Vision 2
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
What is different about the retina and what are the implications of it?
It is part of the CNS as it is an outgrowth of the embryonic diencephalon
myelination and glial support
optic nerve myelinated by oligodendrytes
only starts later so keeps retina transparent and prevents light scattering
blood-brain barrier
protects the neural tissue from fluctuations in plasma composition and toxins but makes drug delivery to retina challenging
What are the layers of the retina from back to front?
black pigmented epithelium
outer nuclear layer
outer plexiform layer
inner nuclear layer
inner plexiform layer
ganglion layer
What is in the outer nuclear layer?
nuclei of photoreceptors
What is in the outer plexiform layer?
synapses between photoreceptors and bipolar
What is in the inner nuclear layer?
nuclei of bipolar cells
What is in the inner plexiform layer?
synapses between bipolar and ganglion cells
What is surprising about the direction of light travel?
it passes through all the layers before it reaches the photoreceptors
What are 2 other types of cells found?
horizontal
amacrine
Where do horizontal cells act?
receive input from photoreceptors and project laterally to influence surrounding BP and PR cells
Where do amacrine cells act?
between bipolar and ganglion
Roughly how many cones vs rods vs ganglion cells?
7 million vs 100 million vs 1 million
What are the 3 main things that have massive impact on how photoreceptors process light?
Negative membrane potential of photoreceptors
Hyperpolarised as response to incoming light
Unique way to react
Sensing light and inhibiting
Response will be graded
Membrane potential that goes negative will increase
Different steps
More intense light is, more negative response will be
Temporal dynamics of return to resting potential
Return is slow for rods
Fast for cones
Big consequences for temporal resolution
Slow decay = summate photons
complex synaptic contacts with bipolar and horizontal cells
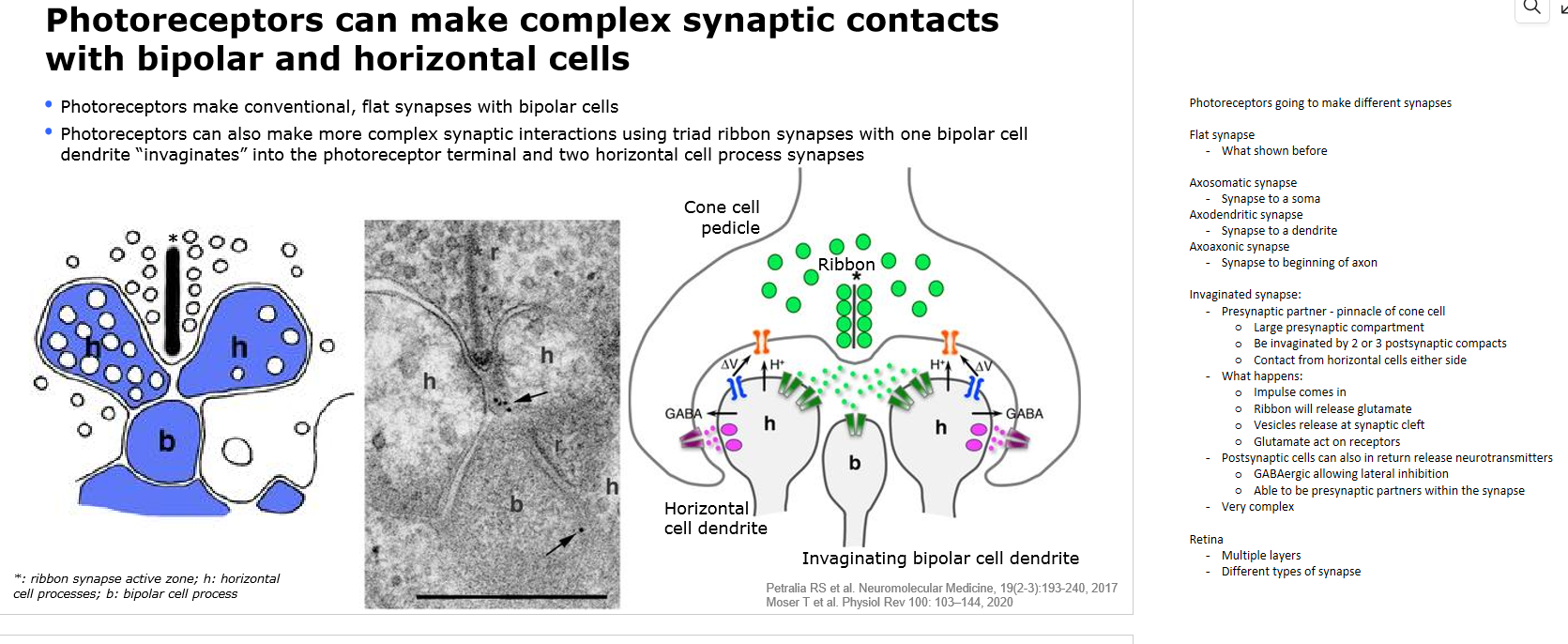
What are the 2 major types of bipolar cells?
ON-response
OFF-response
How does ON bipolar cells work?
metabotropic gluatamate receptors at postsynaptic cleft
they respond to glutamate by hyperpolarising
less glutamate since hyperpolarised PR therefore means depolarisation
How do OFF bipolar cells work?
ionotropic glutamate receptors postsynaptically
these produce classic EPSPs
therefore hyperpolarisation of cone causes hyperpolarisation of bipolar
What does the high diversity (13 types) of bipolar cells indicate?
bipolar cells perform the first elementary operation on visual signals and provide ganglion cells with highly pre-processed inputs
Are there also on and off ganglion cells?
yes
How can you identify on and off cells?
apply spot of light and see change in AP or not
What are the 3 types of ganglion cell type?
midget cells
parasol cells
small bistratified cells
Midget cells?
tiny with small cell bodies and dendritic arbours
only receive input from one bipolar cell
only on or off, not both
Parasol cells?
large with massive soma and arbour
collect input from lot of bipolar cells and PR
only on or off, not both
Small bistratified cells?
dendritic arbour split into two
can have both off and on
As you move from PR to BP to ganglion are there more or less types?
more - processing of light is increasing
What is formed from on and off BP and ganglion cells?
on and off channels where ganglion cels respond to light in the same sense as theur pre-synaptic bipolar cell partners
What is the first neuron in the retina that fires an AP?
ganglion cells
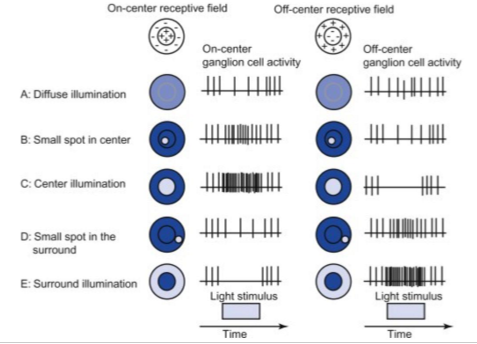
What kinda receptive fields do ganglion cells have?
circular receptive fields with antagonistic center-surround organisation
means in the centre has on response and around edges has off response or vice versa
identified by Kuffler 1953
applied light to centre and then to other areas and observed
Diagram for centre surround organisation?
What are horizontal cells involved in?
lateral inhibition in outer plexiform layer
Don’t understand next slide on light around and how horizontal cells involved
Why are there larger receptor fields further from the fovea?
lots of photoreceptors (rods) converging on one ganglion cell
Since lots of overlapping receptive fields within the visual field what?
not processing same information, signalling complementary visual information simultaneously and in parallel (eg colour, motion)
What are the 3 main parallel pathways from retina through the LGN to V1?
koniocellular
from bistratified
brightness contrast, colour contrast
parvocellular
from midget
detail, colour
magnocellular
from parasol
motion, luminance
Why are there lots of different damage possible in eye?
damage at different points in the visual pathway cause different defects
What did Hubel and Wiesel do?
investigate LGN by shwing different amounts of light to cat and recorded activity of a single neuron???