Session 2: Development of the Limbs
1/72
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
73 Terms
In what week do the limb buds usually appear
4th week
3 multiple choice options
What is the name of the boundary between the ventral & dorsal limb ectoderm
Axial line
2 multiple choice options
What is a motor unit
The muscle fibres innervated by a single motor nerve fibre
2 multiple choice options
Myotome
A group of muscles innervated by a single nerve root
Where does secondary ossification occur?
Epiphysis
3 multiple choice options
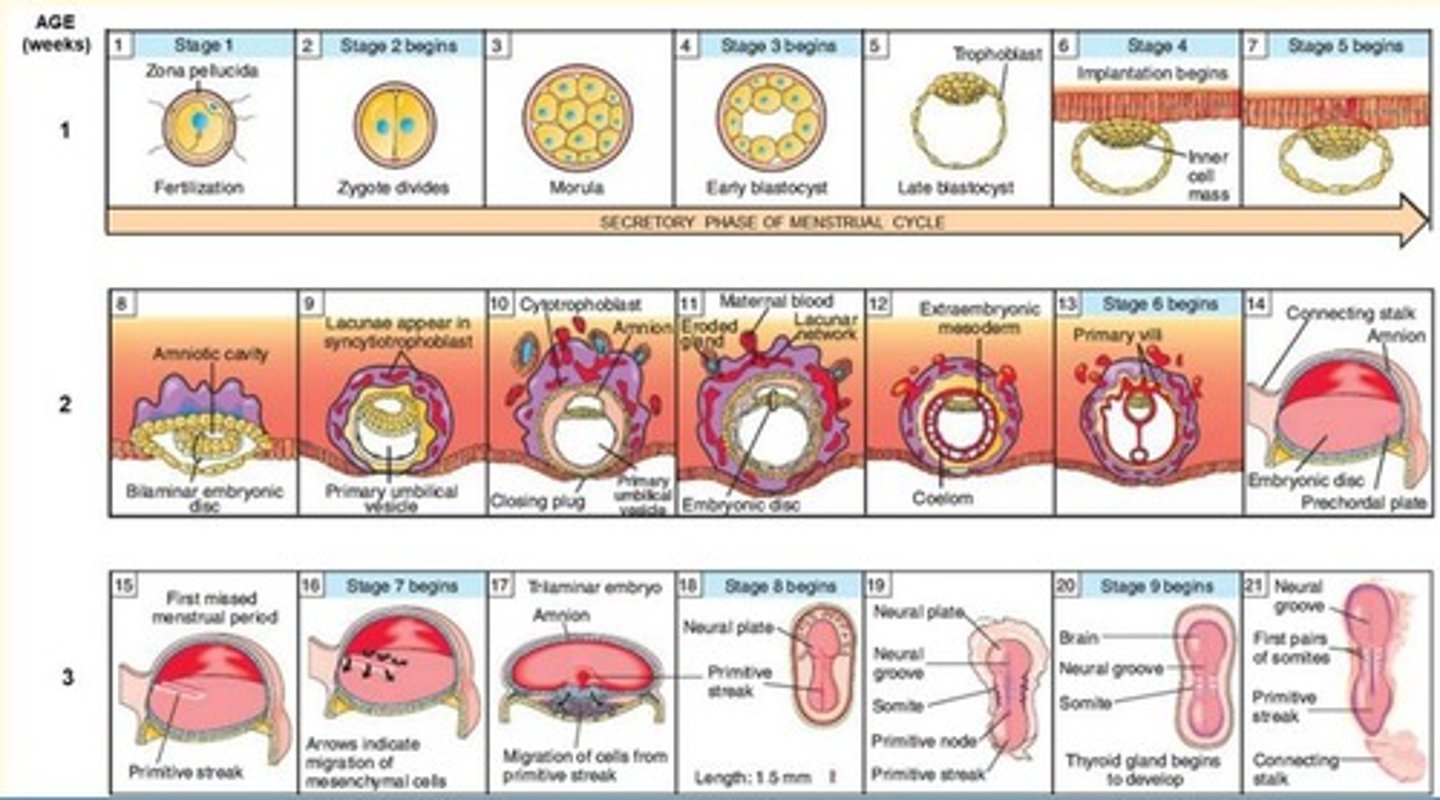
Summarise some key events which happen in first week of development
- Fertilisation
- Zygote division
- Morula
- Blastocyst formation
- Late blastocyst = trophoblast
- Implantation begins = epiblast (inner cell mass)
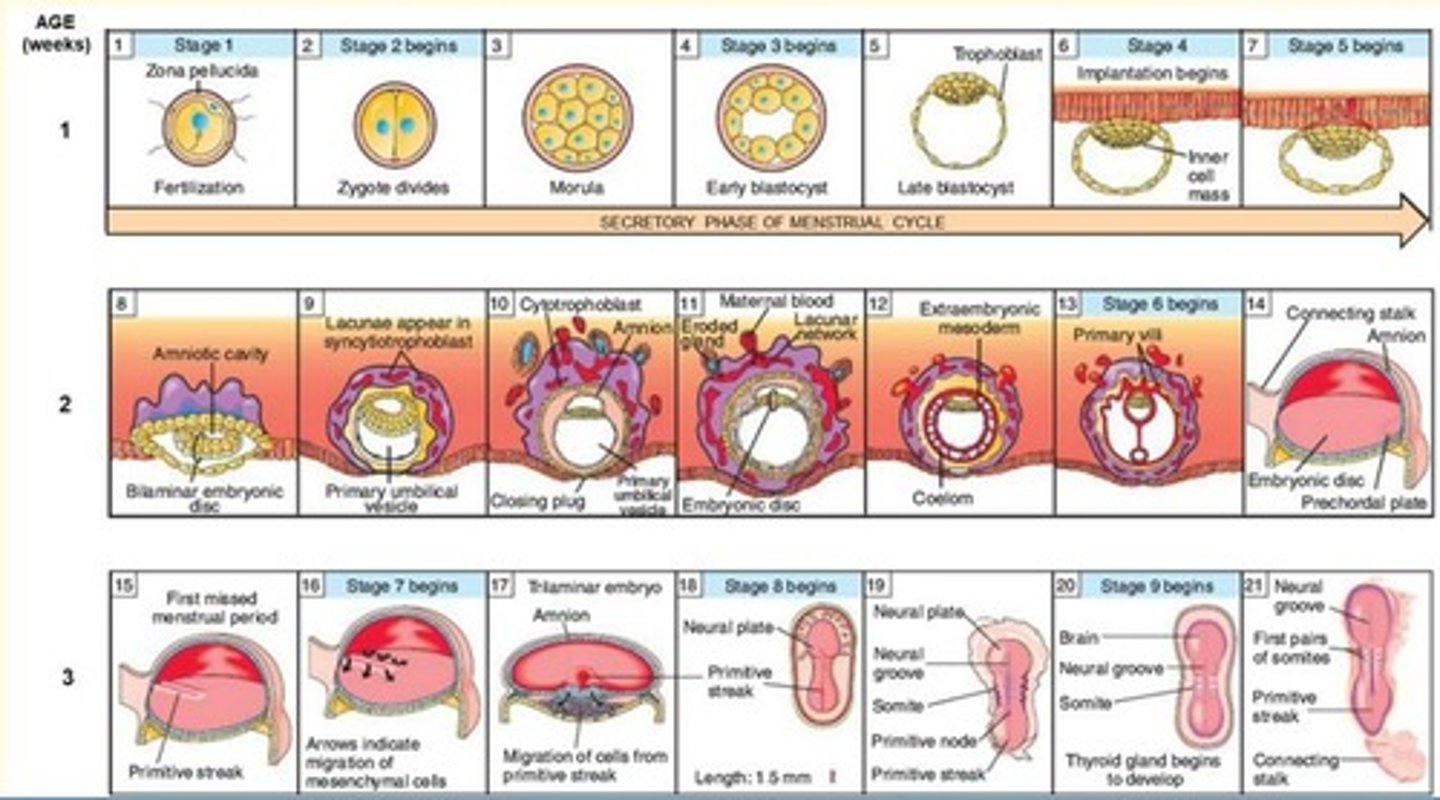
Key events which happen in second week of development
- Formation of the bilaminar embryonic disc
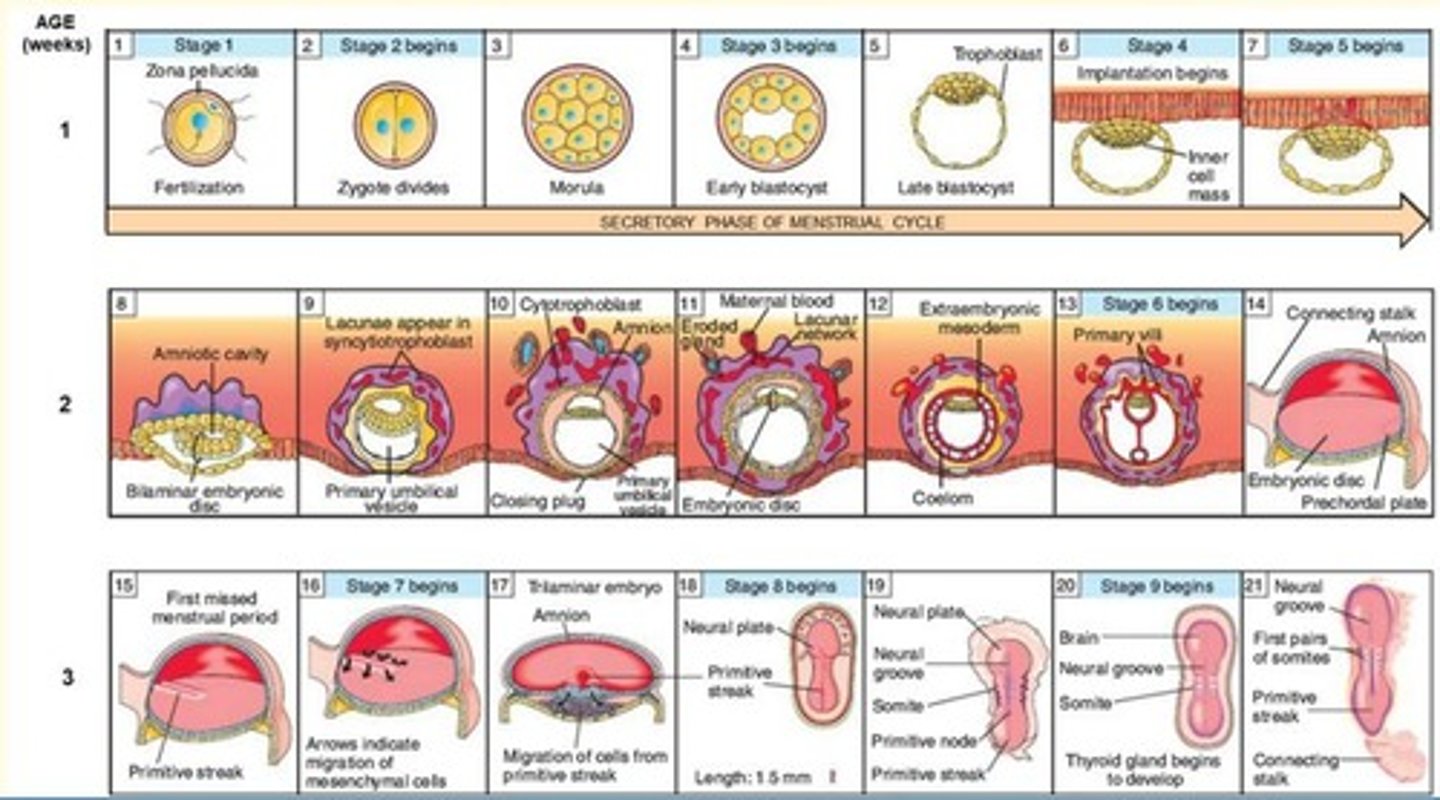
Summarise some key events which happen in third week of development
- Primitive streak formation
- Migration of cells from primitive streak
- Neural plate and neural groove develop
- Formation of the trilaminar embryonic disc from bilaminar
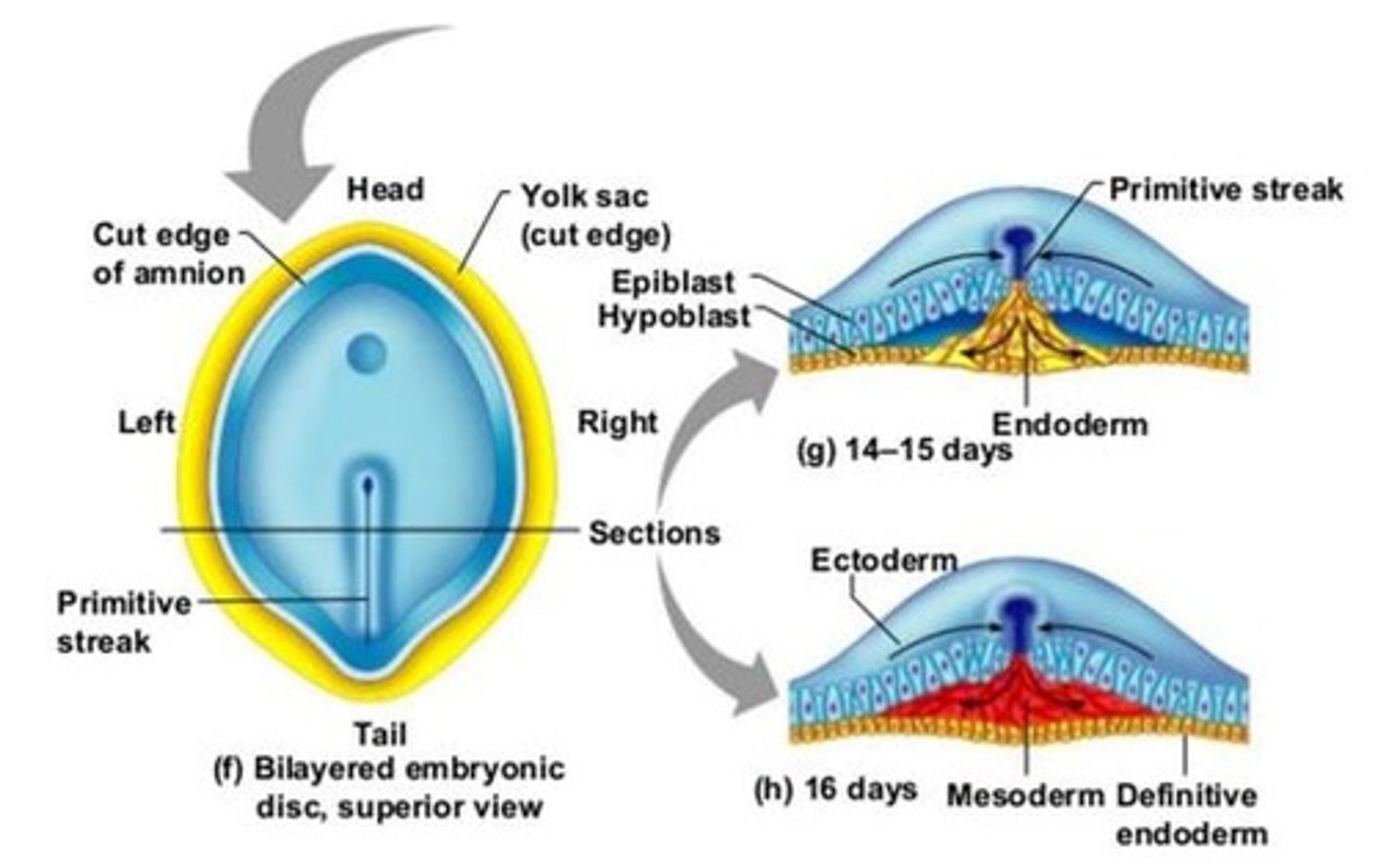
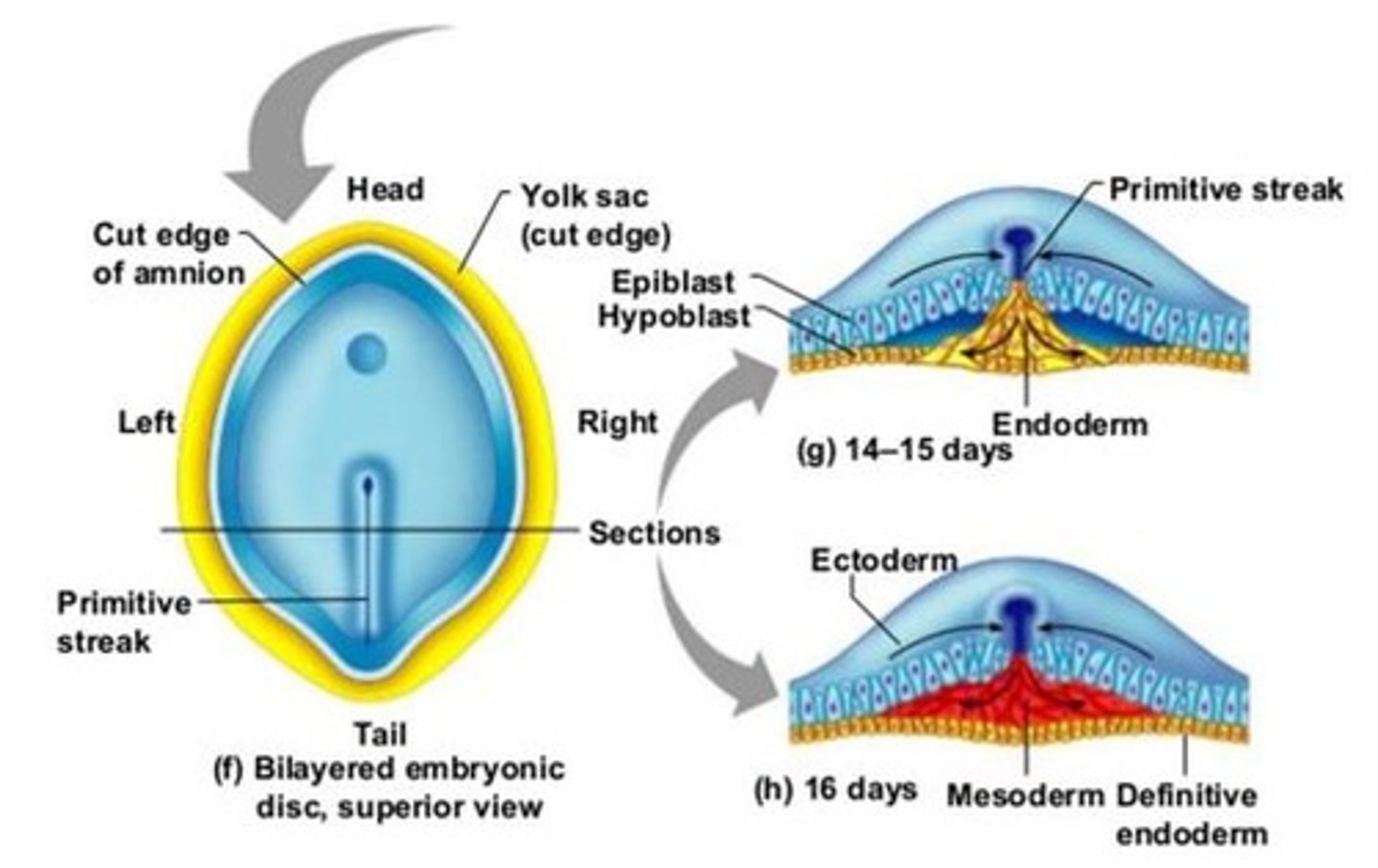
Gastrulation
Process by which bi-laminar embryonic disc is converted into tri-laminar embryonic disc containing three germ layers (ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm).
Gastrulation marks the beginning of ___.
This means that the development of the form and structure of various organs and parts of the body occurs.
Morphogenesis
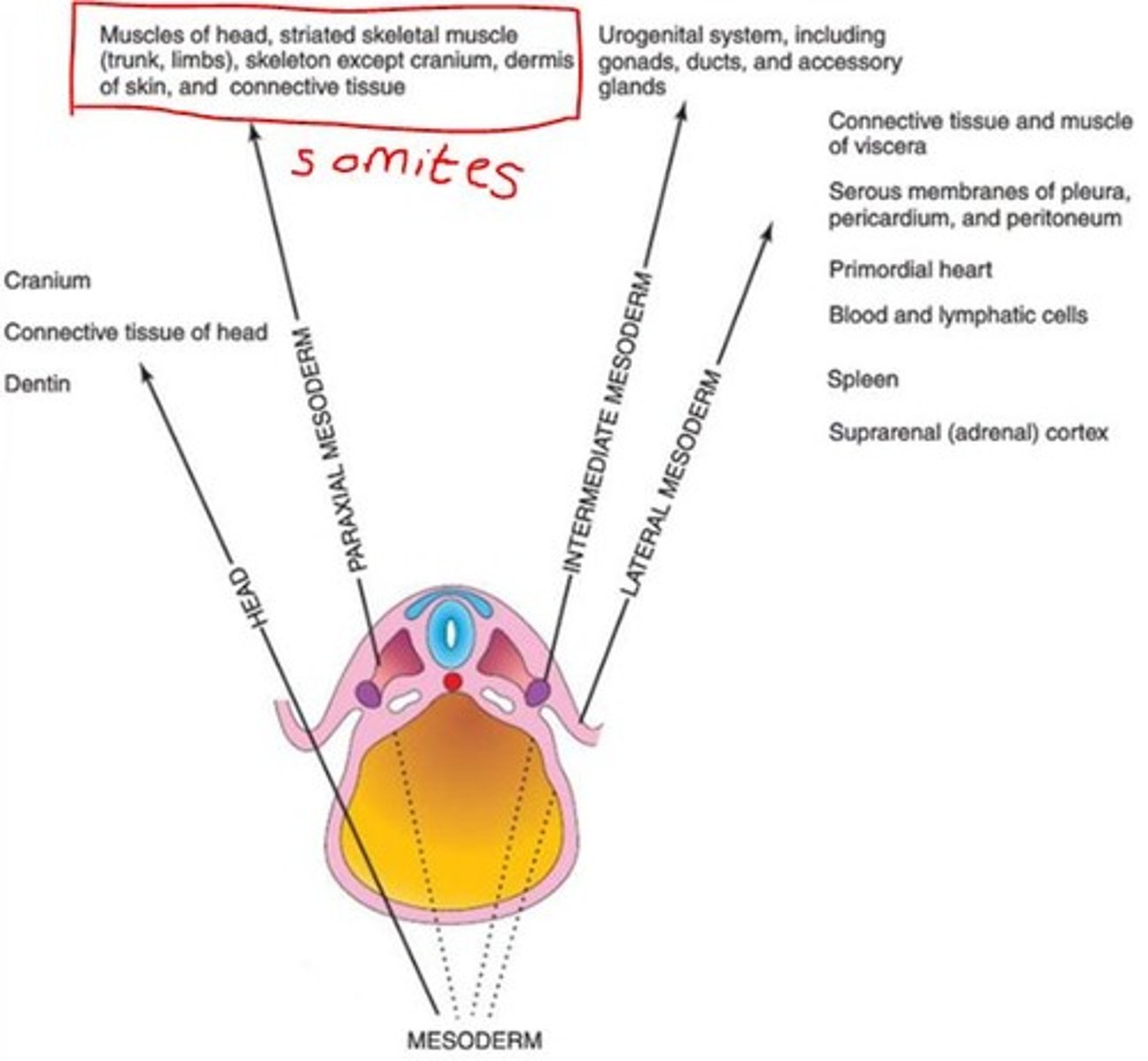
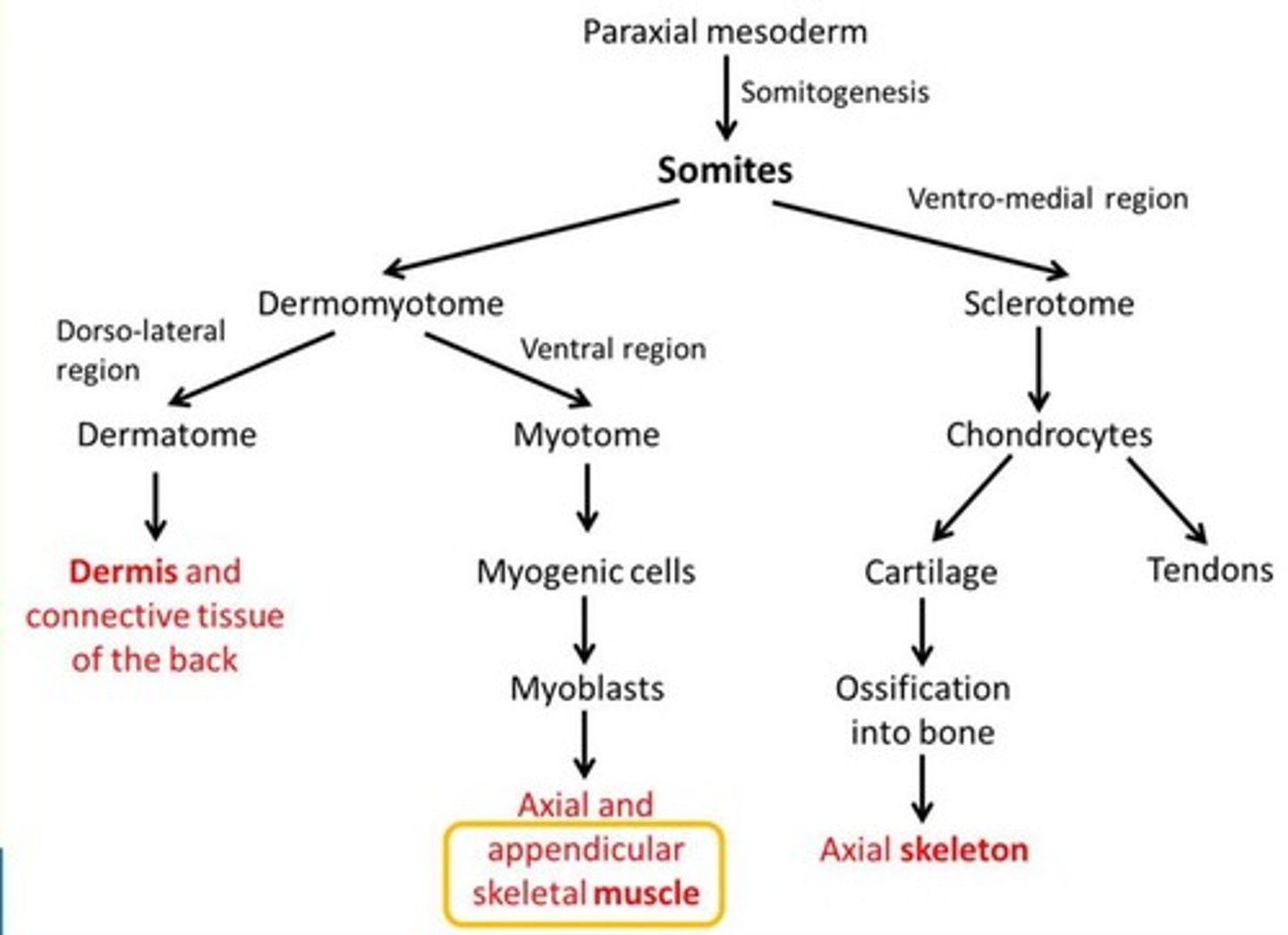
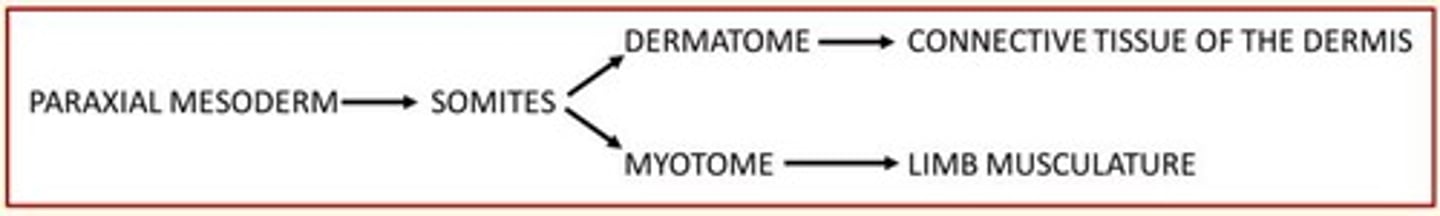
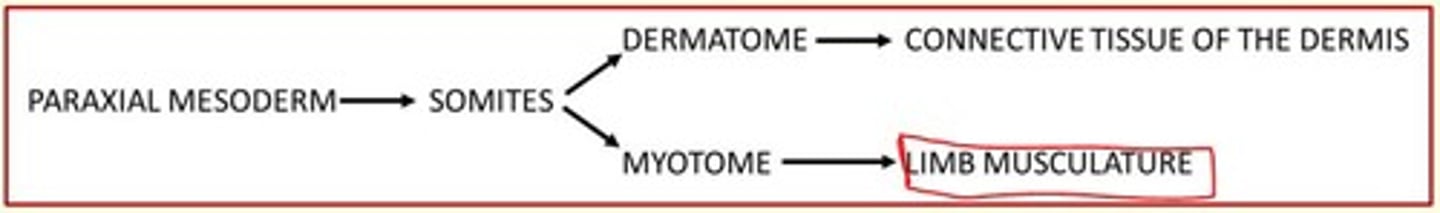
Derivatives of the paraxial mesoderm
Somites
Axial skeleton
Voluntary musculature and dermis
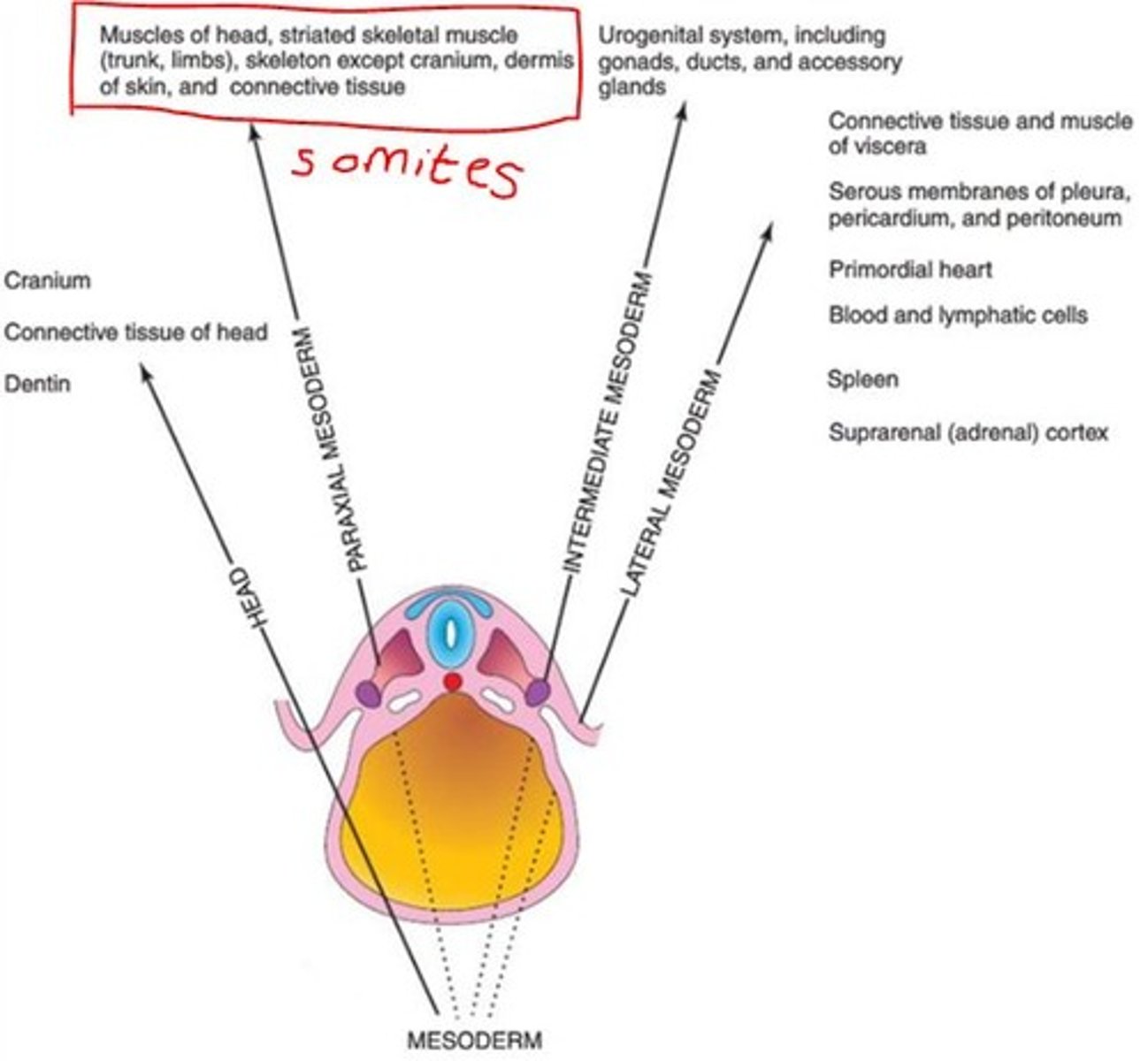
Derivatives of the intermediate mesoderm
Urogenital system (kidney, gonads, testes, etc)
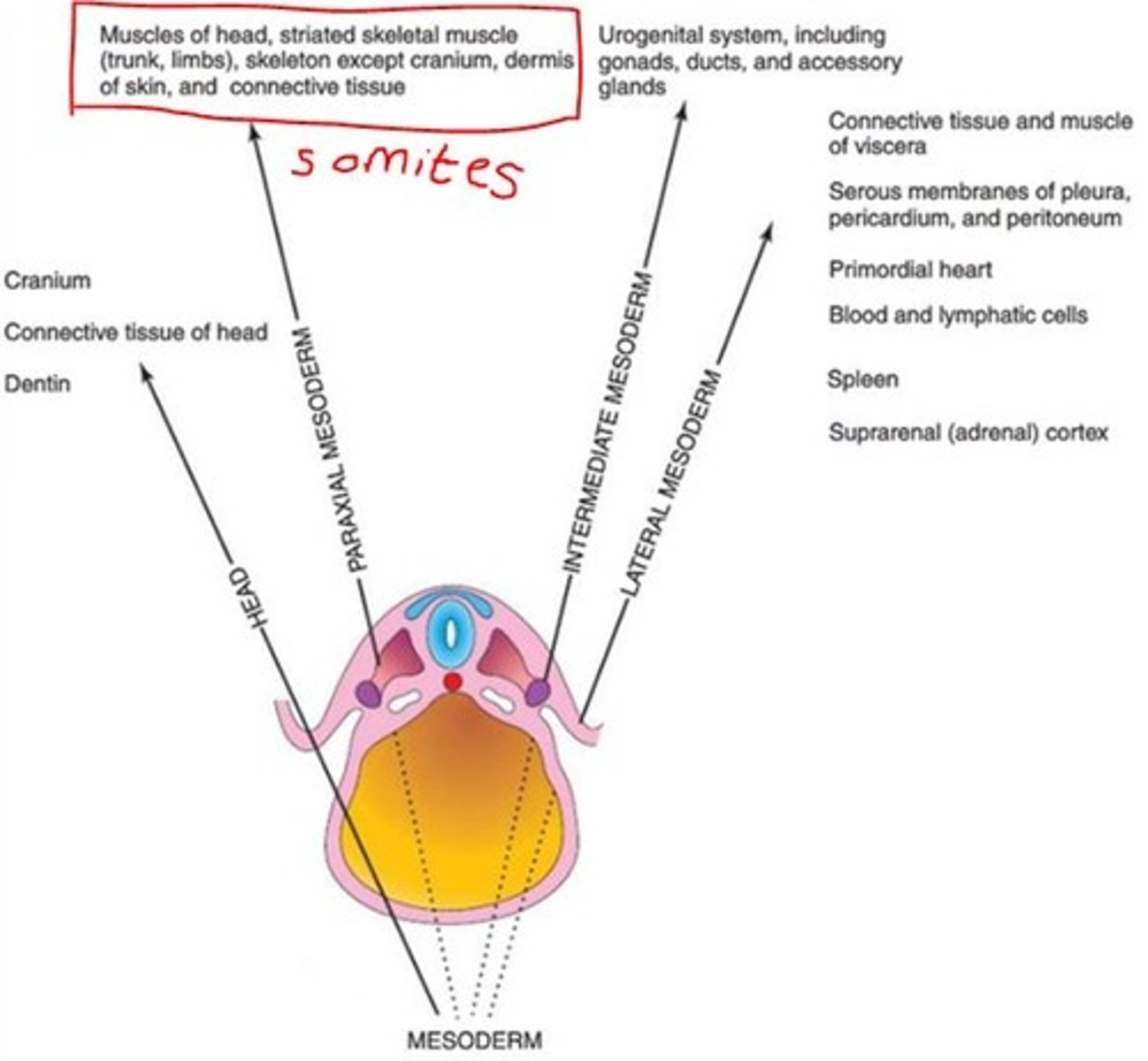
Derivatives of the lateral mesoderm
Smooth muscle of viscera
Connective tissue of viscera
Serous membranes of pleura, pericardium, peritoneum
Primordial heart
Spleen
Suprarenal (adrenal) cortex
Describe the differentiation of the mesoderm which occurs during gastrulation process
During gastrulation, specific regions of epiblast migrate through different parts of primitive node and primitive streak to form the mesoderm.
Epiblast cells migrating at the central and most cranial part of the primitive node will form the ___
Epiblast cells migrating at the central and most cranial part of the primitive node will form the notochord
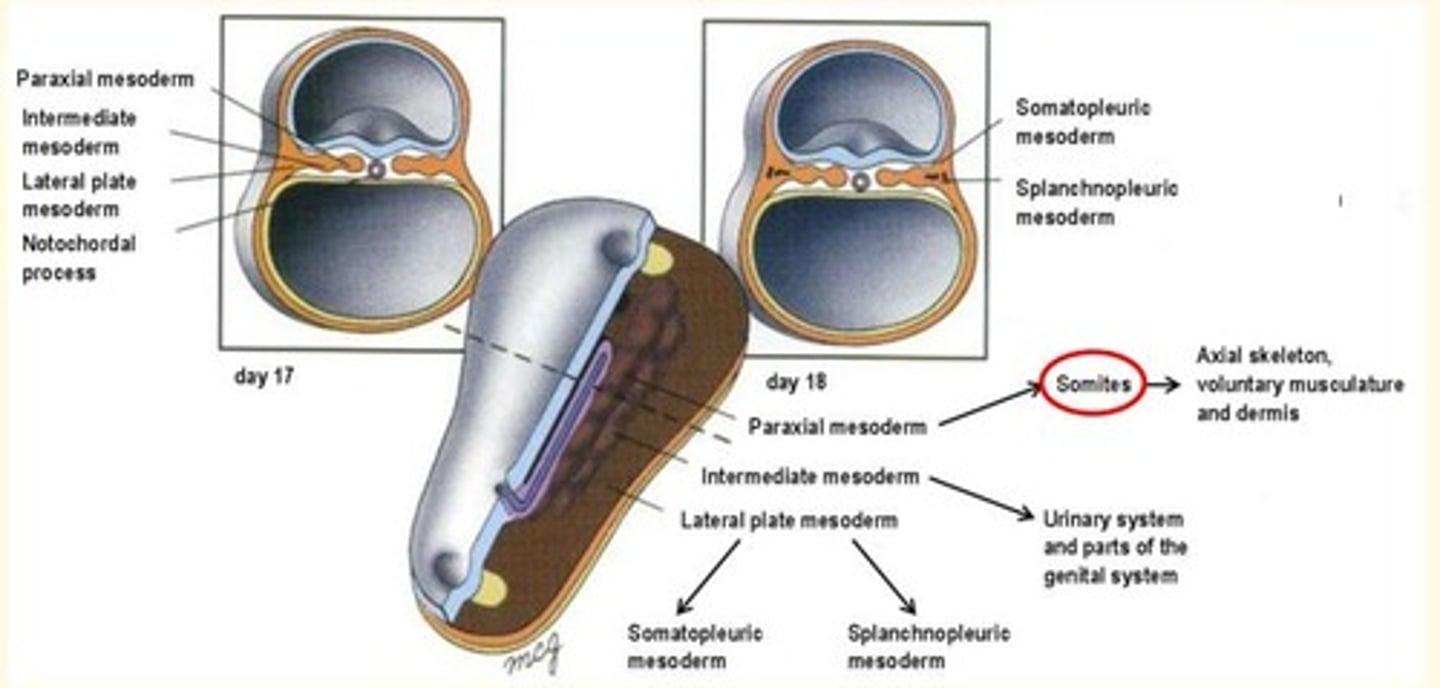
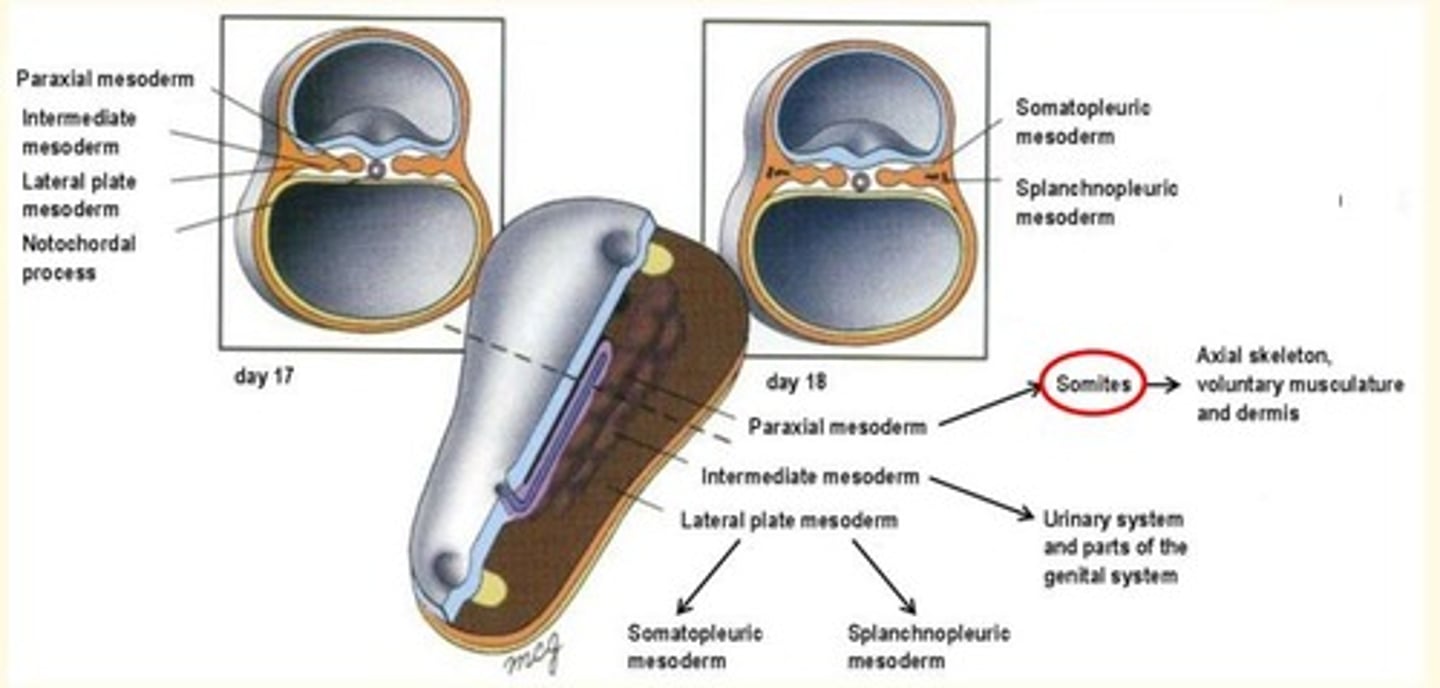
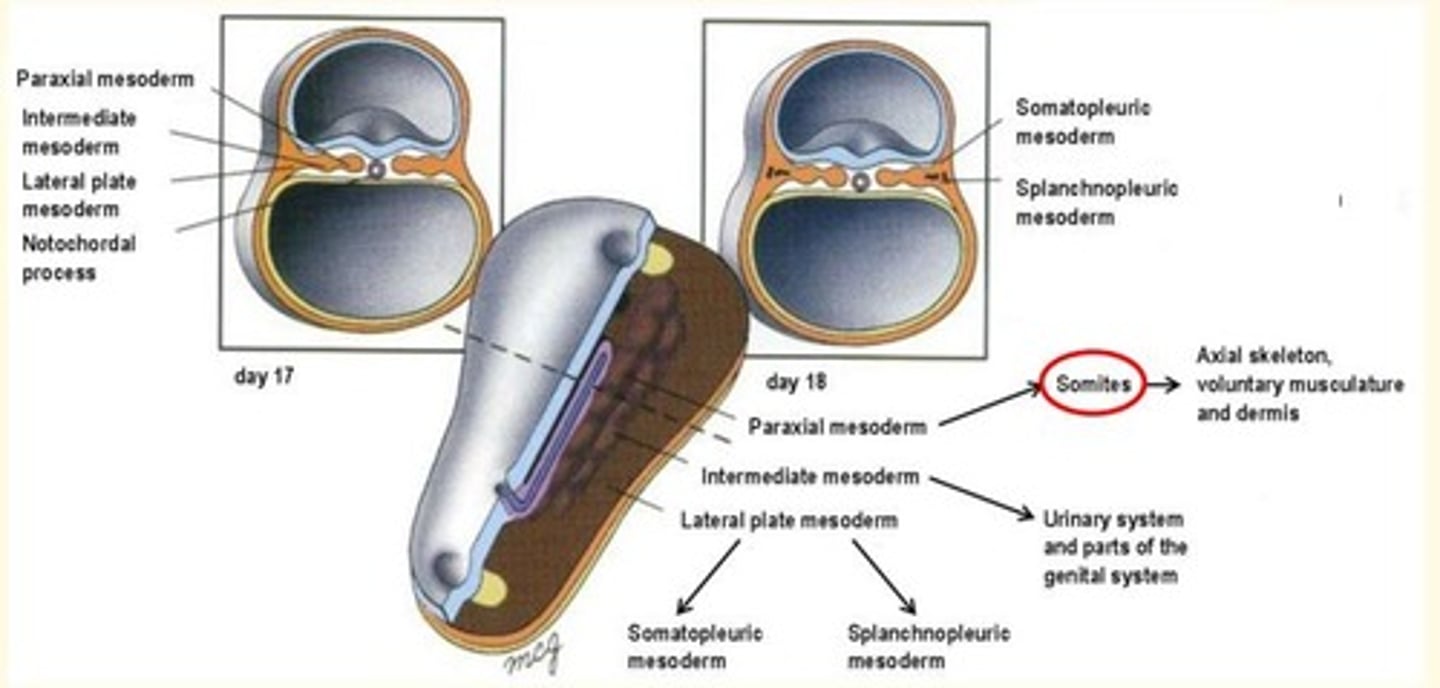
Epiblast cells migrating laterally form the ___, ___ and ___ plate mesoderm
Epiblast cells migrating laterally form the paraxial, intermediate and lateral plate mesoderm
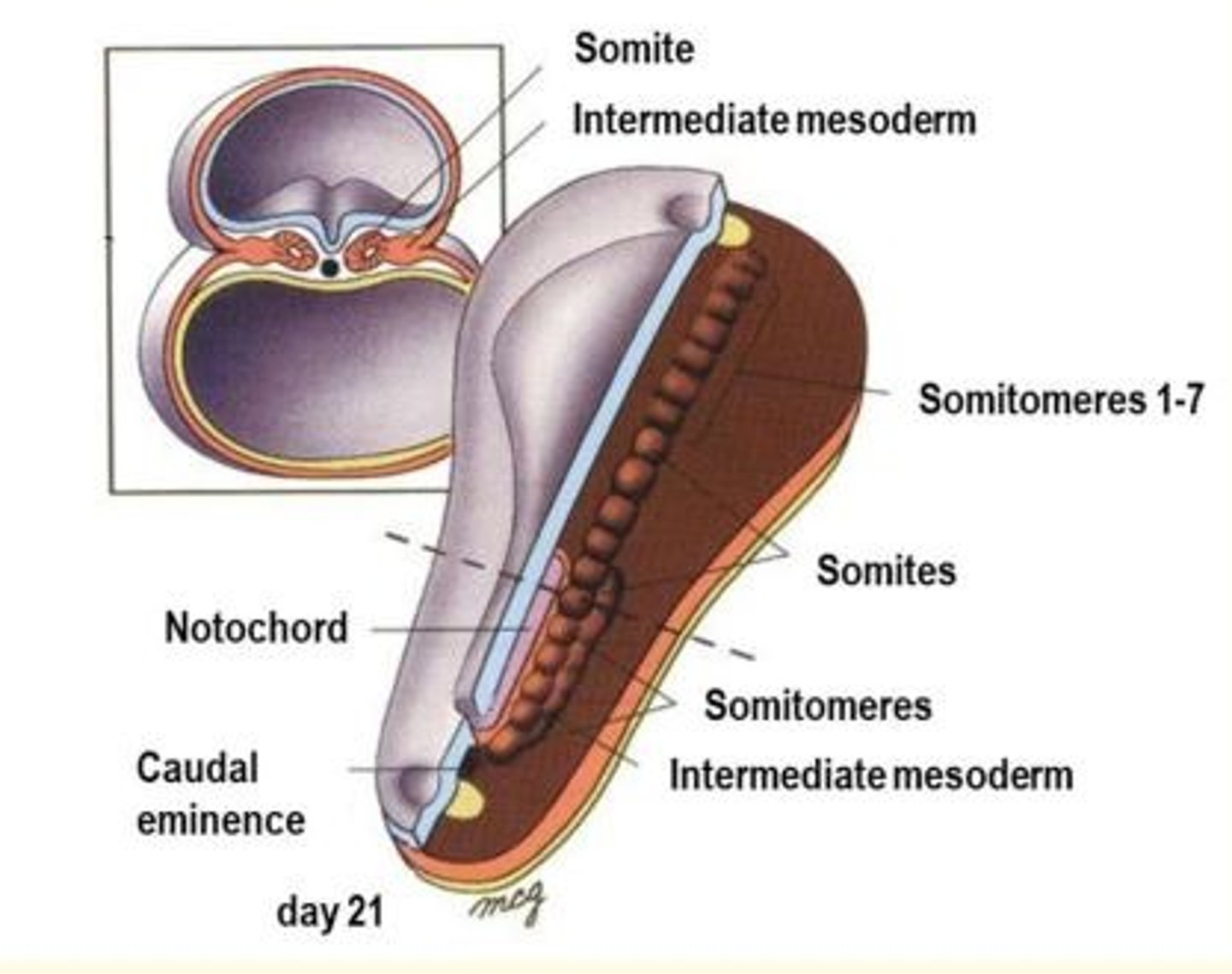
During the ___ week, the paraxial mesoderm starts to be organised into segments called ___.
Toward the end of the ___ week, ___ further organise into ___, on each side of the neural tube.
During the third week, the paraxial mesoderm starts to be organised into segments called somitomeres
Toward the end of the third week, somitomeres further organise into somites, on each side of the neural tube.
The new somites appear in cranio-caudal sequence at a rate of 3 pairs per day, until the end of the 5th week - where 42-44 pairs are present.
As somites mature, various regions become committed to forming only certain cell types.
Sclerotome gives rise to...
Sclerotome gives rise to cartilage cells (chondrocytes) of the vertebrae and ribs, forming the bone component of the axial skeleton (skull bones, ossicles of middle ear, rib cage, sternum, vertebral column)
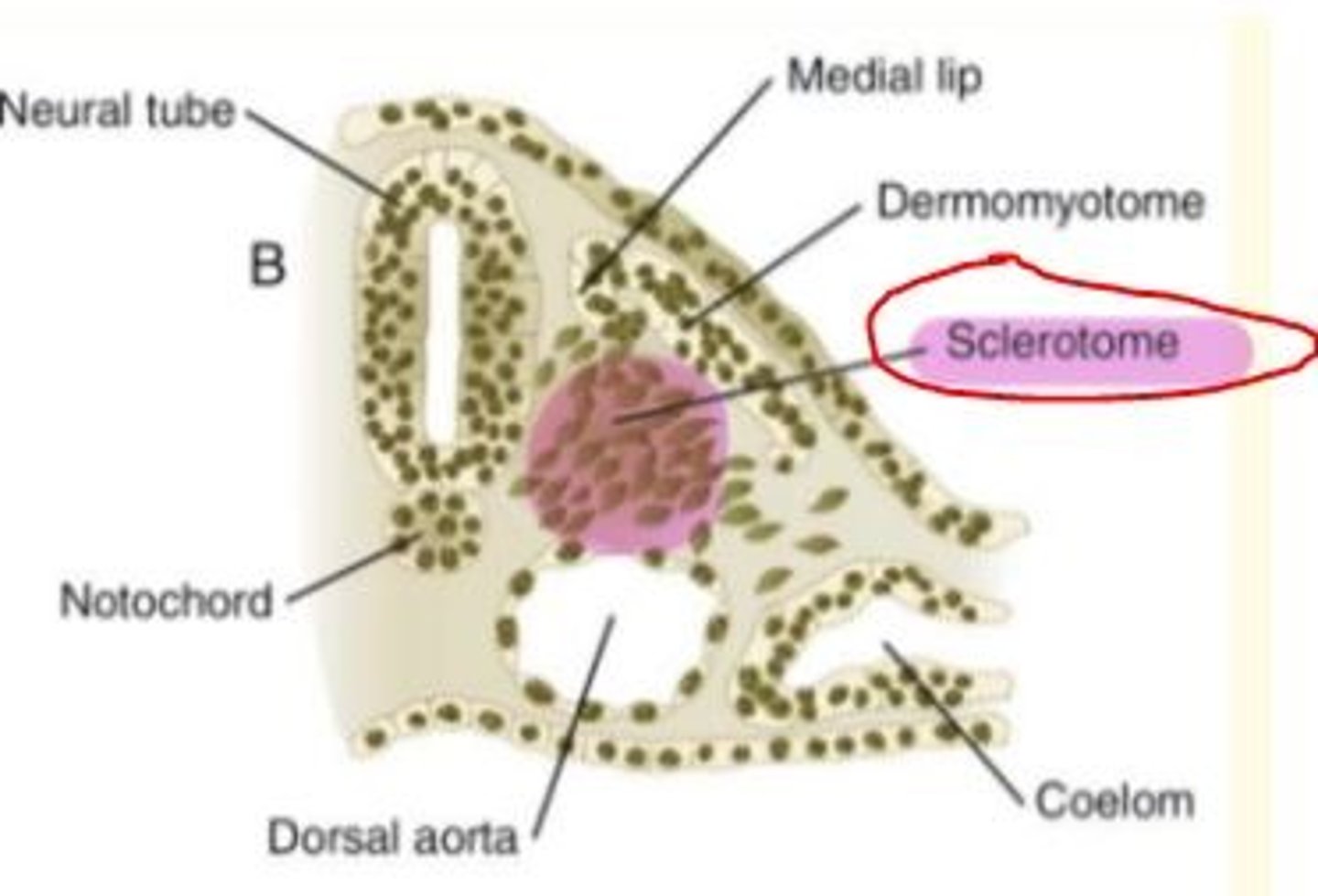
As somites mature, various regions become committed to forming only certain cell types.
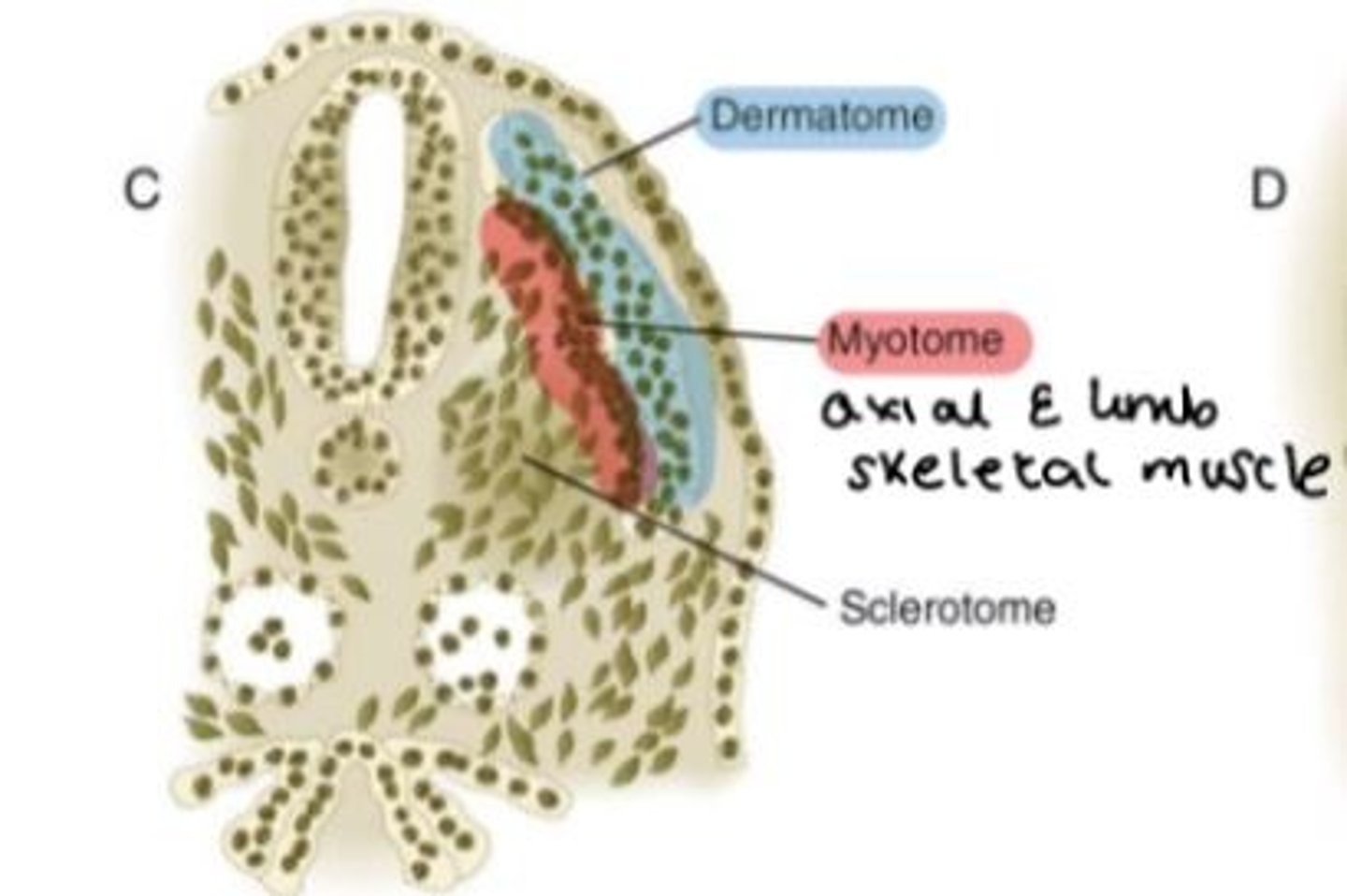
Dermamyotome is a double-layered structure that consists of two parts. What are they?
Dermamyotome is a double-layered structure that consists of...
1) Dermatome = forms dermis of back skin
2) Myotome = cells that divide to form myoblasts which give rise to axial and appendicular limb skeletal muscle
Derivatives of somites (somite differentiation summary)
What are somites?
Transient segmented structures derived from the paraxial mesoderm.
Building blocks of the vertebrate body plan, which are essential for segmentation, bone and musculature development as well as creating a template for the nervous system.
All somites look identical. Why do they form different structures?
Although all somites look identical, they form different structures at different positions along the anterior-posterior axis.
Distinct regions of each somite become specific tissue and cell types as the body develops.
Give some examples of mature cell types derived from somites
Adipocytes
Chondrocytes
Osteocytes
Pericytes
Muscle cells = skeletal, smooth
What do somites determine?
Somites determine the migrating pattern of neural crest cells and spinal nerve axons.
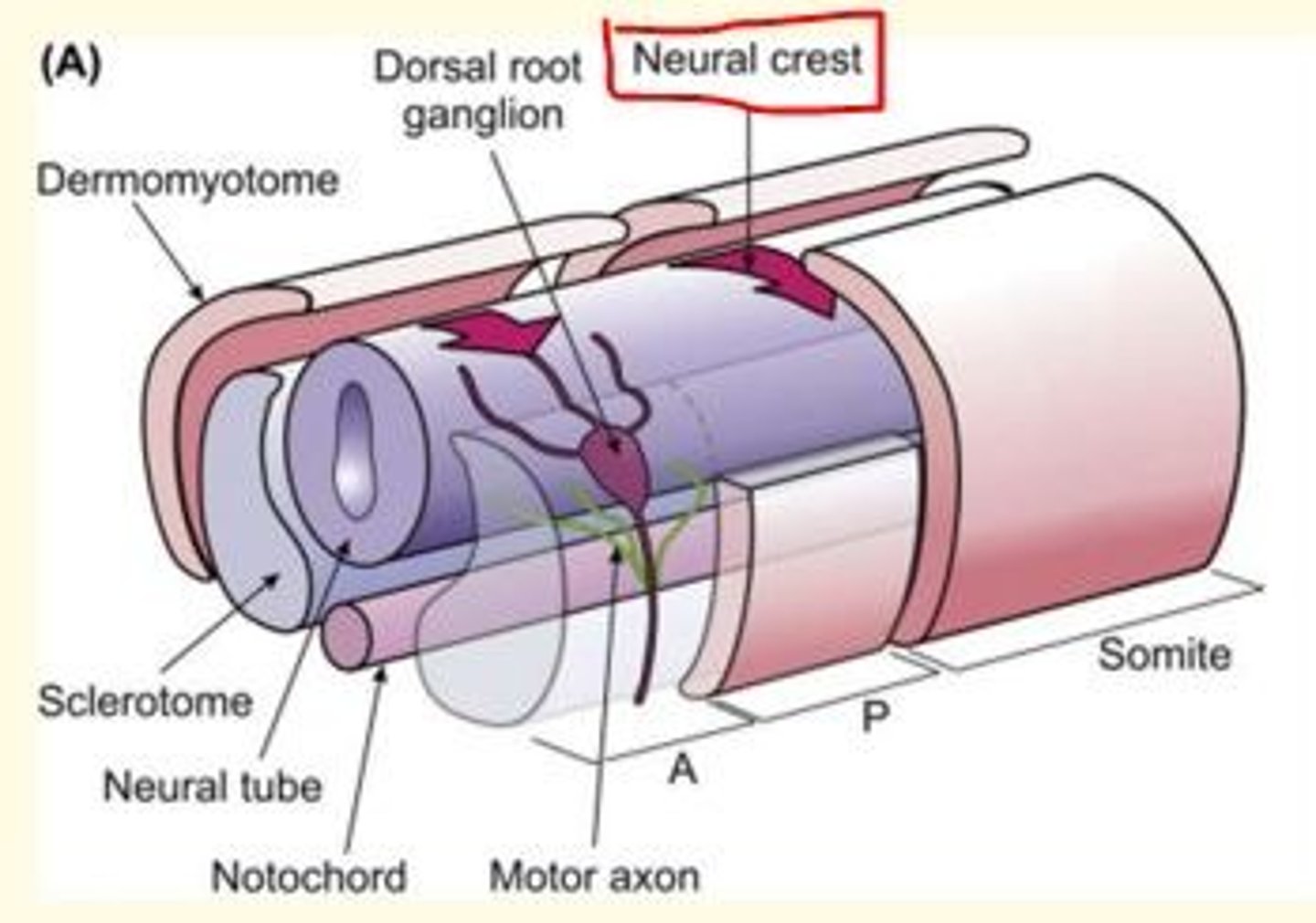
What forms the vertebrae in the developing embryo/fetus?
The resegmentation of the sclerotome forms the vertebrae.
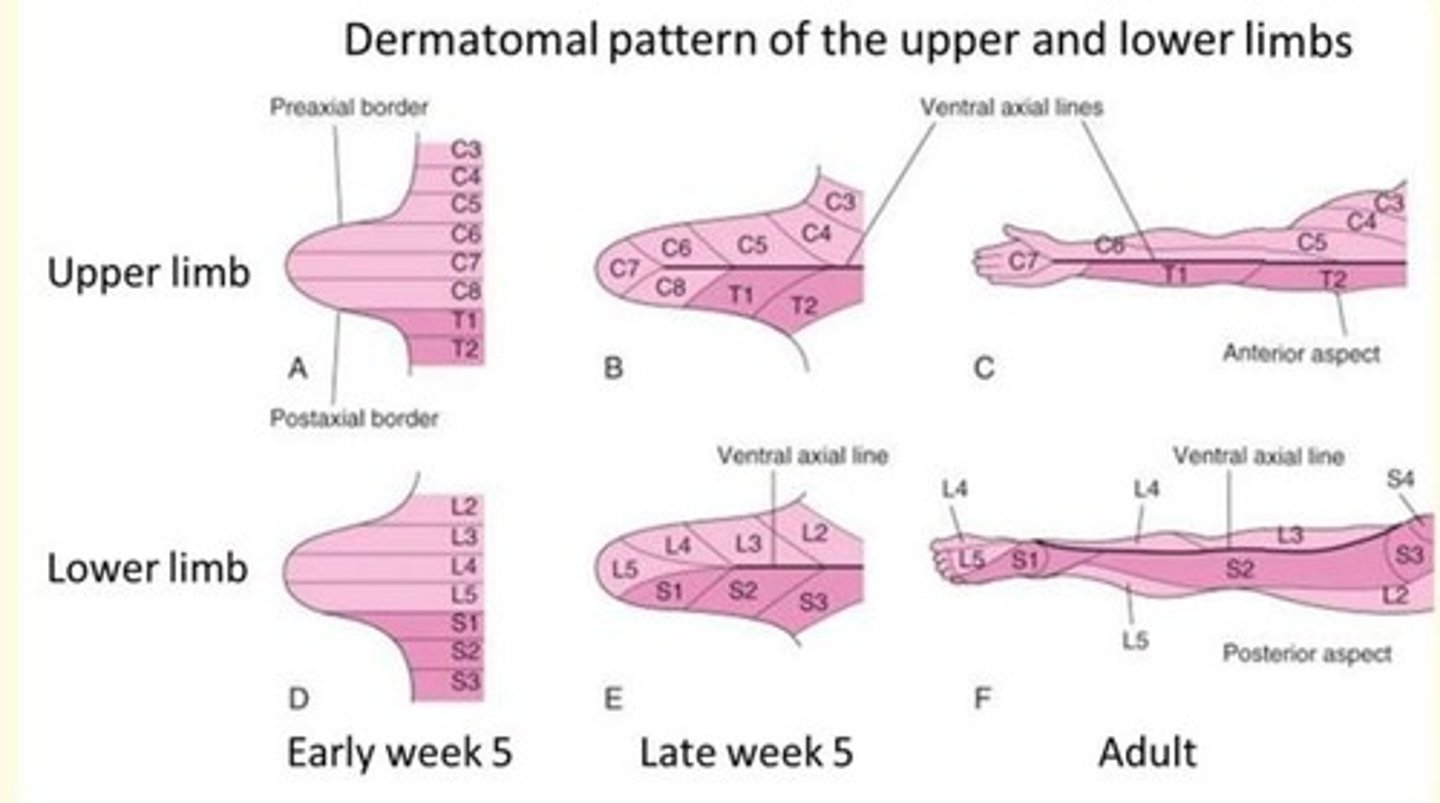
Each myotome and dermatome retains its innervation from its segment of origin: motor and sensory nerves innervate the body wall and limbs in a pattern that is based on the segmental organisation established by the somites.
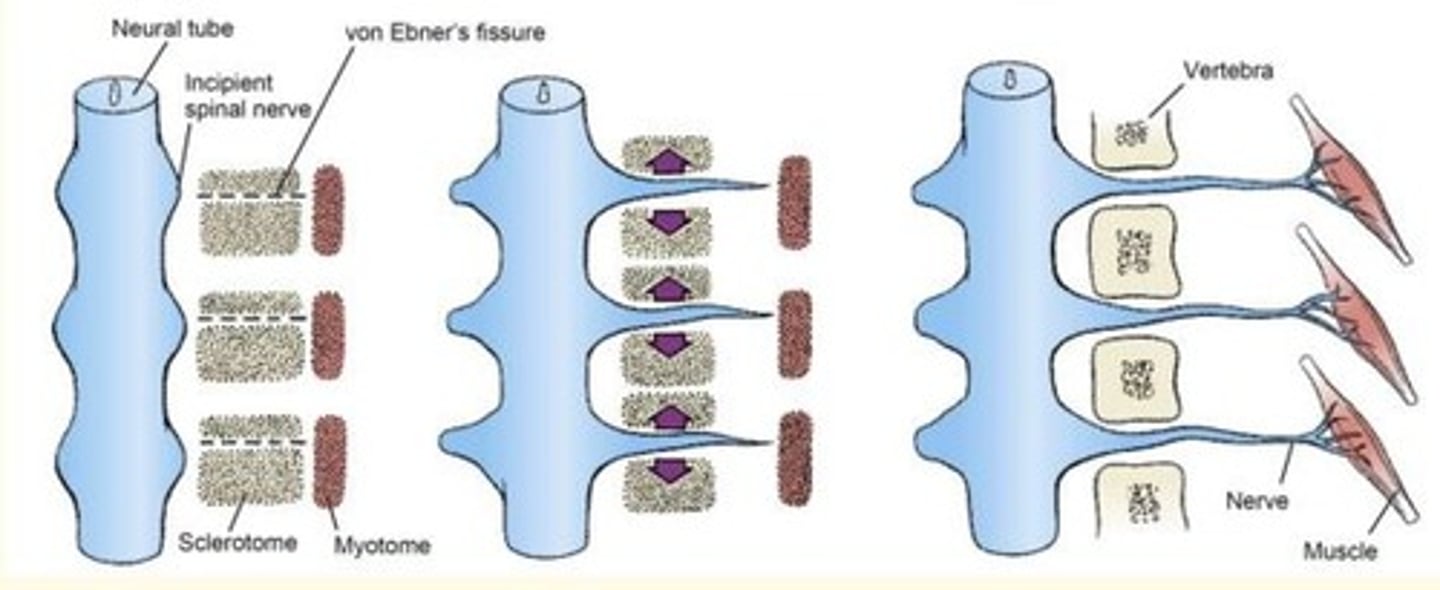
Developmental definition of dermatome and myotome
Dermatome = part of somite that gives rise to dermis
Myotome = part of the somite that gives rise to muscles
Clinical definition of dermatome and myotome
Dermatome = strip of skin supplied by single spinal nerve
Myotome = muscle or group of muscles supplied by a single spinal nerve
The adult body is divided into specific regions called ___
Dermatomes
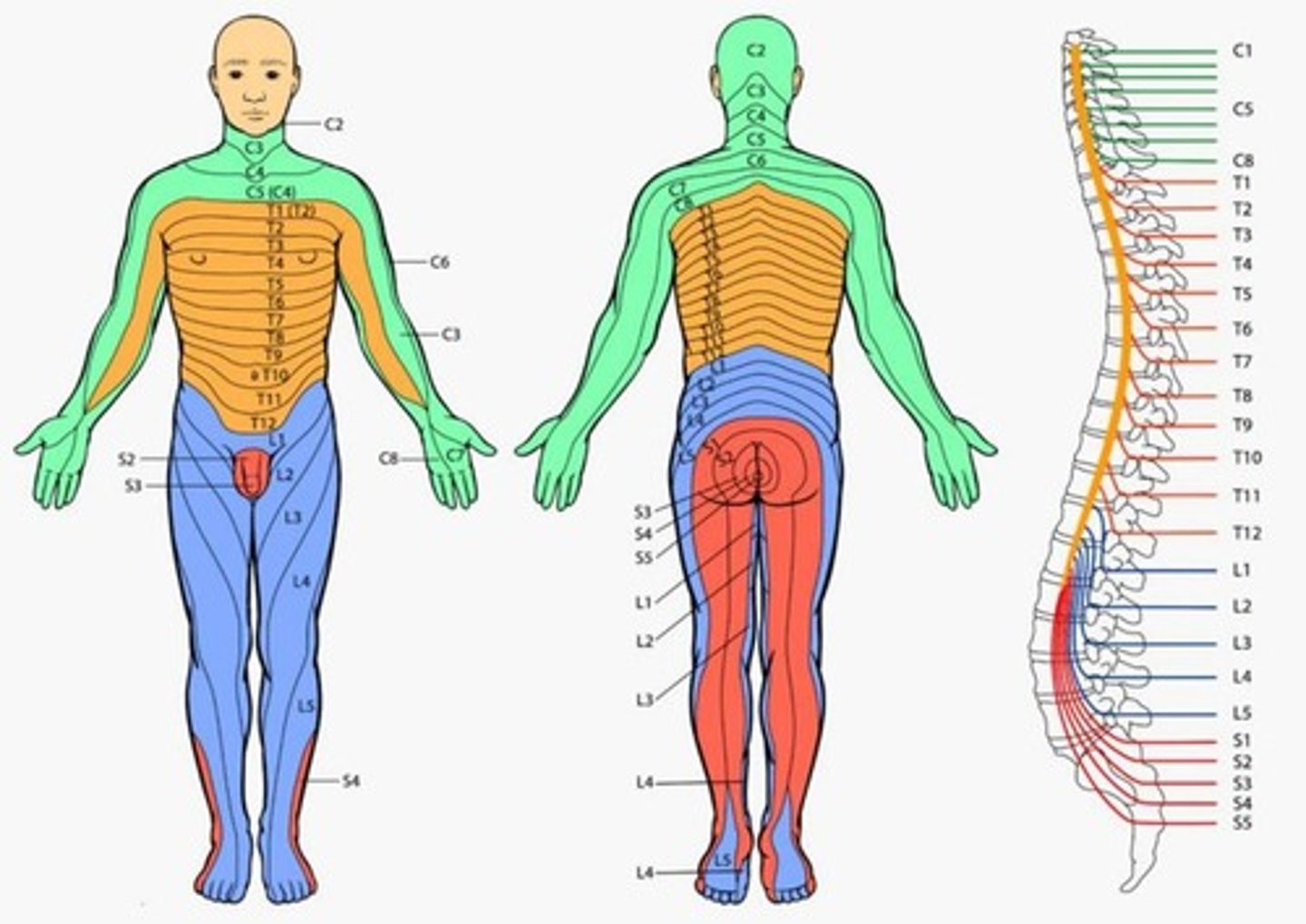
Testing of dermatomes is important because...
It forms the basis of the neurological examination looking for radiculopathy as sensation changes within specific dermatome can help determine the pathological disc level.
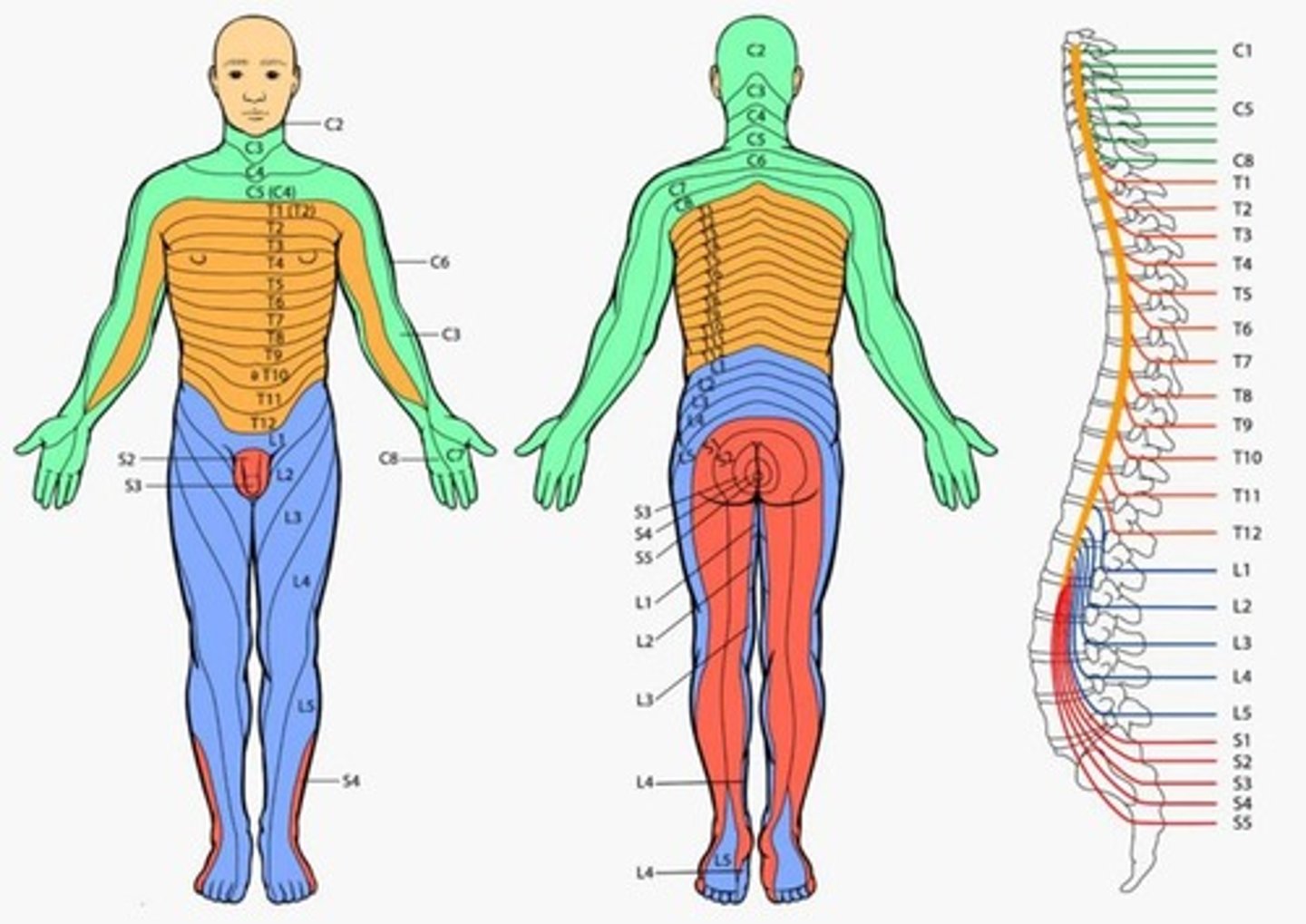
What occurs during the 5th week?
During the 5th week...
Peripheral nerves grow from developing limb (brachial and lumbosacral) plexuses into the mesenchyme of the limb buds
The spinal nerves are distributed in segmental bands, supplying both the dorsal and ventral surfaces of the limb buds.
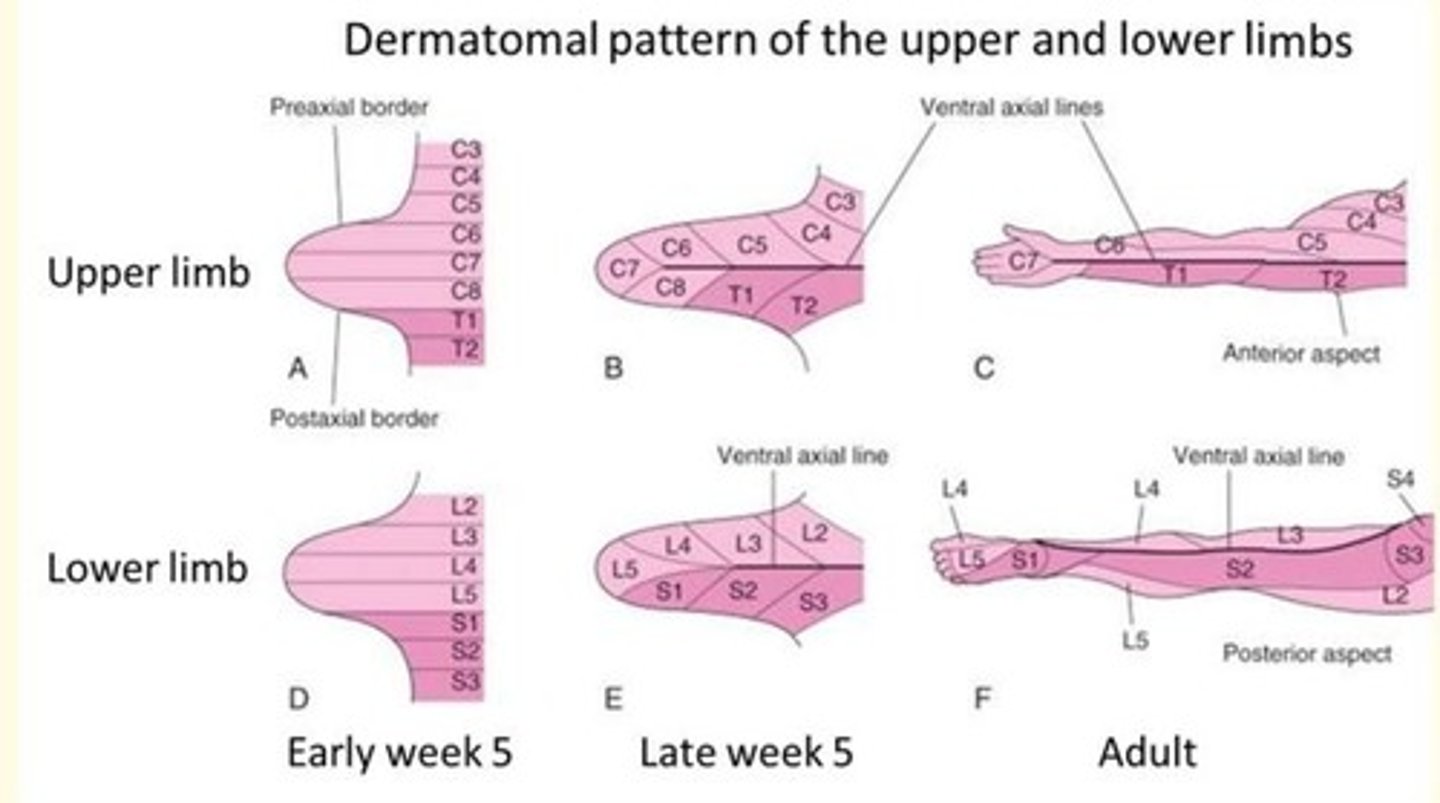
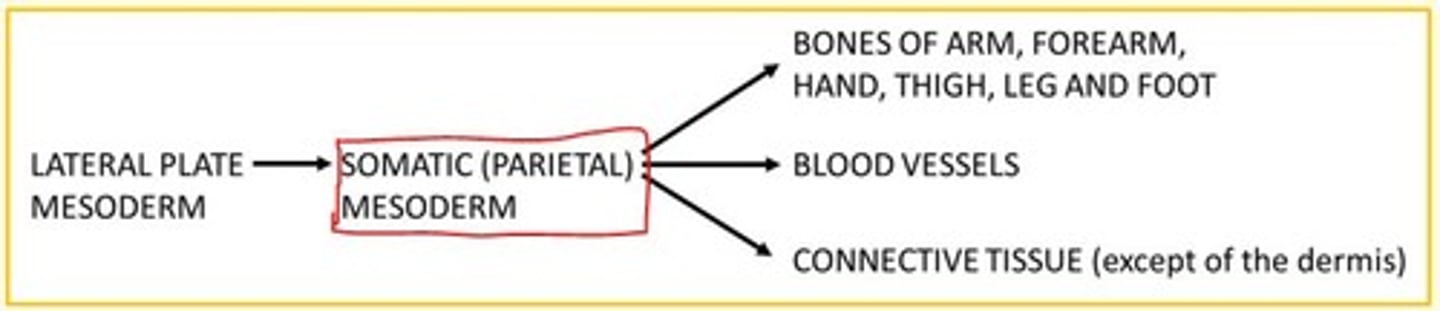
The lateral plate mesoderm becomes the somatic (parietal) mesoderm which develops into the limb ___
Skeleton
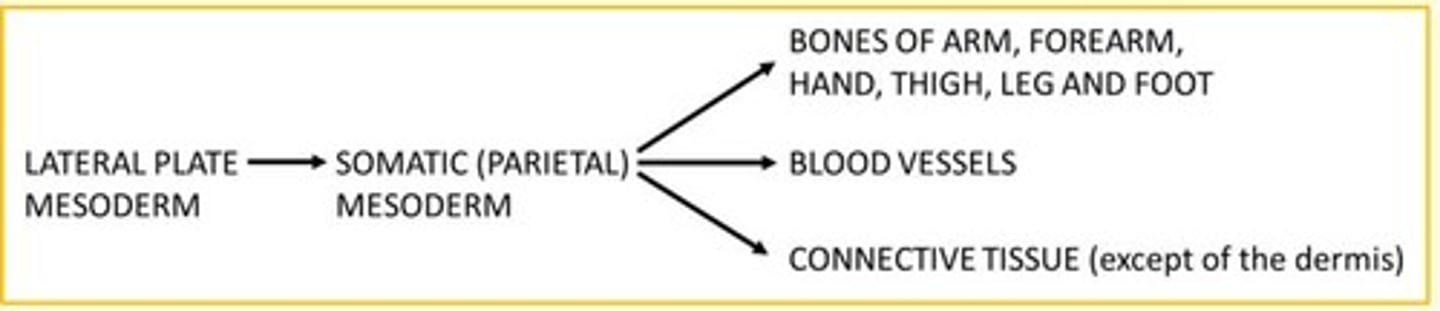
The paraxial mesoderm becomes the ___ which develops into the limb ___
The paraxial mesoderm becomes the somites which develops into the limb musculature
Antero-posterior axis
Extends from the front of the body to the back

Proximo-distal axis
Base to tip (e.g., base of limb to tips of digits)
Dorsal
Back
Back of the hand, top of the foot
Ventral
Front
Palm of the hand, sole of the foot
During what weeks do limb morphogensis occur in the foetus?
Limb morphogensis occurs from the 4th to the 8th week
Upper limb starts (C5 to T1), lower limb development is lagging (L1 to S1).
Limb development (4th - 8th week) begins with the activation of a group of a group of mesenchymal cells from WHICH layer of the mesoderm?
Limb development begins with the activation of a group of mesenchymal cells from the SOMATIC (PARIETAL) layer of the lateral mesoderm that form limb buds.
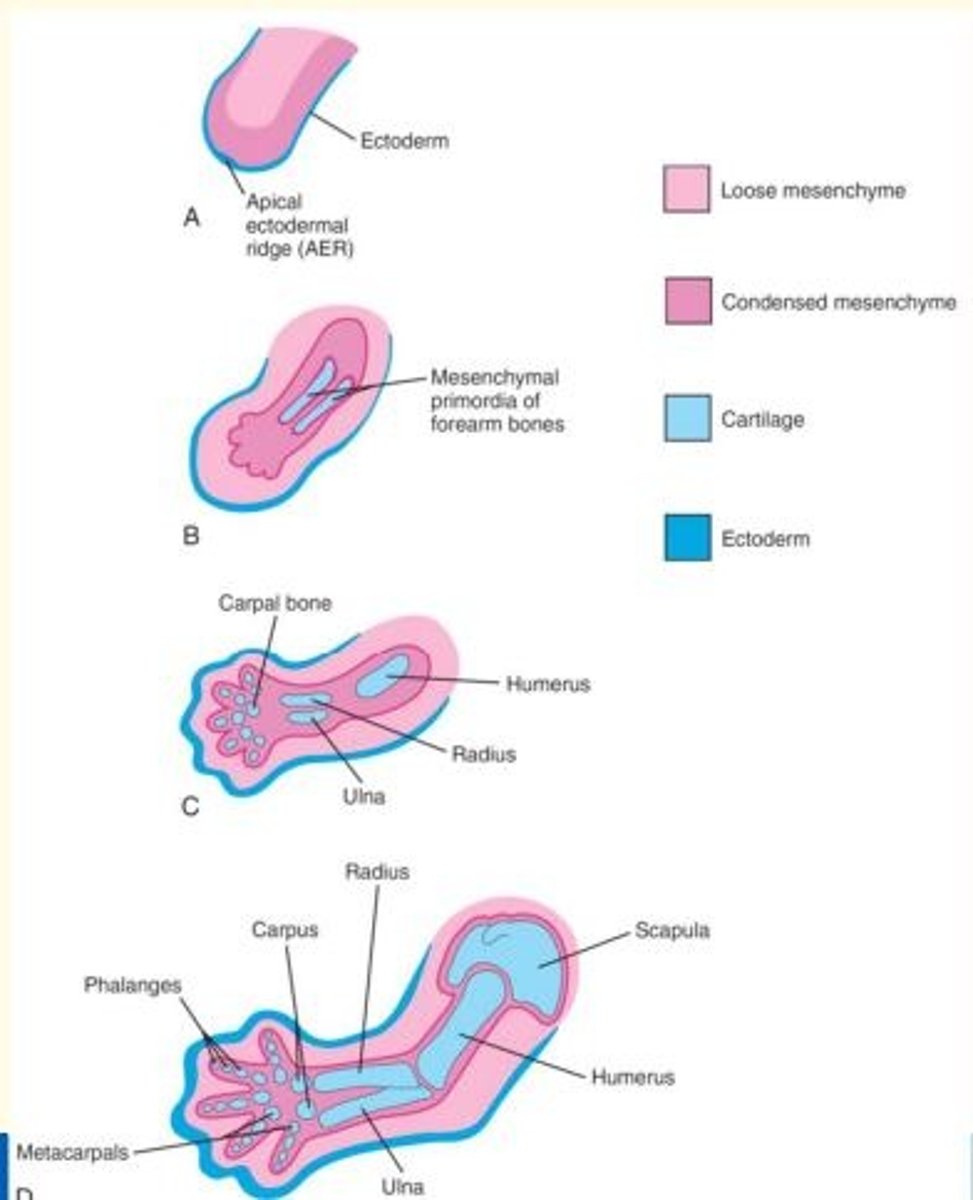
Anatomy of a limb bud
Limb bud consists of mesenchymal core derived from somatic (parietal) layer of lateral plate mesoderm that will form bones and connective tissues of the limb.
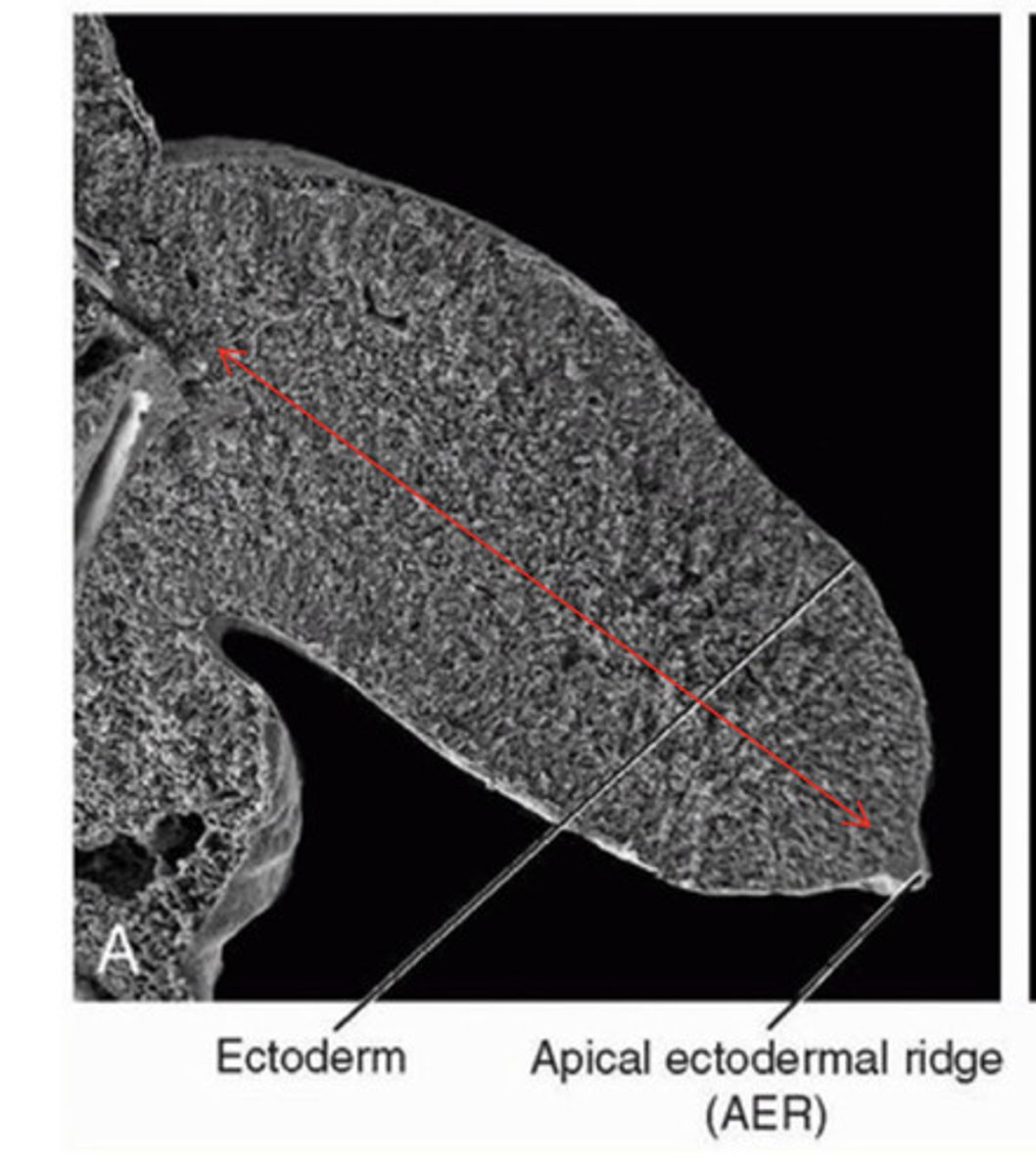
Limb bud is covered by a layer of cuboidal ectoderm.
Apical ectodermal ridge (AER) = ectoderm at the distal border of the limb thickens and forms the AER. This is a specialised multilayered epithelial structure.
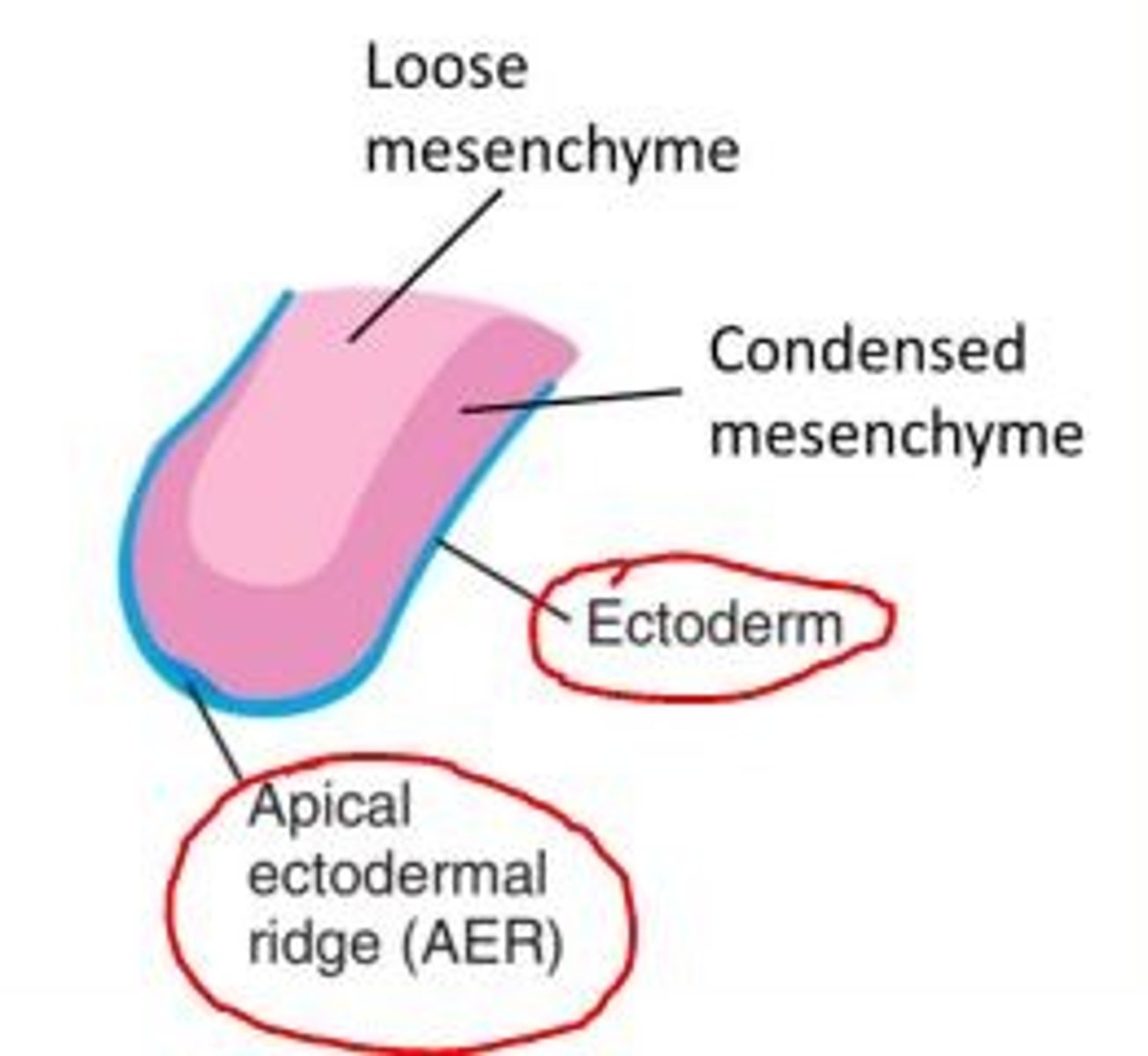
What is the function of the Apical Ectodermal Ridge (AER) in the limb bud?
The AER induces the adjacent mesenchyme to remain as a population of undifferentiated, rapidly proliferating cells called the progress zone.
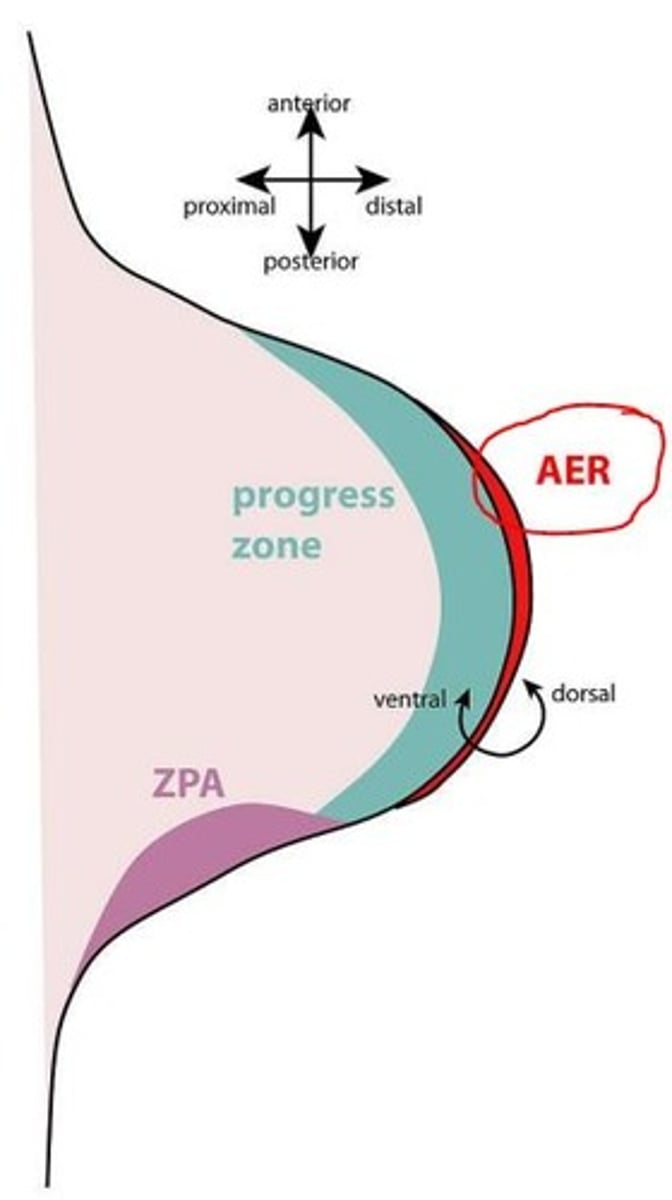
Three functions of the Apical Ectodermal Ridge (AER) in the limb bud
1) Critical for limb bud outgrowth
2) Arranges limb development in proximal to distal direction (establishes proximo-distal axis of limb)
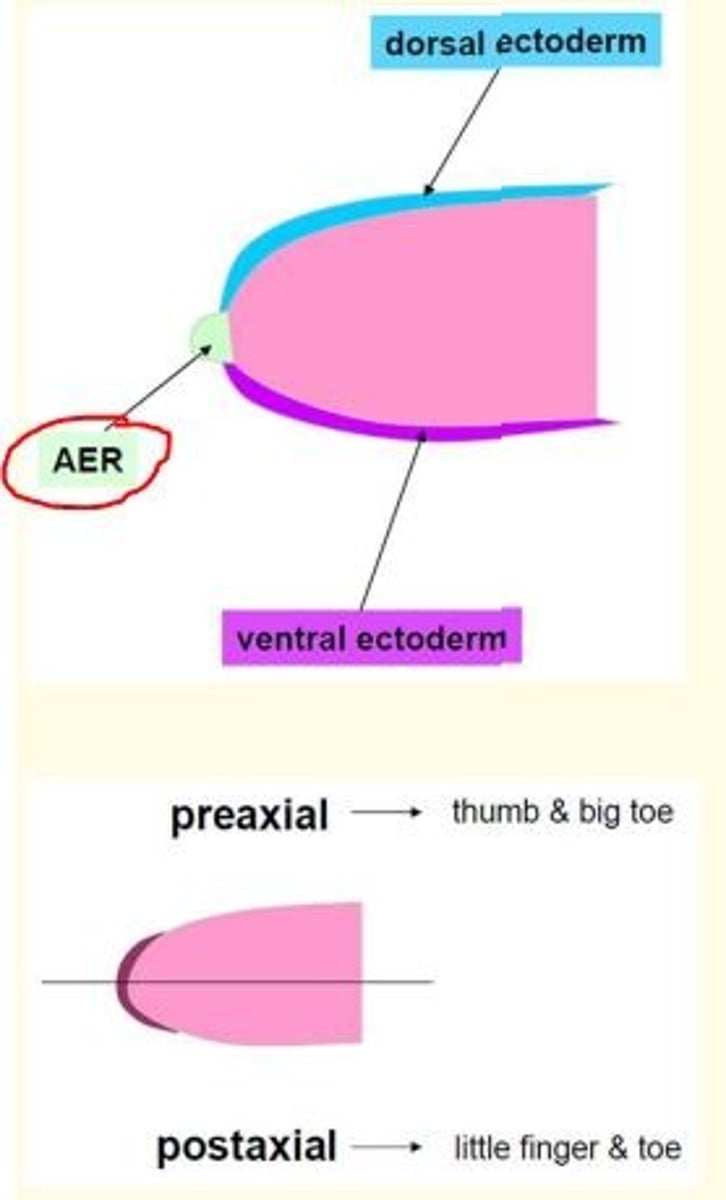
3) AER marks boundary between dorsal and ventral limb ectoderm - dorsoventral patterning
In 6-week old embryos, the terminal portion of the limb buds become flattened to form ___ and ___
In 6-week old embryos, the terminal portion of the limb buds become flattened to form handplates and footplates
By the end of the 6th week of development, mesenchymal tissue in the hand plates has condensed to form ___ ___
By the end of the 6th week of development, mesenchymal tissue in the hand plates has condensed to form finger buds (digital rays)
At the tip of each digital ray, a part of the Apical Ectodermal Ridge (AER) induces the development of the mesenchyme into mesenchymal primordia of the bones (phalanges) in the digits.
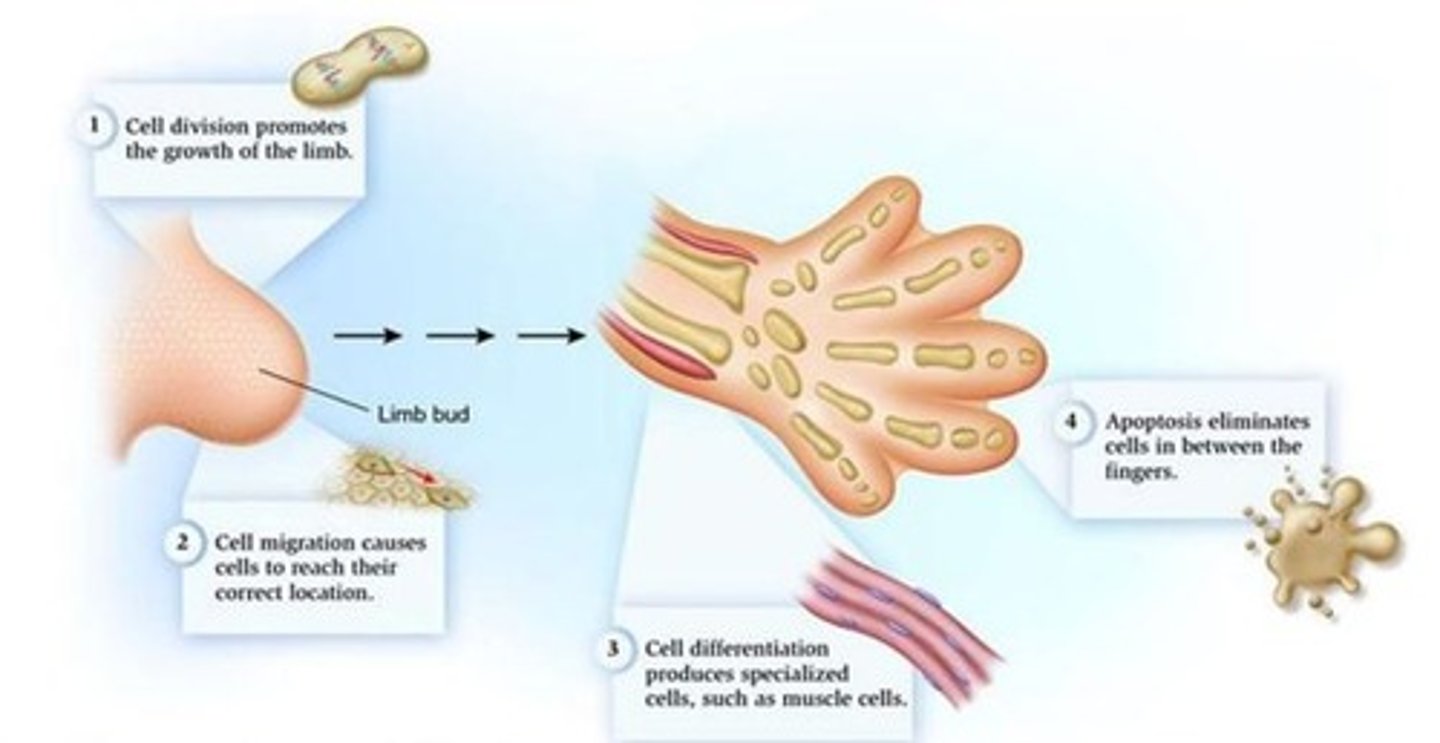
Name four cellular processes which promote limb formation in the developing foetus in the 6th week
1) Cell division promotes growth of the limb
2) Cell migration causes cells to reach their correct location
3) Cell differentation produces specialised cells such as muscle cells
4) Apoptosis eliminates cells in between fingers
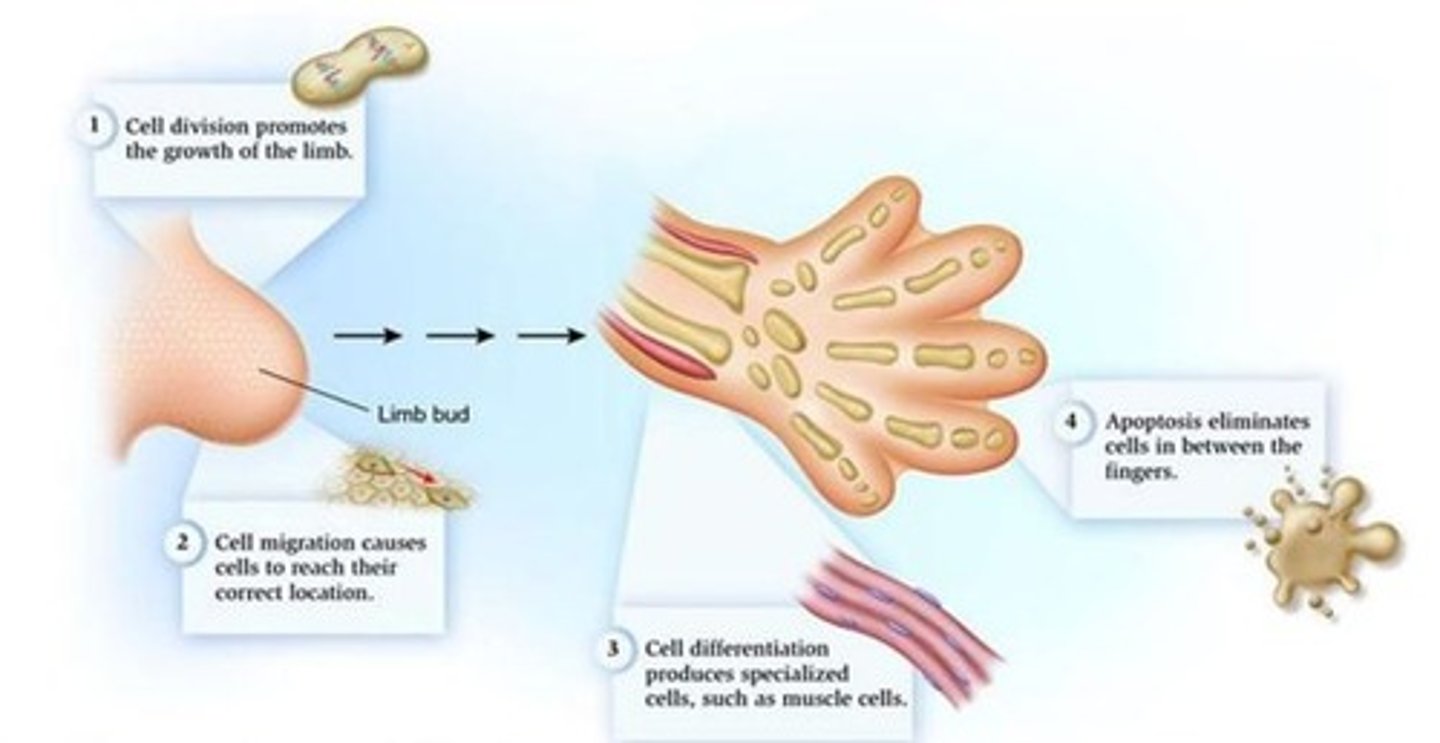
At the end of the 8th week, notches are formed between the digital rays, leading to the formation of separate digits. This is conducted by ___ process
Apoptosis
At what stage, do chondrification centres appear in the limb buds?
Later in the 5th week
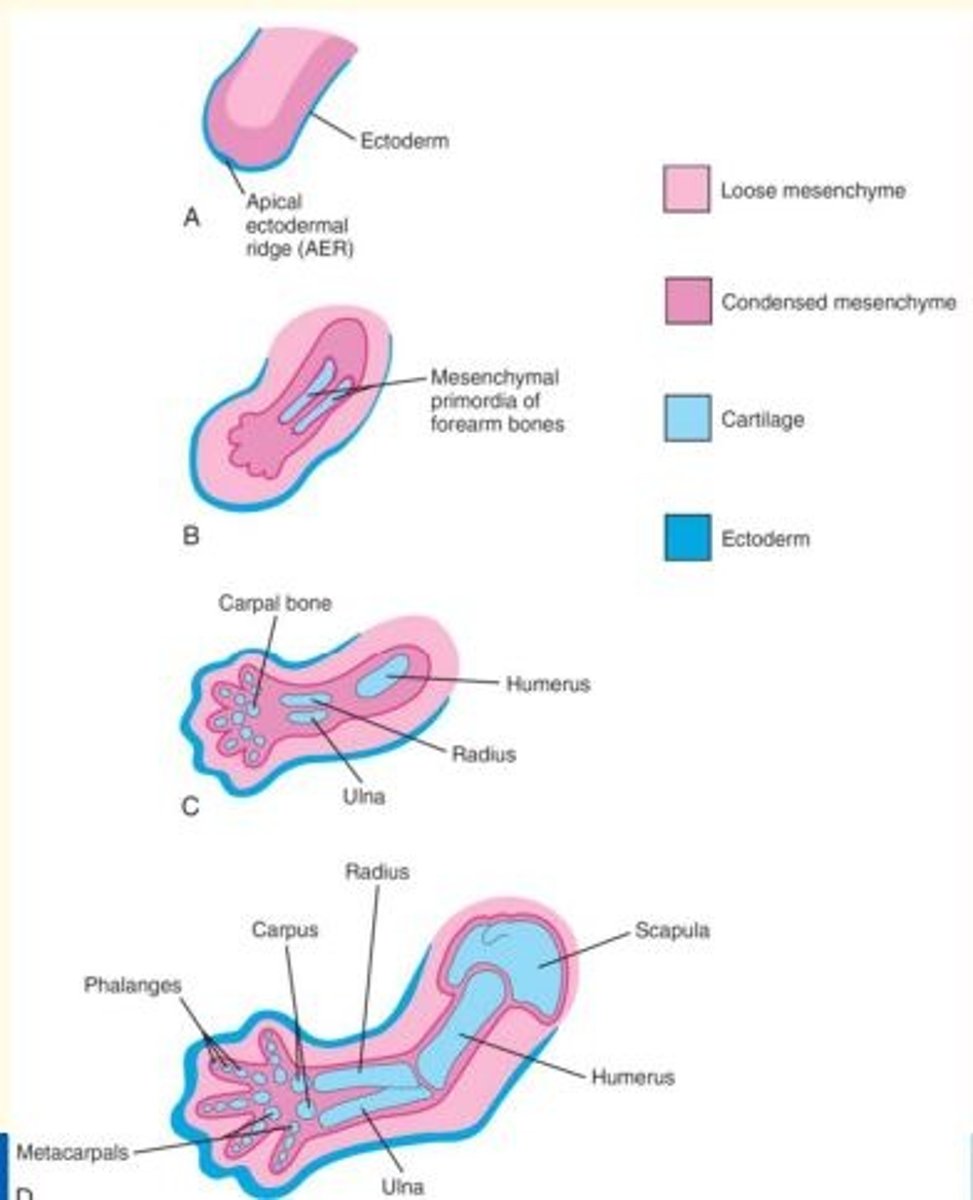
At what stage do mesenchyme cells in the limb buds begin to condense and differentiate into chondrocytes?
During the 6th week, mesenchyme in the limb buds begin to condense and these cells differentiate into chondrocytes.
The mesenchymal bone models in the limbs undergo chondrification to form hyaline cartilage bone models.
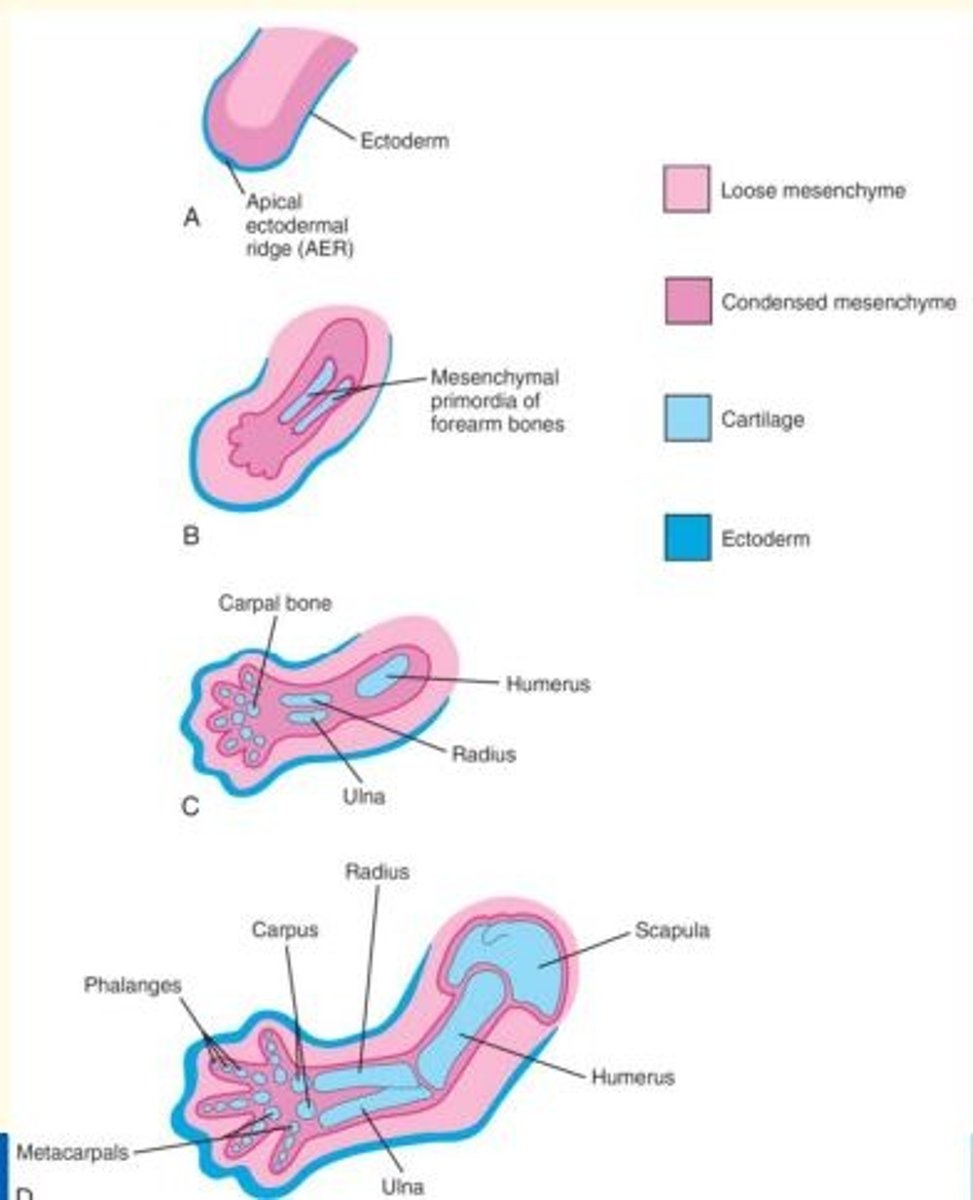
By what week is the entire limb skeleton of the foetus cartilaginous (due to chondrification)?
By the end of the 6th week, the entire limb skeleton is cartilaginous
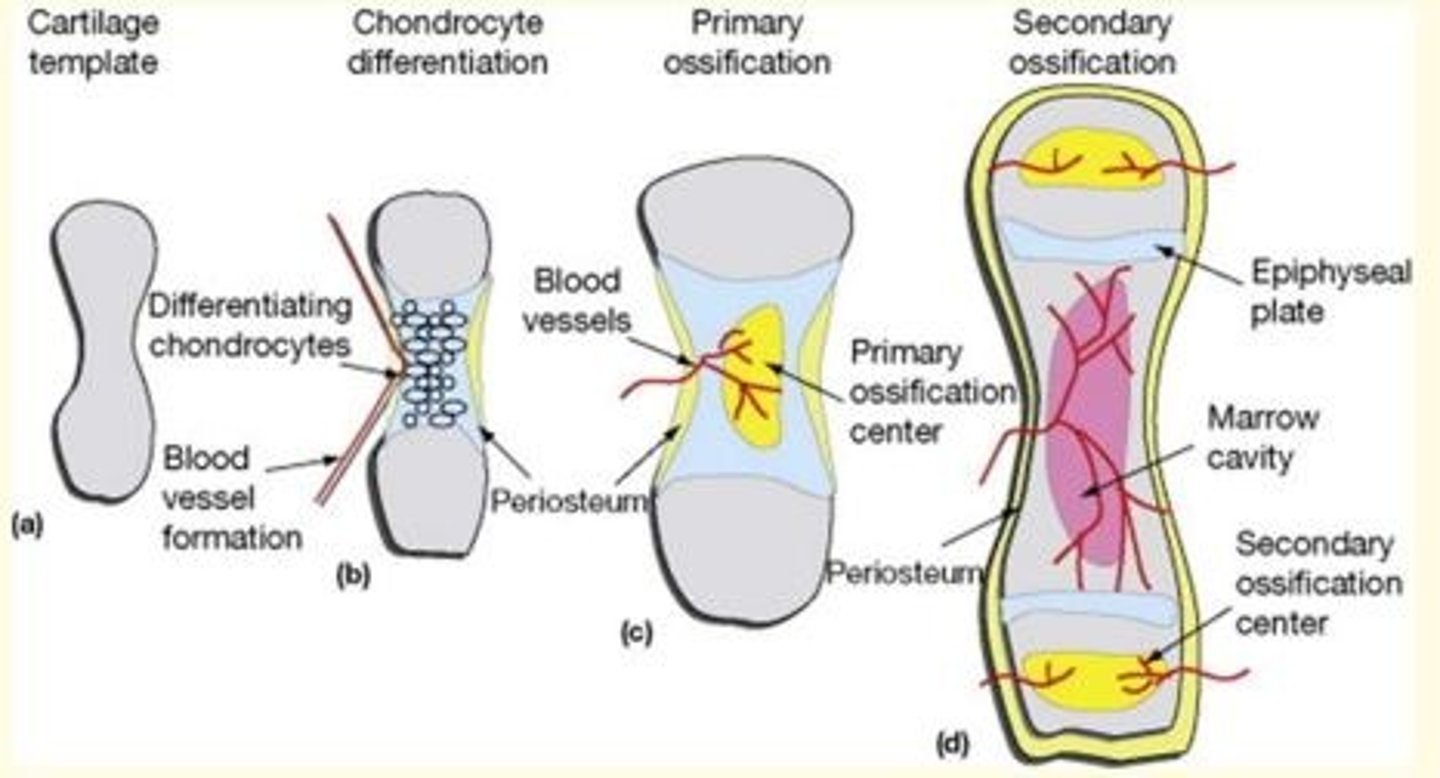
Osteogenesis of the long bones (formation of primary ossification centres in the diaphysis) occurs during which week?
Osteogenesis of the long bones begins in the 7th week from primary ossification centres in the diaphysis of the long bones
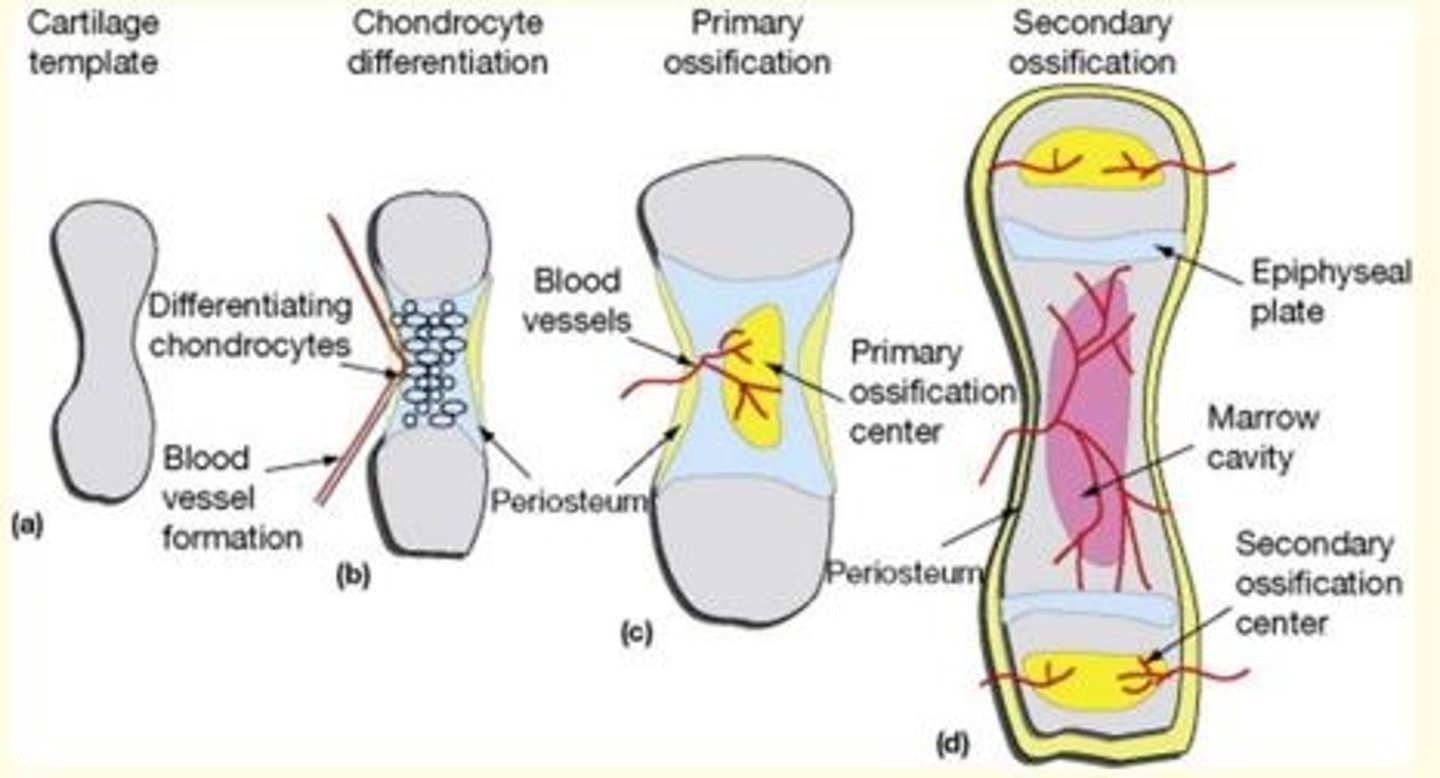
What part of the bone plays an important role in growth in the length of bones?
Epiphyseal growth plates
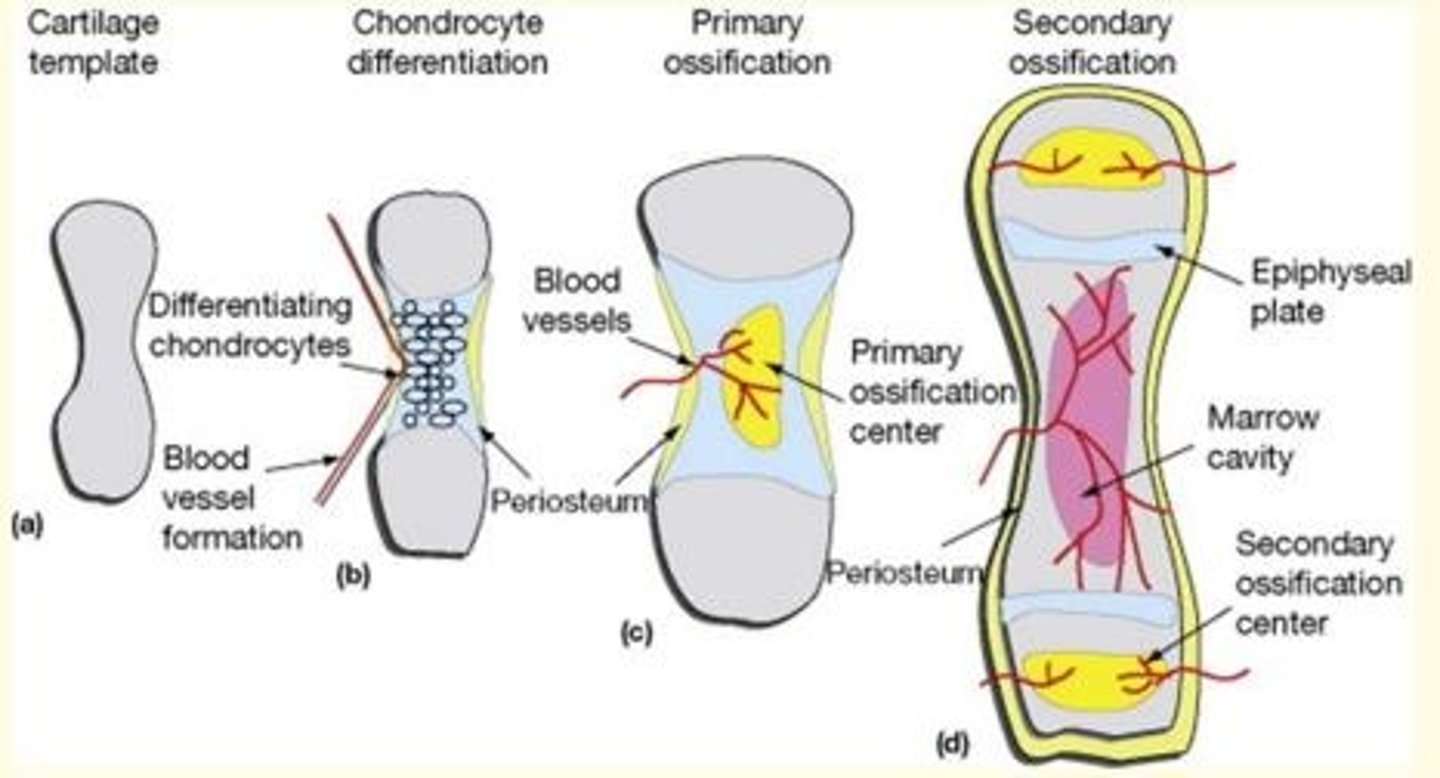
Secondary ossification centres arise in the ___ of the bone
Epiphyses
The musculature of the limb is derived from what type of cells?
Myogenic cells
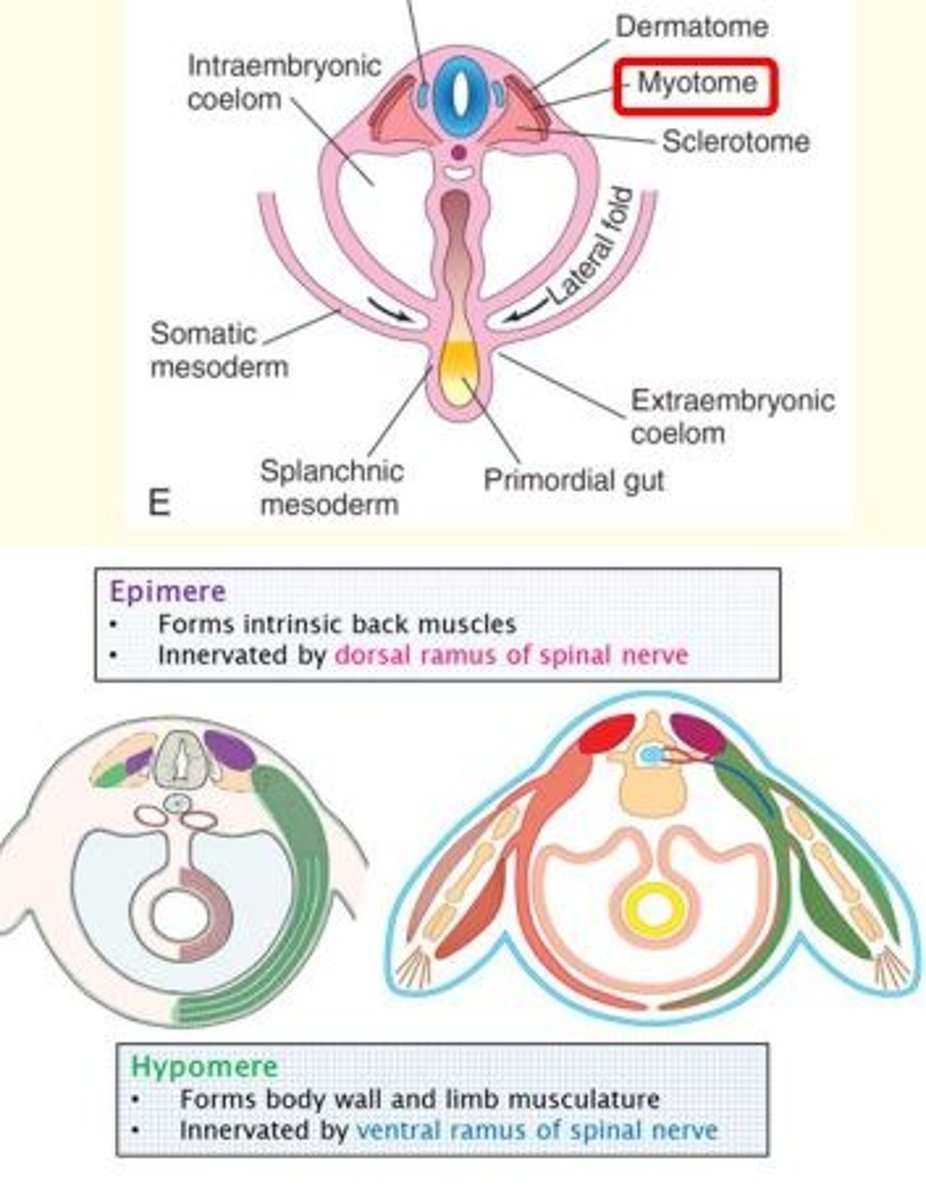
Each myotome is divided into two parts...
A small dorsal region called the ___
A larger ventral region called the ___
A smaller dorsal region called the epimere
A larger ventral region called the hypomere
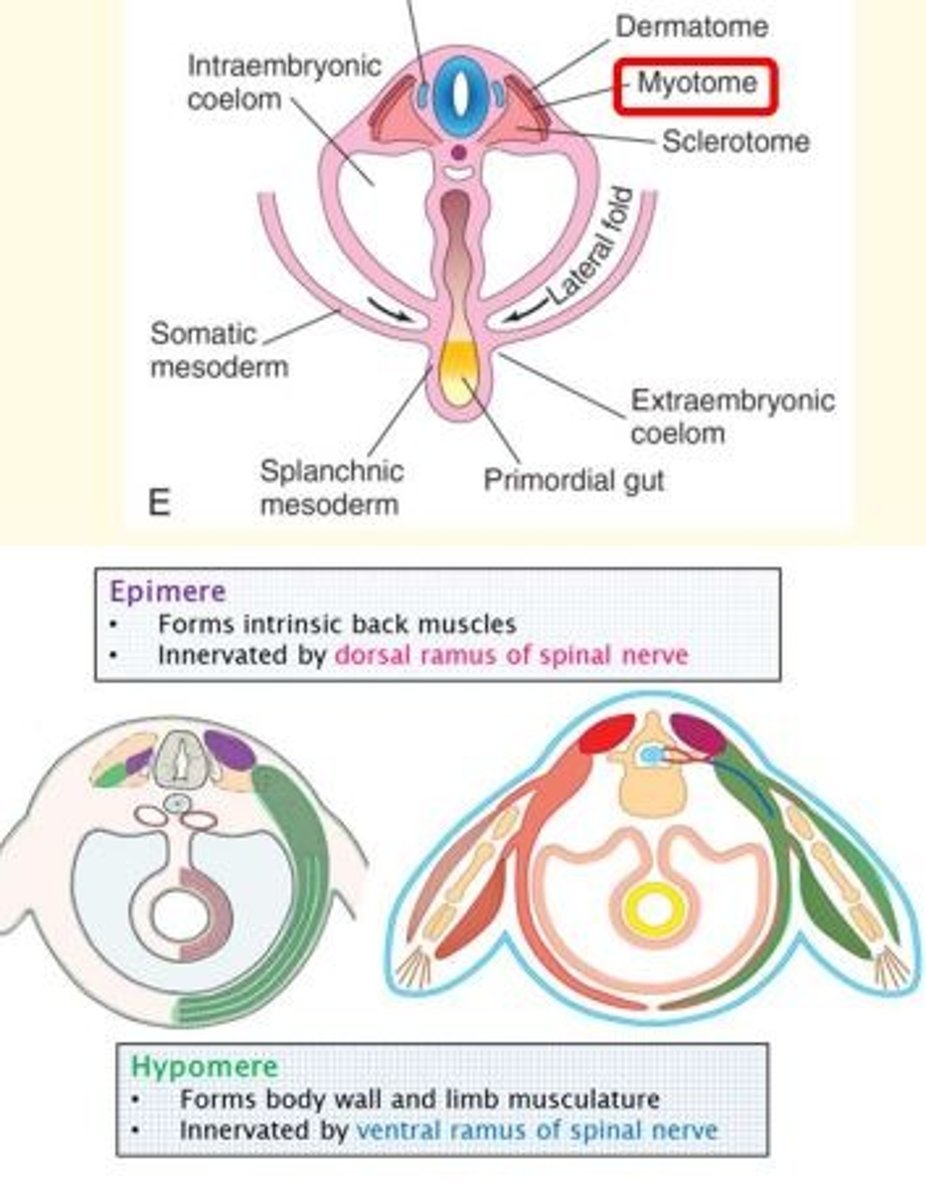
Each myotome is divided into two parts...
A small dorsal region called the epimere
A larger ventral region called the hypomere
What does the epimere form?
The epimere forms the intrinsic back muscles.
It is innervated by the dorsal ramus of the spinal nerve.
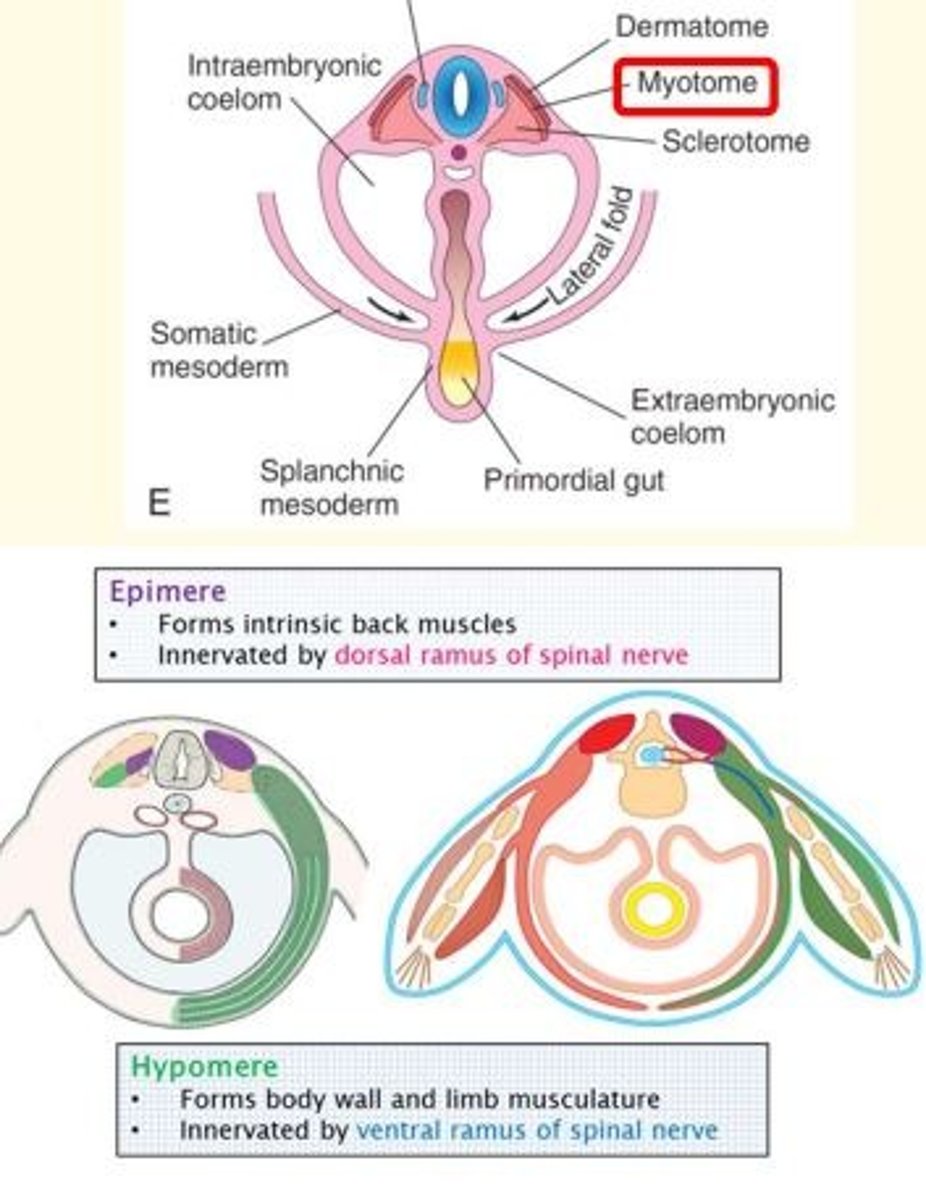
Each myotome is divided into two parts...
A small dorsal region called the epimere
A larger ventral region called the hypomere
What does the hypomere form?
The hypomere forms the body wall and limb musculature.
It is innervated by the ventral ramus of the spinal nerve.
Myogenic cells begin to coalesce into two common muscle masses - what are these?
One is the precursor of the flexor muscle
The other gives rise to the extensor muscles
The stage after this includes the splitting of the common muscle masses into anatomically recognisable precursors of the definitive muscles of the limb.
What important process occurs during 7th week of gestation?
Limb rotation
Upper limb rotates 90◦ laterally
Lower limb rotates 90◦ medially
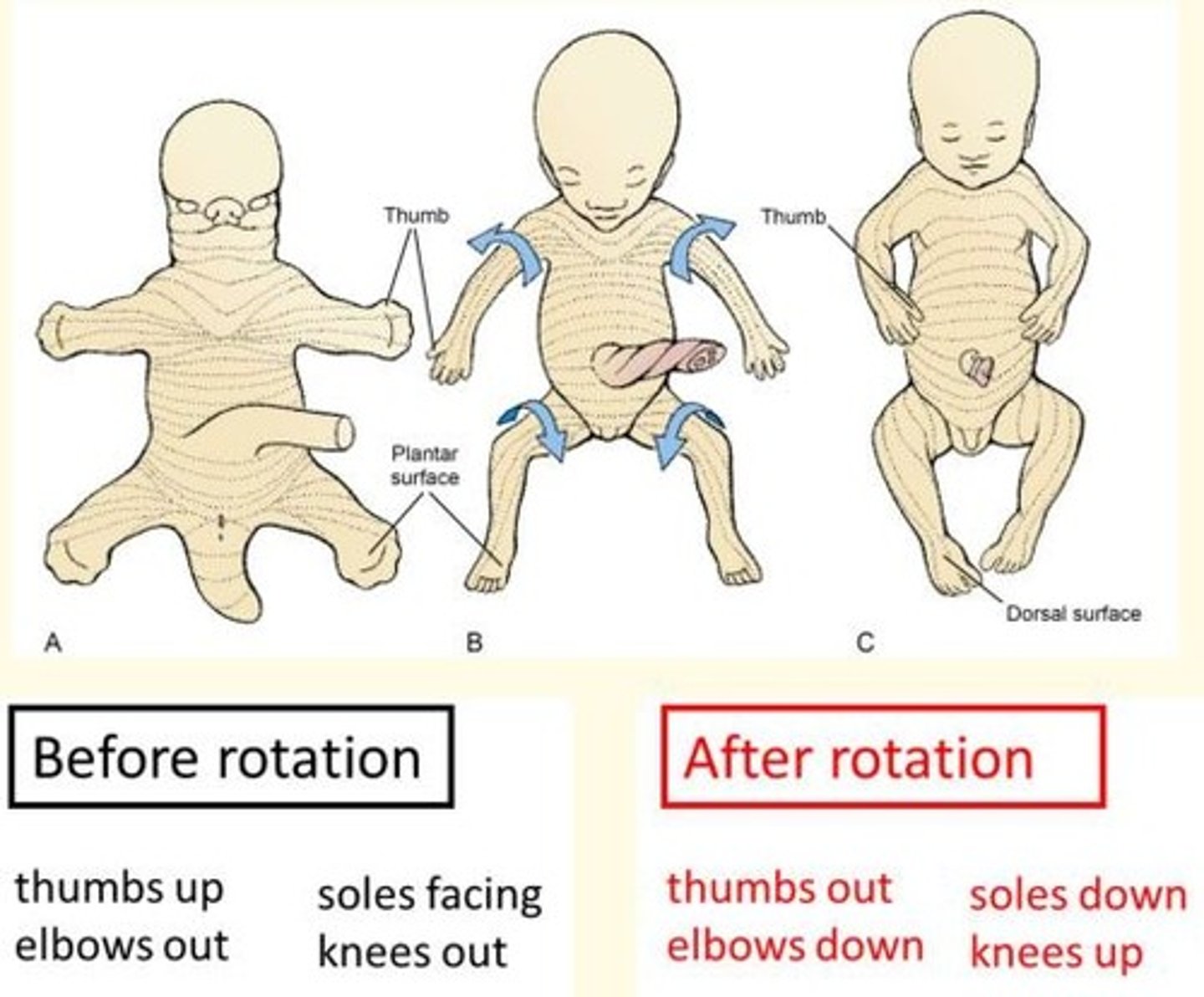
What is the effect of limb rotation during the 7th week of gestation?
Limb rotation causes the originally straight (dermatomal) segmental pattern of lower limb innervation to twist into a spiral.
Causes of limb defects
Usually hereditary
Can be chemically-induced by teratogens e.g., thalidomide
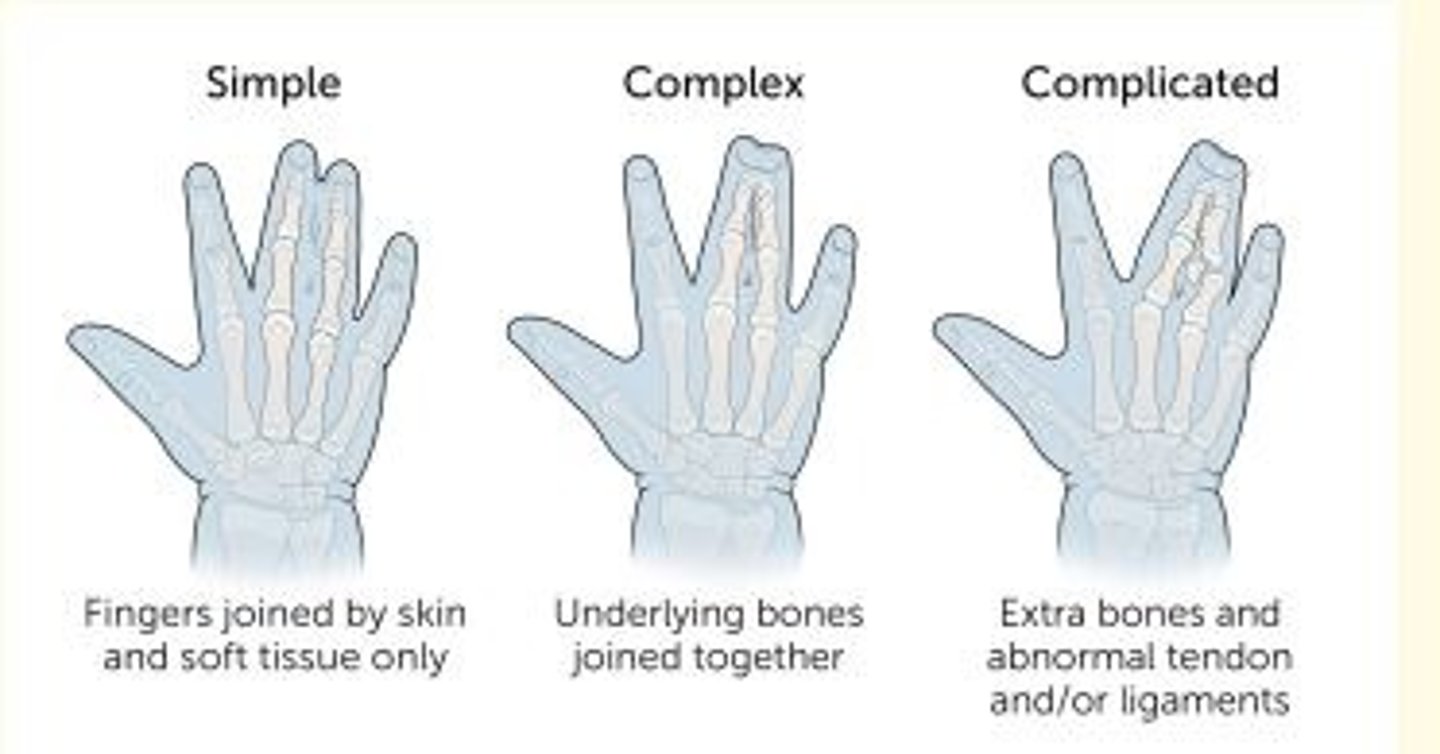
Birth limb defect where two or more digits are fused together
Syndactyly
Birth limb defect where there is supernumerary fingers and/or toes
Polydactyly (also known as hyperdactyly)
Non-syndromic polydactyly
Polydactyly appearing in isolation (not with any syndrome)
Syndromic polydactyly
Polydactyly appearing as part of a syndrome with other associated birth defects
Extremely rare birth defect marked by COMPLETE absence of one or more limbs
Amelia
Birth defect marked by PARTIAL absence of one or more limbs
Meromelia
Thalidomide teratogen associated with what birth defects?
Limb defects (phocomelia - seal limb) and amelia
What two tissues have their shared origin in ectoderm? Does this have any clinical significance?
Skin (including lining of mouth, nostril and anal canal) and nervous tissues (also teeth, sweat glands, hair, nails and dental enamel) are all formed from ectoderm.
There are some important and not uncommon neurocutaneous conditions such as Neurofibromatosis, Sturge Webber Syndrome and Tuberosis sclerosis which have their origin in this shared embryology.
The apical ectodermal ridge (AER)...
Is a ridge of thickened ectoderm at the apex of the developing limb bud
A 9-month old male infant presents to the orthopedic clinic with the defects shown below.
The mother reports excellent health and not taking any medication, alcohol and tobacco at any point during her pregnancy. However, she does mention that she has a cousin and a great aunt who had upper limb defects.
Based on the history, you strongly suspect that this family most likely harbours a mutation that results in the loss or disruption of what class of genes?
HOX genes (e.g. HOXA10)
3 multiple choice options
The way that the upper limb forms embryologically creates multiple compartments as a result of the limb's rotation. Which of the following are correctly paired?
Anterior compartments of the upper limb - Primarily a Flexor Compartment (muscles that produce flexion on the joints)
3 multiple choice options
During development disruption of growth and/or patterning can result in a defect with absence of part of a limb; it is called...
Meromelia
3 multiple choice options
Pattern and initial outgrowth of the limb buds starts to appear...
End of fourth week of development
3 multiple choice options
Describe epimere and hypomere
The musculature divides into two regions.
The epimere goes dorsally to form the erector spinae muscles and is innervated from the (dorsal) posterior ramus of the spinal nerve roots.
The hypomere goes ventrally to form the rest of the musculature and is innervated by the (ventral) anterior ramus of the spinal nerve root.