DNA structure, replication, transcription, translation, and mutations test
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
DNA's function in an organism:
stores and carries genetic information
Structure of DNA:
double helix (double stranded)
What base pairs are in DNA?
A-T
G-C
Components of a nucleotide:
nitrogenous base, phosphate, sugar
What are the bonds between nitrogen bases called
hydrogen bonds
What is RNA's structure?
single stranded
What base pairs does RNA have?
A, U, G, C
What is the relationship between genes and proteins?
A gene is a segment of DNA that carries a code, written in a sequence of nucleotides, which tells the cell how to build a specific protein.
What is transcription?
The process of turning DNA into RNA
Where does transcription take place?
inside the nucleus
What are the three steps of transcription?
initiation, elongation, termination
What happens during initiation in transcription?
RNA polymerase recognizes and binds to a promoter region on double stranded DNA and unwinds the strand

What happens during elongation in transcription?
-RNA polymerase II adds complementary base pairs to DNA template strand
-As elongation occurs, completed portions of mRNA are released

What happens during termination in transcription?
A stop codon is reached which marks the ending of transcription

What is the template strand?
The original strand that is being used to copy and make complementary pairs.
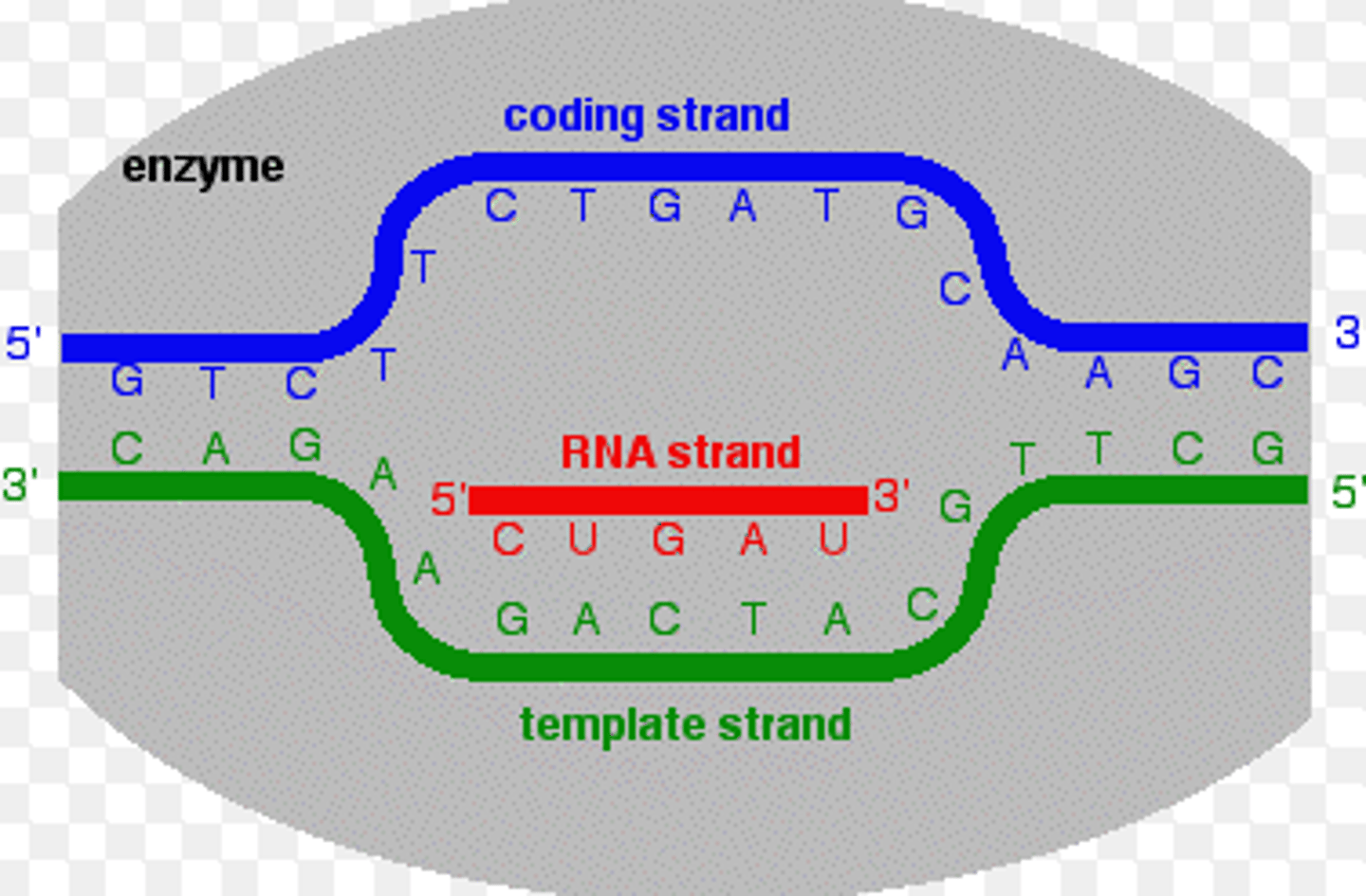
Which strand is the non coding strand?
template strand-(3' to 5')

Which strand is the coding strand?
non-template strand- (5' to 3')

Which strand do you use to identify the amino acid when using the codon chart?
mRNA strand
What is a codon?
a sequence of three nucleotides that together form a unit of genetic code in a DNA or RNA molecule.
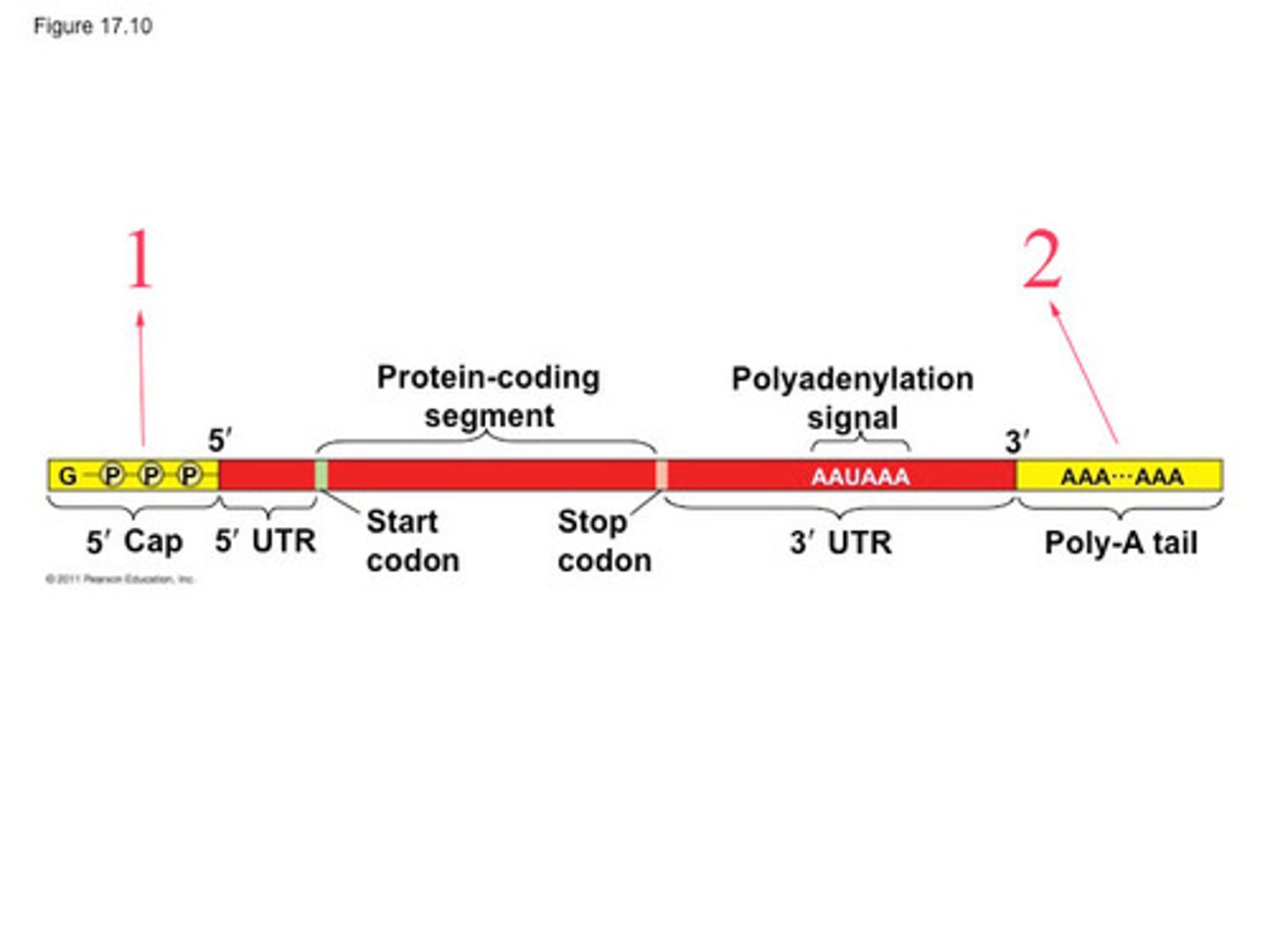
What is an exon?
An exon is a coding region; it gets spliced
What is an intron?
An intron is a non coding region; it gets removed
What is the purpose of the poly-A tail?
The presence of the poly(A) tail increases the stability of the mRNA molecule through the interaction of proteins

What is the purpose of the 5' cap?
Protects from degradation; involved in translation initiation
Why is the splicesome significant?
it removes introns and splices exons; it turns a immature RNA into a mature mRNA
What is mRNA and its function
mRNA (messenger RNA) is the form that carries the instructions for making proteins and is made during transcription.
What is tRNA and its function
tRNA (transfer RNA) is the form that carries amino acids
What is rRNA and its function
rRNA (ribosomial RNA) is the form that makes up part of the structure of the ribosomes
What is translation?
the decoding of an mRNA message into a protein
Where does translation take place?
cytoplasm
What are the 3 steps of translation?
initiation, elongation, termination
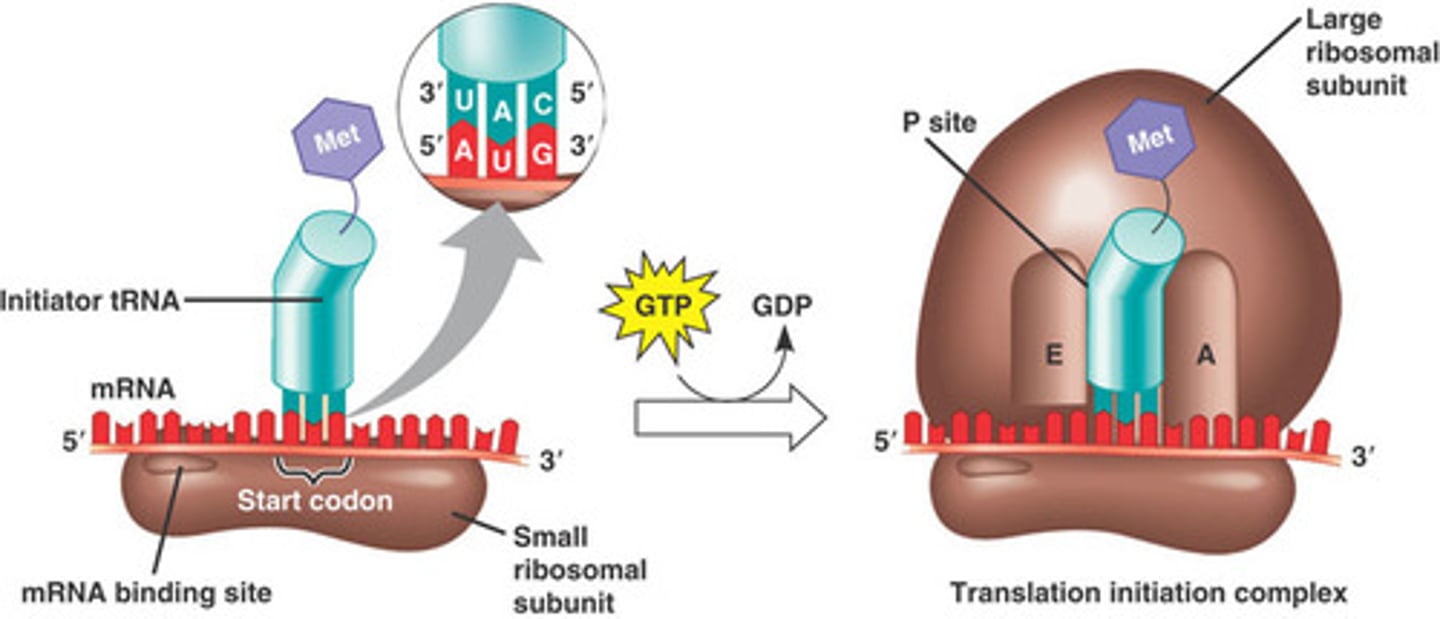
Initiation of translation:
The ribosome attaches to the mRNA at the start codon (AUG).
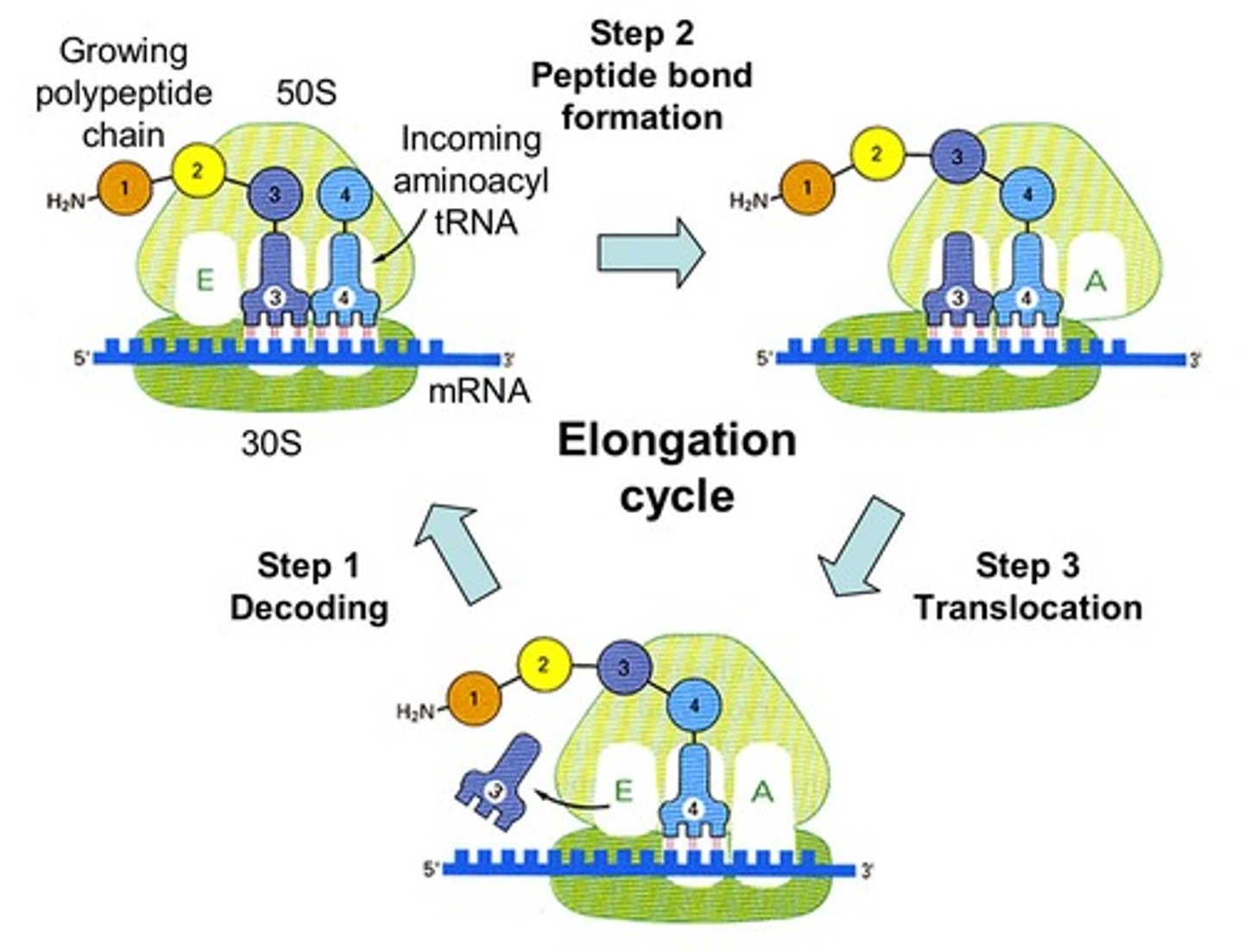
Elongation of translation:
Amino acids are brought and the ribosome helps link these amino acids together, forming a growing protein chain.
Termination of translation:
When the ribosome reaches a stop codon (UAA, UAG, or UGA), translation ends. No tRNA matches these codons, so a release factor helps separate the protein from the ribosome, and the process is complete.

Protein synthesis diagram:
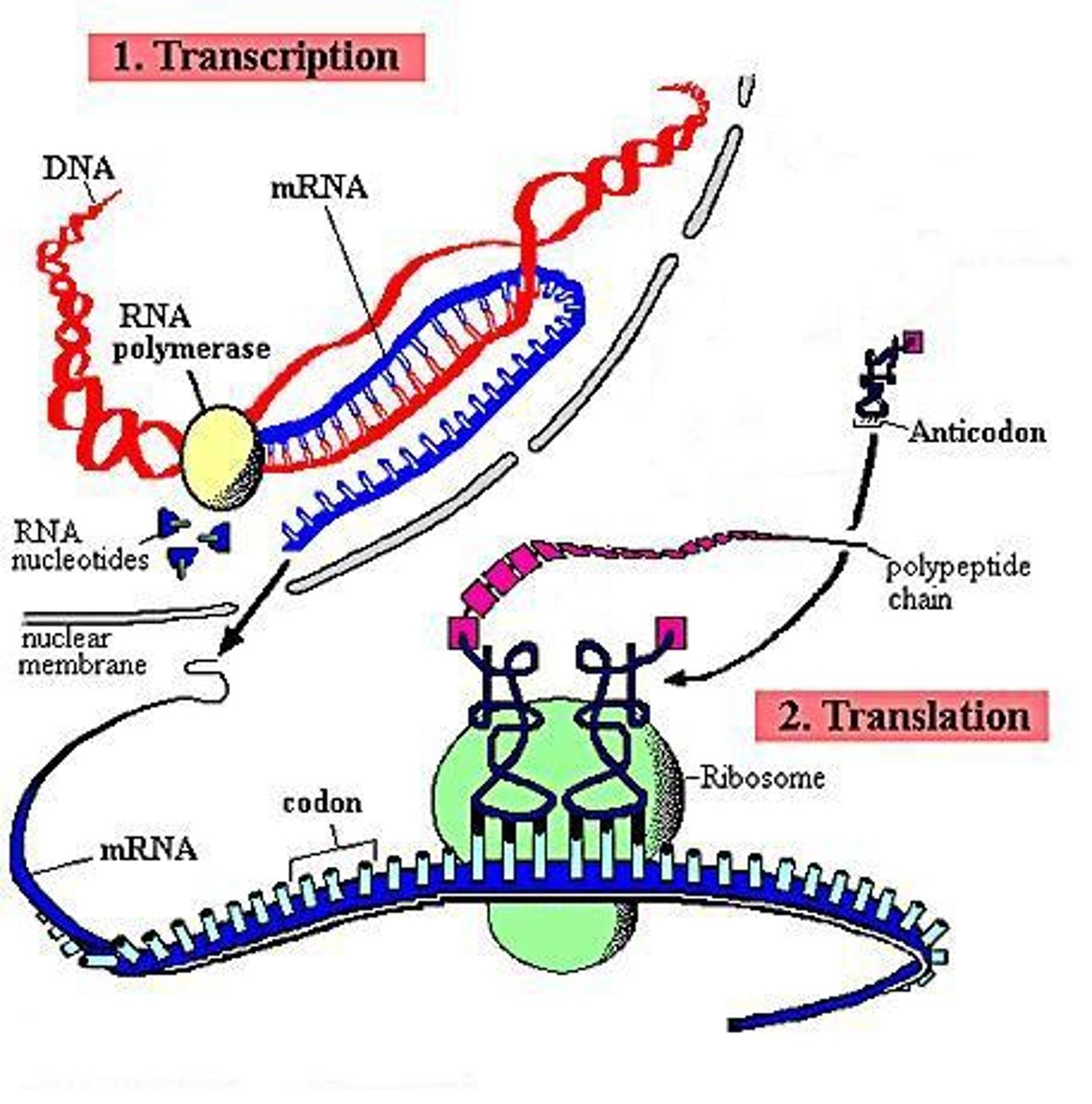
If the DNA codon was AGC what would the mRNA codon be?
UCG
If the DNA code was AAA what would the mRNA be?
UUU
What would amino acid of GUC be?
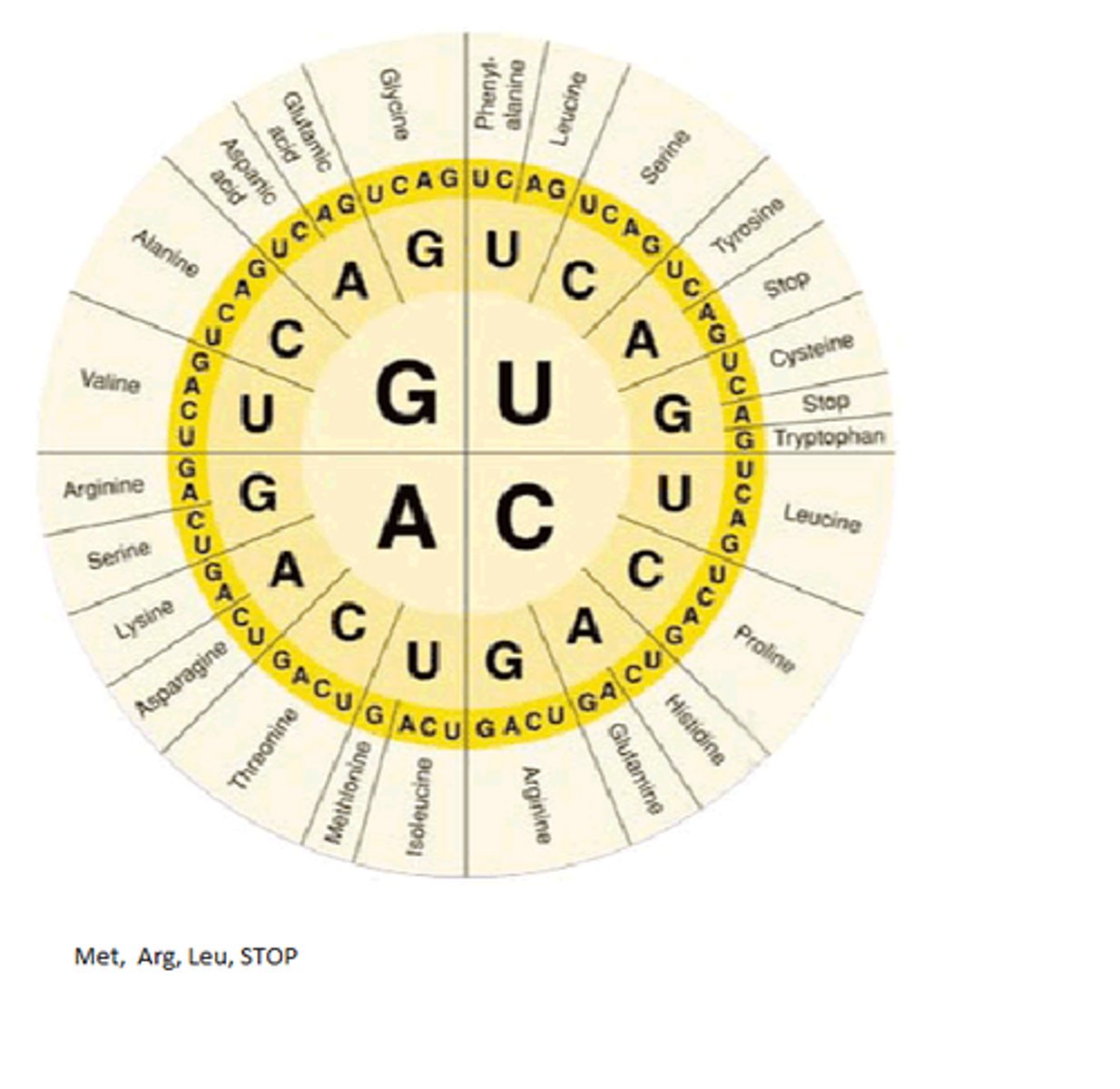
What is a mutation?
change in DNA sequence
What is a point mutation?
a change in a single nucleotide
What is substitution?
When one base is substituted for another
What are the kinds of point mutations?
silent, missense, nonsense
What is a nonsense mutation?
an early stop codon is present- shortening the protein
What is a missense mutation?
one amino acid substituted for another
What is a silent mutation?
no change in protein- the amino acid isn't affected
What is a frameshift mutation?
The "reading frame" is shifted, changing the entire protein.
What are the kinds of frameshift mutation?
insertion and deletion
What happens during insertion?
an extra base is inserted into a codon
What happens during deletion?
a base is removed
Are mutations positive or negative?
They can be both
What is an example of a positive mutation?
lactose tolerance
What is an example of a negative mutation?
sickle cell anemia