Biological Anthropology 002
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
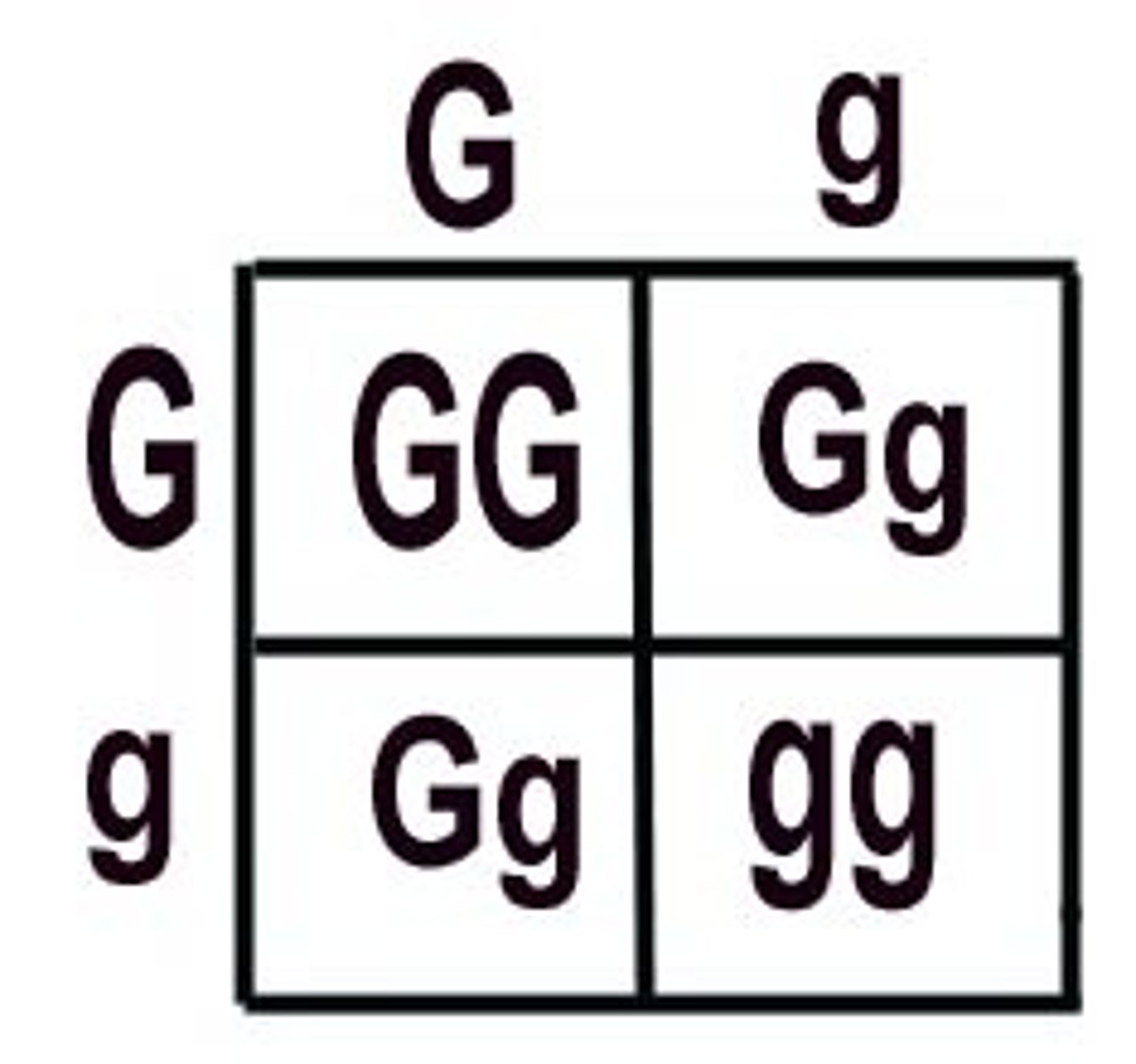
Punnett Square
Visual diagram used to predict the possible genotypes and phenotypes of offspring in a genetic cross
Peppered Moth
Natural Selection
- pre-industrial England the moth was a mottled gray color with camouflage w/the lichen on the trees
- when the coal dust began covering the foliage in the 19th century England, the lichen died, and the tree bark was a darker color
- these moths which were darker were favorably selected
Meiosis
the production of gametes through one DNA replication and two cell (and nuclear) divisions, creating four haploid gametic cells
Cultural, Developmental, Acclimatory adaptations
cultural: the ways humans use cultural knowledge, practices, behaviors to adjust to and thrive in their environment
developmental: the changes an organisms phenotype undergoes during growth and development in response to environmental exposures
acclimatory: the temporary, reversible changes in an organism's physiology that occur in response to environmental stressors
High Altitude
a field that studies how humans have adapted to live in high-altitude environments, typically above 2,500 meters (8,200 ft) above sea level
Proteins
- compose bone and muscle
- hormones
- enzymes
- cellular function
Somatic Cells
Diploid cells that form the organs, tissues, and other parts of an organisms body
Gametes
sexual reproductive cells, ova and sperm, that have a haploid number of chromosomes and that can unite with a gamete of the opposite type to form a new organism
Scientific Method
involves empirical data collection and hypothesis testing
Mendel
- experiments in particular inheritance
- discovered dichotomous variation
- developed a series of postulates about inheritance
Lamarck
- inheritance of acquired characteristics
Mendelion
- basic principles associated with the transmission of genetic material, forming the basis of genetics, including the law of segregation and the law of independent assortment
segregation: asserts that two allele's for any given gene (or trait) are inherited, one from each parent' during gamete production, only one of the allele's will be present in each ovum or sperm
assortment: asserts that the inheritance of one trait does not effect the inheritance of other traits
Polygenic
refers to one phenotypic trait that is affected by two or more genes
Bipedalism
walking on two feet
Adaptive Radiation
the diversification of an ancestral group of organisms into new forms that are adapted to specific environmental niches
Natural Selection
the process by which some organisms, with features that enable them to adapt to the environment, preferentially survive and reproduce, thereby increasing the frequency of those features in the population
Allen's Rule
an ecogeographic principle that explains how the body shape of warm-blooded animals adapts to different climates
Ricket's
- a childhood disease causing soft and weakening bones, directly linked to vitamin D deficiency, which is often caused by inadequate UV radiation exposure
- condition leads to softening and weakening of bones, often resulting in skeletal deformities such as bowed legs or thickened wrists and ankles
ABO Blood System
- a system classifying human blood based on the presence or absence of specific antigens, A, B, on red blood cells
- antigens are determined by inherited allele's the system results in four blood types A, B, AB, and O
Malthus
- inspires Darwin and Wallace in discoveries of natural selection
- was arguing for limits of human population growth not concerned with how species change
- argued that in nature there is a tendency in size, while the availability of resources remains relatively the same
- limits for populations to increase is controlled by availability of resources
Uniformitarianism
the concept that processes that occurred in the geologic past are still at work today
Biological Anthropology
the study of the evolution, variation, and adaptation of humans and their past and present relatives; sometimes called physical anthropology
Linnaeus
- natural scheme of life
- taxonomy
- binomial nomenclature
- homo sapiens (us)
- anis lupus --> wolf
Sexual Dimorphism
observable differences in appearance or behavior between the sexes of the same species
Down syndrome ro
- chromosomal abnormalities
= Non disjunctive errors: the failure of homologous chromosomes to separate properly during cell division
- trisomy