Panic Disorder
1/15
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
16 Terms
How would you explain panic disorder to your patients?
= is an Intense feeling of anxiety and fear in which people often feel as if “they are about to die or go crazy.”
persistent concern or worry about additional panic attacks or their consequences because by the change in hysical or mental sensations or smothering sensation symptoms
discrete occurrences of intense fear or discomfort of sudden onset that are accompanied by a surge of physiological hyperarousal
can occur in the context of any anxiety disorder as well as other mental disorders (e.g., depressive disorders, posttraumatic stress disorder, substance use disorders) and some medical conditions (e.g., cardiac, respiratory, vestibular, gastrointestinal).
How would you explain panic attacks and the 13x possible symptoms to occur?
= is an abrupt surge of intense fear or intense discomfort that reaches a peak within minutes.
consists of a distinct combination of thoughts, emotions, and physical reactions.
During this time, four (or more) of the following 13x symptoms occur:
1. Palpitations, pounding heart, or accelerated heart rate.
2. Sweating.
3. Trembling or shaking.
4. Sensations of shortness of breath or smothering.
5. Feelings of choking.
6. Chest pain or discomfort.
7. Nausea or abdominal distress
8. Feeling dizzy, unsteady, lightheaded, or faint.
9. Chills or heat sensations.
10. Paresthesias (numbness or tingling sensations).
11. Derealization (feelings of unreality) or depersonalization (being detached from oneself).
12. Fear of losing control or “going crazy.”
13. Fear of dying.
Which 6x parts does the Treatment planning of patients with Panic Disorder involves?
Review latest intense panic experience
Physical reactions during the state of panic
Symptom Induction Technique
What thoughts and images were going through patient’s mind during when, notice the reactions
Matching the sensations and catastrophic interpretations
Behavioral experiment to identify and test underlying Assumption
Hierarchy of Fear Ladder
Creating the cognitive panic model —> Intervene in the belief system before the physical reaction start.
Identifying safety behaviors
Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP)
How could thoughts and images of patients with panic disorder look?
“I’m dying now” (e.g., heart attack, stroke)
“I’m losing my mind”
“I am going to faint.”
images of paramedics, losing consciousness, …
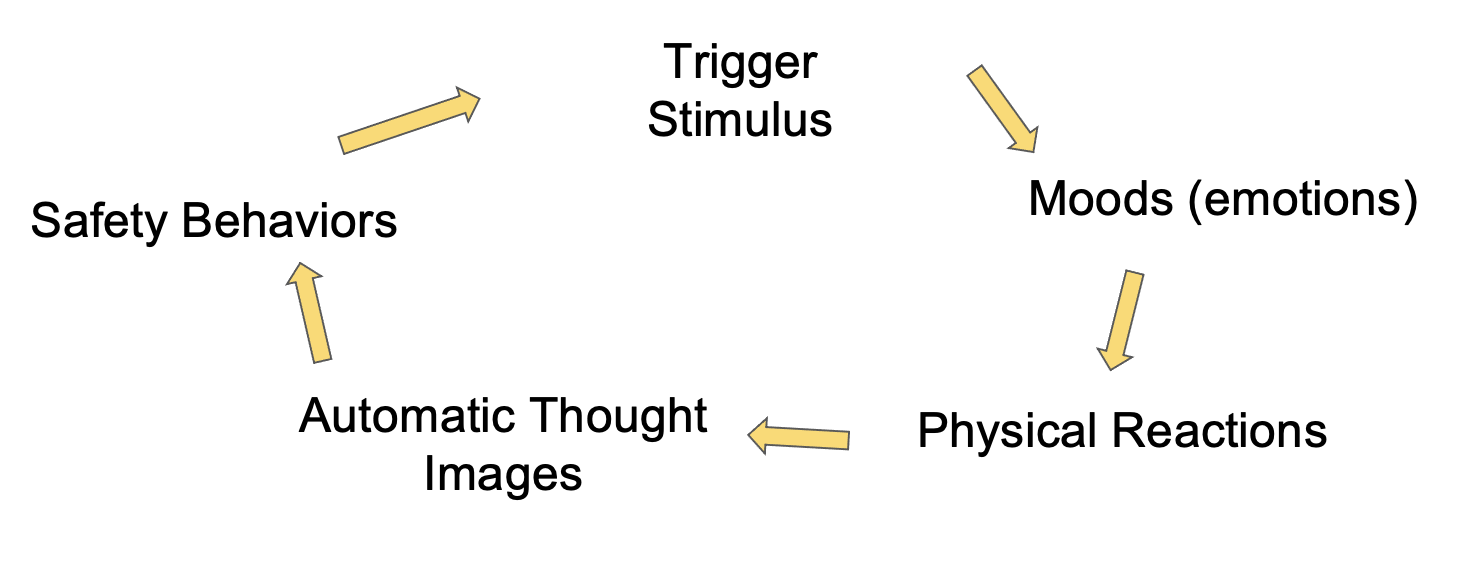
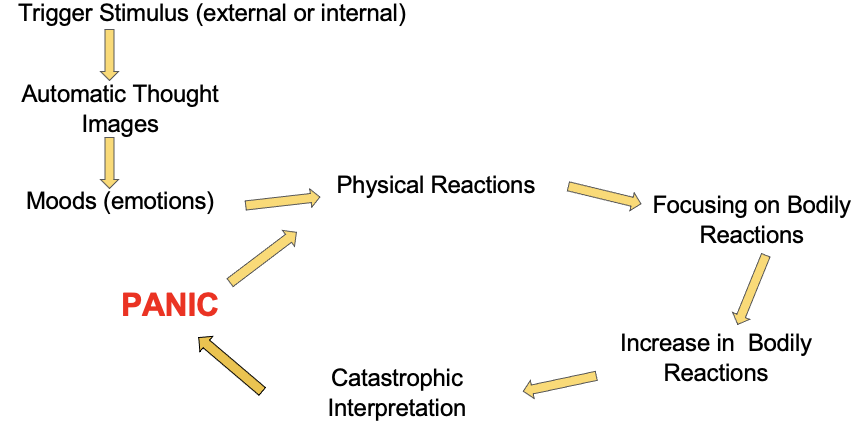
Describe the cognitive model of panic disorder
Example:
Your father died → Something triggers you external
If he dies, I won’t be able to manage life. →automatic thought
I feel nervous and fearful → Mood
I’m getting heart racing and cold sweats → physical reaction
I start to focus on these reactions, which increases the intensity and frequency
I start to have thoughts about the sensations → Interpretation in a catastrophic way, which seems like it confirms my thoughts about physical reaction (“Do I have a heart attack? Fuck seems so with this reactions.”)
I get panic attacks —> Perceive the threat and have again physical reactions
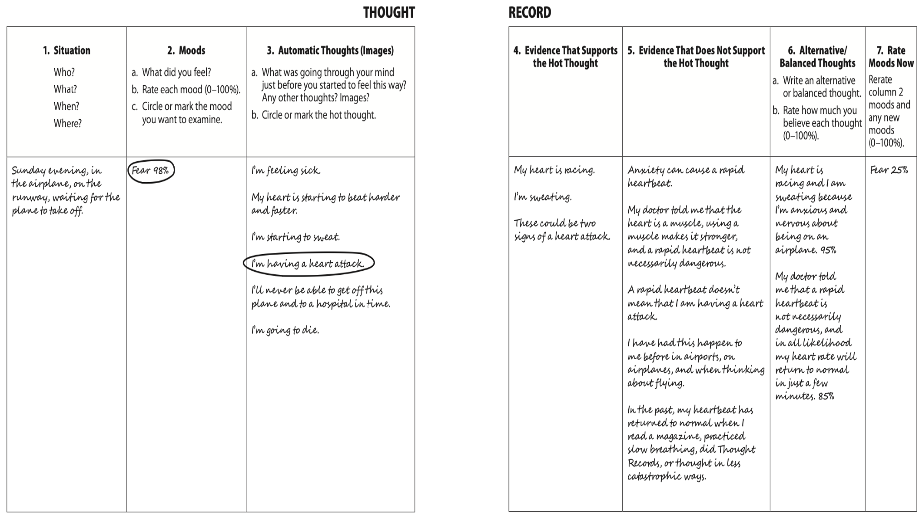
How does a thought record look in patients with panic disorder?
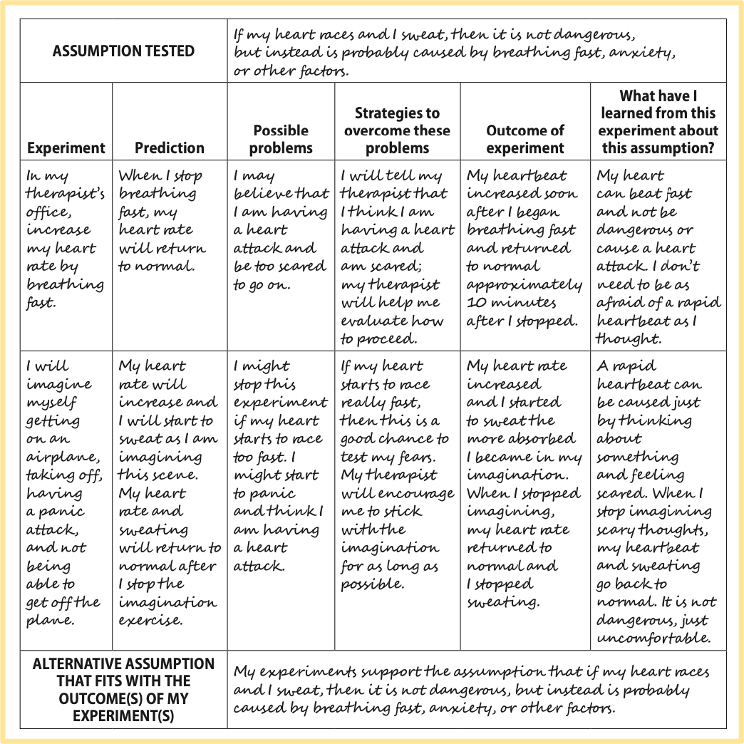
What is the symptom-induction technique and what does it aim?
use of within-session exercises repeatedly to induce the client’s feared physical sensation through treatment
client learns that certain physical sensations are not always frightening, that the physical sensations do not lead to the catastrophic outcome.
What are the 2x conditions for symptom-induction technique clients has to fullfill?
1) any medical contraindications for physically engaging in the exercise?
2) willing to endure a moderate level of discomfort?
Name 13x commonly used techniques for Symptom Induction

Name 6x Guidelines for Planning Behavioral Experiments and Identify and Testing underlying assumptions
1. Write Down the Assumption You Are Testing
2. Make Specific Predictions
3. Break Up Experiments into Small Steps
4. Do a Number of Experiments
5. Problem Solve, Don’t Quit
6. Write Down Your Experiments and Their Outcomes
How does a Behavioral experiment to identify and test underlying Assumption look?
To identify underlying assumptions, put a behavior or situation that triggers a strong emotion into a sentence that begins with “If . . . ”; follow that by “then . . . ” and let your mind complete that sentence.
It is usually necessary to do a number of behavioral experiments in order to fairly test existing assumptions and to develop alternative assumptions that fit your life experiences.
How is Exposure and Response Prevention (ERP) used in a patient with panic disorder?
Anxious patients often engage in avoidance, a coping strategy.
When patients are anxious and significantly avoidant, you will provide a strong rationale for exposing themselves to feared situations.
Fearful → “If I [do this activity], something bad will happen”
ERP helps them identify an activity that is associated with low to moderate discomfort and ask them to engage in this activity.
Then identify a new situation that is just a little more difficult, and encourage frequent exposure until they can do it with relative ease, and so on.
How does the fear-Ladder Hierarchy Technique is used and look?
When you experience high levels of anxiety, it is helpful to develop a hierarchy of the situations, events, or people you fear.
A “hierarchy” is a list, written in order of fear intensity, with the most feared situation or event at the top and the least feared situation at the bottom.
You can think of it as a “Fear Ladder” on which the lowest step describes a situation in which you experience a small amount of fear, and each step up the ladder represents situations in which you experience greater degrees of fear.

What are specific phobias?
= Fear of specific things or situations, such as heights, animals, insects, flying in airplanes.
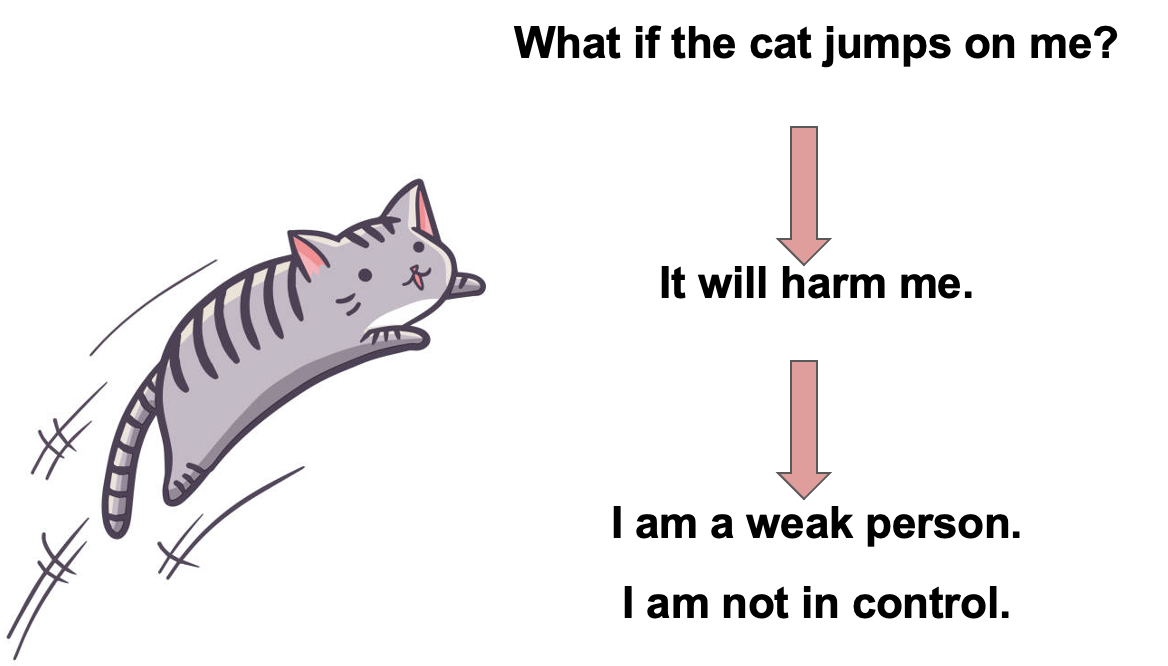
What is Agoraphobia?
= Fear or anxiety about:
1. Using public transportation (e.g., automobiles, buses, trains, ships, planes).
2. Being in open spaces (e.g., parking lots, marketplaces, bridges).
3. Being in enclosed places (e.g., shops, theaters, cinemas).
4. Standing in line or being in a crowd.
5. Being outside the home alone.