Geography #20: Volcanoes
1/14
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
15 Terms
What are the two main types of volanoes?
Strato-volcanoes (composite cone) & Shield Volcano.

What are the main features of a Stratovolcano (Composite Cone)?
Tall, steep-sided cone shape.
Made from layers of ash and lava.
Eruptions are usually explosive.
Lava is thick and sticky (high silica).
Often found at destructive plate margins.
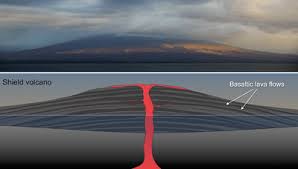
What are the main features of a shield volcano?
Wide, gently sloping sides.
Made mostly from runny lava flows.
Eruptions are usually gentle (effusive).
Lava is thin and runny (low silica).
Often found at constructive margins or hotspots.
What are the main 3 features that a volcano has?
Crater, Vent, Magma Chamber
What is a crater?
The bowl-shaped opening at the top of a volcano where eruptions occur and gas, lava, and ash escape.
What is a vent?
The passage through which magma travels from the magma chamber to the Earth’s surface.
What is a magma chamber?
A large underground store of molten rock that feeds the volcano during eruptions.
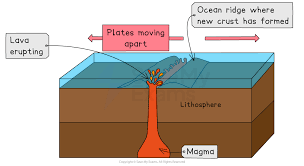
What are the Constructive (Divergent) Plate Boundaries?
It is when plates move apart and magma rises to form a new crust, causing gentle volcanic eruptions.
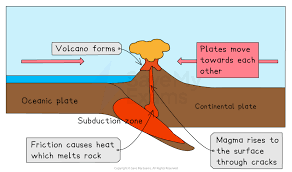
What are the Destructive (Convergent) Plate Boundaries?
The plates move together and the denser plate subducts, causing strong earthquakes and explosive volcanoes.
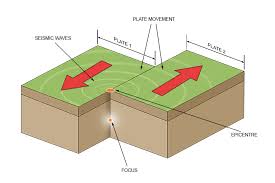
What are the Conservative Plate Boundaries?
When the plates slide past each other, causing strong earthquakes from the friction but no volcanoes.
What are the causes of volcanic eruptions?
Plate Movement - Volcanoes usually form at plate boundaries where plates move apart or where one plate is forced under another (subduction).
Magma Pressure Build-Up - Magma rises from the mantle and pressure builds inside the magma chamber until it erupts.
Gas Pressure - Gases trapped in magma expand as magma rises, increasing pressure and causing explosions.
Weaknesses in the Crust - Magma escapes through cracks or vents in the Earth’s crust.
Hotspots - Some volcanoes form above mantle plumes (hotspots), even away from plate boundaries (e.g. Hawaii).
What are the effects of volcanic eruptions on people?
Loss of Life and Injuries - From lava flows, ash clouds, toxic gases and fast-moving hot flows.
Destruction of Homes and Infrastructure - Buildings, roads and airports can be damaged or buried.
Health Problems - Ash can cause breathing problems and eye irritation.
Loss of Jobs and Income - Farming, tourism and businesses may stop.
Displacement of People - People may have to evacuate or become homeless.
How do volcanoes present hazards for people?
Lava Flows - Hot molten rock can destroy buildings, roads and farmland.
Ash Fall - Ash can damage buildings, contaminate water and cause breathing problems.
Pyroclastic Flows - Fast-moving hot gas and ash flows can destroy everything in their path.
Lahars (Volcanic Mudflows) - Ash mixed with water creates fast-moving mudflows that bury settlements.
Toxic Gases - Gases like sulphur dioxide can harm people, animals and crops.
How do volcanoes present opportunities for people?
Fertile Soils - Volcanic ash breaks down into nutrient-rich soil, good for farming.
Geothermal Energy - Heat from volcanoes can generate electricity.
Tourism - Volcanoes attract tourists, creating jobs and income.
Minerals and Building Materials - Volcanic rocks can be used in construction and industry.
Hot Springs - Used for tourism and sometimes heating.
What can be done to reduce the impacts of volcanoes?
Monitoring and early warning systems – Use gas sensors and satellite imagery to detect signs of eruptions and alert communities in time.
Evacuation plans – Prepare and practice clear evacuation routes and safe zones to move people quickly away from danger.
Land-use planning – Avoid building homes, schools, and critical infrastructure near high-risk volcanic zones.
Lava diversion and barriers – In some cases, engineers can build channels or barriers to redirect lava flows away from settlements.
Public education and drills – Teach communities about volcanic hazards, emergency procedures, and how to respond during eruptions.