
AP U.S. History Other Things You Must Know
1491 - 1607
In 1491, the land was inhabited by various Native American tribes. In 1607, the first permanent English settlement was established in Jamestown, Virginia. During this period, European exploration and colonization of the Americas began, leading to conflicts between Europeans and Native Americans. The transatlantic slave trade also began, bringing enslaved Africans to the Americas. These changes set the stage for the development of the United States as a nation.
Encomienda System
A Spanish labor system that rewarded conquerors with the labor of conquered non-Christian peoples. The laborers were provided with benefits by the conquerors for whom they labored, including military protection and education. Intended to promote conquest and colonization.
Joint-Stock Companies
A company made up of a group of shareholders. Each shareholder invests some money in the company and, in turn, receives a share of the company’s profits.
Dutch East India Company - Controlled spice trade in the East Indies.
Dutch West India Company - Investment company and a sugar industry in Brazil.
English East India Company - Trade in Indian Ocean region.
Pueblo Indians
Native Americans that were located in the Rio Grande region of the southwestern United States, modern day New Mexico and Arizona. Named for their distinct buildings.
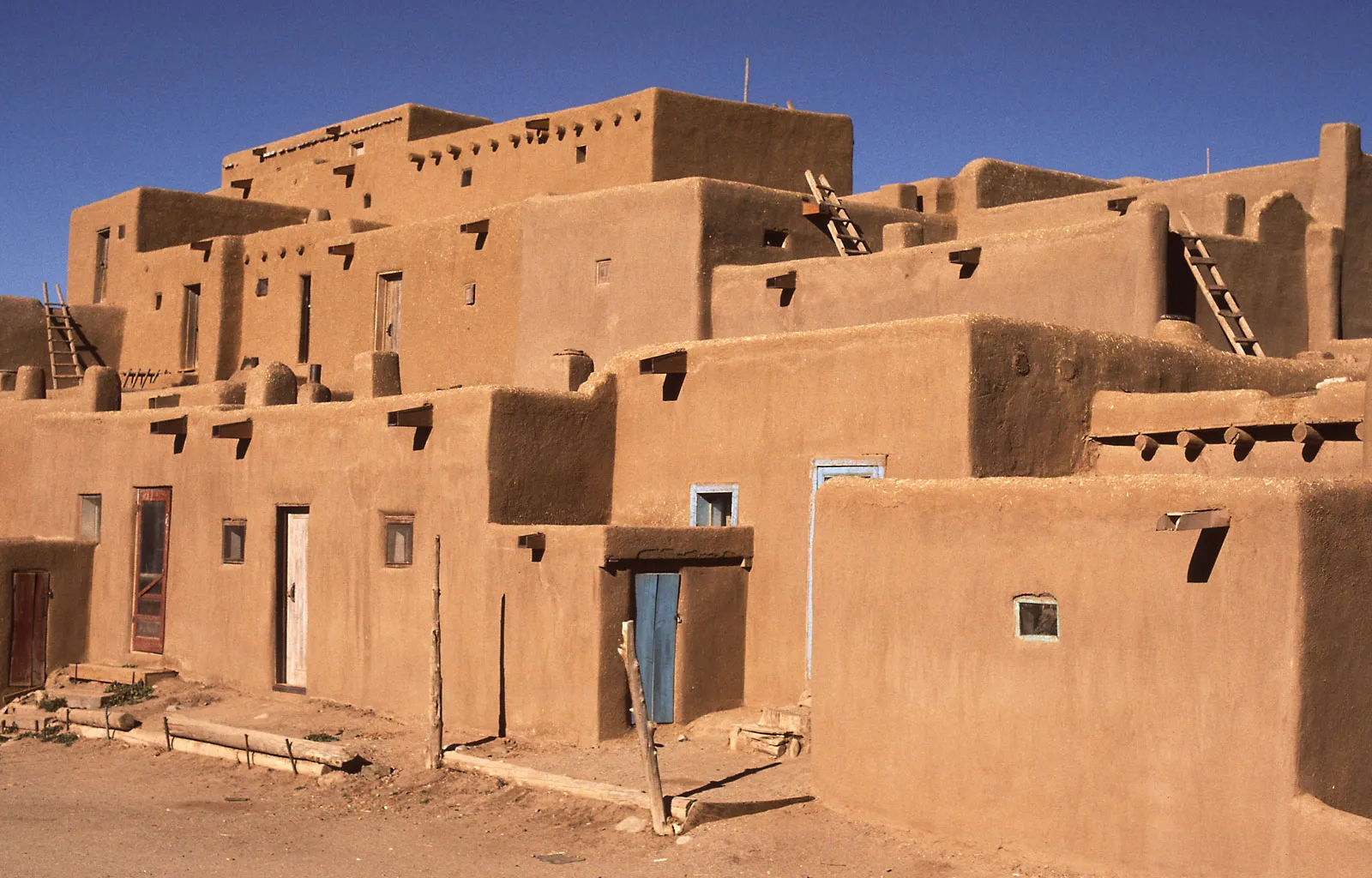

Pueblo Revolt (1680) was an uprising of most of the Pueblo people against the Spanish colonizers in the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo Mexico.
Asiento System
A contract granted by the Spanish crown to an individual or company allowing the holder exclusive rights in the slave trade with Spain’s American colonies. Constituted the principal legal means of supplying slaves to the New World.
Roanoke
One of the first colonization efforts by the British and Sir Walter Raleigh. However, in 1590, the 121 colonists had disappeared without explanation. It has been known as the Lost Colony. Only clues to their disappearance was the words “Croatoan” carved into a tree.
1607 - 1754
During this period, The most notable change included the establishment of the first permanent English settlement in Jamestown, the growth of the slave trade, the expansion of British colonies, the French and Indian War, and the emergence of a distinct American identity. These changes set the stage for the American Revolution and the eventual formation of the United States as an independent nation.
House of Burgesses
The first legislative body in British North America with the purpose of passing laws and maintaining order in the Jamestown Colony of Virginia. It became a representation of the struggle between the crown and the colonists’ desire for self-governance.

Mercantilism
The economic theory that trade generates wealth and is stimulated by the accumulation of profitable balances, which a government should encourage by means of protectionism. The United State’s wealth and power was best gained through increasing exports and reducing imports. Similar to commercialism. Believed in tariffs.
Cash Crops
A crop grown by a farmer for sale rather than for personal use.
Northern Colonies; Barley, oats, and wheat.
Southern Colonies: Cotton, tobacco, rice, and indigo.
Virginia and Maryland: Tobacco
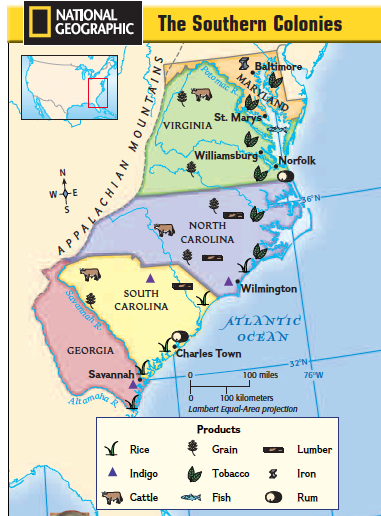
Triangular Trade
The trade between the New World, Britain, and Africa in the shape of a triangle.
New World sends raw materials to Europe.
Europe sends manufactured goods to Africa.
Europe takes slaves and manufactured goods to the New World.
Order of Colonization of Colonies
Virginia - 1607
New York - 1626
Massachusetts Bay - 1630
Maryland - 1633
Rhode Island - 1636
Connecticut - 1636
New Hampshire - 1638
Delaware - 1638
North Carolina - 1653
South Carolina - 1663
New Jersey - 1664
Pennsylvania - 1682
Georgia - 1732
1754 - 1800
During this period, the most notable change included the French and Indian War, the American Revolution, the drafting of the Constitution, and the establishment of the federal government. These events led to the formation of a new nation, with a unique system of government and a growing sense of national identity. Additionally, the period saw significant economic growth, as well as the expansion of slavery and the displacement of Native American populations.
Bill of Rights
Compromised of the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. Inspired by Jefferson and written by James Madison. Adopted in 1791.
Freedom of speech, press, assembly, protest, and religion.
Right to bear arms.
Homeowners cannot be forced to let soldiers take over their home.
No unreasonable search and seizure.
Double jeopardy, no compensation, no self-incrimination, due process of law, and a fair trial.
Speedy and public trial, trial by impartial jury, and right of a lawyer.
Jury trial in Federal civil cases.
No excessive bail and fines or cruel and unusual punishment.
All rights not listed, belong to the people, not the government.
Federal Government only has those powers delegated in the Constitution.
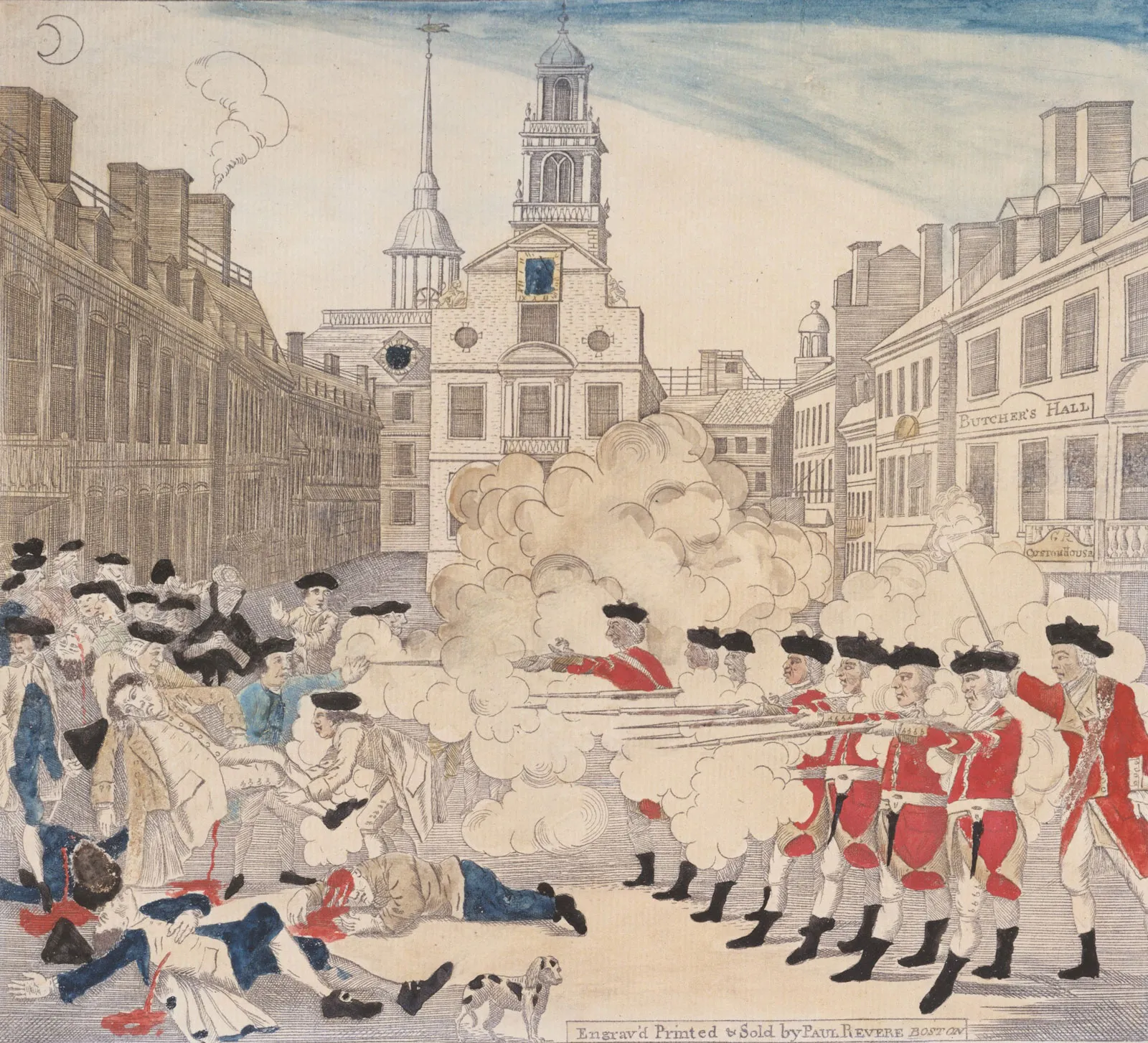
Boston Massacre
A confrontation in Boston of March 5, 1770, in which a group of 9 British soldiers killed 5 people in a crowd of hundreds of people. The colonists were verbally and physically harassing the soldiers.

Boston Tea Party
An American political and mercantile protest, against the British Parliament’s tax on tea, by the Sons of Liberty in Boston on December 16, 1773. “No taxation without representation.”
Checks and Balances
The ability of each branch to respond to the actions of the other branches. Each branch of government can change acts of the other branches.
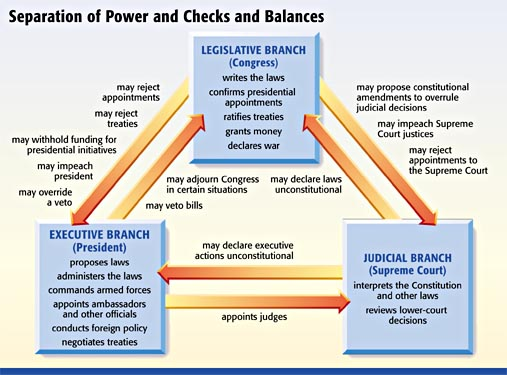
The Constitution
The Constitution is the supreme law of the United States. It was written by James Madison, Washington, Jefferson, Adams, Franklin, Hamilton, and Jay in 1787. It outlines the framework of the federal government and establishes the three branches of government: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. It also outlines the rights and freedoms of American citizens, including the Bill of Rights, and the process for amending the Constitution.
Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence is a document that was adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776. It declared that the thirteen American colonies were no longer subject to British rule and were now free, independent states. The document outlines the colonists' grievances against the British government and asserts that all men are created equal and have certain unalienable rights, including life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. It also states that governments derive their power from the consent of the governed and that the people have the right to alter or abolish a government that becomes destructive to these ends.
Sons of Liberty
Founded in 1765 by Samuel Adams and John Hancock. A loosely organized, sometimes violent, political organization active in the 13 colonies founded to advance the rights of the colonists and to fight taxation by the British government. Known for the Boston Tea Party, Gaspee Affair, and the Attack on John Malcolm.
1800 - 1848
During this period, the country expanded its territory through the Louisiana Purchase and the Mexican-American War, which led to the acquisition of new states. The Industrial Revolution brought about changes in manufacturing and transportation, leading to urbanization and the growth of cities. The issue of slavery became increasingly contentious, leading to the Civil War. Women's rights and the abolitionist movement gained momentum during this time as well.
Embargo Act
The Embargo Act of 1807 was a general trade embargo on all foreign nations in response to the British and French interference with U.S. merchant ships during the Napoleonic Wars. It devastated American shipping exports and cost the American economy about 8 percent in decreased gross national product. Exports declined by 75% and imports declined by 50%.
War of 1812
Fought by the United States and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America. It was caused by British limiting American trade with Europe and impressment, recruitment by force. Britain won the War of 1812. It increased patriotism in the U.S. and its respect from other countries. Federal Party lost power.
Hartford Convention
Series of meetings from December 15, 1814 to January 5, 1815, in Hartford Connecticut calling on the Federal Government to protect New England and to supply financial aid to New England’s badly battered trade economy. It was feared that this would cause New England’s secession from the Union.
Tariff of Abominations
Passed in 1828. It sought to protect northern and western agricultural products from competition with foreign imports. The tax on foreign goods resulted in the raised cost of living in the South and cutted into the profits of New England’s industrialists. It targeted the most frequently imported items to New England.
Cult of Domesticity
System of cultural beliefs or ideals in the 19th century that governed gender roles in upper and middle class society. Women should exist in the private, domestic sphere of the home, and should not venture into the public sphere for work like men do. Based on the theory of scientific sexism.
Monroe Doctrine
Articulated by James Monroe in 1823. A foreign policy position that opposes / forbids European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. Any intervention in America’s politics by foreign powers is potentially hostile.
Marbury v. Madison
James Madison refused to deliver William Marbury a commission, from John Adams, as justice of the peace. It established the principle of judicial review, American courts have the power to strike down laws and statuses that they find to violate the Constitution.
1844 - 1877
This period saw the expansion of the country's territory, the rise of industrialization, the abolition of slavery, and the end of the Civil War. The country also experienced political and social upheavals, including the emergence of new political parties, the growth of the women's suffrage movement, and the rise of labor unions. These changes transformed the United States into a more modern and diverse nation.
Emancipation Proclamation
Issued by Abraham Lincoln in 1863. Declared “that all persons held as slaves” within the rebellious states “are, and henceforward shall be free.” It proclaimed the freedom of slaves and slaves could enlist in the Union Army.
Fugitive Slave Act
Passed by Congress in 1850 in part of the Compromise of 1850. Required that slaves (most being runaways) be returned to their owners, even if they were in a free state.
The Missouri Compromise
Led by Henry Clay in 1820. Authorized the people of the Missouri territory to form a constitution and state government, and for the admission of such state into the Union on an equal footing with the original states, and to prohibit slavery in certain territories.
Main entered as a free state.
Missouri entered as a slave state.
36’30” line established as the dividing line regarding slavery.
Kansas-Nebraska Act
Drafted by Stephen A. Douglas in 1854. Territorial organic act that created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska. Repealed the Missouri Compromise, creating two new territories, and allowed for popular sovereignty. Led to Bleeding Kansas, a slavery vs anti slavery activist movement to gain votes.
The Surrender at Appomattox Court House
Fought in Virginia, on the Morning of April 9, 1865, was one of the last battles of the American Civil War. Confederate general Robert E. Lee surrendered his army to Union general Ulysses S. Grant in order to prevent unnecessary destruction to the South. Brought the war in Virginia to an end.
1865 - 1898
This period was marked by the end of the Civil War, the abolition of slavery, and the Reconstruction era. The country experienced rapid industrialization, urbanization, and westward expansion. The government implemented policies that favored big businesses, and the economy grew rapidly. The Spanish-American War in 1898 marked the emergence of the US as a global power.
Gilded Age
The growth of industry and a wave of immigrants. Production of iron and steel rose dramatically and western resources like lumber, gold, and silver increased the demand for improved transportation. Fortunes were made and lost. Problems like dangerous working conditions, monopolies, and business corruption occurred.
Laissez-Faire Economics
Developed by the French Physiocrats during the 18th century. An economic philosophy of free-market capitalism that opposes government intervention. Allows companies to take risks and invest in the economy. The opposite of communism.
JP Morgan, John D. Rockefeller, and Andrew Carnegie
JP Morgan: American financier and investment banker who dominated corporate finance on Wall Street. Financed the reorganization of railroads, insurance companies, and banks.
John D. Rockefeller: American business magnate and philanthropist. Considered to be the wealthiest American of all time. Founder of the Standard Oil Company - the first great industrial monopoly in the world.
Andrew Carnegie: Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Led the expansion of the steel industry and became one of the richest Americans in history. Called for the rich to use their wealth to improve society. Goal to improve efficiency by making supplies more reliable and eliminating the middleman.
Horizontal Integration
Used by John D. Rockefeller. Joining or consolidating with one’s competitors to create a monopoly.
Vertical Integrations
Pioneered by Andrew Carnegie. Combine into one organization at all phases of manufacturing. Makes supplies more reliable and improved efficiency.
Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890
The first Antitrust law. Authorized the federal government to institute proceedings against trusts in order to dissolve them. Made cartels and price-fixing illegal in the United States. Limit all behaviors that restrained free trade. It was to broad and did not define key terms leading to narrow judicial interpretations.
The New South
Envisioned a post-reconstruction southern economy modeled on the North’s embrace of the industrial revolution - economic regeneration, sectional reconciliation, racial harmony, and the gospel of work. Birmingham and Alabama prospered from iron and steel manufacturing. The rest of the south prospered from mining and furniture production. Cigarette rolling machines. The introduction of the textile mills in the South.
Homestead Strike
Tensions between steel workers and management caused an industrial lockout and strike that began on July 1, 1892, culminating in a battle in which strikers defeated private security agents at Carnegie Steel Company.
1890 - 1945
During this period, the country experienced rapid industrialization, urbanization, and immigration. The Progressive Era brought about reforms in politics, labor, and social issues. The US also became a major world power after its involvement in World War I and World War II. The Great Depression of the 1930s led to the implementation of the New Deal policies, which aimed to stimulate the economy and provide relief to those in need. Overall, this period marked a time of transformation and growth for the United States.
Roosevelt Corollary
Not only were the nations of the Western Hemisphere not open to colonization by European powers but that the United States had the responsibility to preserve order and protect life and property in those countries (Latin America).
“Speak Softly, and Carry a Big Stick.”
Theodore Roosevelt’s Big Stick Ideology, the policy of carefully mediated negotiation (“speak softly”) supported by the unspoken threat of a power military (“big stick”). Negotiation but having strength in case of emergencies.

Transcontinental Railroad
Any continuous rail line connecting a location on the U.S. Pacific coast with one or more of the railroads of the nation’s eastern trunk line rail system. It revolutionized travel, connecting areas of the West with the East. Previously, it would take months of travel. Negative impact on the Plains Indians as they had to move away from the railroad.
Wilson’s 14 Points
Woodrow Wilson’s war address to Congress on April 2, 1917 about the U.S. needing to enter the war.
Open diplomacy without secret treaties.
Economic free trade on the seas during war and peace.
Equal trade conditions.
Decrease armaments among all nations.
Adjust colonial claims.
Evacuation of all Central Powers from Russia and allow it to define its own independence.
Belgium to be evacuated and restored.
Return of Alsace-Lorraine region and all French territories.
Readjust Italian borders.
Austria-Hungary to be provided an opportunity for self-determination.
Creation of a Turkish state with guaranteed free trade in the Dardanelles.
Creation of an independent Polish state.
Creation of the League of Nations.
Great Depression
Economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. Period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. Led to the Wall Street stock market crash. Effect of overproduction, executive inaction, ill-timed tariffs, and an inexperienced Federal Reserve.
Manhattan Project
A research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. Made using the newly recognized fission process. Sparked a nuclear arms race during the Cold War.
Potsdam Conference
Held in the Soviet occupation zone to allow the three leading Allies (Soviet Union, United Kingdom, and the United States) to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistake of the Paris Peace Conference.
Germany would be occupied by the allies and be demilitarized and disarmed.
Judicial systems to be purged of Nazi influence.
Freedom of speech, press, and religion.
1948-1980
The post-World War II era saw a booming economy, the rise of the middle class, and the beginning of the Civil Rights Movement. The 1950s were marked by conformity and consumerism, while the 1960s brought about social and political upheaval, including the Vietnam War and the counterculture movement. The 1970s were characterized by economic recession, energy crises, and the Watergate scandal. Overall, these decades were a time of great change and transformation in American society.
Scopes Monkey Trial
American legal case in 1925 in which a high school teacher, John T. Scopes, was accused of violating Tennessee’s Butler Act, which had made it illegal for teachers to teach human evolution in any state-funded school. Brought hordes of spectators and reporters to Dayton. Some believe the whole trial was planned in order to bring tourists to the city.
Bay of Pigs
A failed military landing operation of the southwestern coast of Cuba in 1961 by Cuban exiles, covertly financed and directed by the United States. It was aimed at overthrowing Fidel Castro’s communist government. It failed because the exiles immediately came under heavy fire when they landed.

Cuban Missile Crisis
A direct and dangerous confrontation (brink of nuclear war) between the United States and the Soviet Union during the cold war. Both sides came to an agreement by the Soviets removing the missiles out of Cuba in exchange that the U.S. would not invade the Island and would remove their missiles out of Italy and Turkey.
Red Scare
The promotion of a widespread of fear of a potential rise of communism, anarchism or other leftist ideologies by a society or state. In the United States, many feared recent immigrants who embraced (or not) communist, socialist, or anarchist ideology.
The Kent State Massacre
Killing of four and wounding of nine unarmed college students by the Ohio National Guard on the Kent State University campus. It triggered a nationwide student strike that forced hundreds of Universities to close an destroying the Nixon administration, in addition to Watergate. The students were protesting, sources say with fire, when they were shot.
1980-Present
In this period, the economy has shifted from a manufacturing-based to a service-based industry, resulting in job losses and income inequality. The country has become more diverse, with an increase in immigration and a growing minority population. Technological advancements have revolutionized communication and transformed the way people live and work. The political landscape has also changed, with a shift towards more polarized and divisive politics. Additionally, there have been significant social changes, including the legalization of same-sex marriage and the #MeToo movement.
Détente
The easing of hostility or strained relations, especially between countries. This was between the United States and its two major Communist rivals, the Soviet Union and China. Examples include treatiest and Nixon’s attempt to pull out of Vietnam.
Domino Theory
The theory that a political event in one country will cause similar events in neighboring countries. A communist government in one nation would quickly lead to communist takeovers in neighboring states.
Fall of the Berlin Wall
November 9, 1989. As the Cold War began to thaw across Europe and the political reforms inside the Soviet bloc, the spokesman for East Berlin’s Communist Party announced that starting at midnight, citizens of East Germany were free to cross the country’s borders.

Attacks of September 11, 2001
Also called 9/11. A series of airline hijackings and suicide attacks committed by al-Qaeda.
(2 Planes) New York - 2,750 deaths
Pentagon - 184 deaths
Pennsylvania - 40 deaths
Caused emotional distress, death, long term health problems,stock market panic, Afghanistan War, tightened security measures within the United States airports, government buildings, and sports venues, expanded the FBI search and surveillance powers, and created a Department of Homeland Security.

Affordable Care Act
Signed into law by Barack Obama in 2010. Expand access to insurance, increase consumer protections, emphasize prevention and wellness, improve quality and system performance, expand the health workforce, and curb rising health care costs.
Sources
List of Concepts
https://www.albert.io/blog/frequently-tested-ap-us-history-terms-concepts/
Information
AP U.S. History Other Things You Must Know
1491 - 1607
In 1491, the land was inhabited by various Native American tribes. In 1607, the first permanent English settlement was established in Jamestown, Virginia. During this period, European exploration and colonization of the Americas began, leading to conflicts between Europeans and Native Americans. The transatlantic slave trade also began, bringing enslaved Africans to the Americas. These changes set the stage for the development of the United States as a nation.
Encomienda System
A Spanish labor system that rewarded conquerors with the labor of conquered non-Christian peoples. The laborers were provided with benefits by the conquerors for whom they labored, including military protection and education. Intended to promote conquest and colonization.
Joint-Stock Companies
A company made up of a group of shareholders. Each shareholder invests some money in the company and, in turn, receives a share of the company’s profits.
Dutch East India Company - Controlled spice trade in the East Indies.
Dutch West India Company - Investment company and a sugar industry in Brazil.
English East India Company - Trade in Indian Ocean region.
Pueblo Indians
Native Americans that were located in the Rio Grande region of the southwestern United States, modern day New Mexico and Arizona. Named for their distinct buildings.

Pueblo Revolt (1680) was an uprising of most of the Pueblo people against the Spanish colonizers in the province of Santa Fe de Nuevo Mexico.
Asiento System
A contract granted by the Spanish crown to an individual or company allowing the holder exclusive rights in the slave trade with Spain’s American colonies. Constituted the principal legal means of supplying slaves to the New World.
Roanoke
One of the first colonization efforts by the British and Sir Walter Raleigh. However, in 1590, the 121 colonists had disappeared without explanation. It has been known as the Lost Colony. Only clues to their disappearance was the words “Croatoan” carved into a tree.
1607 - 1754
During this period, The most notable change included the establishment of the first permanent English settlement in Jamestown, the growth of the slave trade, the expansion of British colonies, the French and Indian War, and the emergence of a distinct American identity. These changes set the stage for the American Revolution and the eventual formation of the United States as an independent nation.
House of Burgesses
The first legislative body in British North America with the purpose of passing laws and maintaining order in the Jamestown Colony of Virginia. It became a representation of the struggle between the crown and the colonists’ desire for self-governance.

Mercantilism
The economic theory that trade generates wealth and is stimulated by the accumulation of profitable balances, which a government should encourage by means of protectionism. The United State’s wealth and power was best gained through increasing exports and reducing imports. Similar to commercialism. Believed in tariffs.
Cash Crops
A crop grown by a farmer for sale rather than for personal use.
Northern Colonies; Barley, oats, and wheat.
Southern Colonies: Cotton, tobacco, rice, and indigo.
Virginia and Maryland: Tobacco

Triangular Trade
The trade between the New World, Britain, and Africa in the shape of a triangle.
New World sends raw materials to Europe.
Europe sends manufactured goods to Africa.
Europe takes slaves and manufactured goods to the New World.
Order of Colonization of Colonies
Virginia - 1607
New York - 1626
Massachusetts Bay - 1630
Maryland - 1633
Rhode Island - 1636
Connecticut - 1636
New Hampshire - 1638
Delaware - 1638
North Carolina - 1653
South Carolina - 1663
New Jersey - 1664
Pennsylvania - 1682
Georgia - 1732
1754 - 1800
During this period, the most notable change included the French and Indian War, the American Revolution, the drafting of the Constitution, and the establishment of the federal government. These events led to the formation of a new nation, with a unique system of government and a growing sense of national identity. Additionally, the period saw significant economic growth, as well as the expansion of slavery and the displacement of Native American populations.
Bill of Rights
Compromised of the first ten amendments to the United States Constitution. Inspired by Jefferson and written by James Madison. Adopted in 1791.
Freedom of speech, press, assembly, protest, and religion.
Right to bear arms.
Homeowners cannot be forced to let soldiers take over their home.
No unreasonable search and seizure.
Double jeopardy, no compensation, no self-incrimination, due process of law, and a fair trial.
Speedy and public trial, trial by impartial jury, and right of a lawyer.
Jury trial in Federal civil cases.
No excessive bail and fines or cruel and unusual punishment.
All rights not listed, belong to the people, not the government.
Federal Government only has those powers delegated in the Constitution.
Boston Massacre
A confrontation in Boston of March 5, 1770, in which a group of 9 British soldiers killed 5 people in a crowd of hundreds of people. The colonists were verbally and physically harassing the soldiers.

Boston Tea Party
An American political and mercantile protest, against the British Parliament’s tax on tea, by the Sons of Liberty in Boston on December 16, 1773. “No taxation without representation.”
Checks and Balances
The ability of each branch to respond to the actions of the other branches. Each branch of government can change acts of the other branches.

The Constitution
The Constitution is the supreme law of the United States. It was written by James Madison, Washington, Jefferson, Adams, Franklin, Hamilton, and Jay in 1787. It outlines the framework of the federal government and establishes the three branches of government: the legislative, executive, and judicial branches. It also outlines the rights and freedoms of American citizens, including the Bill of Rights, and the process for amending the Constitution.
Declaration of Independence
The Declaration of Independence is a document that was adopted by the Continental Congress on July 4, 1776. It declared that the thirteen American colonies were no longer subject to British rule and were now free, independent states. The document outlines the colonists' grievances against the British government and asserts that all men are created equal and have certain unalienable rights, including life, liberty, and the pursuit of happiness. It also states that governments derive their power from the consent of the governed and that the people have the right to alter or abolish a government that becomes destructive to these ends.
Sons of Liberty
Founded in 1765 by Samuel Adams and John Hancock. A loosely organized, sometimes violent, political organization active in the 13 colonies founded to advance the rights of the colonists and to fight taxation by the British government. Known for the Boston Tea Party, Gaspee Affair, and the Attack on John Malcolm.
1800 - 1848
During this period, the country expanded its territory through the Louisiana Purchase and the Mexican-American War, which led to the acquisition of new states. The Industrial Revolution brought about changes in manufacturing and transportation, leading to urbanization and the growth of cities. The issue of slavery became increasingly contentious, leading to the Civil War. Women's rights and the abolitionist movement gained momentum during this time as well.
Embargo Act
The Embargo Act of 1807 was a general trade embargo on all foreign nations in response to the British and French interference with U.S. merchant ships during the Napoleonic Wars. It devastated American shipping exports and cost the American economy about 8 percent in decreased gross national product. Exports declined by 75% and imports declined by 50%.
War of 1812
Fought by the United States and its indigenous allies against the United Kingdom and its allies in British North America. It was caused by British limiting American trade with Europe and impressment, recruitment by force. Britain won the War of 1812. It increased patriotism in the U.S. and its respect from other countries. Federal Party lost power.
Hartford Convention
Series of meetings from December 15, 1814 to January 5, 1815, in Hartford Connecticut calling on the Federal Government to protect New England and to supply financial aid to New England’s badly battered trade economy. It was feared that this would cause New England’s secession from the Union.
Tariff of Abominations
Passed in 1828. It sought to protect northern and western agricultural products from competition with foreign imports. The tax on foreign goods resulted in the raised cost of living in the South and cutted into the profits of New England’s industrialists. It targeted the most frequently imported items to New England.
Cult of Domesticity
System of cultural beliefs or ideals in the 19th century that governed gender roles in upper and middle class society. Women should exist in the private, domestic sphere of the home, and should not venture into the public sphere for work like men do. Based on the theory of scientific sexism.
Monroe Doctrine
Articulated by James Monroe in 1823. A foreign policy position that opposes / forbids European colonialism in the Western Hemisphere. Any intervention in America’s politics by foreign powers is potentially hostile.
Marbury v. Madison
James Madison refused to deliver William Marbury a commission, from John Adams, as justice of the peace. It established the principle of judicial review, American courts have the power to strike down laws and statuses that they find to violate the Constitution.
1844 - 1877
This period saw the expansion of the country's territory, the rise of industrialization, the abolition of slavery, and the end of the Civil War. The country also experienced political and social upheavals, including the emergence of new political parties, the growth of the women's suffrage movement, and the rise of labor unions. These changes transformed the United States into a more modern and diverse nation.
Emancipation Proclamation
Issued by Abraham Lincoln in 1863. Declared “that all persons held as slaves” within the rebellious states “are, and henceforward shall be free.” It proclaimed the freedom of slaves and slaves could enlist in the Union Army.
Fugitive Slave Act
Passed by Congress in 1850 in part of the Compromise of 1850. Required that slaves (most being runaways) be returned to their owners, even if they were in a free state.
The Missouri Compromise
Led by Henry Clay in 1820. Authorized the people of the Missouri territory to form a constitution and state government, and for the admission of such state into the Union on an equal footing with the original states, and to prohibit slavery in certain territories.
Main entered as a free state.
Missouri entered as a slave state.
36’30” line established as the dividing line regarding slavery.
Kansas-Nebraska Act
Drafted by Stephen A. Douglas in 1854. Territorial organic act that created the territories of Kansas and Nebraska. Repealed the Missouri Compromise, creating two new territories, and allowed for popular sovereignty. Led to Bleeding Kansas, a slavery vs anti slavery activist movement to gain votes.
The Surrender at Appomattox Court House
Fought in Virginia, on the Morning of April 9, 1865, was one of the last battles of the American Civil War. Confederate general Robert E. Lee surrendered his army to Union general Ulysses S. Grant in order to prevent unnecessary destruction to the South. Brought the war in Virginia to an end.
1865 - 1898
This period was marked by the end of the Civil War, the abolition of slavery, and the Reconstruction era. The country experienced rapid industrialization, urbanization, and westward expansion. The government implemented policies that favored big businesses, and the economy grew rapidly. The Spanish-American War in 1898 marked the emergence of the US as a global power.
Gilded Age
The growth of industry and a wave of immigrants. Production of iron and steel rose dramatically and western resources like lumber, gold, and silver increased the demand for improved transportation. Fortunes were made and lost. Problems like dangerous working conditions, monopolies, and business corruption occurred.
Laissez-Faire Economics
Developed by the French Physiocrats during the 18th century. An economic philosophy of free-market capitalism that opposes government intervention. Allows companies to take risks and invest in the economy. The opposite of communism.
JP Morgan, John D. Rockefeller, and Andrew Carnegie
JP Morgan: American financier and investment banker who dominated corporate finance on Wall Street. Financed the reorganization of railroads, insurance companies, and banks.
John D. Rockefeller: American business magnate and philanthropist. Considered to be the wealthiest American of all time. Founder of the Standard Oil Company - the first great industrial monopoly in the world.
Andrew Carnegie: Scottish-American industrialist and philanthropist. Led the expansion of the steel industry and became one of the richest Americans in history. Called for the rich to use their wealth to improve society. Goal to improve efficiency by making supplies more reliable and eliminating the middleman.
Horizontal Integration
Used by John D. Rockefeller. Joining or consolidating with one’s competitors to create a monopoly.
Vertical Integrations
Pioneered by Andrew Carnegie. Combine into one organization at all phases of manufacturing. Makes supplies more reliable and improved efficiency.
Sherman Antitrust Act of 1890
The first Antitrust law. Authorized the federal government to institute proceedings against trusts in order to dissolve them. Made cartels and price-fixing illegal in the United States. Limit all behaviors that restrained free trade. It was to broad and did not define key terms leading to narrow judicial interpretations.
The New South
Envisioned a post-reconstruction southern economy modeled on the North’s embrace of the industrial revolution - economic regeneration, sectional reconciliation, racial harmony, and the gospel of work. Birmingham and Alabama prospered from iron and steel manufacturing. The rest of the south prospered from mining and furniture production. Cigarette rolling machines. The introduction of the textile mills in the South.
Homestead Strike
Tensions between steel workers and management caused an industrial lockout and strike that began on July 1, 1892, culminating in a battle in which strikers defeated private security agents at Carnegie Steel Company.
1890 - 1945
During this period, the country experienced rapid industrialization, urbanization, and immigration. The Progressive Era brought about reforms in politics, labor, and social issues. The US also became a major world power after its involvement in World War I and World War II. The Great Depression of the 1930s led to the implementation of the New Deal policies, which aimed to stimulate the economy and provide relief to those in need. Overall, this period marked a time of transformation and growth for the United States.
Roosevelt Corollary
Not only were the nations of the Western Hemisphere not open to colonization by European powers but that the United States had the responsibility to preserve order and protect life and property in those countries (Latin America).
“Speak Softly, and Carry a Big Stick.”
Theodore Roosevelt’s Big Stick Ideology, the policy of carefully mediated negotiation (“speak softly”) supported by the unspoken threat of a power military (“big stick”). Negotiation but having strength in case of emergencies.

Transcontinental Railroad
Any continuous rail line connecting a location on the U.S. Pacific coast with one or more of the railroads of the nation’s eastern trunk line rail system. It revolutionized travel, connecting areas of the West with the East. Previously, it would take months of travel. Negative impact on the Plains Indians as they had to move away from the railroad.
Wilson’s 14 Points
Woodrow Wilson’s war address to Congress on April 2, 1917 about the U.S. needing to enter the war.
Open diplomacy without secret treaties.
Economic free trade on the seas during war and peace.
Equal trade conditions.
Decrease armaments among all nations.
Adjust colonial claims.
Evacuation of all Central Powers from Russia and allow it to define its own independence.
Belgium to be evacuated and restored.
Return of Alsace-Lorraine region and all French territories.
Readjust Italian borders.
Austria-Hungary to be provided an opportunity for self-determination.
Creation of a Turkish state with guaranteed free trade in the Dardanelles.
Creation of an independent Polish state.
Creation of the League of Nations.
Great Depression
Economic shock that impacted most countries across the world. Period of economic depression that became evident after a major fall in stock prices in the United States. Led to the Wall Street stock market crash. Effect of overproduction, executive inaction, ill-timed tariffs, and an inexperienced Federal Reserve.
Manhattan Project
A research and development undertaking during World War II that produced the first nuclear weapons. Made using the newly recognized fission process. Sparked a nuclear arms race during the Cold War.
Potsdam Conference
Held in the Soviet occupation zone to allow the three leading Allies (Soviet Union, United Kingdom, and the United States) to plan the postwar peace, while avoiding the mistake of the Paris Peace Conference.
Germany would be occupied by the allies and be demilitarized and disarmed.
Judicial systems to be purged of Nazi influence.
Freedom of speech, press, and religion.
1948-1980
The post-World War II era saw a booming economy, the rise of the middle class, and the beginning of the Civil Rights Movement. The 1950s were marked by conformity and consumerism, while the 1960s brought about social and political upheaval, including the Vietnam War and the counterculture movement. The 1970s were characterized by economic recession, energy crises, and the Watergate scandal. Overall, these decades were a time of great change and transformation in American society.
Scopes Monkey Trial
American legal case in 1925 in which a high school teacher, John T. Scopes, was accused of violating Tennessee’s Butler Act, which had made it illegal for teachers to teach human evolution in any state-funded school. Brought hordes of spectators and reporters to Dayton. Some believe the whole trial was planned in order to bring tourists to the city.
Bay of Pigs
A failed military landing operation of the southwestern coast of Cuba in 1961 by Cuban exiles, covertly financed and directed by the United States. It was aimed at overthrowing Fidel Castro’s communist government. It failed because the exiles immediately came under heavy fire when they landed.

Cuban Missile Crisis
A direct and dangerous confrontation (brink of nuclear war) between the United States and the Soviet Union during the cold war. Both sides came to an agreement by the Soviets removing the missiles out of Cuba in exchange that the U.S. would not invade the Island and would remove their missiles out of Italy and Turkey.
Red Scare
The promotion of a widespread of fear of a potential rise of communism, anarchism or other leftist ideologies by a society or state. In the United States, many feared recent immigrants who embraced (or not) communist, socialist, or anarchist ideology.
The Kent State Massacre
Killing of four and wounding of nine unarmed college students by the Ohio National Guard on the Kent State University campus. It triggered a nationwide student strike that forced hundreds of Universities to close an destroying the Nixon administration, in addition to Watergate. The students were protesting, sources say with fire, when they were shot.
1980-Present
In this period, the economy has shifted from a manufacturing-based to a service-based industry, resulting in job losses and income inequality. The country has become more diverse, with an increase in immigration and a growing minority population. Technological advancements have revolutionized communication and transformed the way people live and work. The political landscape has also changed, with a shift towards more polarized and divisive politics. Additionally, there have been significant social changes, including the legalization of same-sex marriage and the #MeToo movement.
Détente
The easing of hostility or strained relations, especially between countries. This was between the United States and its two major Communist rivals, the Soviet Union and China. Examples include treatiest and Nixon’s attempt to pull out of Vietnam.
Domino Theory
The theory that a political event in one country will cause similar events in neighboring countries. A communist government in one nation would quickly lead to communist takeovers in neighboring states.
Fall of the Berlin Wall
November 9, 1989. As the Cold War began to thaw across Europe and the political reforms inside the Soviet bloc, the spokesman for East Berlin’s Communist Party announced that starting at midnight, citizens of East Germany were free to cross the country’s borders.

Attacks of September 11, 2001
Also called 9/11. A series of airline hijackings and suicide attacks committed by al-Qaeda.
(2 Planes) New York - 2,750 deaths
Pentagon - 184 deaths
Pennsylvania - 40 deaths
Caused emotional distress, death, long term health problems,stock market panic, Afghanistan War, tightened security measures within the United States airports, government buildings, and sports venues, expanded the FBI search and surveillance powers, and created a Department of Homeland Security.

Affordable Care Act
Signed into law by Barack Obama in 2010. Expand access to insurance, increase consumer protections, emphasize prevention and wellness, improve quality and system performance, expand the health workforce, and curb rising health care costs.
Sources
List of Concepts
https://www.albert.io/blog/frequently-tested-ap-us-history-terms-concepts/
 Knowt
Knowt
