7. Epithelial Tissue
1/35
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
36 Terms
Epithelial tissue
-lines the surface of the body and cavities
-responsible for the formation of glands
-Faces Lumen without cells´
Epithelial tissue Functions
-Secretion, Protection and Absorption
-sensory
What is always below epithelial tissue
Connective Tissue
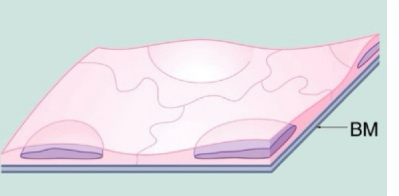
Basement membrane
specialized basal surface that separates it from the underlying connective tissue
Basal Membrane components
basal laminate + reticular lamina
Apical Surface and functions
Surface of Epithelium, secretion, absorption and movement of contents.
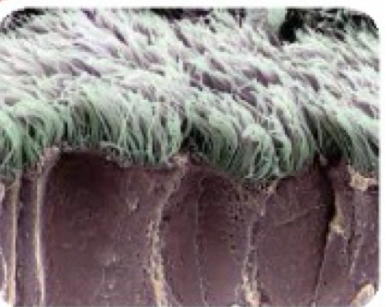
Cilia
-hairlike extensions of the apical plasma membrane
-contains atonement → motility
-respiratory tract and female reproductive system
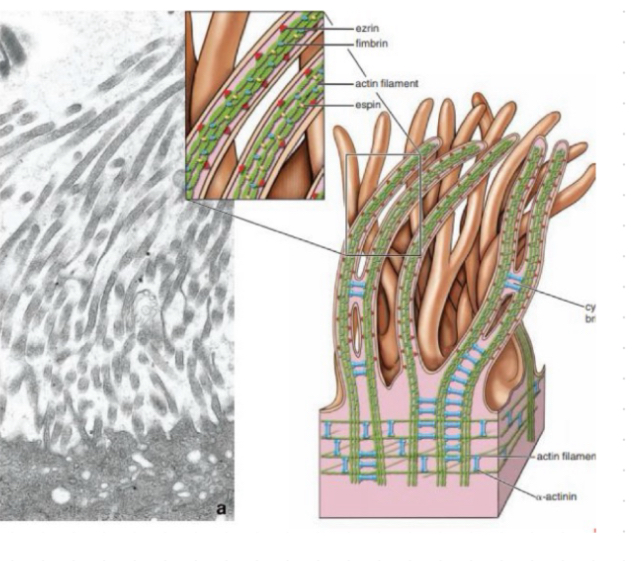
Microvilli:
-fingerlike cytoplasmic projections
-apical surface of most columnae epithelial cells
-increase absorption
-not motile
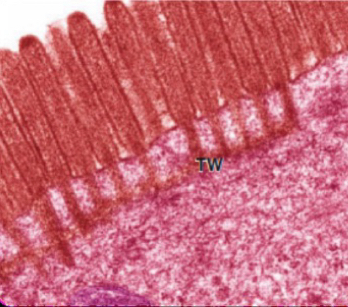
Stereocilia
-unusually long, immobile microvilli
-inner ear and male reprdoctive part
Lateral surfaces
in contact with neighboring cells.
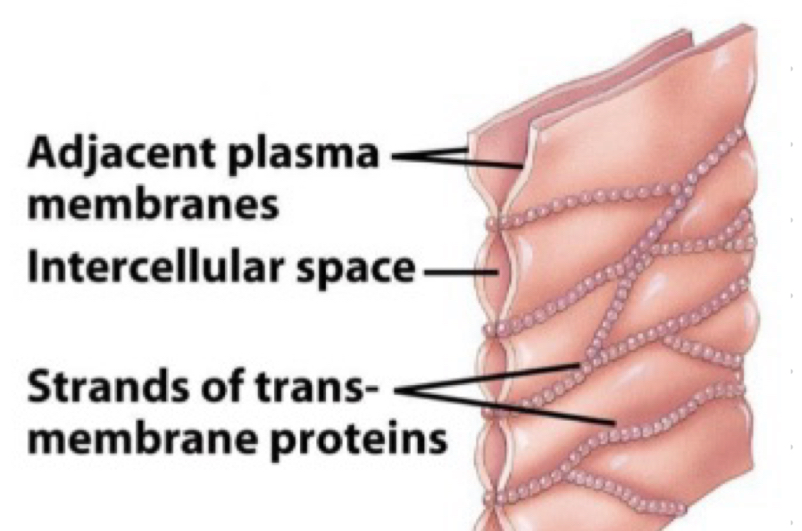
Tight junction
-near apical surface
-seal off intercellular space
-keep cell polarity
-keep epithelial cells tightly attached
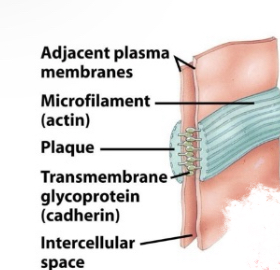
Adherens junctions - belt desmosome
-anchoring points for cytoskeleton
-Provide mechanical attachment via actin filaments - stabilize
-single continuous layer
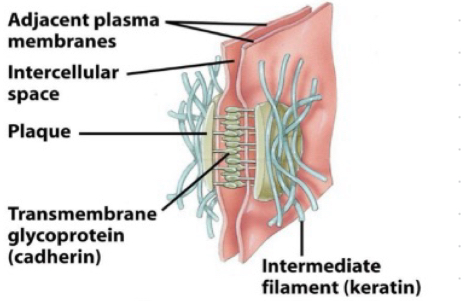
Desmosomes
-Strong spot-like adhesions; connect intermediate filaments.
-two dense attachment plaques
-transmembrane glycoprotein
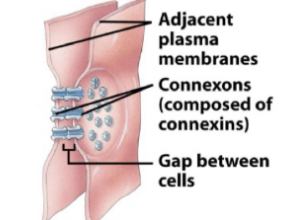
Communicating junctions
-Allow communication and ion exchange between cells.
Basal surface
attached to the basement membrane

Hemidesmosome
-adhering junction of basal plasma to basement membrane
-attach of epithelial cells to basement membrane
Classification by Embryonic Origin: Ectoderm
Skin and glands
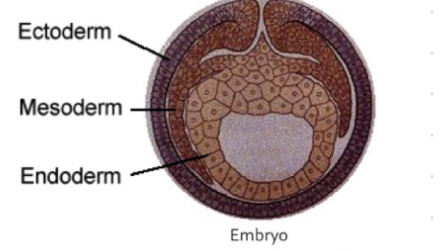
Classification by Embryonic Origin: Mesoderm
Endothelium and Mesodelium
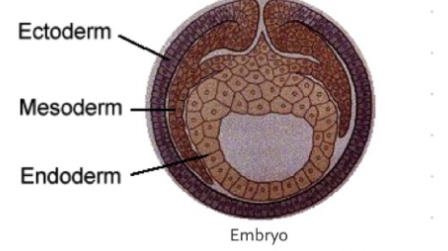
Classification by Embryonic Origin: Endoderm
Gastrointestinal coatingand respiratory coating
Coating epithelium
Continuous sheet, one or several layers, covering body surfaces.
Glandular epithelium
participates in the secretion of molecules, forming structures called glands.
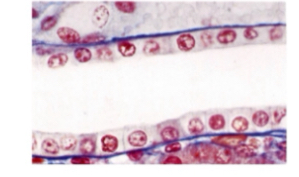
Simple
-single layer of cells
-Little protection
-cilia and micrvolli
Simple cuboid
-single layer of cells
-squares with visible nucleus
Simple flattened
-single layer
-flattened cells
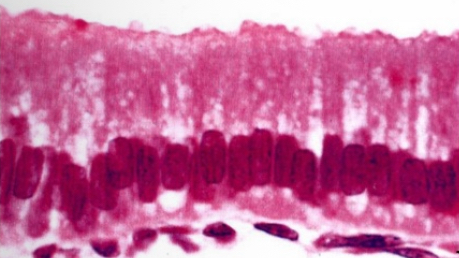
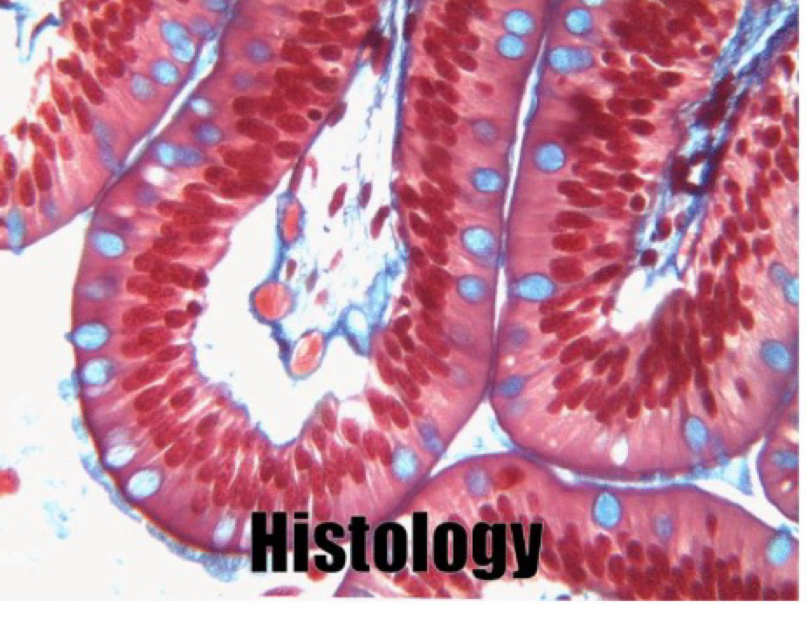
Simple columnar / cylindrical
-single layer
-column = säulen
Stratified
-two or more layers
-protective function
-basal cells cuboidal

Stratified squamous non keratinized
-most common
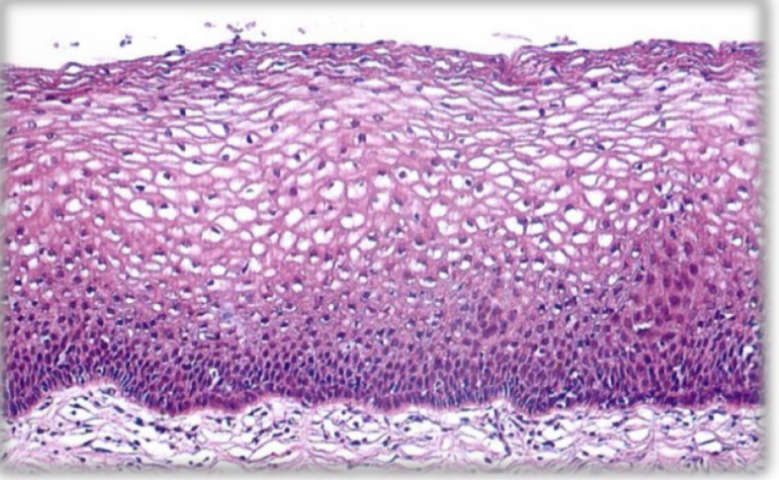
Stratified flattened or squamous non keratinized
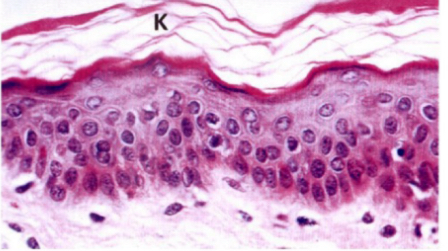
Stratified keratinized squamous
-additional protective keratin layer
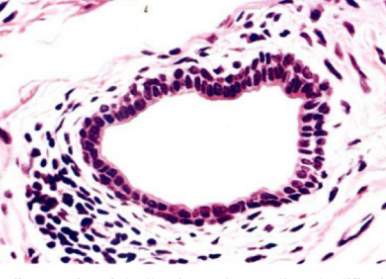
stratified cuboid
-two or three layers Of cuboidal cells
-robust lining
-.rare
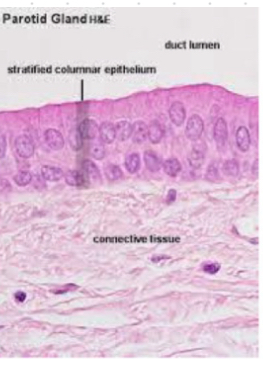
Stratified Columnar or cilyndrical
-cells are columnar

Pseudostratified
-cells rest at Basal membrane
-nuclei near basal membrane
-goblet
Cilia + many layers of cell
Pseudodostratified
Respiratory truck epithelium
Pseudostratified
Keratin on surface + dark line
99% Skin
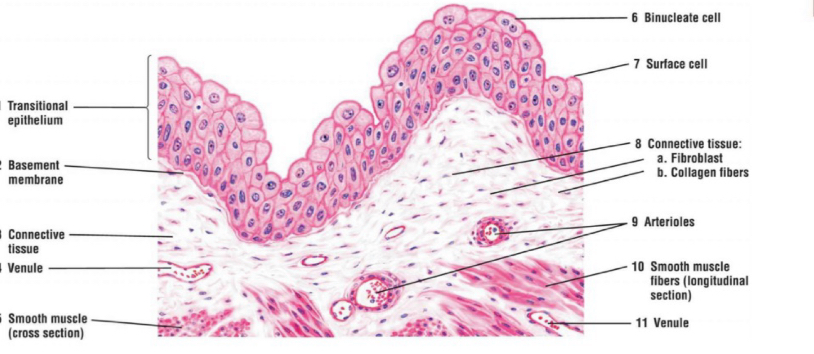
Stratified Transitional
-polygonal cells
-wave