Mirrors
1/4
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
5 Terms
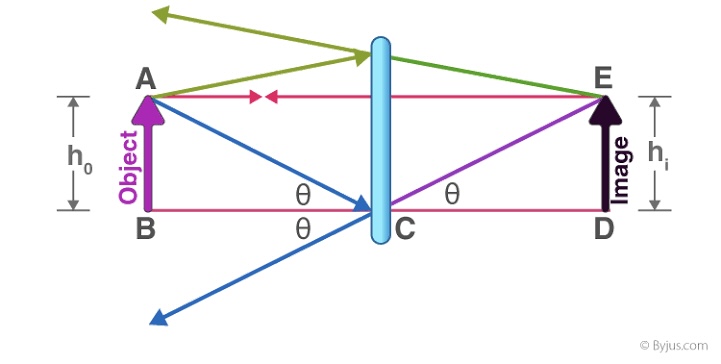
What type of image does a plane mirror form?
Virtual, upright, same size as the object, and located an equal distance behind the mirror
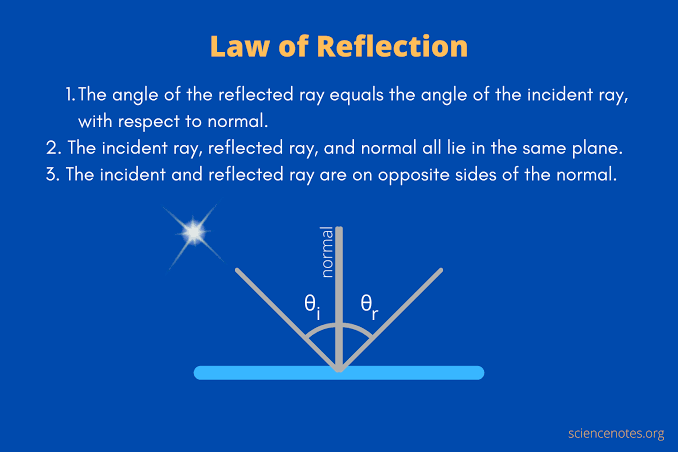
What is the rule the law of reflection states?
Angle of incidence equals angle of reflection, both measured from the normal.
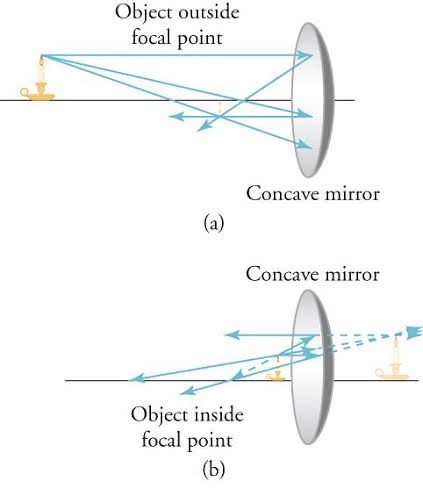
What happens when an object is placed outside the focal length of a concave mirror?
It creates a real, inverted image (outsize). If inside the focal length, the image is virtual, upright, and magnified .
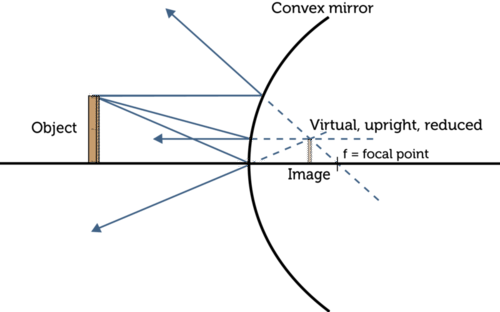
What kind of images do convex mirrors always produce?
Virtual, upright, and smaller (diminished) images.
What is the mirror equation, and how is magnification (m) defined?
Mirror equation: 1/f = 1/do + 1/di. Magnification: m = hi/ho = –di/do (negative = inverted, positive = upright) .
