GCSE WJEC Food Preparation and Nutrition - Food, nutrition and health
1/217
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
218 Terms
Macronutrient
A nutrient that the human body needs in large amounts
Protein
A macronutrient made from chains of amino acids
Uses of protein
- Growth E.g. nails, hair and muscle mass
- Repair of muscles, tissues and organs
- Maintenance E.g. enzymes and antibodies
11
Number of non-essential amino acids. (ones that the body can make)
9
Number of essential amino acids. (ones that the body can't make, so must be eaten)
High biological value (HBV)
Sources of protein that contain all of the essential amino acids
Sources of HBV
- Meat / poultry
- Fish
- Dairy
- Soya / quinoa
Low biological value (LBV)
Sources of proteins that do not contain all the essential amino acids
Sources of LBV
- Peas
- Nuts
- Pulses
- Spinach
Protein complementation
Combining different sources of LBV proteins to provide all the essential amino acids. E.g. hummus and pita individually do not provide all the essential amino acids, but together they do
Dietary reference values (DRV)
Estimates for the amount of nutrients people should have in their diet
DRV of protein
55g for men
45g for women
Varies of protein requirement
- Children need more for growth
- Physically active people need more for growth and repair
- Pregnant women need 6g more for foetal development
- Lactating people need more for baby development
Protein excess
Pressure and strain on kidneys and liver (could lead to organ failure)
Protein deficiency
- Growth reduction
- Weakened immune system
- Weakened digestive system (nutrients aren't taken up)
- Oedema (fluid build up leading to swelling)
- Kwashiorkor (swollen organs, loss of muscle mass)
Vegetarian
Someone who doesn't eat products sourced from killing animals (meat, gelatine, etc.)
Alternative sources of protein
- Soya
- Mycoprotein
- TVP
- Tofu
Soya
- Plant based HBV source
- Must be cooked to remove toxicity
Mycoprotein
- Made from mushroom fungus and egg white / potato starch
- Replacement for poultry
- Comes in chunks, mince and fillets
TVP
- Textured vegetable protein. Made from soya flour (ground soya beans)
- Baked dough with meat-like texture
- Replacement for sausages, burgers and ready meals
Tofu
- Made from curdling soya milk
- Varying texture depending the amount of liquid it contains
- Used in desserts, dips, stir fries
Properties of alternative proteins
- Not much flavour
- Good at absorbing flavour (prepare with sauces, marinades, etc.)
Lipid
A macronutrient made from chains of fatty acids. Either fats (solid) or oils (liquid)
Uses of lipid
- Concentrated source of energy (twice as much as protein and carbs)
- Source of fat soluble vitamins (A and D)
- Source of essential fatty acids (omega 3 and 6)
- Forms an insulating layer to keep us warm
- Forms a protective layer around organs and bones
- Makes cholesterol (substance in cell membranes)
Triglyceride
A lipid made of 3 fatty acid molecules and one glycerol molecule
Glycerol
A three-carbon alcohol to which fatty acids are covalently bonded to make fats and oils.
Fatty acids
Chains of carbon and hydrogen that forms the monomer of lipids
Saturated fatty acids
Fatty acids that contain the maximum amount of hydrogen atoms as possible (only C-C single bonds)
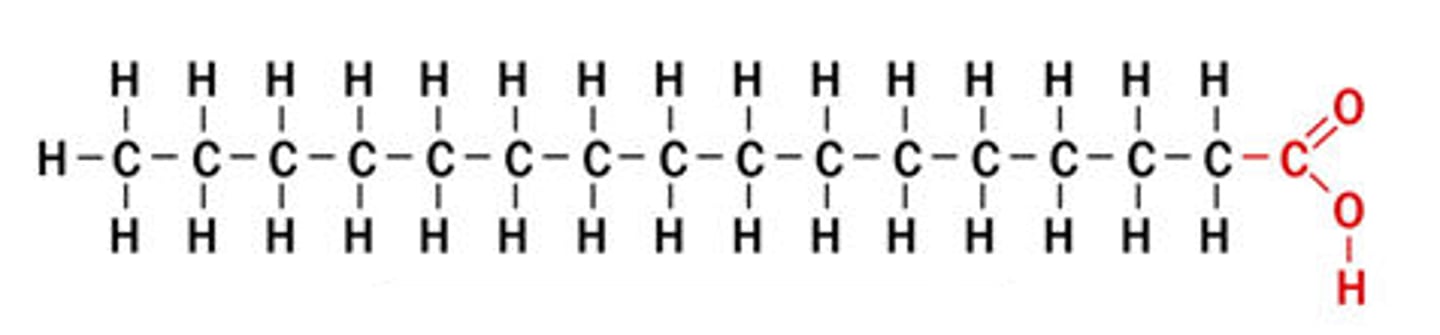
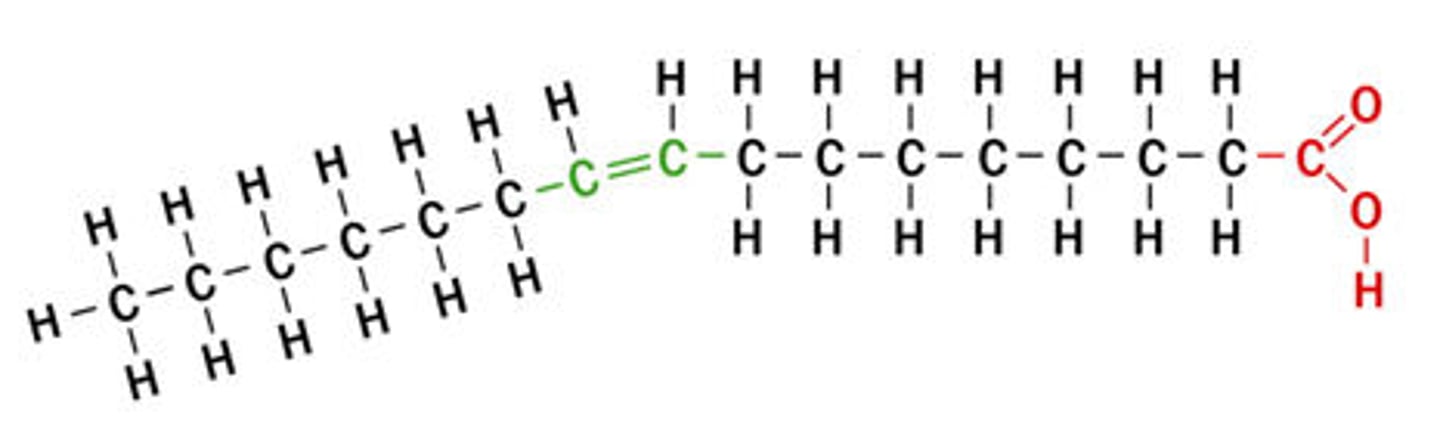
Unsaturated fatty acids
Fatty acids that do not contain the maximum amount of hydrogen atoms (contain C=C double bonds)
Saturated lipid
- Solid at room temperature (fat)
- Generally come from animal sources, but also come from some plant sources
- Excess consumption can lead to cardiovascular disease

Unsaturated lipid
- Liquid at room temperature (oil)
- Generally come from plant sources)
- Lowers blood cholesterol
- Can be either monounsaturated or polyunsaturated

Monounsaturated lipid
- Contain one C=C double bond
- Found in olive oil, nuts and avocado
Polyunsaturated lipid
- Contain multiple C=C double bond
- Found in sesame oil, soybean oil, seeds and oily oil
Essential fatty acids
The fatty acids that the body can't produce (omega-3 and omega-6)
Omega-3
- Found in oily fish and seeds
- Improve brain function and reduces risk of heart disease
Omega-6
- Found in chickens, nuts, vegetable oils
- Lowers blood cholesterol and reduces inflammation
35%
Proportion of daily food energy that should come from fat
DRV of lipid
70g
20g of which coming from saturates
Lipid excess
- Weight gain, especially build up around organs which leads to strain
- Obesity
- Increased cholesterol levels, restricting blood flow and high blood pressure
Lipid deficiency
- Vitamin deficiency
- Weight loss
- Less insulation (colder)
- Less protection
Carbohydrate
A macronutrient made chains of carbon based molecules. Can be simple or complex
Intrinsic sugar
Sugar that occurs naturally in food. E.g. fruit and vegetables
Extrinsic sugar
Sugar added to food by manufacturers. E.g. cakes and sweets
Added Sugar
Provides energy but nothing else so is sometimes referred to as 'empty calories'
Starch
- How plants store glucose
- Found in potatoes, bread, pasta, rice and cereals
- These foods also contain other nutrients including B vitamins, iron, calcium and fibre
Digesting carbohydrates
- Sugar and starch is broken down into glucose, which is absorbed and used for energy (respiration)
Monosaccharides
- A simple sugar
- The most basic sugar molecules. E.g. glucose, fructose
Disaccharides
- A simple sugar
- Two monosaccharides joined together. E.g. sucrose is made of glucose and fructose
Effect of simple sugars
Rapidly digested making blood sugar levels rise quickly and short burst of energy. Often come from high GI foods
Polysaccharides
- A complex sugar
- A polymer of lots of monosaccharides. E.g. starch is a chain of glucose molecules
Effect of complex sugars
Digested slowly, causing a slow steady burst of energy. Often come from low GI levels
Glycaemic index
The scale of how quickly carbohydrates affect blood sugar levels
High GI foods
- Mainly simple sugars
- Digested quickly and cause a rapid rise in sugar levels
- Include watermelon, white bread / pasta / rice
Low GI foods
- Mainly complex sugars
- Digested slowly causing a gradual rise in blood sugar levels
- Include peaches, brown bread / pasta / rice, porridge
50%
Proportion of daily food energy that should come from carbohydrates
5%
Proportion of daily food energy that should come from sugars
Of which sugars
The part of Uk food labelling that helps people separate their sugar intake fro their carb intake
Carbohydrate excess
- Converted into fat (obesity)
- Dental caries (decay)
- Fluctuating blood sugar levels, this can lead to Type 2 diabetes
Carbohydrate deficiency
- Reduced blood sugar levels, this can lead to hunger, dizziness and tiredness
- Fat is used for energy instead
- Protein is used for energy, which leads to loss of muscle mass
Micronutrient
Essential nutrients needed by the body in small or trace amounts
Vitamins
Organic compounds needed by the body in small amounts but are still essential
Fat soluble vitamins
Organic compounds that are soluble in fat and are therefore found in fatty foods. Vitamins A, D, E, K
Uses of vitamin A
- Eyesight
- Healthy immune system
- Healthy skin
Sources of vitamin A
- Retinol, which is found in liver, butter, oily fish and egg
- Carotene, which is found in margarine and yellow fruit and veg
DRV of vitamin A
0.7 mg for men
0.6 mg for women
Vitamin A excess
- Weaken bones
- Harm to foetuses
- Fatal in extreme circumstances
Vitamin A deficiency
- Night blindness
- Weak immune system
- Stunted growth
Uses of Vitamin D
- Absorb various minerals
- Teeth and bone development
Sources of vitamin D
- Oily fish
- Egg yolks
- Produced by the body when exposed to sunlight
DRV of vitamin D
0.01 mg
Vitamin D excess
Hypercalcemia - kidney damage
Nausea
Constipation
Vitamin D deficiency
Bone diseases such as:
- Osteomalacia (bone become soft)
- Rickets and osteoporosis (bones become brittle)
Uses of thiamin (B1)
- Improved nervous system
- Energy release from food
Sources of thiamin (B1)
- Pasta
- Eggs
- Liver
- Peas
Thiamin (B1) deficiency
- Tiredness
- Weak muscles
- Beriberi (disease that affects the heart, vessels and nervous system)
Uses of riboflavin (B2)
- Energy release from food
- Tissue repair
Sources of riboflavin (B2)
- Dairy
- Eggs
- Leafy greens
Riboflavin (B2) deficiency
- Dry skin
- Sore throat
- Sores around the mouth
Uses of niacin (B3)
- Healthy nervous system
- Energy release from food
- Healthy skin
Sources of niacin (B3)
- Wheat
- Nuts
- Meat
- Fish
Niacin (B3) deficiency
Pellagra (disease causing fatigue, depression and memory loss)
Uses of folic acid (B9)
- Growth of babies
- Production of red blood cells
- Essential to have high levels at conception to avoid birth defects
Sources of folic acid (B9)
- Liver
- Peas
- Leafy greens
Folic acid (B9) deficiency
- Anaemia
- Weak muscles
- Mouth sores
- Spina Bifida in newborns
Uses of Cobalamin (B12)
- Production of red blood cells
- Healthy nervous system
Uses of ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
- Protection from infection and allergies
- Healthy blood vessels
- Healing wounds
- Absorption of iron
Sources of ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
- Citrus
- Strawberries
- Green veg
- Potatoes
Excess ascorbic acid (vitamin C)
- Stomach pain
- Diarrhoea
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C) deficiency
- Anaemia
- Scurvy (tiredness and bleeding gums)
- Increased risk of cancer
Preparation of fruit and vegetables
- Prepare the just before you need them to retain vitamin C
- Steam or microwave them
- Don't chop into small pieces as it increases surface area
- Peel thinly or not at all as most nutrients are just below the skin
Minerals
Chemical elements, usually metals, that are needed by the body in small amounts, but are still essential
Uses of calcium
- Strong teeth and bones
- Healthy nerves and muscles
- Blood clotting
Sources of calcium
- Dairy
- Hard water
- Green leafy veg
- Tofu
Calcium excess
- Kidney stones
- Hypercalcemia
- Kidney damage
Calcium deficiency
- Rickets
- Osteoporosis
- Slowed blood clotting
Uses of iron
- Forms haemoglobin
- Forming proteins
Sources of iron
- Meat
- Dark green vegetables
Iron excess
- Stomach pains
- Nausea
- Constipation
- Death
Iron deficiency
- Anaemia
- Heat palpations
- Headaches
Uses of potassium
- Cardiovascular health
- Controlling fluid balance
- Works with sodium to control muscles and nerves