Chapter 29 Seedless plants
1/25
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
26 Terms
Evolution
Genetic change in a population of
organisms over time
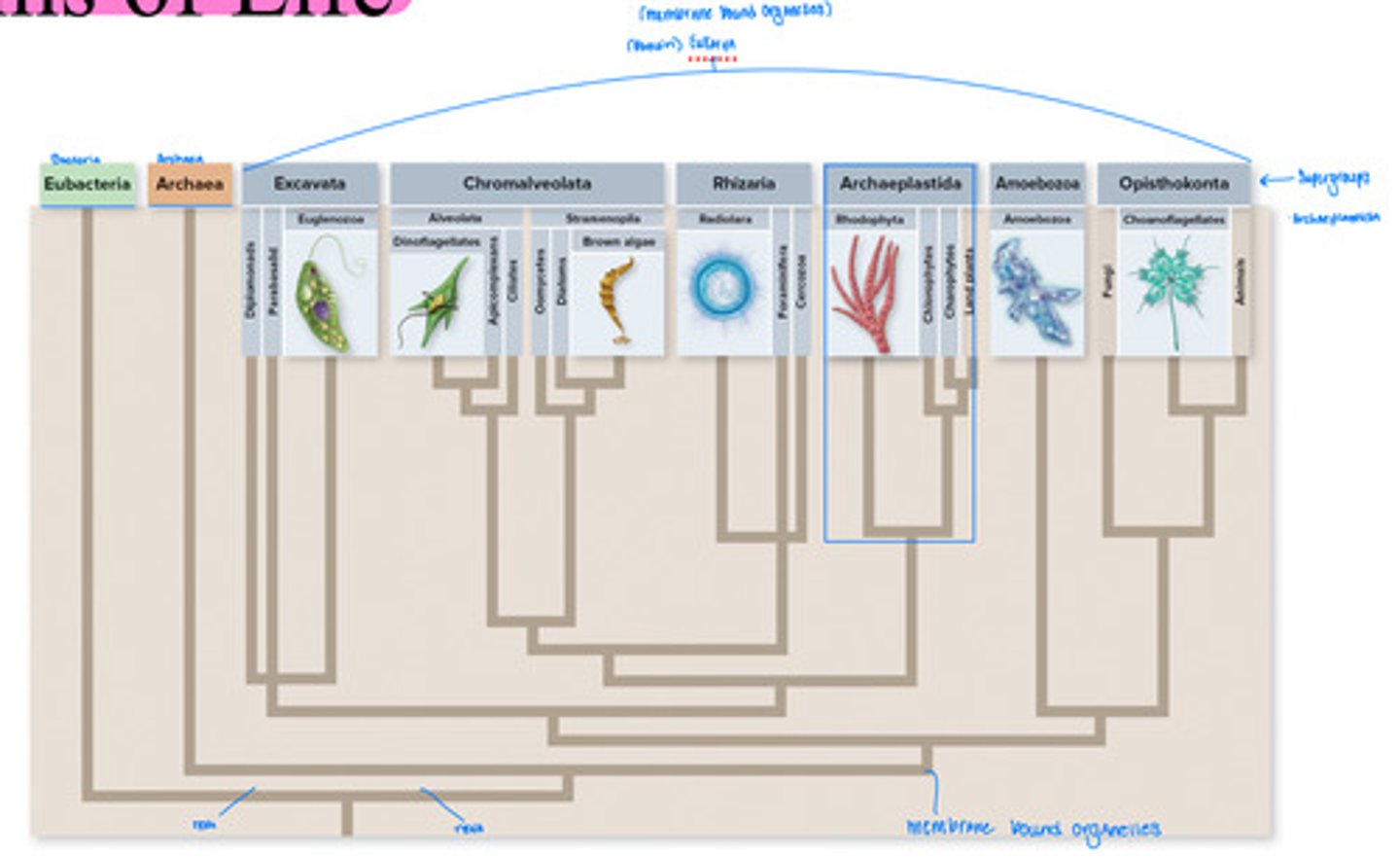
Domains of life
All supergroups fall under the domain of Eukarya. They are all membrane bound organisms. We are focusing on supergroup archaeplastida.
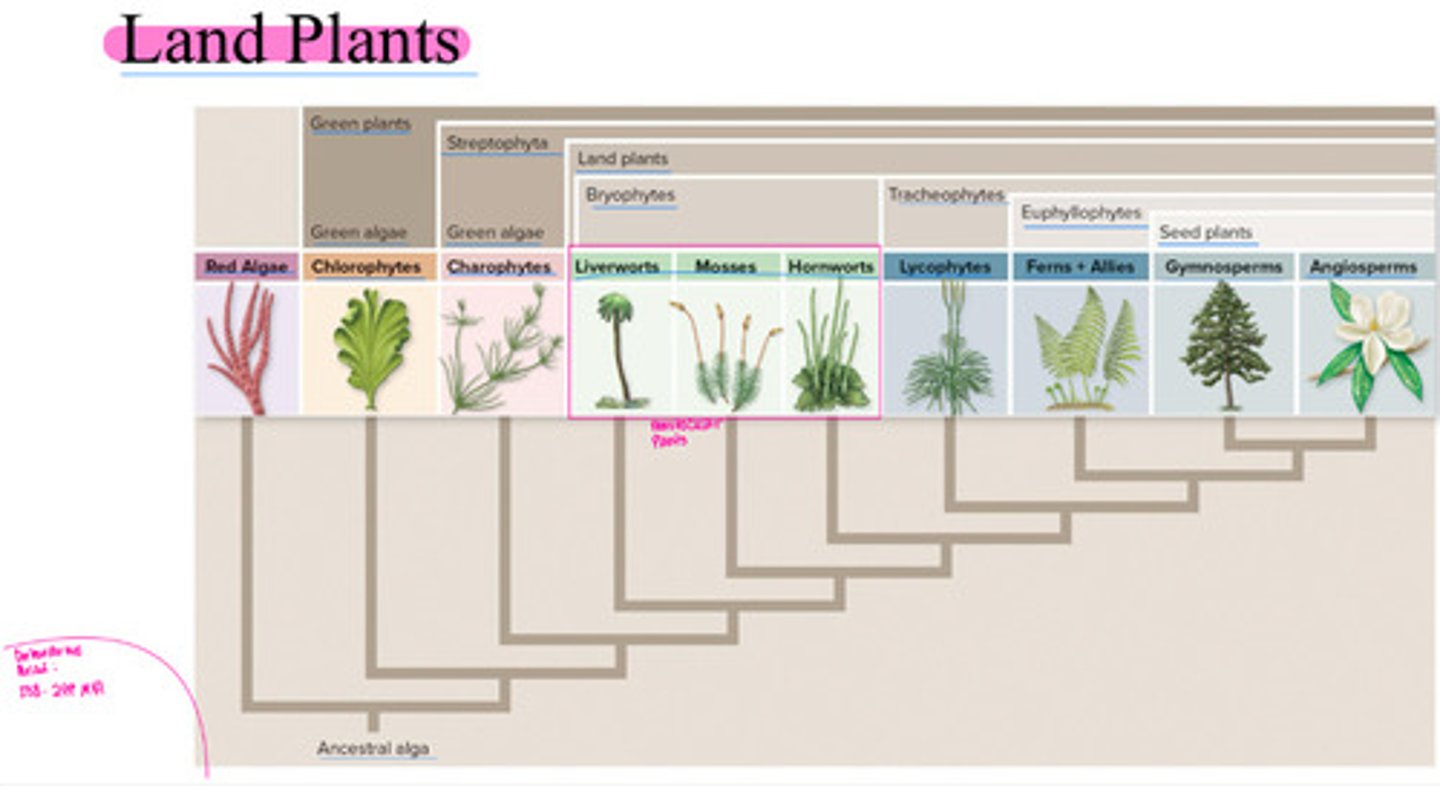
Land plants
Domain:
Supergroup:
Kingdom:
Know this taxonomy!!!
Domain: Eukarya
Supergroup: Archaeplastida
Kingdom: Plantae
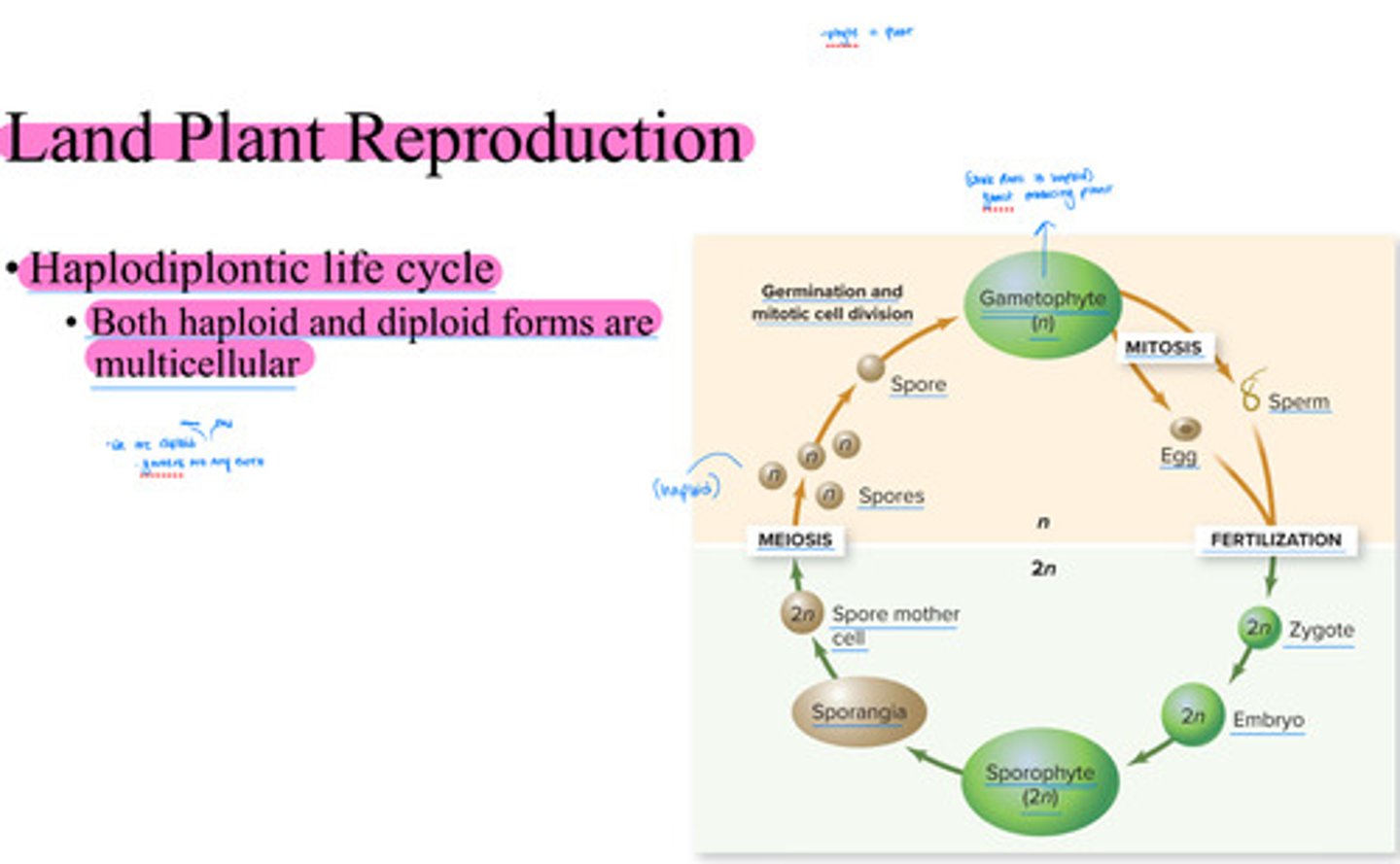
Land Plant Reproduction
• Haplodiplontic life cycle
• Both haploid and diploid forms are
multicellular
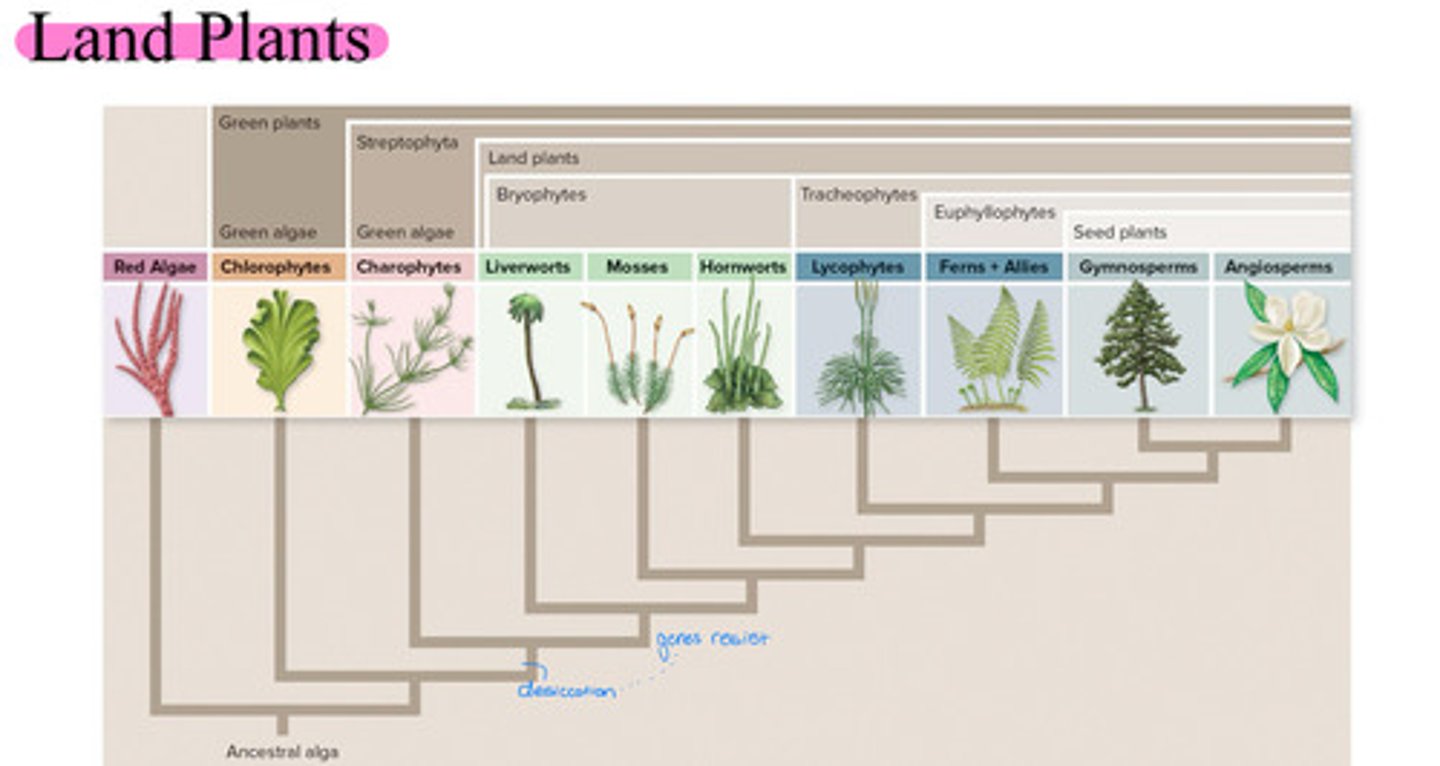
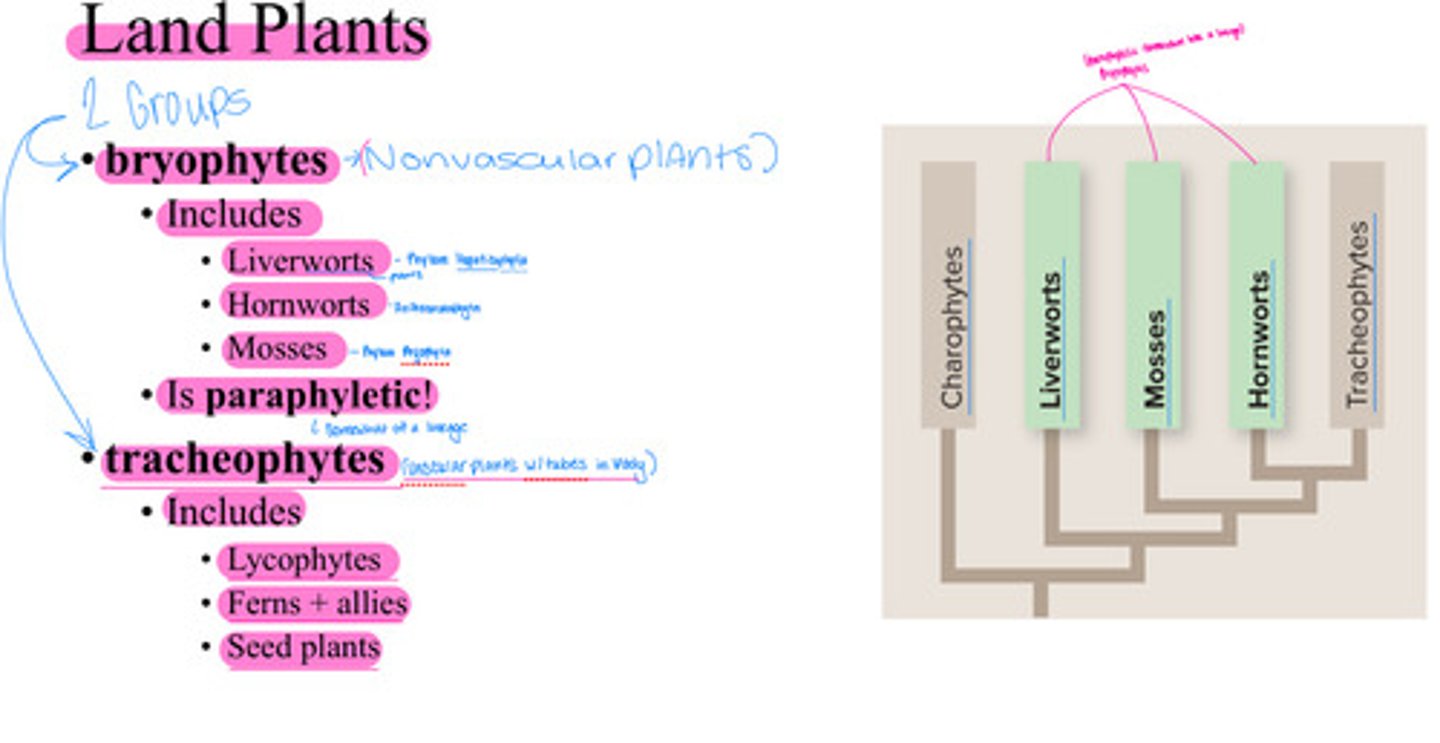
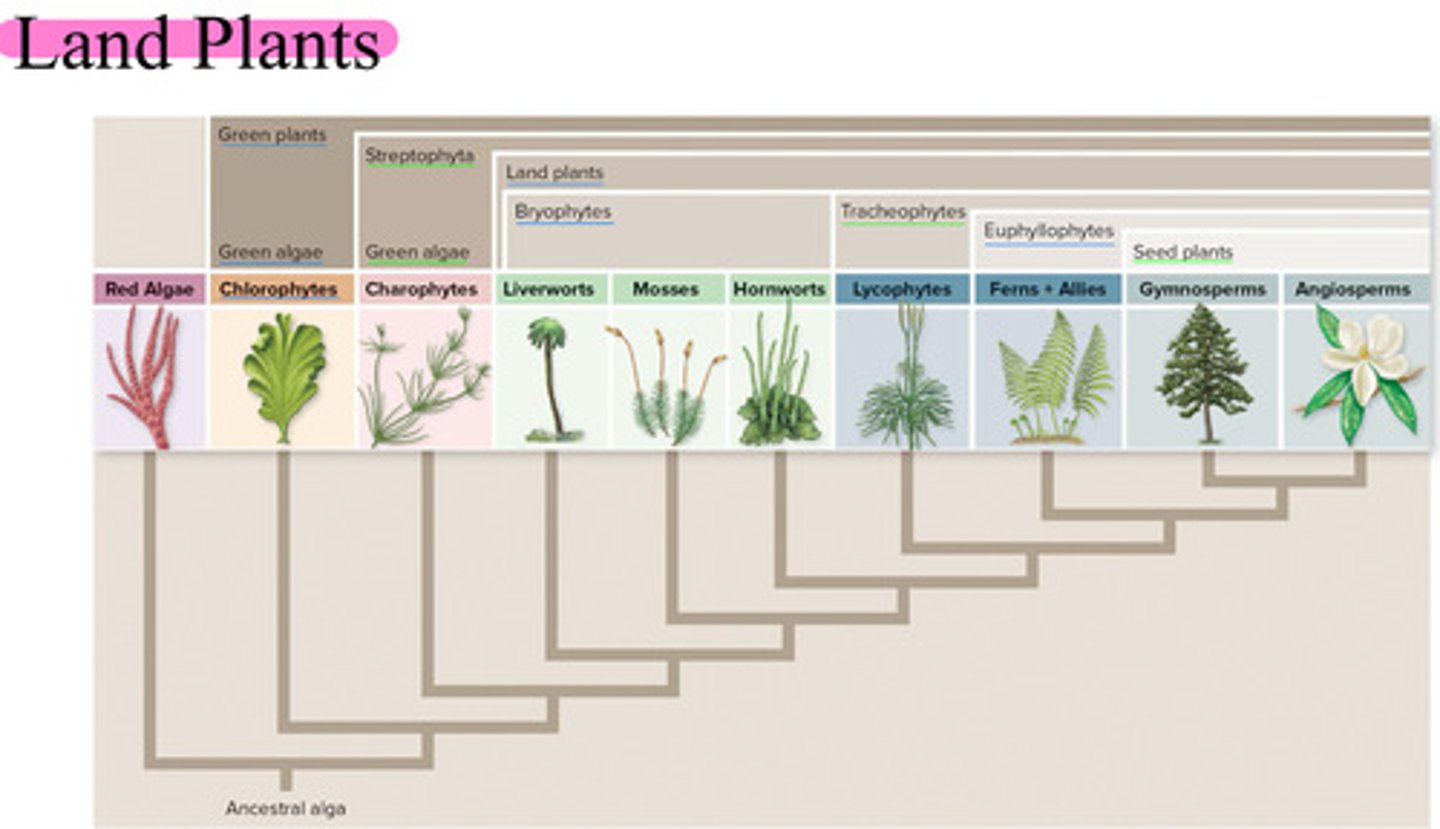
Land Plants
• bryophytes
Includes:
• Liverworts
• Hornworts
• Mosses
• Is paraphyletic!
• tracheophytes
Includes:
• Lycophytes
• Ferns + allies
• Seed plants
Land Plants
• bryophytes ( non-vascular plants )
Includes:
• Liverworts - Phylum Hepaticophyta
• Hornworts - Phylum Anthoceratophyta
• Mosses - Phylum Brophyta
• Is paraphyletic! ( somewhat of a lineage )
• tracheophytes ( vascular plants with tubes in their bodies )
Includes:
• Lycophytes
• Ferns + allies
• Seed plants
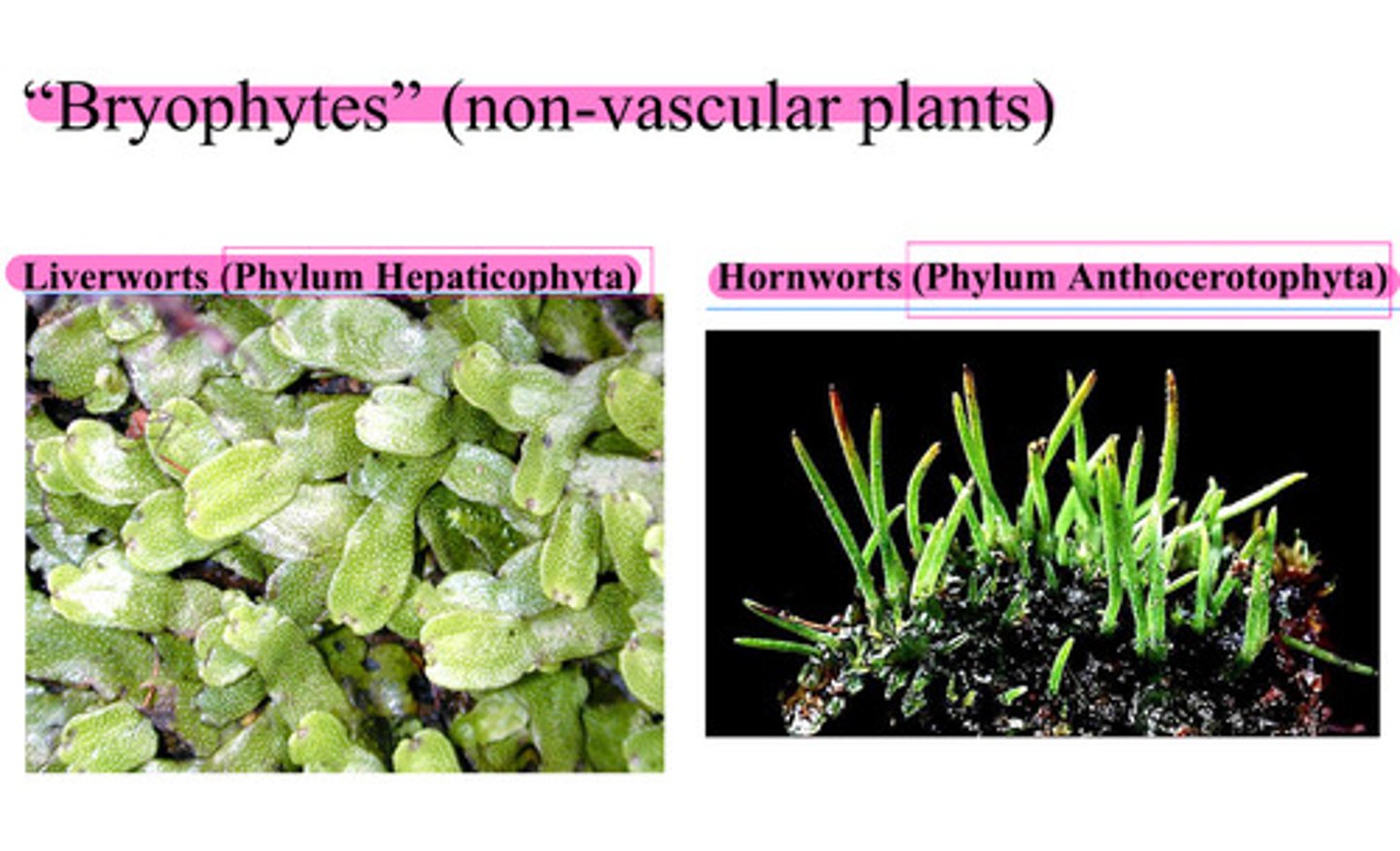
"Bryophytes" (non-vascular plants)
- Liverworts (Phylum Hepaticophyta)
- Hornwarts ( Phylum Anthocerotophyta )
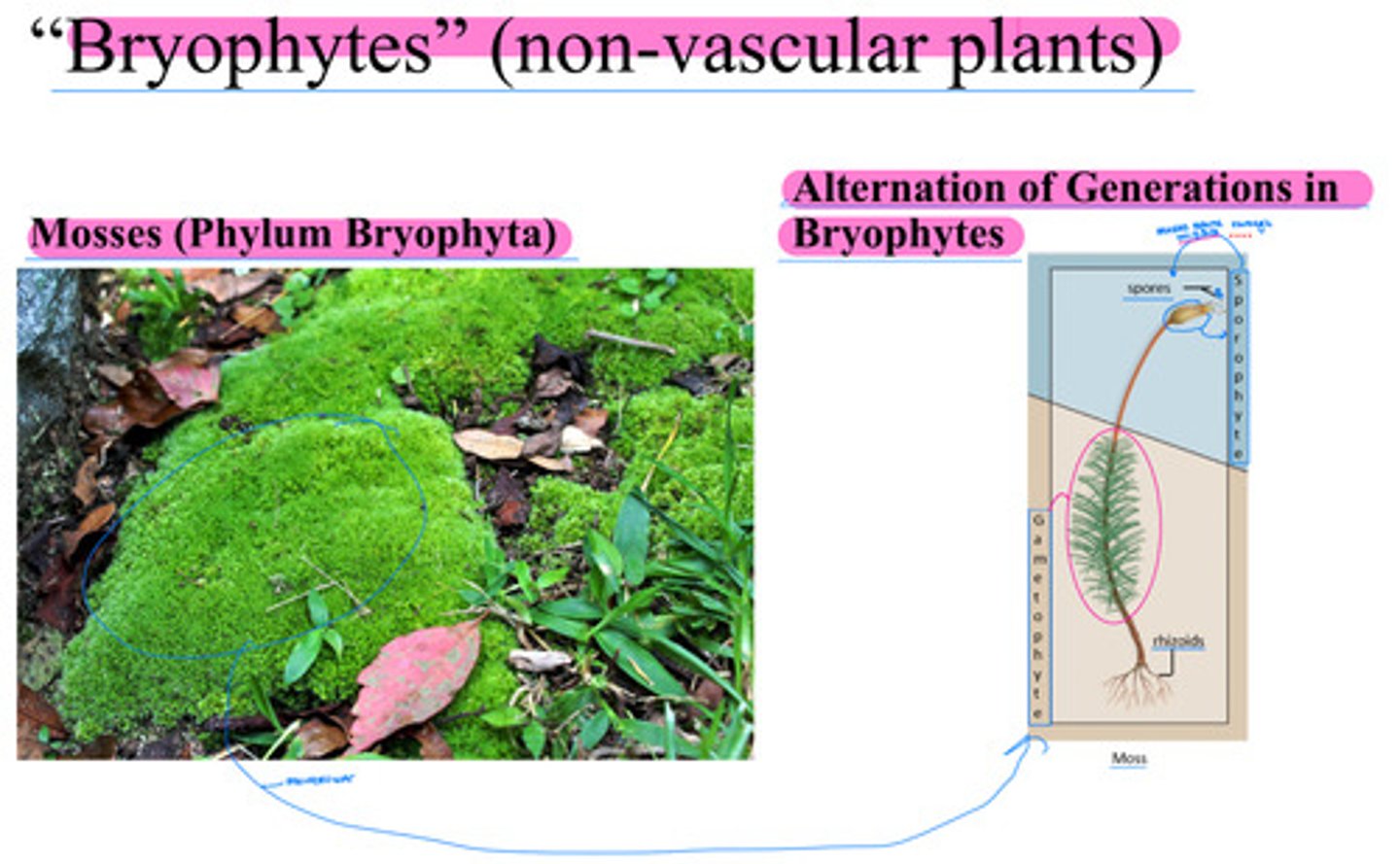
"Bryophytes" (non-vascular plants)
- Mosses (Phylum Bryophyta)
- Alternation of Generations in
Bryophytes
See notes written on slide
"Bryophytes" (non-vascular plants)
Sphagnum moss - holds water well
- used for landscaping / retaining water
Peat moss - ( Dead ) this is the moss she was telling us about the dead bodies being found in.

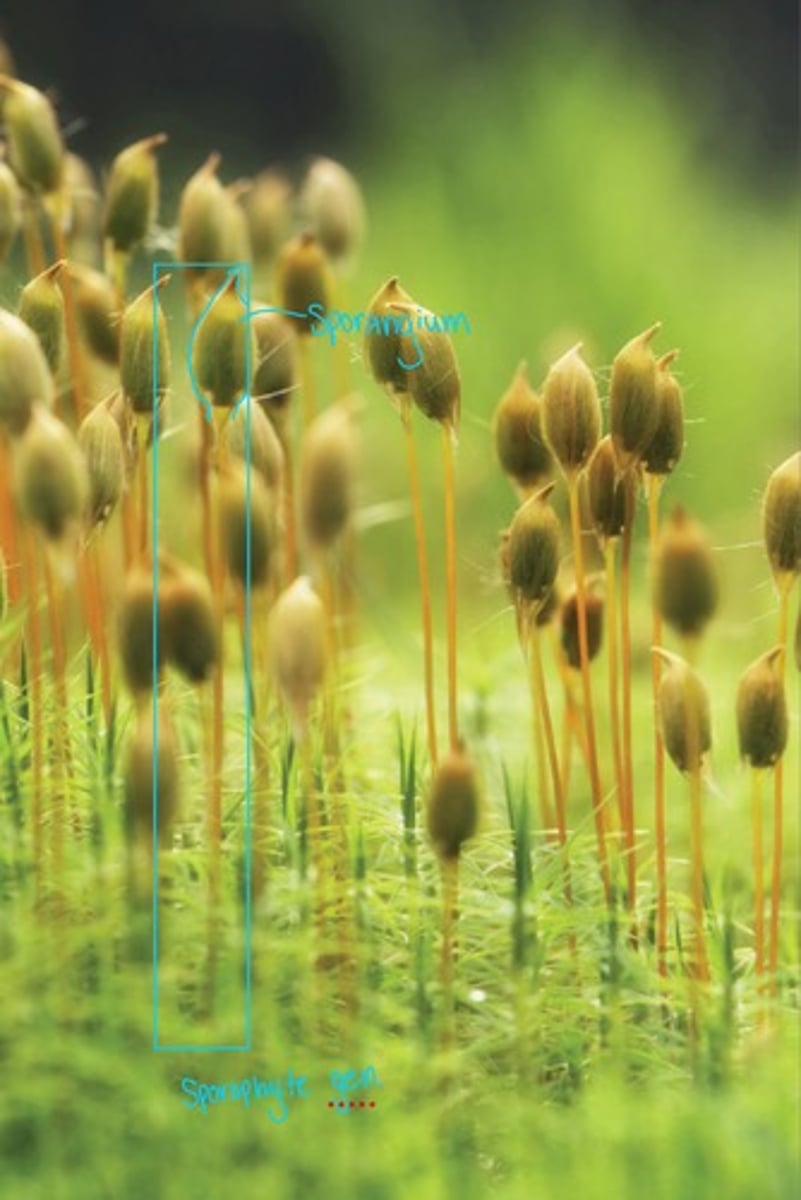
Moss Reproduction
• Archegonium
• Antheridium
• Sporangium
• Rhizoids
Moss Reproduction
• Archegonium - ( females ) produce eggs
• Antheridium - ( males ) produce sperm ( flagellated )
^ both form the gametagaria ( will house spores )
• Sporangium - makes spores. Is 2n ( diploid )
• Rhizoids - not true roots, act as anchors
* mosses don't have vascular tissue
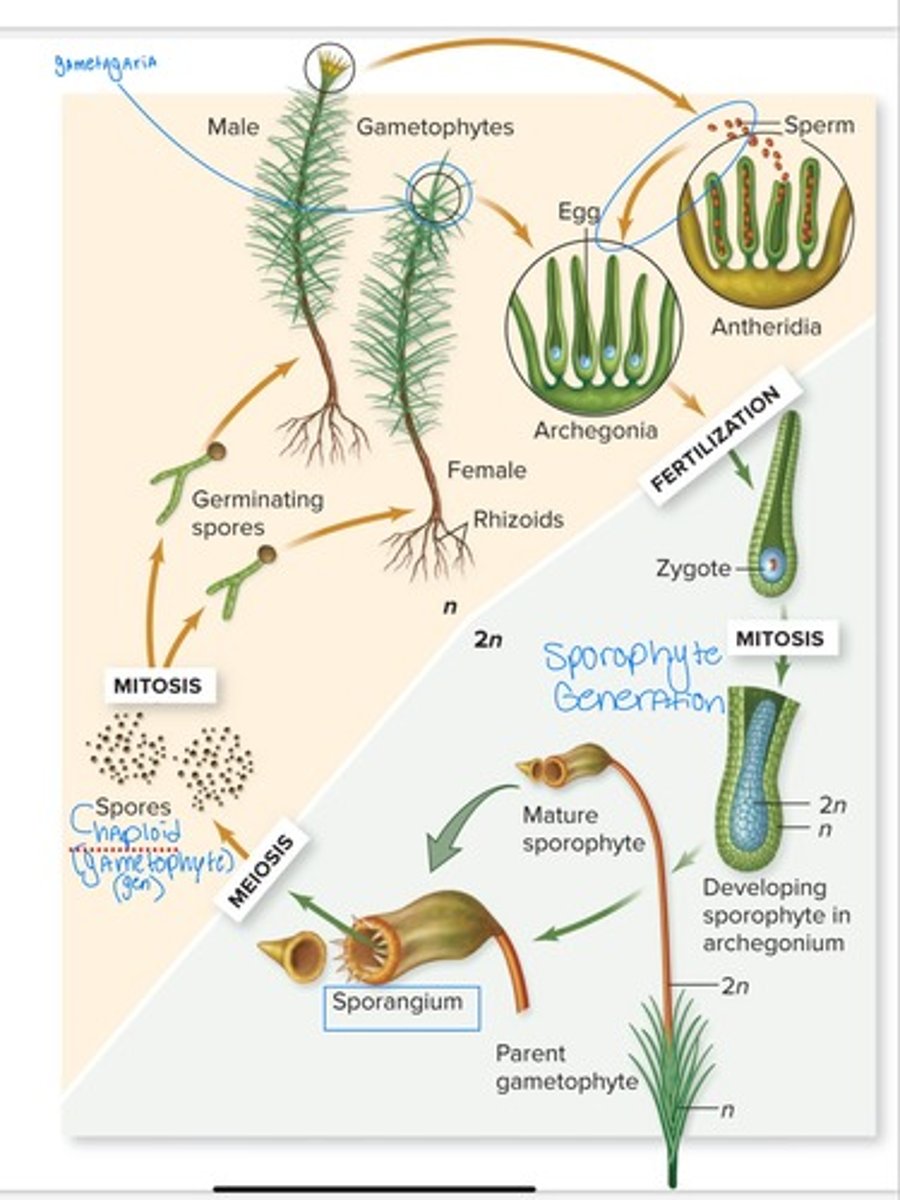
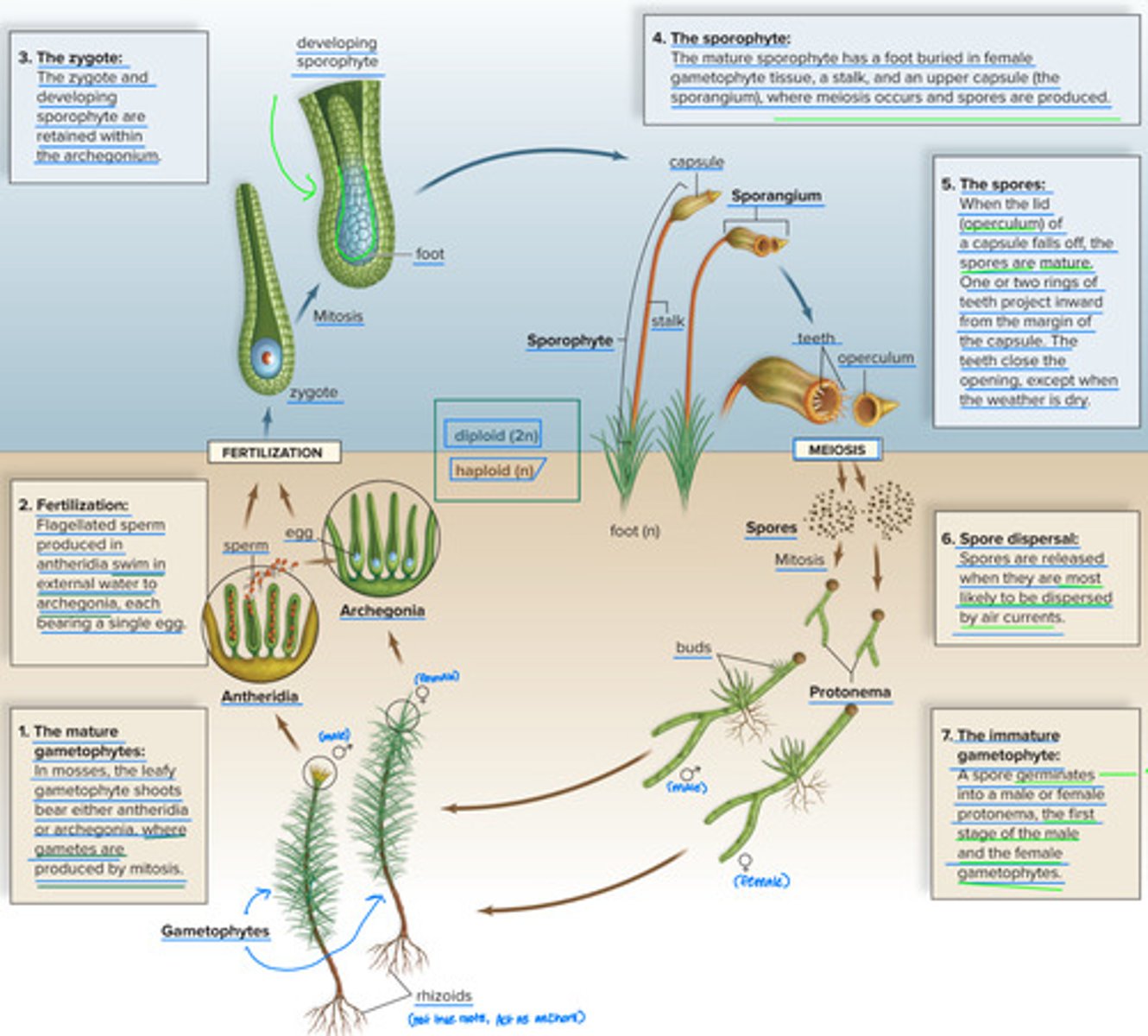
Moss reproduction, broken down step-by-step
1. The mature. Gametophytes :
In Mosses, the leafy gametophyte shoots bear either antheridia or archaegonia. Where gametes are produced by mitosis.
2. Fertilization :
Flagellated sperm produced in antheridia swim in external water to archegonia , each bearing a single egg.
3. The Zygote :
The zygote and developing sporophyte are retained within the archegonium .
4. The sporophyte :
The mature sporophyte has a foot buried in female gametophyte tissue, a stalk, and an upper capsule ( the sporangium ), where meiosis occurs and spores are produced.
5. The spores :
When the lid ( operculum ) of a capsule falls off, the spores are mature. One or two rings of teeth project inward from the margin of the capsule, the teeth close the opening, except when the weather is dry.
6. Spore dispersal :
Spores are released when they are most likely to be dispersed by air currents .
7. The immature. Gametophyte :
*see slide, ran out of words here.
What is this structure?
Generation : sporophyte
Structure : sporangium

Land Plants
Land plants are adapted for terrestrial life
• Vascular plants = tracheophytes
• Vascular system made of
• Xylem
• Phloem
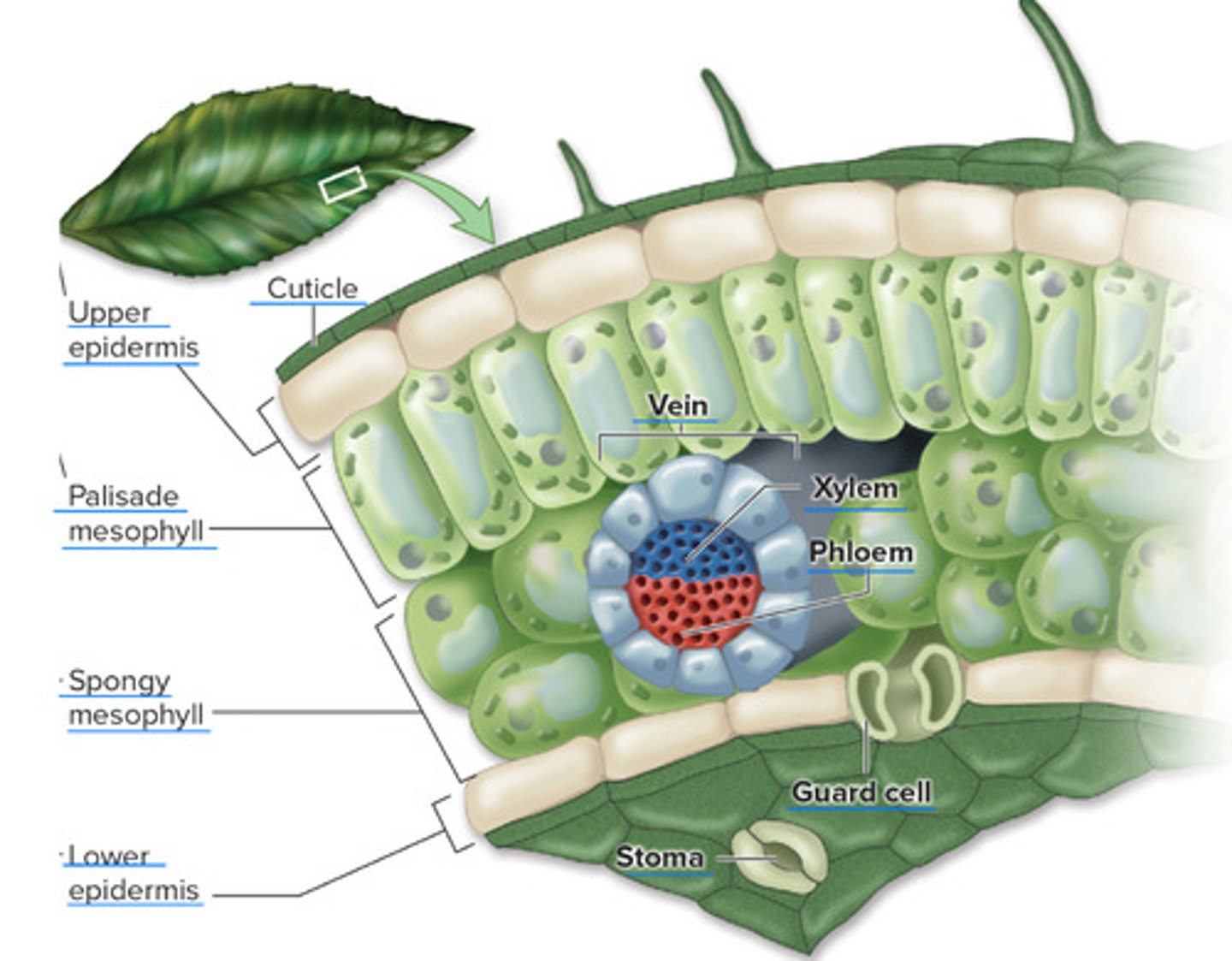
Land plants are adapted for terrestrial life
• Vascular plants = tracheophytes - these can grow to a certain height due to their piping to reach sunlight / bryophytes can’t grow as high
• Vascular system made of : ( 2 special tissues )
• Xylem - transport water ( moves water from roots to the rest of the plant )
• Phloem - transport sugar, nutrients, and hormones through the plant
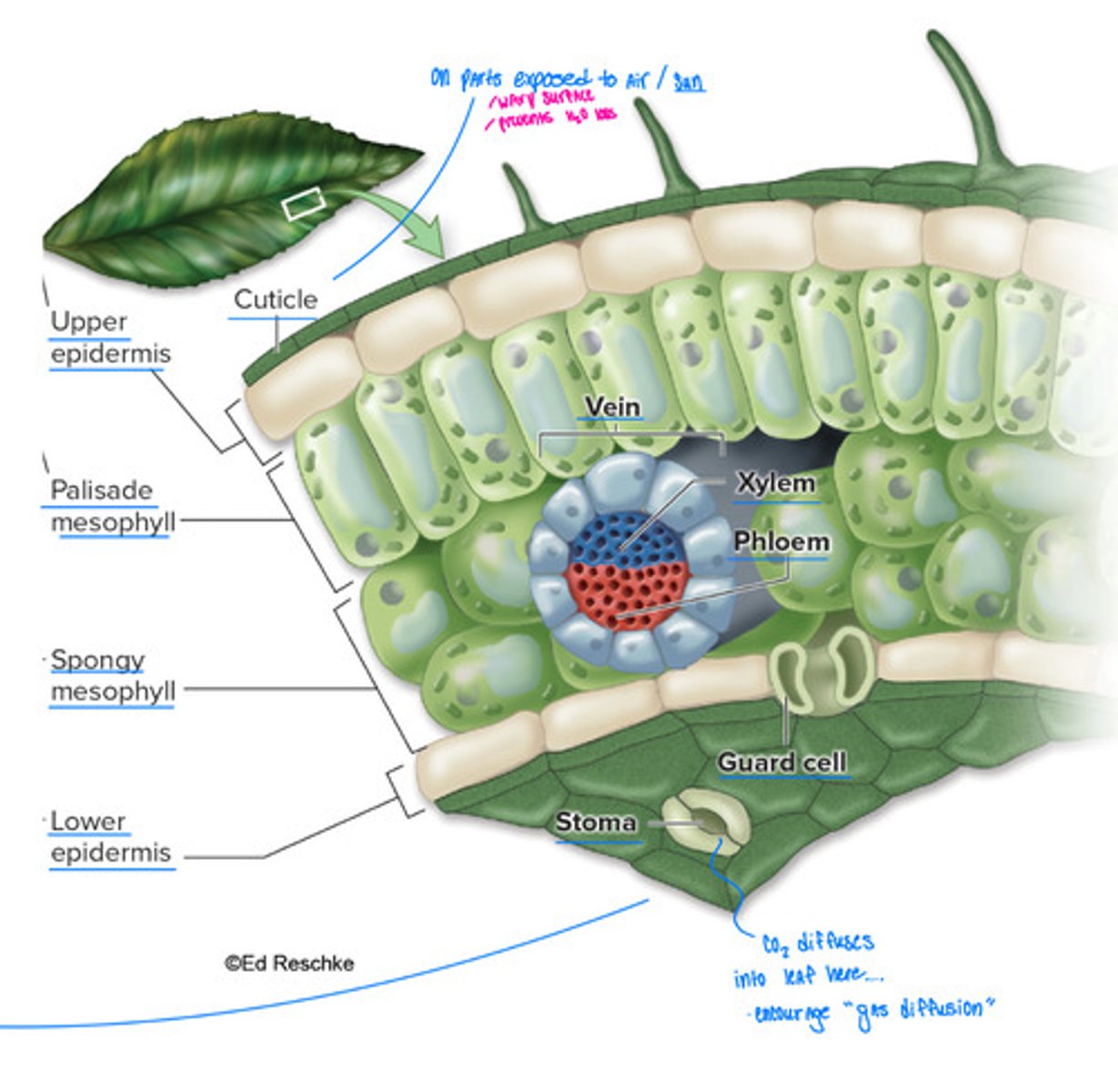
Land plants are adapted for terrestrial life
- Impermeable cuticle on parts exposed to air ( waxy surface, prevents H2O loss )
- stomata - tiny openings on leaves and stems, facilitate gas diffusion.
Review: Alternation of Generations
• Sporophyte = spore plant
• Sporangia cells undergo meiosis
• Produces haploid spores
• Gametophyte = gamete plant
• Produces gametes
• Names tell you the reproductive
cells each generation produces
Review: Alternation of Generations
• Sporophyte ( big leafy part / undergoes meiosis ) ( creates spores ( 1n )= spore plant
• Sporangia cells undergo meiosis
• Produces haploid spores
• Gametophyte ( dominant generation in bryophytes ) = gamete plant
• Produces gametes
• Names tell you the reproductive
cells each generation produces
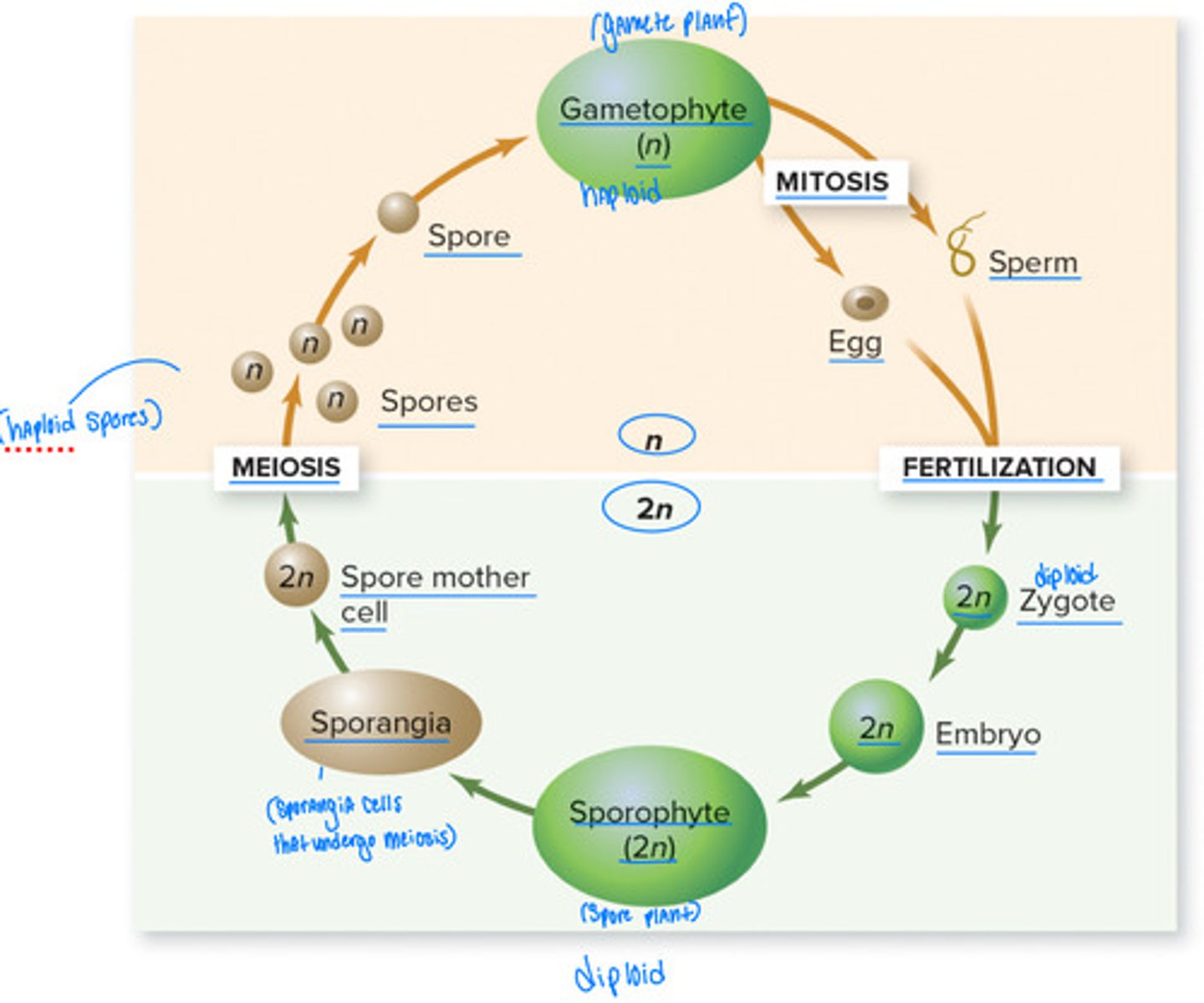
Tracheophytes = Vascular plants
• Dominant sporophyte generation
• What is the dominant generation in
Division “Bryophyta”?Gametophytes
• Three groups of tracheophytes
• Phylum Lycophyta
• Phylum Pterophyta
• Seed plants
Tracheophytes
• Stems evolved first, then roots
• Roots evolved twice in plants!
• Leaves evolved twice in plants!
Tracheophytes
• Stems evolved first, then roots
- Roots anchor plant in substrate
- roots help meet H2O demand, which results in larger plants
• Roots evolved twice in plants!
- lycophytes - lycophyta diverged before roots evolve
• Leaves evolved twice in plants
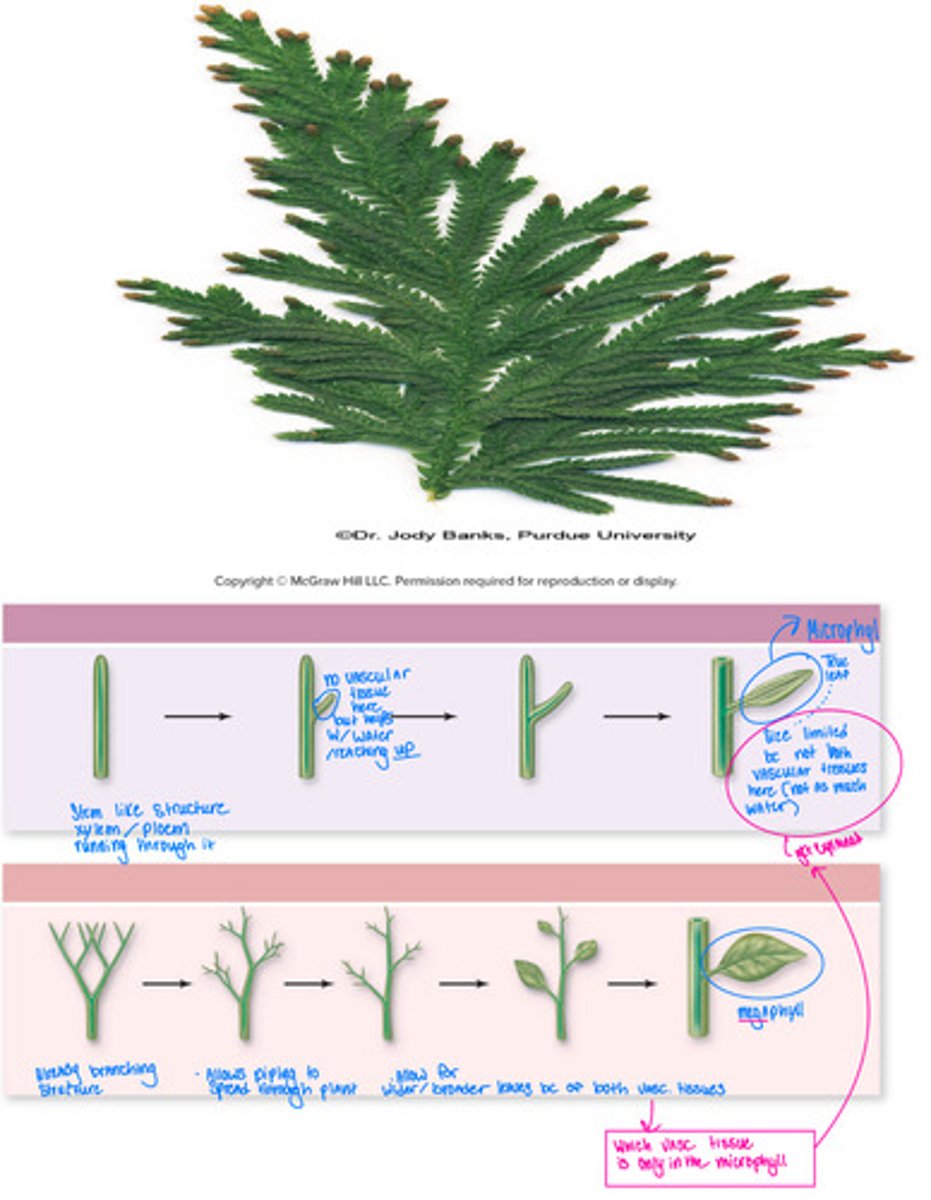
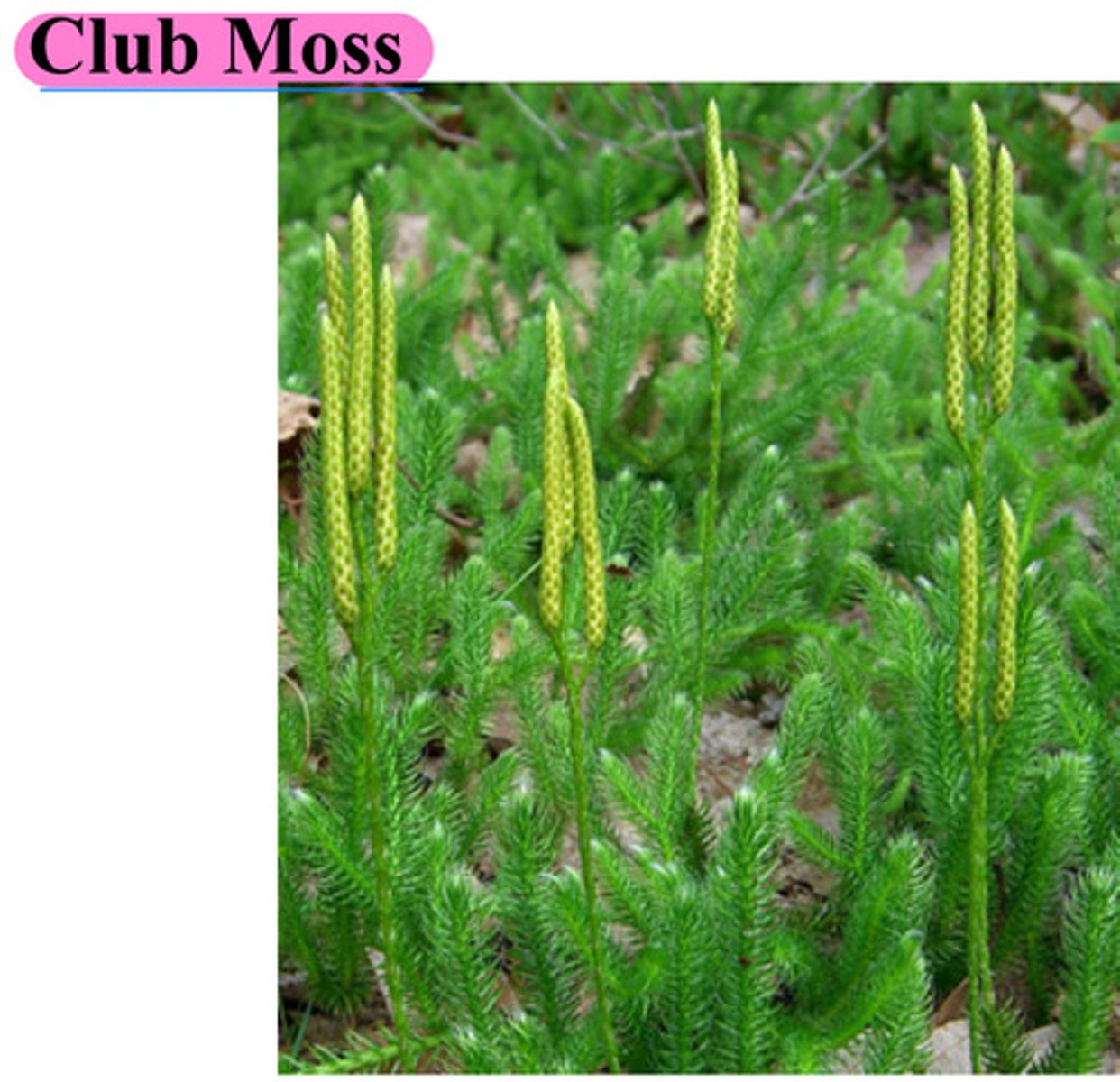
Phylum Lycophyta (vascular plants)
Club Moss
Evolution of Vascular Tissues
• Tracheophytes =
• Vascular tissues create:
• Stems
• Roots
• Xylem
• Phloem
Phylum Lycophyta (vascular plants)
Club Moss
Evolution of Vascular Tissues
• Tracheophytes =
• Vascular tissues create:
• Stems
• Roots
• Xylem - transports water
• Phloem - transports sugar

Phylum Lycophyta (vascular plants)
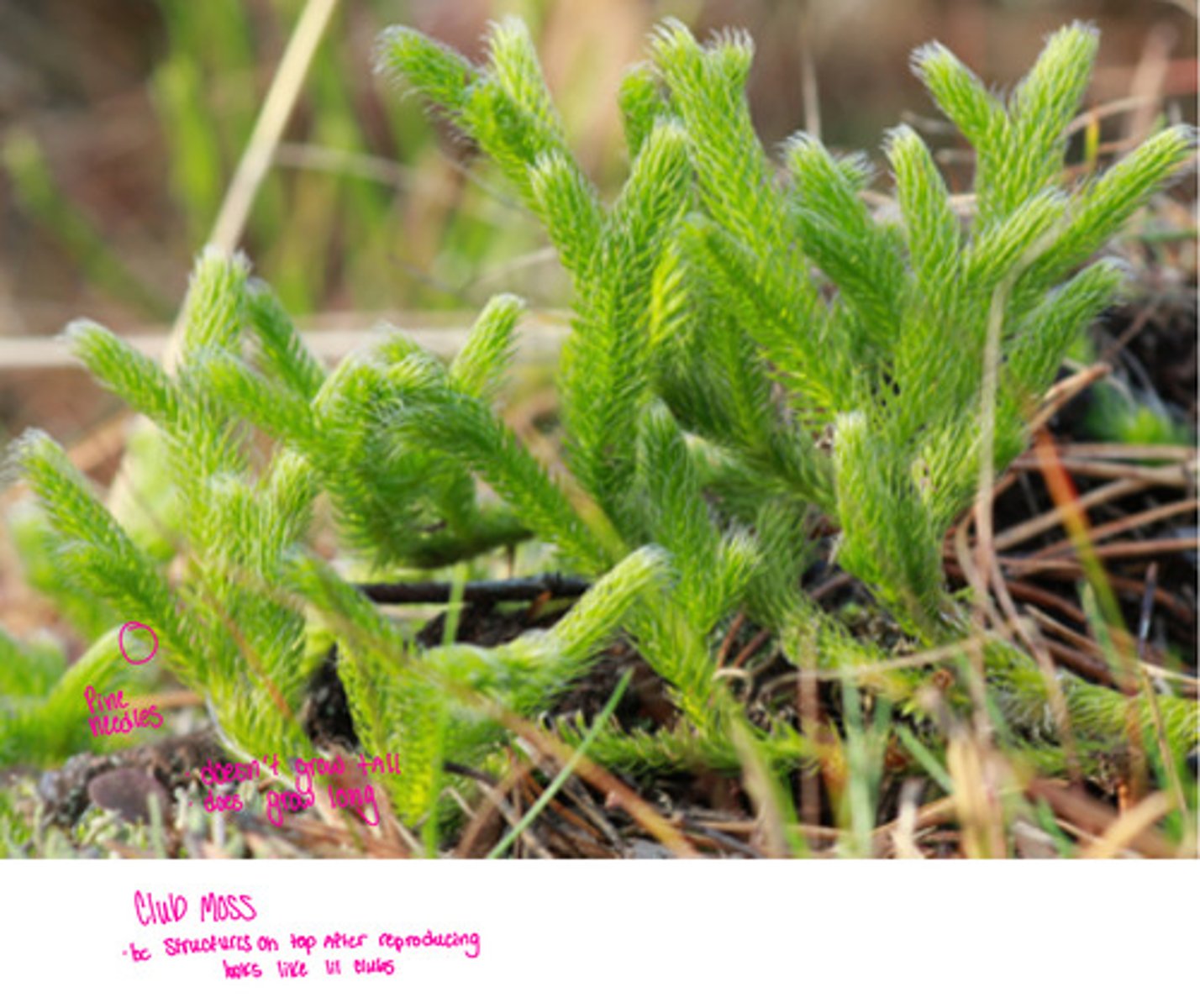
• Small leaves with unbranched
veins
• Specialized leaves carrying
spores are clustered in structures
called strobili ( this is the plural form, singular form is strobilus )
Club moss ( because structures on top after reproducing look like little clubs )
-Pineneedles
- doesn’t grow tall
- does grow long

Phylum: Pterophyta (vascular plants)
• Pteridophyta = ferns and allies
• Water is still required for
reproduction
• Carries flagellated sperm to eggs
• Whisk ferns have no roots or
leaves
• Vascular tissues in the stem
* ferns are found in shady places
* whisk ferns belong in pterophyte group
* no roots, leaves, has blobs, not a bryophyte
* an example of loss of characters would be you can’t see their megaphylls
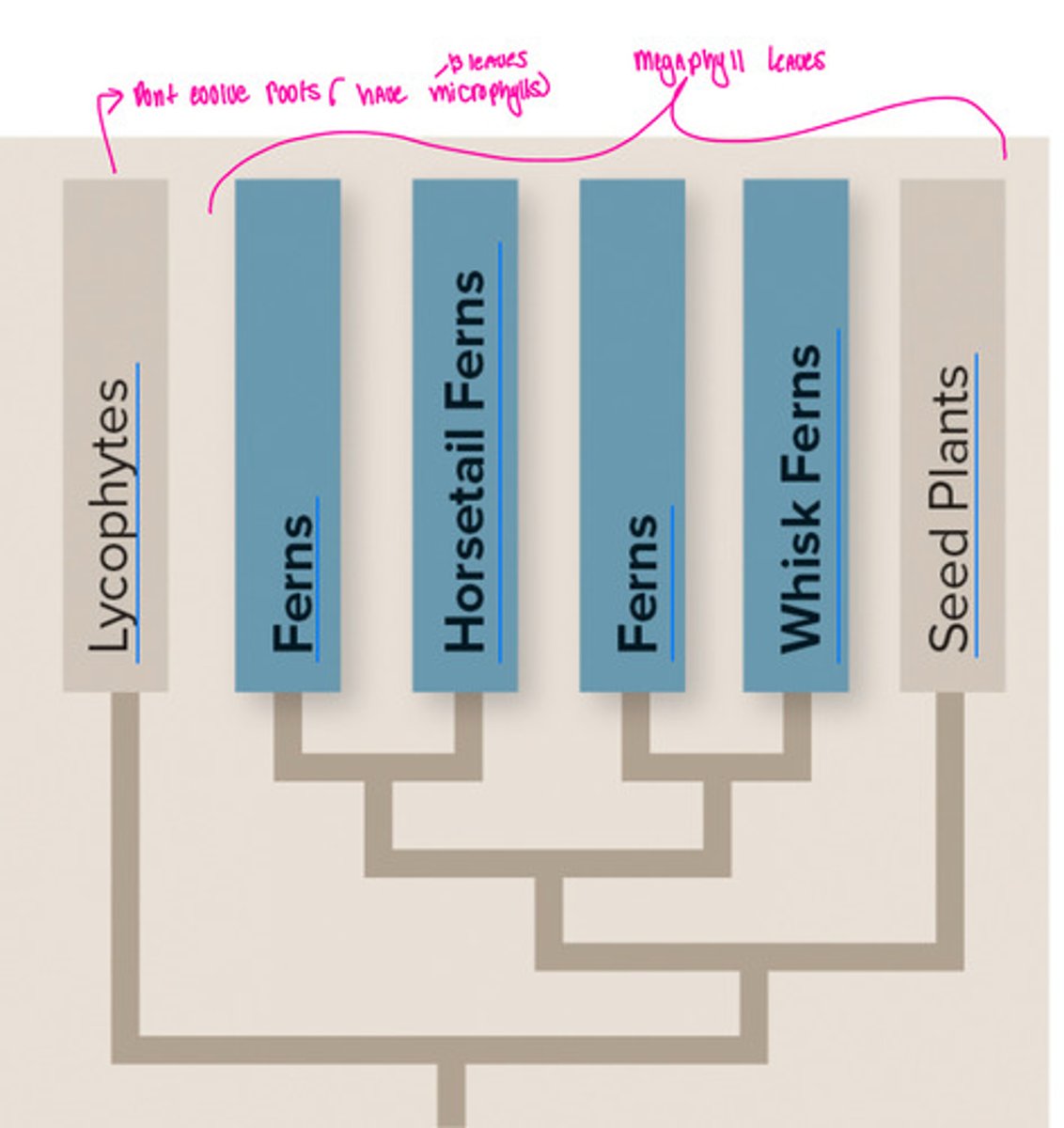
Phylum: Pterophyta (vascular plants)
- whisk ferns
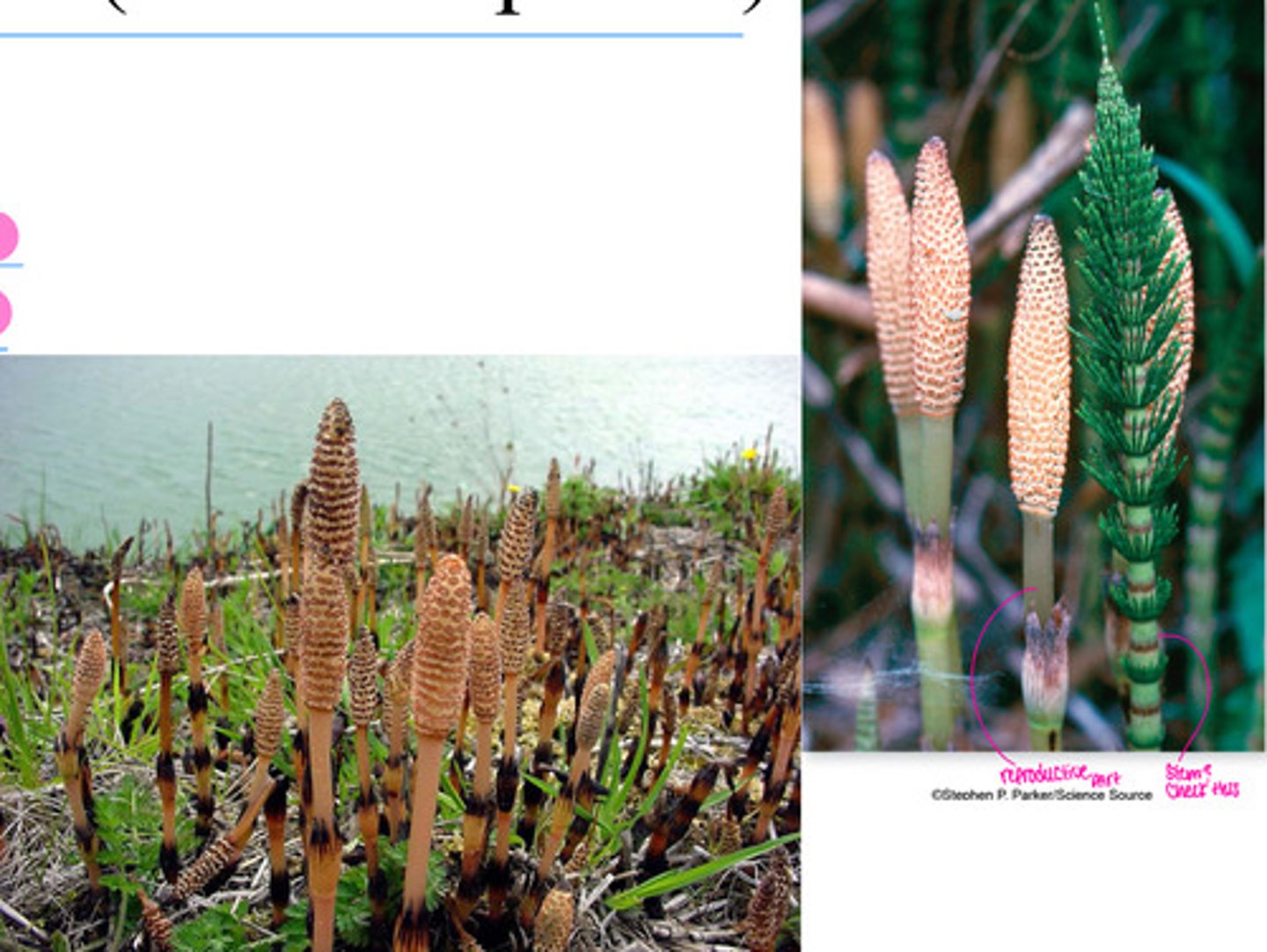
- Horsetails
( for horsetails - before plastics you needed these to scrub. They pull silica up out of the ground. Silica is hard and gritty. You can’t eat it. They used to cut them, slice them, and boom you have a scrub brush. they call them scouring rushes.)

Phylum: Pterophyta (vascular plants)
Horsetails (Equisetum) (<- genus)
• “Scouring rushes” due to the
silica stored in their hollow
stems
• Diuretic properties

Phylum: Pterophyta (vascular plants)
Alternation of Generations and ferns
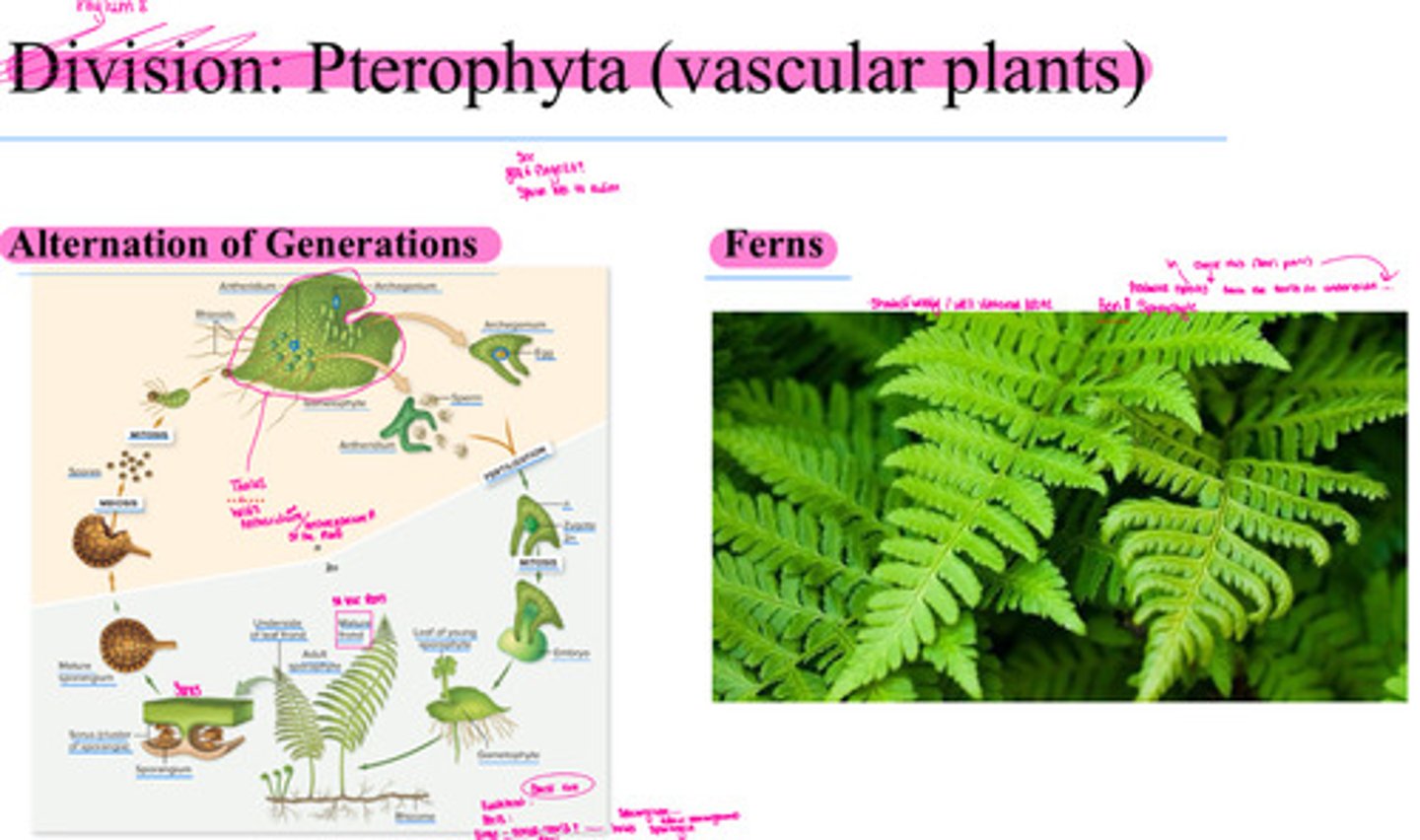
Phylum: Pterophyta (vascular plants)
Ferns
• 11,000 species of ferns today
• Fern forests in what is now New
England have turned into coal
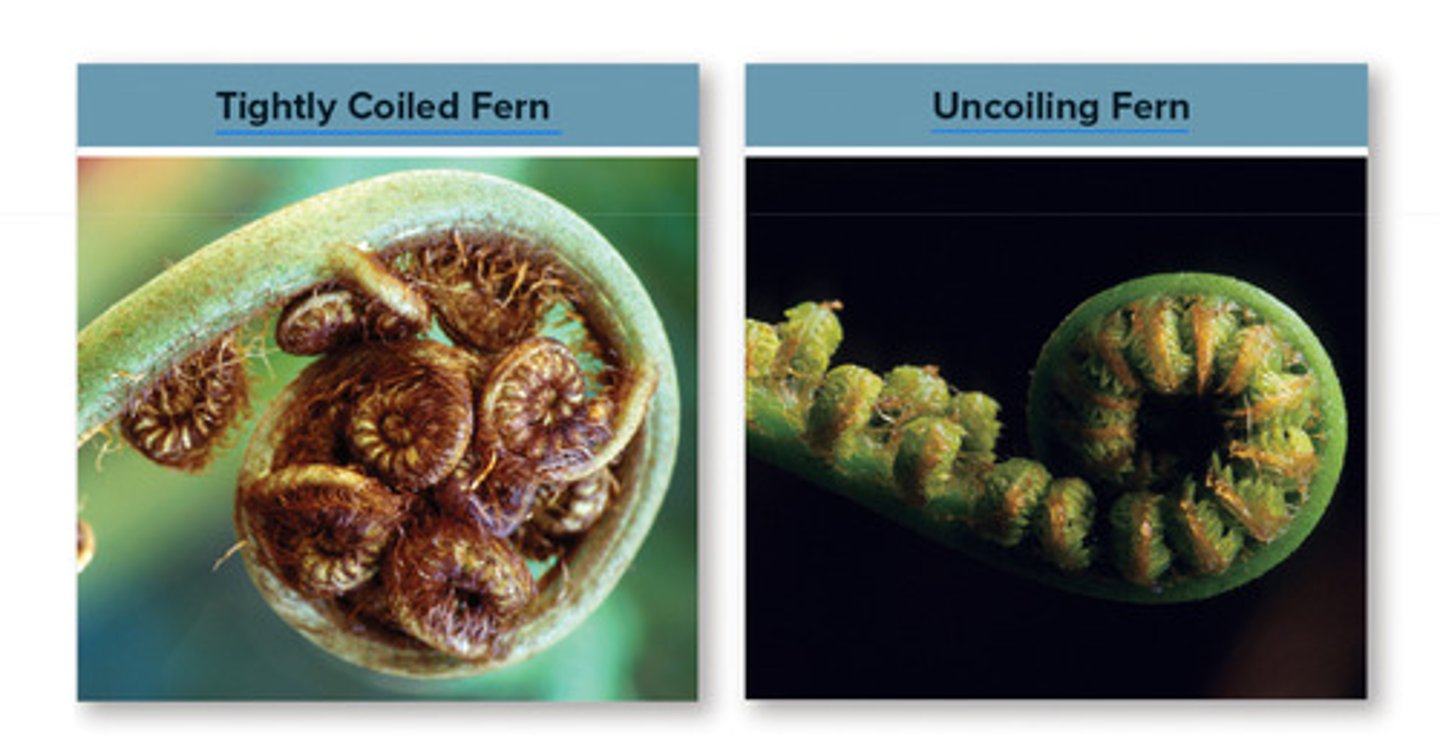
• Fiddleheads emerge from soil
and allow fronds to expand in air
( coal kicked off an Industrial Revolution, carbon emissions rise, why? Answer w recording )
Land plants