APC 12- Homeostasis 2
1/16
Earn XP
Description and Tags
negative feedback ,positive feedback loops,role of autonomic system , role of endocrine systme , how cardiovascular system is regulated to control blood pressure and cardiac output ,how the kidneys contribute to regulation of blood pressure and how negative feedback loops control the release of thyroid hormone and cortisol
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
17 Terms
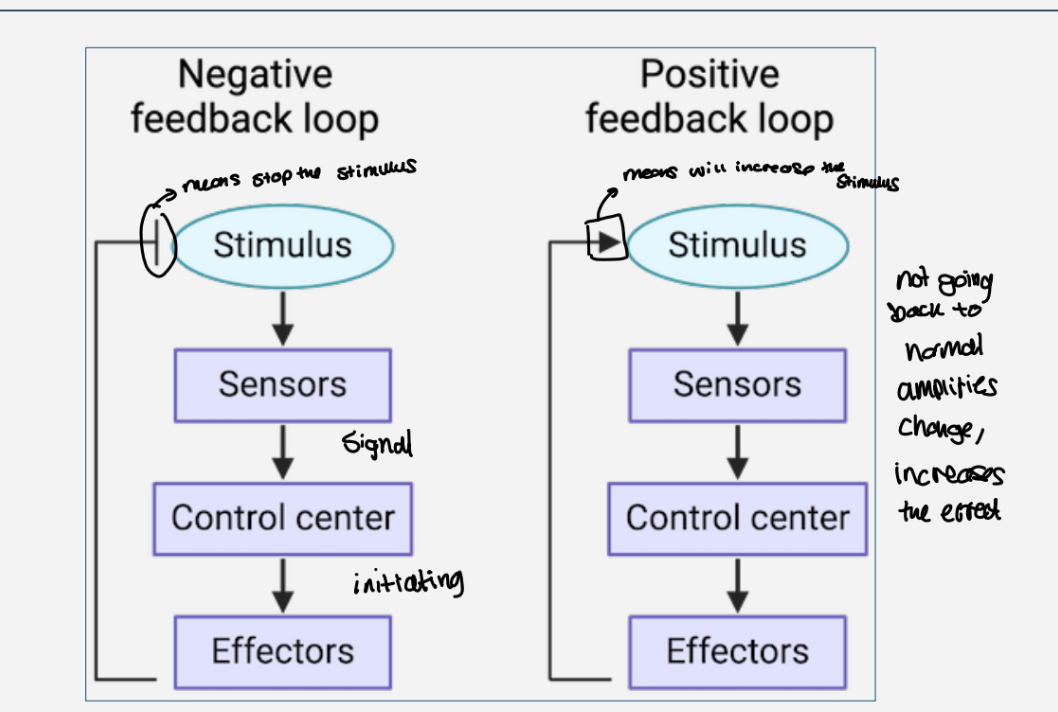
Summarise negative and positive feedback loops
negative - means that the stimulus stops , back to normal
positive - the stimulus is increases ,does not go back to normal ,it amplifies the change
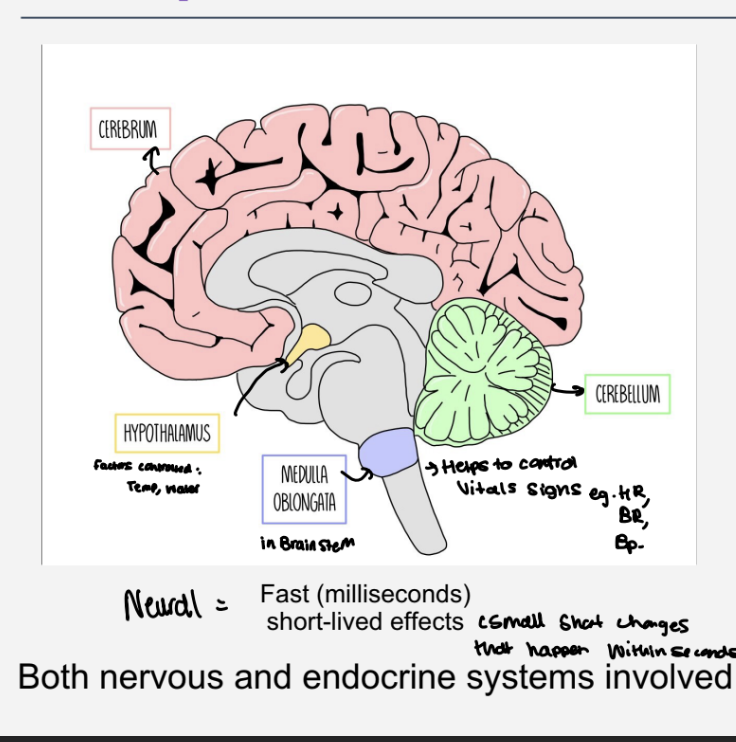
Summary of neural control
fast - within milliseconds ,short lived effects
cerebrum
hypothalamus- controls temp ,water
, medulla oblongata - in brainstem and controls vital signals - hr,br,bp
cerebellum
automatic control of body systems
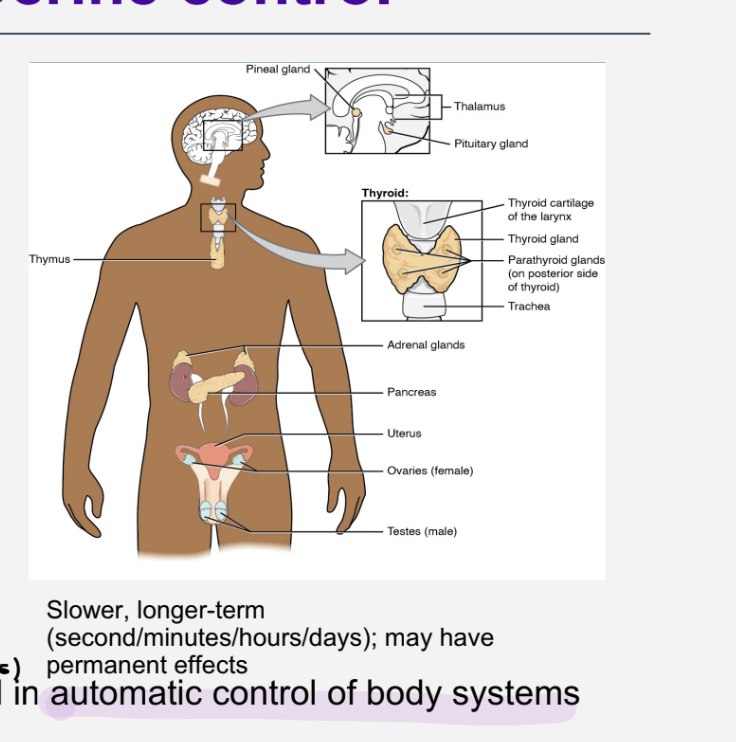
summary of endocrine system
slower
longer tern - min,days ,hours
may have permanent effect
automatic control of body systems
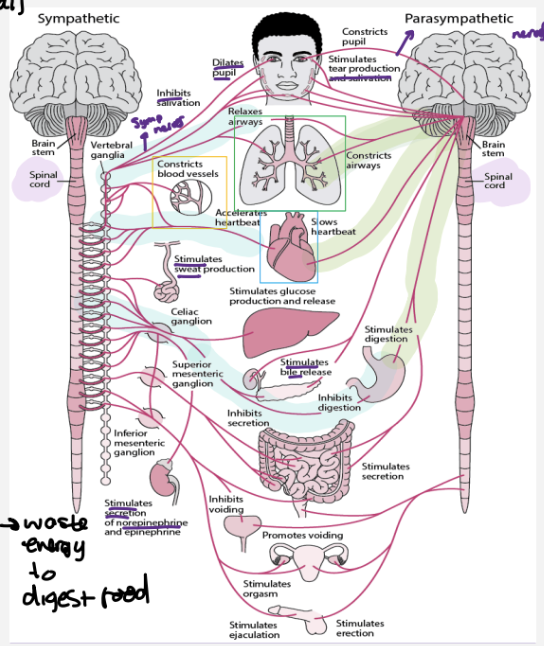
What are the 2 main branches the autonomic nervous system consist of ?
sympathetic branch :
increases heart rate
relaxes ( opens) airways
contracts most blood vessels - so increase blood pressure
also inhibits digestive processes - waste energy digesting food
happens during emergency/stressful situations
the fight or flight response
noradrenaline neurotransmitter
parasympathetic branch :
slows heart rate
usually when resting
contricts ( closes ) airways
also stimulates digestive processes
the rest and digest response
acetylcholine neurotransmitter
signals travel down spinal cords , have sympathetic nerves and parasympathetic = both equally control the body
What does the autonomic regulation of the cardiovascular system involve ?
involves
heart rate = 60-100
blood pressure
have cluster of cells that are myogenic
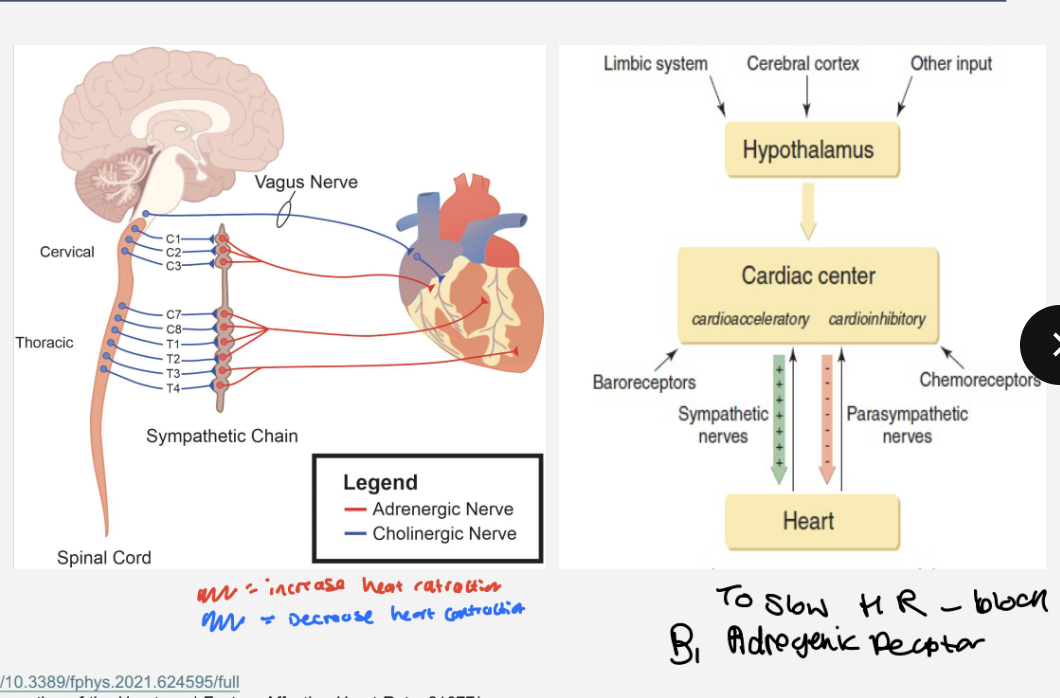
How does the regulation of the heart rate work ?
at rest the sinoatrial node sets that pace of the heart
the cardiac centre in the medulla modulates heart rate
Accelerate HR
activates the cardiac nerve
via the sympathetic response releases neurotransmitter noradrenaline
noradrenaline released acts on b1 adrenergic increasing the electrical impulses
Decrease HR
activates the vagus nerve
via the parasympathetic response releases acetylcholine neurotransmitter decreases rate of depolarisation
acetylcholine acts on M 2 muscarinic receptors
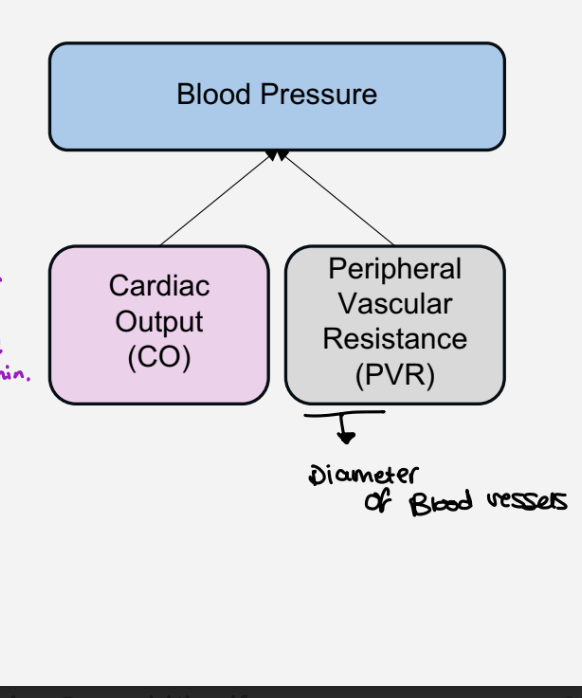
What is blood pressure ?
Pressure exerted by the blood upon the walls
of the blood vessels’
What factors does arterial blood pressure depend on ?
cardiac output (CO) - amount of blood pumped out of the left ventricle in 1 minute
Peripheral Vascular Resistance ( PVR) - diameter of blood vessels
Note - if CO or PVR increase ,BP will increase
What factors affect cardiac output ?
CO= Heart rate ( -70bpm) x Stroke Volume ( -70ml )
= 4900ml = 5L
Heart rate is controlled by the cardiac centre in the medulla
SV is controlled by hypothalamus and kidney ( adh , raas system )
stroke volume - volume of blood ejected from the left ventricle
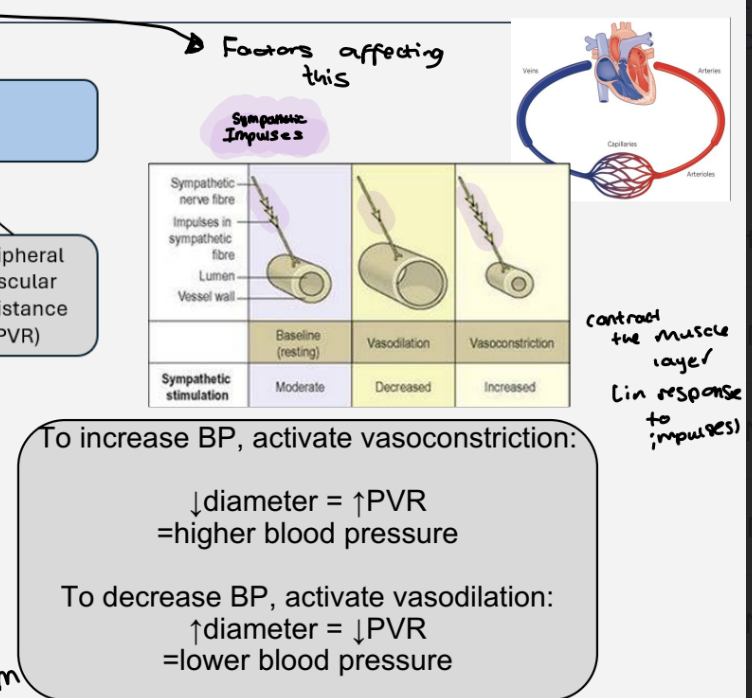
What factors affect PVR ?
the diameter of blood vessels
sympathetic impulses affect the diameter of the blood vessels
less impulses - vasodilation
more impulses - vasoconstriction
to increase BP ,activate vasoconstriction - decreased diameter ,increased pvr = higher blood pressure
to decrease Bp , activate vasodilation - diameter increased , decreased PVR = lower blood pressure
What are the 2 ways blood pressure can be controlled ?
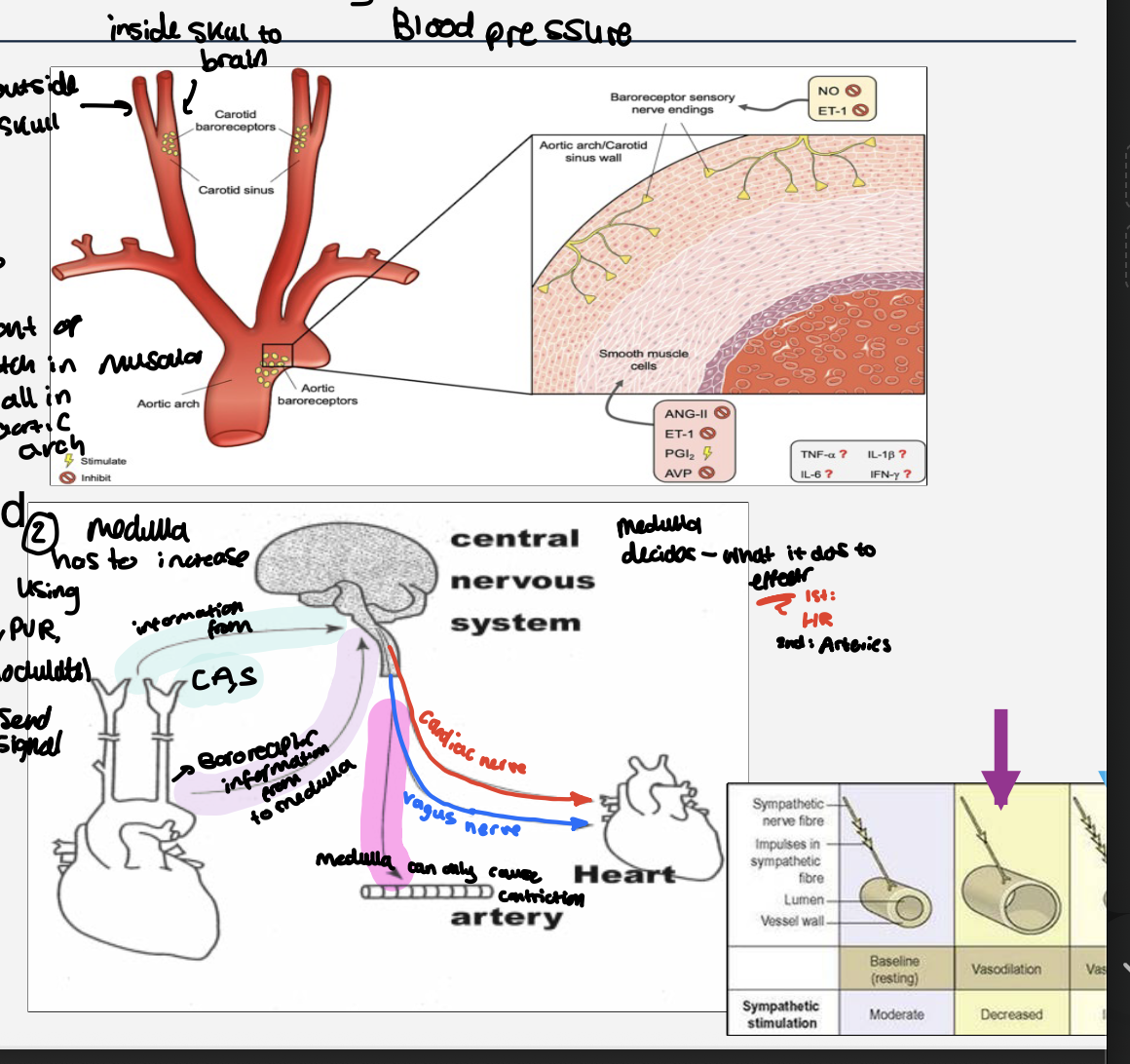
Arterial baroreceptors - the first way the body controls blood pressure ,short term
RAAS system ( renin - angiotensin - aldosterone - system ) - longer term
What is the first way used to control blood pressure ?
Arterial Baroreceptors
bp changes = stimulus ,
Detected by baroreceptors - neuron clusters in muscle wall:
aorta, carotid sinus ( carotid artery ) - sense the amount of stretch in muscular walls in the aortic arch
if blood pressure too low
if the stretch is lower than the range
medulla has to increase using co ,pvr
impulse sent to the cardiac centre
the cardiac accelerator nerve activated
heart rate increases , the cardiac output increase
PVR increases - vasoconstriction
note- medulla only can constrict
If blood pressure is too high
if the stretch is higher than the range
medulla sends the impulses to the cardiac centre
the vagus nerve activated
the heart rate decreases , the cardiac output decreases
PVR Decreases - vasodilation
What can control blood pressure ?
Increasing blood volume increases blood pressure
2 main ways of fluid balance ,modulate blood volume
Hypothalamus controls blood volume ( ADH)
Kidneys control blood volume ( RAAS)
kidneys - dehydration ,more conc ions ,detected by hypothalamus ,adh released ,kidney conserve water aquaporins in the walls open -take in more water
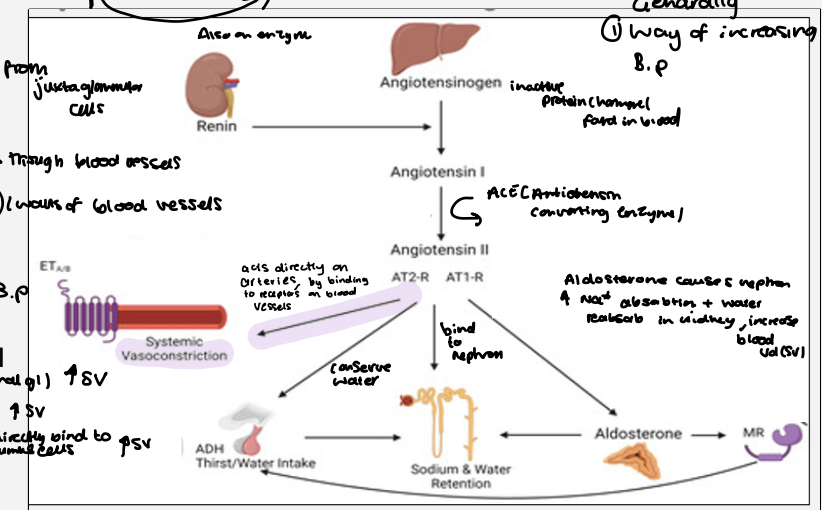
How can blood pressure been controlled by the RAAS System ?
raas- renin- angiotensin - aldosterone system
renin ( hormone) released from nephrons in juxtaglomerular cells in the kidney in response to low blood pressure ,low sodium in the kidney or sympathetic activation
renin converts angiotensinogen ( inactive hormone) into angiotensin ( active form) , this flows through the blood vessels in the lungs
it binds to angiotensin converting enzyme which converts angiotensin 1 into angiotensin 2 carried around the body
angiotensin 2 increases blood pressure by :
binding to receptors in arteries causing systemic vasoconstriction increasing pvr
binds to receptors on adrenal glands - aldosterone released increased na absorption and water reabsorption in kidney increasing sv
Directly binds to nephron increasing sodium and water reabsorption in kidney , increasing SV
Adh release from hypothalamus cells conserving water
overall - RAAS raises blood pressure and restores circulating volume
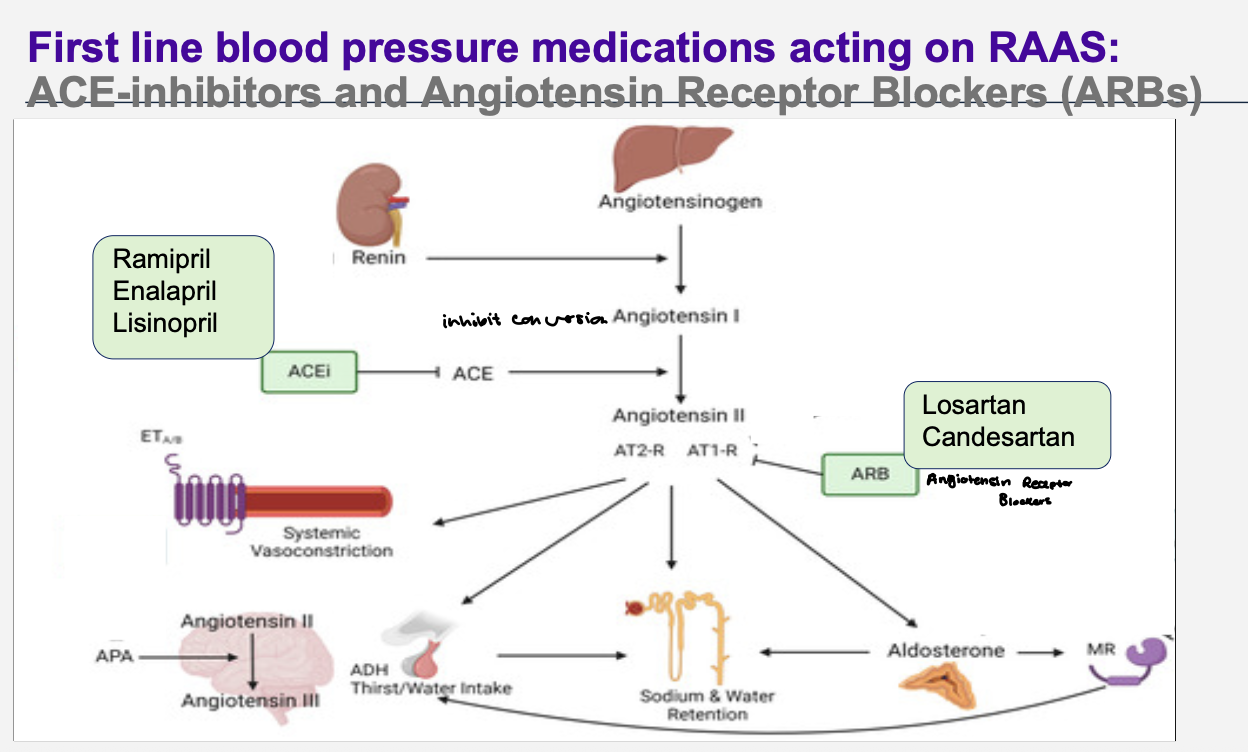
What are the drugs used that affect the raas system to lower blood pressure ?
Describe the regulation of thyroid hormones - negative feedback
thyroid hormone- controls metabolic rate of every cell in the body
Early morning - hypothalamus releases TRH (thyrotropin-releasing hormone)
• TRH stimulates pituitary to release thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH)
• TSH stimulates thyroid to release TH (T4/T3- different forms)
• High TH inhibits TRH and TSH
• TH has stable half life (T3 1 day; T4 7 days) so levels remain relatively stable
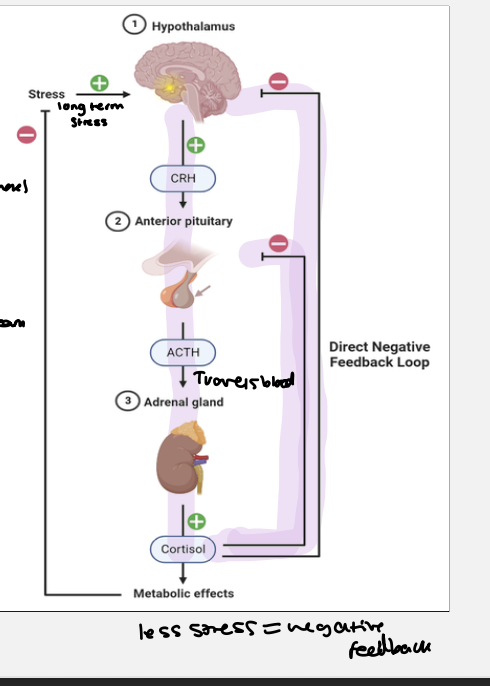
Describe the regulation of cortisol - negative feedback
linked to circadian rhythm
• Early morning CRH ( corticotropin - releasing - hormone) released
• Stimulates ACTH ( adrenocorticotropic hormones) from the anterior pituitary
• ACTH stimulates adrenal glands (on top of kidney)
• Adrenal gland releases Corticosteroid hormones (mainly
Cortisol)
• Cortisol causes increased glucose, protein and lipid
availability in stressful situations, providing more nutrients
for energy
• When cortisol levels rise during the morning, cortisol
inhibits CRH and ACTH
• Cortisol levels fall slowly, cycle repeats
• This negative feedback loop is known as the Hypothalamic-
Pituitary-Axis (HPA)