Topic 5 - Solar Energy, Atmospheric Heating and Global Temperature
1/33
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
What is the Electromagnetic spectrum? (EM spectrum)
Energy that comes from the Sun and other stars. It is made of different wavelengths of energy.
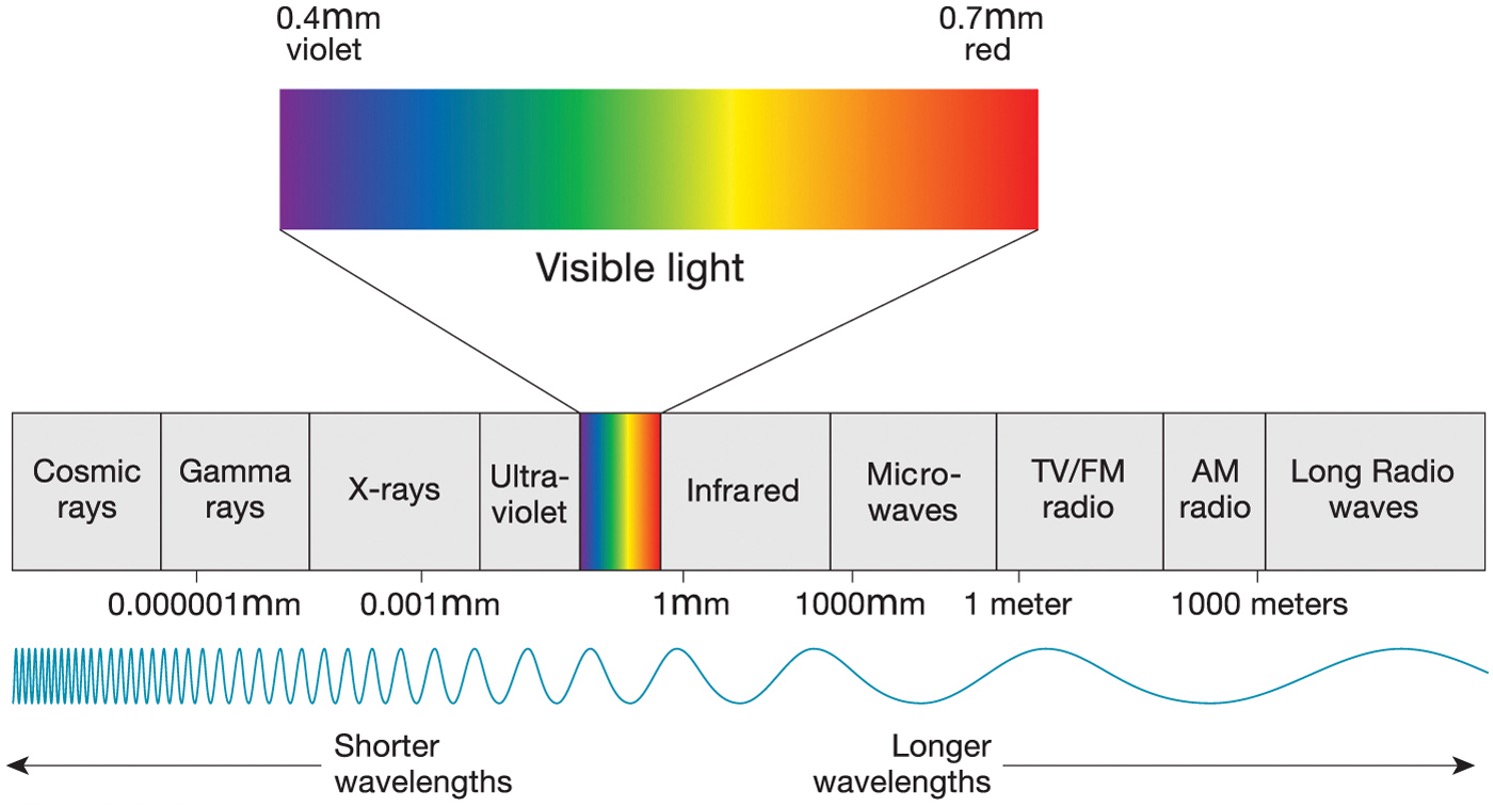
What part of the EM spectrum can our eyes see?
the visible light
What is a wavelength?
The distance between two wave crests, or two wave troughs, is the wavelength.
Which wavelengths are more damaging to organic material?
short wavelengths
Incoming solar radiation
is considered short wave and consists mostly of visible light, IR and UV radiation
Outgoing thermal radiation
is emitted by Earth itself is in the thermal IR portion of the spectrum and is considered long wave
Which wavelengths are considered less damaging?
long wave
What is Incoming Solar Radiation?
the amount of solar energy that reaches earth’s surface
What does the curvature of Earth have to do with insolation?
Because Earth is curved, the Sun's rays are not evenly received across it. This explains why temperature varies so much across the globe.
When energy reaches earth but it is spread out over a larger area closer to the poles …
When it is spread out, the intensity of the solar rays diminishes/decreases, it gets “diluted”
Why is it so hot between latitudes 23.5 degrees N and S?
Because on a certain day of the year you can be directly under the sun
Insolation at Earth's surface - what patterns do you see?
Insolation is the highest at the subtropical highs – the great world deserts are at these latitudes
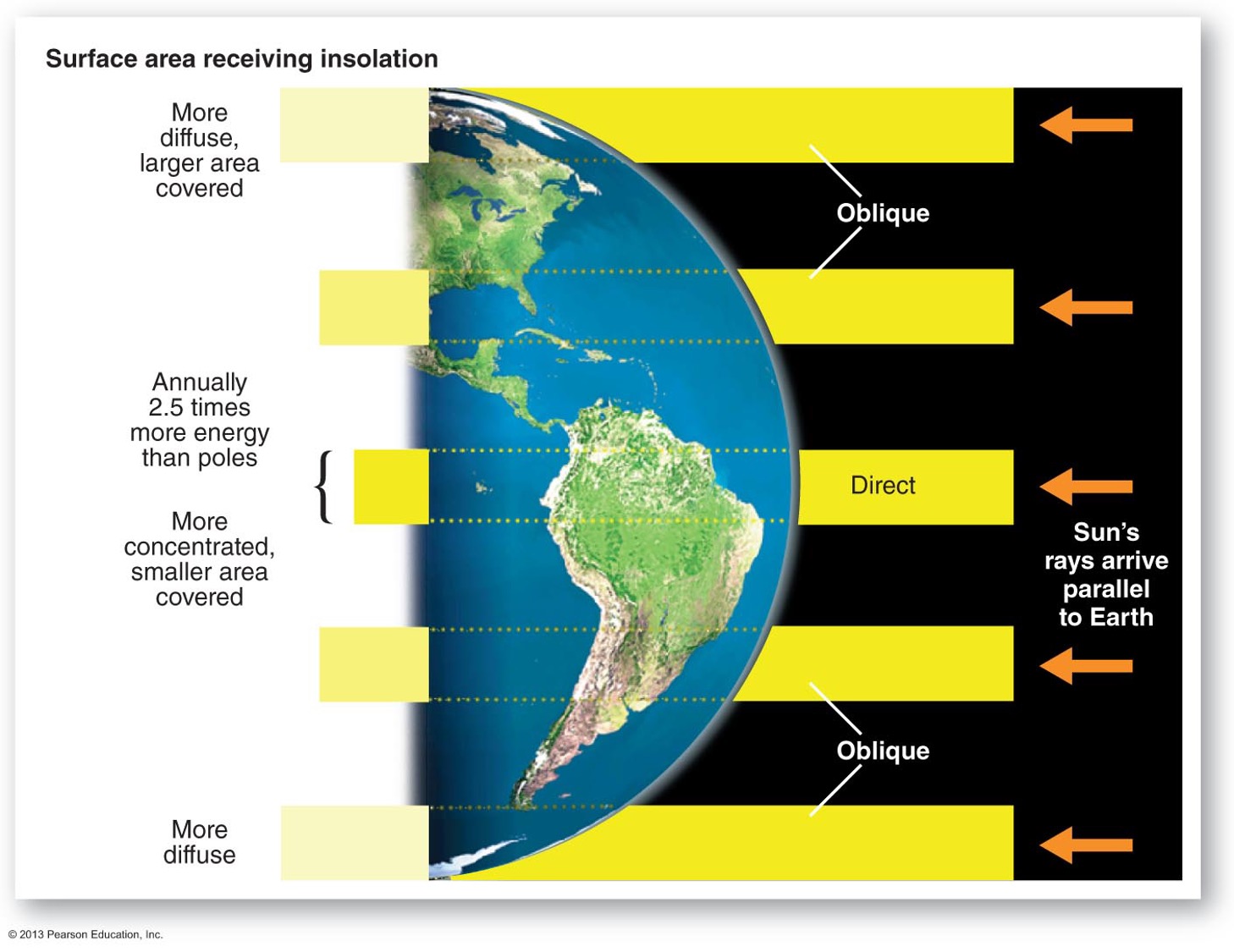
What three physical processes help reduce the amount of energy ultimately being received?
scattering, absorption and reflection
What is scattering(aka diffuse radiation)?
Incoming solar rays bounce off of aerosols in the atmosphere
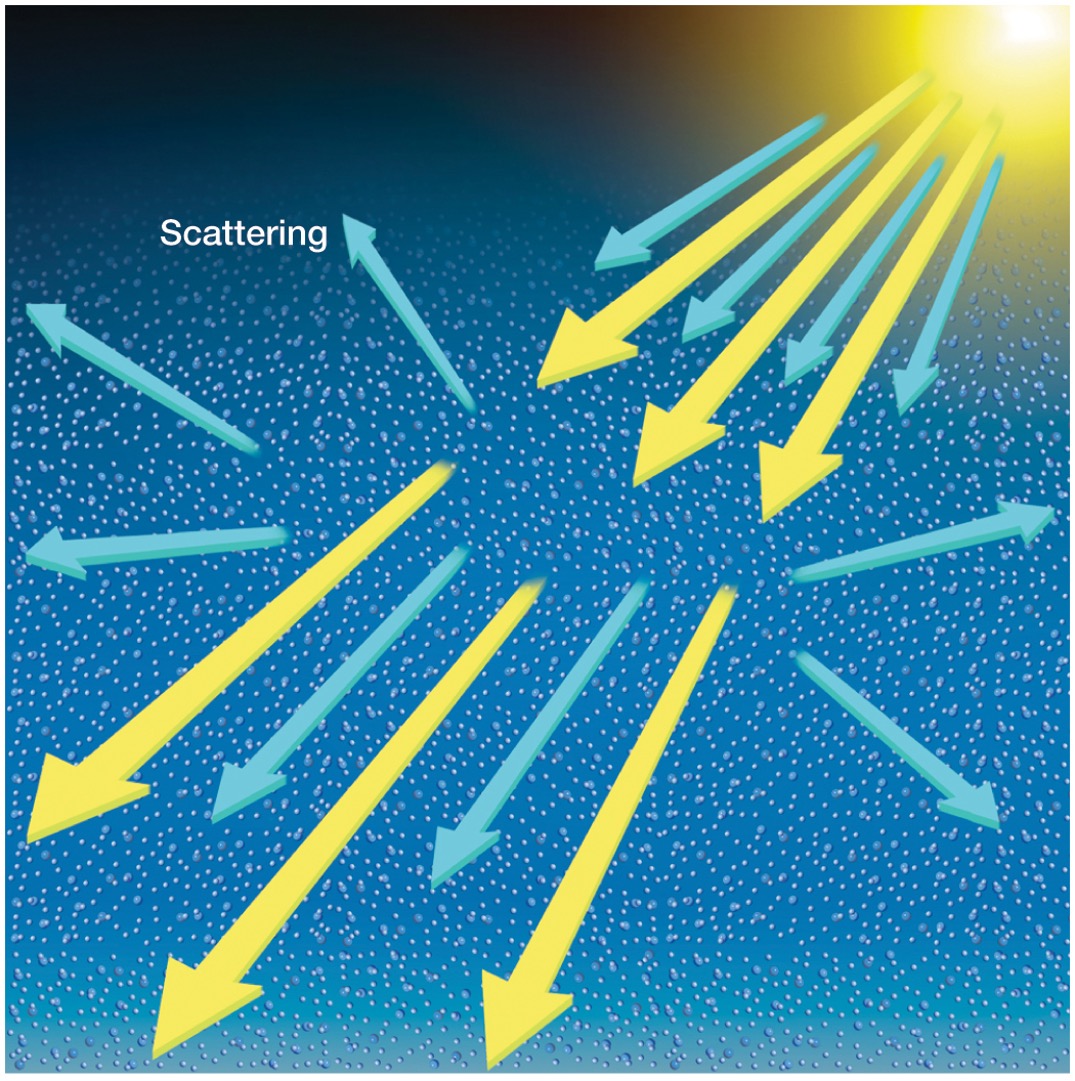
Why does scattering happen?
The rays get scattered and change direction. The energy of the scattered wavelength stays the same
What is refraction?
As the Sun's rays enter our atmosphere, they pass from one medium to another

What is albedo? What is the relationship to Reflection?
Refers to how reflective a surface is – not necessarily shiny
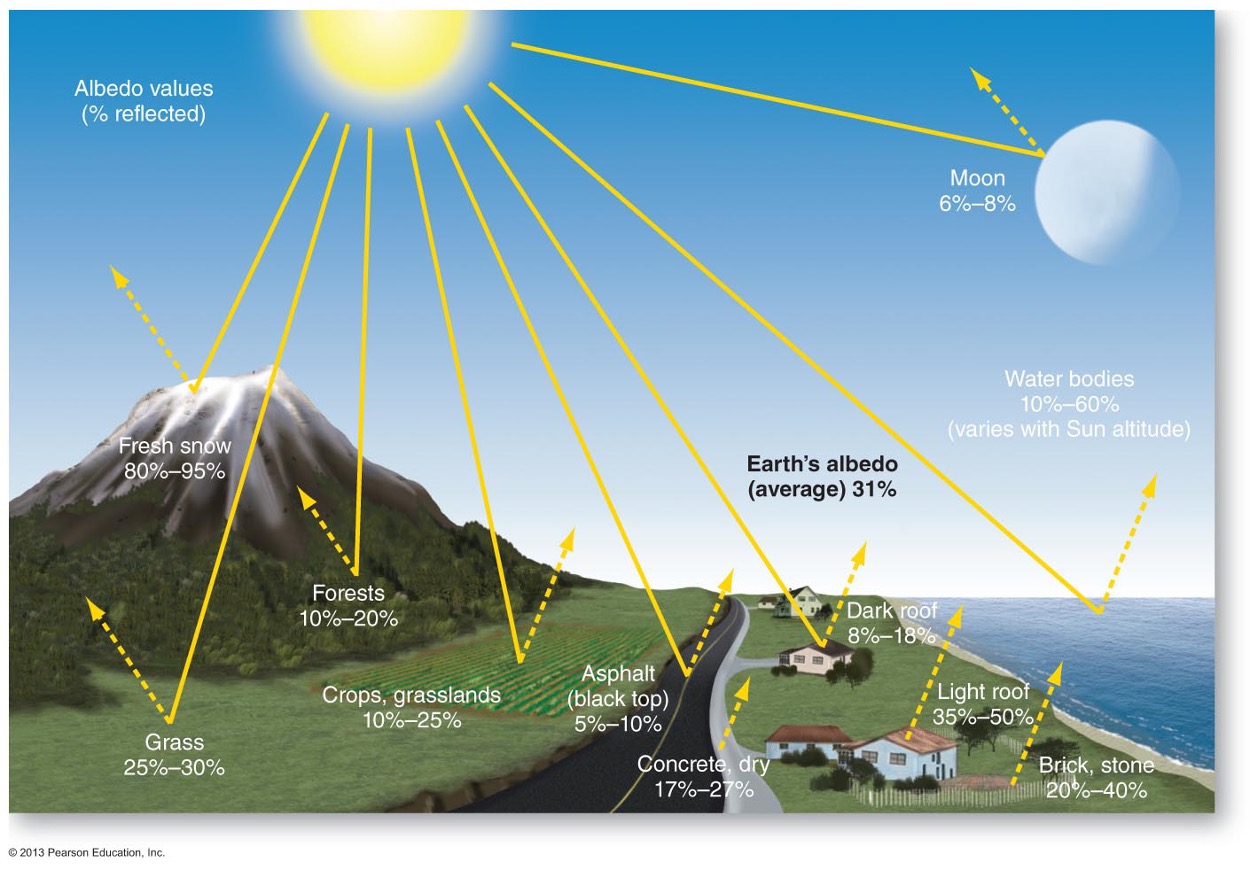
What does 100% albedo mean?
all light energy is reflected
What does 0% albedo mean?
all light energy is absorbed
What are some examples of high albedo?
white and other light colors, snow and ice
What are some examples of low albedo?
black and dark colors, green vegetation, asphalt
What causes albedo to change?
global warming, seasons, urbanization, deforestation
What is positive feedback ?
because a change continues to occur in response to the input
What is an example of positive feedback?
icefields melting lead to more dark surface showing. This increases absorption, which increases the surface temperature and the cycle continues.
What is absorption?
All insolation that is not scattered or reflected gets absorbed.
How does the sun’s energy get moved around in three ways?
conduction, convection and advection
What is conduction?
Transfer of heat energy from surface-to-surface, or in the air, molecule to molecule. (Direct contact, direct transfer) (ex: coffee mug)
What is convection?
Up and down movement of fluids due to differences in temperature (hot air rises, cold air sinks) (convection goes up and down) Ex: air and water both rise up and sink down
cold air …
sinks
hot air ….
rises
what is advection?
Side to side movement of fluids due to differences in temperature
How is earth directly warmed by solar energy?
Insolation
How is earth indirectly warmed by solar energy?
Reflection of the heat from all sources
Water’s specific heat - What is specific heat?
The amount of energy required to raise 1 g. of water 10 C.