Anatomy- Lab Exam
1/130
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
131 Terms
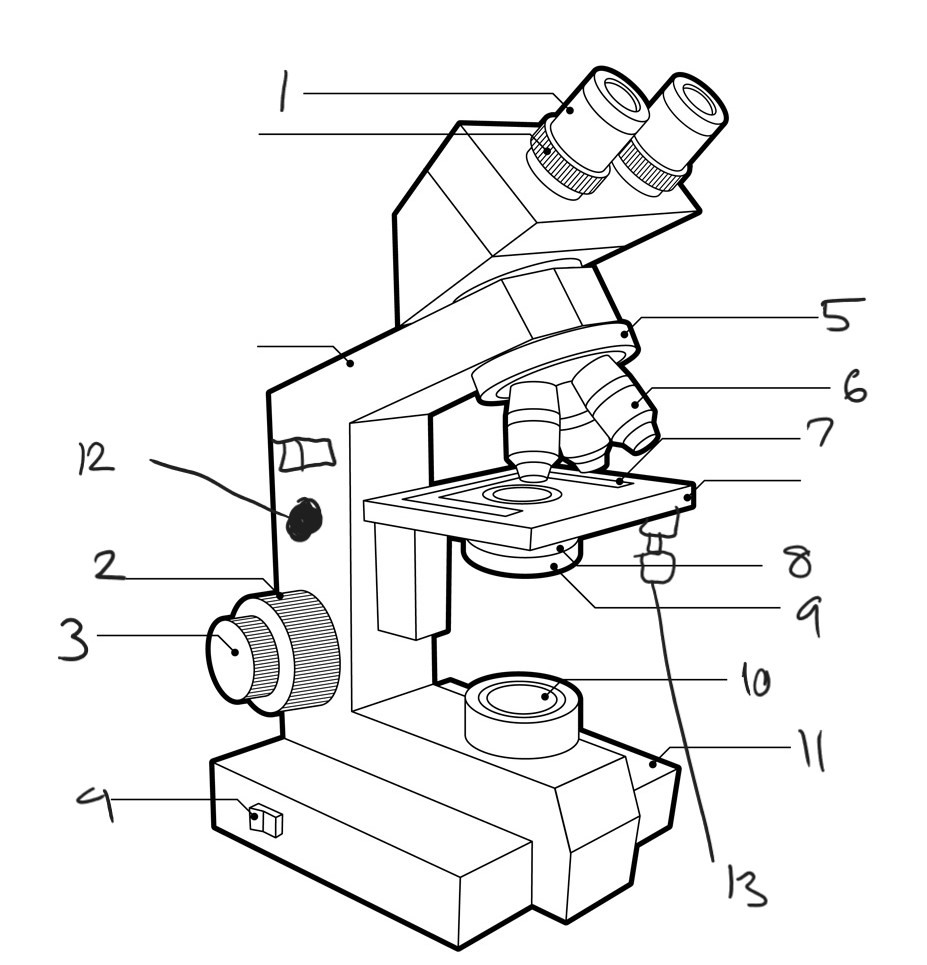
Label diagram
ocular lens
course focus knob
fine focus
power switch
rotating nosepiece
object lenses
stage control
condenser
diaphragm lever
lamp
base
lamp brightness control knob (other side)
stage control knobs
ocular lens
lens in a microscope or telescope that is closest to the eye of the viewer
used to magnify the image formed by the objective lens or mirror and allows the viewer to see the enlarged image.
10x
objective lens
lens in optical instruments, such as microscopes and telescopes
responsible for gathering and focusing light onto the focal point
usually located at the front of the instrument and has a larger diameter compared to other lenses in the system
4x, 10x, 40x, and 100x
base
sturdy bottom part that provides stability and support for the entire microscope
typically flat and wide to prevent the microscope from tipping over during use
The base also houses the illuminator or light source in some microscopes, providing the necessary light for viewing specimens
course focus knob
big knob on left side
moves stage up and down
don’t use after setting it with the 4x
condenser
responsible for focusing and directing light onto the specimen
located below the stage
helps to enhance the resolution and brightness of the image.
diaphragm lever
used to control the amount of light passing through the specimen.
located below the condenser
can be adjusted to regulate the intensity and focus of the light.
By manipulating the diaphragm lever, the user can enhance contrast and improve visibility of the specimen.
fine focus knob
It allows for precise adjustment of the focus of the microscope's objective lens, enabling clear and detailed viewing of the specimen under observation
lamp
provide light for the specimen being observed
it helps to enhance visibility and clarity by directing light onto the sample.
mechanical stage
platform that holds the specimen slide in place and allows for precise movement and positioning
typically consists of two knobs or controls that control the horizontal (x-axis) and vertical (y-axis) movement of the stage
This enables the user to easily navigate and focus on different areas of the specimen under the microscope
rotating nosepiece
device that holds multiple objective lenses.
By rotating the nosepiece, different objective lenses can be brought into position, allowing for different levels of magnification and focus.
This feature enables users to easily switch between lenses without having to manually remove and insert them, making it more convenient and efficient for microscopy.
stage clip
mechanism used to hold a slide or specimen in place on the stage of the microscope.
It ensures that the slide remains steady and secure during observation and allows for precise positioning of the specimen under the microscope's objective lenses.
stage control knobs
allow users to adjust the position and movement of the microscope stage
typically include a coarse adjustment knob for larger movements and a fine adjustment knob for more precise positioning
By turning these knobs, users can move the stage horizontally or vertically to focus on different areas of the specimen being observed.
tube
the microscope's eyepiece or ocular lens
look through to observe the specimen.
connects eyepiece to the objective lenses, allowing the light from the specimen to pass through and be magnified.
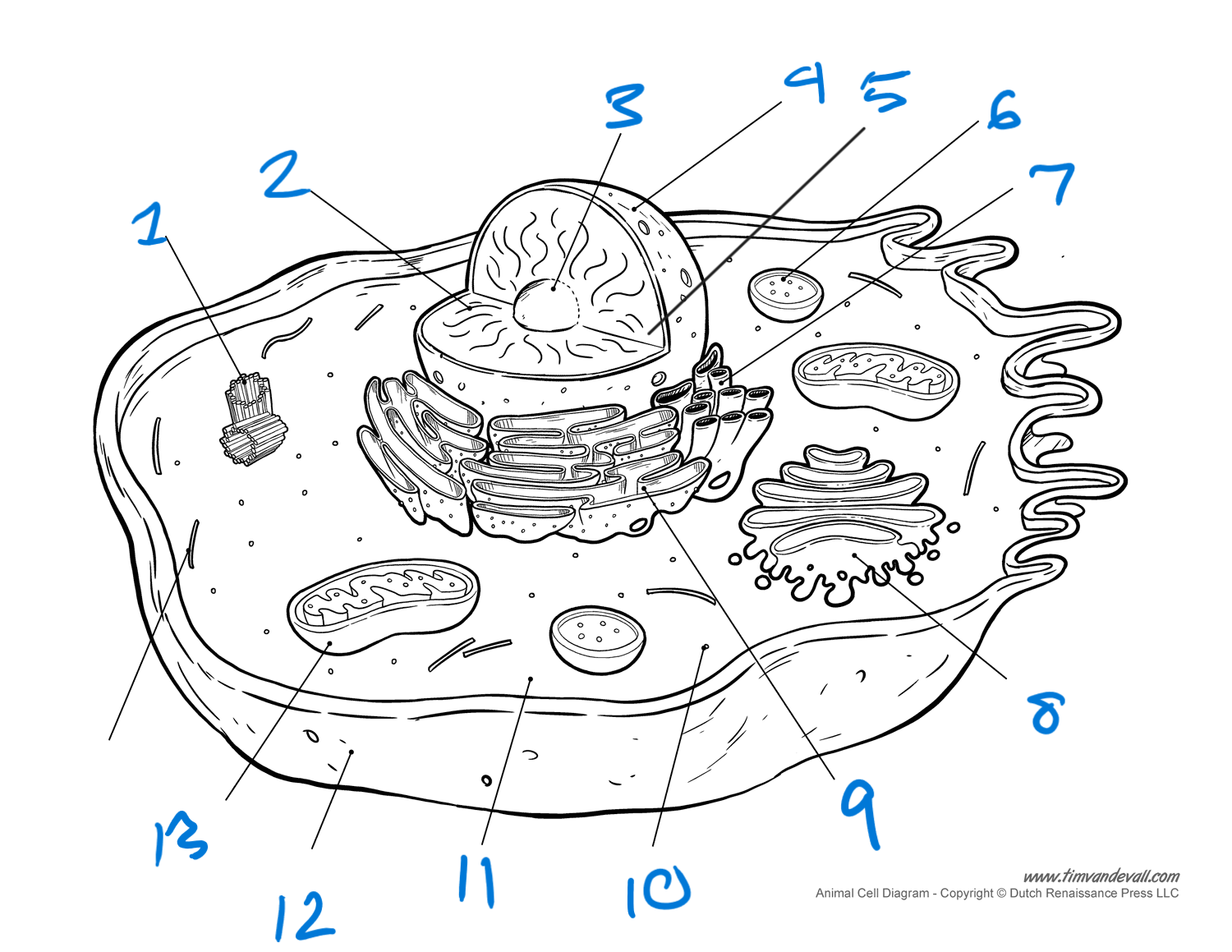
label cell
centrioles (in centrosomes)
chromatin
nucleolus
nuclear membrane (envelope)
nucleus
lysosome'
SER
golgi bodies
RER
ribosomes
cytoplasm
plasma membrane
mitochondria
nucleus
membranous
double membrane
control center
has DNA, RNA, proteins, and nucleolus
nucleolus/nucleoli
non-membranous
ribosome synthesis
contains DNA, RNA, and proteins
mitochondria
membranous
ATP synthesis
double membrane
has own protein, RNA, and DNA
ribosomes
non-membranous
rRNA for translating
2 types: free and bound
free- suspended in cytosol, makes proteins for nucleus, mitochondria, and cytosol
bound- attached to RER, makes protein for everywhere else
rough ER
membranous
makes secretory, lysosomal, and secretory proteins
smooth ER
membranous
makes lipids and steroid hormones
attached to RER
golgi apparatus
sorts, packages, and finalizes proteins/lipids to cell membrane, lysosomes, or for secretions
centrosomes
non-membranous
organizes microtubules and spindle apparatus (cell division)
has 2 centrioles and a pericentriolar matrix
nuclear membrane
double membrane'
covers nucleus
protects genetic material
chromatin
unwounded DNA
found in nucleus
cytoplasm
area between nuclear and cell membrane
2 components- organelles and cytosol
organelles: functioning structures of cell
cytosol: gel-like component, water and suspension of carbs, lipids, and proteins, may have inclusions (melanin or glycogen)
mitosis
essential for growth and repair of cells
1 cell divides into 2 diploid
genetically identical
interphase
first stage of cell division
3 stages: G1, S, G2
G1 (interphase)
growth and metabolism
centrosome replication begins
S (interphase)
chromatin replicates and is attached by centromeres
kinetochore proteins form
G2 (interphase)
growth and metabolism
makes enzymes and specific proteins needed for cell division
prophase
chromatin condenses into chromsomes
nucleoli and envelope disappear
centrosomes move to opposite poles
microtubules form spindle apparatus and attach to kinetochore proteins
spindle moves chromosomes toward cell equator
metaphase
46 chromosomes line up along cell equator
anaphase
spindle shortens, pulls kinetochores apart, separating centromeres
46 chromsomes move to each pole
cytokinesis begins
telophase
chromsomes uncoil to chromatin
nucleoli and nuclear membrane reappear
spindle disappears
cytokinesis
division of cytosol
meiosis
produces gamete
1 diploid (zygote) = 4 haploid cells
prophase I
homologous chromsomes attach to each other = tetrads
crossing over occurs (genetic diversity)
normal prophase activities
metaphase I
23 tetrads line across cell equator
anaphase I
tetrads separate and migrate to opposite poles (46 chromsomes)
telophase I
normal telophase activities
no homologous chromsomes (crossed over)
2 haploid daughter cells formed
meiosis II
same as meiosis I but with 23 chromosomes instead of 46
prophase Il, metaphase ll, anaphase ll, and telophase ll
homologous chromosomes
pair of chromosomes
get one from each parent
same length
same centromere position
same genes (not always same alleles)
present in mitosis and meiosis I
separated in anaphase II
diploid cells
2n
refers to number of chromosomes
has homologous chromsomes
46 chromosomes
haploid
n
refers to number of chromosomes
does not have homologous chromsomes
23 chromosome
sister chromatids
formed in S in interphase
exact same genetically
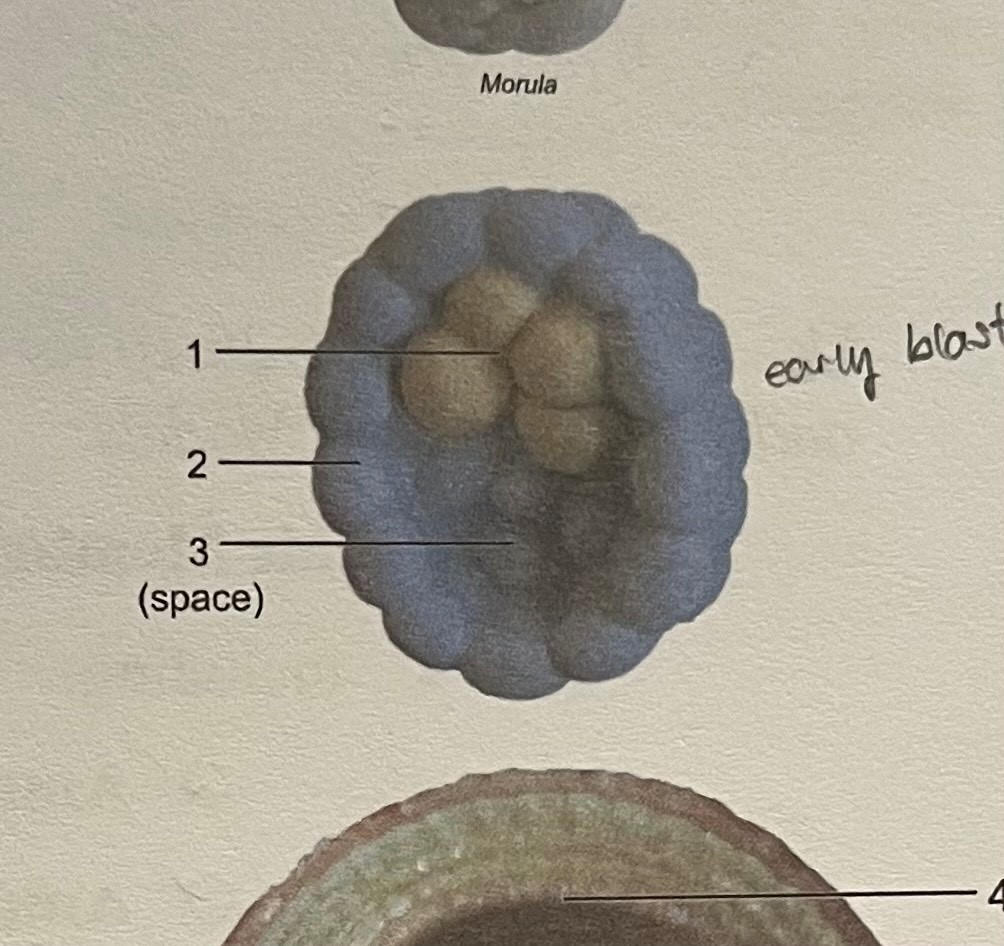
label
embryoblast (inner cell mass)
trophoblast
blastocyst cavity
(early blastocyst)
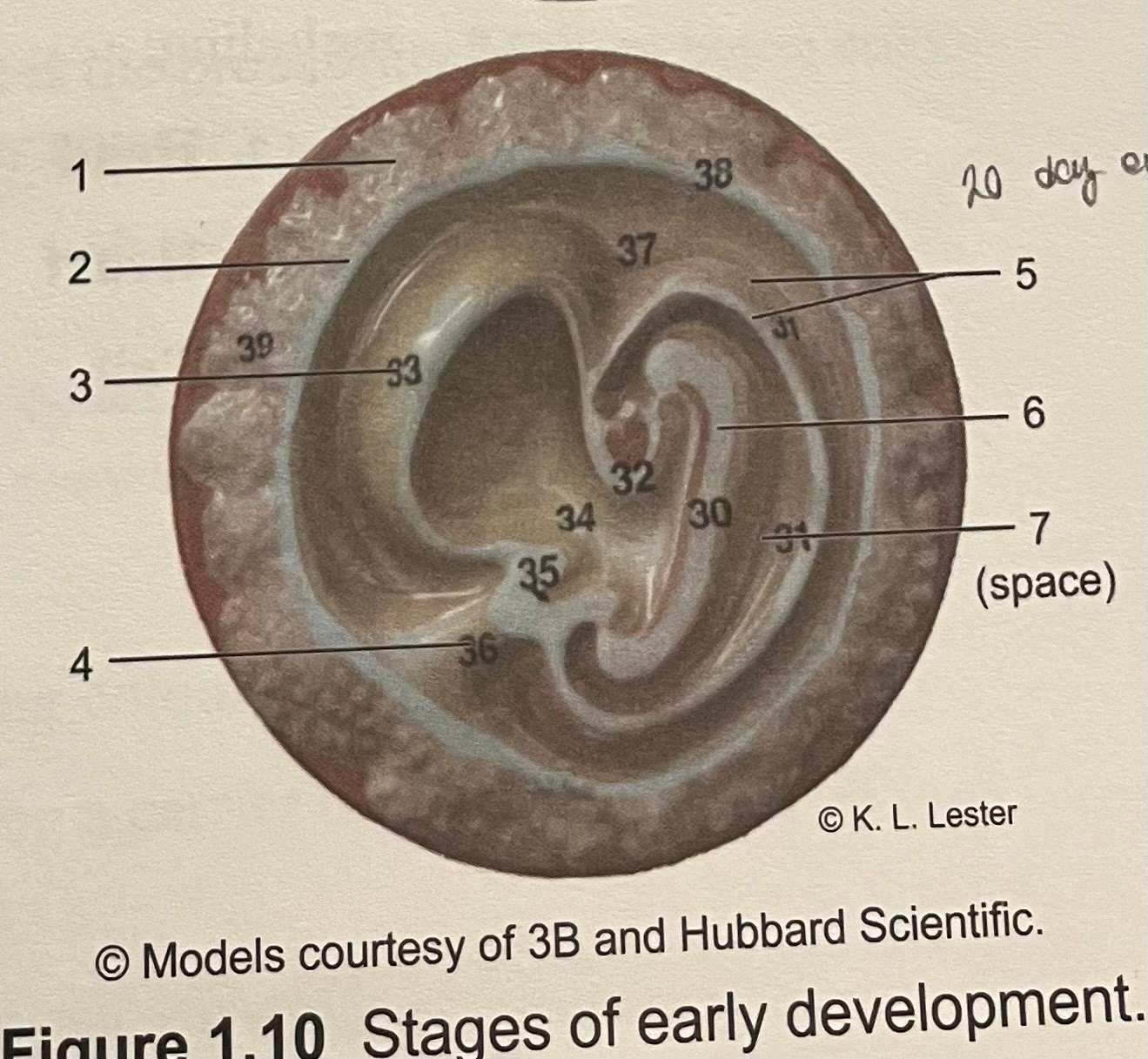
label
embryonic disc
yolk sac
chorion
amnion
amnion cavity
epiblast
hypoblast
(20 day embryo)
label
chorionic villi
chorion
yolk sac
umbilical cord
amnion
embryo
amnionic cavity
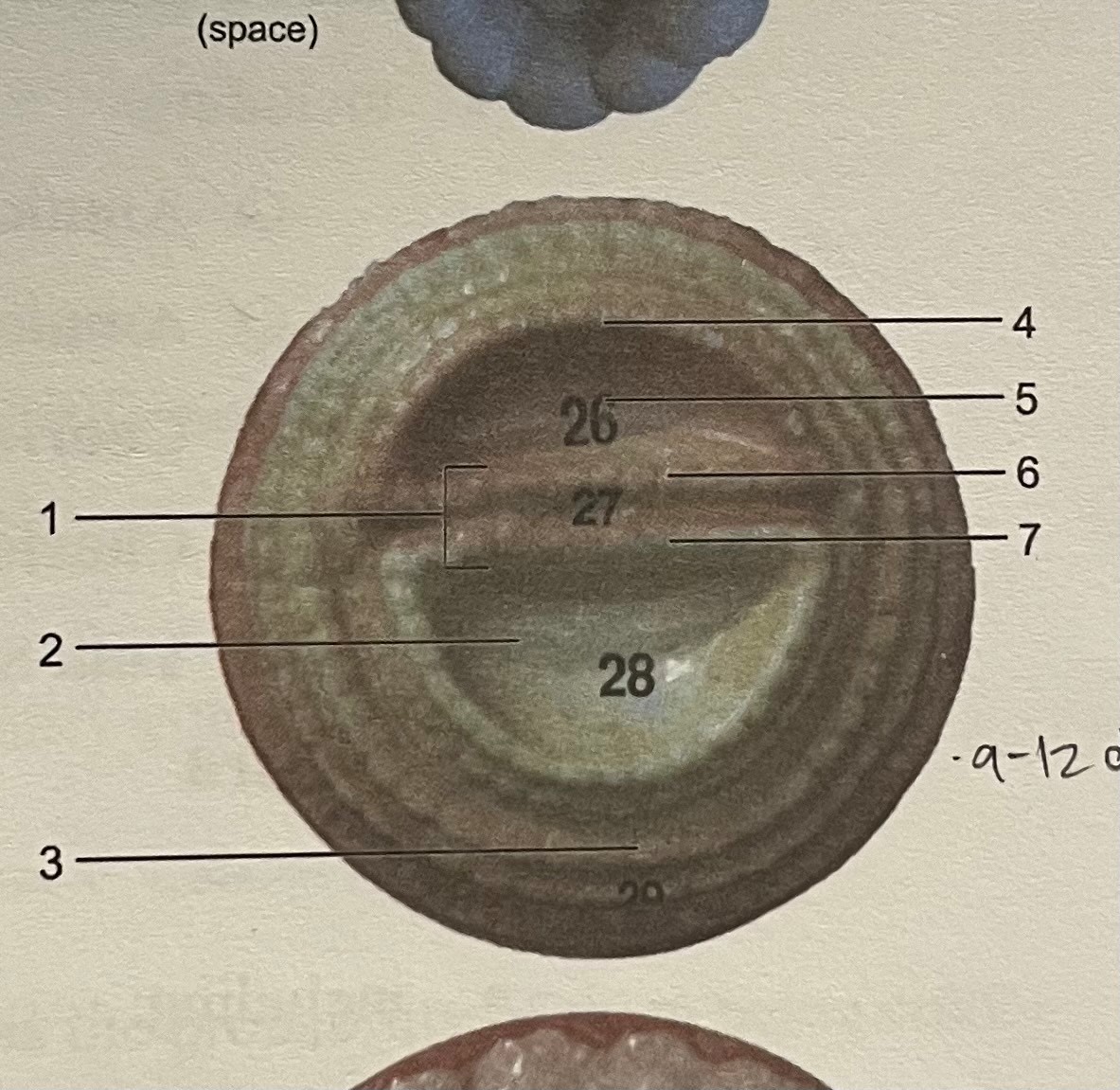
(9-12 day embryo)

label
chorionic villi
umbilical cord
amnion
ammonic cavity
chorion
embryo
yolk sac
(4 week embryo)
zygote
diploid
fertilized egg
goes through rapid miotic divisions called cleavage divisions
morula
solid ball of 16-32 cells
occurs after 72 hours of fertilization
no differentiation of cells (blastomeres)
blastocyst
hollow sphere of cells
occurs after 6 days
differentiation of cells
forms blastocyst cavity, embryoblast, and trophoblast
embryoblast
inner cell mass
cells divide and differentiate to form embryo
forms bilayer embryonic disc: epiblast and hypoblast
hypoblast
undergoes mitosis to form yolk sac
epiblast
will undergo mitosis to form: amnion (with amnion cavity) and 3 germ layers
amnion
fluid filled cavity that surrounds embryo with amnionic fluid
function of fluid- shock absorption and temp regulation
ectoderm
will form nervous system and epidermis of skin
mesoderm
will form muscles, most bones, cardiovascular system, and dermis of skin
endoderm
will form epithelial linings of digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems and their associated glands
yolk sac
derived from hypoblast
forms part of gut (gastrointestinal tract)
produces earliest blood cells and vessels
source of primordial germ cells (reproductive cells)
trophoblast
made of trophoblast cells
cells divide and differentiate to form chorion
chorion
from trophoblast cells
surrounds all embryonic membranes
chorionic villi- projections of chorion containing blood vessels that will form fetal part of placenta
implantation
attachment of blastocyst to endometrium of uterine wall after 6 days
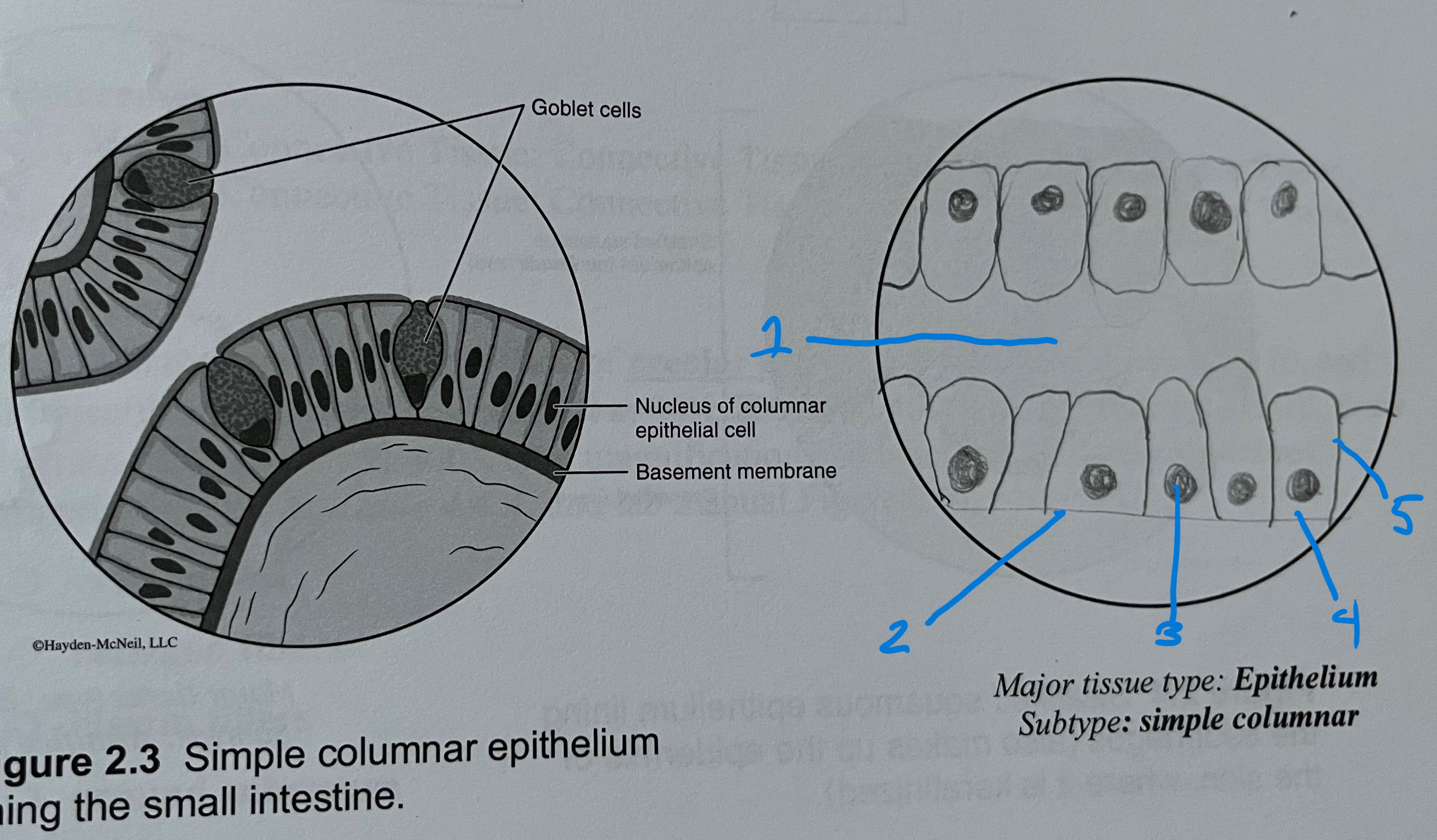
label
stratified columnar
free surface
basement membrane
nucleus
cytoplasm
cell membrane
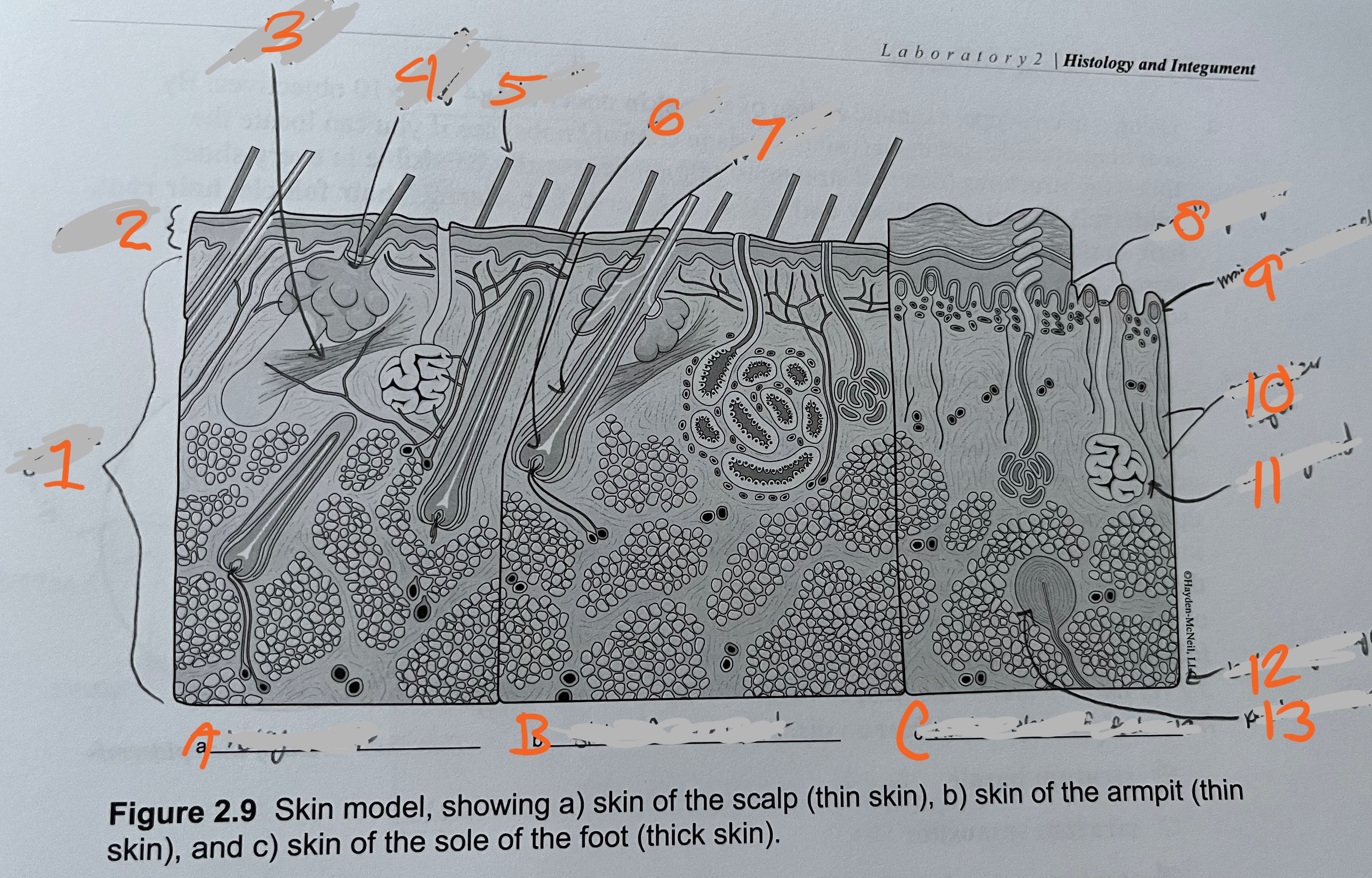
label
dermis
epidermis
arrector pili muscle
sebaceous glad
hair shaft
hair root
fair follicle
papillary layer
meisner’s corpuscle
recticular layer
sweat gland
bottom layer (hyperdermis)
pacinian corpuscles
A. hairy scalp
B. skin of armpit
C. hairless skin of foot sole
(skin model)
label
cell membrane
cytoplasm
free surface
nucleus
basement membrane
label
ground substance
nucleus
collagen fibers
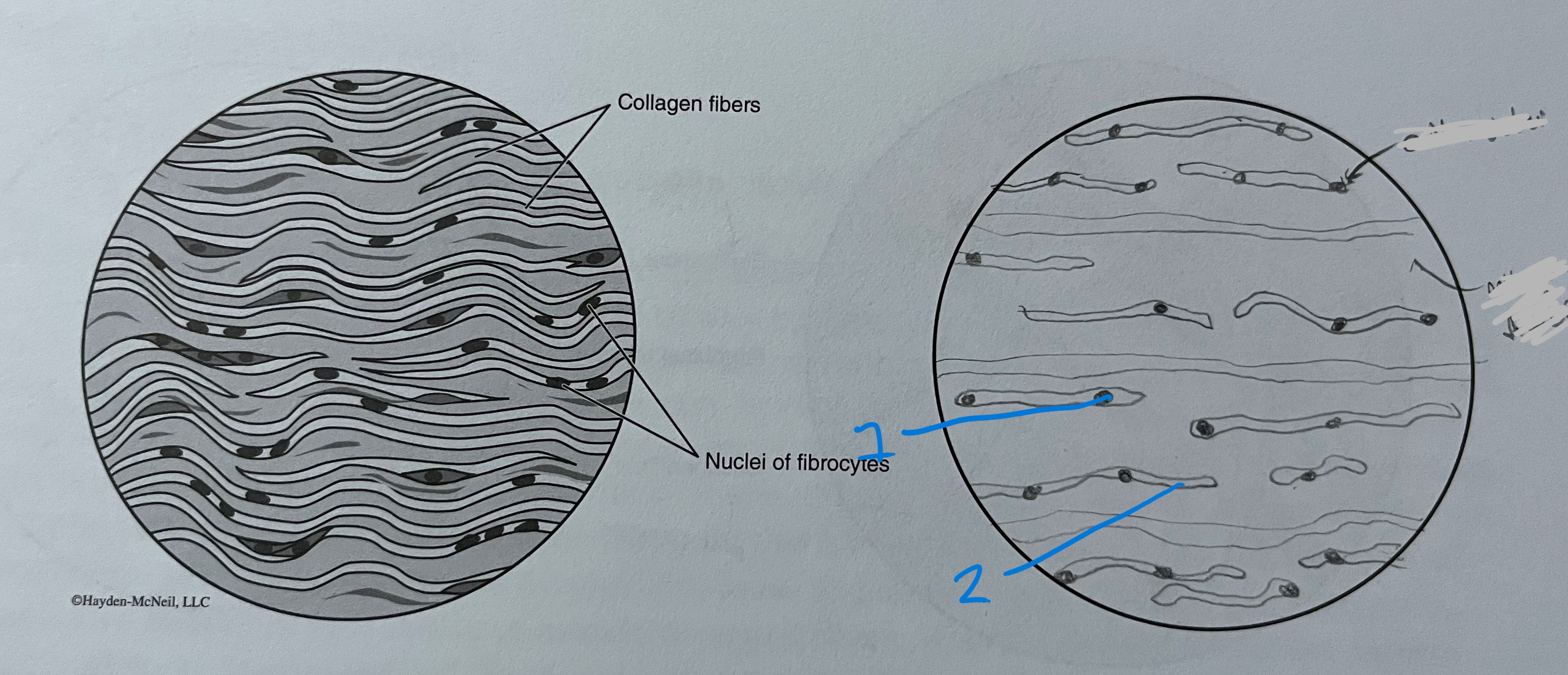
label
dense regular
nucleus
collagen fibers
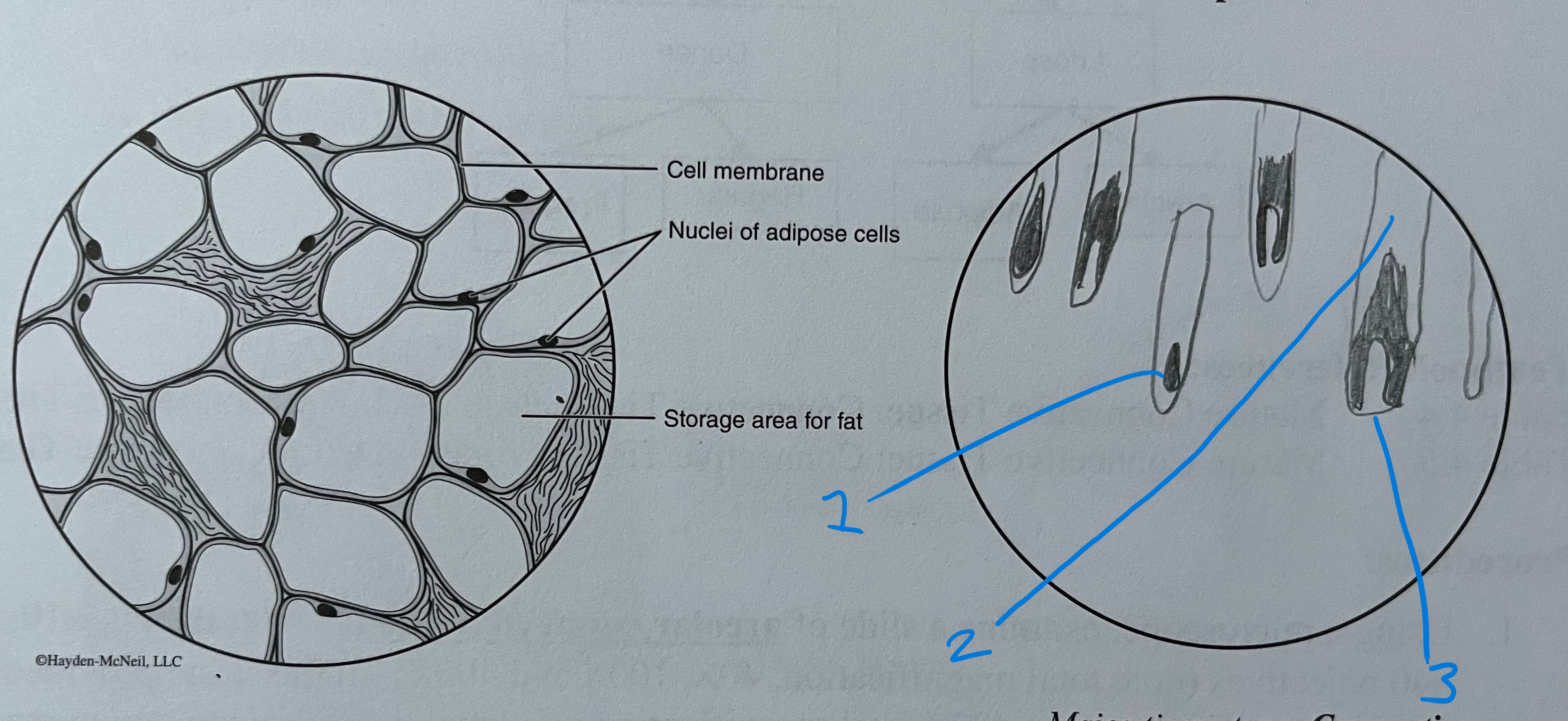
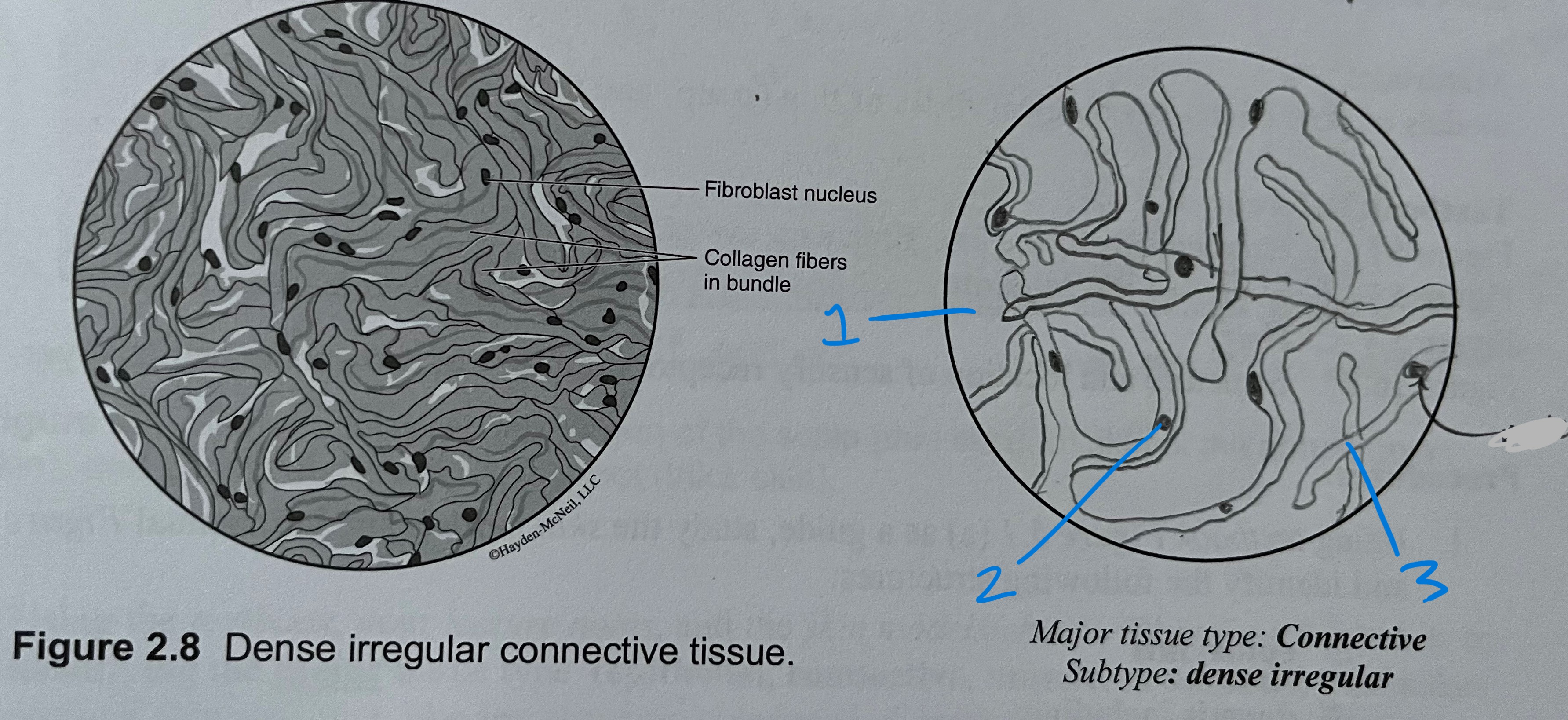
label
adipose CT
nucleus
lipid (fat) droplets in vacuoles
cell membrane
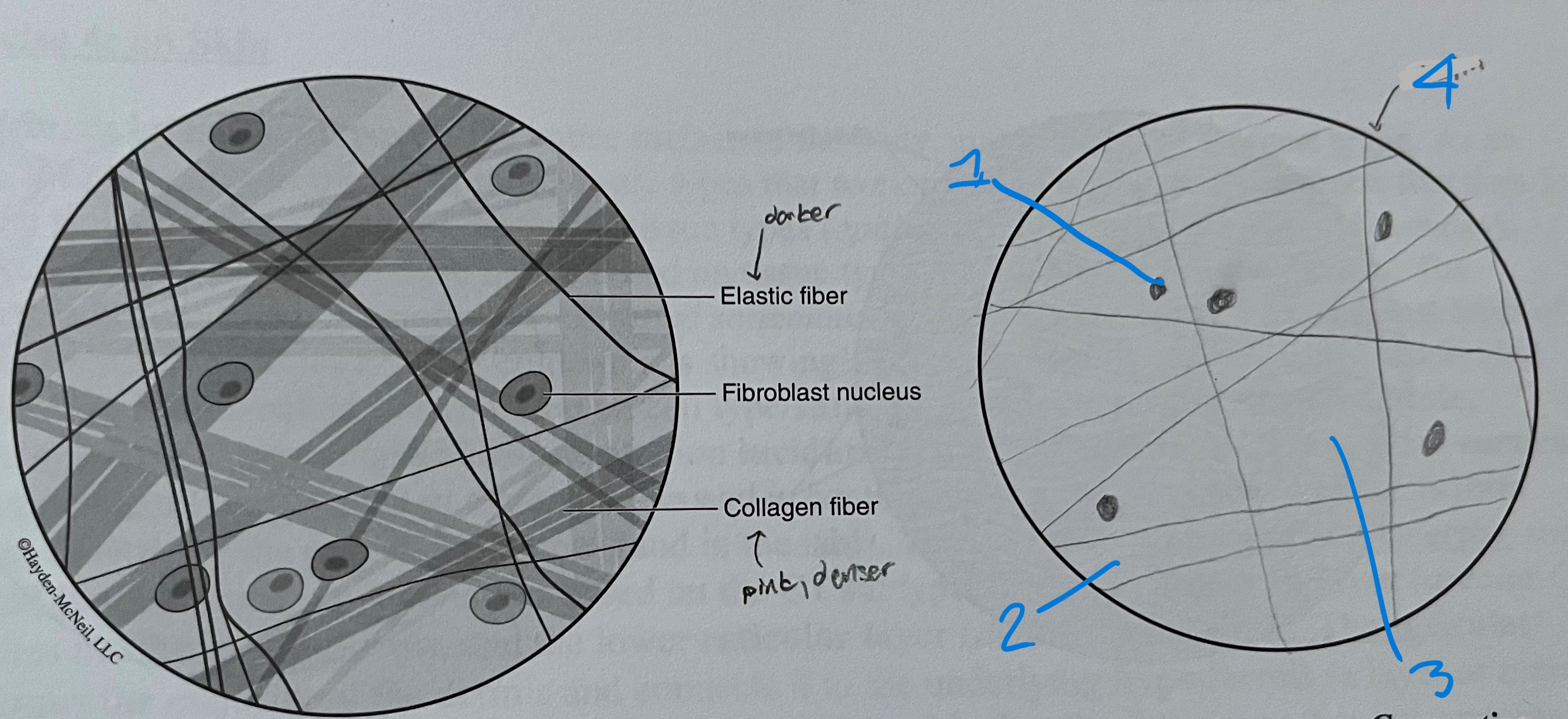
label
areolar ct
nucleus
collagen fibers (pink, denser)
ground substance
elastin fibers (usually darker)
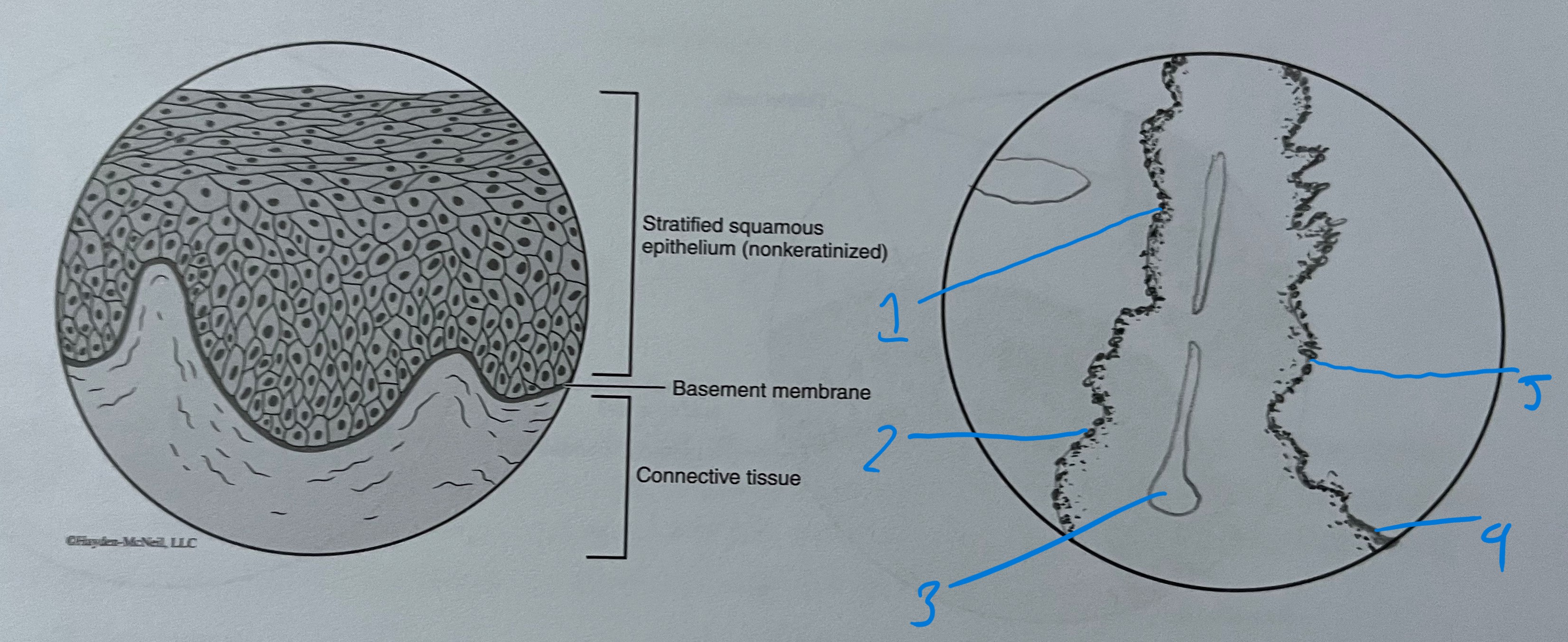
label
stratified squamous
cytoplasm
nucleus
free surface
cell membrane
basement membrane
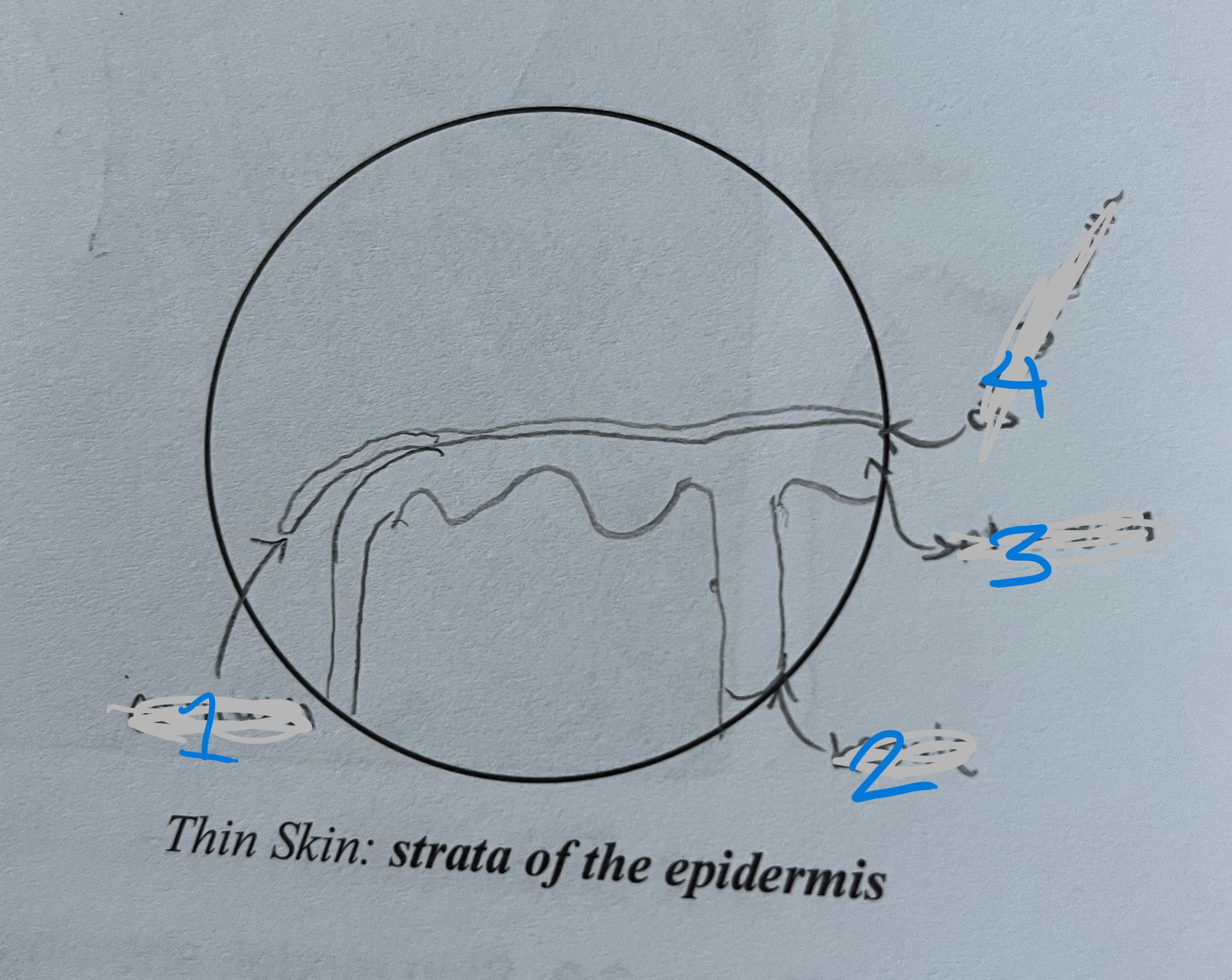
label
stratum corneum
stratum basale
stratum spinosum
stratum grandulosum
(thin skin)
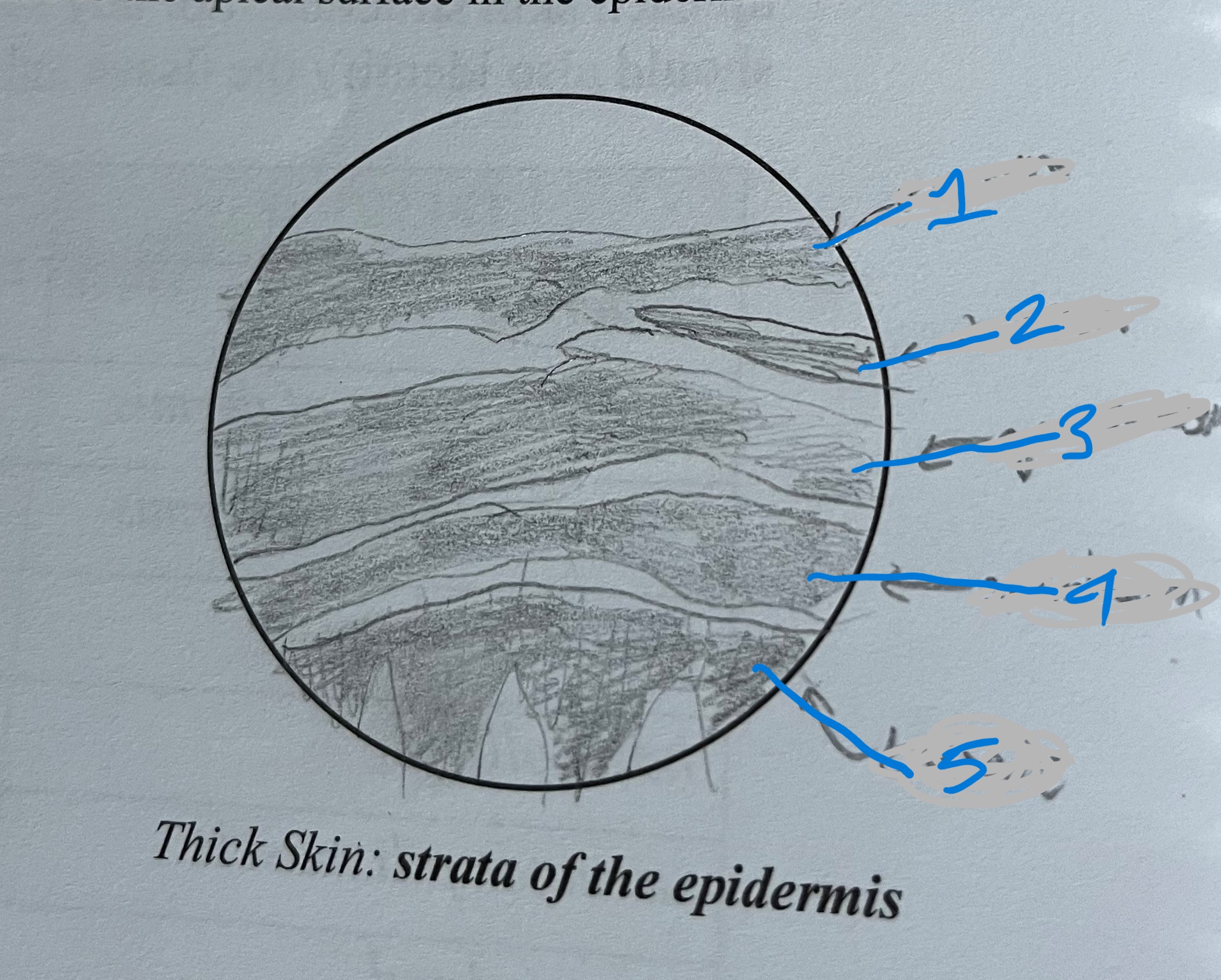
label
stratum corneum
stratum lucidum
stratum granulosum
stratum spinosum
stratum basale
(thick skin)
epithelial tissue
covers/lines surface of body/cavities
have a free layer
surface attached to basement membrane (CT)
types of epithelial tissues
based off layering and cell shape
stratified, simple, transitional, pseudostratified, and glandular
simple epithelial
1 layer '
allows exchange of molecules for absorption and secretion
simple squamous
1 layer
flat or squashed cells
ex. lungs
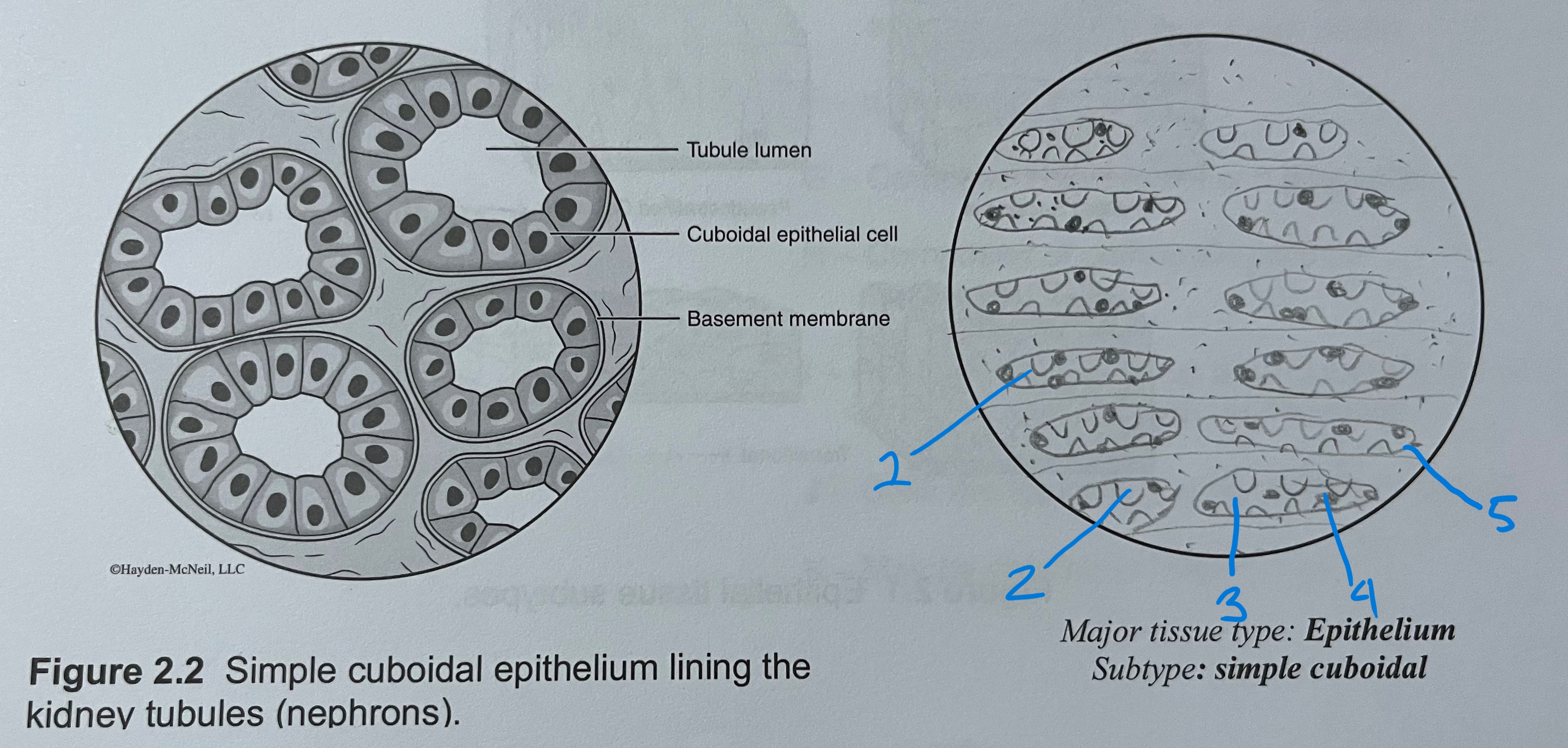
simple cuboidal
1 layer
cube shaped
ex. kidneys
simple columnar
1 layer
long and thin
ex. stomach and small intestine
stratified squamous
more than 1 layer
flat
ex. skin
stratified cuboidal
more than 1 layer
cube shaped
ex. duct of salivary gland
stratified columnar
more than 1 layer
long and thin
ex. linings of urethra
connective tissue
supports and connects tissue
if cells are far apart, separated by extracellular matrix
extracellular material give CT subtypes with identifying characteristics
variable vascularity
CT cell types
BLAST- creates matrix
CYST- maintains matrix
CLAST- breaks down matrix
CT subtypes
bone, blood, CT proper, cartilage
bone
cells- osteoblasts, osteoclasts matrix, osteocytes
ground substance- hydroxyapatite (inorganic Ca++ ions and phosphate salts) and organic components
fibers- collagen
blood
cells- RBC and WBC
matrix (fluid)- plasma (fibers, water, and ground substance)
CT proper
cells- fibroblasts, fibrocytes except adipose tissue (adipocytes)
types: dense CT and loose CT
areolar CT
loose CT
loosely arranged collagen and elastin fibers are surronded by ground substance (hyaluronic acid)
highly vascular
ex. lamina propria
adipose CT
loose CT
very little matrix
highly vascular
cells large (adipocytes), store triglyceride
loose CT
2 types: areolar and adipose
dense CT
many fibers (fiber proteins)
little ground substance
poorly vascular
2 types: dense regular CT and dense irregular CT
dense regular CT
collagen fibers running in same direction
ex. ligaments and tendons
dense irregular CT
collagen fibers arranged irregularly
ex. dermis of skin
cartilage
cells- chondroblasts, chondrocytes
fibers- collagen and elastin
ground substance- chondroitin sulphate and hyaluronic acid
avascular
ex. hyaline cartilage of trachea, ribs, and ends of long bones
glandular tissue
for secretion
if epithelial cells form a gland, cell shapes and layering are no longer used for classifications
2 types- exocrine glands and endocrine glands
exocrine glands
secretes body products onto body surface or into cavities
unicellular or multicellular
unicellular exocrine
secretes mucus onto tracts of the digestive, respiratory, urinary, and reproductive systems
ex. goblet cells
multicellular exocrine
consists of secretory and duct cells
ducts are connect secretions to body surface or cavities)
ex. sweat, sebaceous, mammary, digestive, etc