Chemistry of Life pt. 2
1/24
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
25 Terms
Carbohydrates
energy and strucutre
simple sugars or complex molecules including sugars (carbon, hydrogen, oxygen)
Hydrogen and oxygen 2:1 ratio
Monosaccharides, disaccharides, and polysaccharides.
Monosaccharide/monomer of carbohydrates
Simple sugar
glucose (C6H12O6) - produced in photosynthesis, broken down in cellular respiration for energy for cells *
5 carbon monosaccahrides used in genetic molecules & high energy molecules like ATP
used for short term energy
rings/cyclics
“watered carbon”
Disaccharides/two monomers of carbohydrates
sucrose, maltose, lactose
glycosidic linkage
Polysaccharides/polymers of carboyhydrates
Cellulose, starch
less sweet
long strands of glucose linked by glycosidic bonds, used for storage or structural support in plants and animals.
Cellulose (p) Chitin (a)
cellulose - support of cell wall
chitin -cell walls of fungi, exoskeleton for insects
need rummen to digest
hard bonds to break
Starch (p) Glycogen (a)
Starch - Energy storage for plants
Glycogen - energy storage for animals (muscle and liver)
easily broken bonds
Lipids
long term energy
hydrophobic/non-polar, insoluble because of hydrocarbon tail
no polymers
Fats, phospholipids, steroids, oils, wax
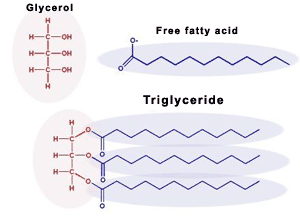
Fats
glycerol (alcohol w/ 3 carbons) + three fatty acids (long)
saturated and unsaturated vary in number and location of double bonds (hydrogden number)
essential fatty acids must be obtained through diet
saturated vs unsaturated
saturated (BAD) - animals, no double bonds, solid at room temp.
unsaturated (good!) - plants/fish, double bonds (cis or trans), liquid at room temp.
triglyciderides
fats, oils, wax
ester linkage - dehydration synthesis to bond glycerol & 3 fatty acids
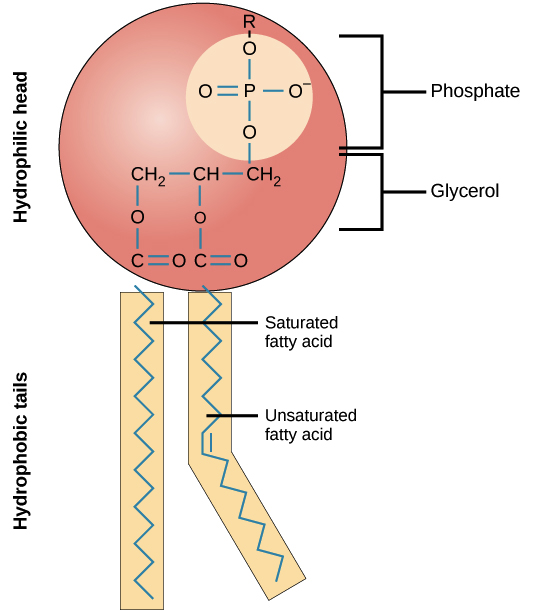
phospholipid
modified triglyceride
amphiphatic - polar head and non polar tail
major component of cell membranes
steroids
four carbon rings
cholesterol - needed in cell membrane
low density bad, high density good
makes cell membrane less fluid
Proteins
Most complicated
20 amino acids
50% of material in cells
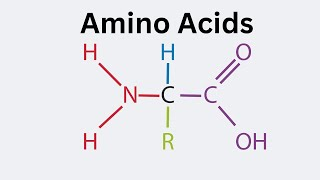
amino acids
amino group, carboxyl, hydrogen, R group. Held by peptide bonds
forms polypeptide chains
give proteins shape and structure
all are polar
amino to left side, will be positive
carbonyl to right side, will be negative
R group determines the charge
disulfite bridges
between 2 sulfate group
structures
primary, secondary, tertiary, quaternary
structure determines the function
primary
order of amino acids that make up the protein
secondary
alpha helix or beta sheet
results from hydrogen bonds on polypeptide backbone (NCC Backbone)
teritary
interaction of R groups
nonpolar or polar
charged R groups have ionic bonds
Quaternary
more than one polypeptide
ionic and covalent
Nucleic Acids
DNA and RNA
DNA had one less oxygen - deoxyribose
RNA is ribose
DNA
genetic info to build proteins
four nitrogenous bases (adenine, cytosine, thymine, guanine) held by hydrogen bonds
five carbon sugar/pentose + phosphate group + nitrogenous base
sugar phosphate backbone, double helix
AGCT
A and G are purines, two rings
C and T are pyrimidines, one ring
RNA
One strand
uracil instead of thymine
mRNA, tRNA, rRNA
used in protein synthesis
speed up chemical reactions
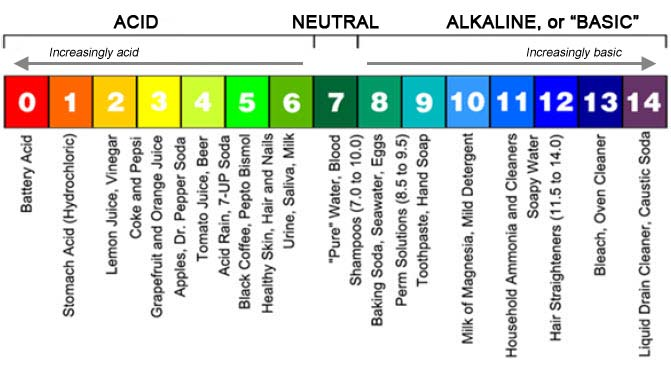
pH acids and bases
pH of four is ten times more than 5.
pH of five is ten times less than four