CLIN PATH: EXAM #2 (DERM LEC CCs)
1/87
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
88 Terms
Pt presents with keratin hyperplasia & proliferating cells in the stratum basale + stratum spinosum due to T cell activation & cytokine release. This causes greater epidermal thickness & accelerated epidermis turnover. What Dx has this typical pathophys?
Psoriasis
Pt presents with plaques (M/C) that are raised, well-demarcated, pink-red plaques or papules with thick silvery white scales. M/C on the extensor surfaces of the elbows/knees, scalp, & nape of the neck. Usually pruritic. What Dz do you suspect?
Psoriasis
___________________:
• Vacuoles appear in the lower epidermis
• Colloid bodies are also present
• Mature lesions are composed of CD8 cytotoxic T cells
Lichen Planus
PE for ___________________:
- 6 p's: purple, polygonal, planar, pruritic, papules or plaques with fine scales & irregular borders that may also have Wickham striae (fine white lines on the skin lesions or on the oral mucosa). May also develop Koebner's phenomenon (new lesions at sites of trauma - also seen in psoriasis). Nail dystrophy. May cause scarring alopecia.
Lichen Planus
______________: fine white lines on the skin lesions or on the oral mucosa. Characteristic in Lichen Planus.
Wickham striae
Common sites of _________________:
•Flexor surfaces of the extremities
•Genital skin
•Mucous membranes
Lichen Planus
This Dz is characterized by "target lesions" consisting of three components: a monomorphous pattern of dusky, central area or blister, a dark red inflammatory zone surrounded by a pale ring of edema, and an erythematous halo on the extreme periphery of the lesion. M/C on acral surfaces (extremities and trunk).
Erythematous Multiforme
This Dz clinically manifests as a negative Nikolsky sign (no epidermal attachment).
Erythematous Multiforme
In __________________ "target lesions" distributed acrally with no mucosal membrane involvement.
Erythematous Multiforme (Minor)
In _______________________ "target lesions" acrally progressing centrally + mucosal membrane involvement (oral, genital, or ocular). No epidermal detachment.
Erythematous Multiforme (Major)
In Erythematous Multiforme, a sparse inflammatory infiltrate = _____________________.
keratinocyte necrosis
In Erythematous Multiforme, the target-like appearance reflects what?
Zones of inflammatory rxn and damage(middlepartdiesoff)
Erythematous Multiforme MAJOR encompasses:
• ____________________:
• Profound mucosal involvement +/- cutaneous lesions
Stevens-Johnson syndrome
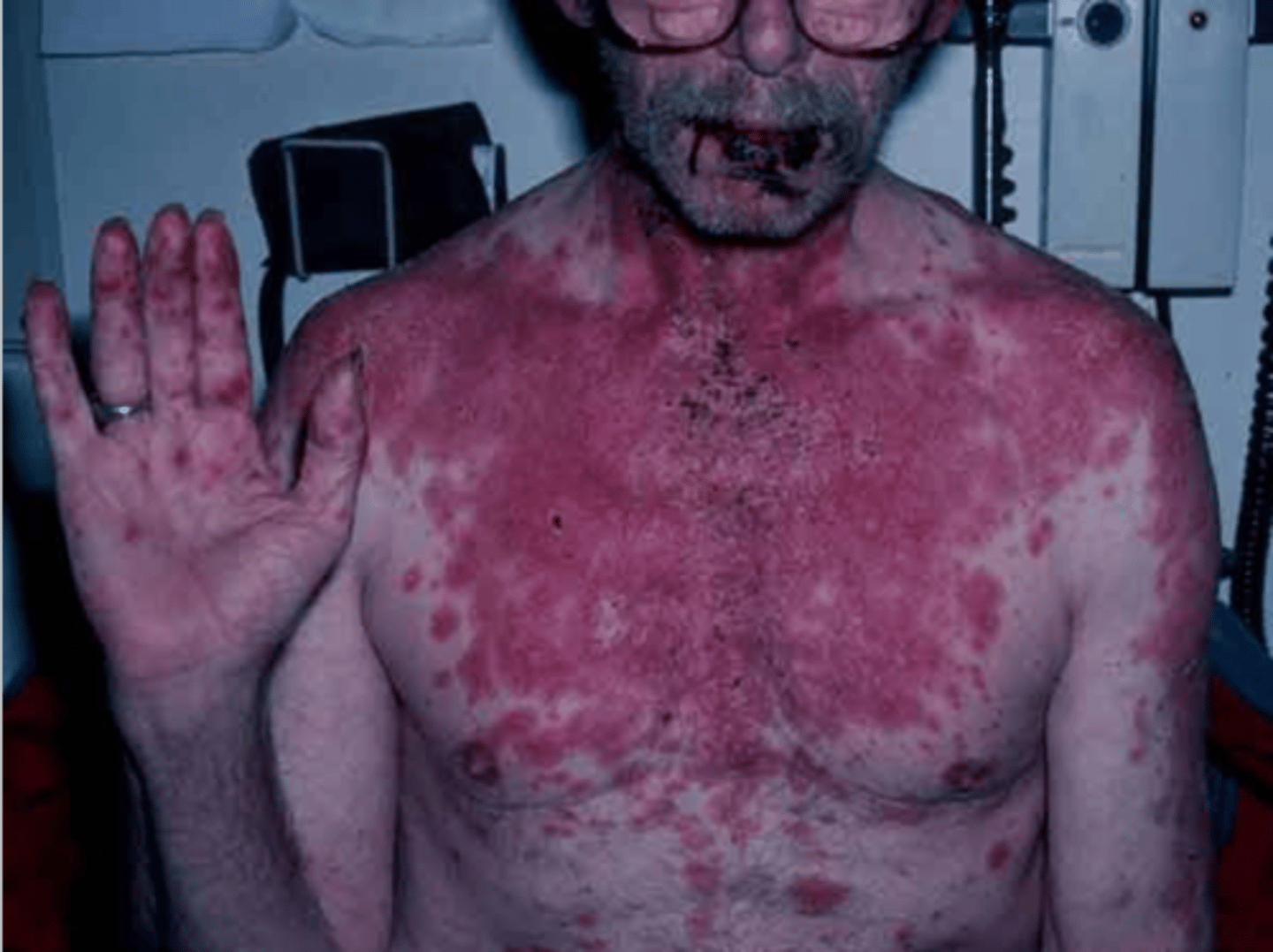
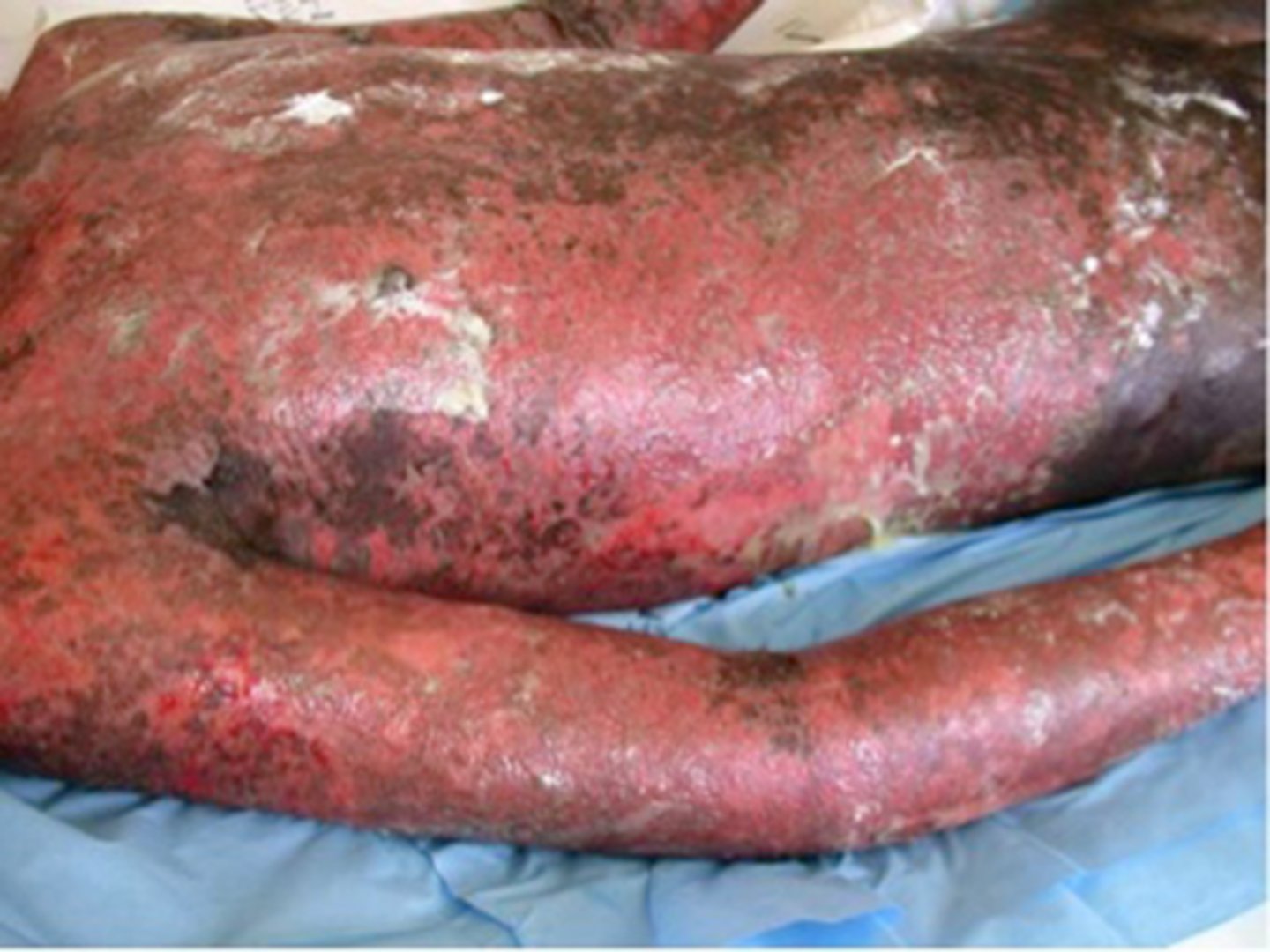
Erythematous Multiforme MAJOR encompasses:
____________________:
• Cause - idiosyncratic drug rxn
• Large areas of skin & mucosa become necrotic with secondary vesiculation
Toxic epidermal necrolysis
______________ is a autoimmune disorder leading to blister formation & severe pruritus. Primarily seen in the elderly. It is a Type II hypersensitivity rxn - IgG autoantibodies against hemidesmosomes & basement membrane zone causing subepidermal blistering.
Bullous pemphigoid
This Dz clinically manifests as a prodrome of pruritus with eczematous or urticarial plaques followed by tense large bullae that don't rupture as easily most commonly involving the groin, axilla, trunk, & flexural areas. Blister roof contains epidermis.
Bullous pemphigoid
Life-threatening, chronic autoimmune blistering disorder of the mucous membranes and skin. Type II hypersensitivity rxn where autoantibodies (IgG) agains desmoglein, a component of the desmosome, lead to acantholysis (separation of the dermis).
Pemphigus vulgaris
__________________ is a disease of the skin and mucous membranes only
Bullous pemphigoid
______________: Inflammatory disorder affecting small blood vessels of the skin --> eruption of reddish or violaceous papules, a pattern known as palpable purpura.
Leuokocytoclastic Vasculitis
________________: Lesions develop in crops --> indiv lesions persist a few days, less than 1 month
Leuokocytoclastic Vasculitis
Pt presents with palpable purpura post-streptococcal infection x 3 days. What Dz do you suspect?
Leuokocytoclastic Vasculitis
Histopath/Pathogen of Leuokocytoclastic Vasculitis: Inflammatory reaction involving blood vessels in association with an accumulation of ______________________
necrotic nuclear (leukocytoclastic) debris
The erythematous or purpuric quality of ___________________ --> numerous erythrocytes that accumulate in the dermis of fully developed lesions.
Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis
Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis can develop at any site, but mainly _________________.
lower extremities
In Leukocytoclastic Vasculitis, _____________ (M/C), can also be vesicopustules, necrotic papules and ulcers
purpuric lesions
Spongiotic Dermatitis pattern example: ___________________
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Vesiculobullous Dermatitis pattern example: ________________
Bullous pemphigoid
Vasculitis pattern example: _________________________
Leuokocytoclastic Vasculitis
___________________: nickel (M/C worldwide), poison ivy, oak or sumac; other metals, chemicals (eg, fragrances, glue, hair dyes), detergents, cleaners, acids, prolonged water exposure.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
_____________________: Type IV hypersensitivity rxn (T-cell mediated - delayed by days.)
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Pt presents with erythematous papules or vesicles (may be linear or geometric). Often associated with localized pruritus, stinging, or burning. May ooze, develop edema, & progress to blisters or bullae/vesicles.
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
The term “______________” refers to edema of the epidermis, which separates keratinocytes from one another
spongiosis
Spongiotic dermatitis is accompanied by a variable amount of ________________.
perivascular inflammation
In Spongiotic dermatitis, the infiltrate is typically composed of ______________, but eosinophils are often concurrently
lymphocytes
In Allergic Contact Dermatitis, first exposure may not yield a rxn but the pt is now _________________.
sensitized
Type IV Hypersensitivity _______________: allergen binds to endogenous protein --> creation of foreign protein
Induction phase
Type IV Hypersensitivity Induction Phase:
__________________ engulf the complex, partially degrade it, migrate to lymph nodes & present antigenic fragments on cell surfaces with MHC-II molecules --> allergen complex --> T cell receptors bind with the allergen complex --> T cells clone themselves.
Langerhans' cells
Type IV Hypersensitivity Induction Phase:
Langerhans’ cells engulf the complex, partially degrade it, migrate to lymph nodes & _________________" --> allergen complex --> T cell receptors bind with the allergen complex --> T cells clone themselves.
present antigenic fragments on cell surfaces with MHC-II molecules
Type IV Hypersensitivity Induction Phase:
Langerhans’ cells engulf the complex, partially degrade it, migrate to lymph nodes & present antigenic fragments on cell surfaces with MHC-II molecules --> allergen complex --> ______________________ with the allergen complex --> T cells clone themselves.
T cell receptors bind
Type IV Hypersensitivity Induction Phase:
Langerhans’ cells engulf the complex, partially degrade it, migrate to lymph nodes & present antigenic fragments on cell surfaces with MHC-II molecules --> allergen complex --> T cell receptors bind with the allergen complex --> _____________________.
T cells clone themselves.
Type IV Hypersensitivity: Elicitation phase
Antigen appears again --> ___________________ process the antigen & migrate to lymph nodes --> T cell presentation also occurs at the site of contact - because now they are recognized --> Inflammatory cytokines create an amplification loop --> clinically recognized dermatitis
Langerhans' cells
Type IV Hypersensitivity: Elicitation phase
Antigen appears again --> Langerhans’ cells process the antigen & migrate to lymph nodes --> _______________________ because now they are recognized --> Inflammatory cytokines create an amplification loop --> clinically recognized dermatitis
T cell presentation also occurs at the site of contact
Type IV Hypersensitivity: Elicitation phase
Antigen appears again --> Langerhans’ cells process the antigen & migrate to lymph nodes --> T cell presentation also occurs at the site of contact - because now they are recognized --> _______________________ --> clinically recognized dermatitis
Inflammatory cytokines create an amplification loop
Type IV Hypersensitivity: Elicitation phase
Antigen appears again --> Langerhans’ cells process the antigen & migrate to lymph nodes --> T cell presentation also occurs at the site of contact - because now they are recognized --> Inflammatory cytokines create an amplification loop --> _____________________
clinically recognized dermatitis
Common causes of ___________________:
- Rhus dermatitis – often appears linear
• Poison ivy
• Poison oak
• Nickel allergy
• Soaps and detergents
Allergic Contact Dermatitis
Panniculitis pattern (inflammation of the fat layer below the skin) example: ________________________
Erythema Nodosum
What is the M/C form of panniculitis?
Erythema Nodosum
Pt presents with painful, erythematous, inflammatory nodules seen on the B/L anterior shins (range in colors from pink, red to purple.) Pt had a streptococcal infection and coccidioidomycosis (fungal) 1 month ago. They also have Sarcoidosis and take OCPs (estrogen exposure). What Dz do you suspect?
Erythema Nodosum
What disease happens in Women > men (3:1) with an etiology: end result of inflammation, infection, Strep pharyngitis, Meds, sulfonamides, Hormones (including pregnancy), OCs containing estrogen, Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD)
Erythema Nodosum
Panniculitis pattern: Erythema Nodosum
- Inflammation occurs in septal divisions btwn _____ compartments
fat
Panniculitis pattern: Erythema Nodosum
• Infiltrate consists of _________________________________
lymphocytes, histiocytes, granulocytes (neutrophils & eosinophils)
Panniculitis pattern: Erythema Nodosum
• Septa thicken & can become ______________ depending upon the infiltrate & duration of rxn
fibrotic
Panniculitis pattern: Erythema Nodosum
• Fat necrosis often spreads to the sc lobules
• Can appear as ____________________ or small stellate clefts within the macrophages
foamy (lipid-laden) macrophages
Panniculitis pattern: Erythema Nodosum
• Immunologic: Believed to be a delayed-type (type IV) hypersensitivity rxn in the ________________
•May involve Immune complex deposition in septum
septal fat
Nodular dermatitis pattern: _____________________
Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
What nodular dermatitis often presents on the face with nodular granulomas that can occur in the pulmonary tree & other viscera?
Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
20 y/o AA Female presents with Granulomas (collections of tissue macrophages) are present in the dermis. PMHx includes: Löfgren’s syndrome, Lupus pernio, and TB (M tuberculosis).
Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
What Dz occurs when Antigens induce T cells --> cytokines --> recruit macrophages to the site?
Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
Nodular dermatitis pattern: Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
• _________________- limit the extent of response
CD8 suppressor cells
Nodular dermatitis pattern: Cutaneous Sarcoidosis
• _________________ direct the immune response
CD4 helper cells
CXR and bone radiographs with findings suggestive of ________________ or skin biopsy
sarcoidosis
Folliculitis and Perifolliculitis Pattern: __________
Acne
This Dz commonly presents as follicle-based comedones, inflammatory papules, or pustules on face, neck, chest and back
Acne
Disfiguring __________________ with severe scarring does not occur before puberty.
nodulocystic acne
Numerous inflamed pustules and papules with central black plugs --> _____________________
open comedones or "blackheads"
__________________ is manifest as a widened follicle with a dense keratin plug within its infundibulum
Comedonal acne
__________________ ("blackheads") --> follicular orifice is open. Incomplete blockage.
Open comedones
_________________ ("whiteheads") --> orifice is normal, and follicle is plugged below the skin surface. Complete blockage.
Closed comedones
Closed comedones ("whiteheads"): _______________ may accompany the keratinous plug with the follicular canal, creating a pustular lesion
Neutrophils
Inflammatory acne lesions are a consequence of follicles that have ruptured with resultant spillage of keratinous debris into the perifollicular dermis, evoking a dense inflammatory reaction with a mixture of _______________________.
neutrophils, lymphocytes, and histiocytes
4 components to develop acne lesions:
• Folliculosebaceous unit is plugged by keratin
• Sebum production
• Overgrowth of Cutibacterium (formerly Propionibacterium) acnes
• ______________________
Secondary inflammatory process
4 components to develop acne lesions:
• Folliculosebaceous unit is plugged by keratin
• Sebum production
• _____________________________
• Secondary inflammatory process
Overgrowth of Cutibacterium (formerly Propionibacterium) acnes
4 components to develop acne lesions:
• Folliculosebaceous unit is plugged by keratin
• ______________________
• Overgrowth of Cutibacterium (formerly Propionibacterium) acnes
• Secondary inflammatory process
Sebum production
4 components to develop acne lesions:
• ________________________
• Sebum production
• Overgrowth of Cutibacterium (formerly Propionibacterium) acnes
• Secondary inflammatory process
Folliculosebaceous unit is plugged by keratin
ACNE:
1. Keratinocytes becomes sticky & fail to slough -->________________
follicular plugging
ACNE:
2. Increased sebum within the follicle acts as a food source for C. acnes --> __________________
bacterial overgrowth
ACNE:
3. Sebum degrades to lipids & free fatty acids --> _______________________
expansion of follicular canal
ACNE:
4. C. acnes recruits neutrophils --> ____________________
pustule formation
ACNE:
5. Neutrophilic enzymes weaken the ___________________ --> releases large amounts of inflammatory reactants into dermis
follicle wall --> rupture
ACNE:
6. Lymphocytes, macrophages & neutrophils respond.
• The comedone is now transformed into: ____________________
Inflamed papule, Pustule, Nodule of acne
ACNE:
7. Follicular rupture & intense 2° rxn may create profound ___________
scarring
In what population does the following occur:
• Maternal androgens stimulate enlargement of sebaceous glands --> Increased sebum production
• Sebum promotes C. acnes overgrowth --> acne
Neonates
In what population does the following occur:
• Androgens stimulate enlargement of sebaceous glands" sebum production in face, neck, chest & back
• Onset may be gradual or rapid
Puberty
__________ clinical manifestations:
• Follicle based comedones, inflammatory papules, or pustules
• Widened follicle with dense keratin plug within its infundibulum
Acne
What two Dz can present as a component of Acne?
PCOS and SAPHO
What Acne classification?
- Few to several papules/pustules (generally < 10) and no nodules
Mild Acne
What Acne classification?
- Several to many papules/pustules (10 - 40) along with comedomes (10 - 40) and few to several nodules
Moderate Acne
What Acne classification?
- Numerous or extensive papules/pustules and many nodules
Severe Acne