dental terms + radiography review
1/60
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
61 Terms
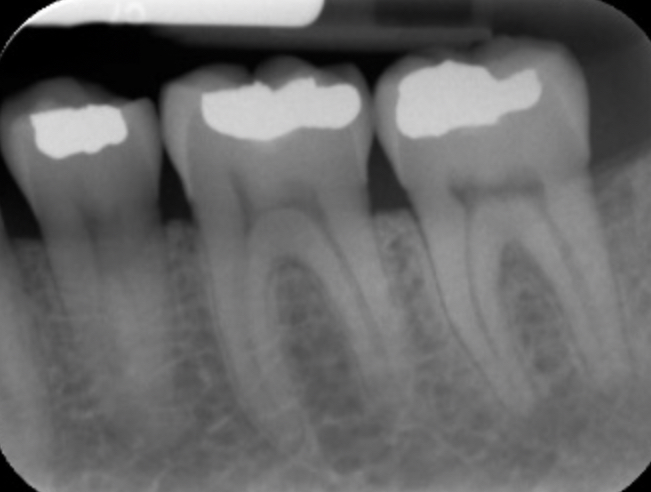
periapical radiographs
identifies abscess, cysts, and granuloma’s that occur at the apex of a tooth's root, appears radiolucent (dark) , indicates bone loss and decay
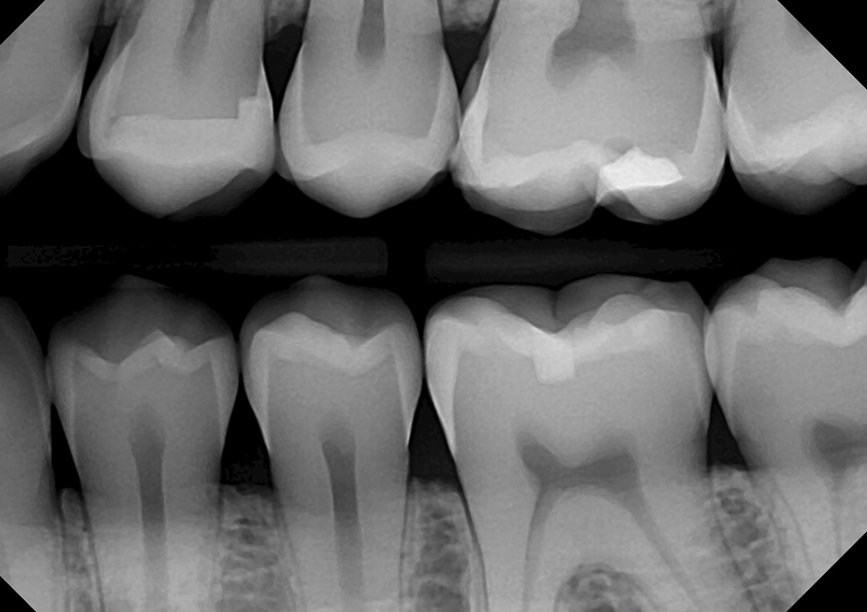
bitewing radiographs
used to detect cavities, interproximal caries, and monitor overall dental health. can also capture both upper and lower teeth in one image.
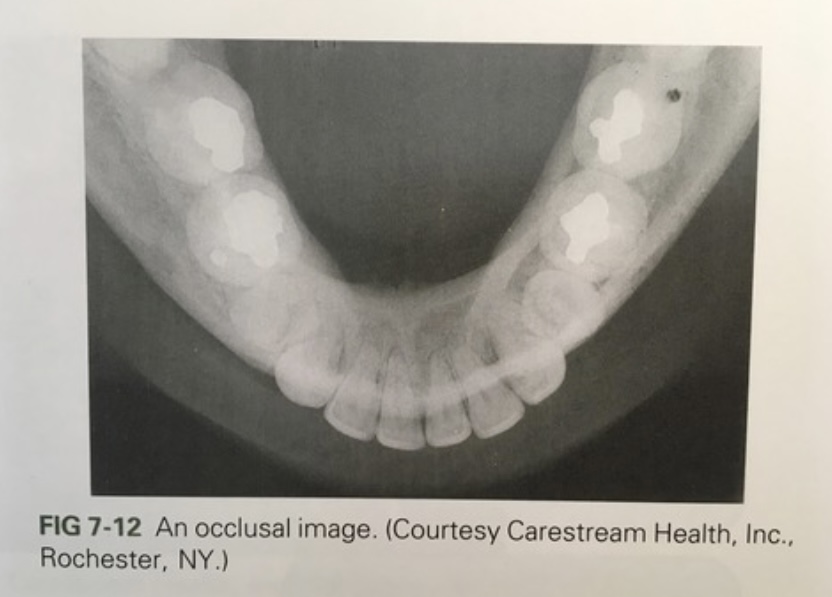
occlusal radiographs
taken by placing film against biting surface of teeth to visualize larger areas of maxilla and mandible and detect abnormalities.
adult film size = #4 ; child film size = #2 ; small pediatric = #0
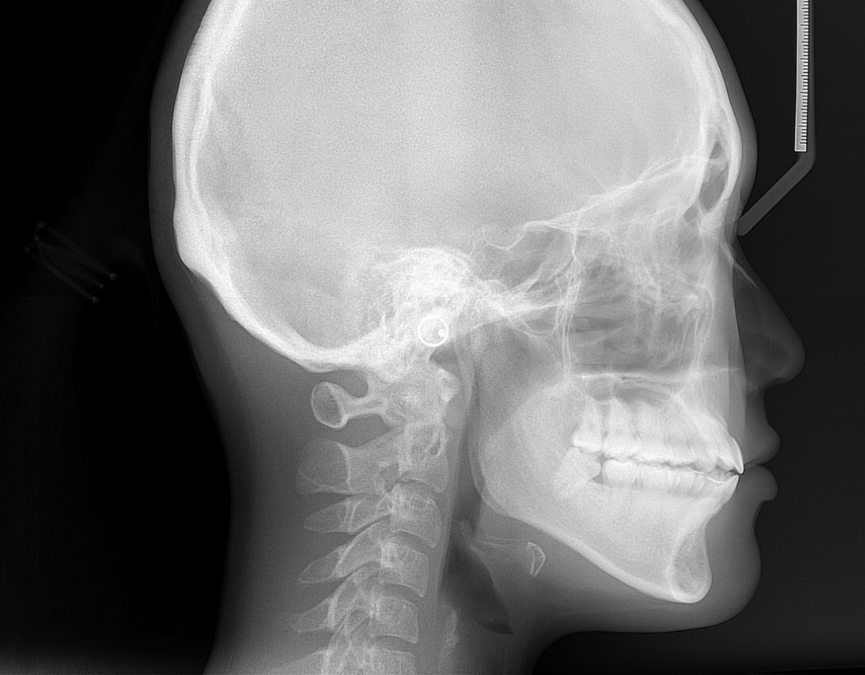
cephalometric radiographs
side profile radiograph containing skull, teeth, and neck. used primarily by orthodontists to assess bone growth and development.
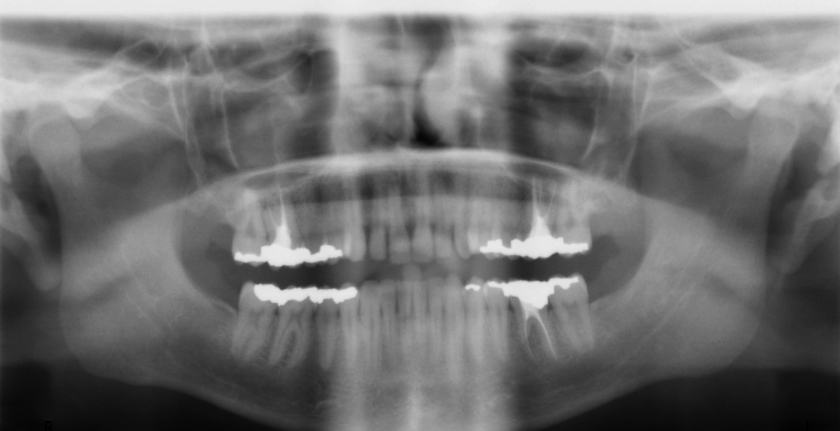
panoramic
wide view x-ray of the teeth, jaws, and surrounding structures, allowing for the assessment of dental abnormalities, wisdom teeth positioning, and jaw-joint issues.
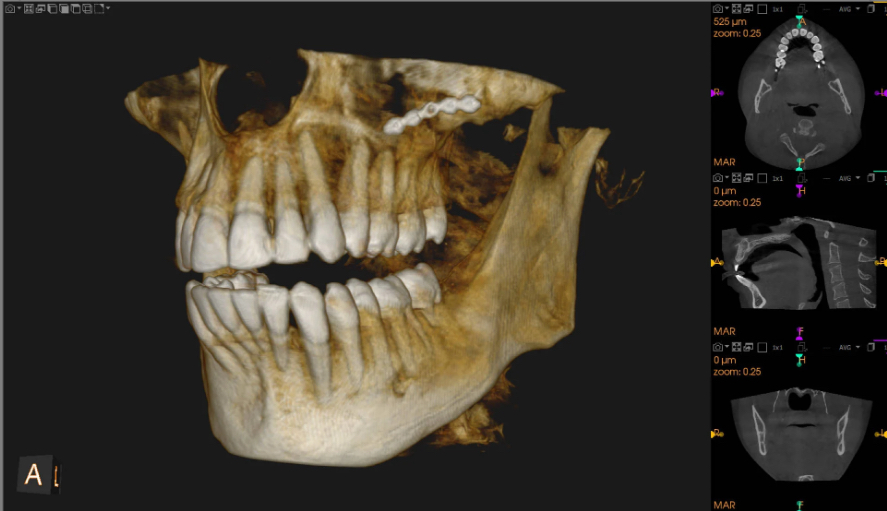
Cone Beam Computed Tomography (CBCT)
3D imaging technique used to provide detailed views of dental structures, soft tissue, nerves, and bones. used for root canals, implant planning, viewing jaw structure, and assessment of bone growth
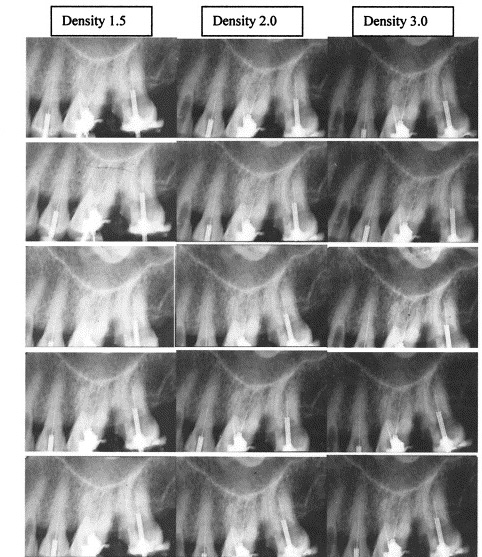
density
overall darkness of an image

bite-wing block
device used to hold digital sensors in place during radiograph
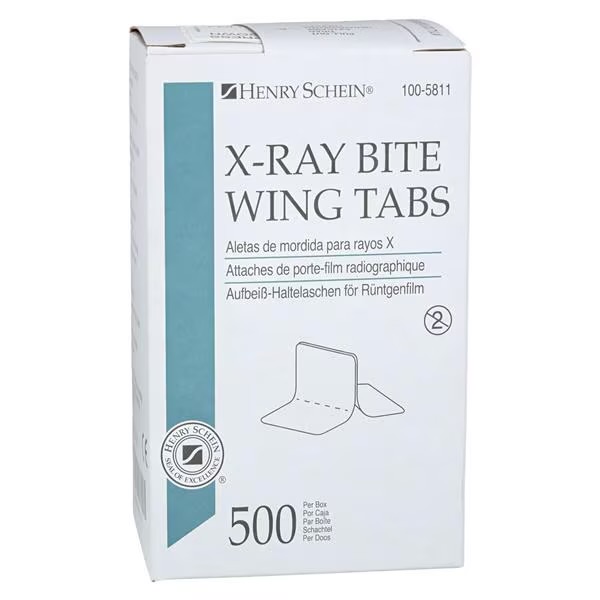
bite-wing tab
small adhesive tab used to hold digital sensors against the teeth
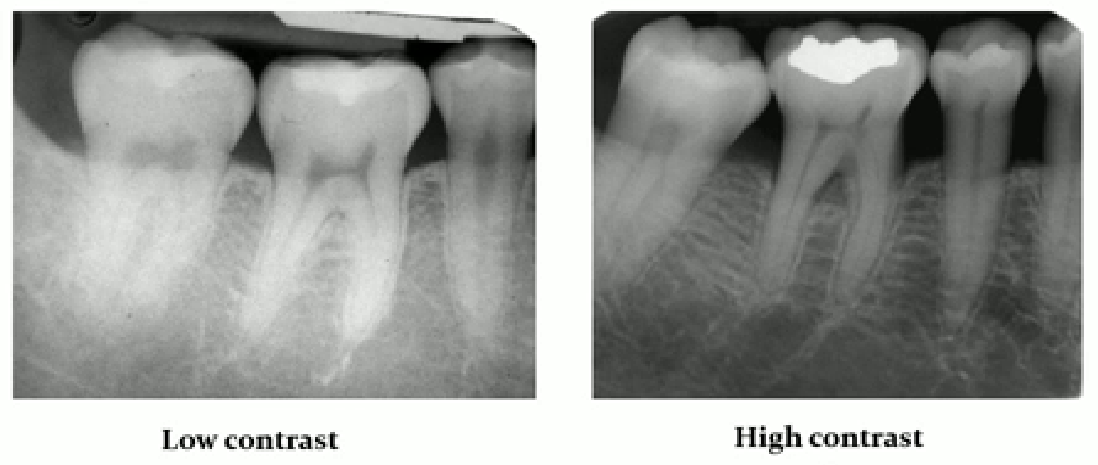
contrast
controls light and dark shades of an image
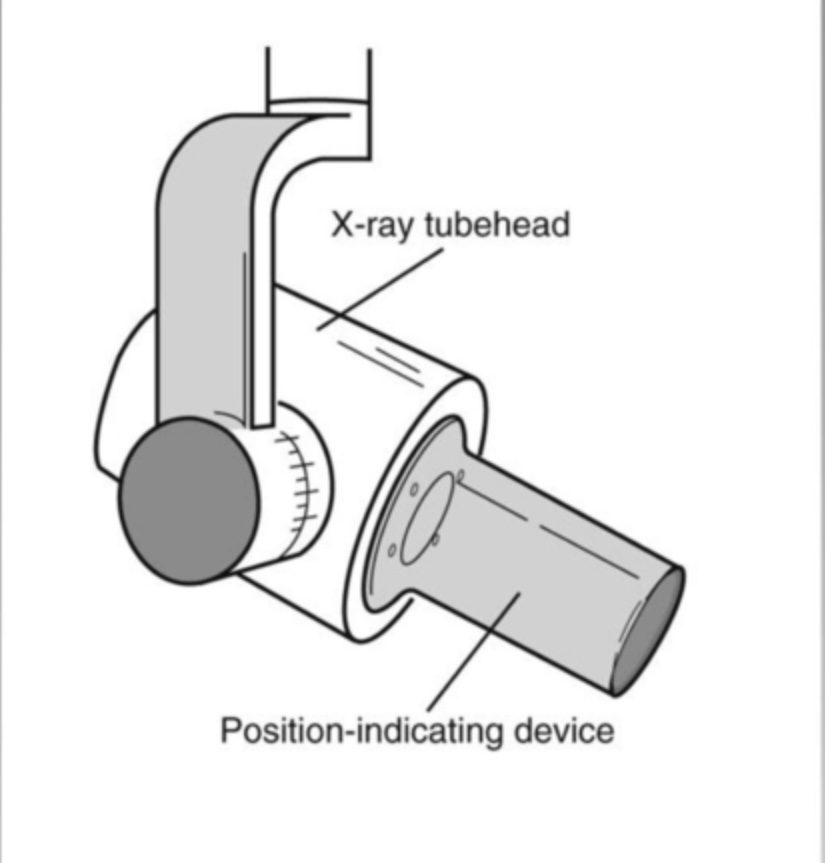
position indicating device (PID)
aiming device used to direct the x-ray beam accurately towards the image receptor (after use, it’s disinfected)
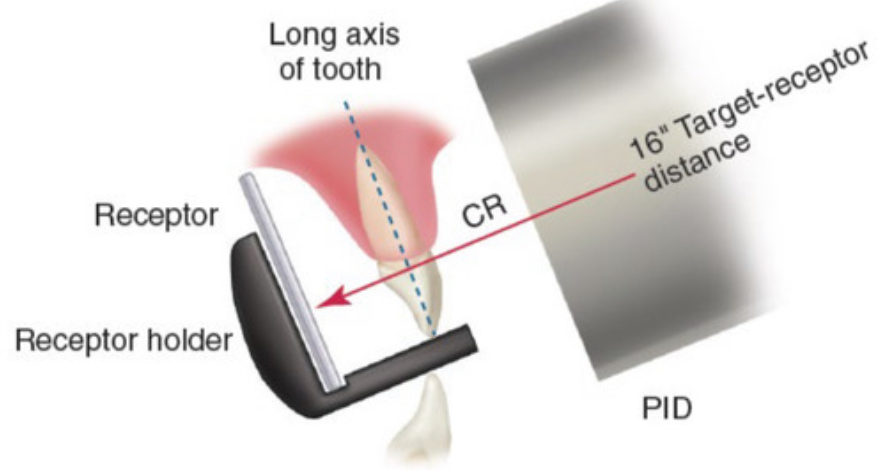
paralleling technique
technique that uses an image receptor placed parallel to the long axis of the long axis of the tooth with an x-ray beam directed perpendicular (⊥) to both the film and the tooth
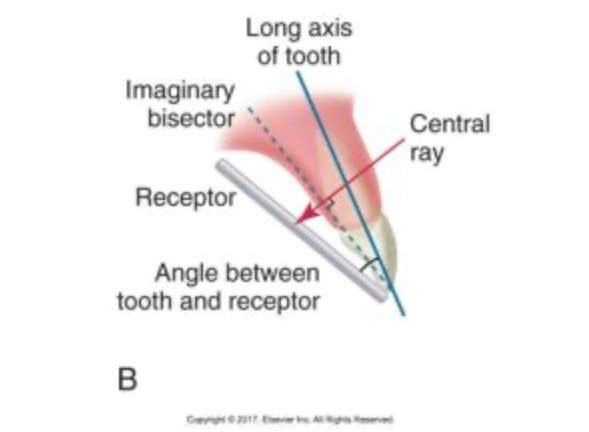
bisecting technique
a technique where the image receptor is aligned against the angle between the tooth and the film, directing the x-ray beam perpendicularly to the bisecting line
pros: useful against shallow palates
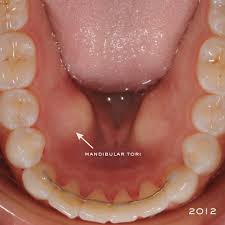
tori
bony growths in oral cavity (maxillary/mandibular), may obstruct receptor placement
PID / Central Ray placement errors
incorrect positioning may lead to image distortion
tubehead placement
horizontal error = overlapping contacts
vertical error = image elongation / foreshortening

photostimuable phosphor (PSP)
an image storing system which captures and stores X-ray images for later processing (can be scratched, MUST be deleted after use or else double images)

complementary metal-oxide semiconductor (CMOS)
converts X-rays into digital signals for immediate display and analysis (fast&accurate) CCD (Charged-Couple Device) and CMOS are same thing
legal requirements
HIPAA - image privacy, confidential records should not be discussed (patient name must not be disclosed)
Retention - must keep images for 7+ years (pediatric dentists must keep until 18+)
Transfer - must comply with patient consent and new dental provider must request images (only by copy, not OG images)
Ownership - legally the dental office owns images, but patient has rights to them
Charting - document date (listed first), type of radiograph, reason for image
anatomy of skull
⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀⠀
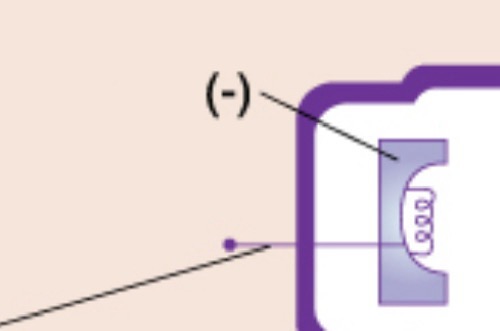
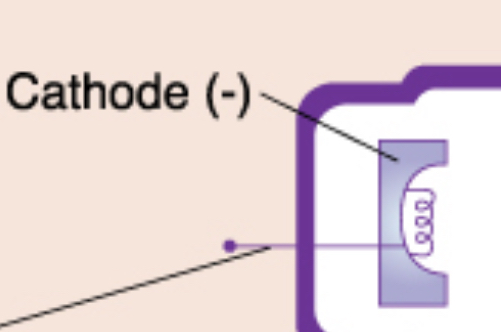
cathode (-)
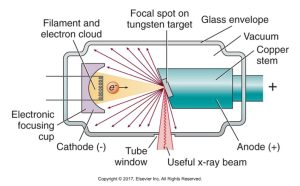
negatively charged electrode in an X-ray tube that emits electrons when heated
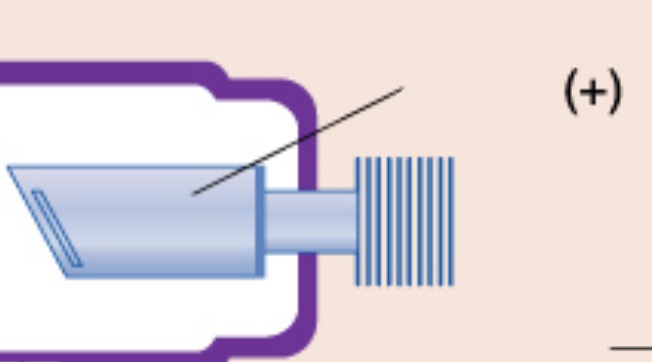
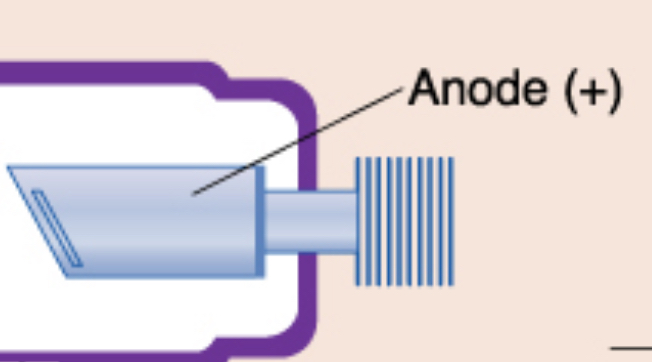
anode (+)
positive electrode, purpose is to convert electrons into x-ray photons
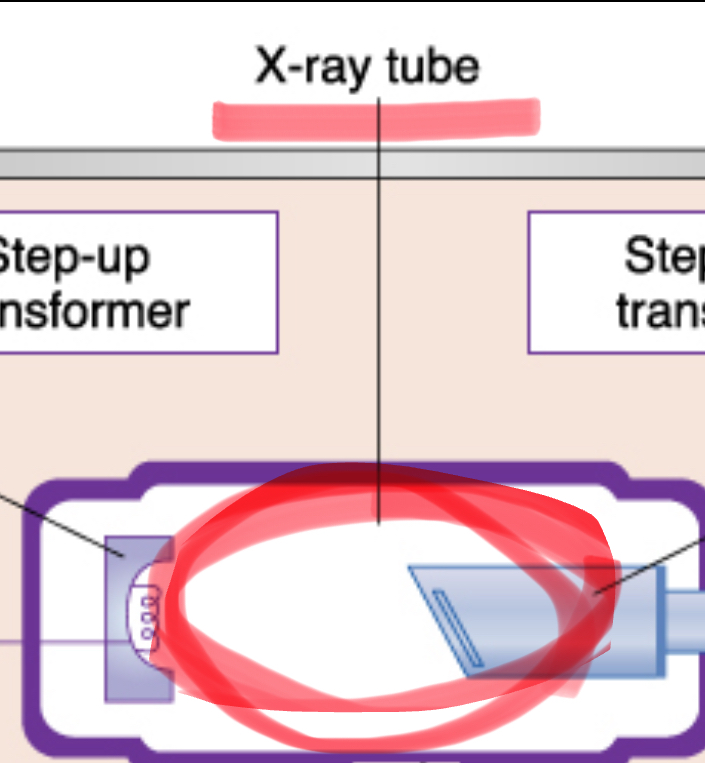
x-ray tube
the heart of the x-ray generating system
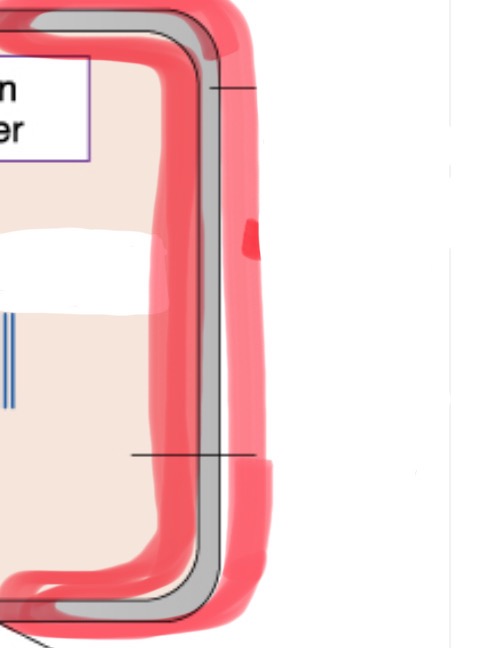
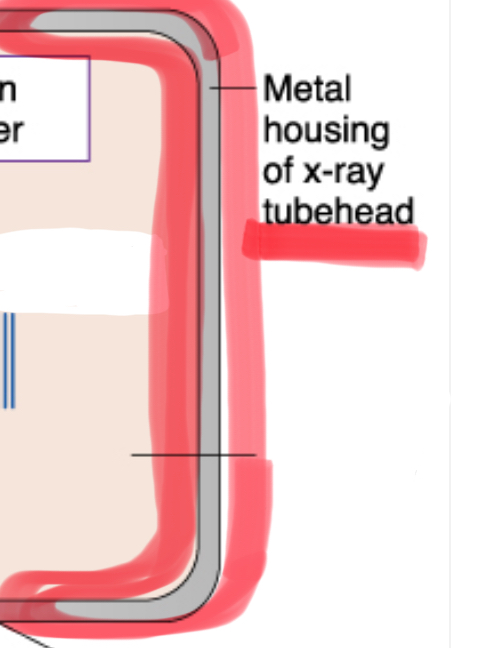
metal housing of tubehead
protects and encloses the x-ray tube, preventing radiation leakage and ensuring safety during imaging procedures
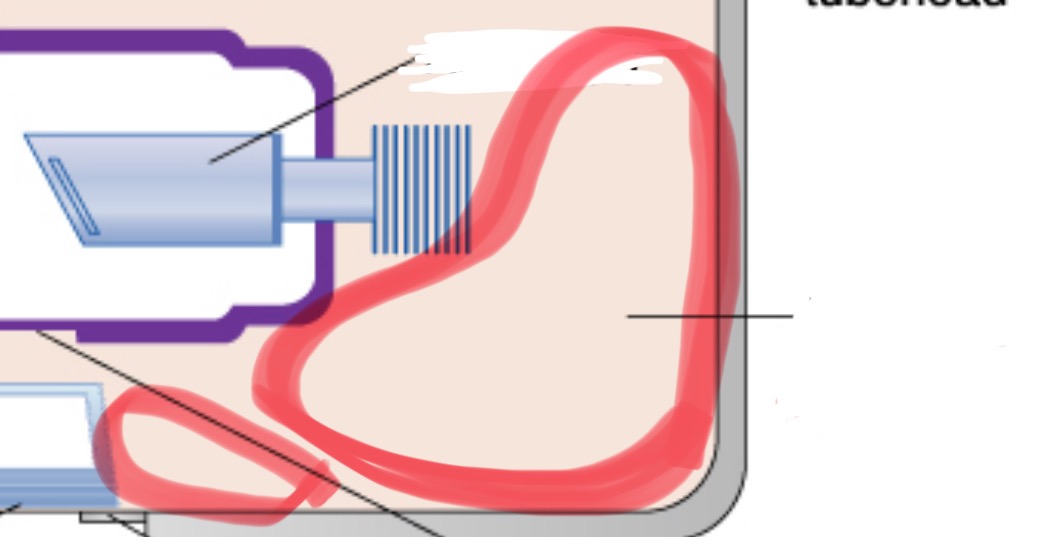
insulating oil
prevents overheating by absorbing the heat created by the production of x-rays
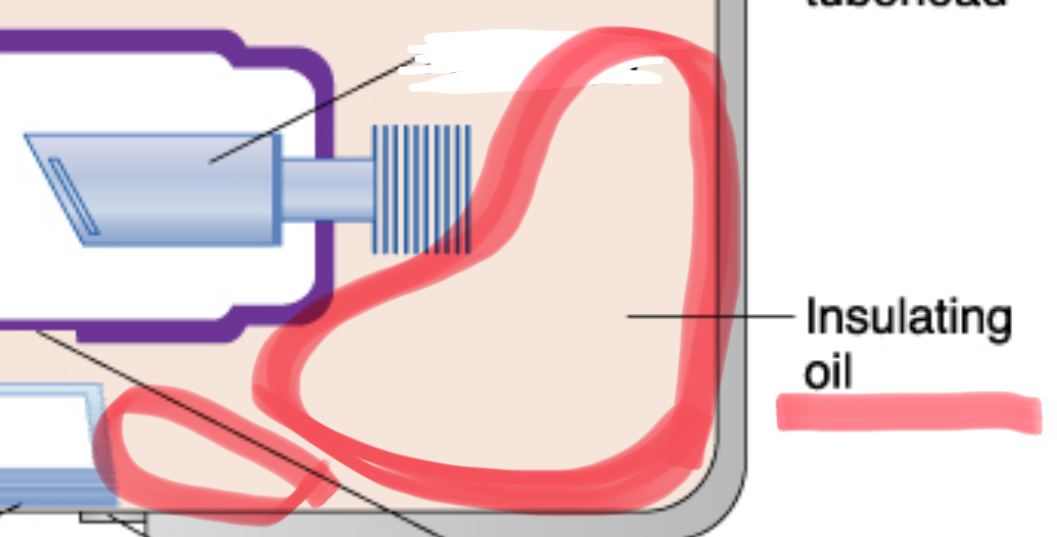
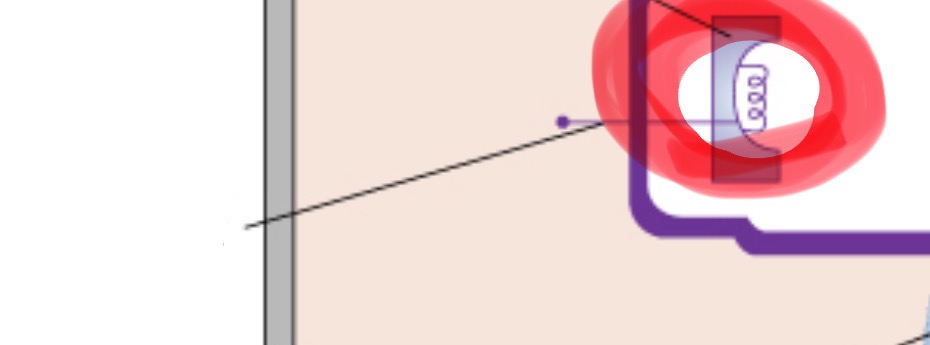
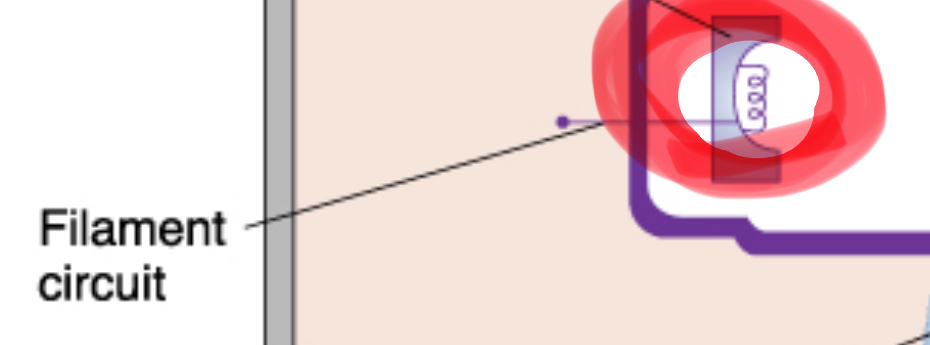
tungsten filament
coiled wire made of tungsten (metal) which produces electrons when heated
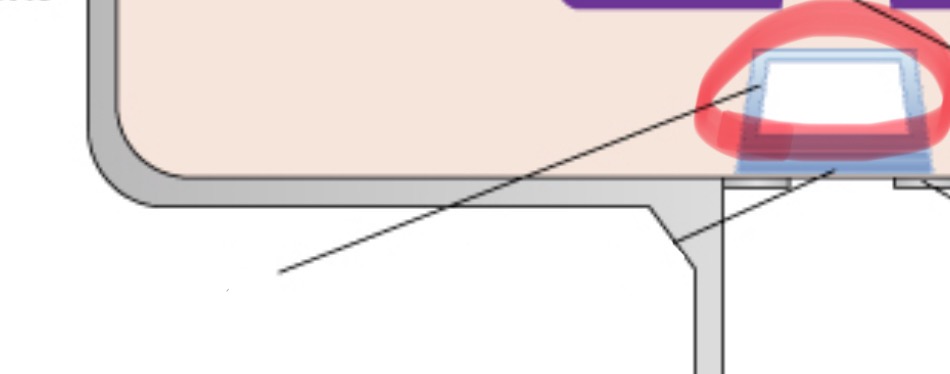
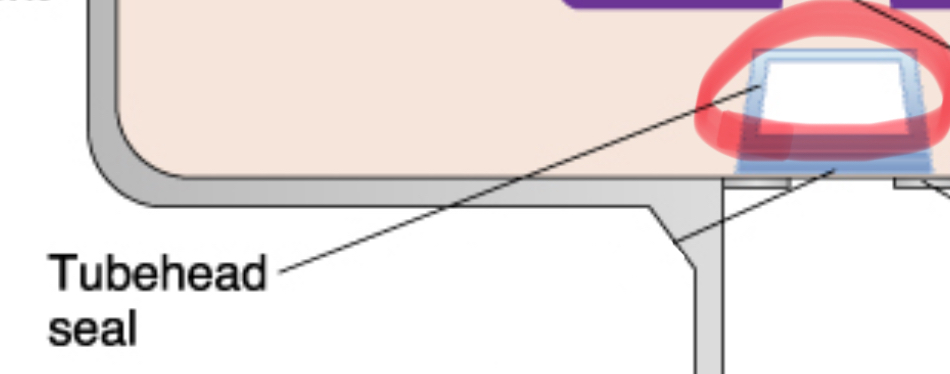
⠀tube head seal
allows the exit of xrays from the tube head. seals the oil inside tube head and acts as a filter to X-ray beam
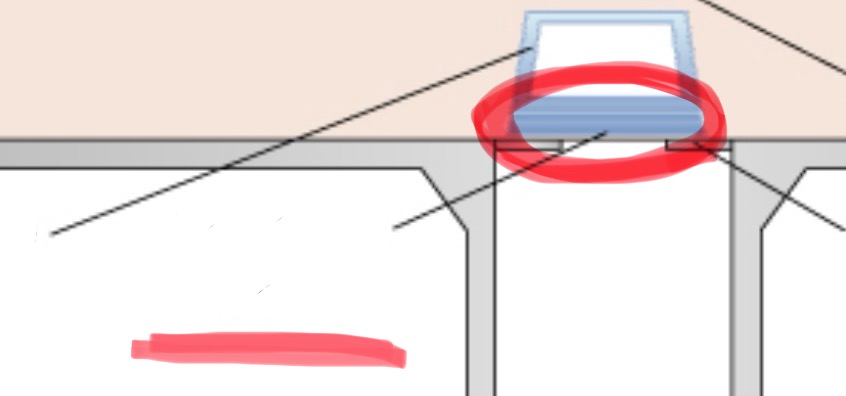
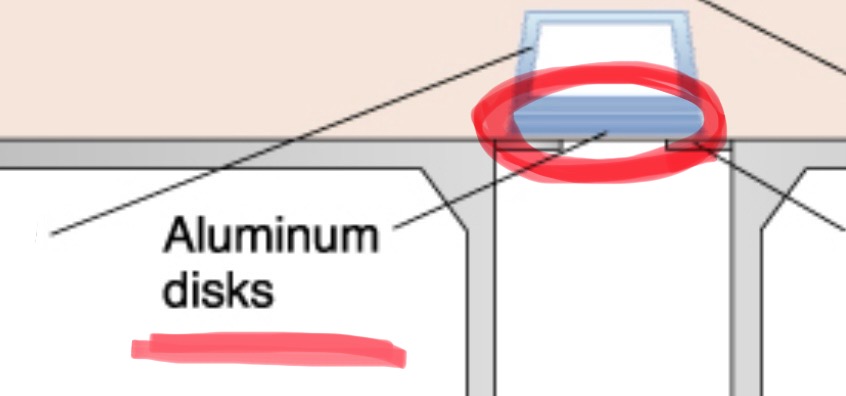
aluminum disks
added filtration. filters out low energy, long wavelength x-rays
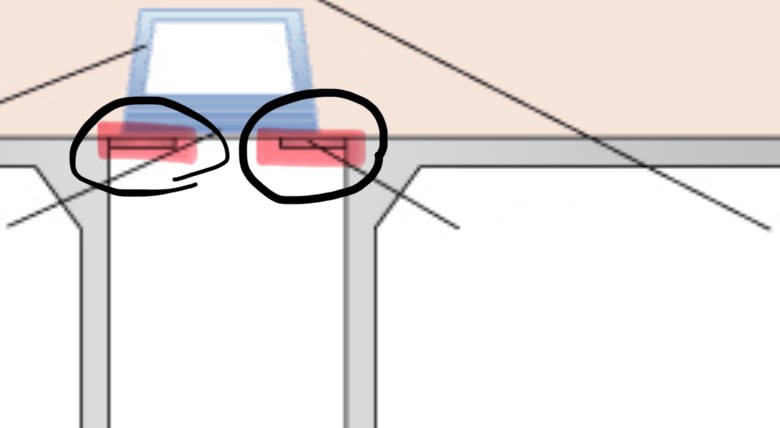
collimator
restricts the size and shape of the x-ray beam
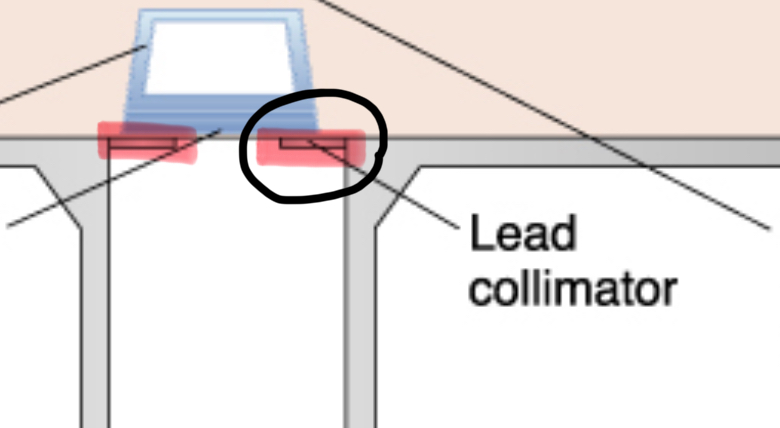
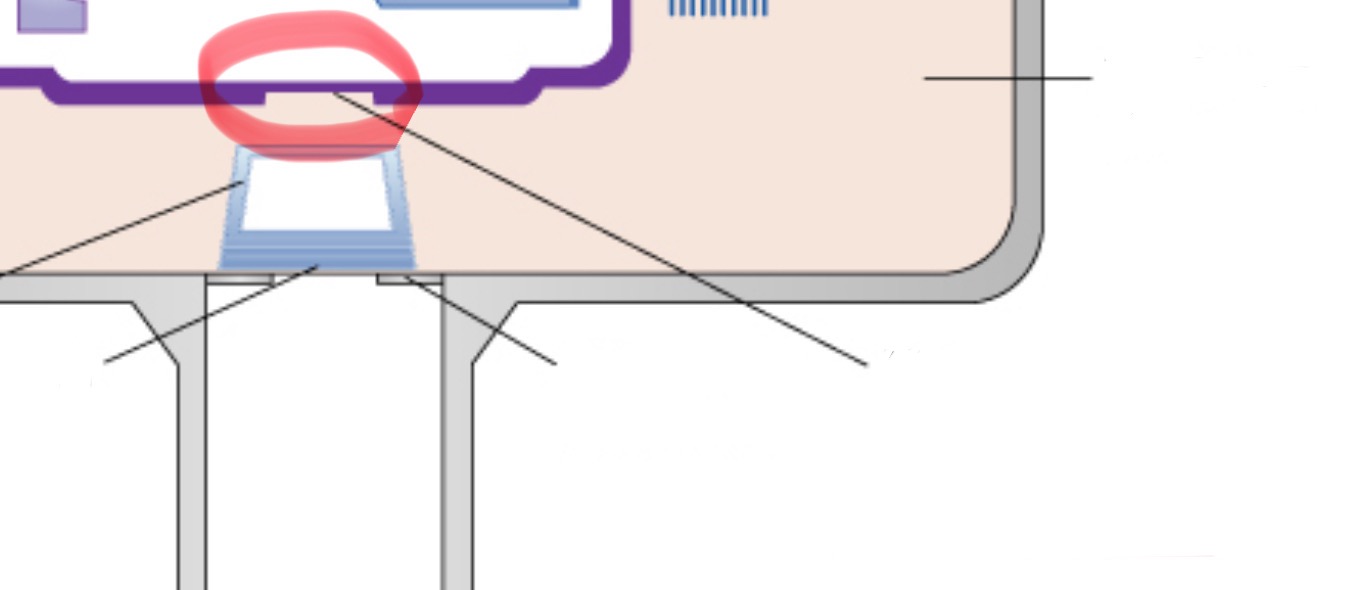
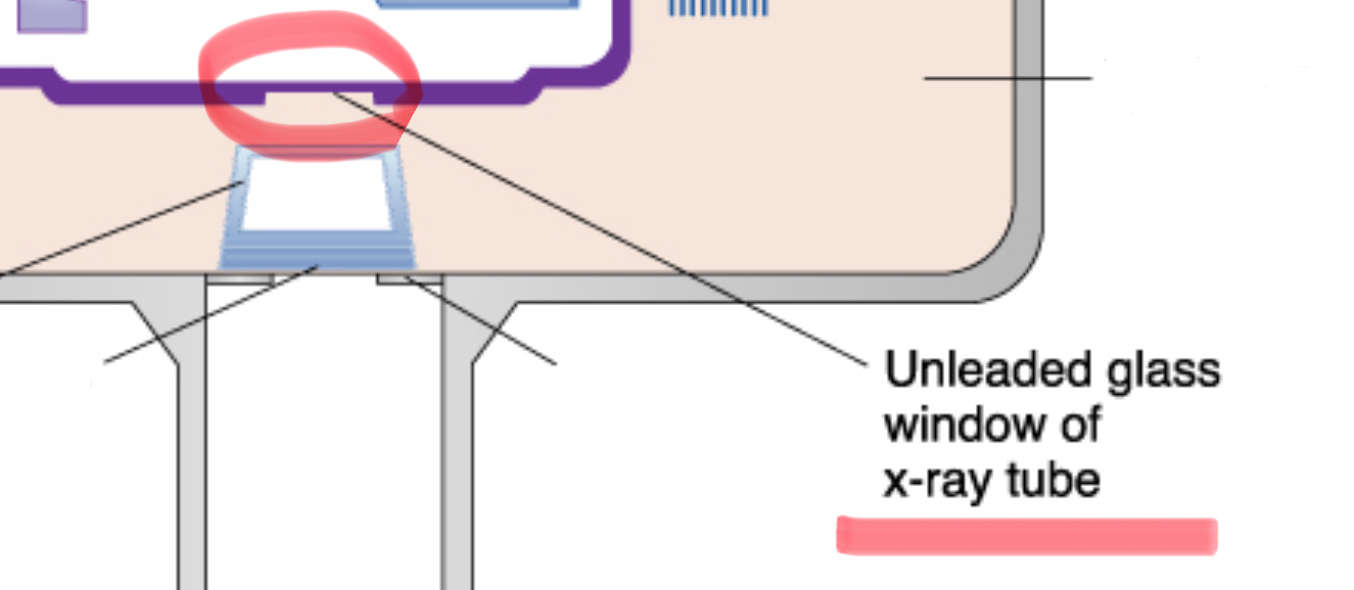
unleaded glass window of tube head
allows x-rays to exit the tube while preventing leakage of radiation, directs beam right toward the aluminum disks, lead collimator, and PID
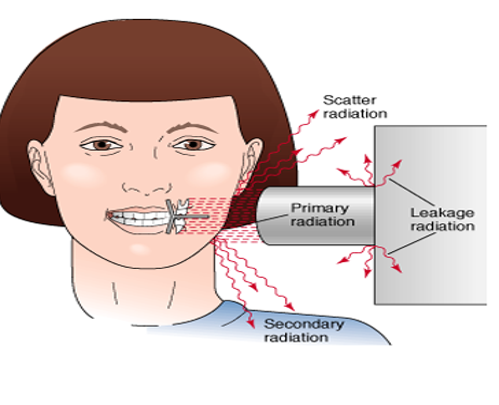
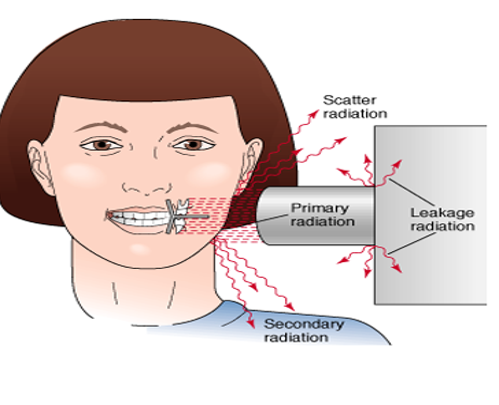
primary radiation
xrays emitted directly from the x-ray tube that have not been altered or scattered
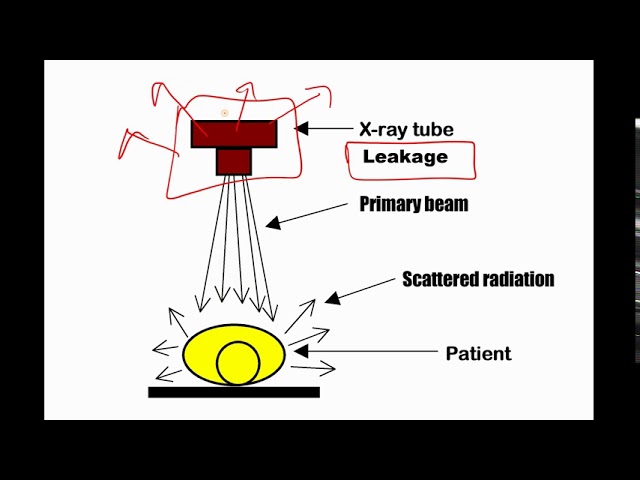
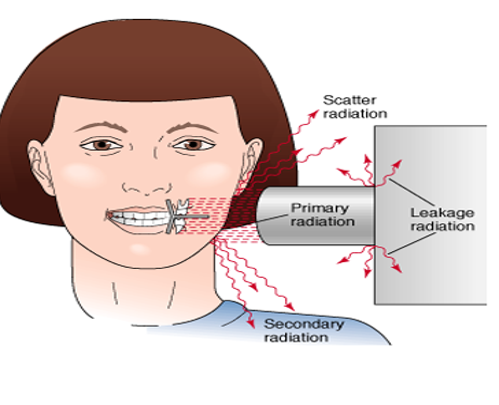
secondary radiation
x-radiation (high energy radiation) created when primary radiation interacts with matter (patient, equipment, or wall)
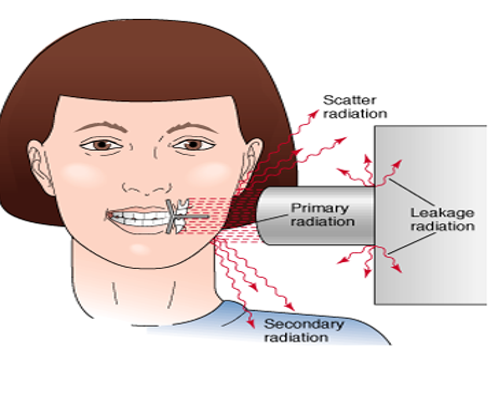
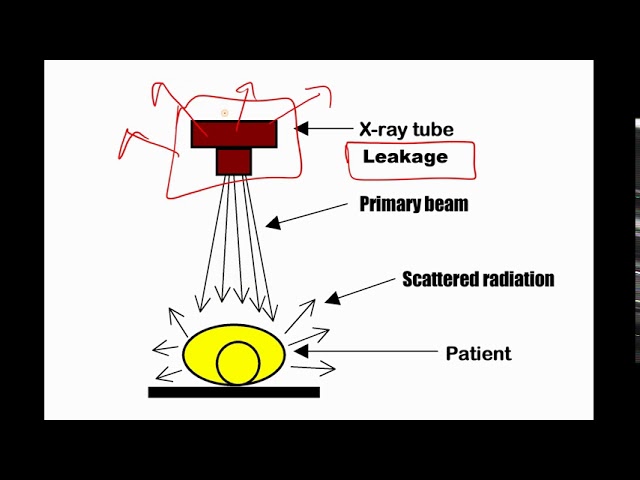
scatter radiation
a form of secondary radiation that occurs when deflected (direction changes after an interaction) from its original path after interacting with matter
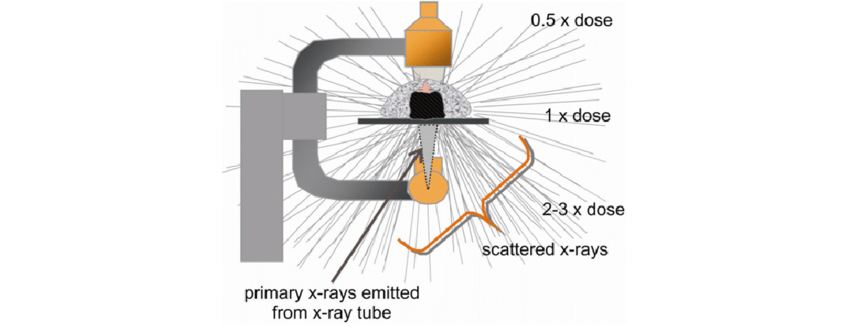

leakage radiation
x-rays that escape from the tube-head’s (checked for annually)
3 consistent parts of x-ray unit
control panel, extension arm, tube head
The two types of filtration
inherent and added filtration
Inherent filtration
takes place when the primary beam passes through the glass window of the xray tube, the insulating oil, and tubehead seal
- Approx. 0.5-1.0 mm
acute exposure
large dose in a short period of time
chronic exposure
small doses over a long period of time
latent exposure
time between exposure to ionizing radiation (powerful energy which creates charged particles called ions) and appearance of symptoms
kVp (kilovoltage peak)
affects the penetration and quality of the x-rays produced (controls density) , recommended amount is 60-70 kV
mA (milliamperage)
quantity (amount) of the X-ray beam, 1/1000 of an ampere, ranges from 7 to 15 mA (must not exceed or else overheating)
Aluminum filtration of a x-ray machines operating at or below 70kVp
1.5 mm aluminum
Aluminum filtration of a x-ray machines operating at or above 70kVp
2.5 mm aluminum
results from increasing exposure time
darker image (too dark = overexposure)
results from decreasing exposure time
lighter image (too light = underexposure)
ALARA means ?
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
somatic effects
only affects the individual exposed to radiation
genetic effects
passed down to offspring (through reproductive cells)
most to least sensitive to radiation (in order)
reproductive cells (sperm/eggs), bone marrow, thyroid, lungs, skin, the eye, muscle, nerves
The maximum permissible dose (mpd) per year for radiation workers is ___ rems/millisieverts a year?
0.5 rems, or 50mSv a year
Meaning of EPA
Environmental Protection Agency
units of radiation measurements & conversion
roengten equivalent man - rem
roengten - R
Sievert - Sv
gray - Gy
Coulombs per kg - C/kg
Gy to Rad: 1 Gy = 100 rad
Sv to Rem: 1 Sv = 100 rem
Rad to Gy: 1 rad = 0.01 Gy
Rem to Sv: 1 rem = 0.01 Sv
cumulative mpd per year
10 mSv/year times age in years
sterilization
to make free from bacteria and other microorganisms, often through heat or chemicals (such as forceps, scalers, beam alignment device, sensor positioning device)
disinfection
the process of reducing harmful microorganisms from objects and surfaces, typically through the use of wipes/sprays ((PID, extension arms, tube head, lead apron (after each use), PSP (must erase))
barriers
prevents radiation exposure and minimizes cross-contamination, includes physical barriers such as walls, lead aprons, and plastic covers. (including but not limited to the dental chair, control panel, tubehead, digital sensor, countertops, computer keyboard, headrest of chair)
Before x-ray exposure:
adjust chair
adjust headrest
place lead apron
place barriers
After x-ray exposure:
dispose of contaminated items
take reusable equipment to sterilization
remove lead apron
Asepsis
the state of being free from disease-causing contaminants, ensuring a sterile environment
Antiseptic
a substance that prevents infection by killing or inhibiting the growth of pathogens