practical
1/69
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
70 Terms
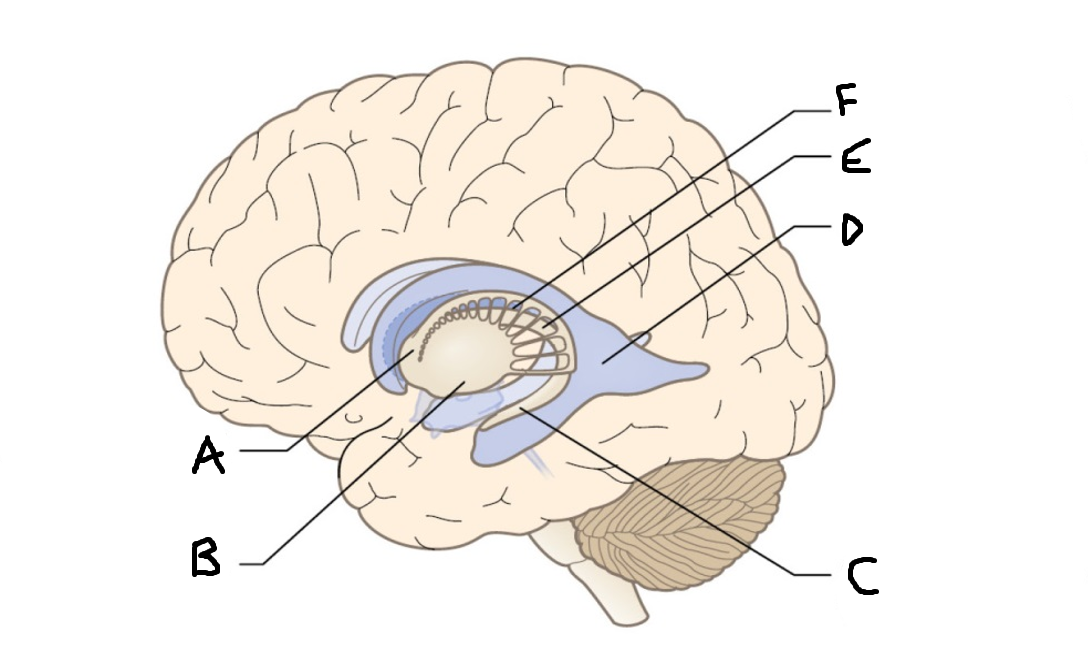
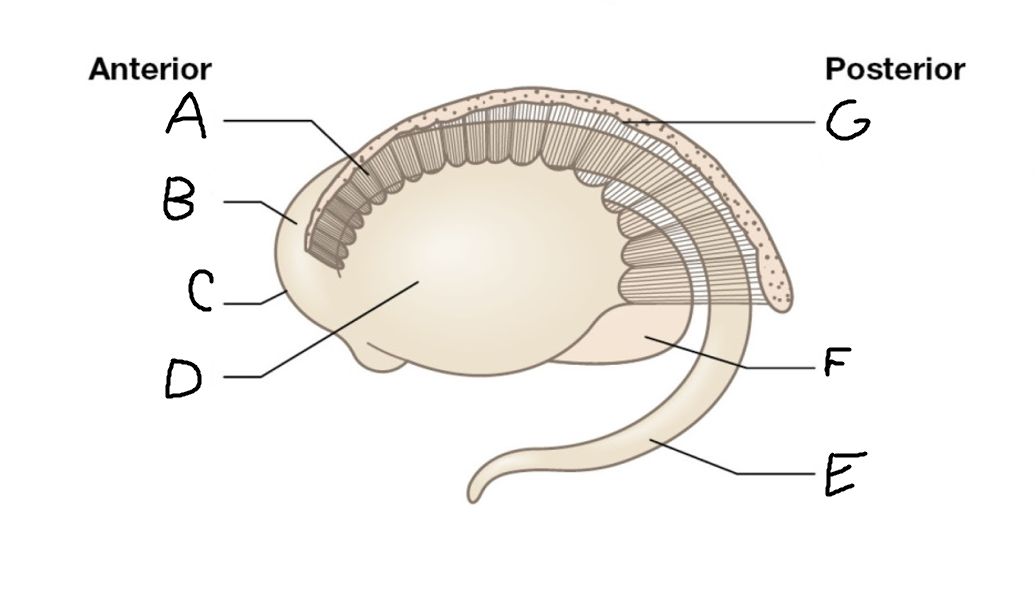
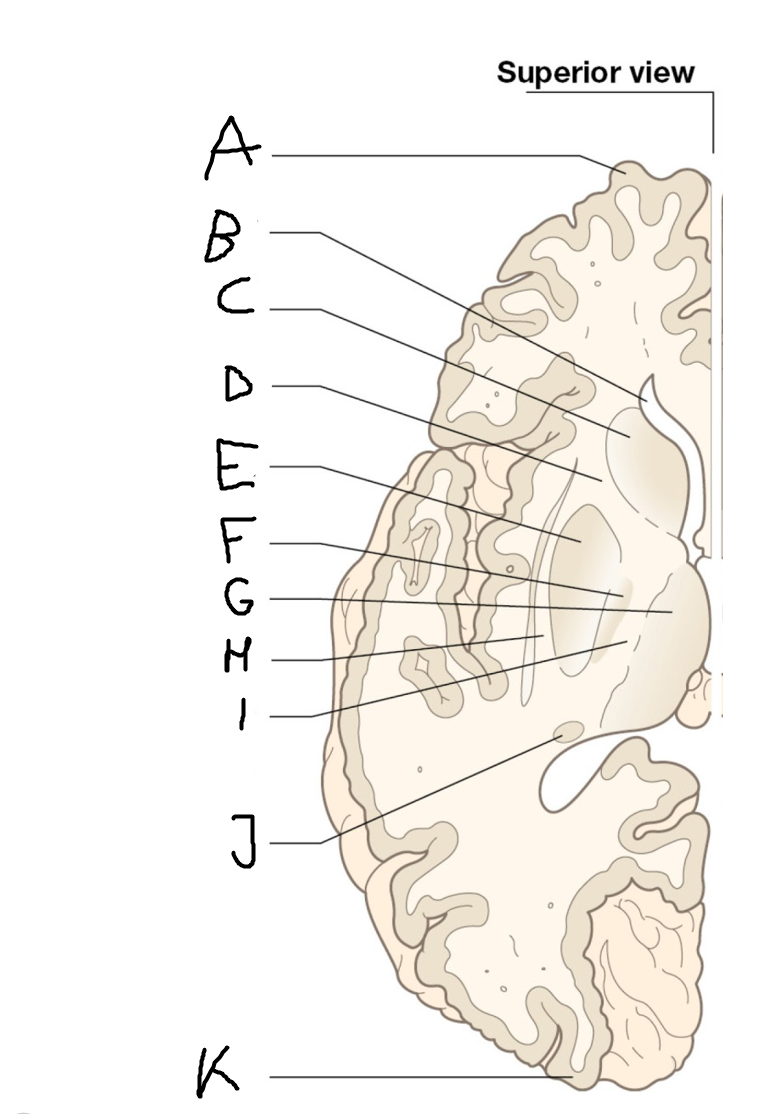
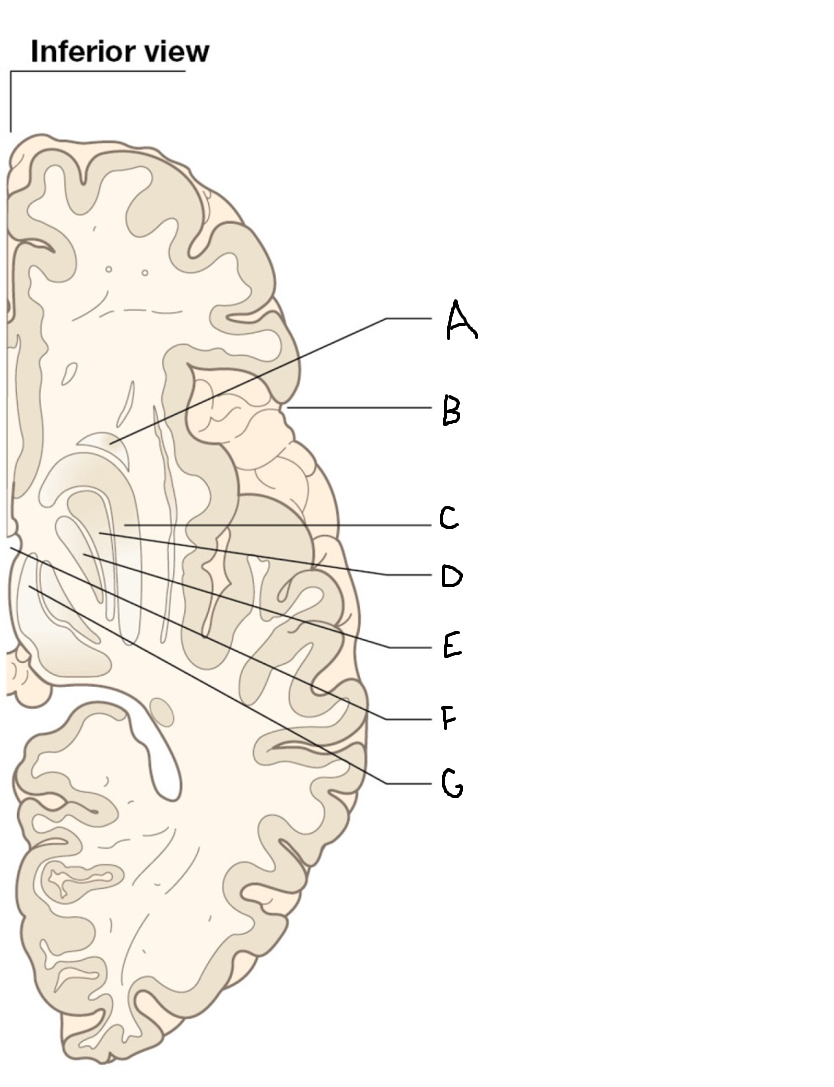
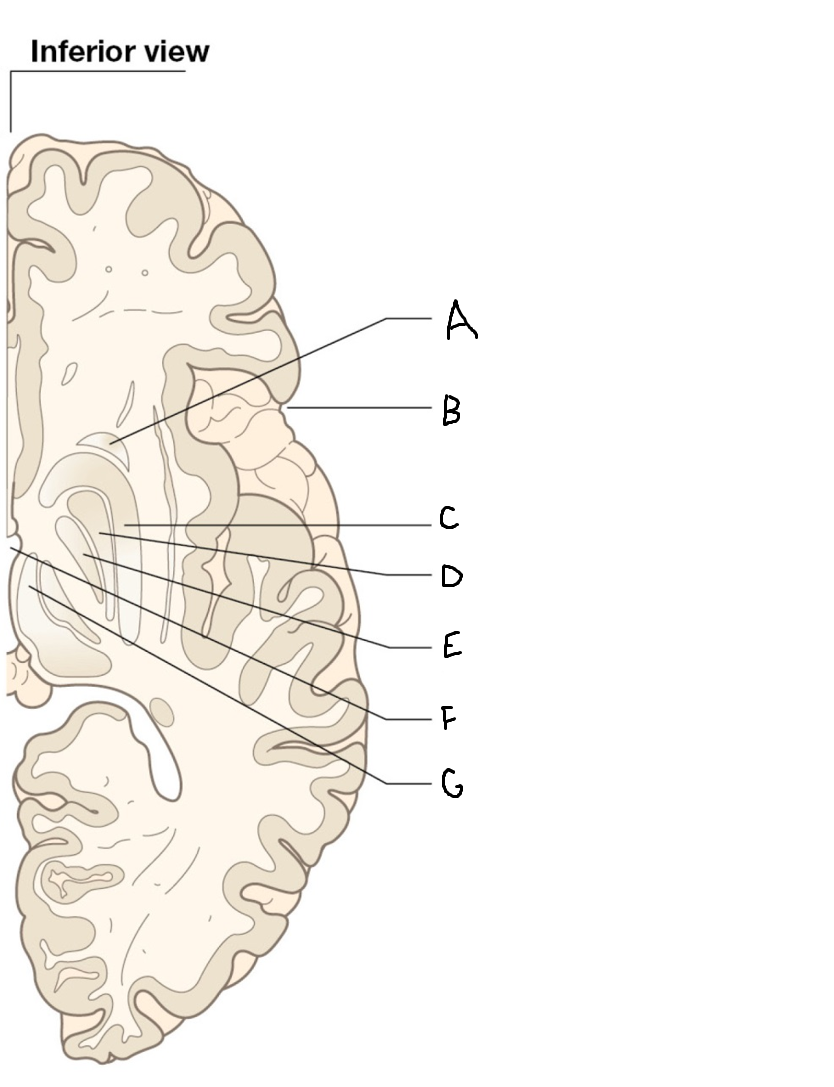
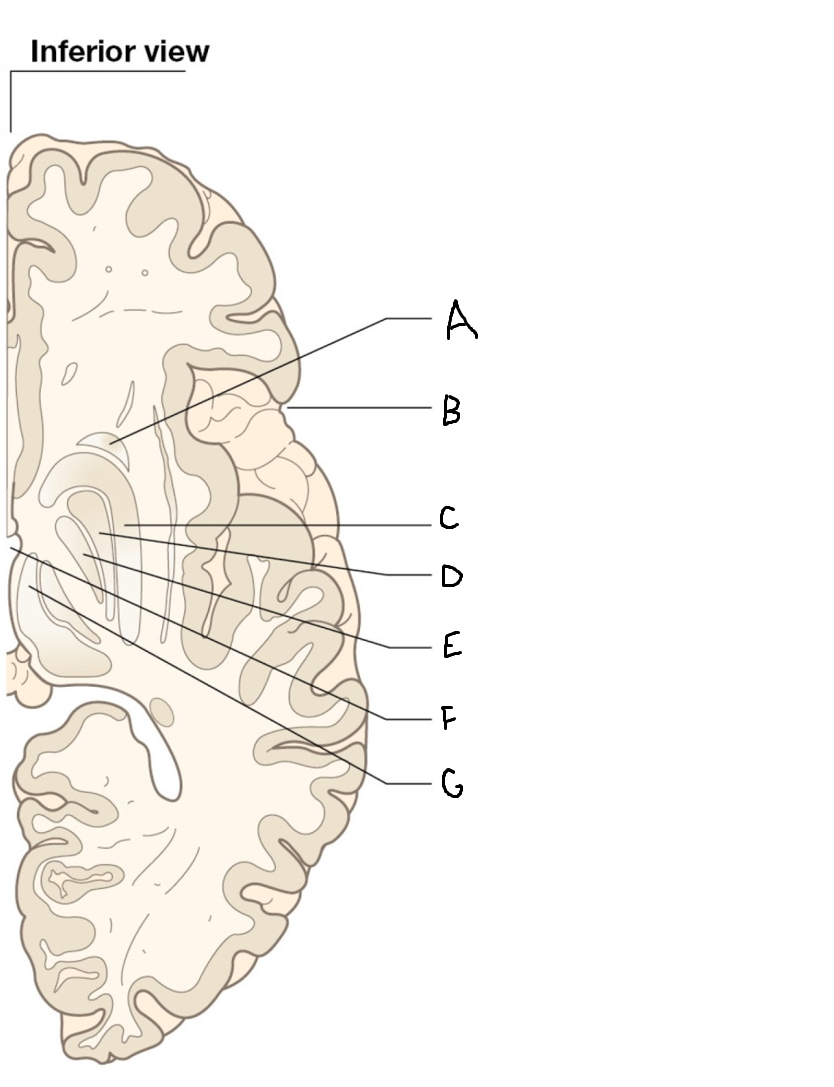
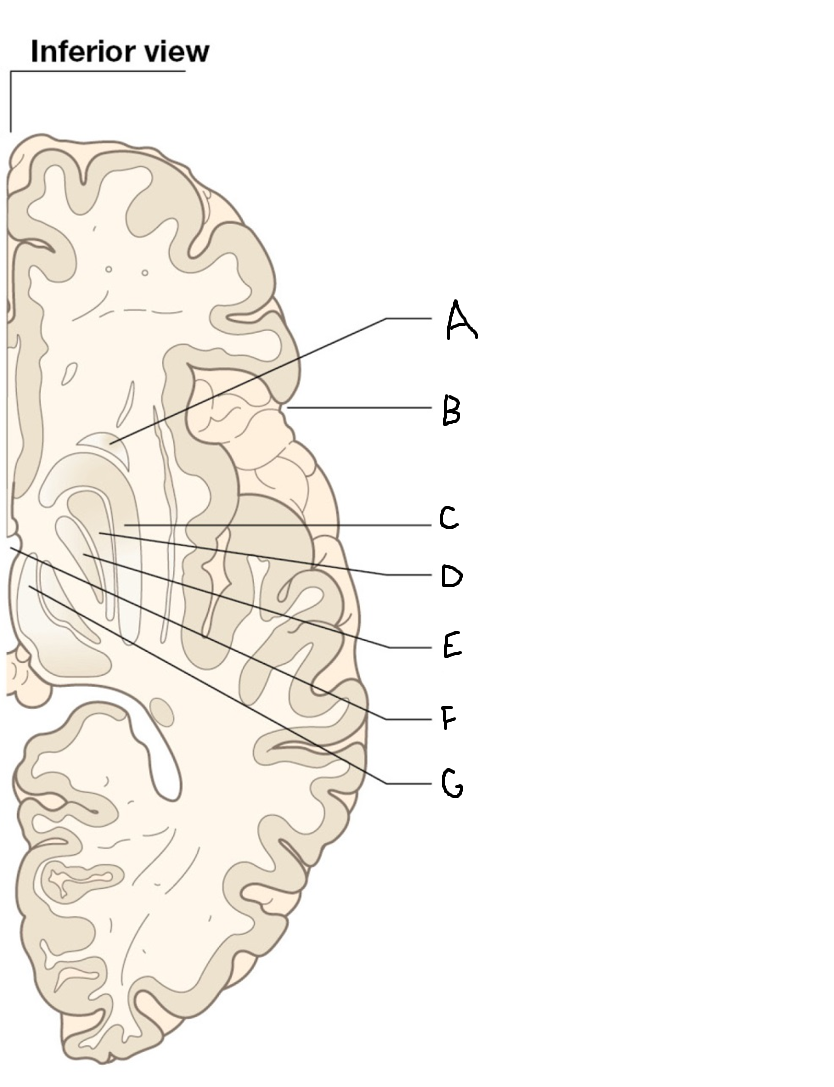
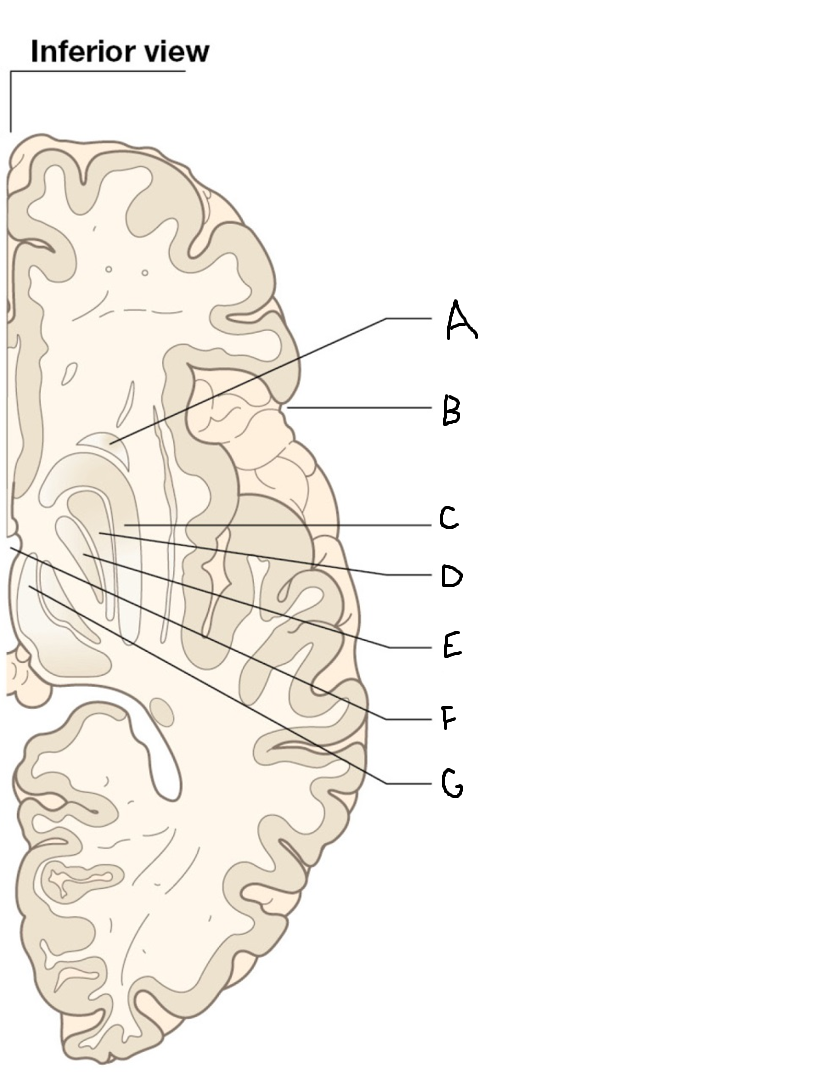
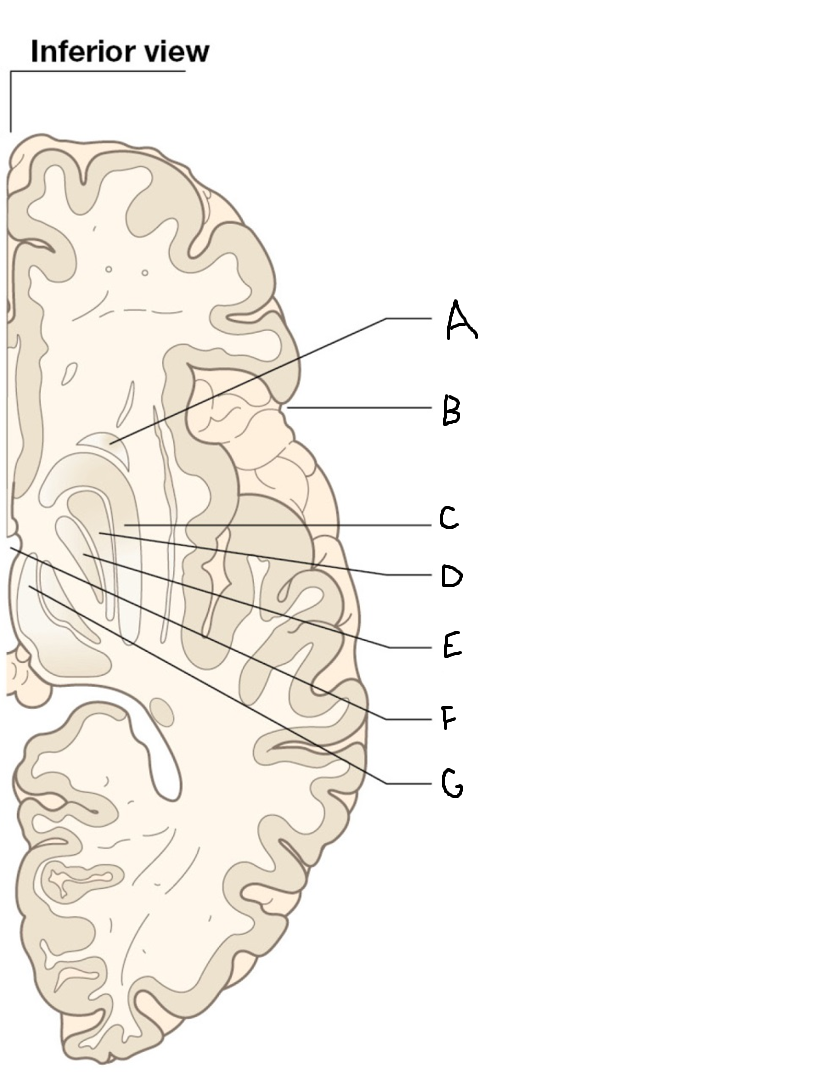
caudate nucleus head
A
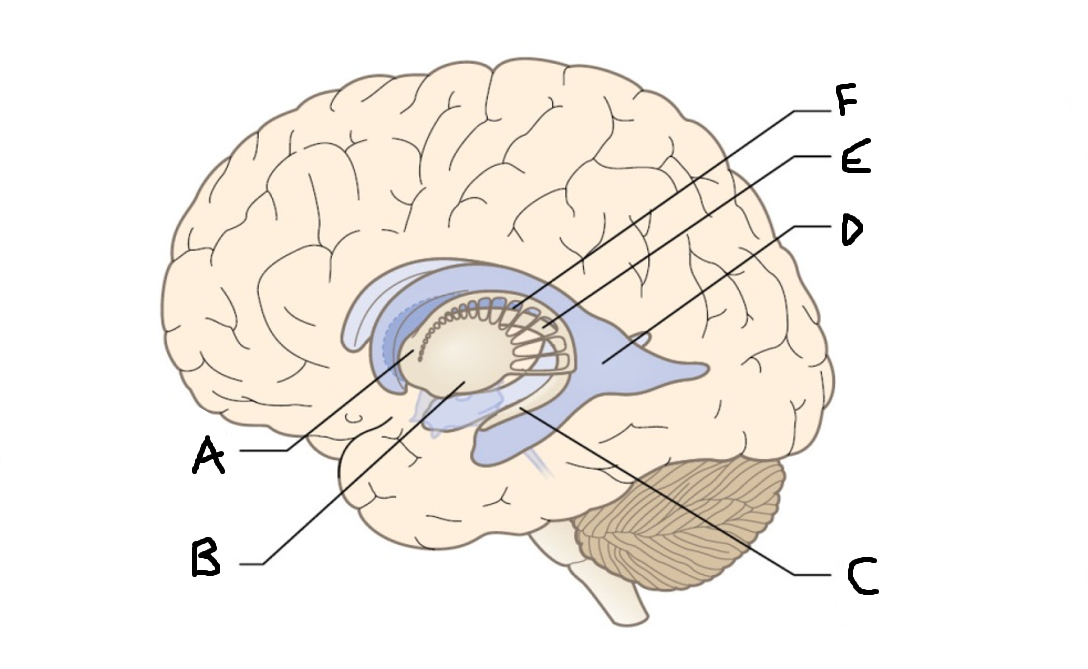
Putamen
B
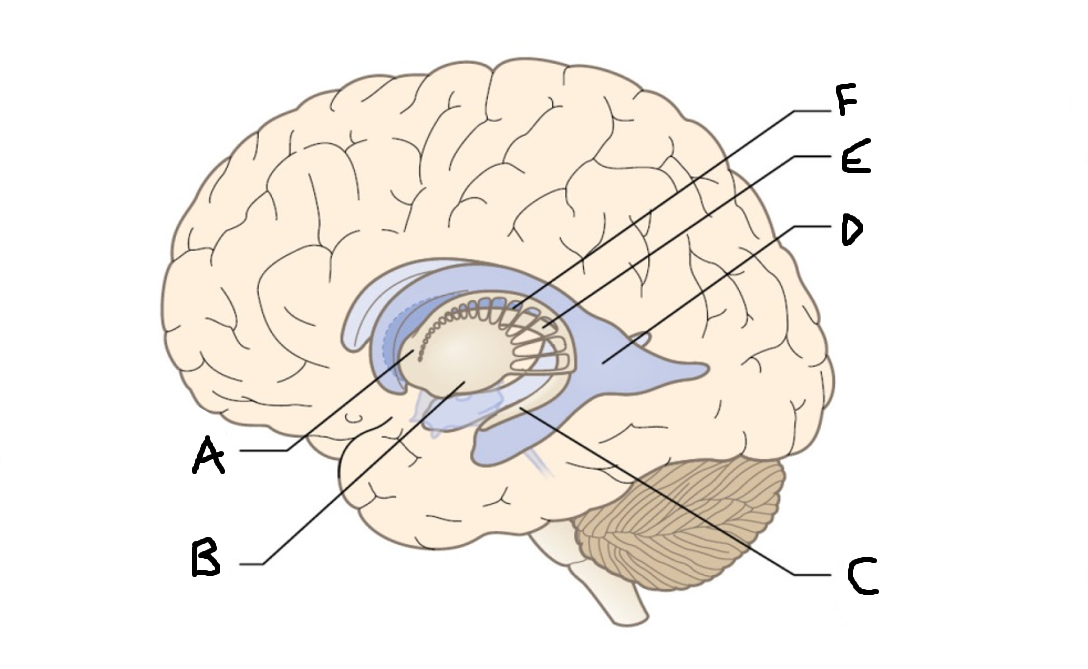
caudate nucleus tail
C
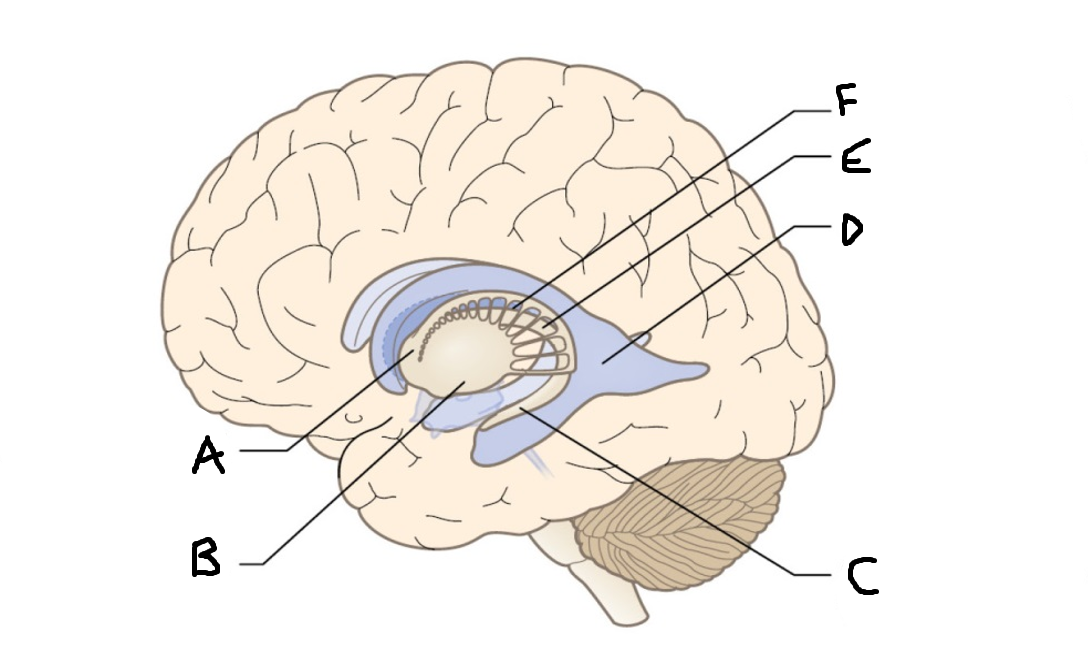
Lateral ventricle
D
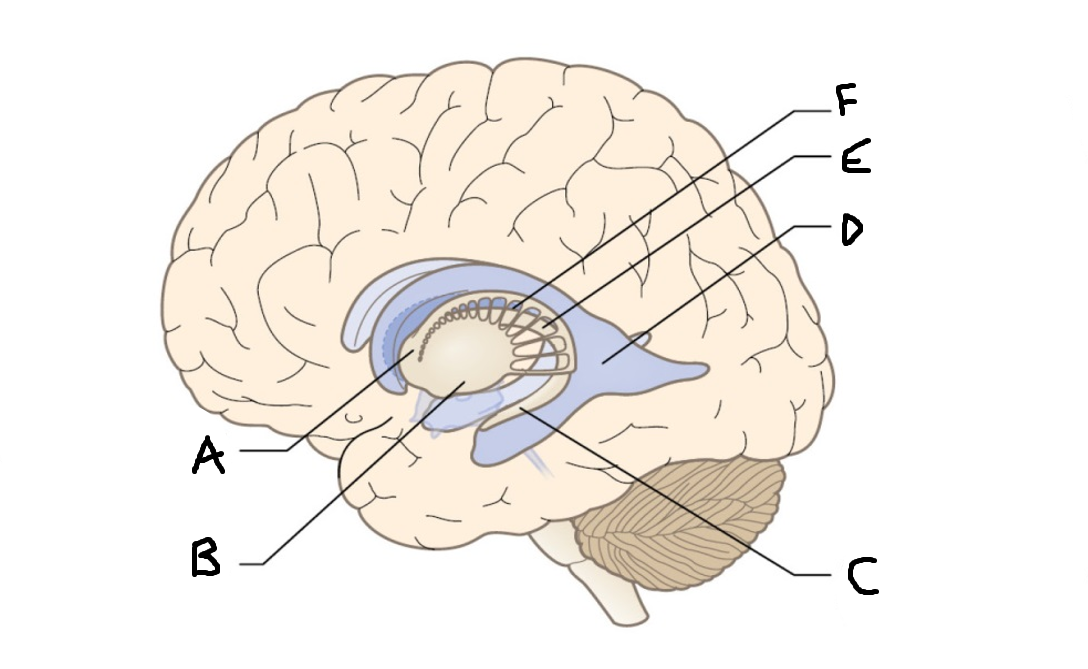
caudate nucleus body
E
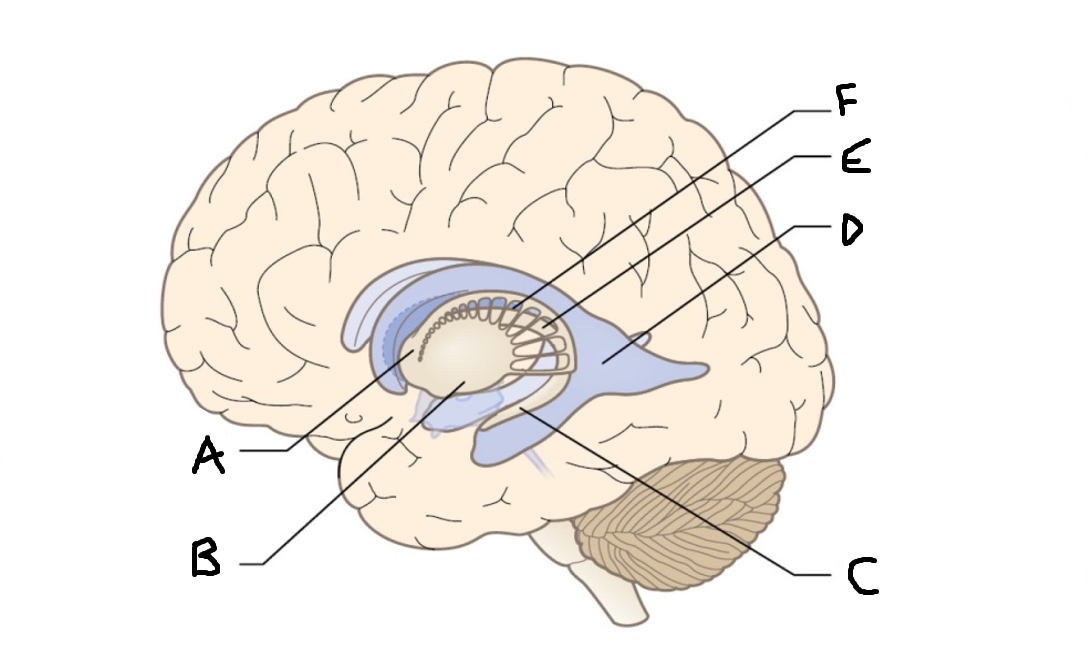
internal capsule
F
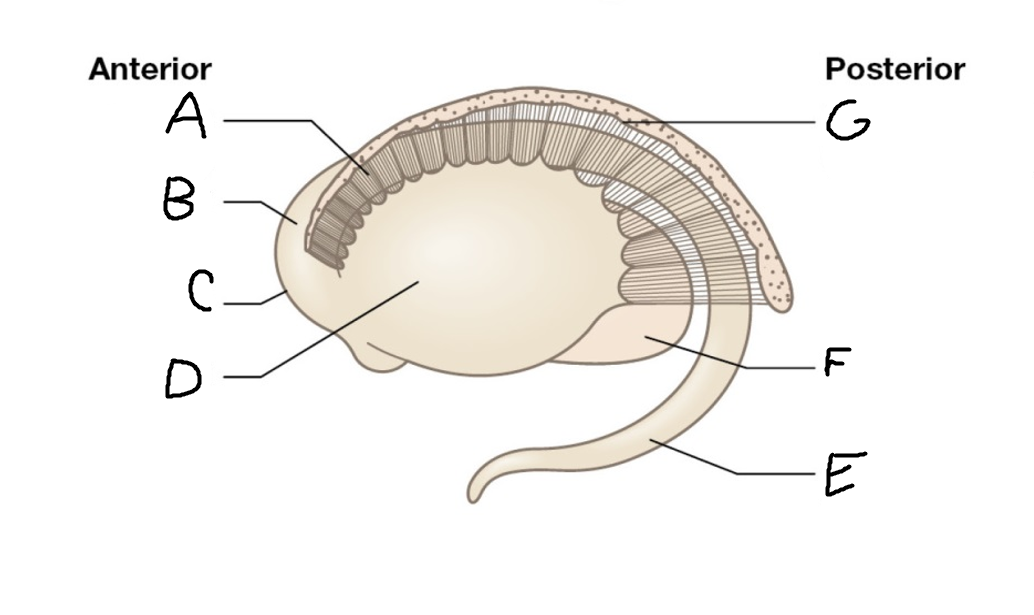
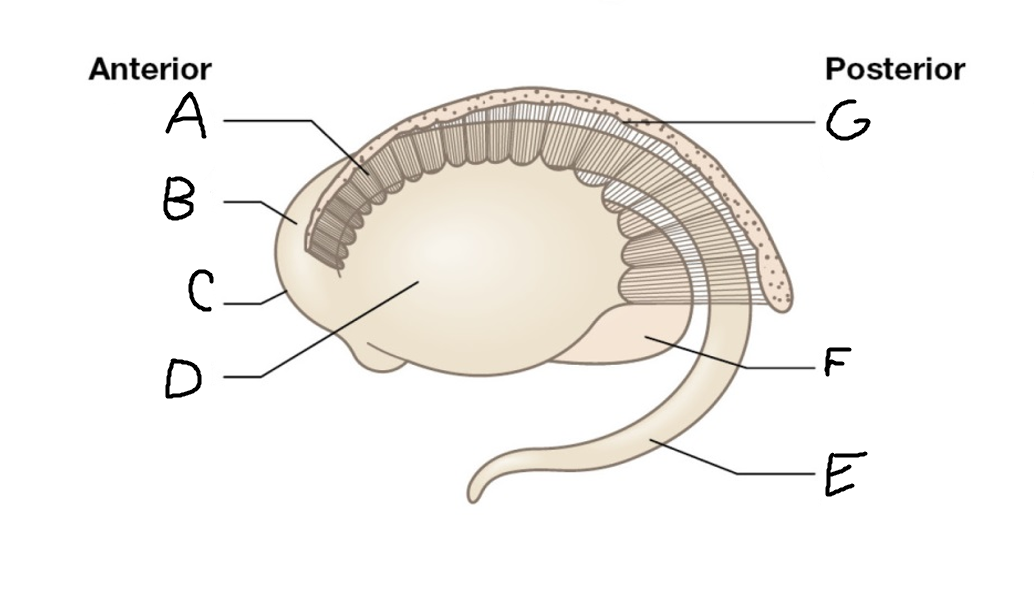
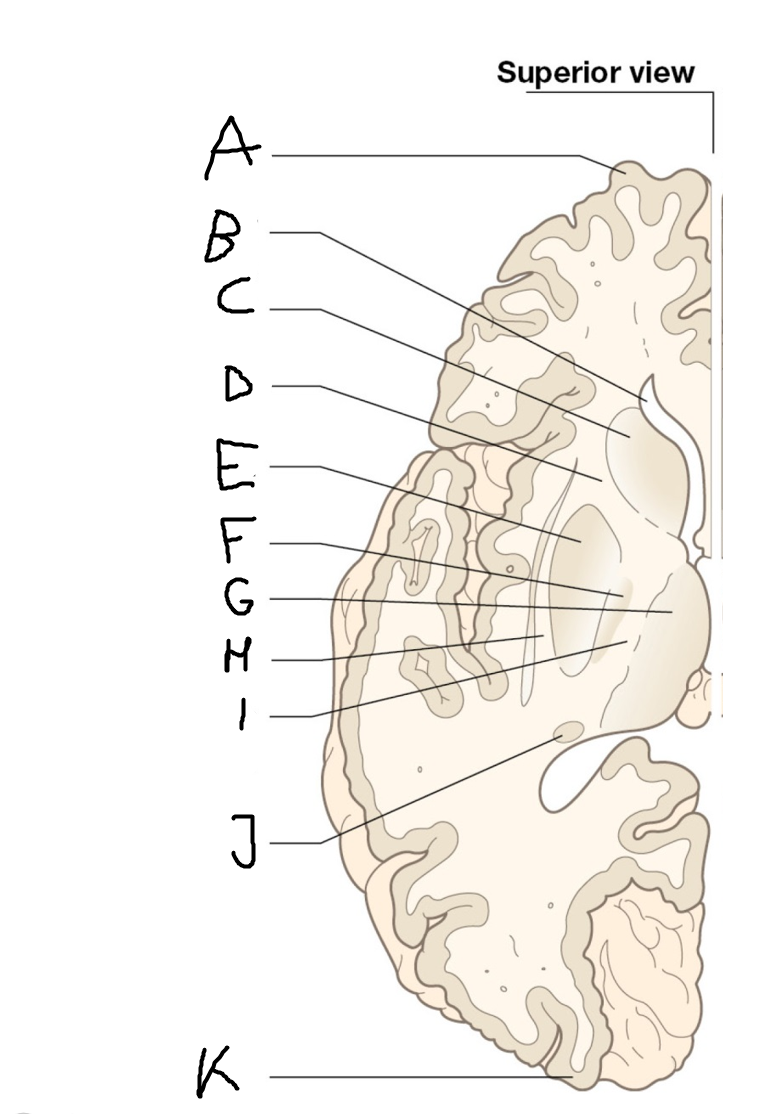
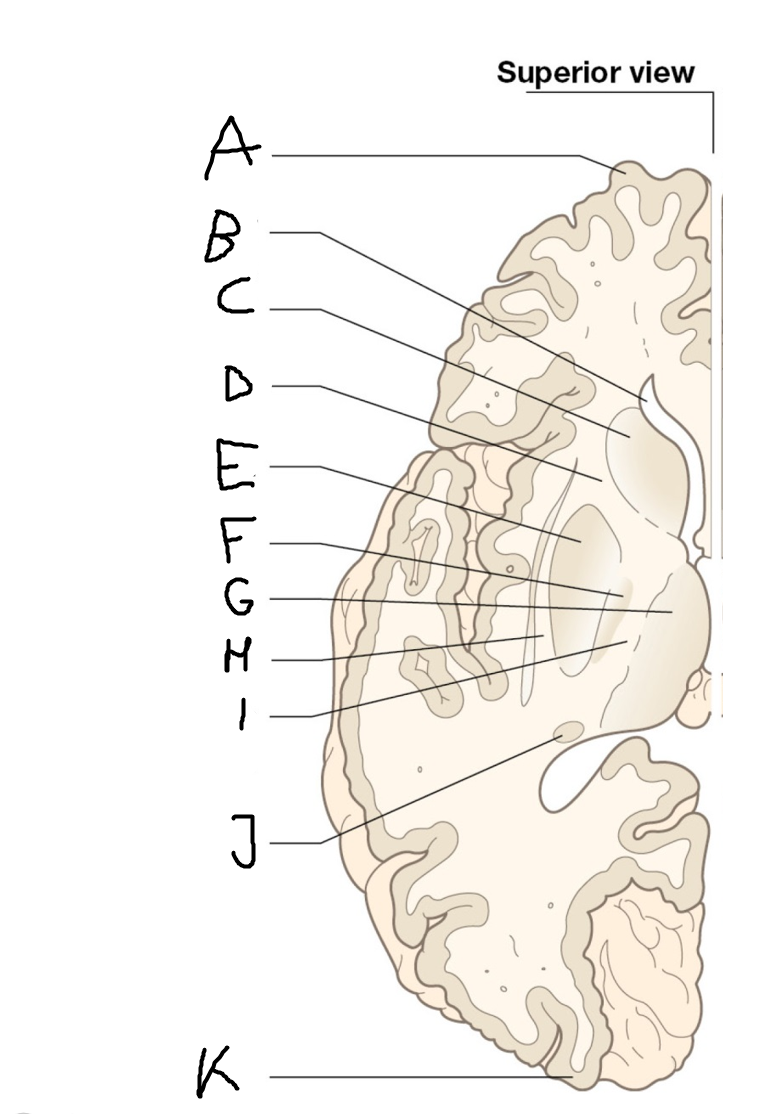
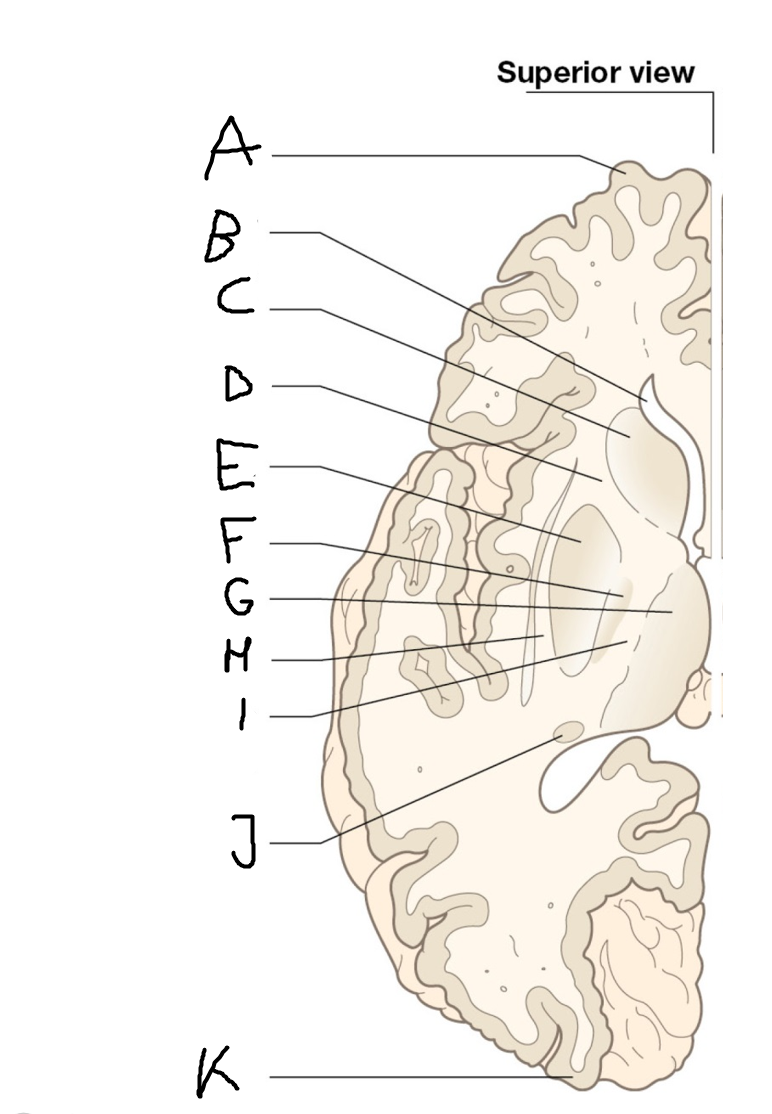
A
internal capsule (anterior limb)
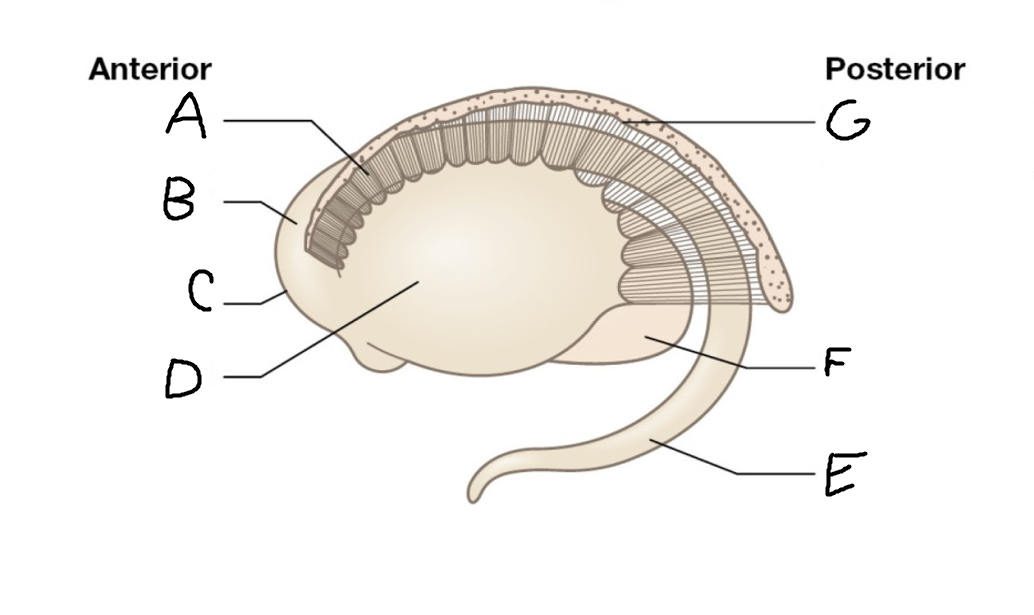
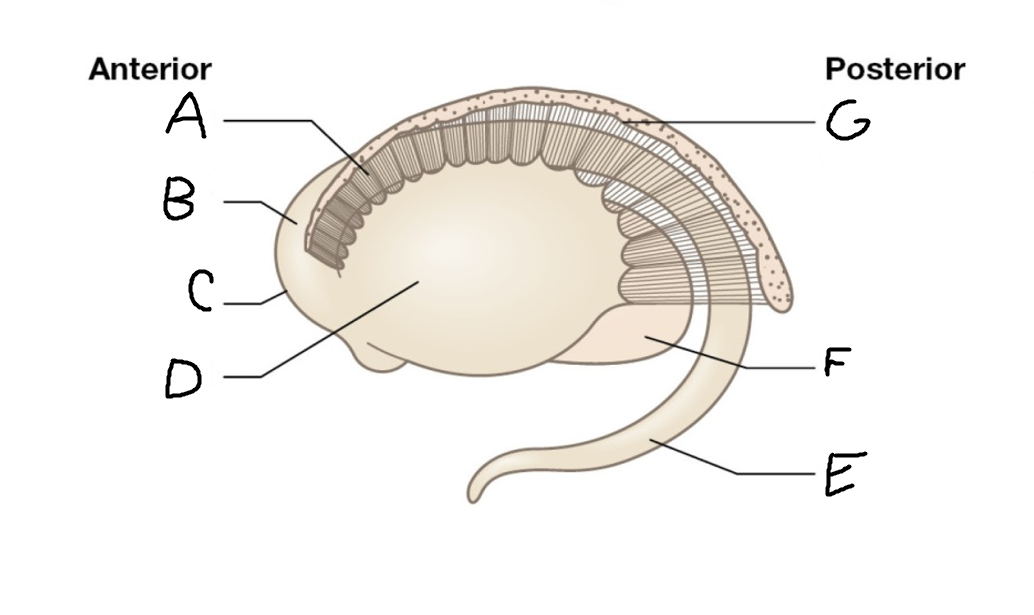
B
caudate nucleus body
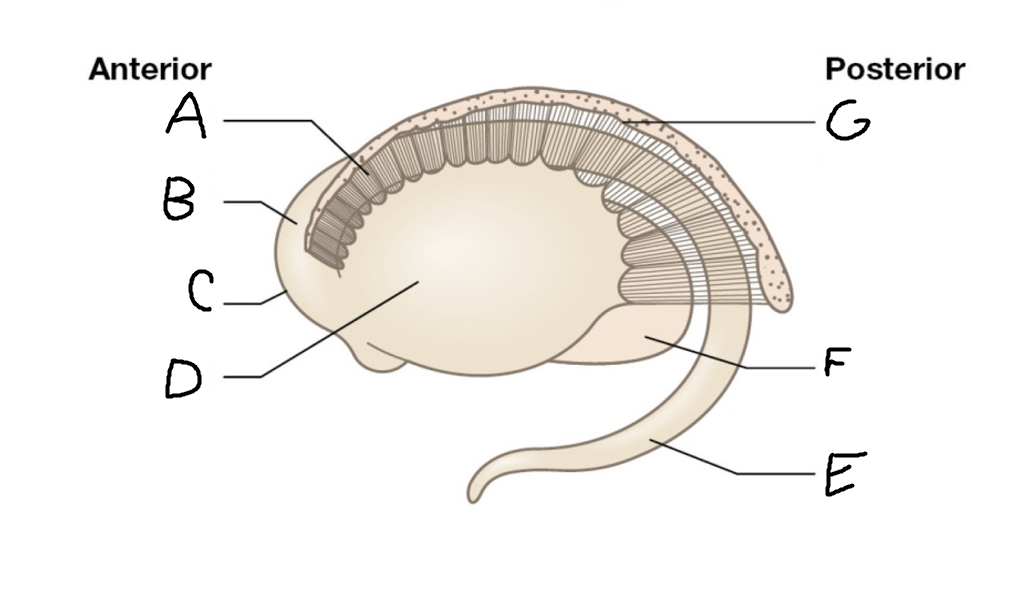
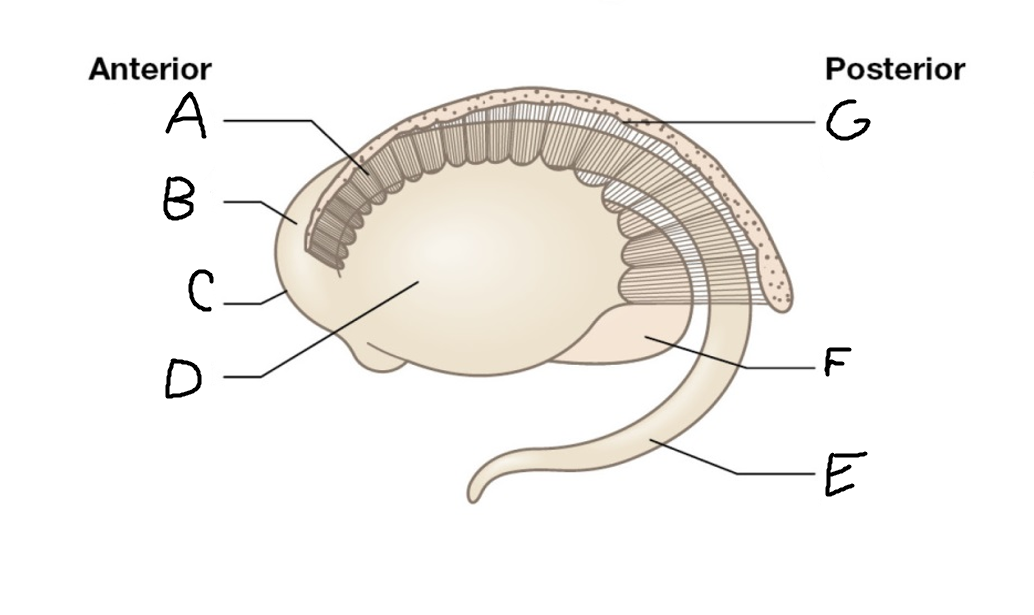
C
caudate nucleus head
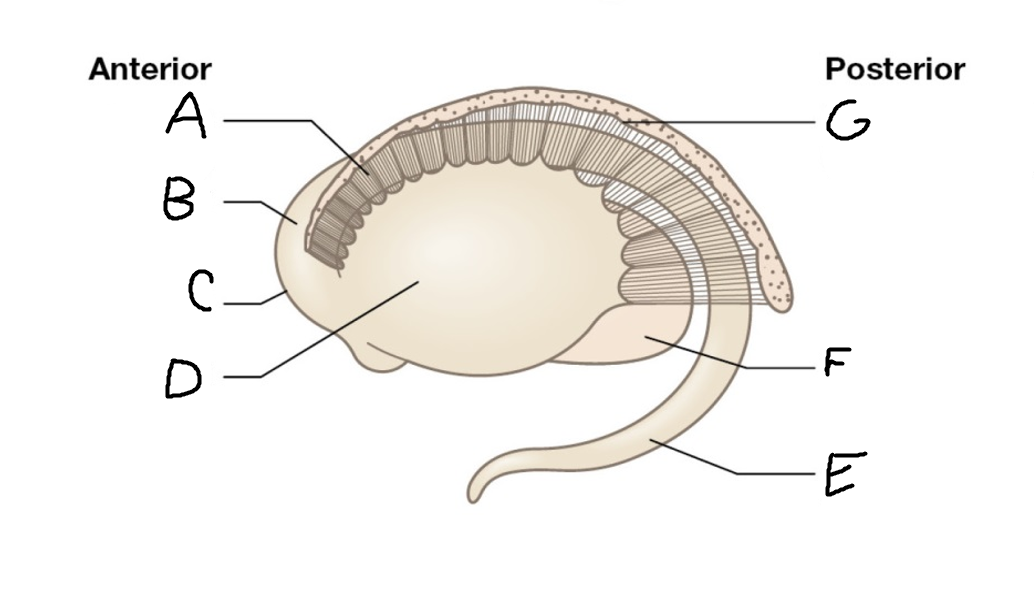
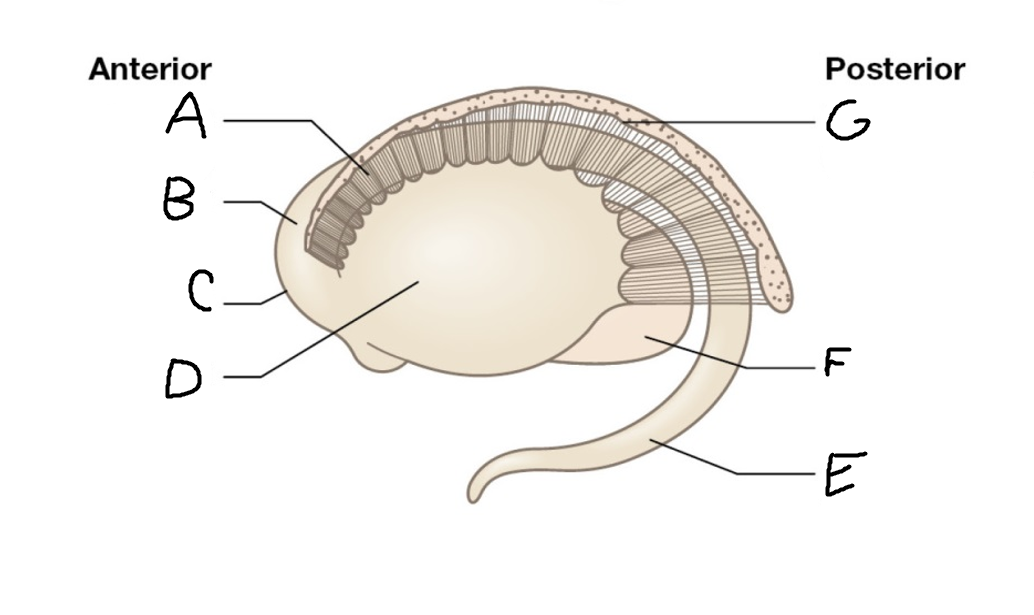
D
putamen
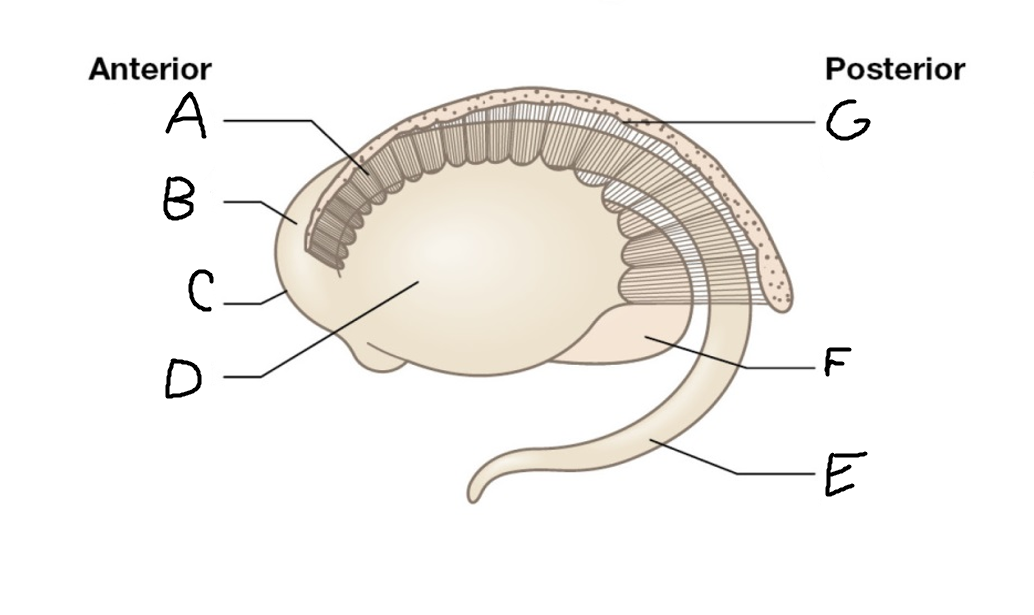
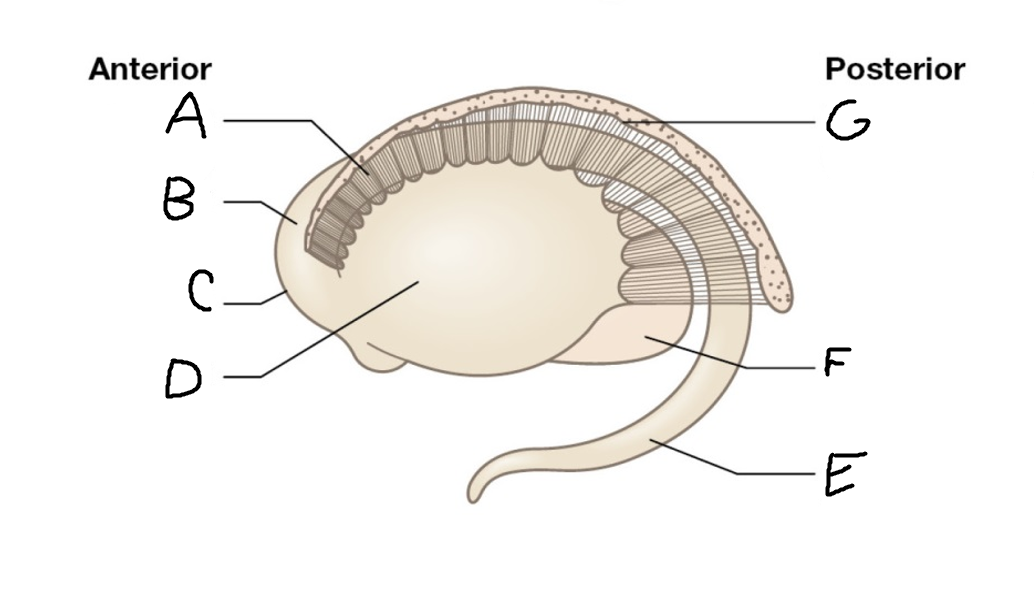
E
caudate nucleus tail
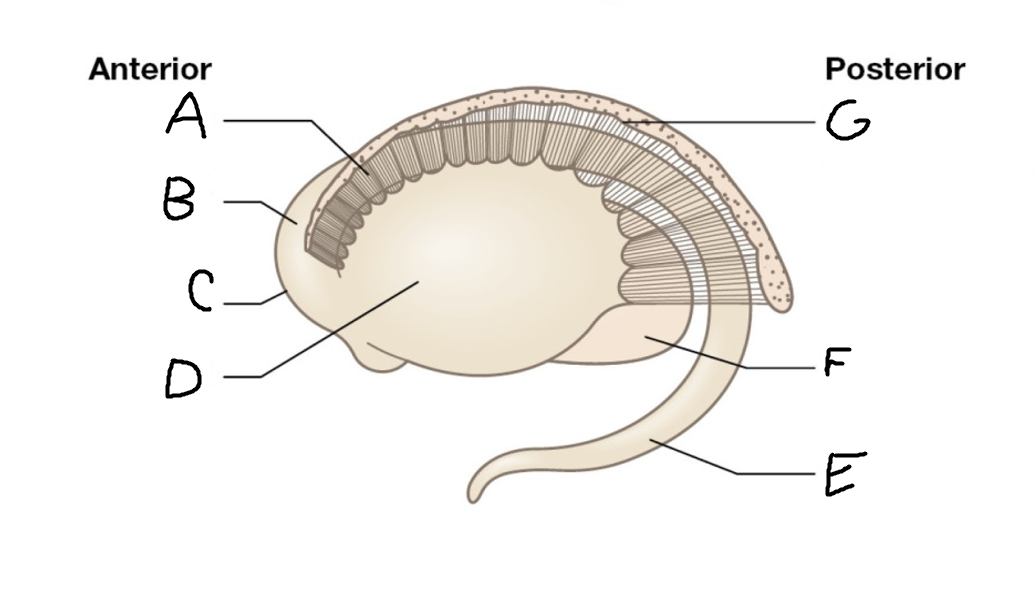
F
thalamus
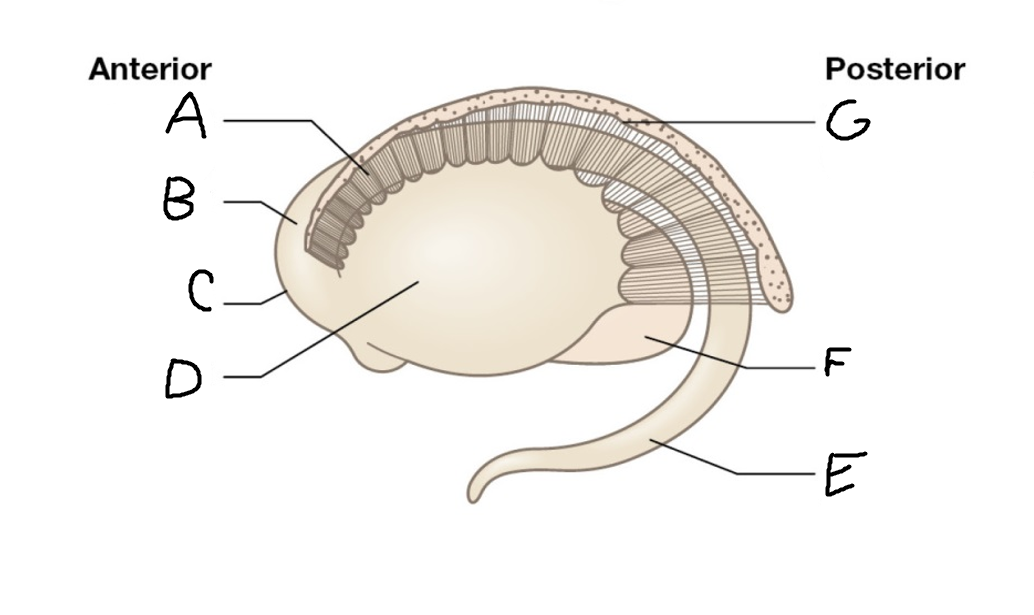
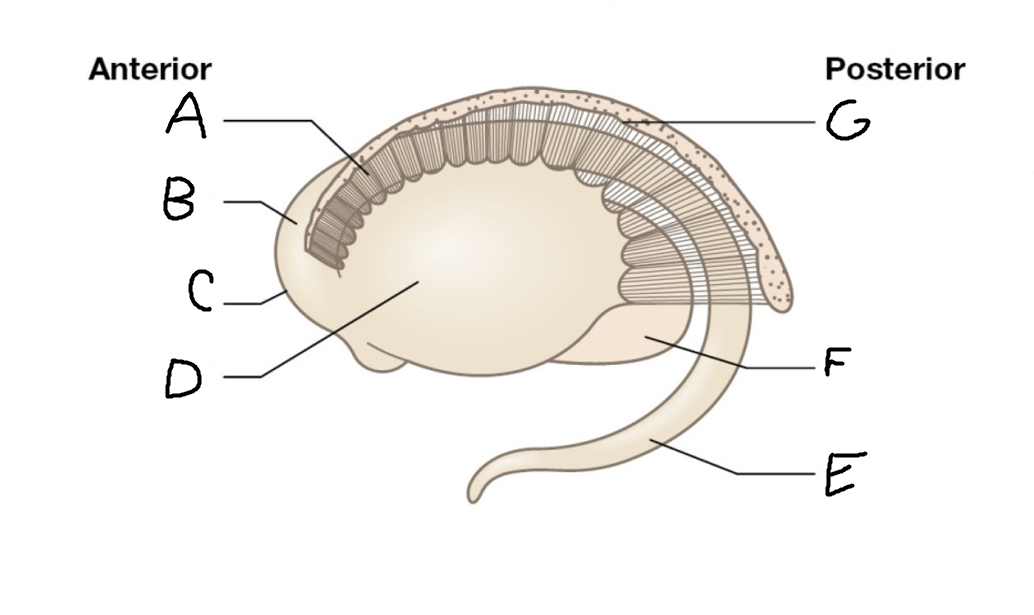
G
internal capsule (posterior limb)
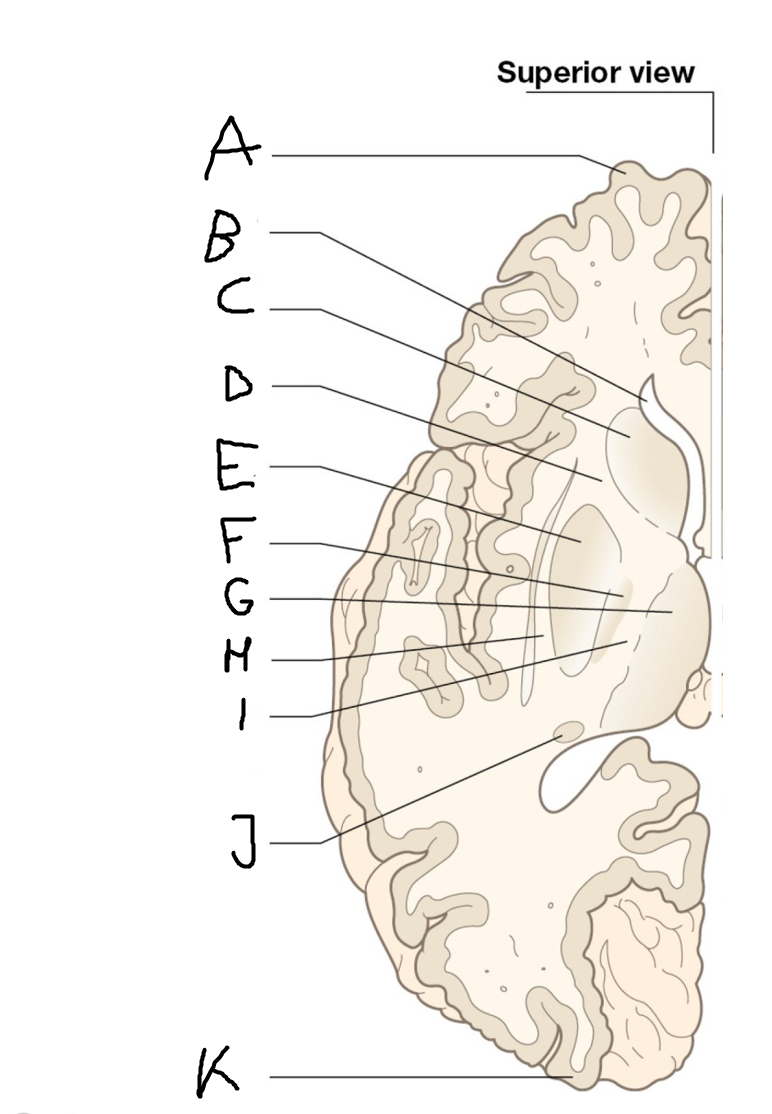
B
anterior horn of lateral ventricle
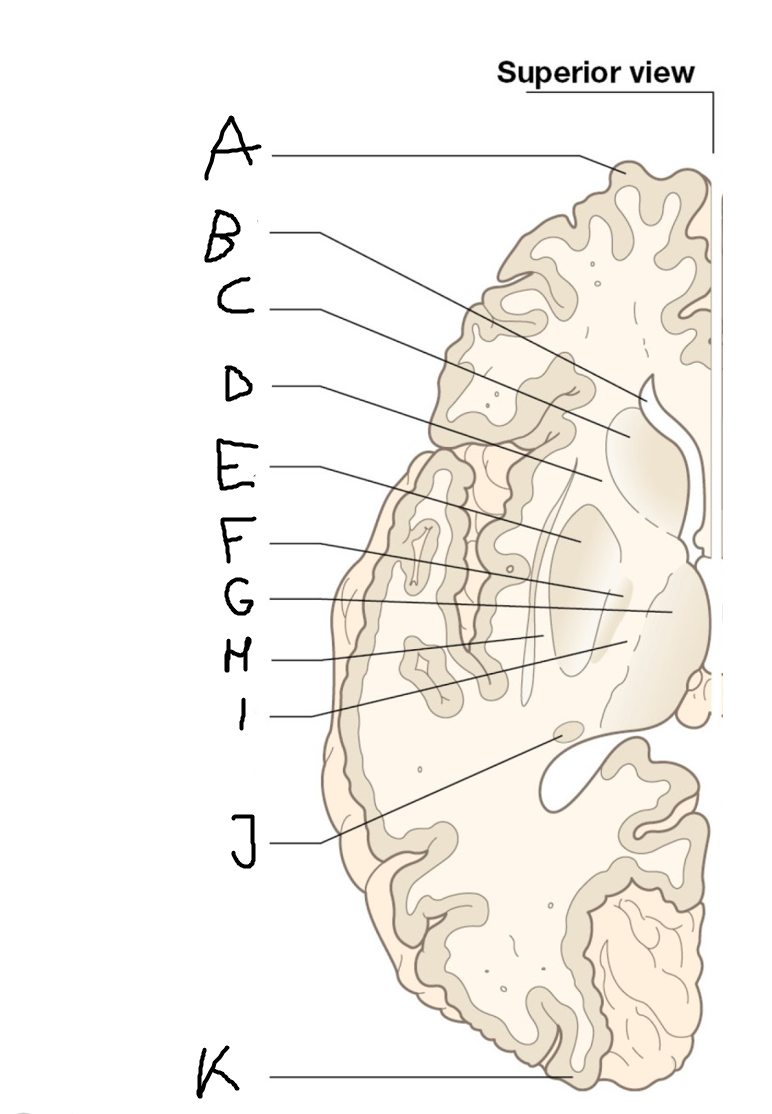
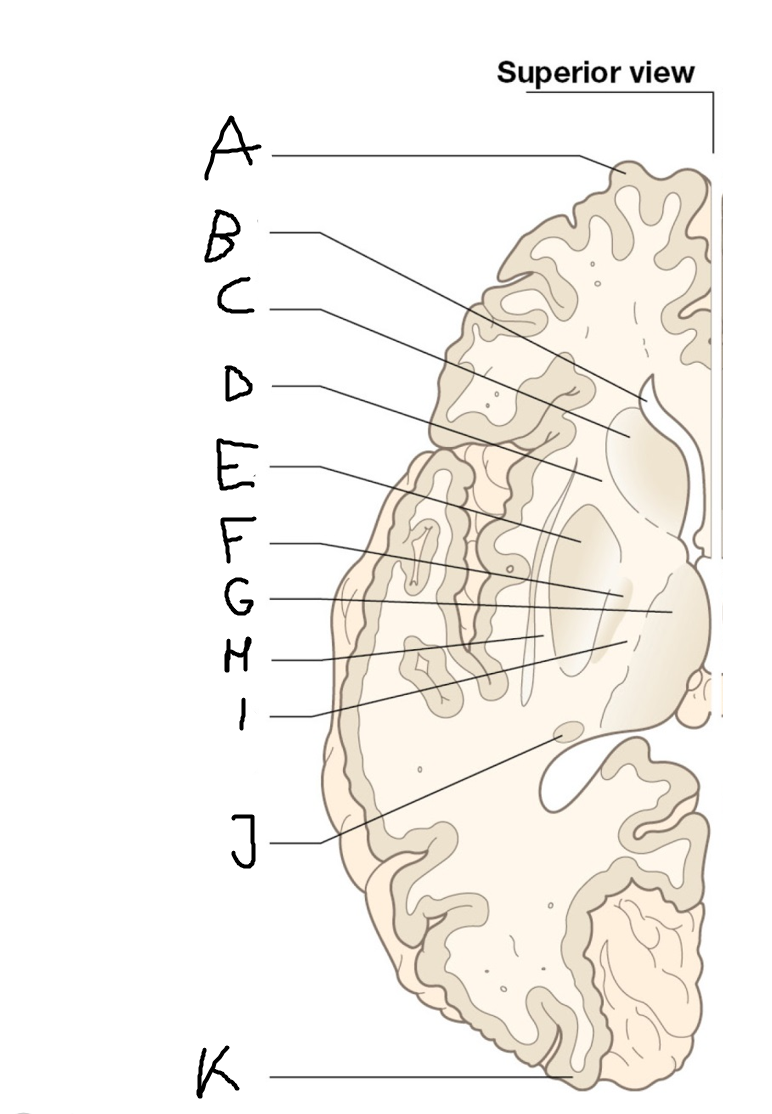
C
head of caudate nucleus
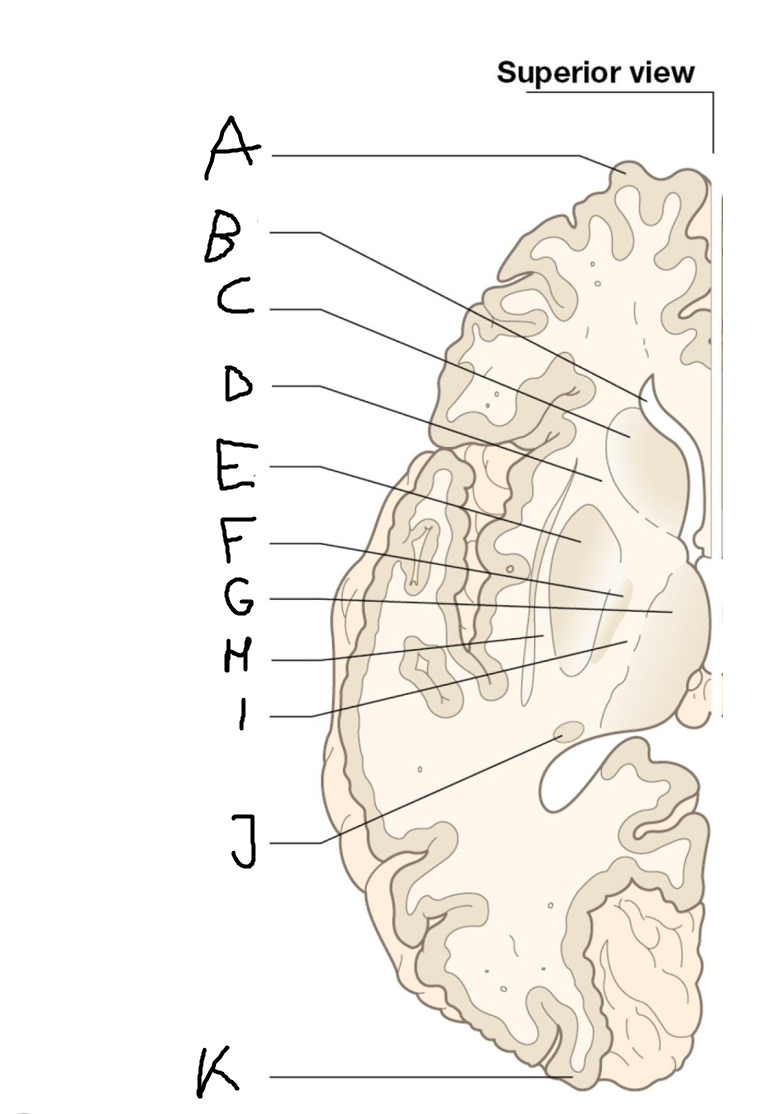
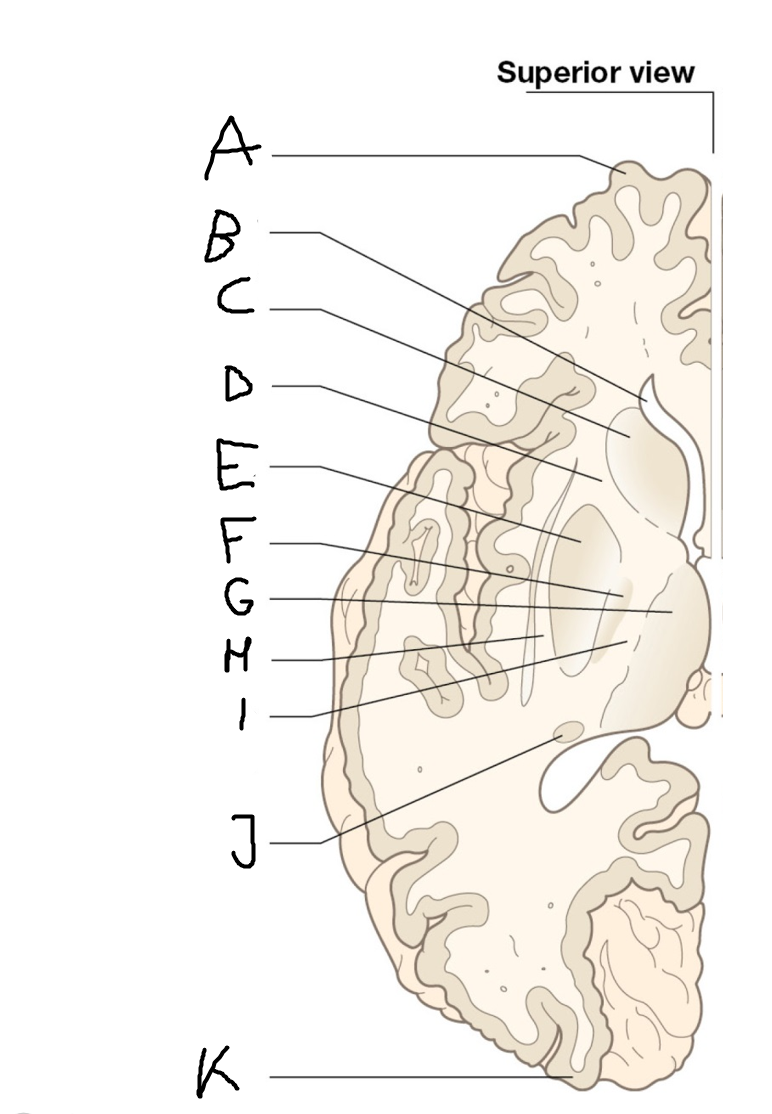
D
internal capsule (anterior limb)
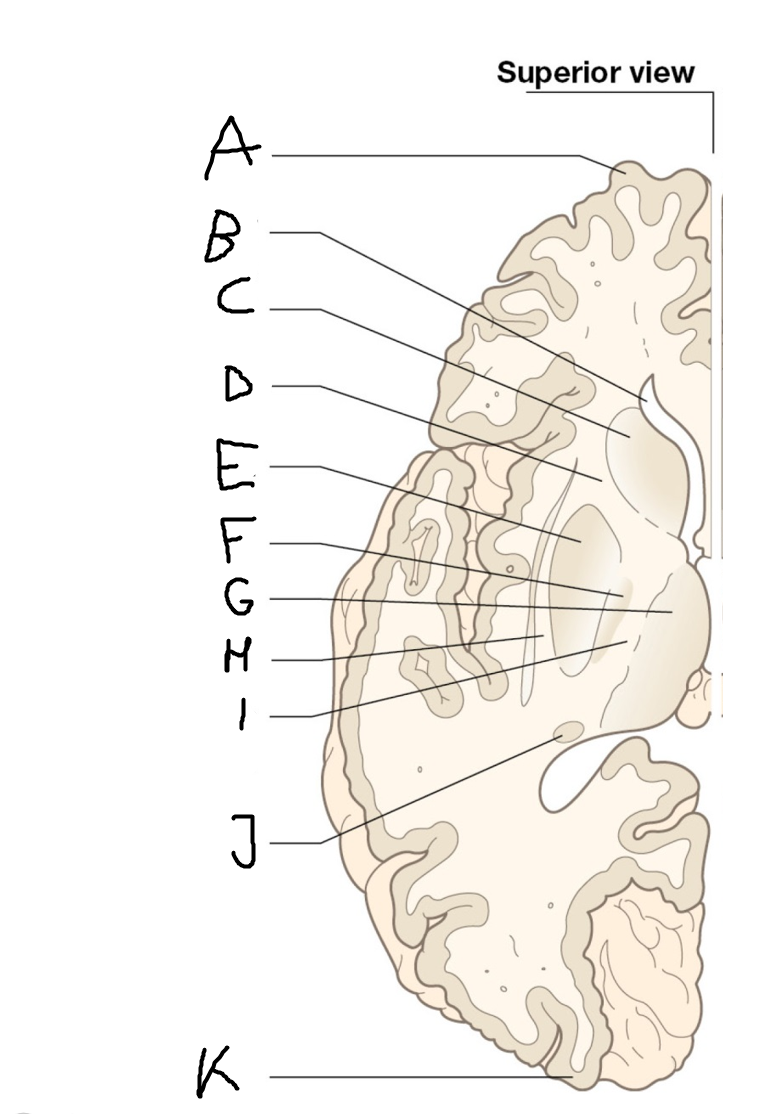
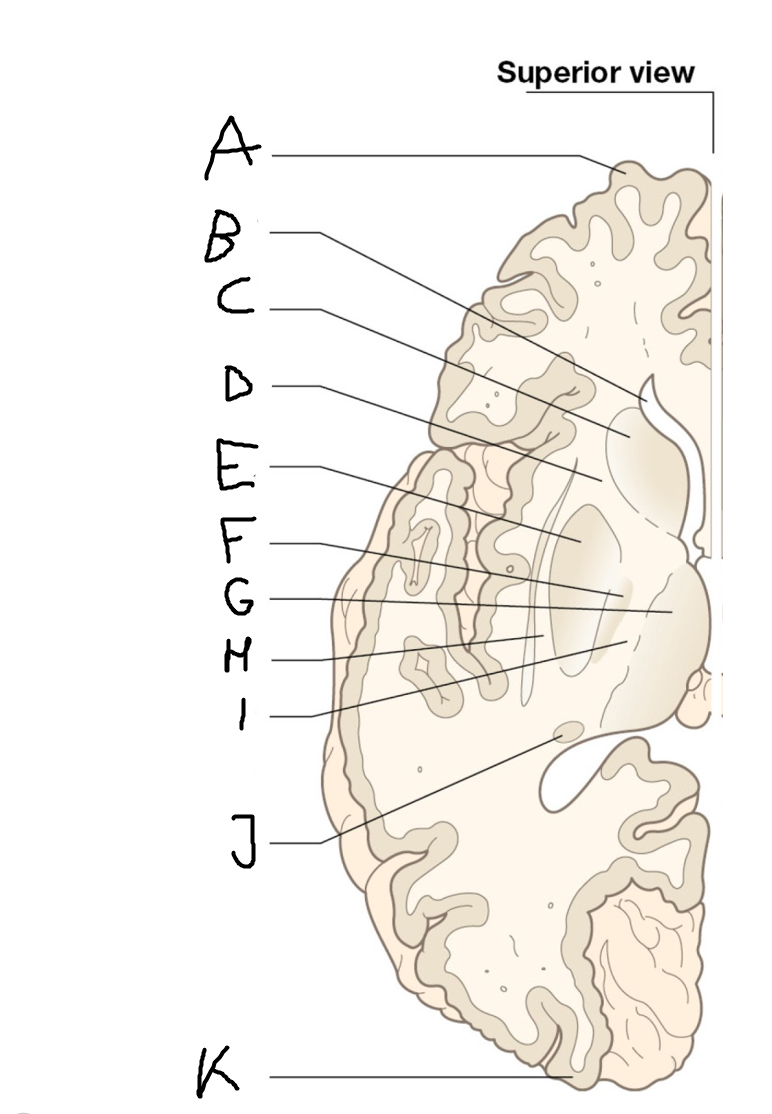
E
putamen
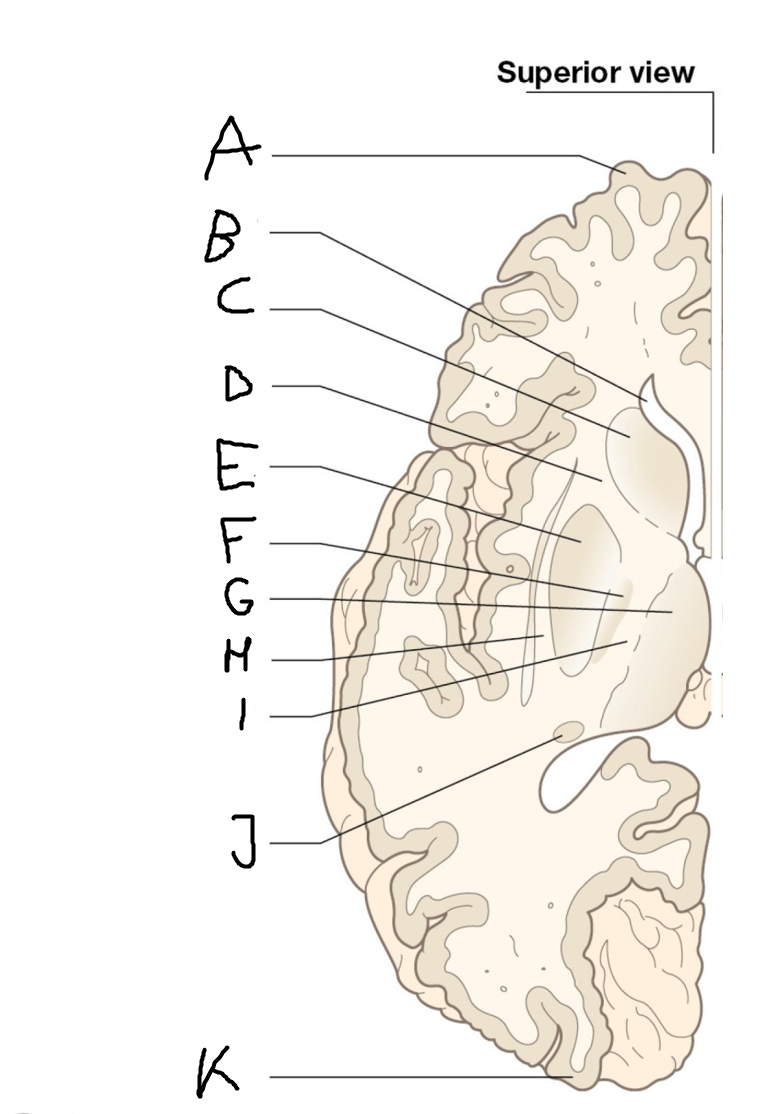
F
globus pallidus
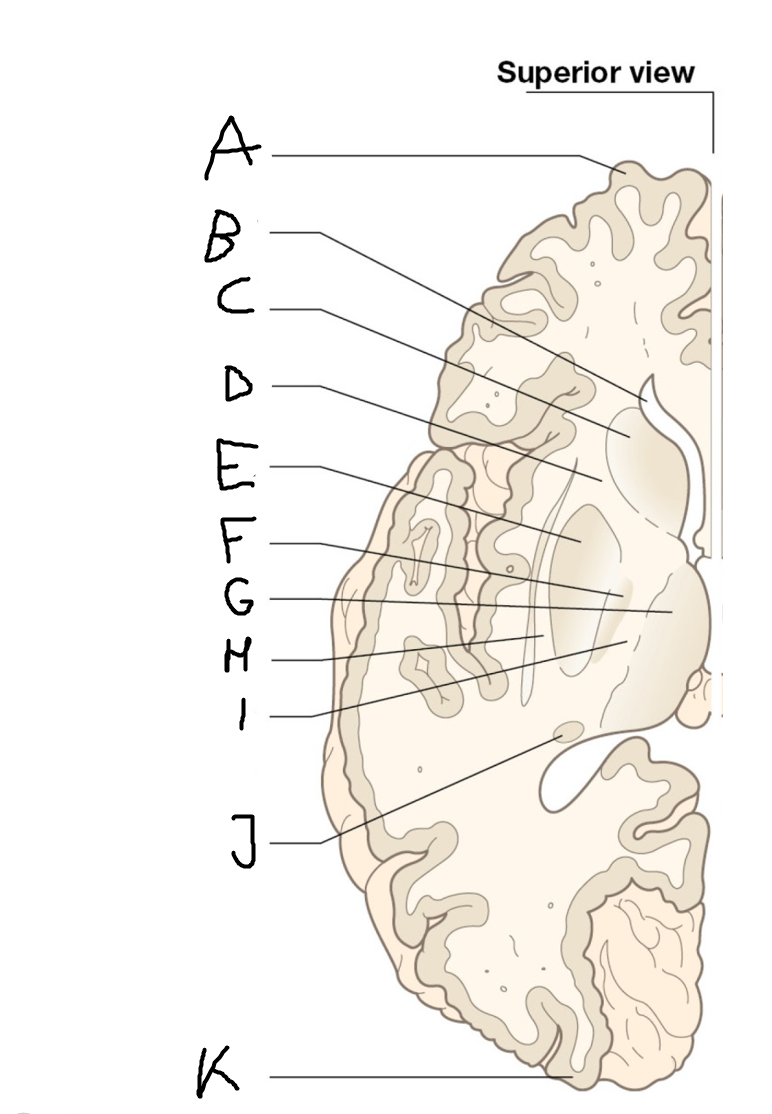
G
Thalamus
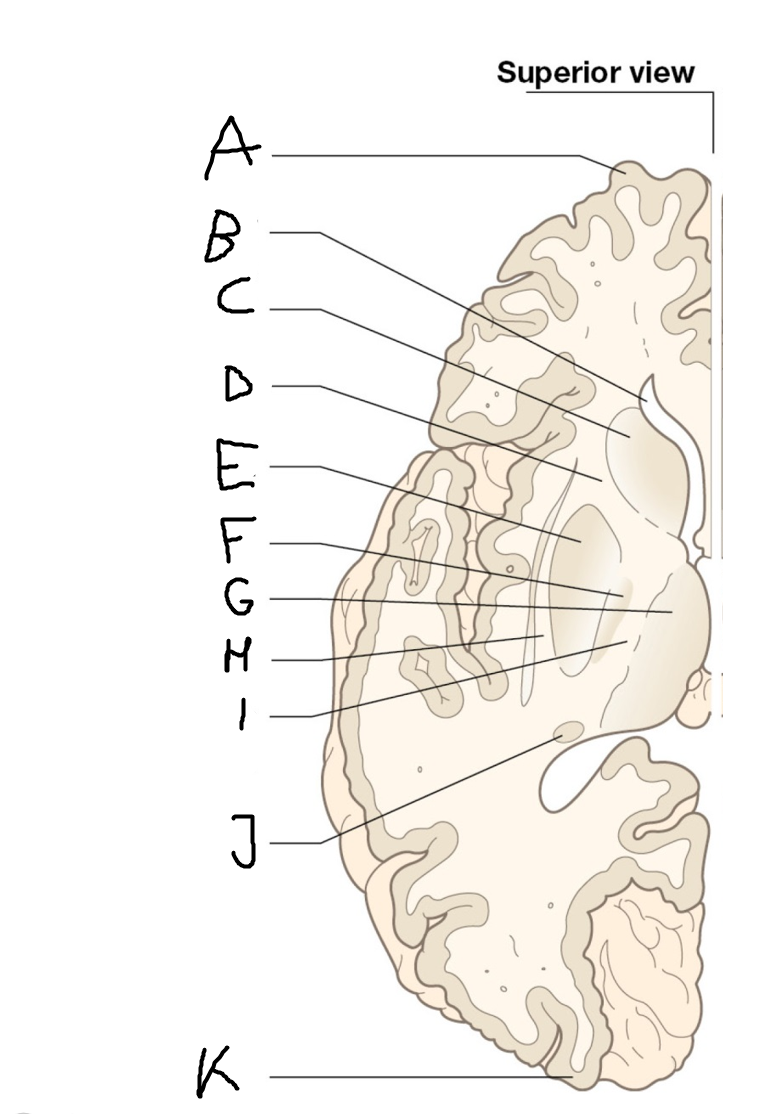
H
External capsule
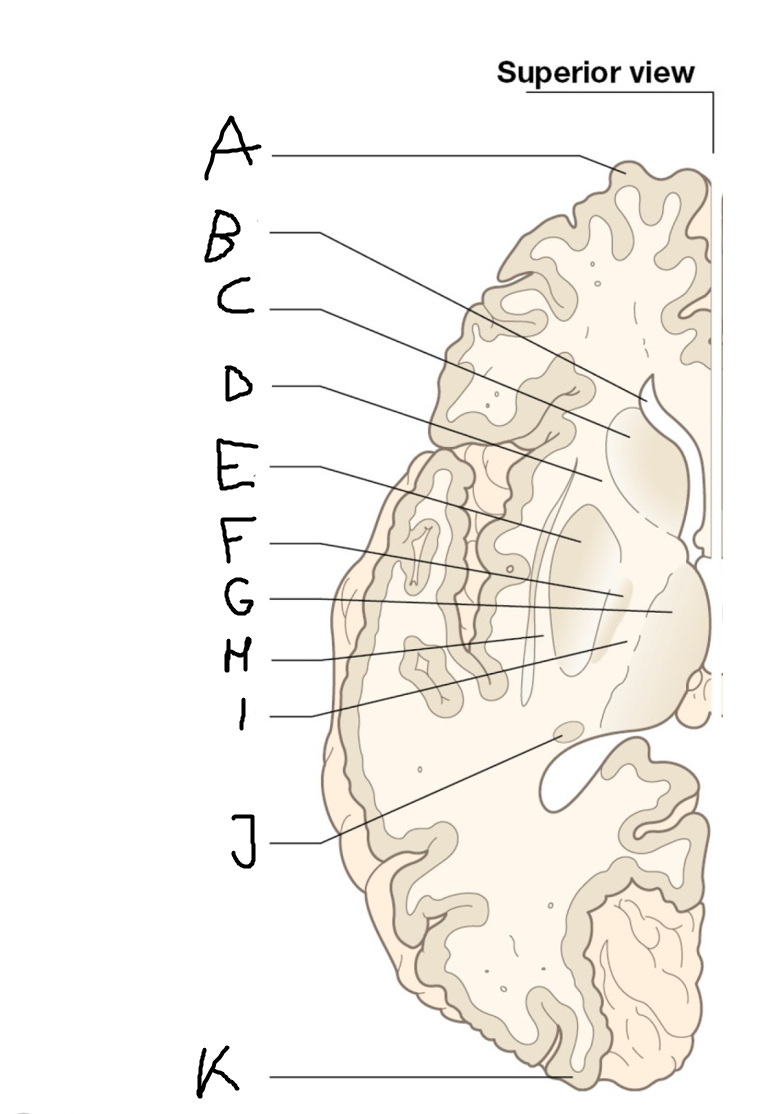
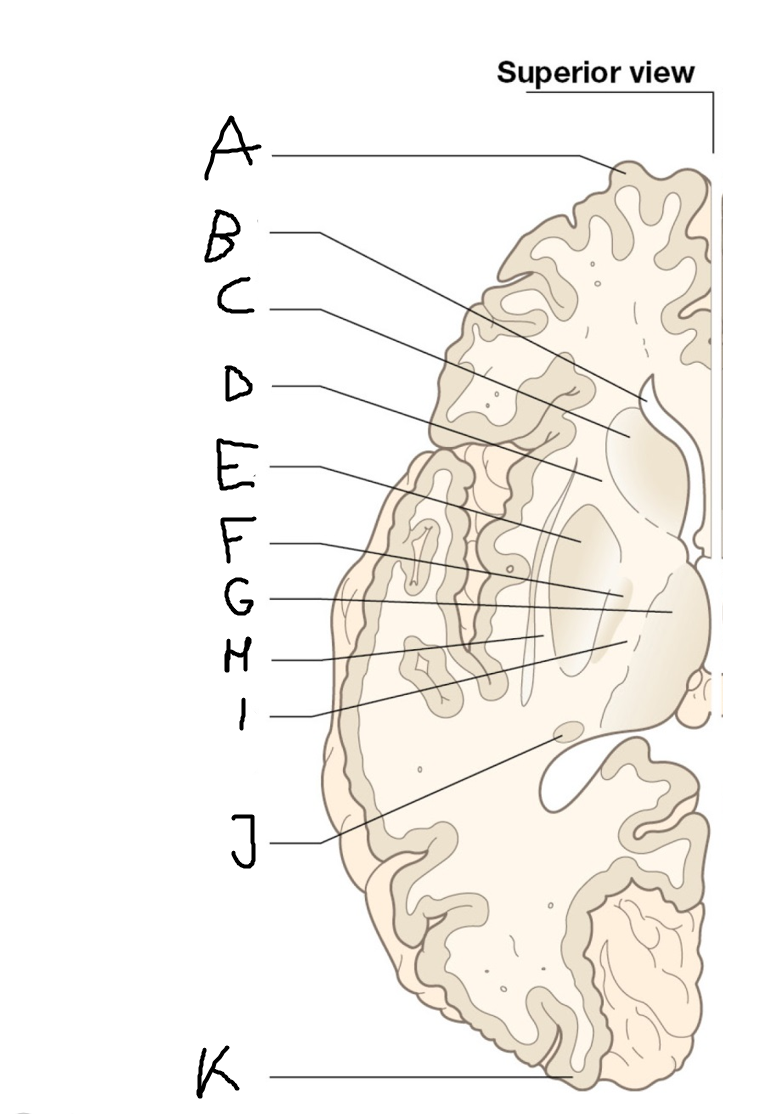
I
internal capsule (posterior limb)
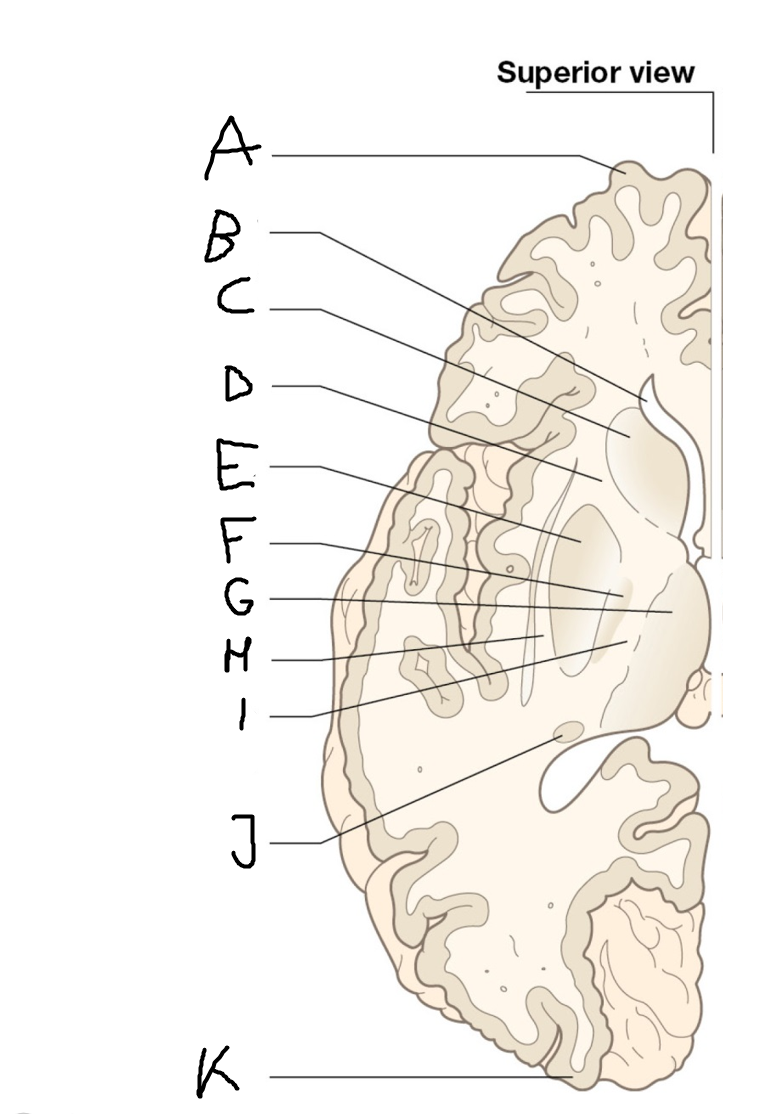
J
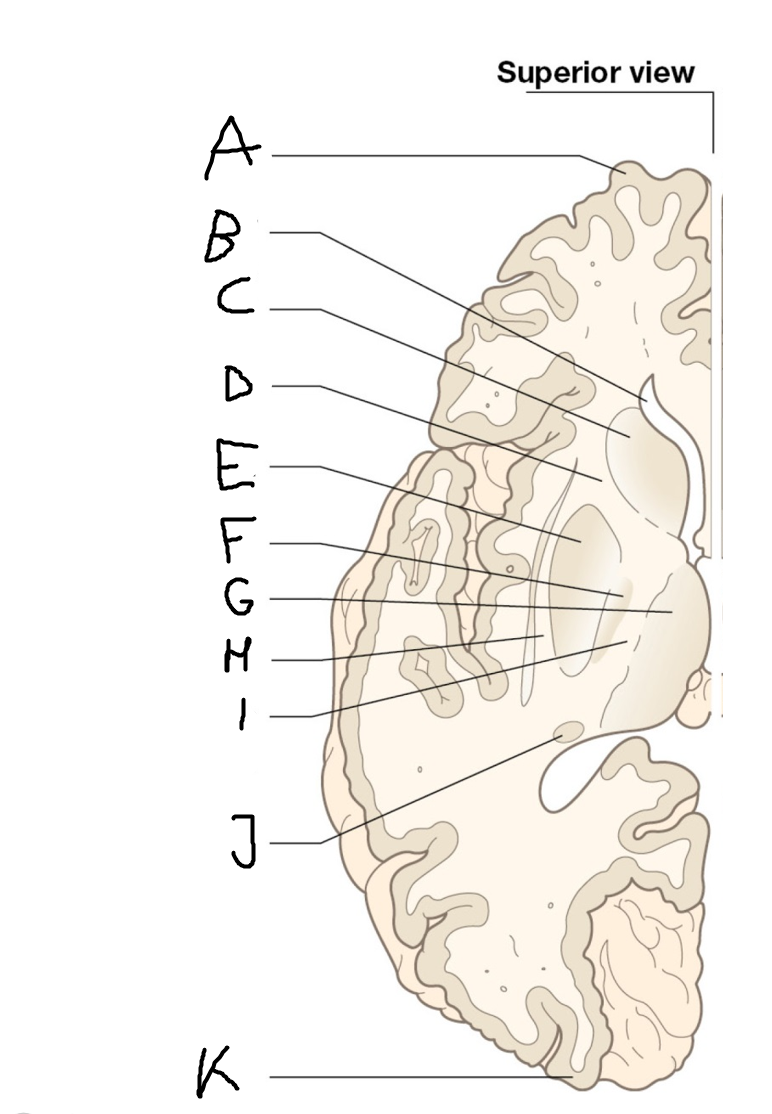
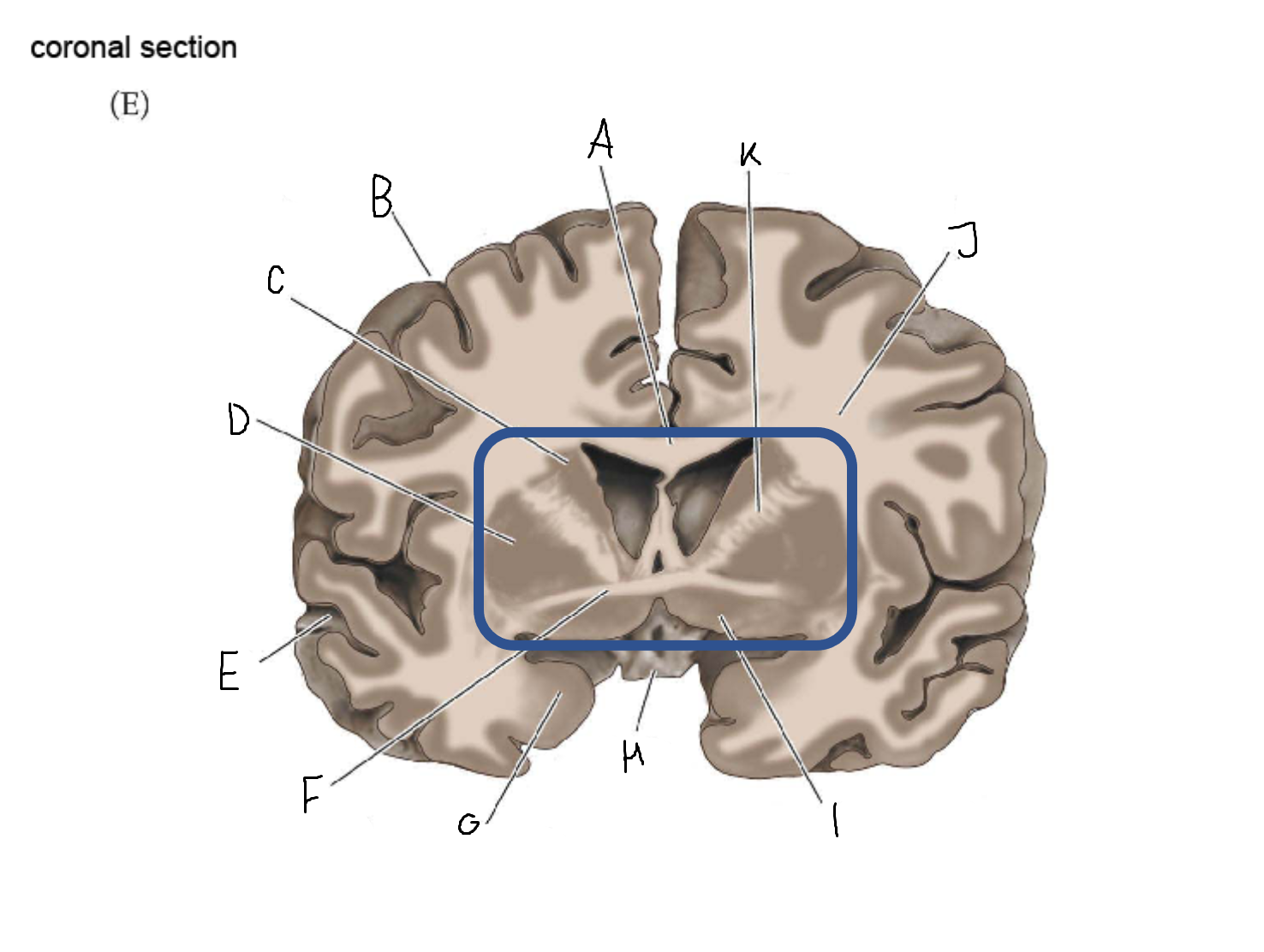
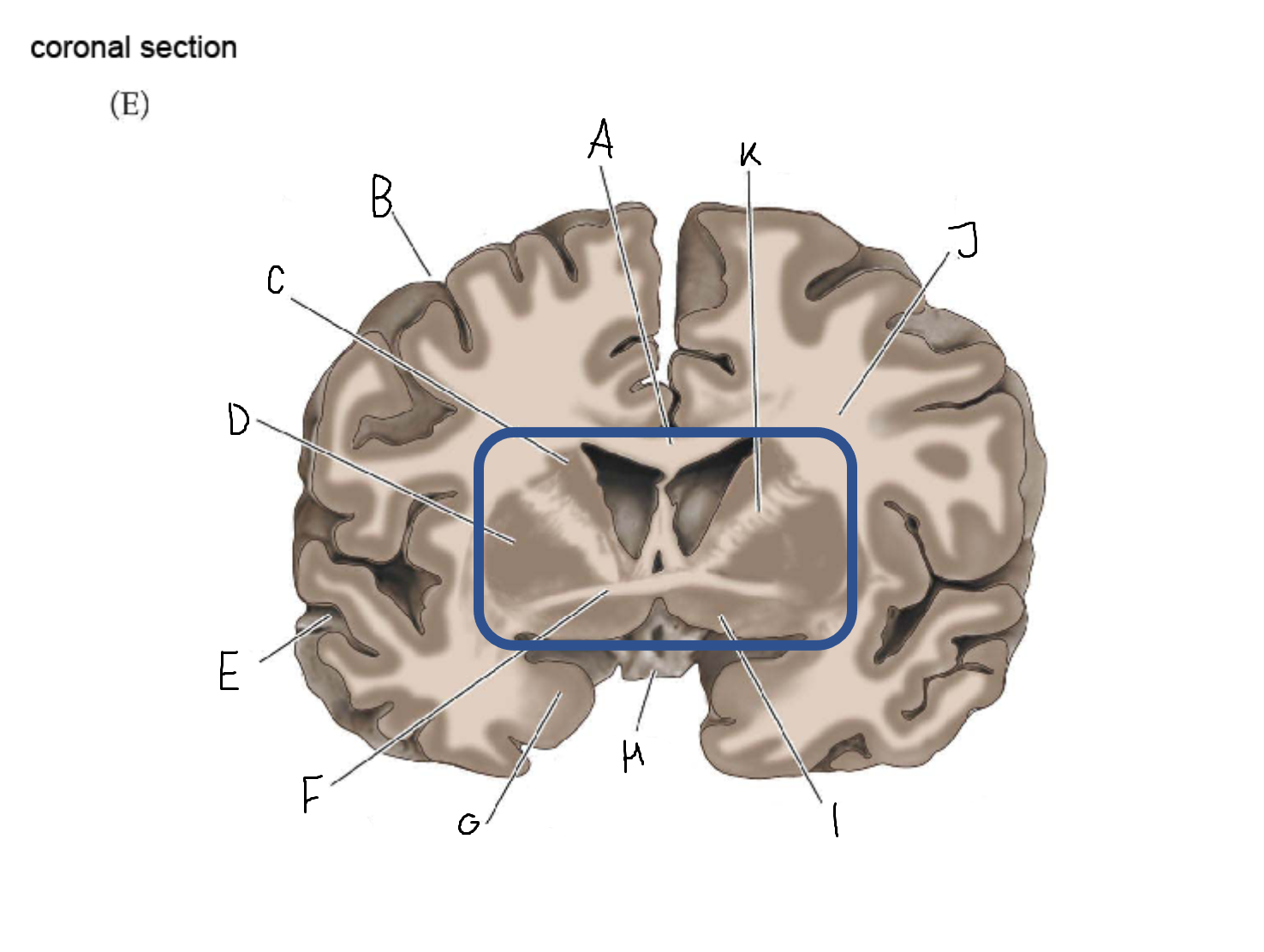
tail of caudate nucleus
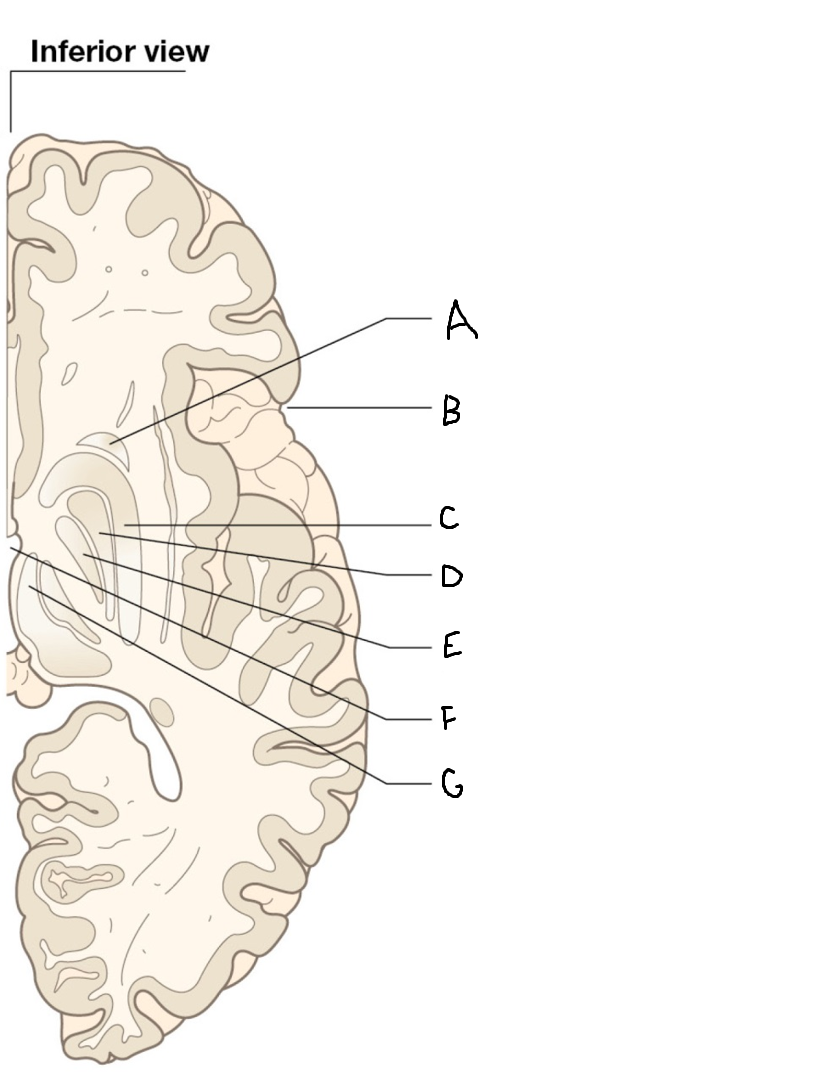
A
head of caudate nucleus
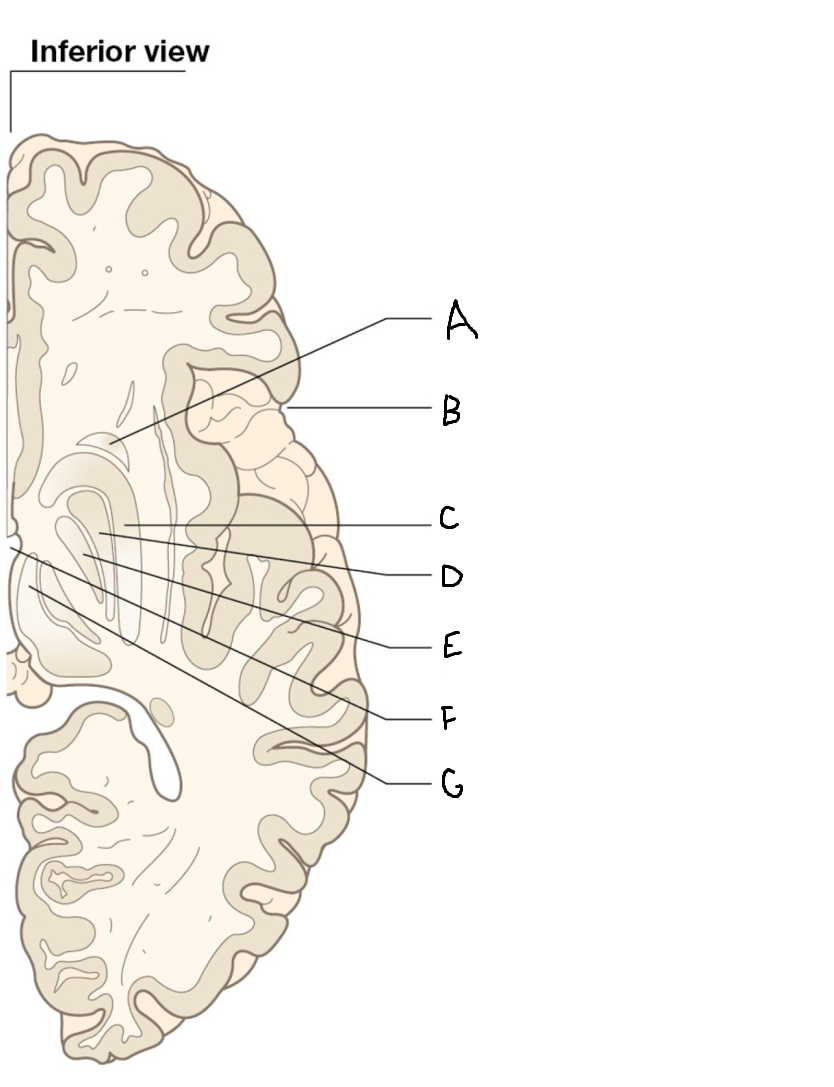
C
putamen
D
external segment of globus pallidus
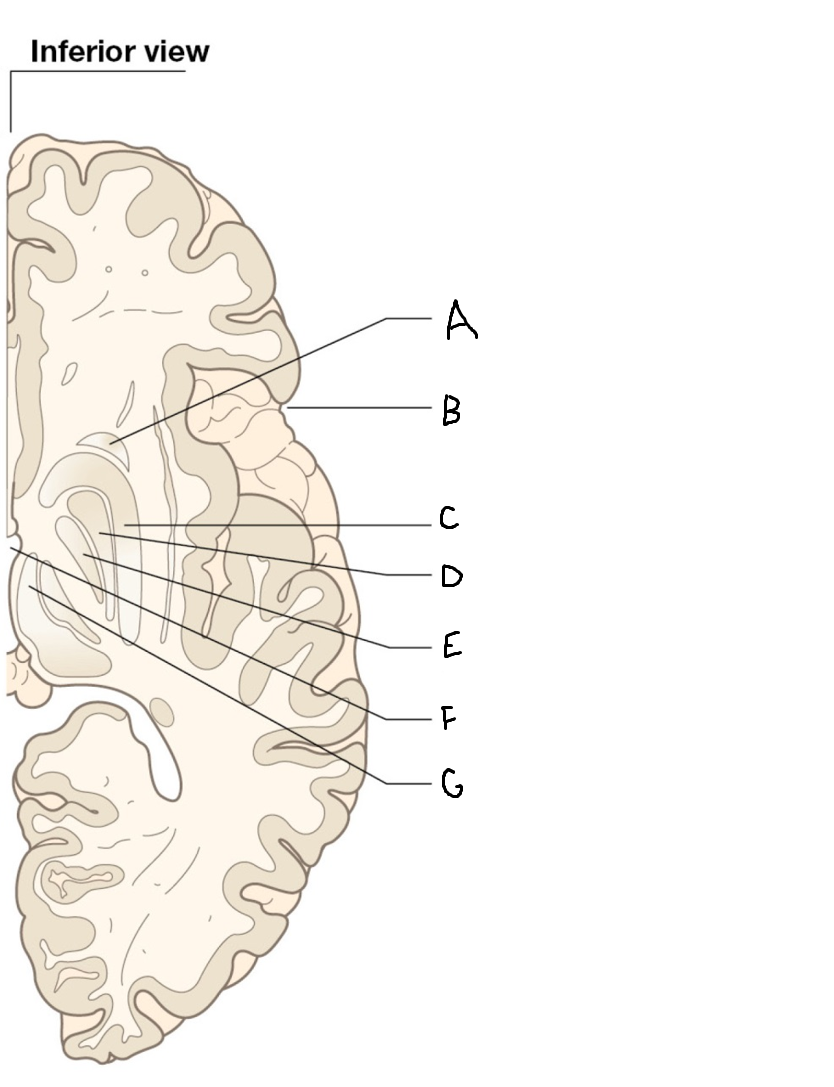
E
internal segment of globus pallidus
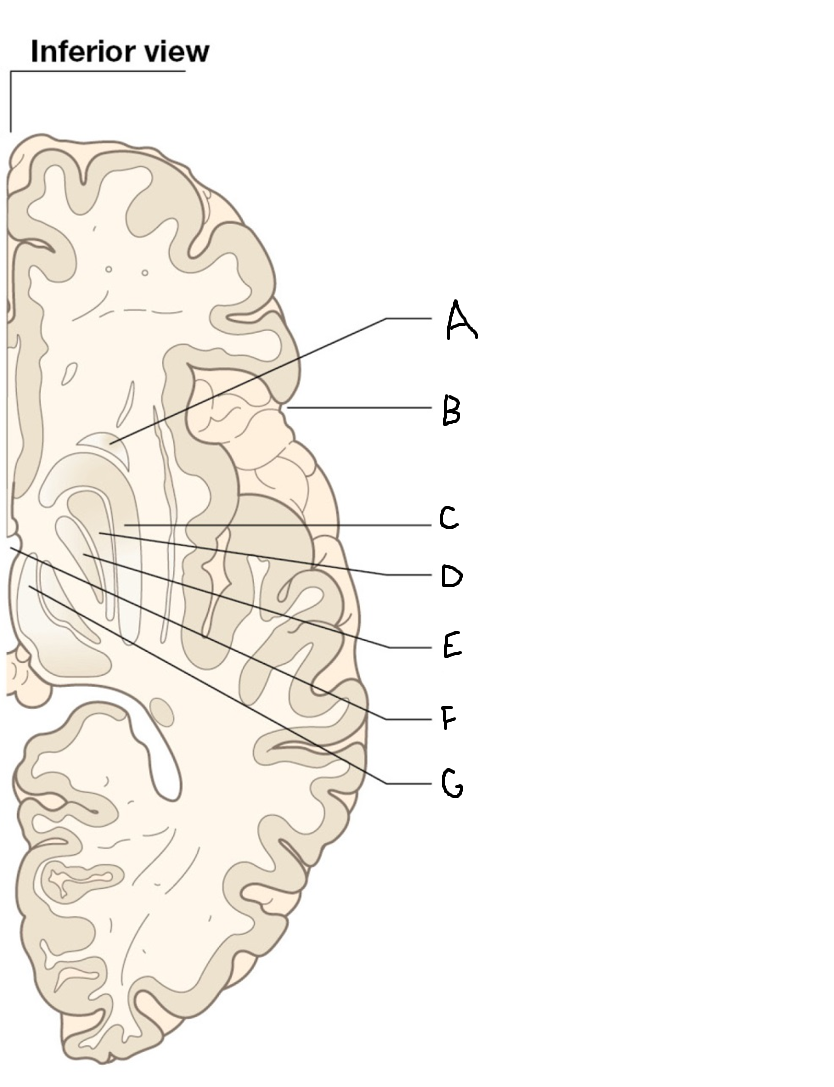
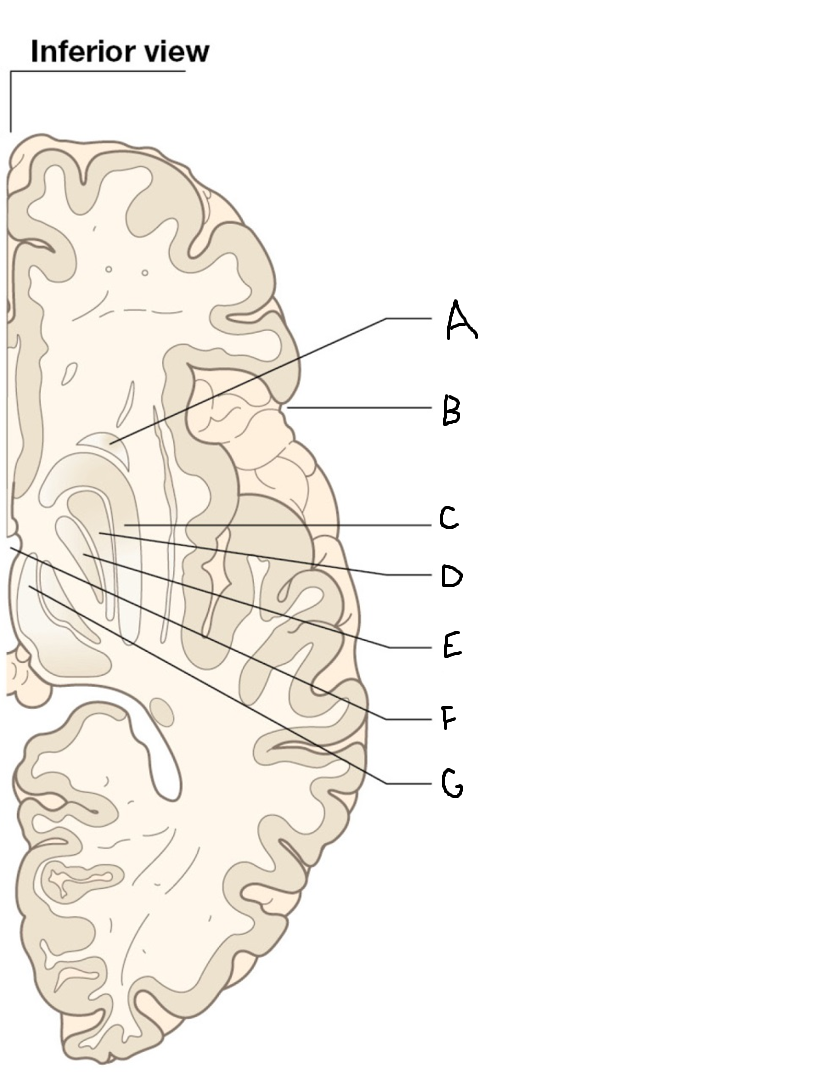
F
third ventricle
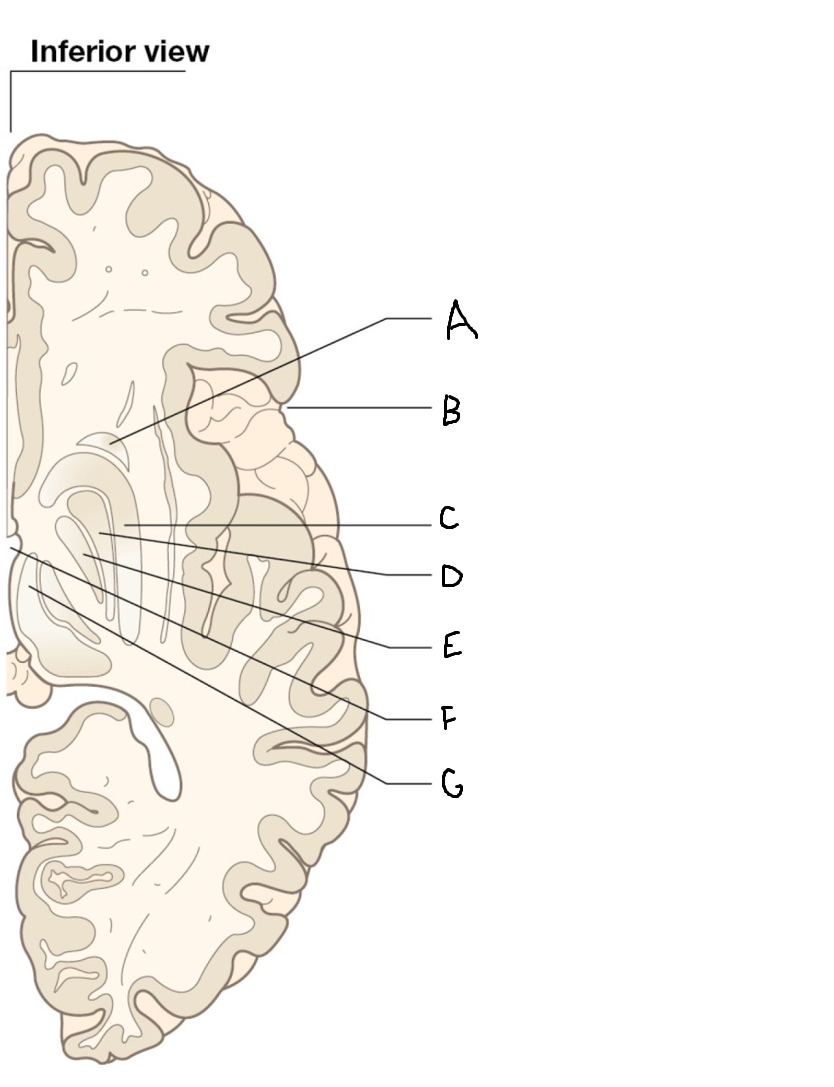
G
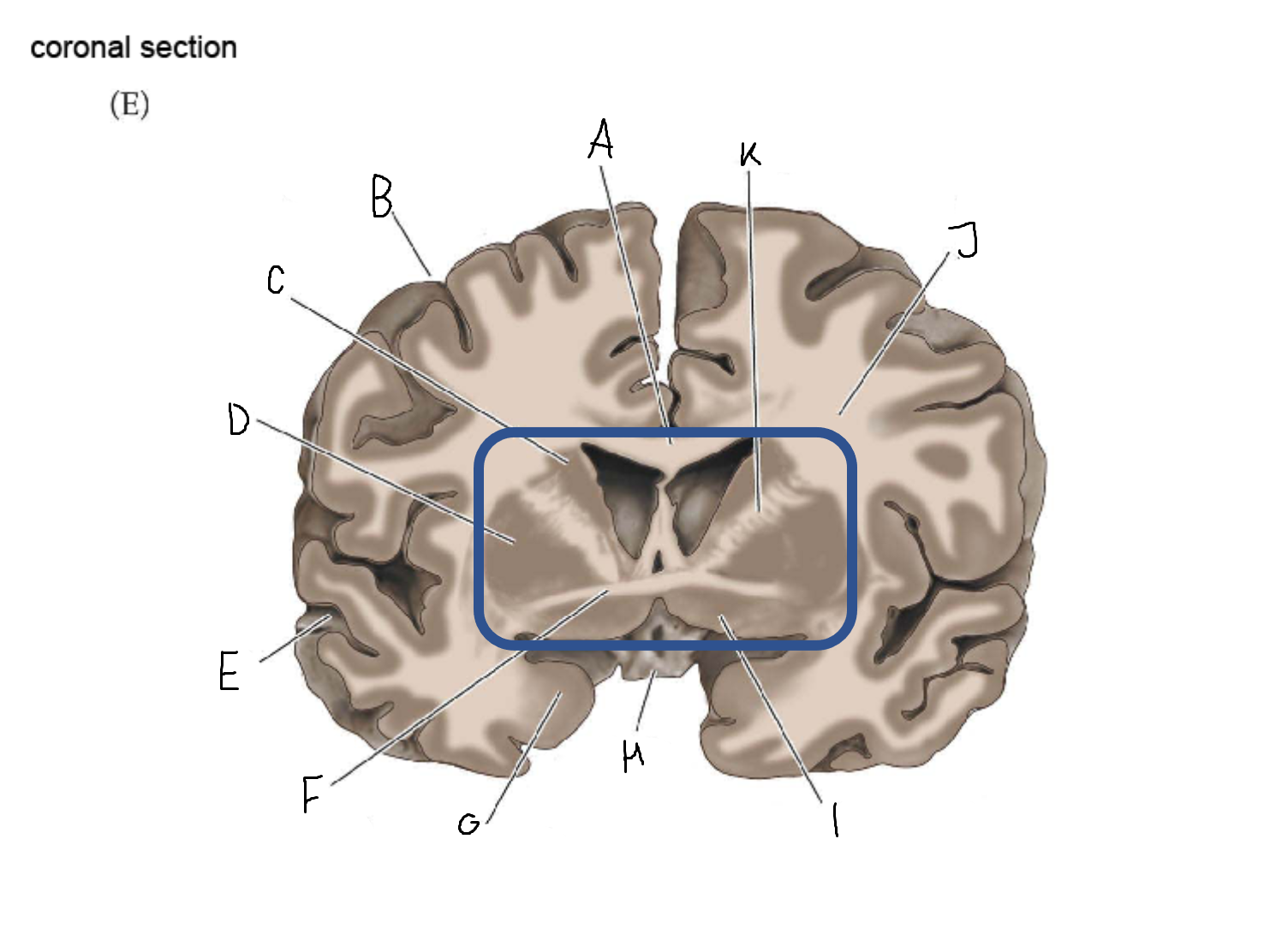
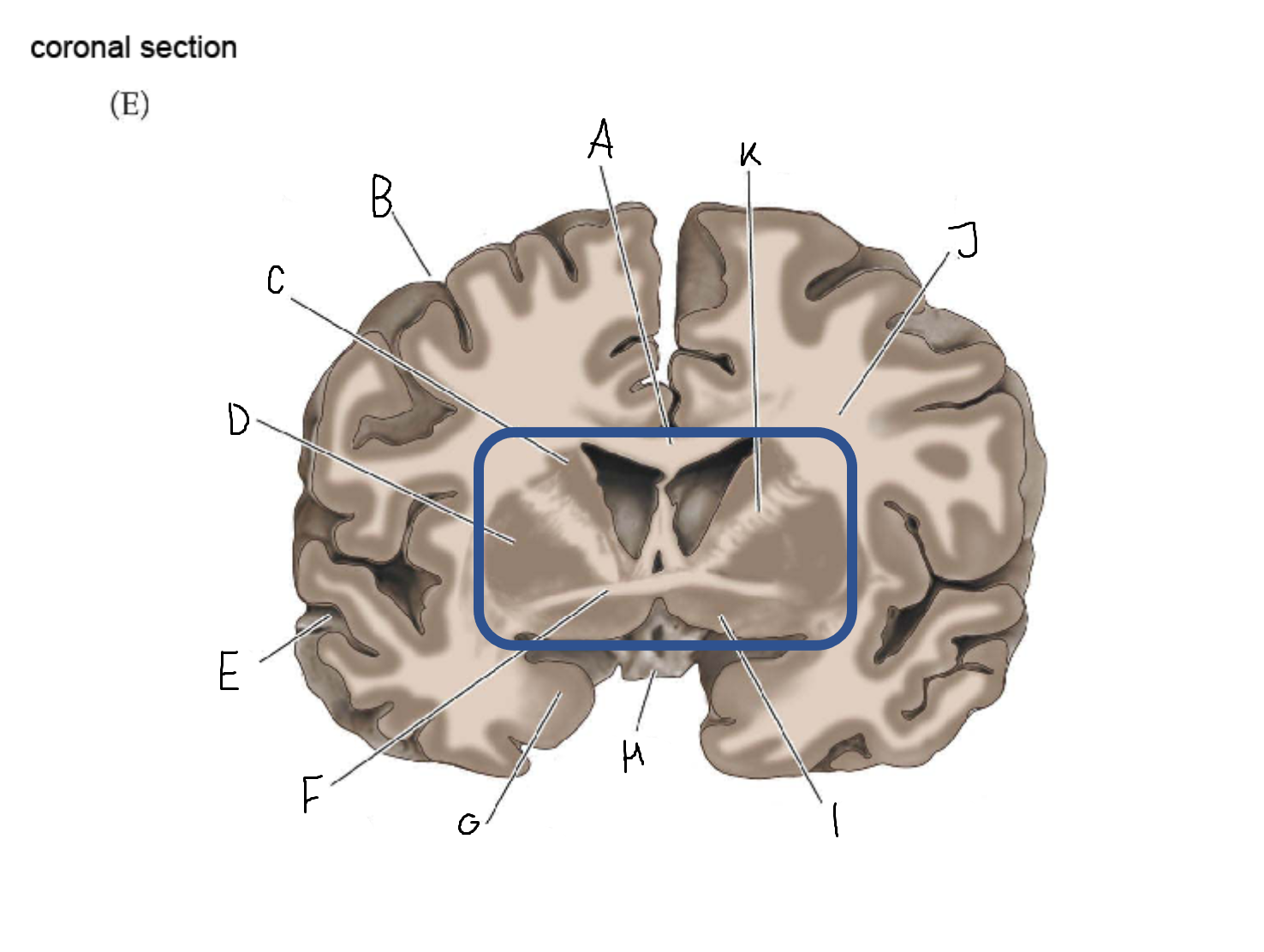
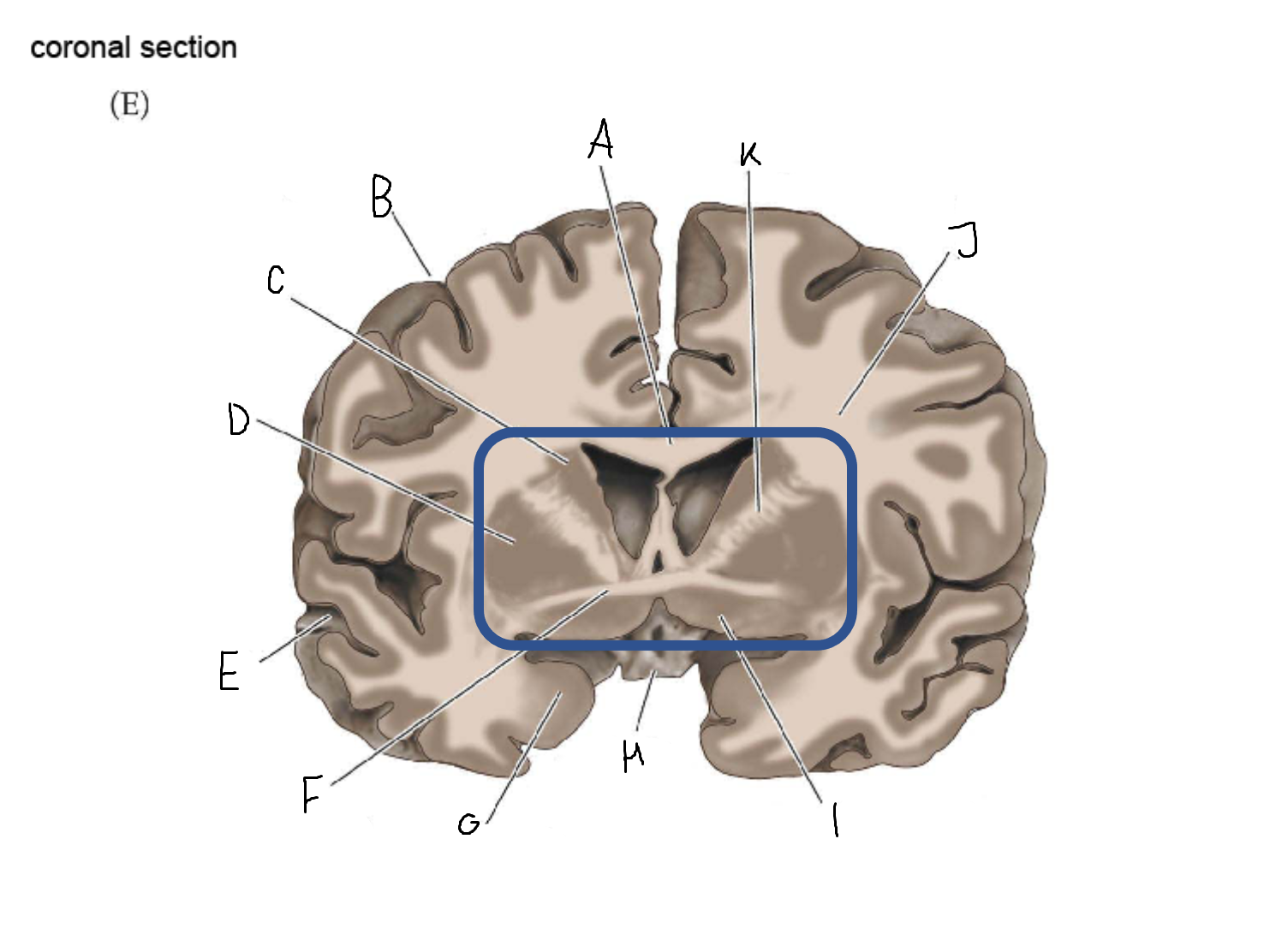
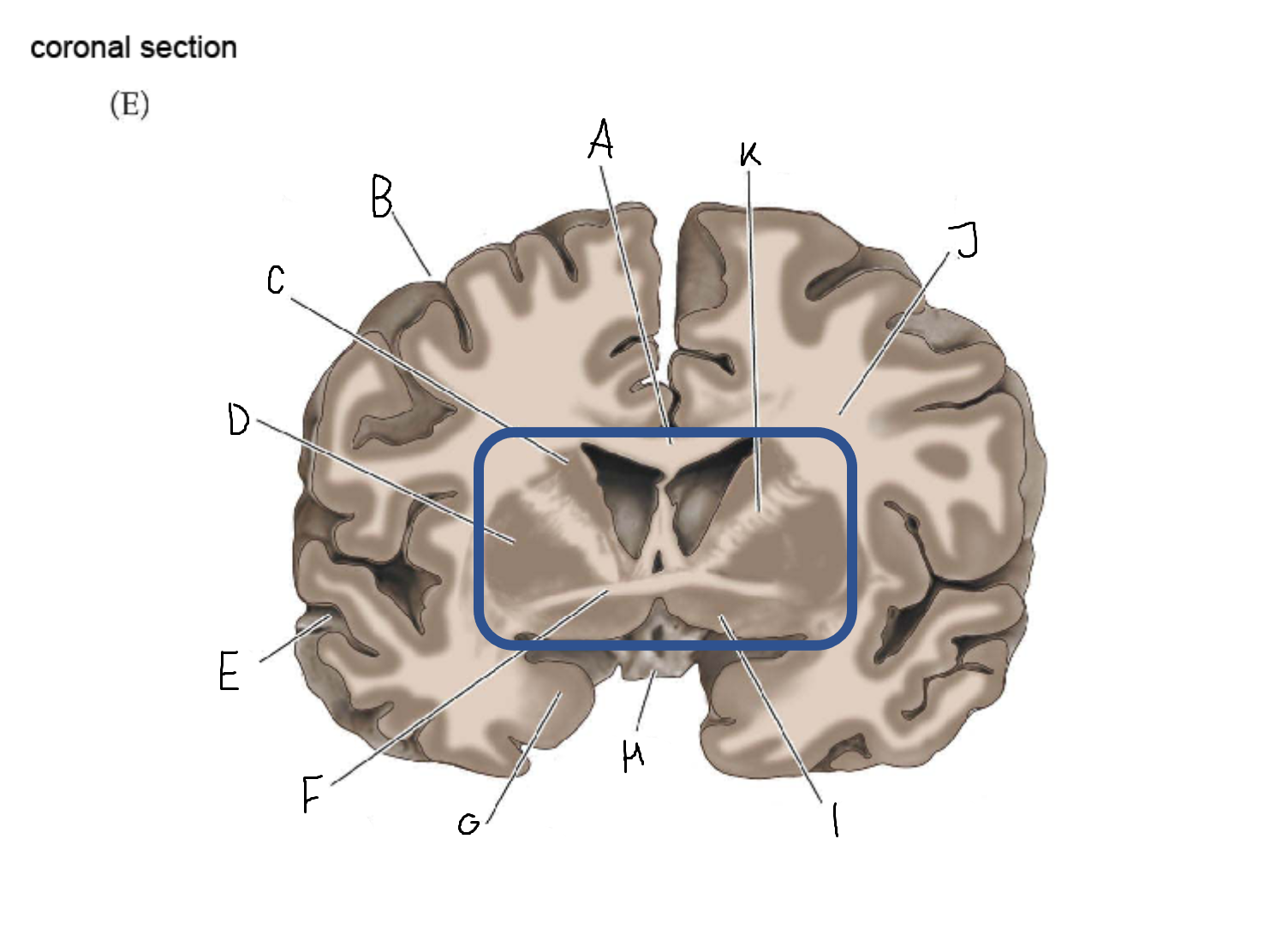
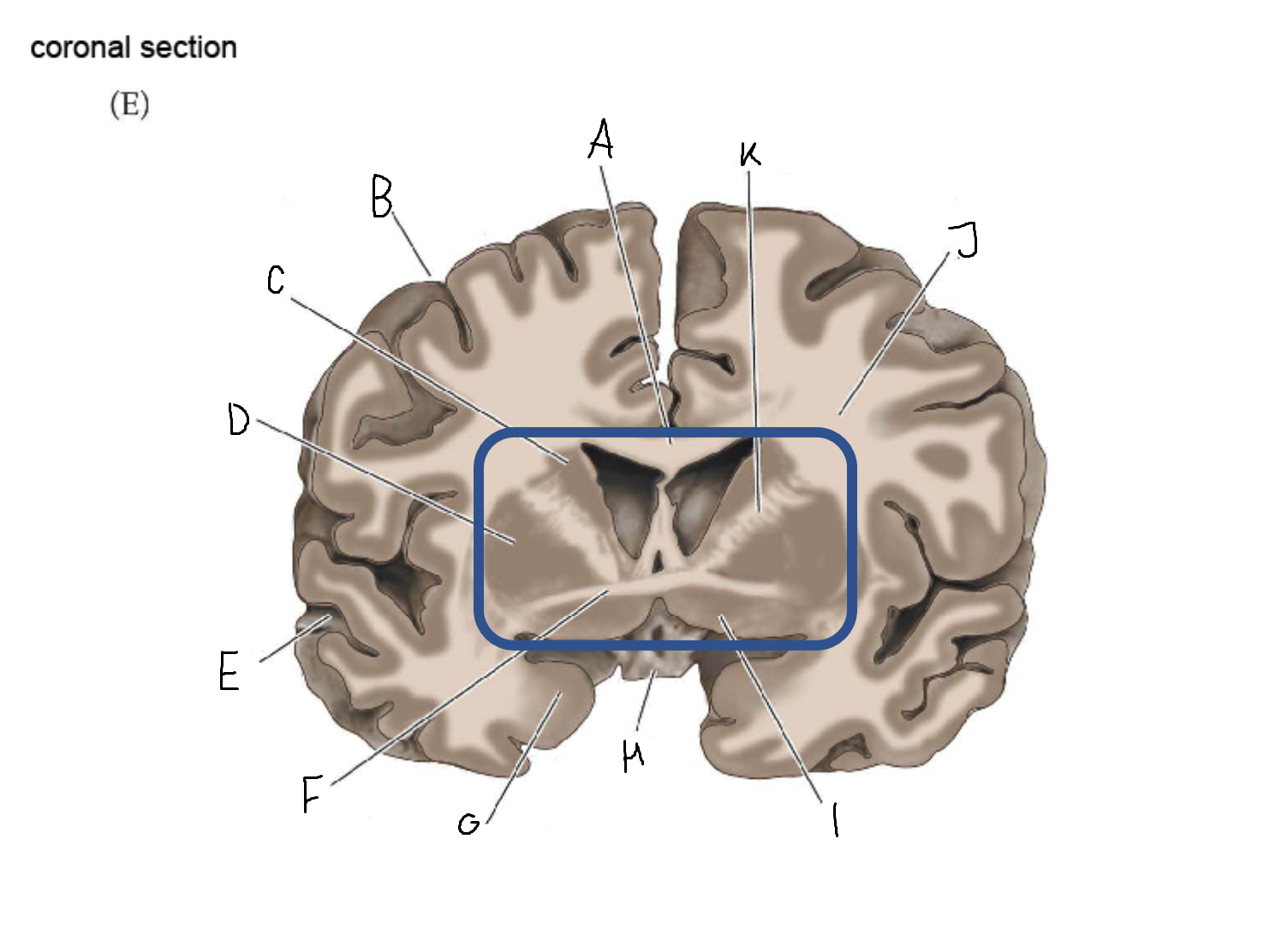
thalamus
A
corpus callosum
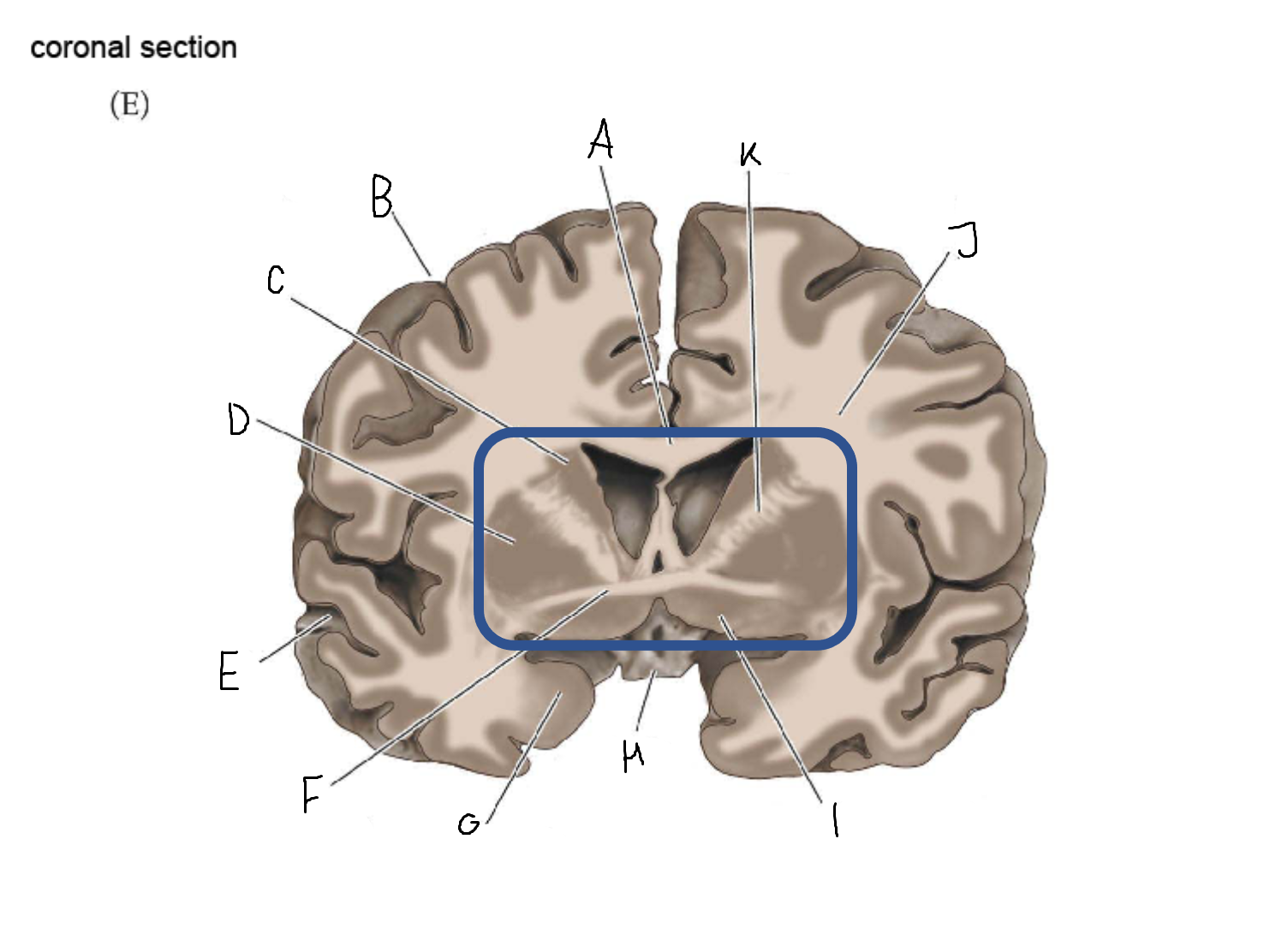
B
cerebral cortex
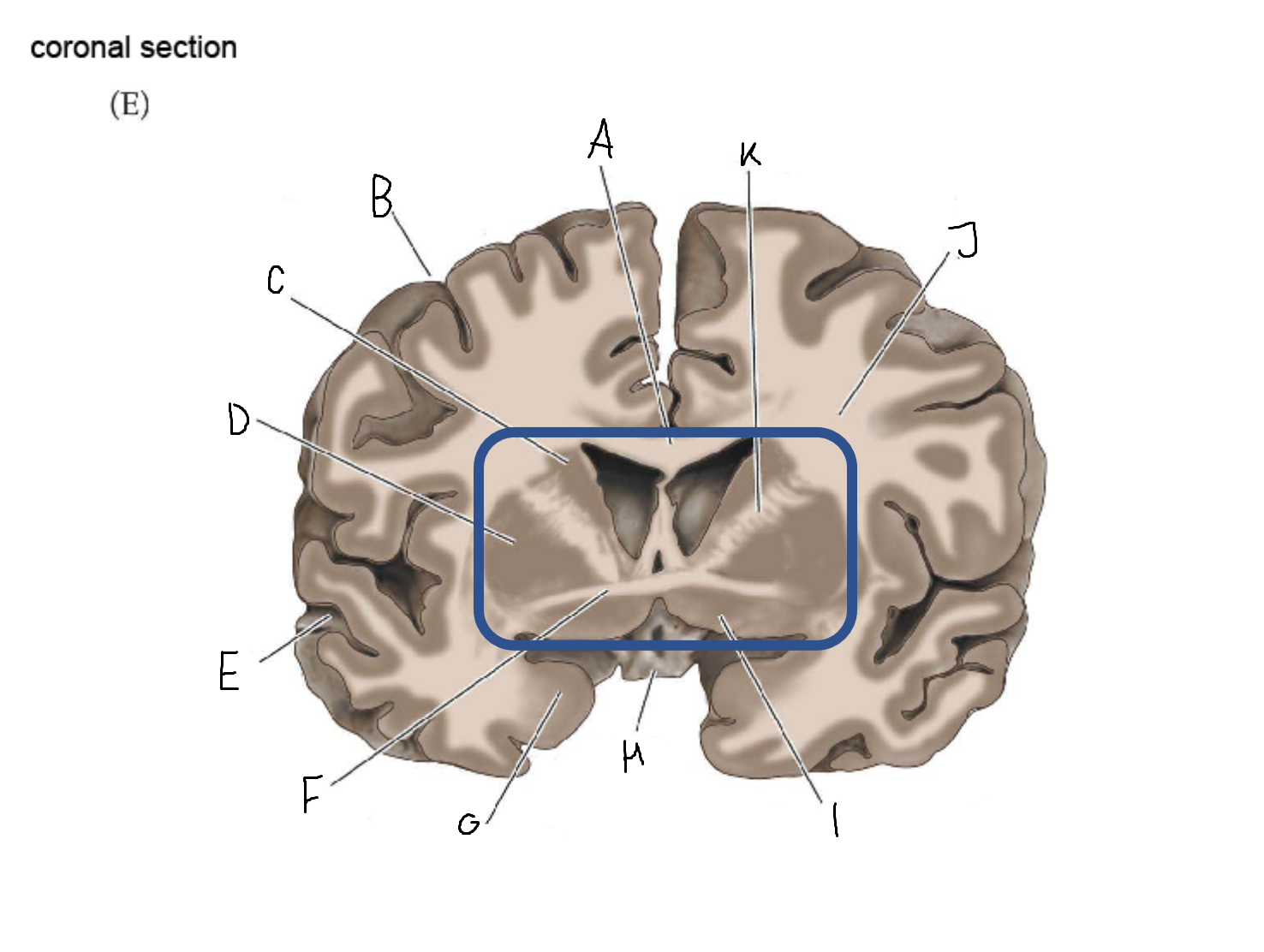
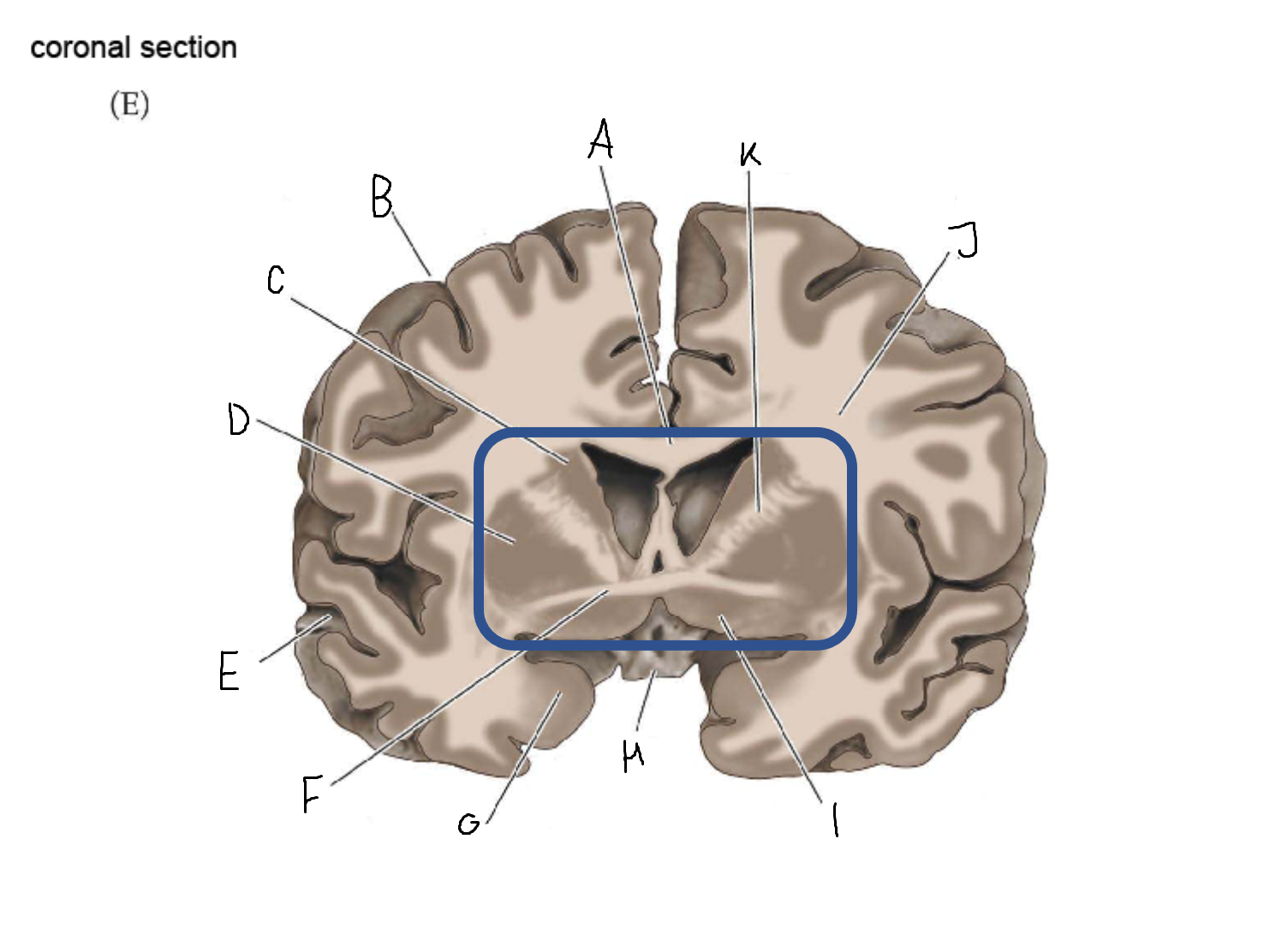
C
caudate
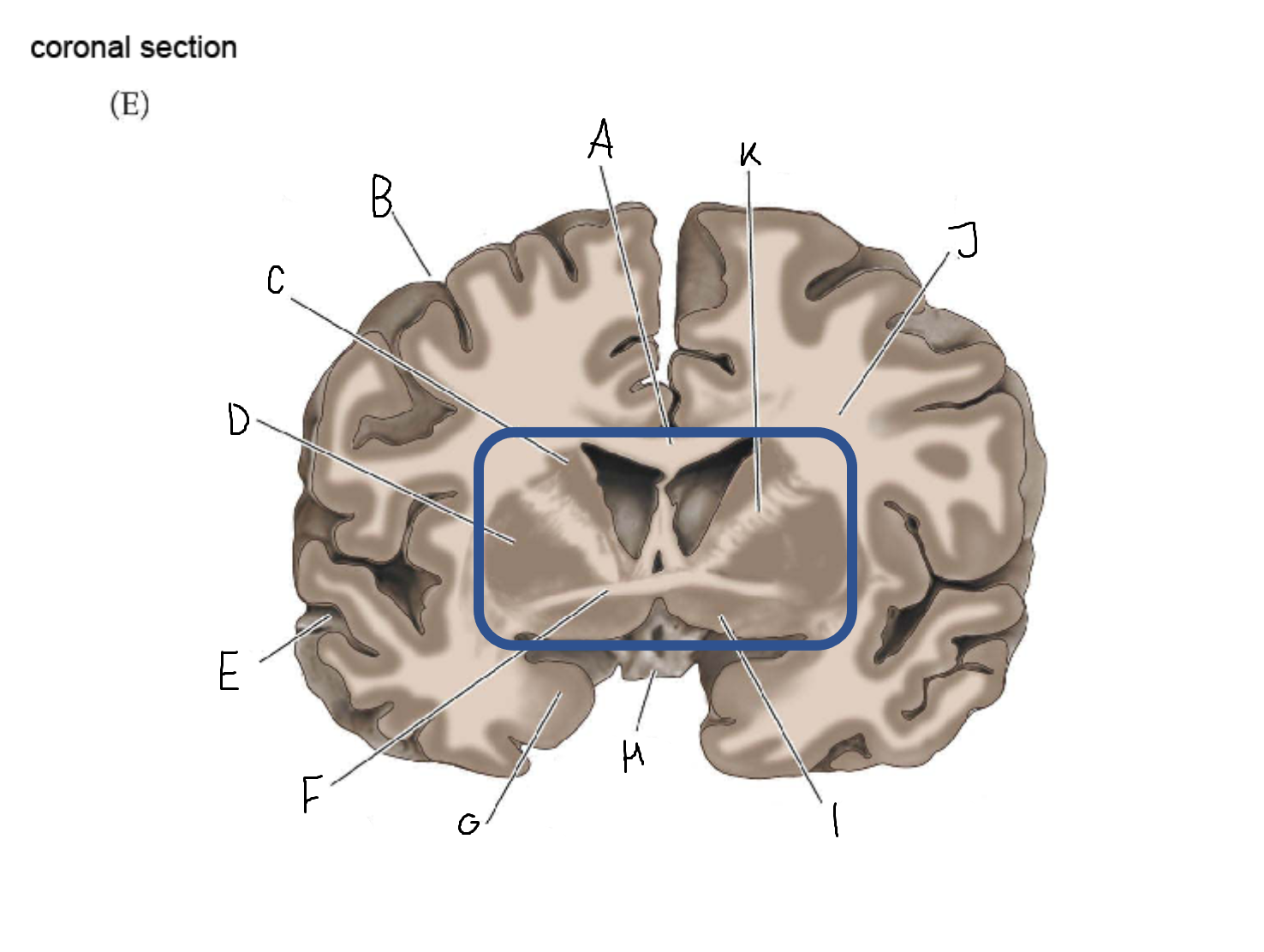
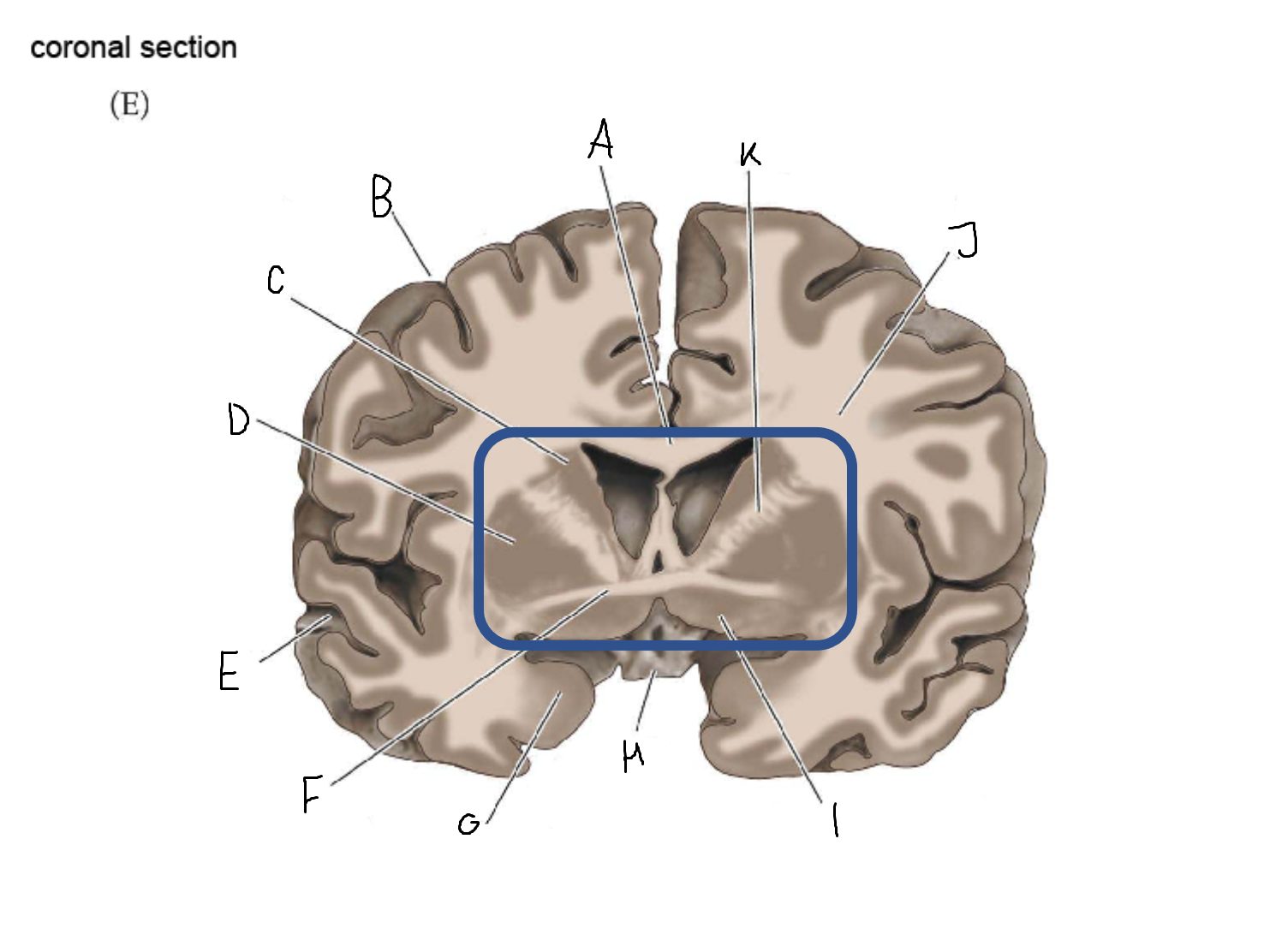
D
putamen
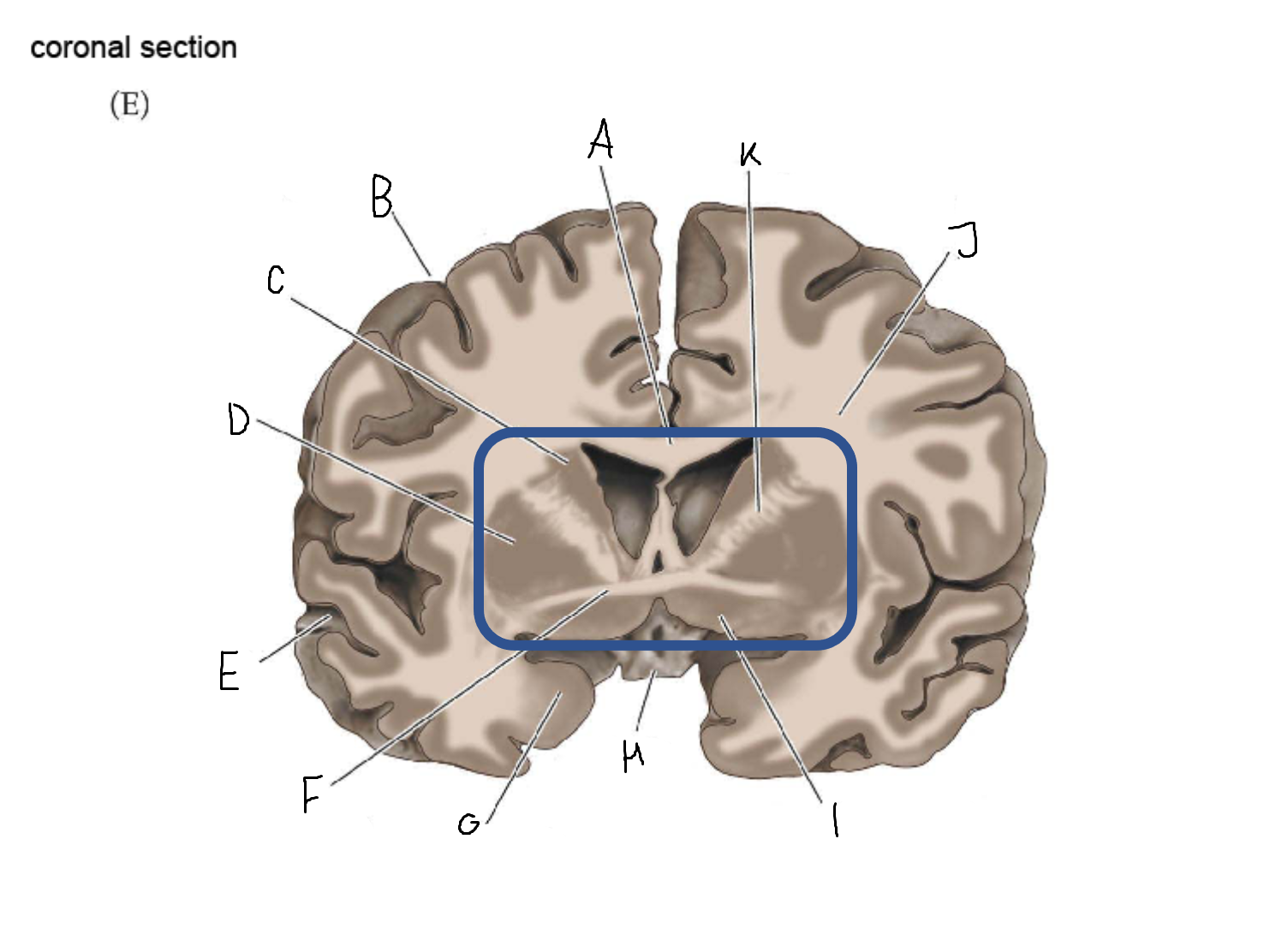
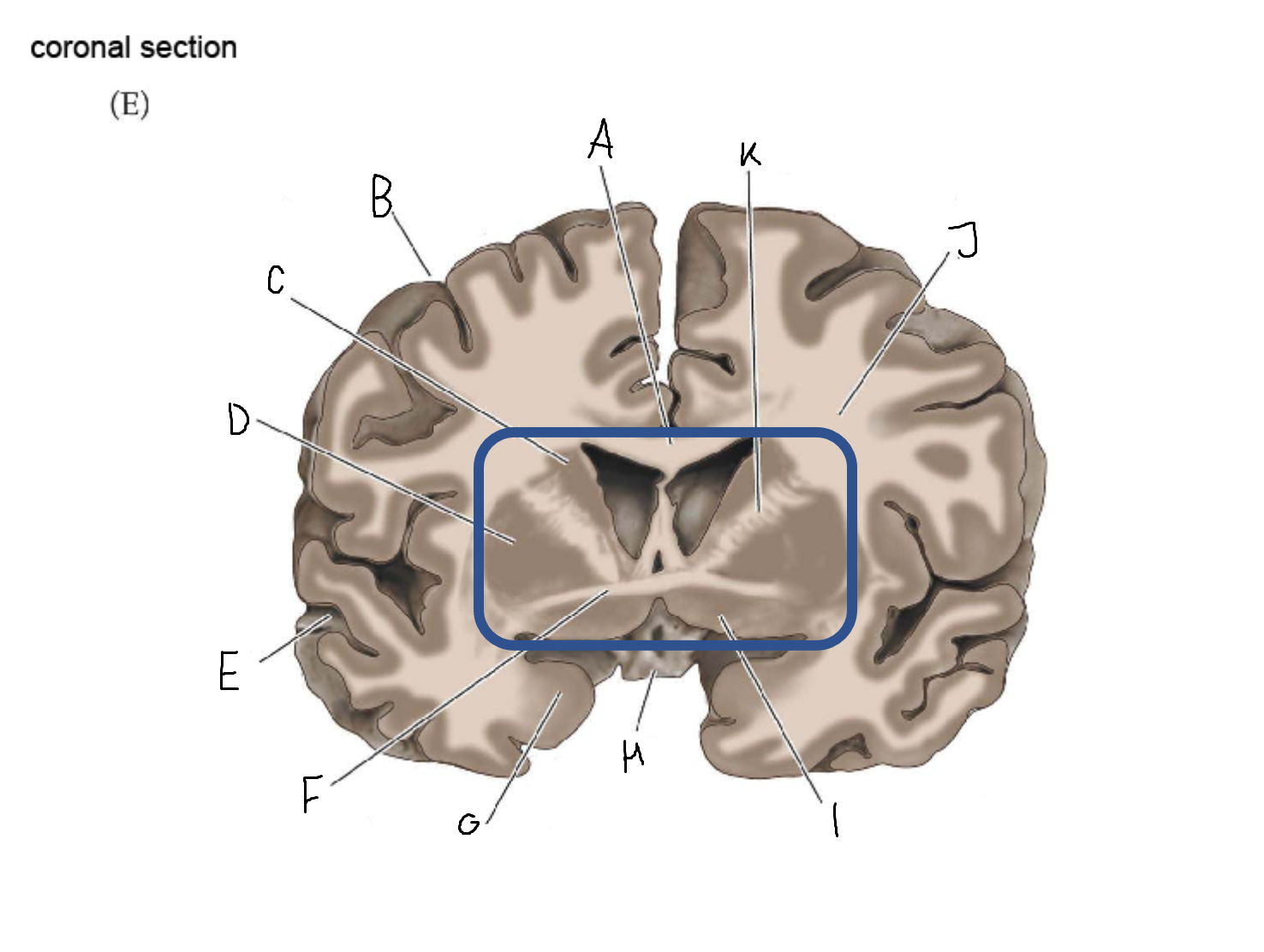
F
anterior commissure
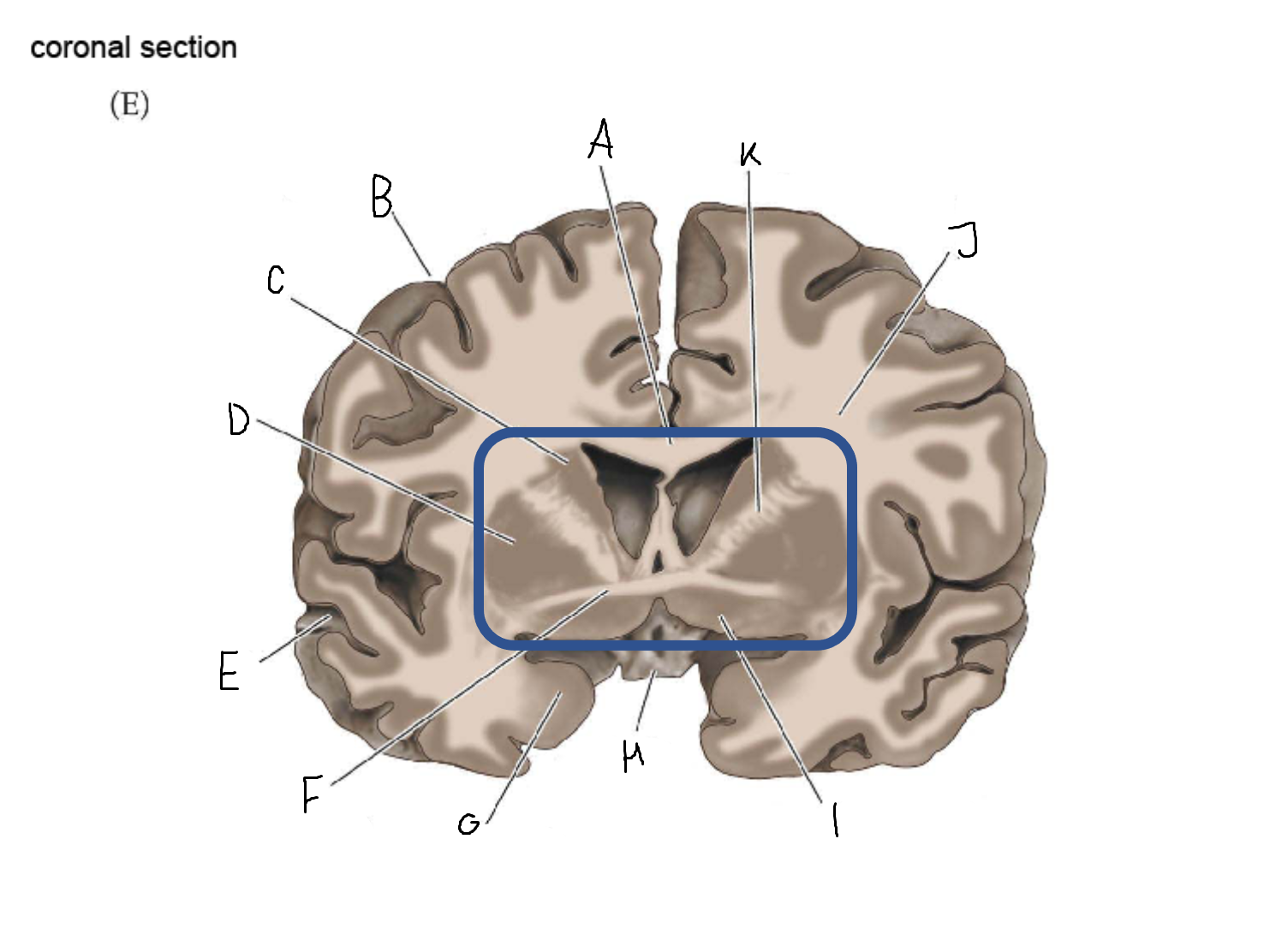
G
amygdala
H
optic chiasm
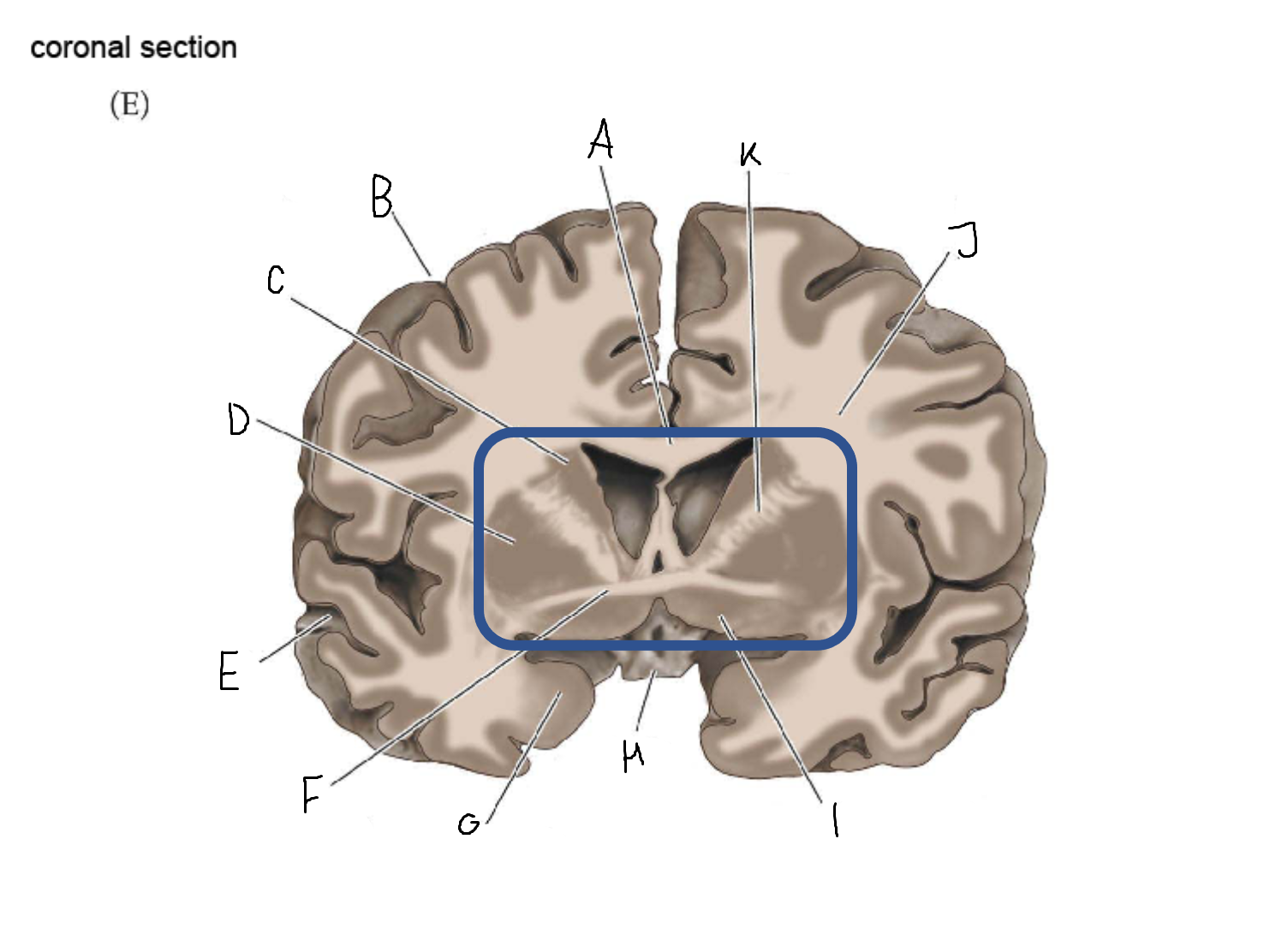
I
basal forebrain nuclei
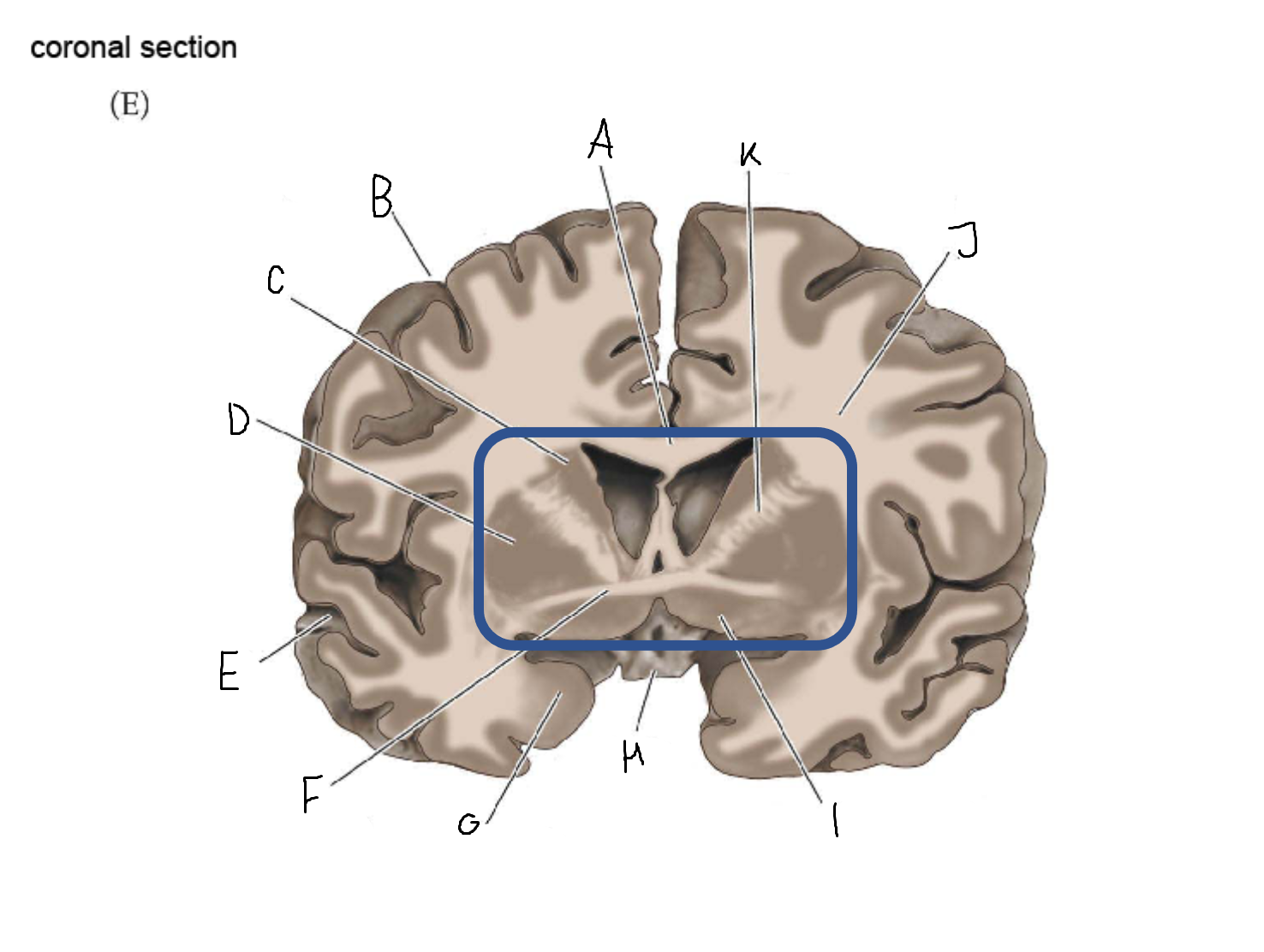
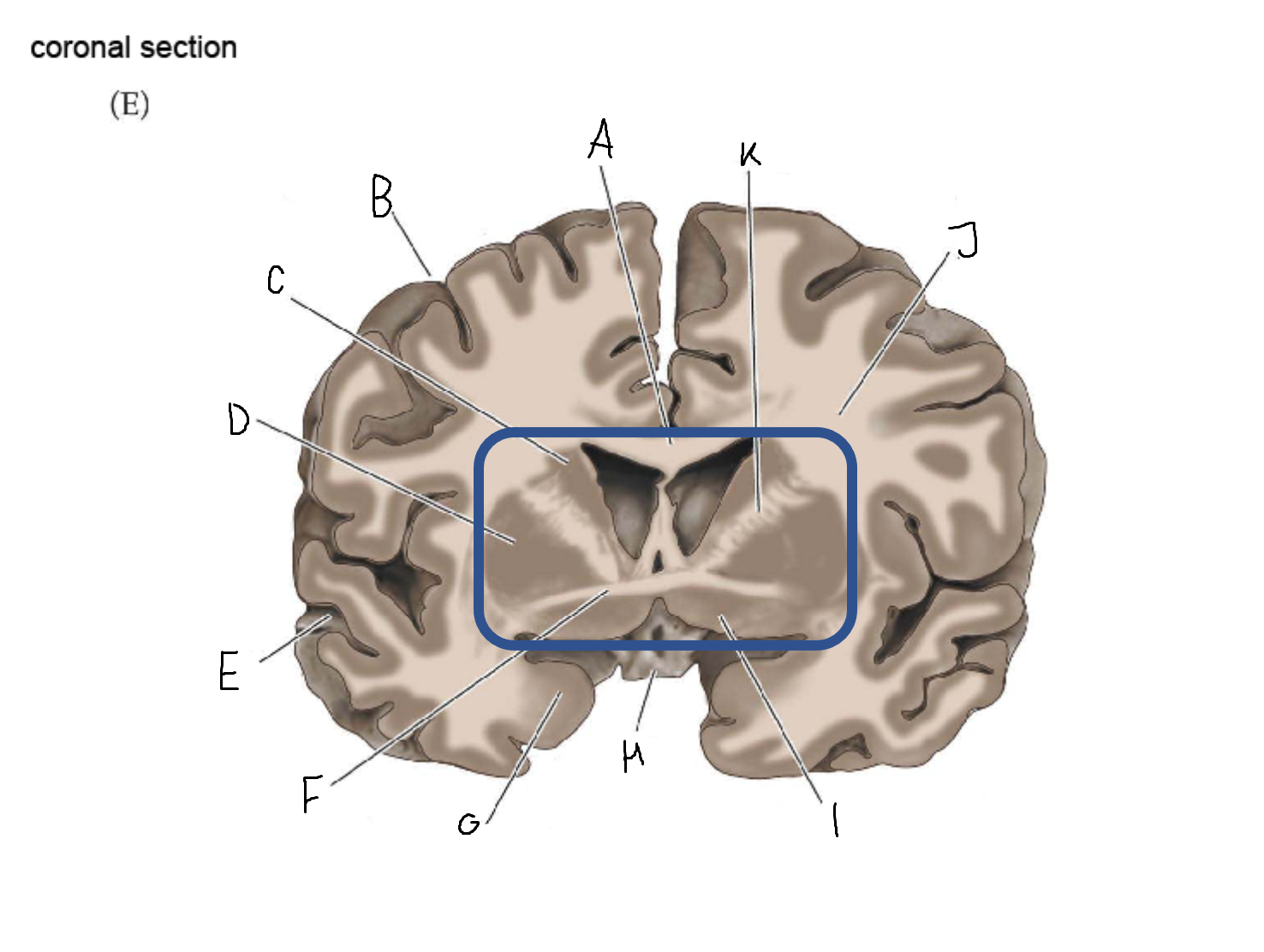
K
internal capsule
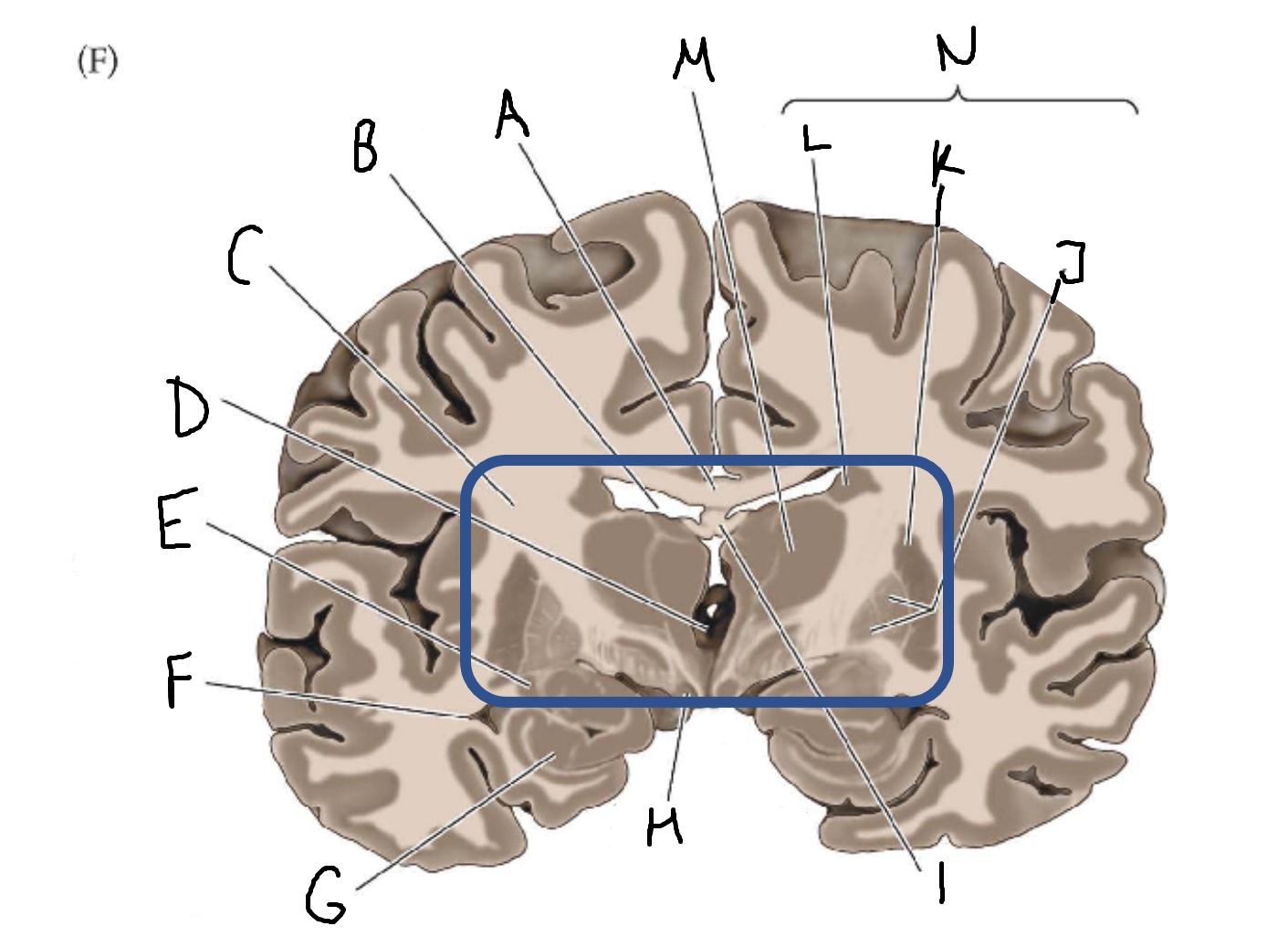
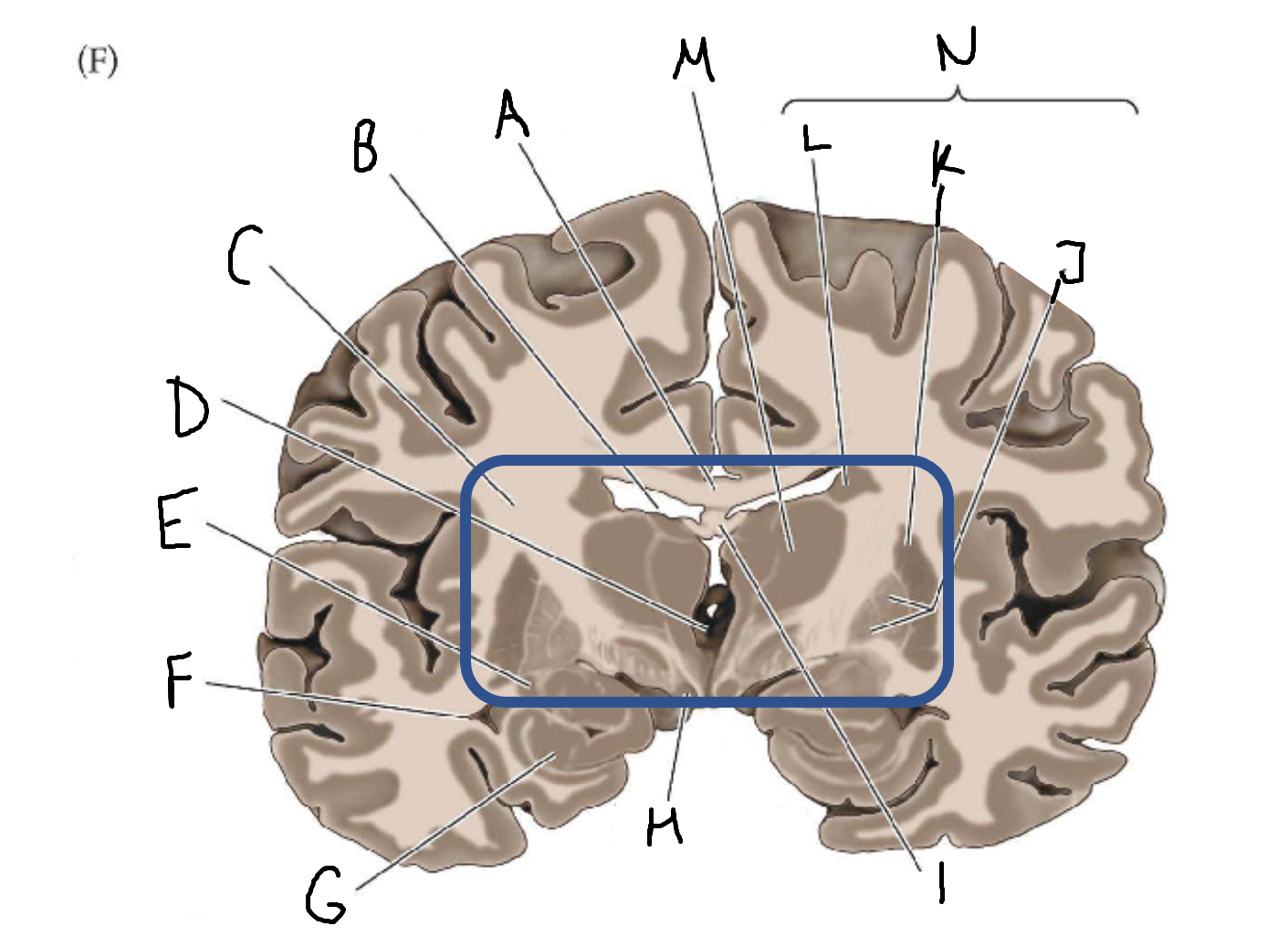
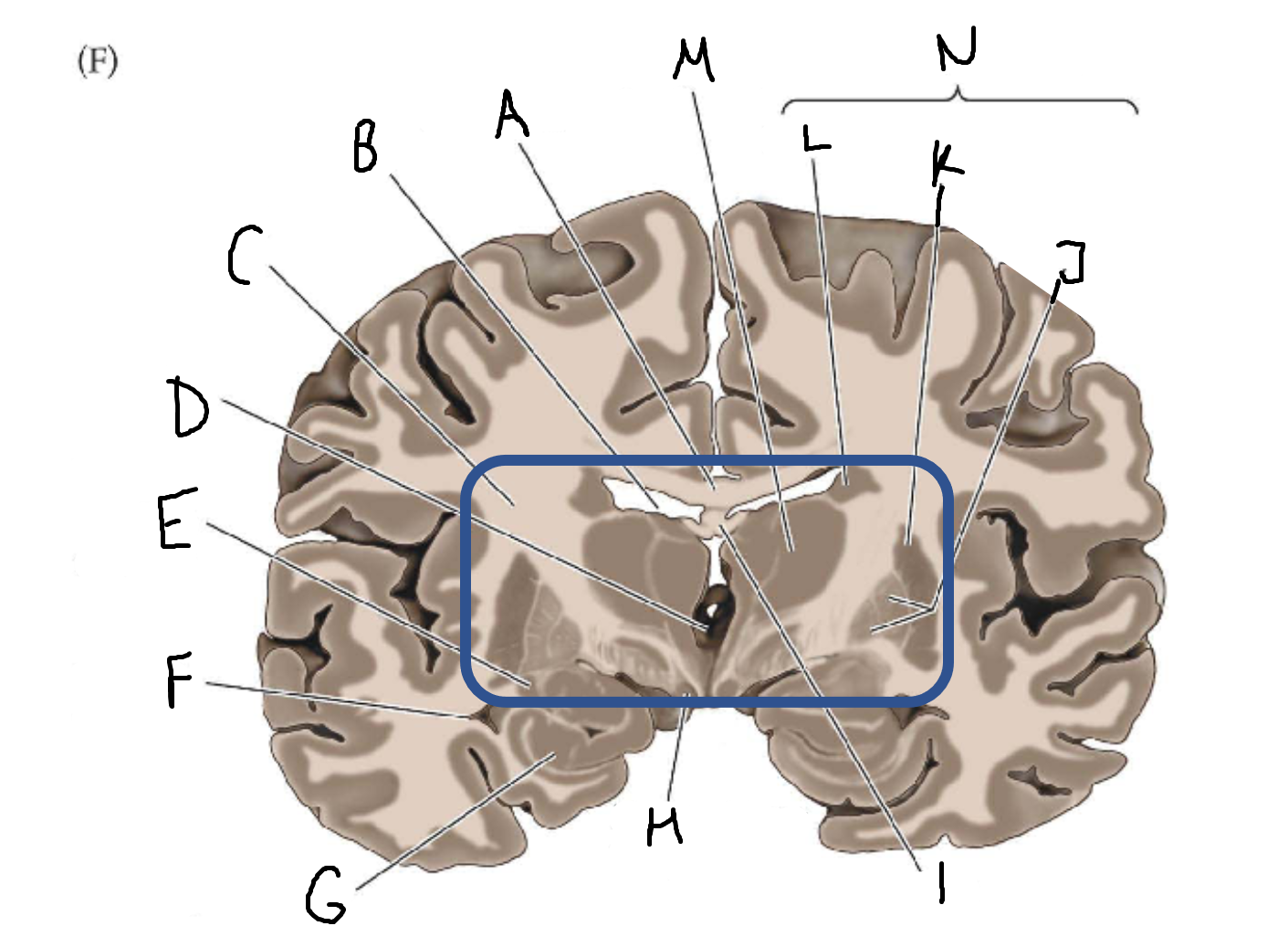
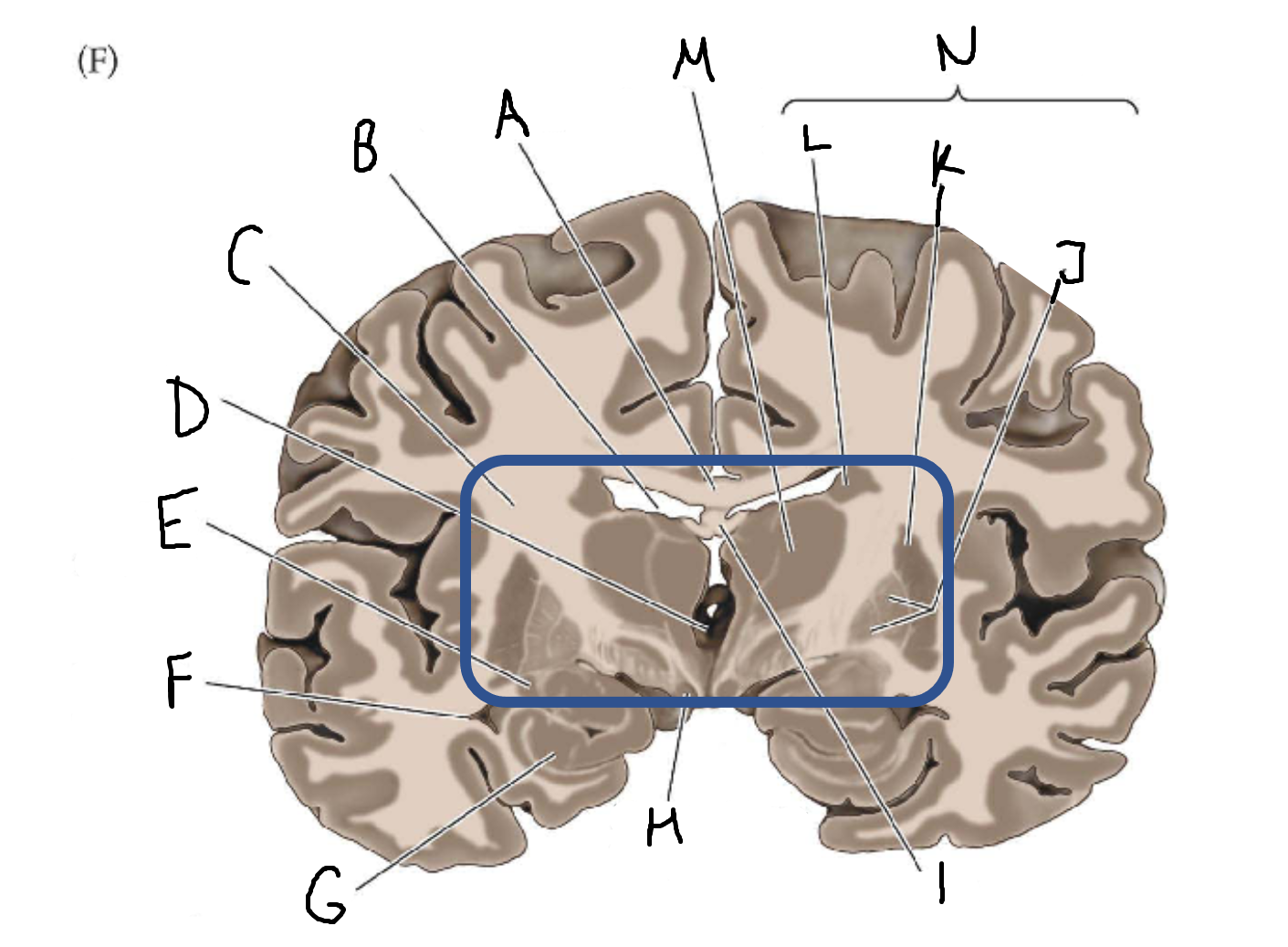
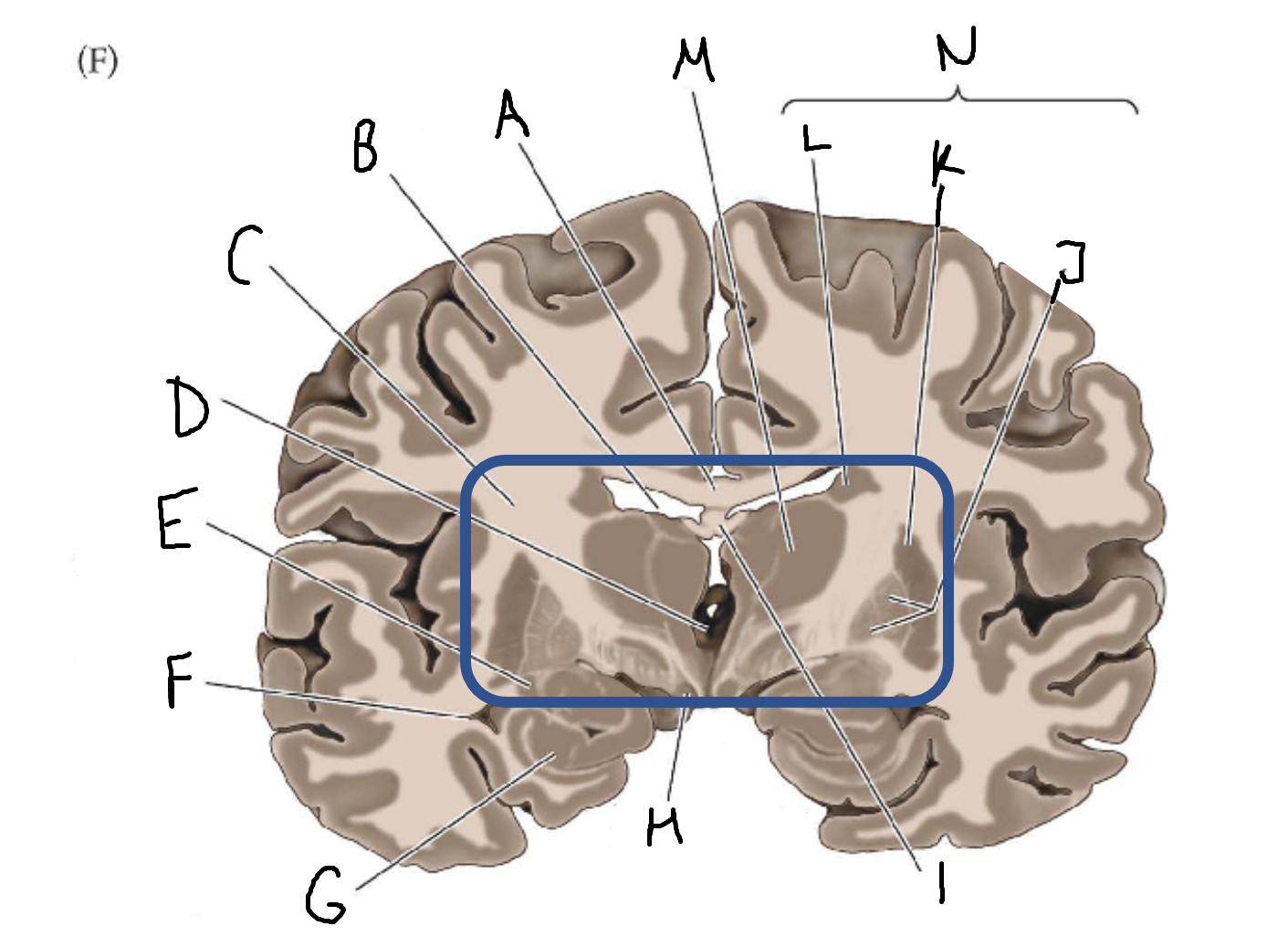
A
corpus callosum
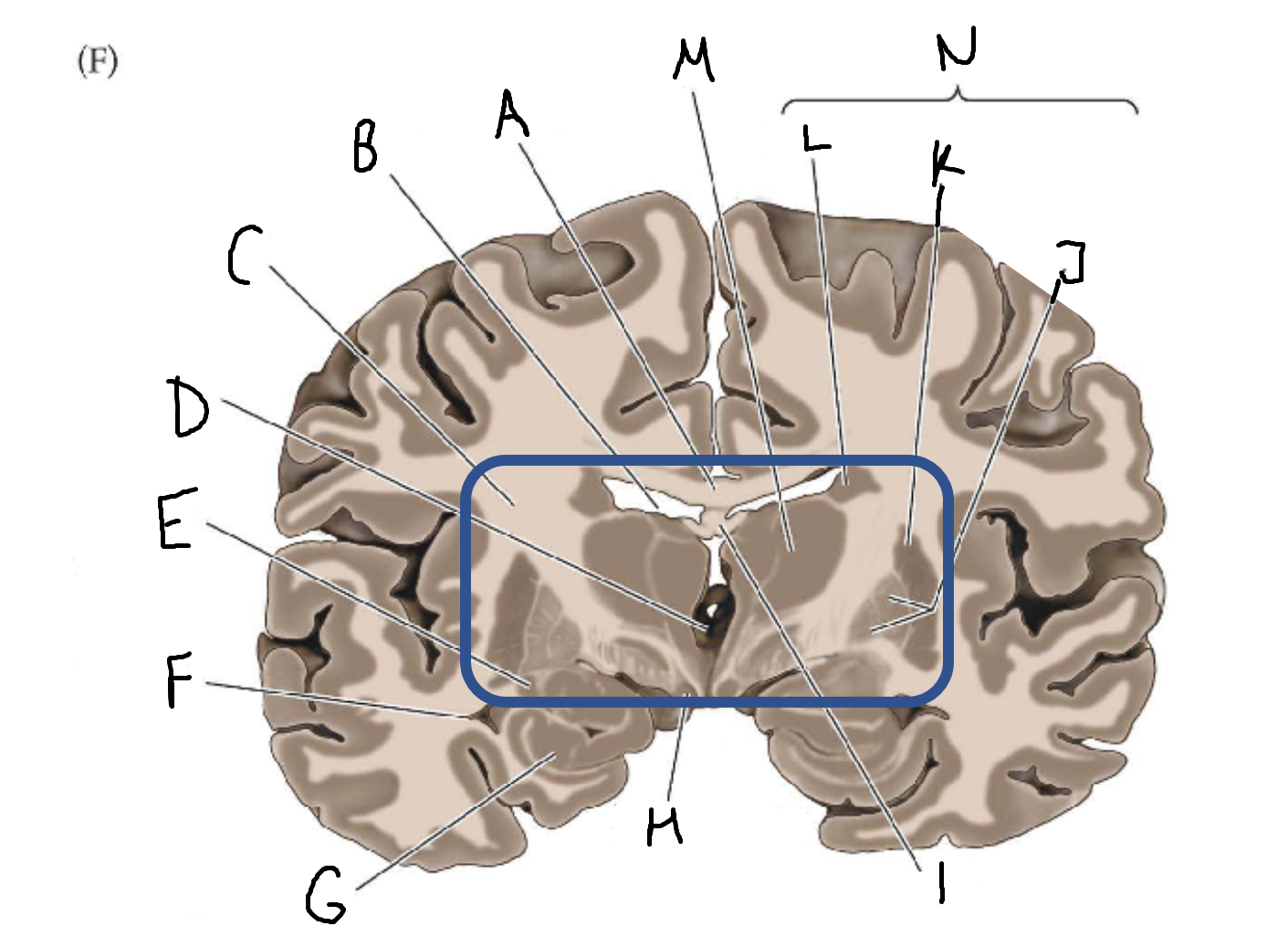
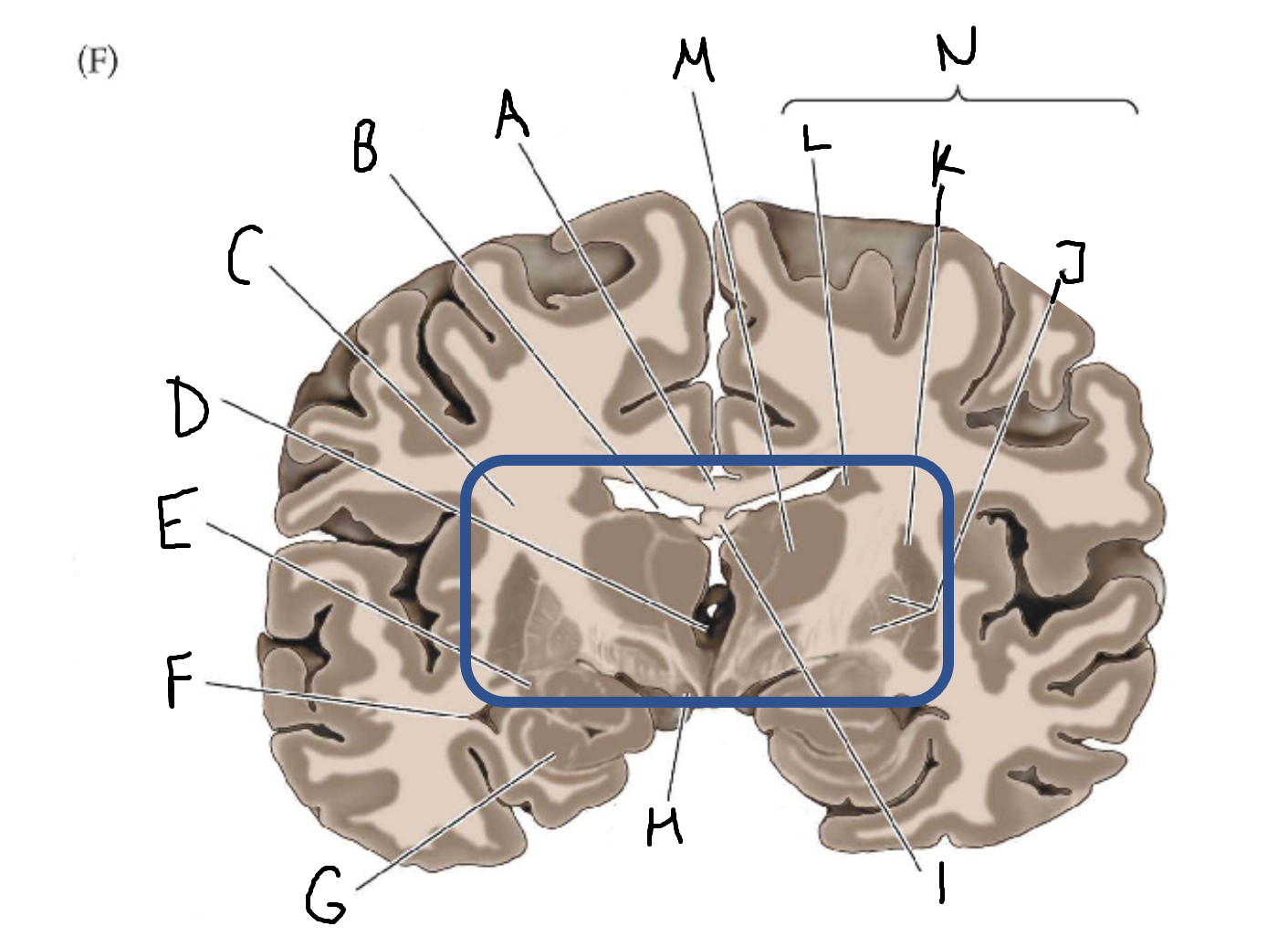
B
lateral ventricle
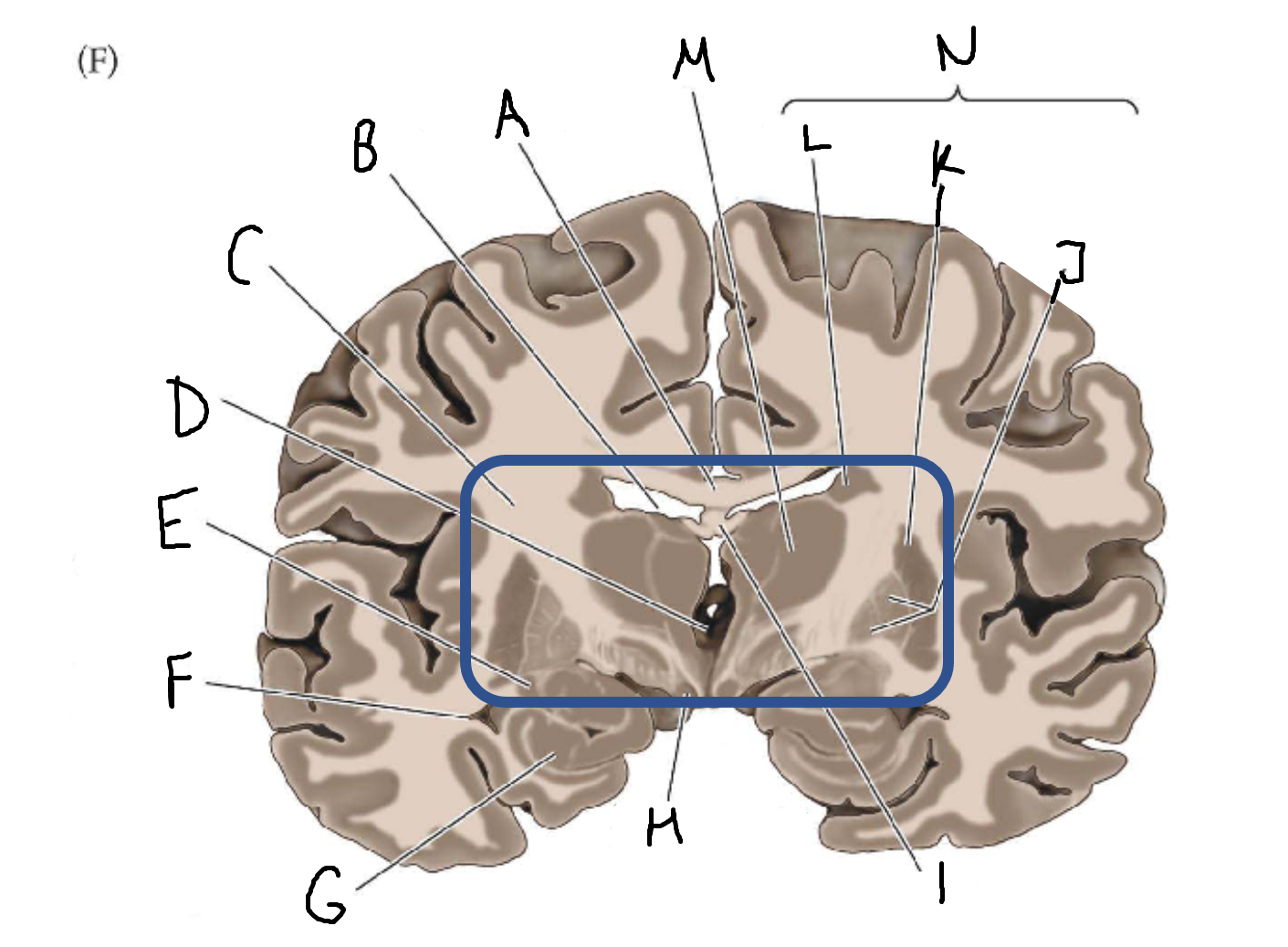
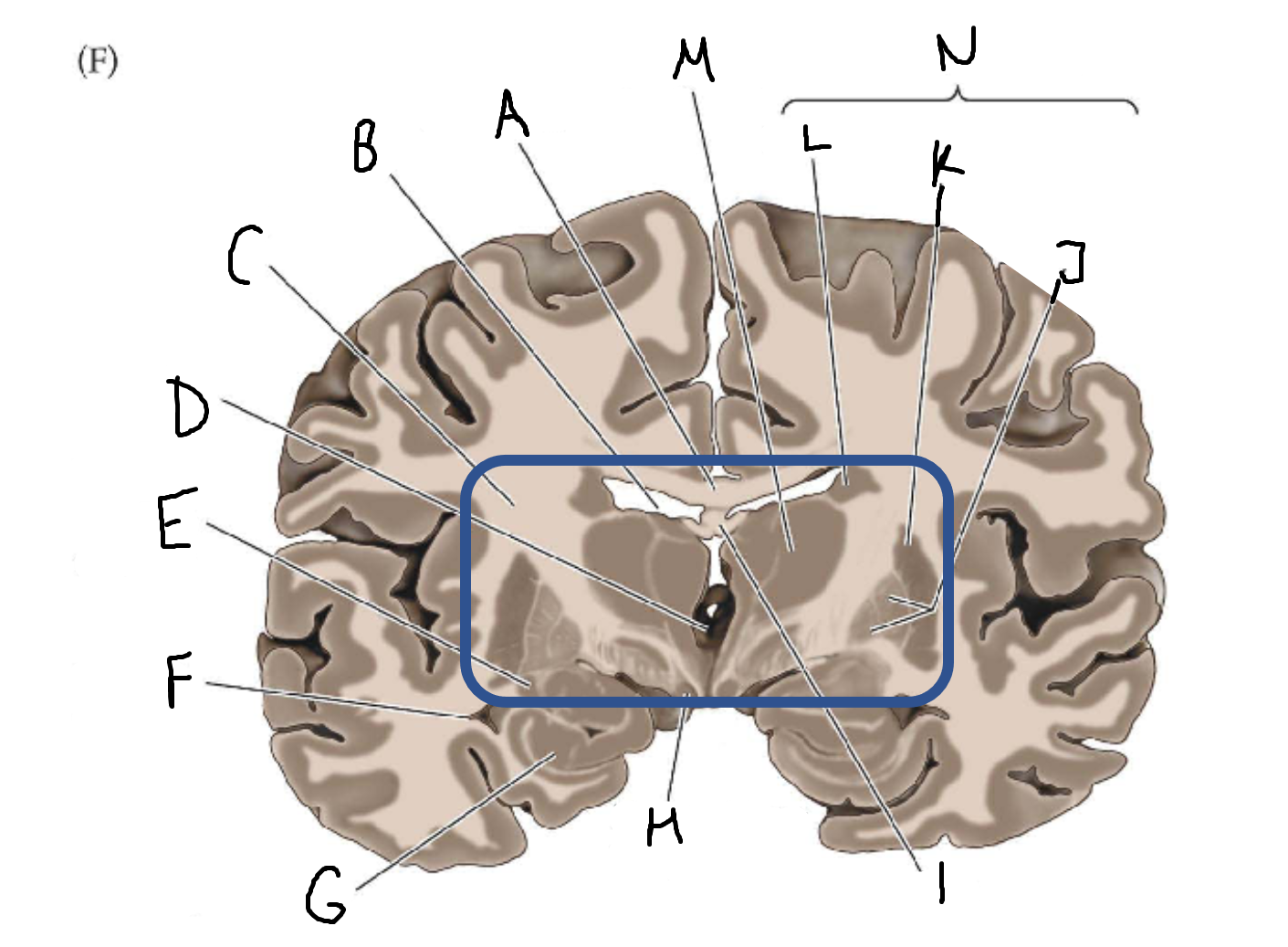
C
internal capsule
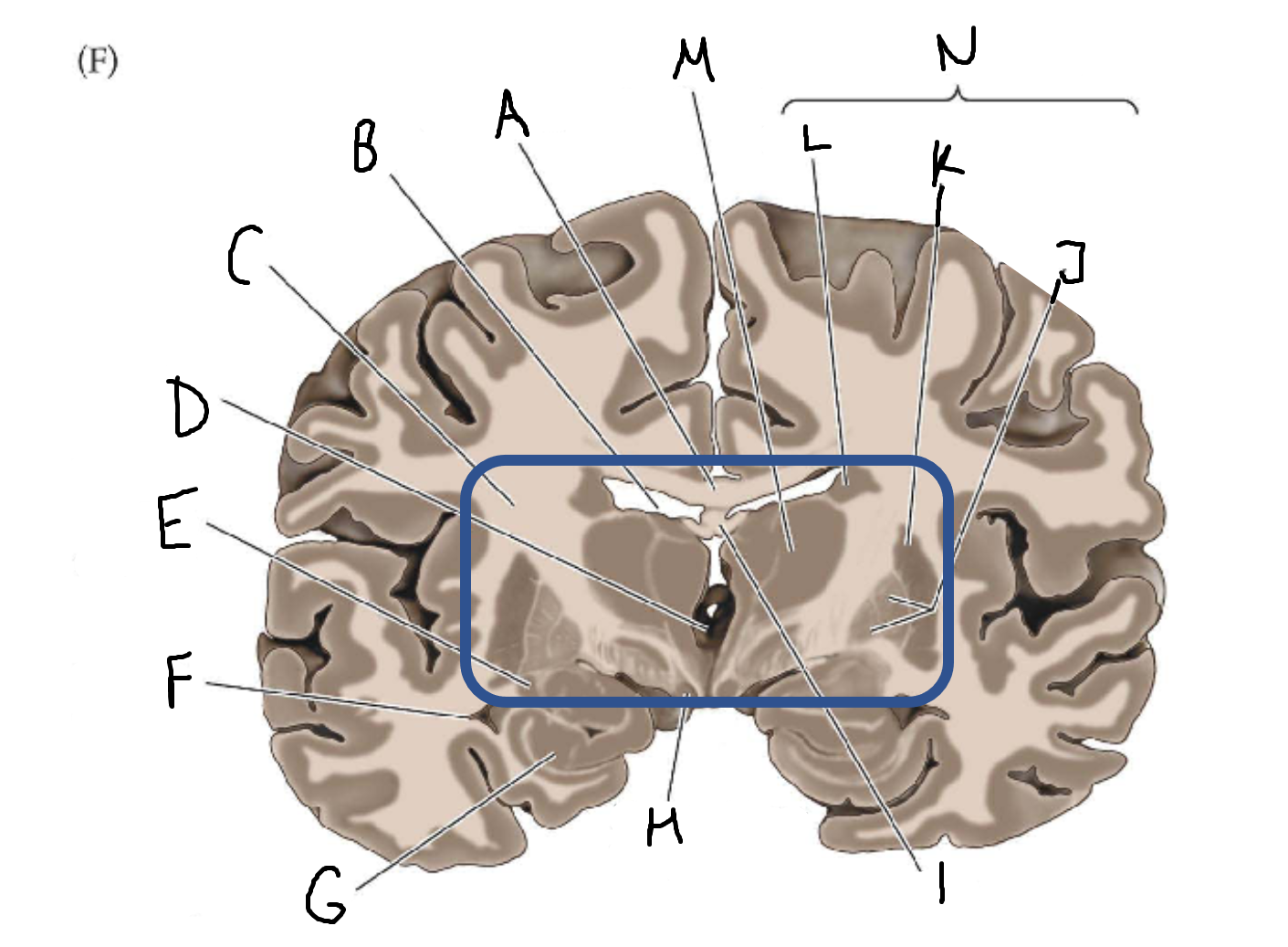
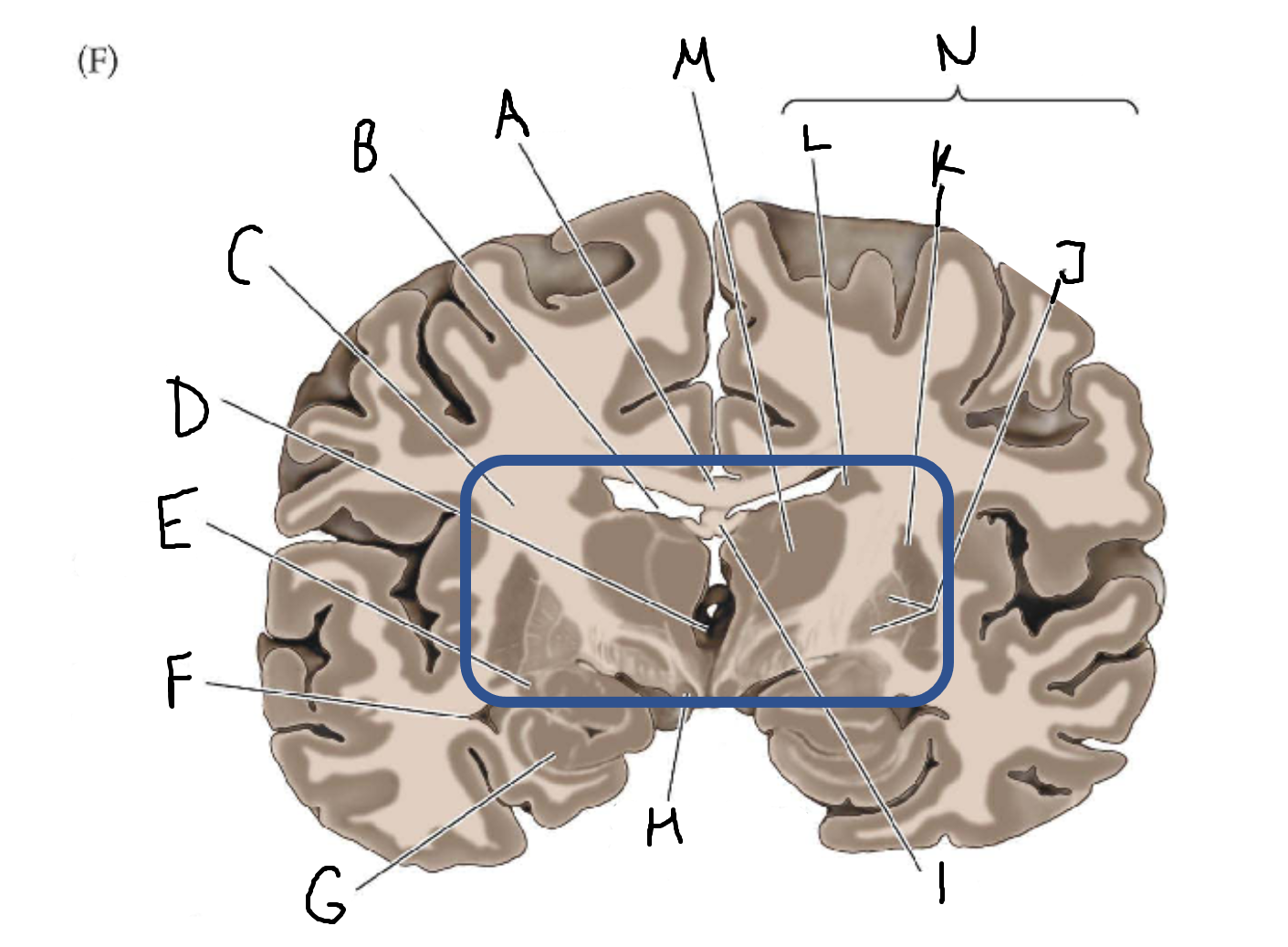
D
third ventricle
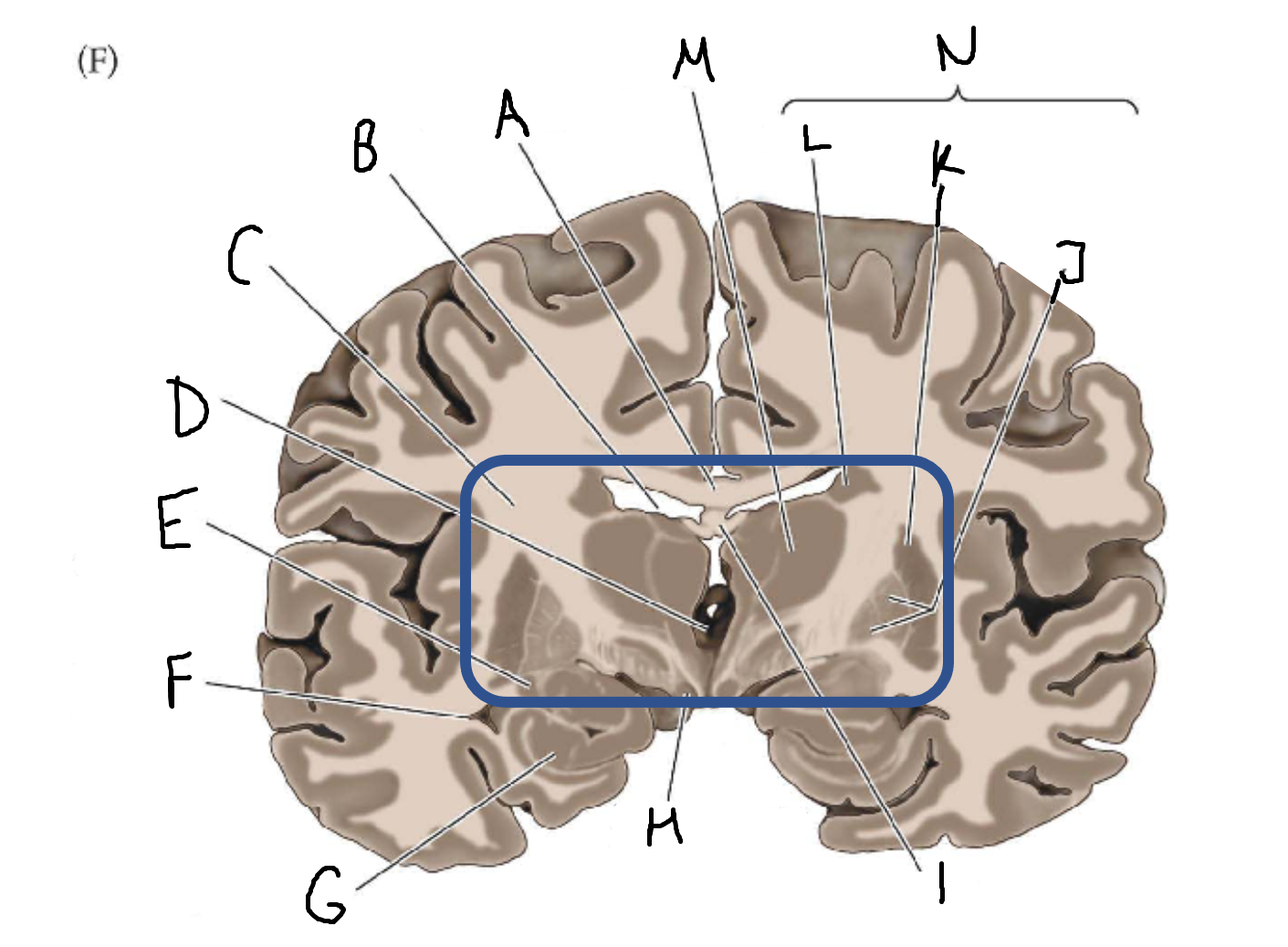
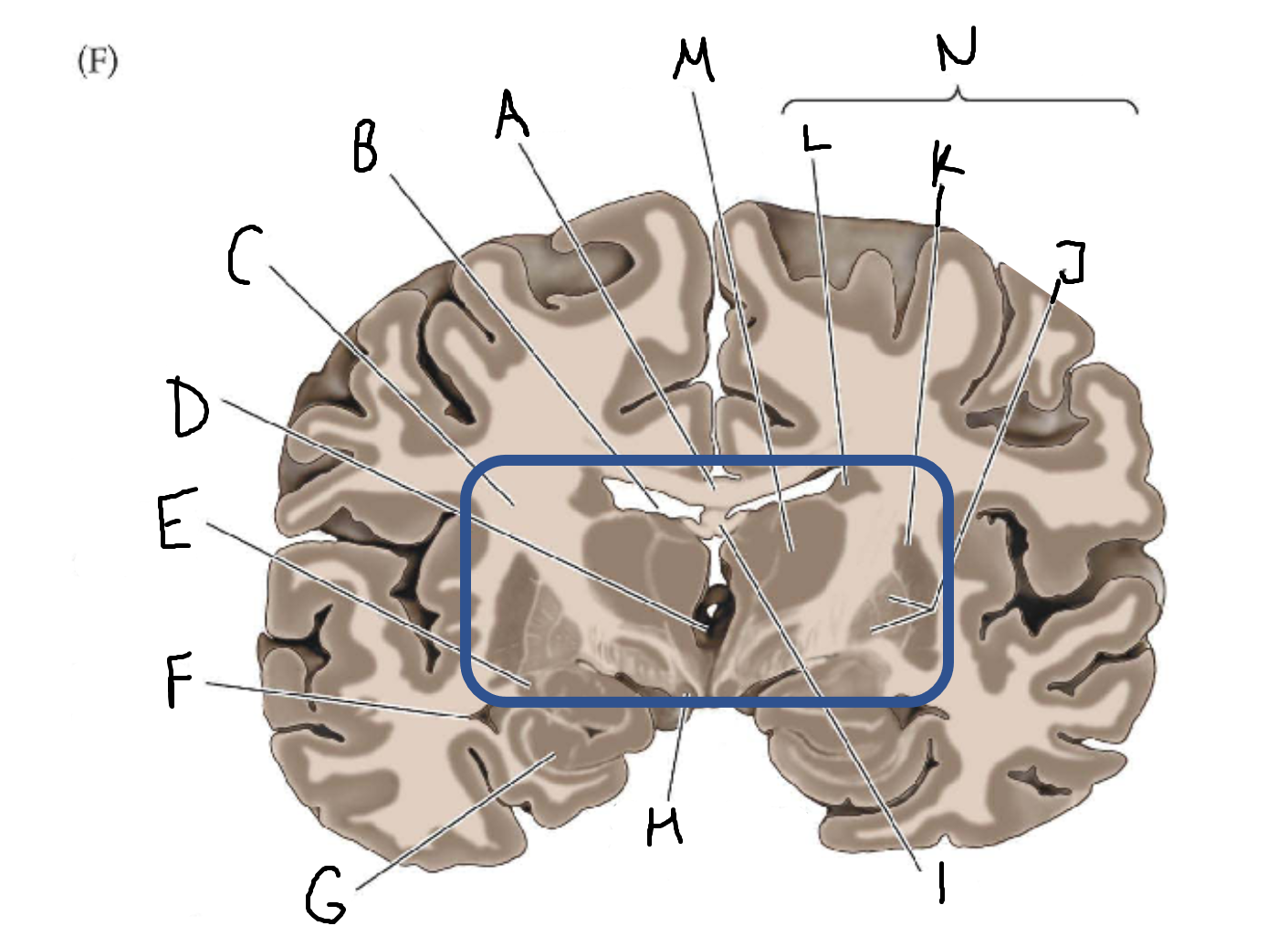
E
tail of caudate nucleus
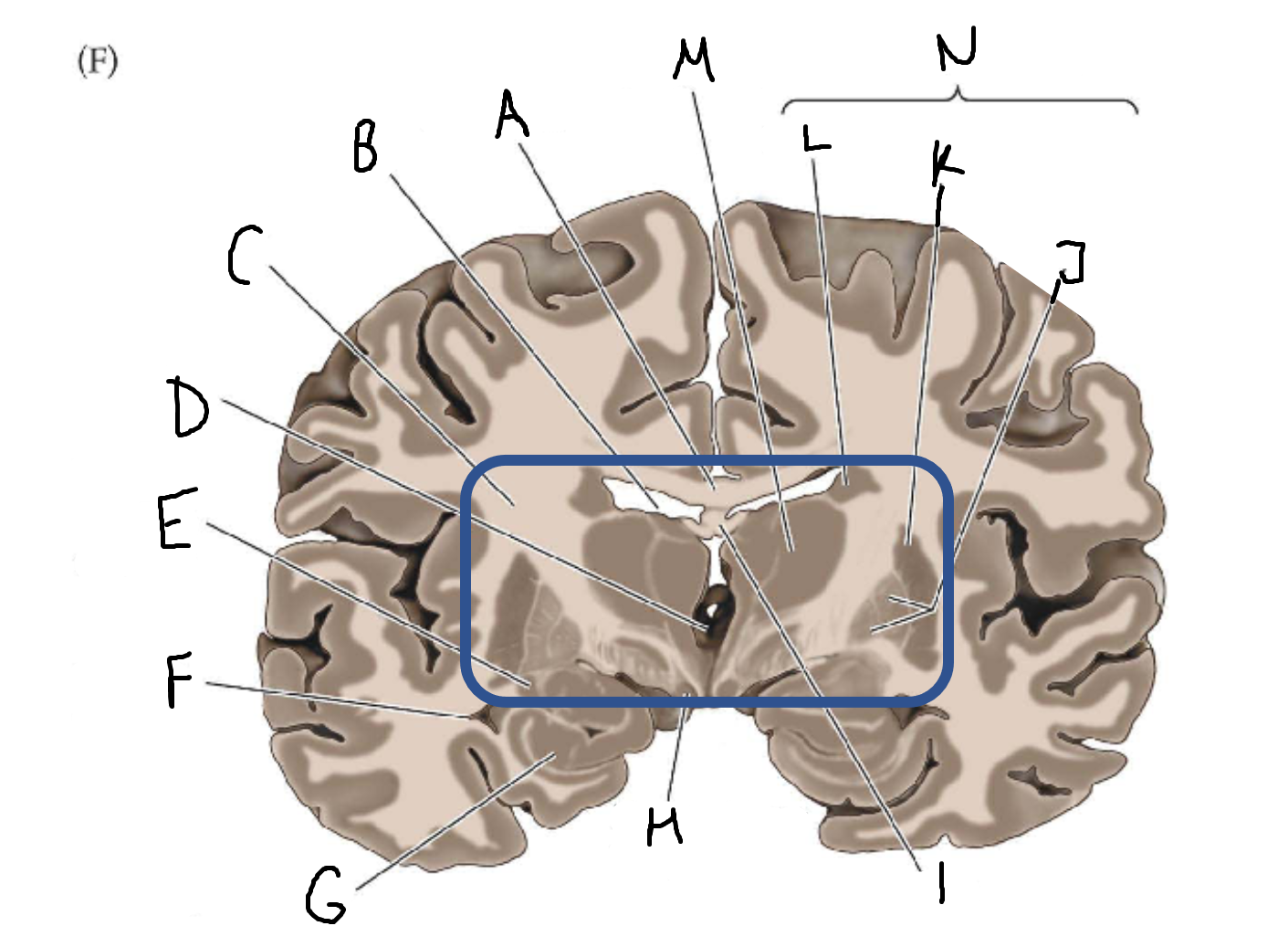
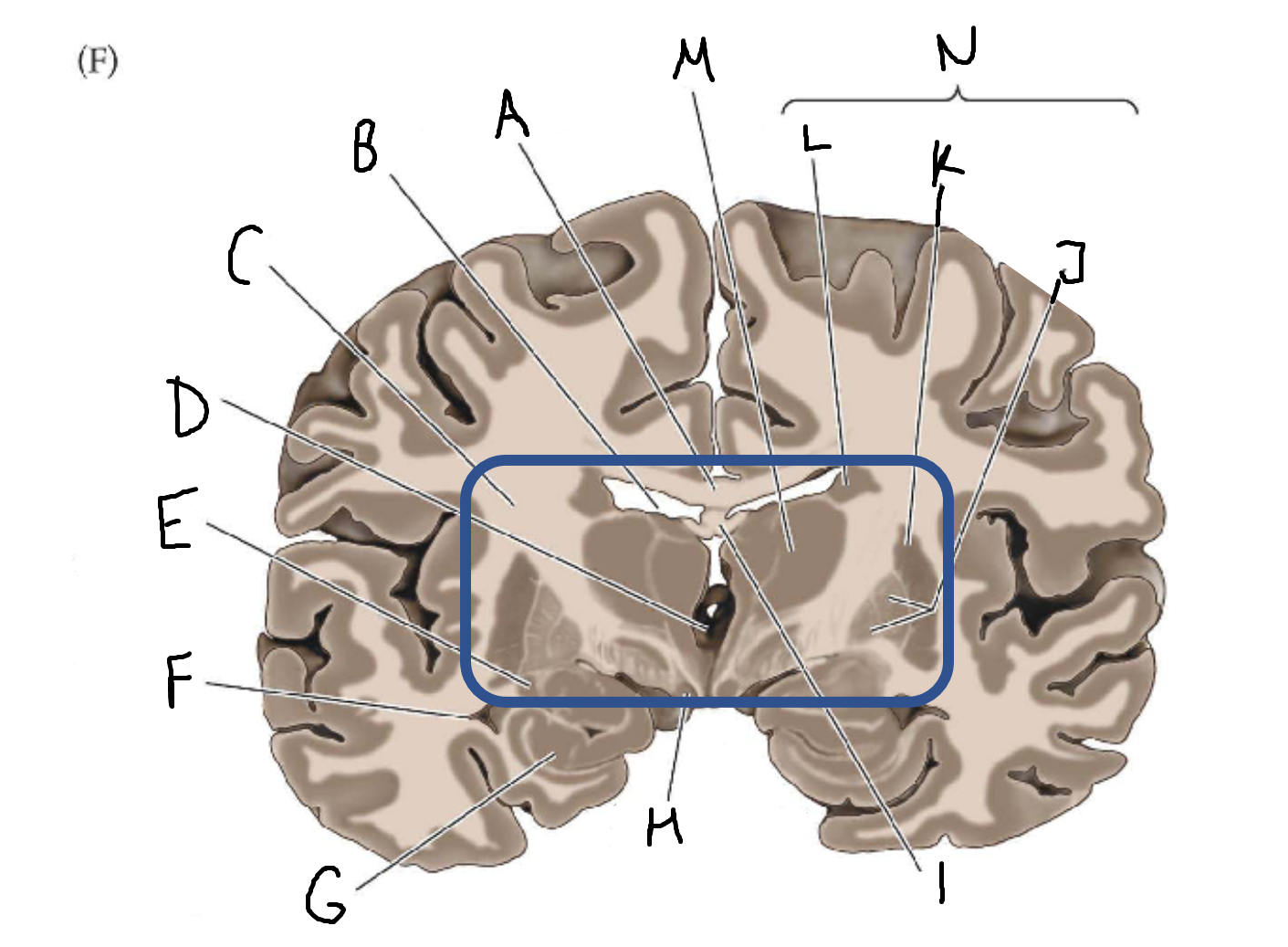
F
lateral ventricle
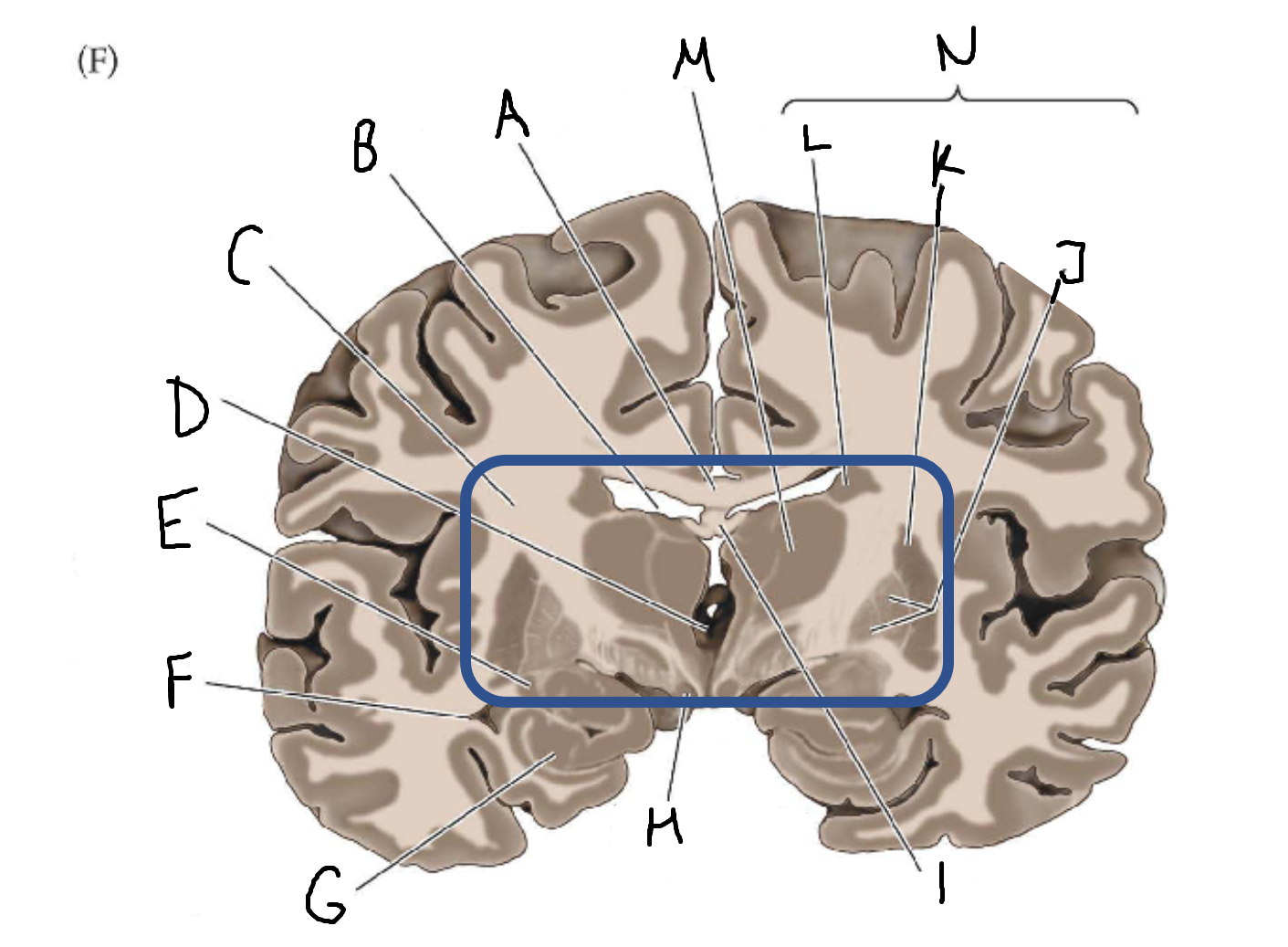
G
hippocampus
H
mammillary body
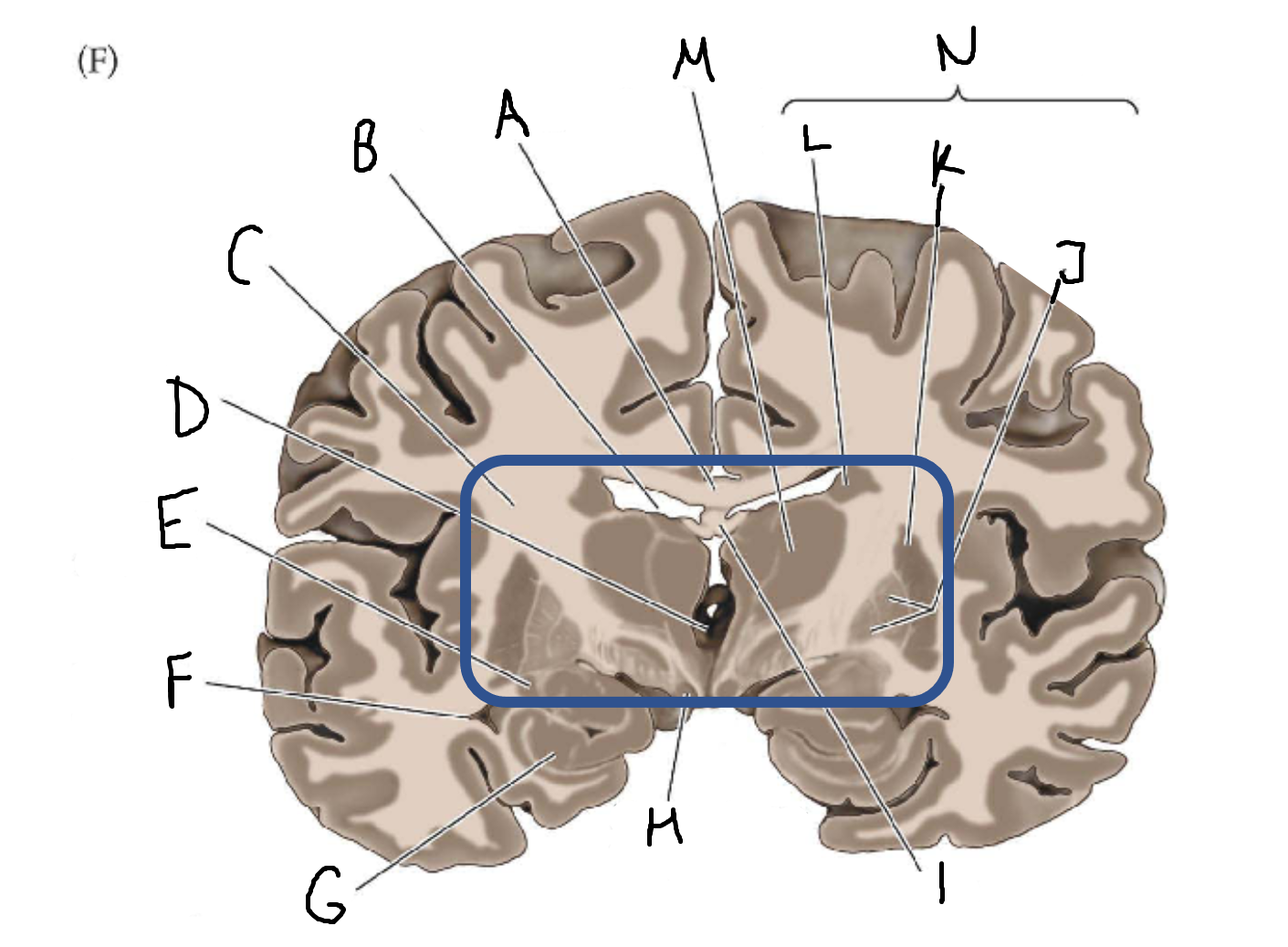
I
fornix
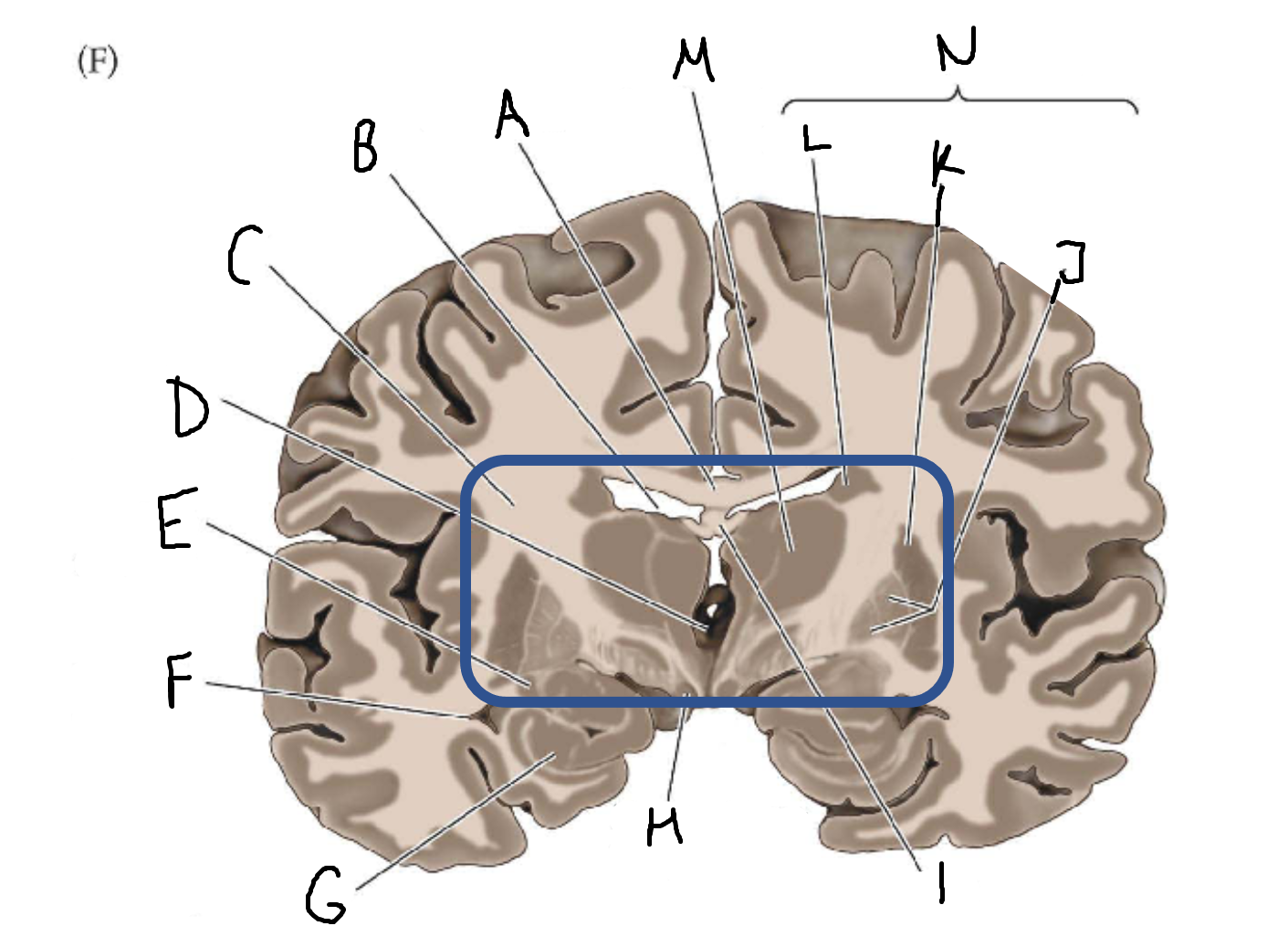
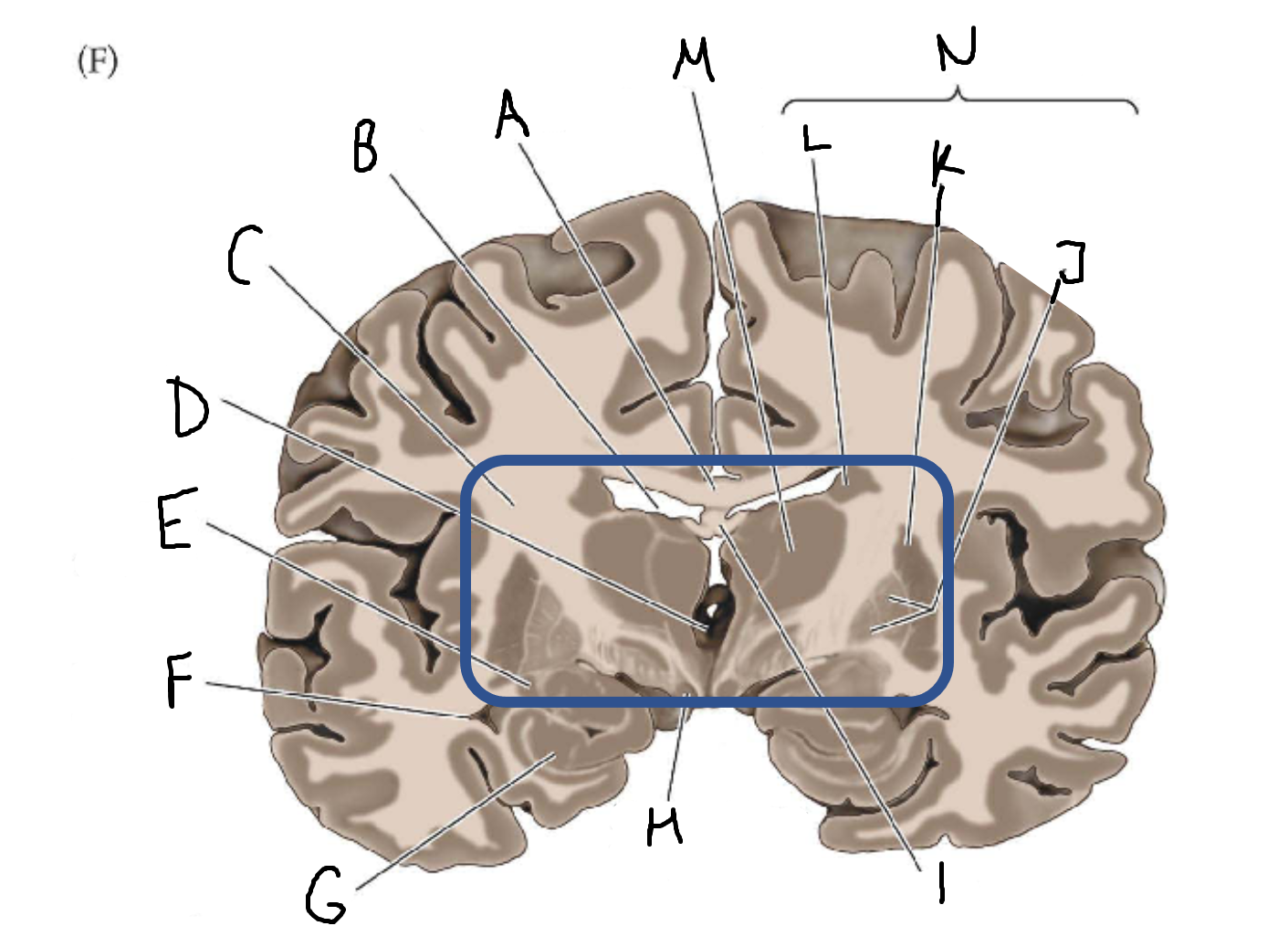
J
globus pallidus
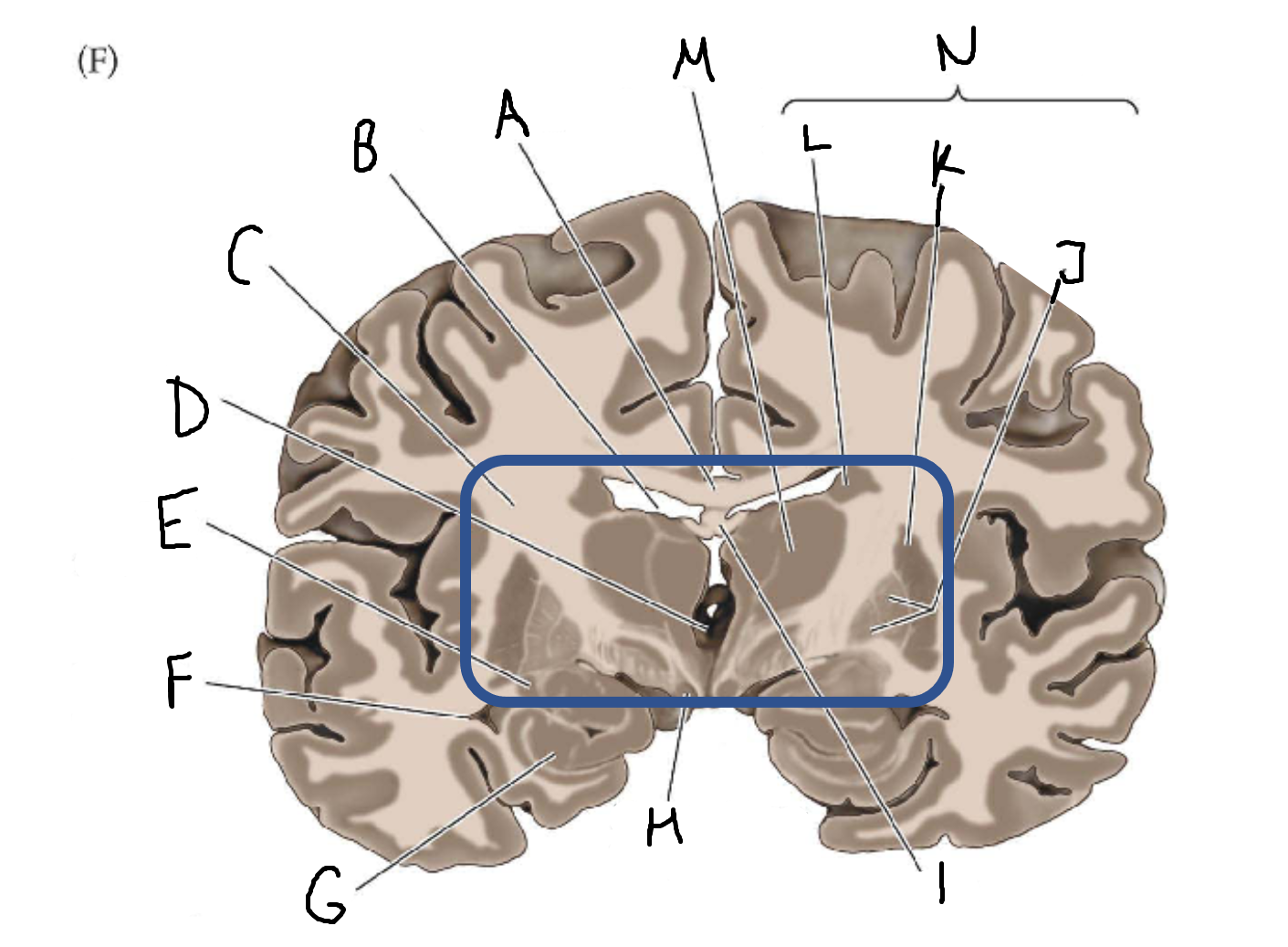
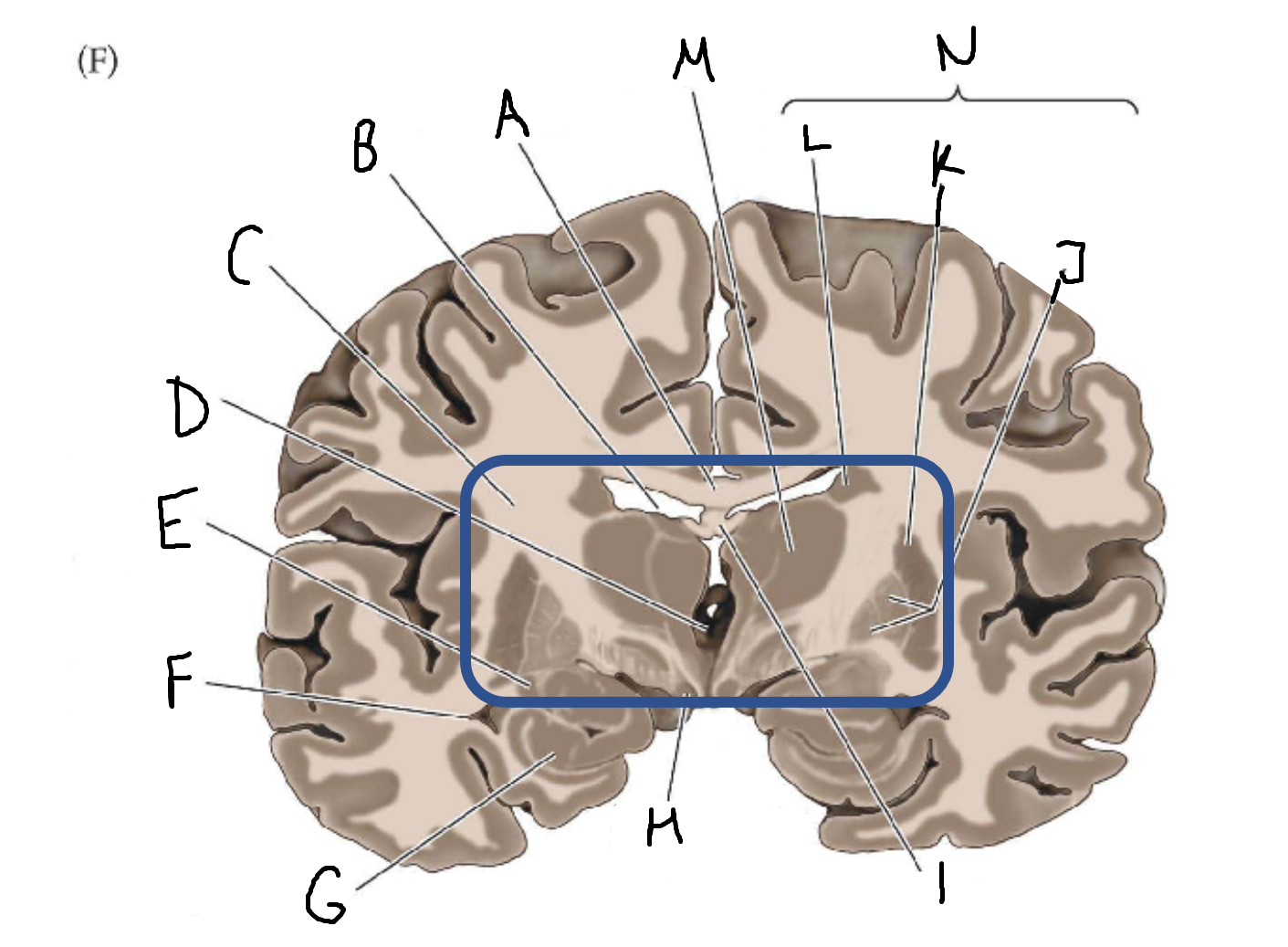
K
putamen
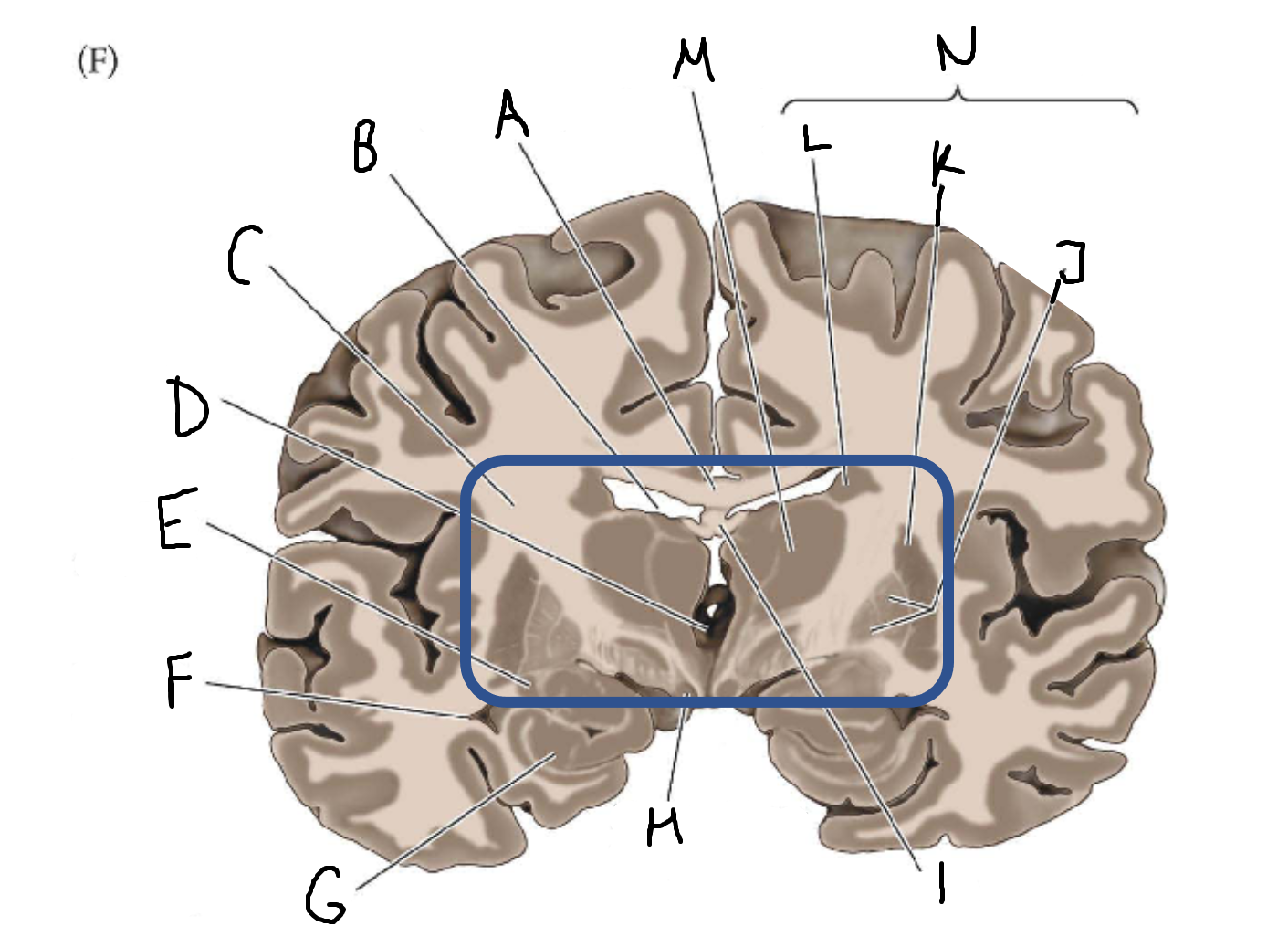
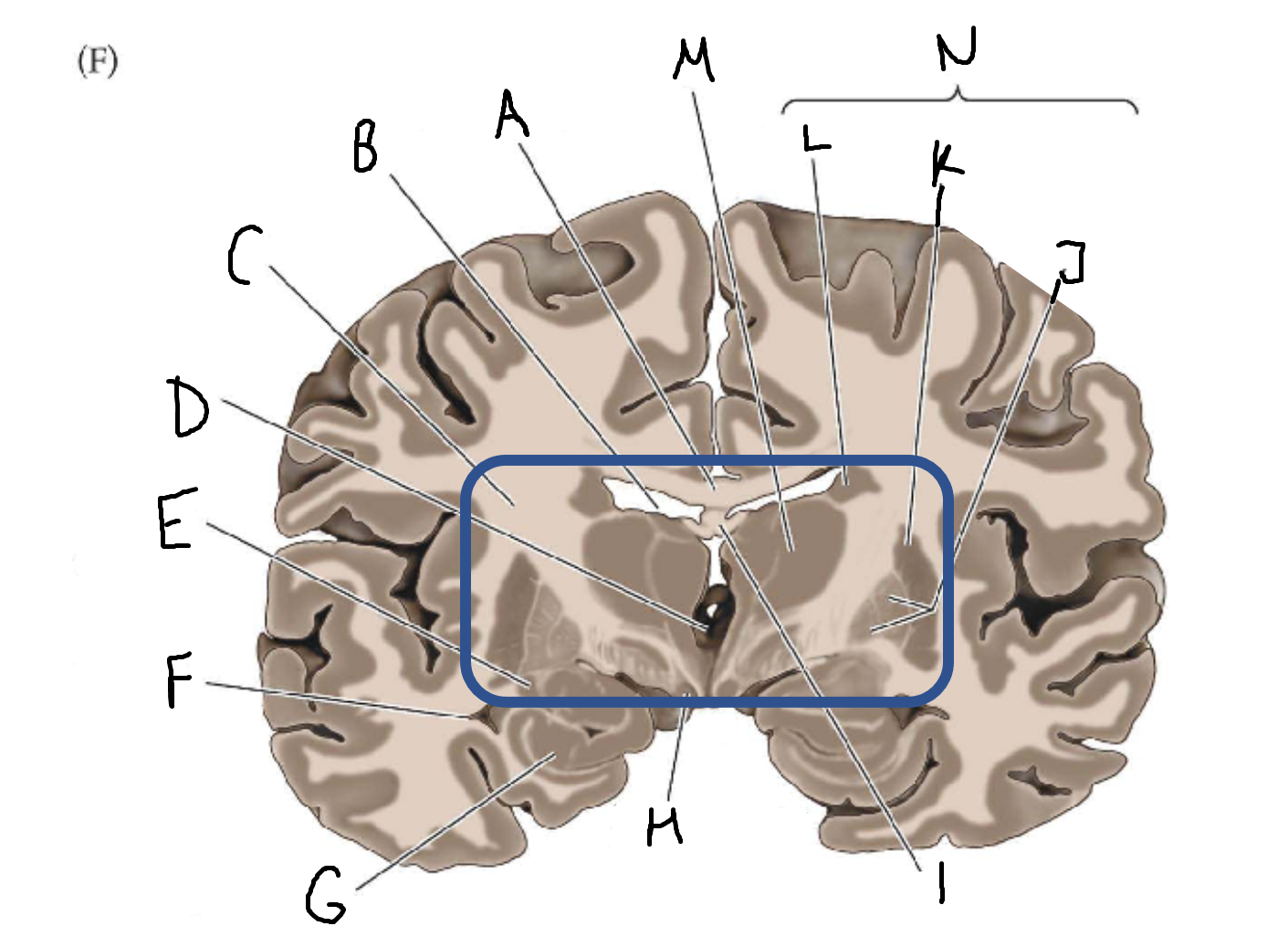
L
caudate
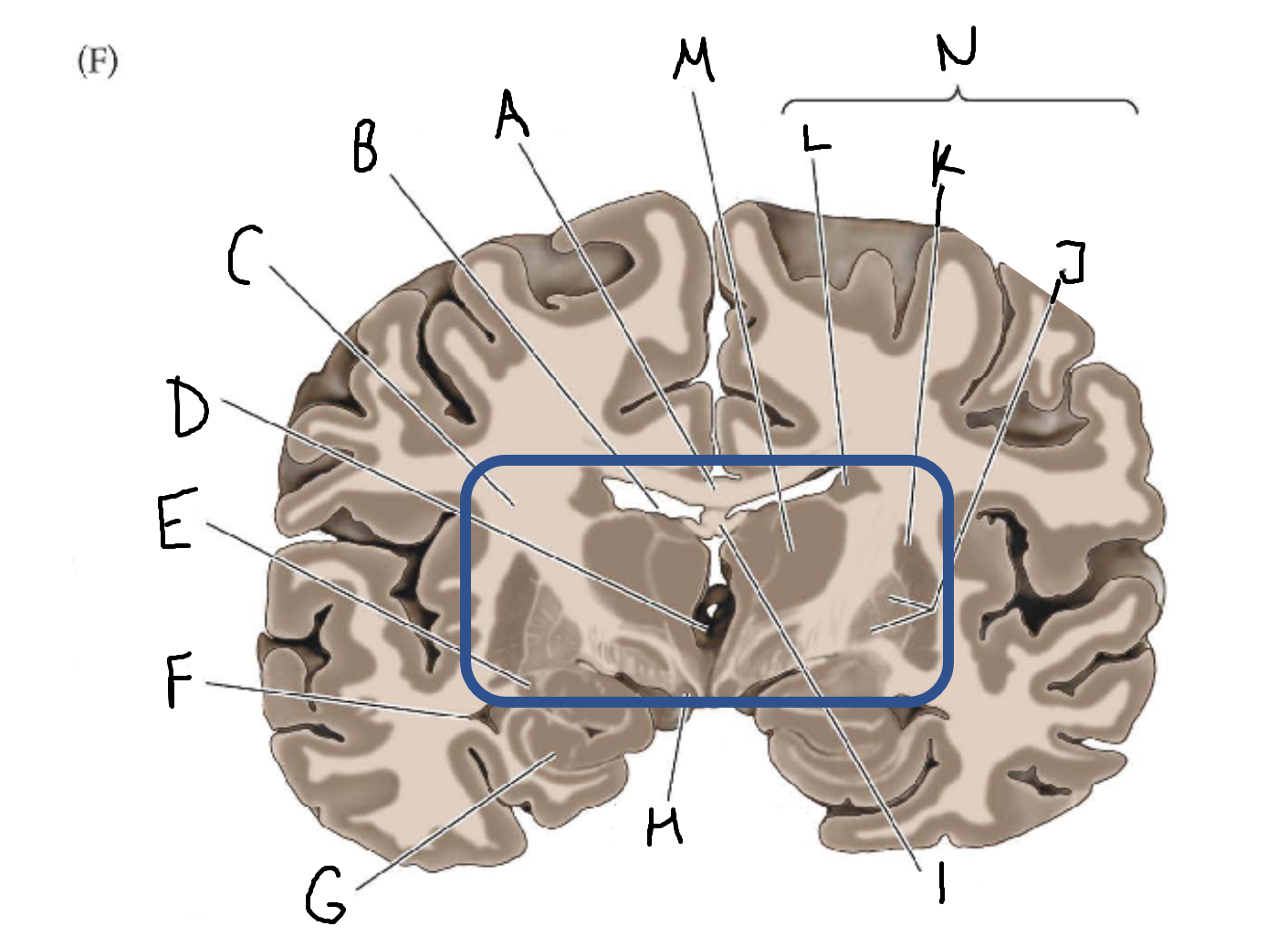
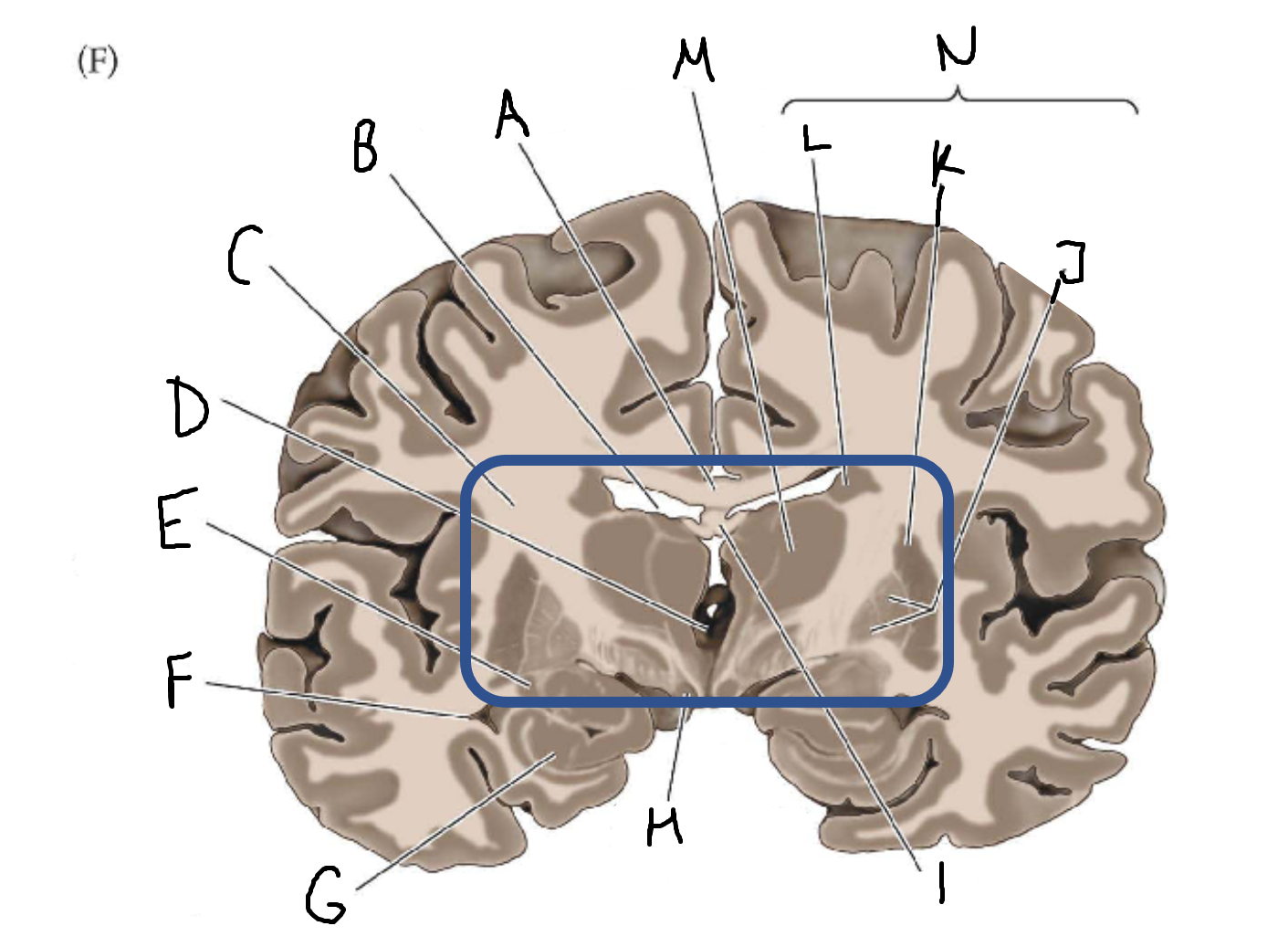
M
thalamus
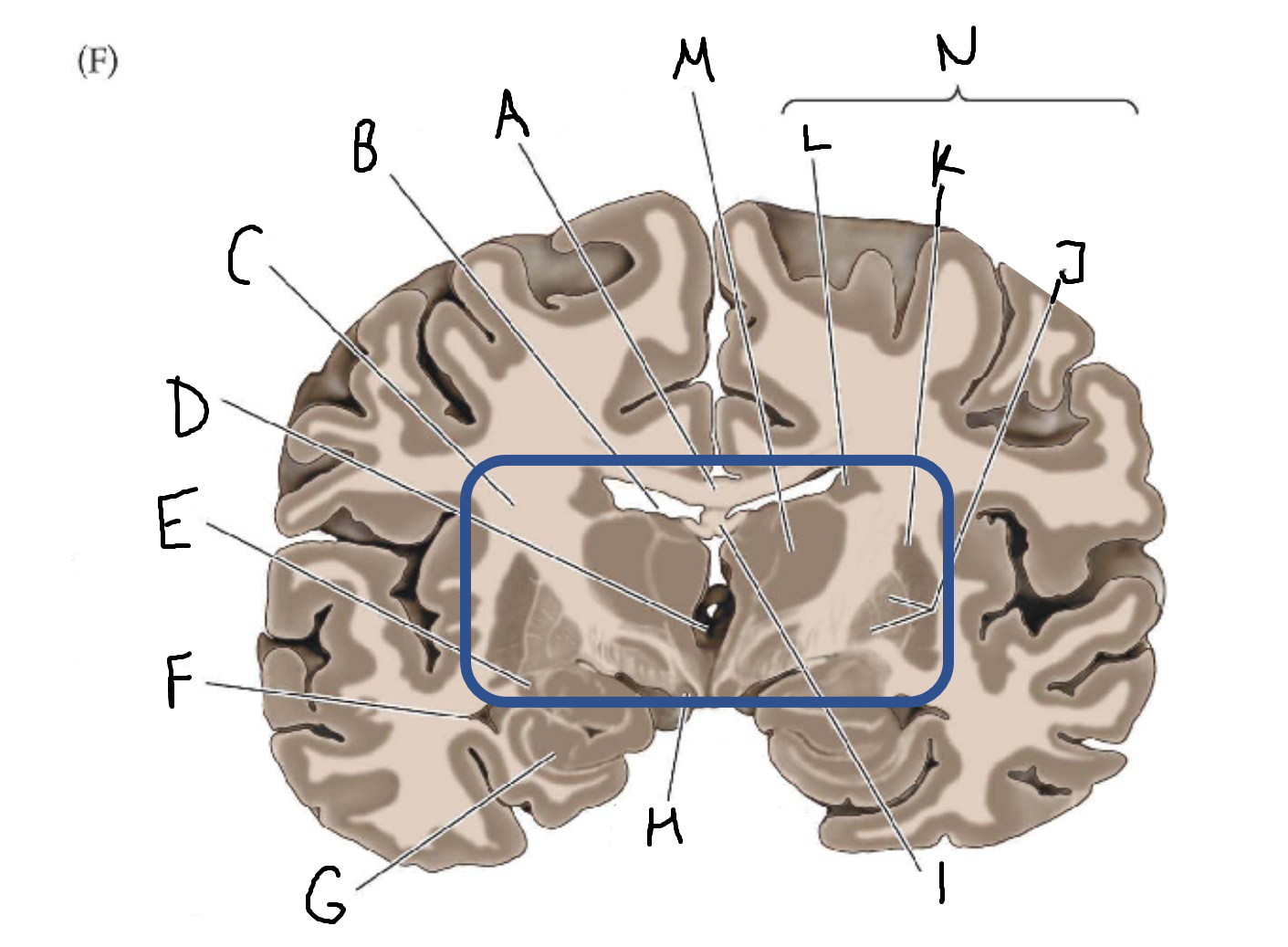
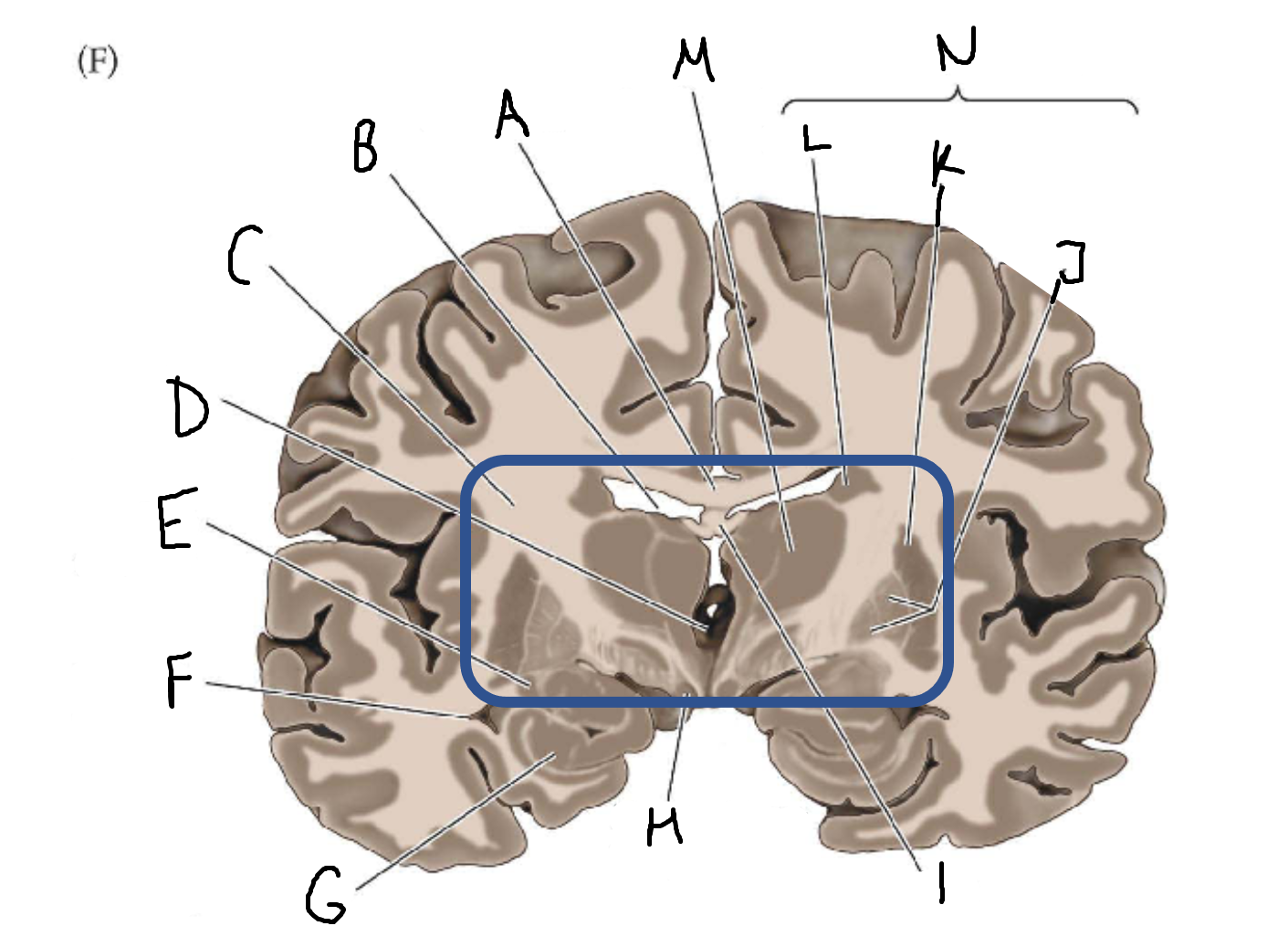
N
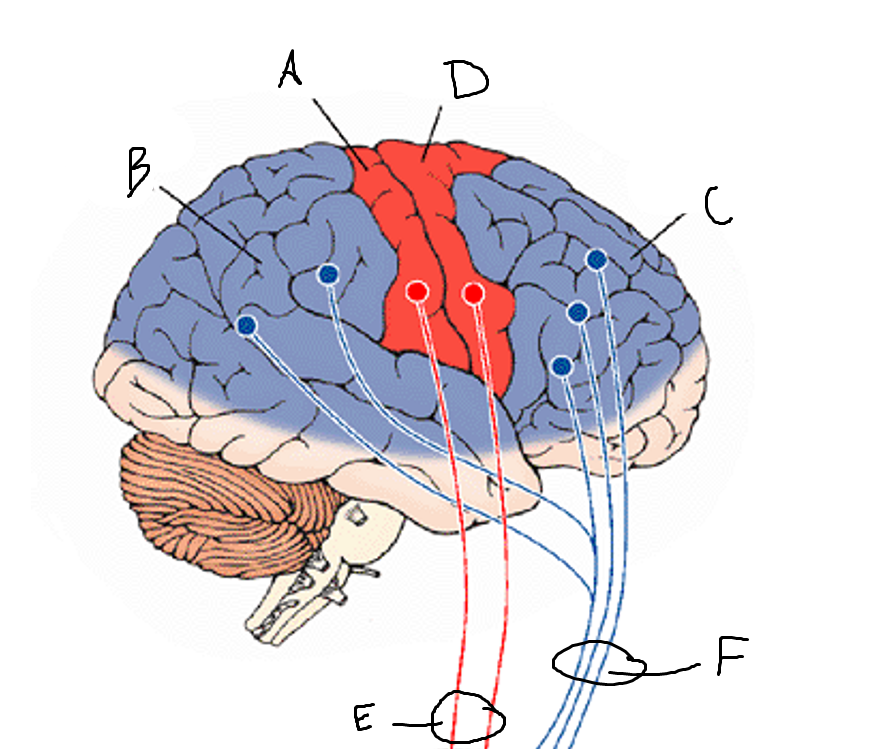
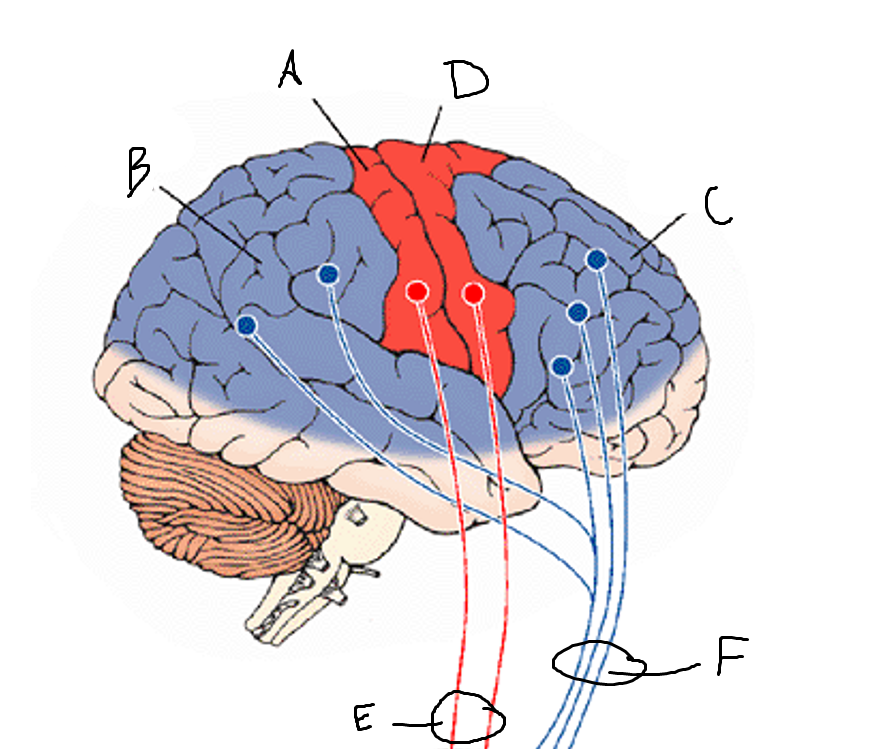
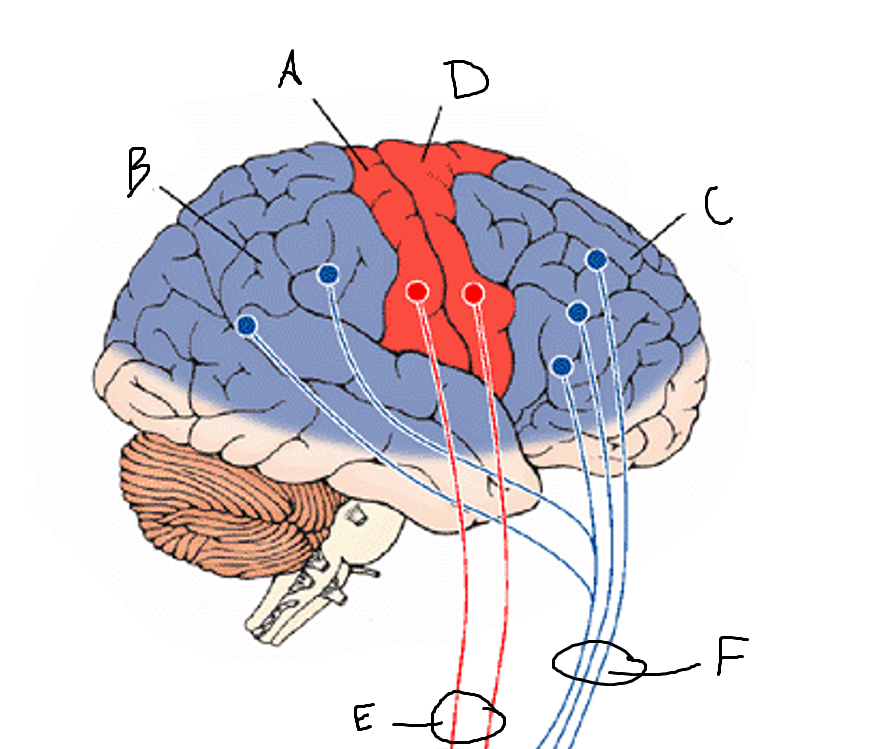
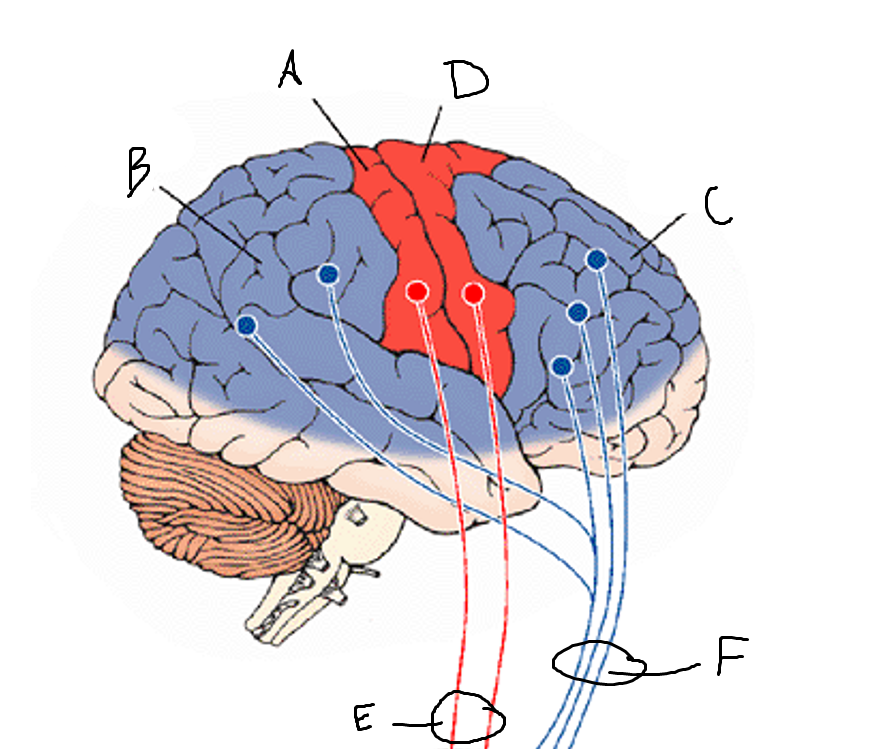
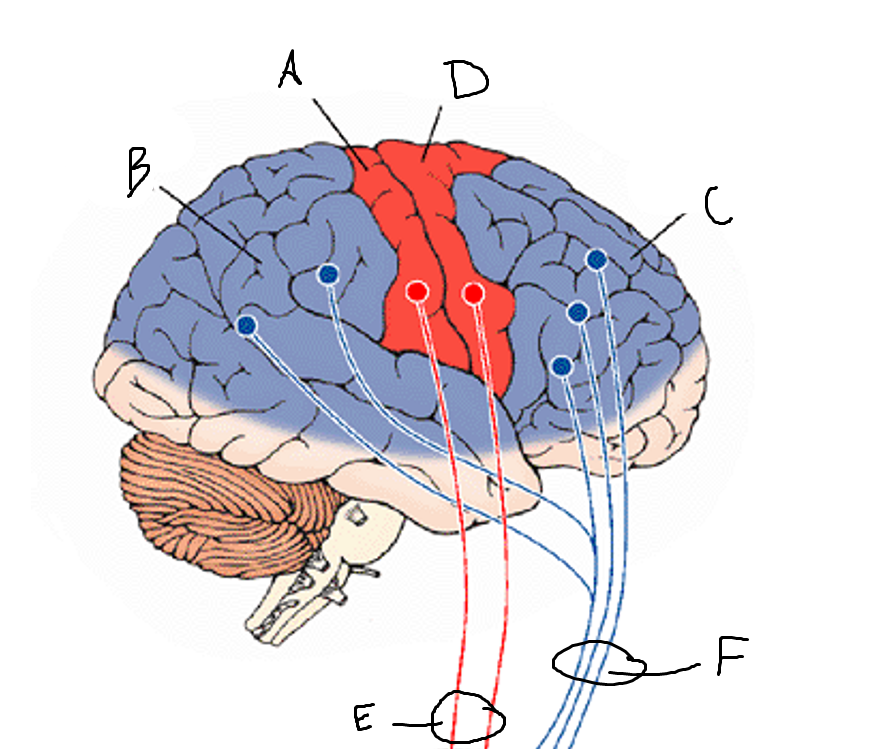
basal ganglia
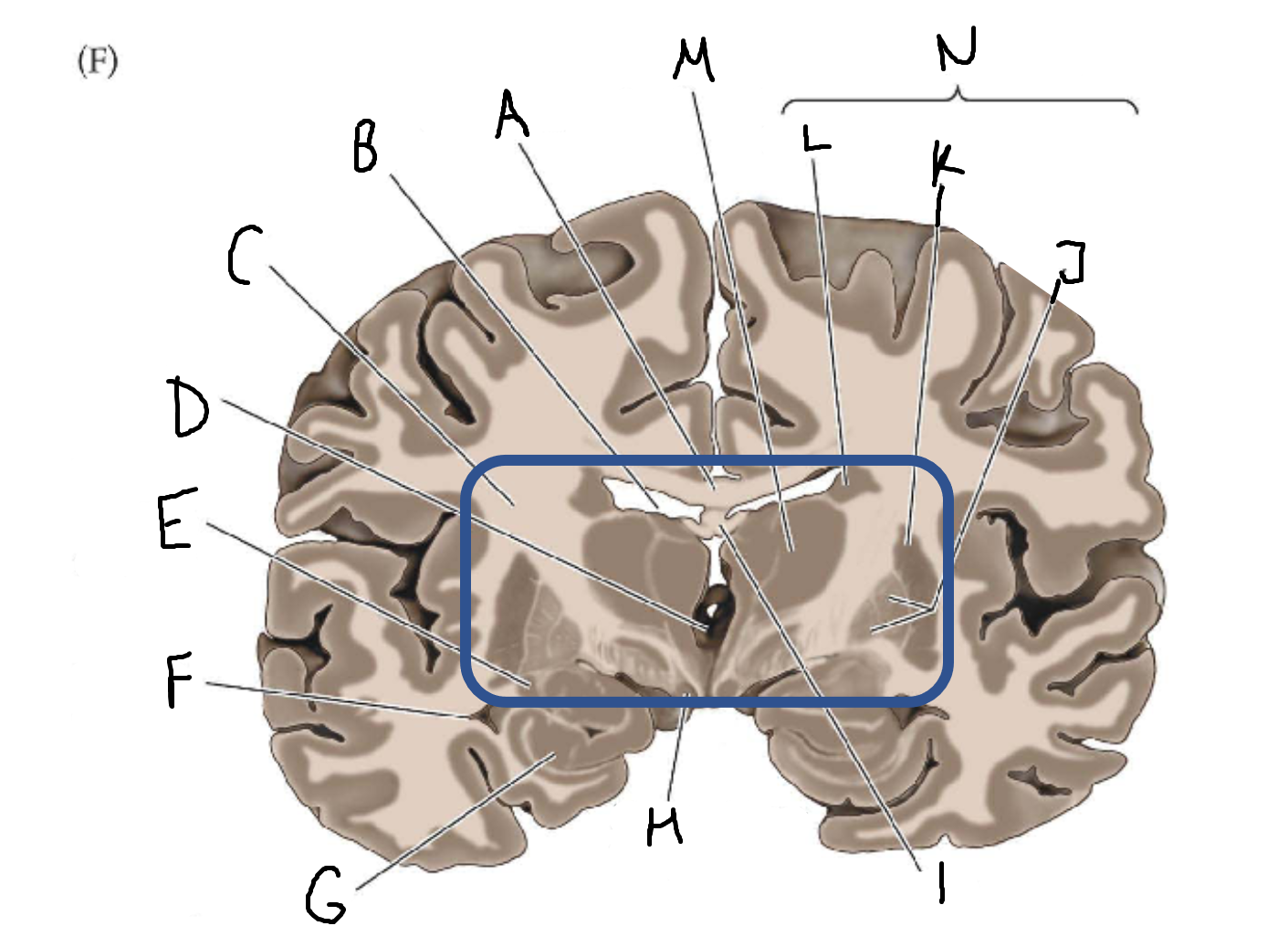
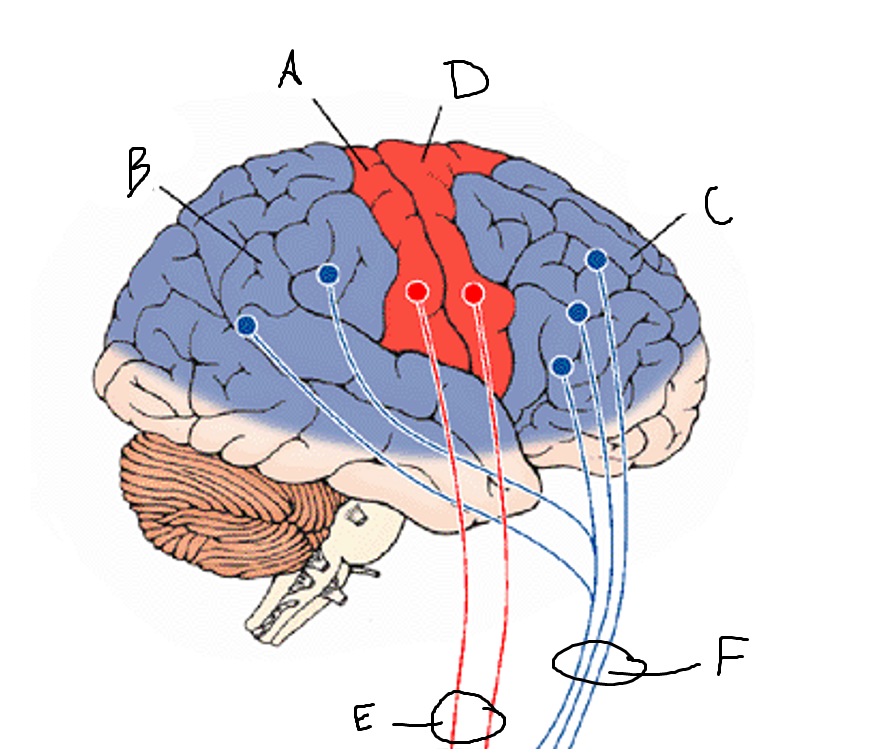
A
somatosensory cortex
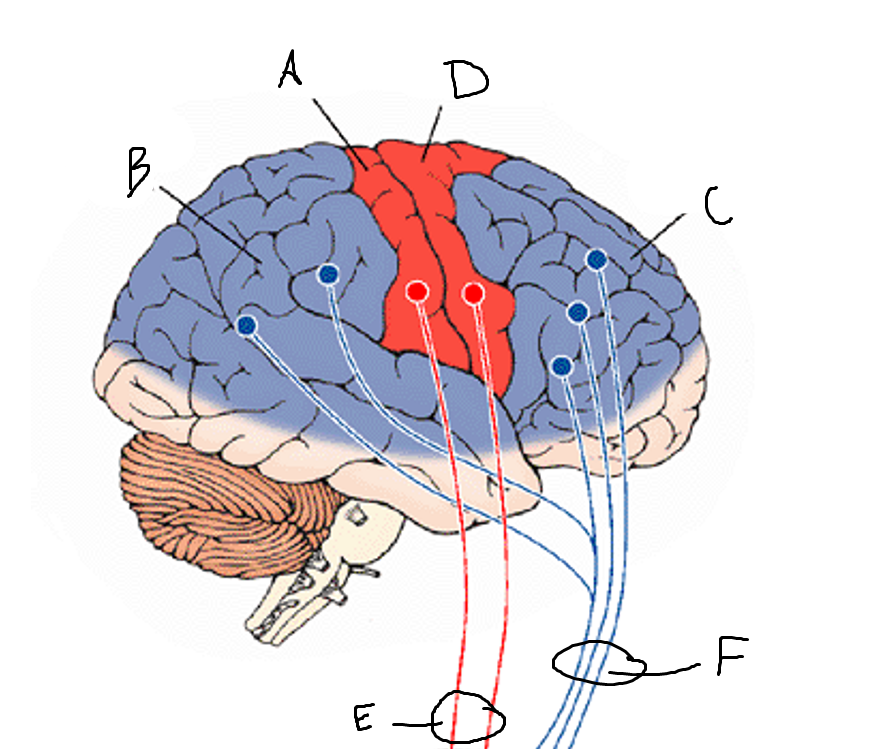
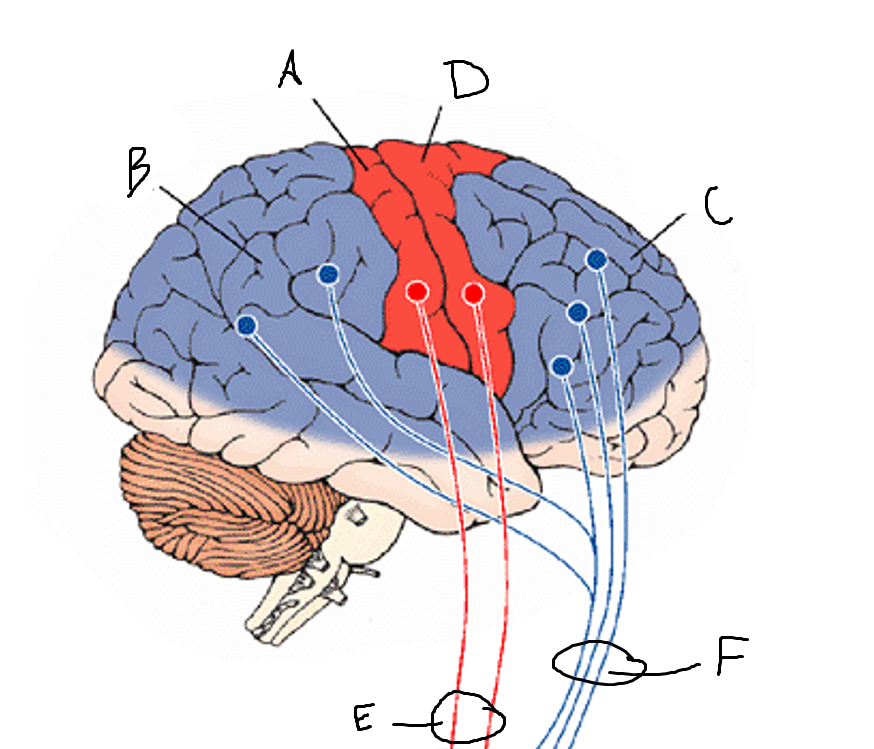
B
parietal association cortex
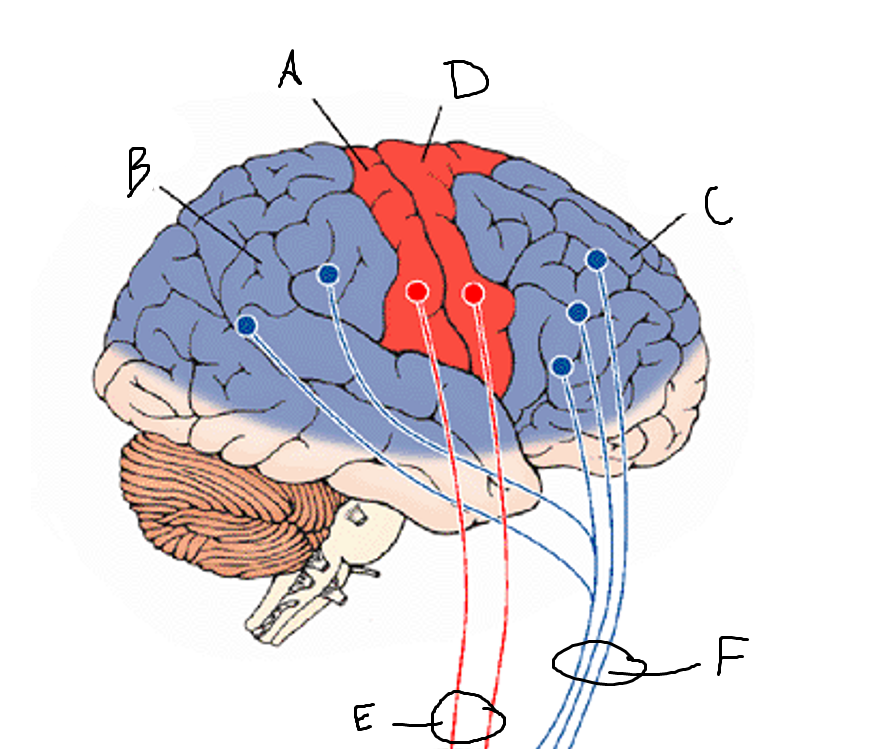
C
frontal and prefrontal cortices
D
primary motor cortex
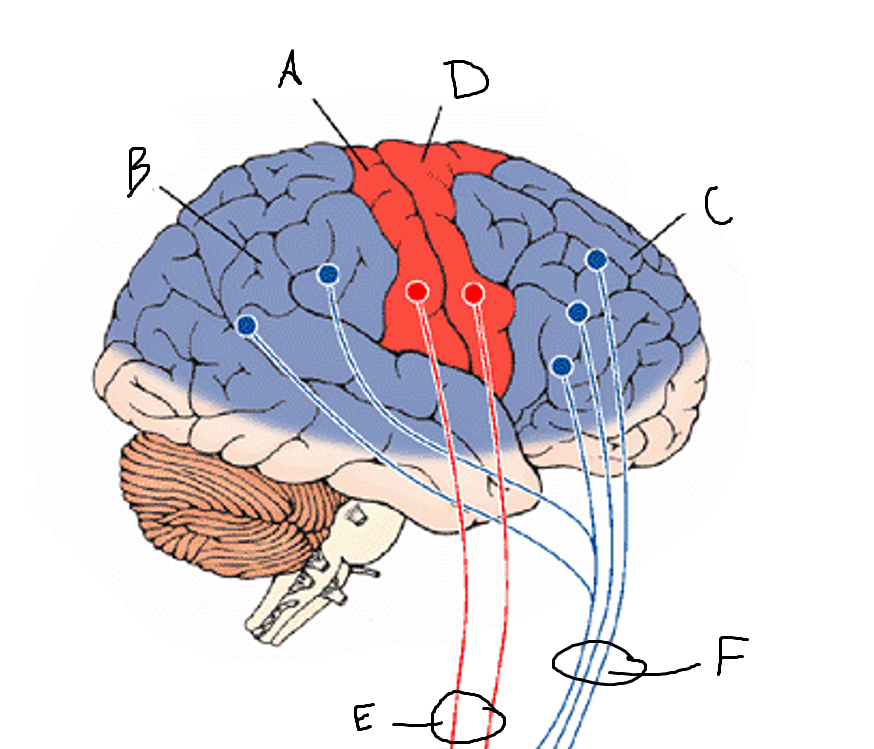
E (where are the projections?)
putamen
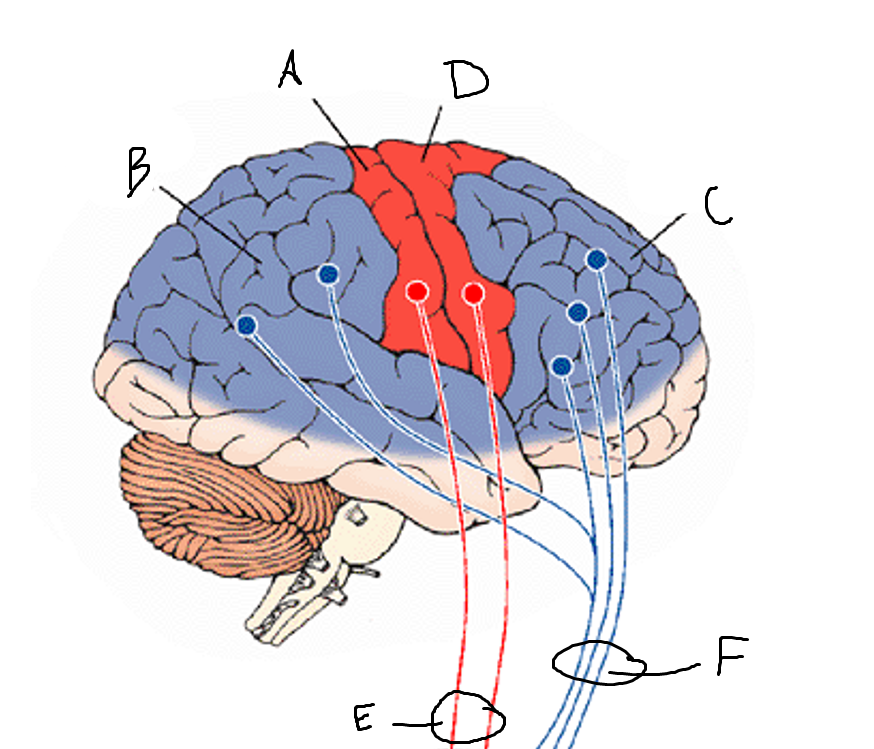
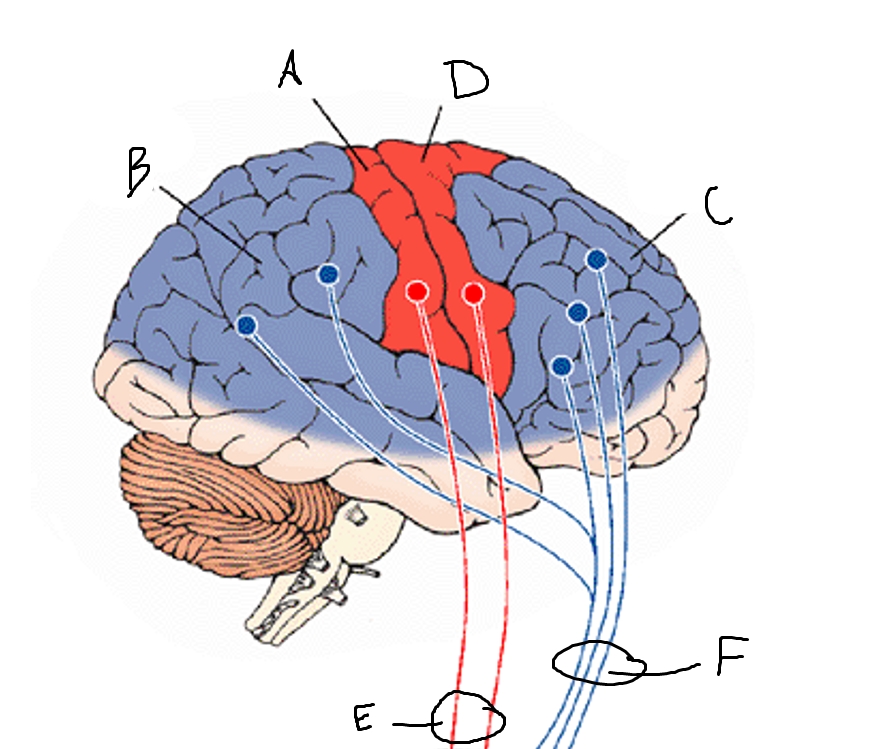
F (where are the projections?)
caudate
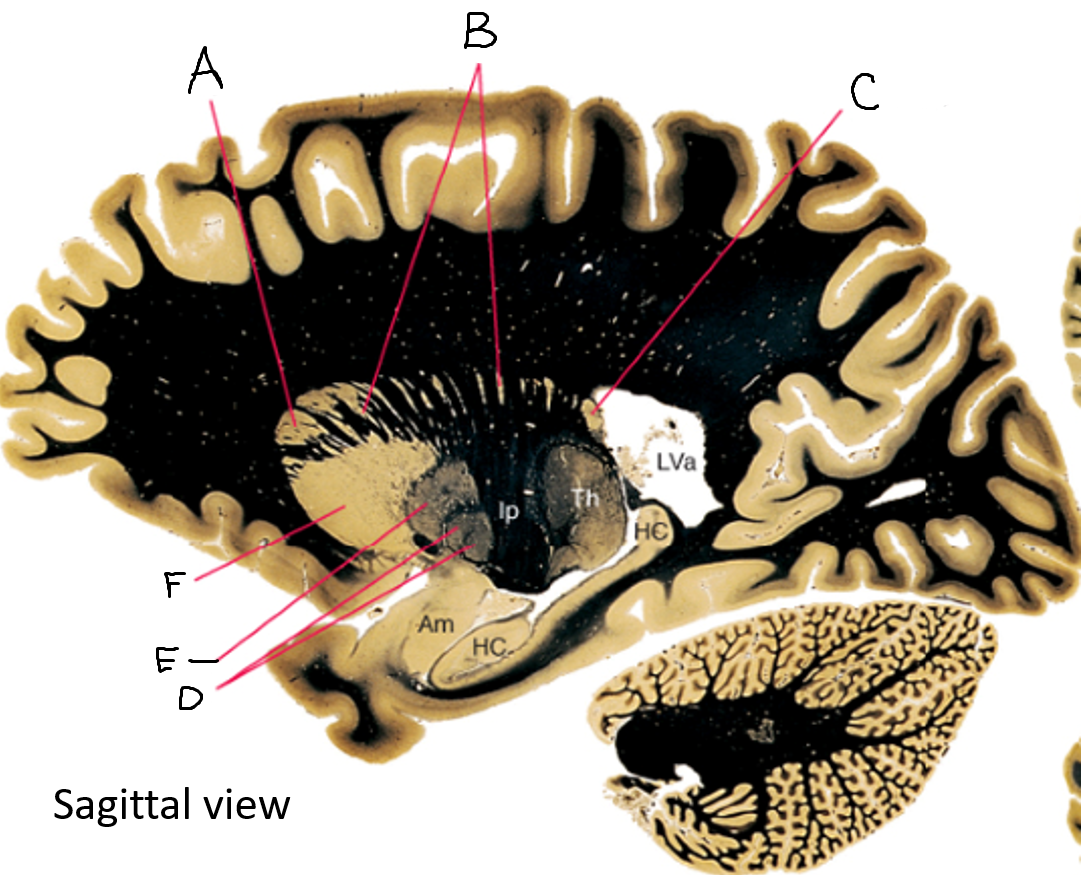
A
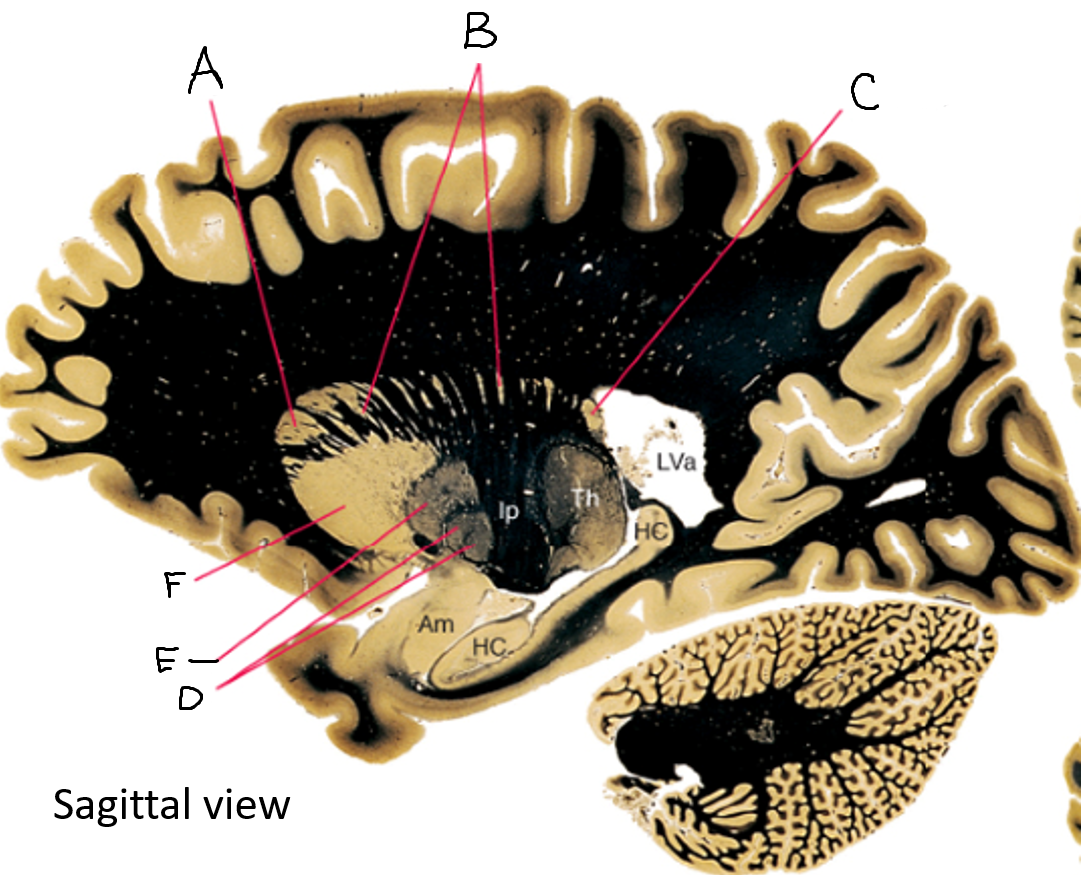
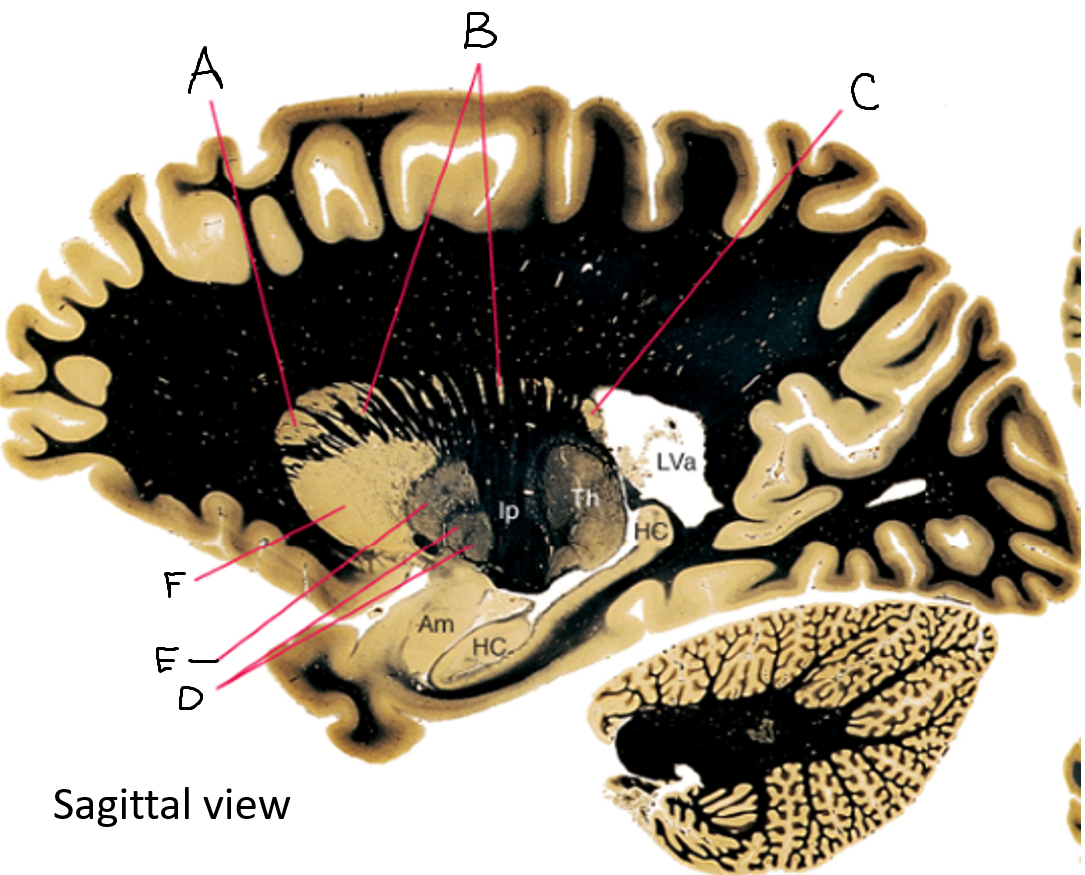
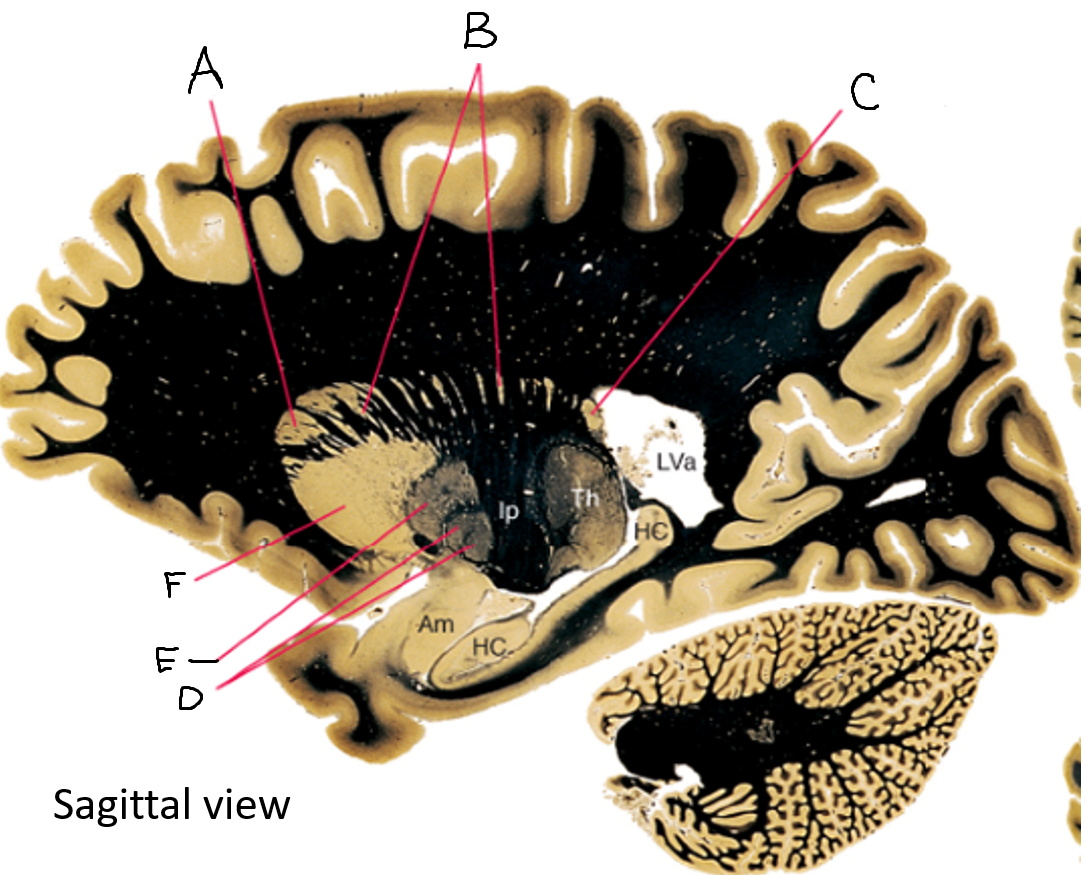
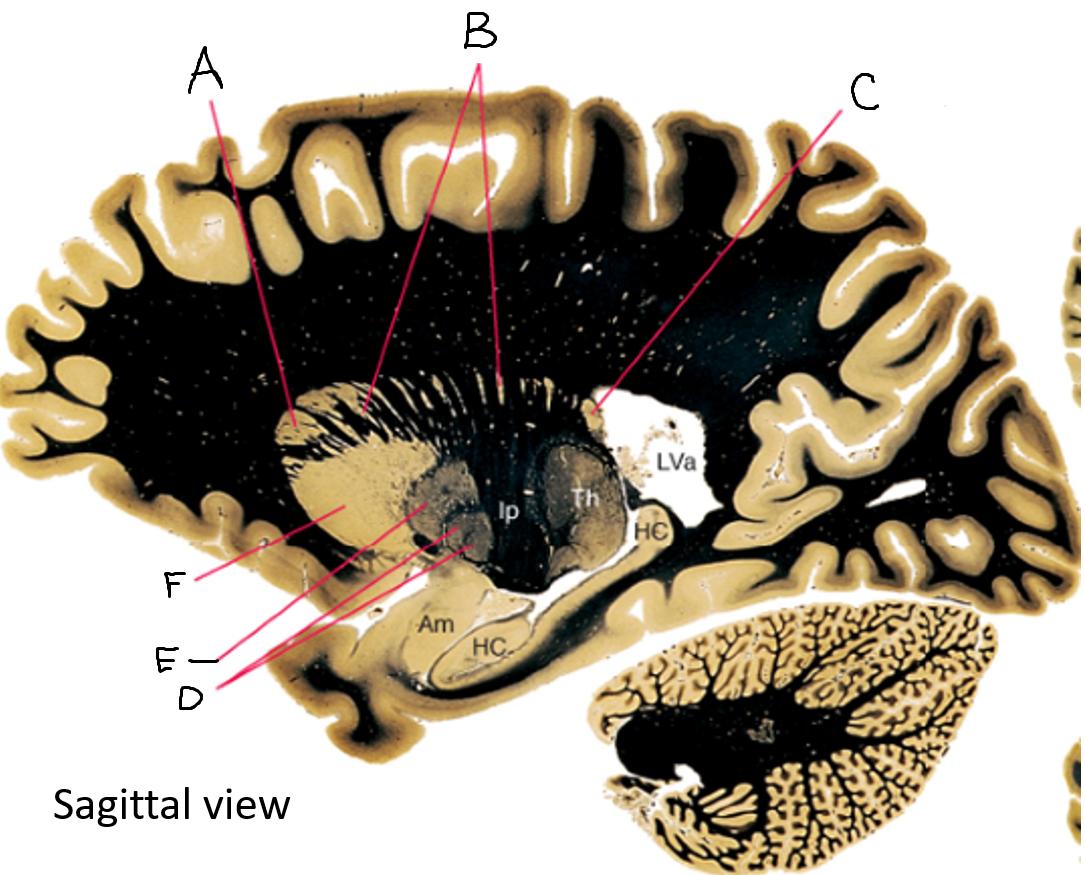
caudate nucleus head
C
caudate tail
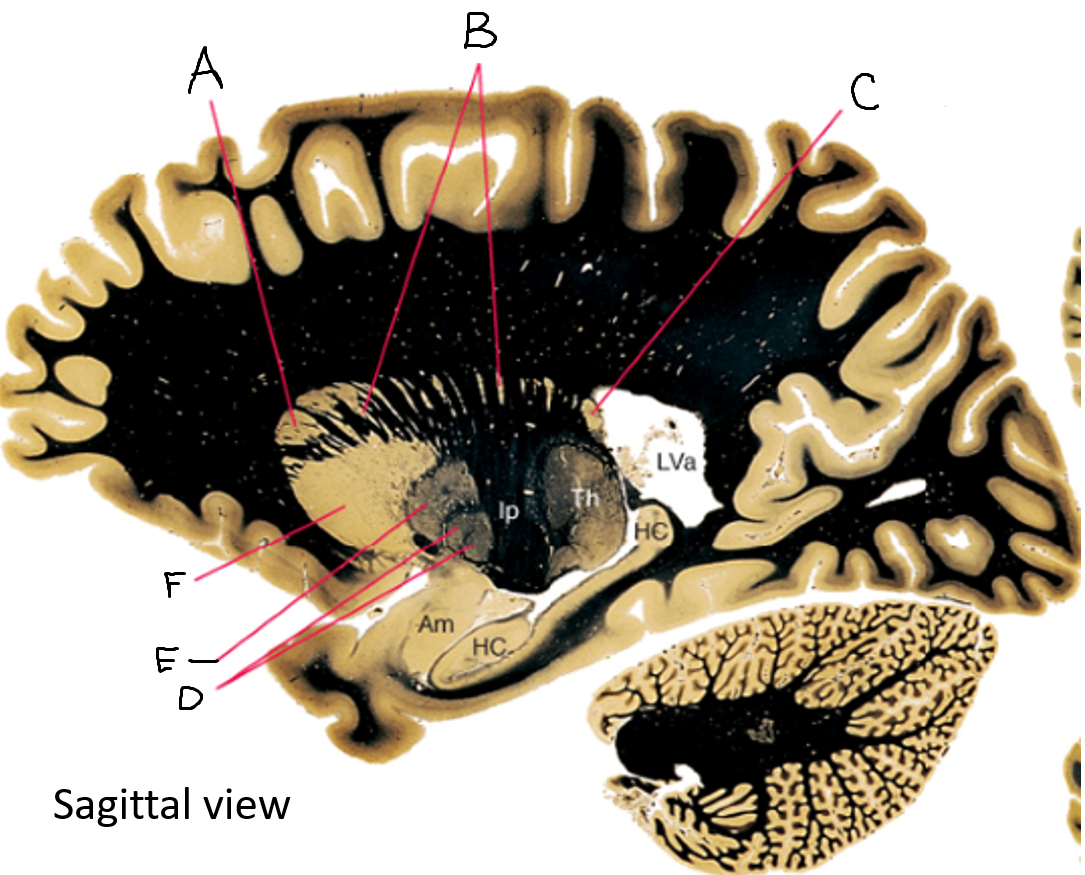
D
globus pallidus (internal segment)
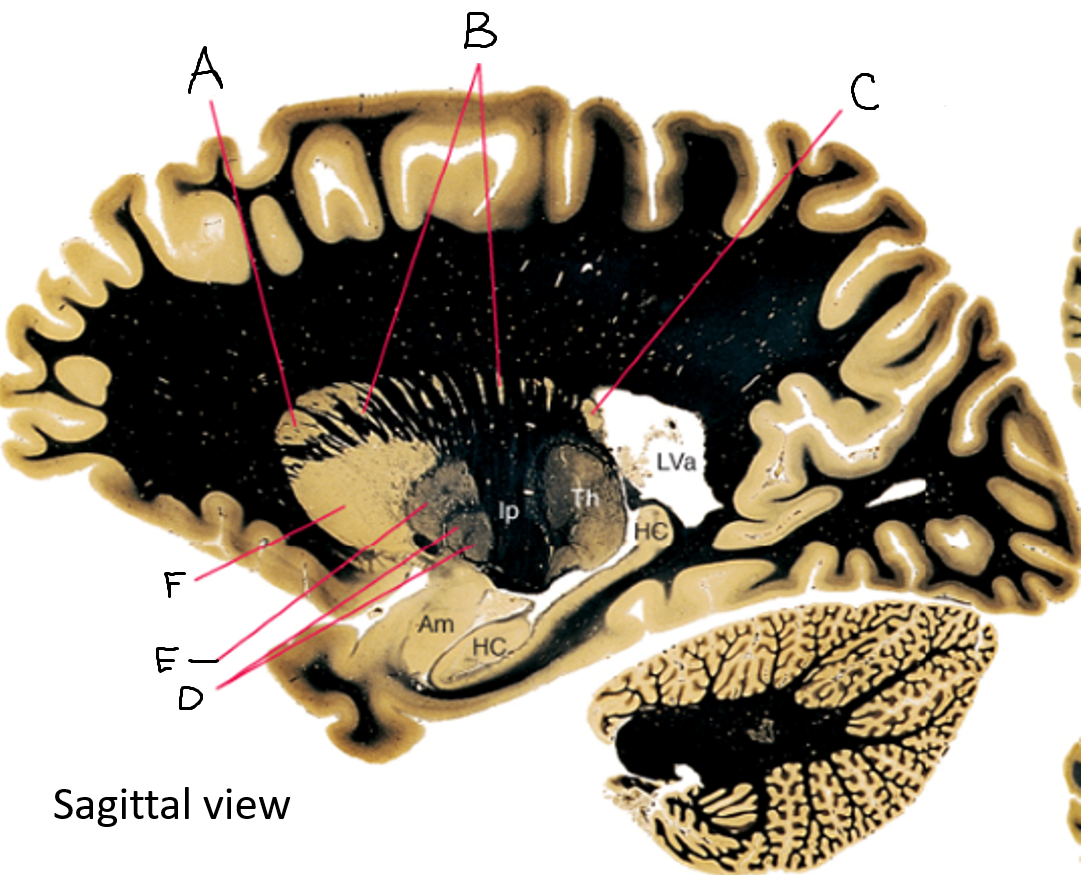
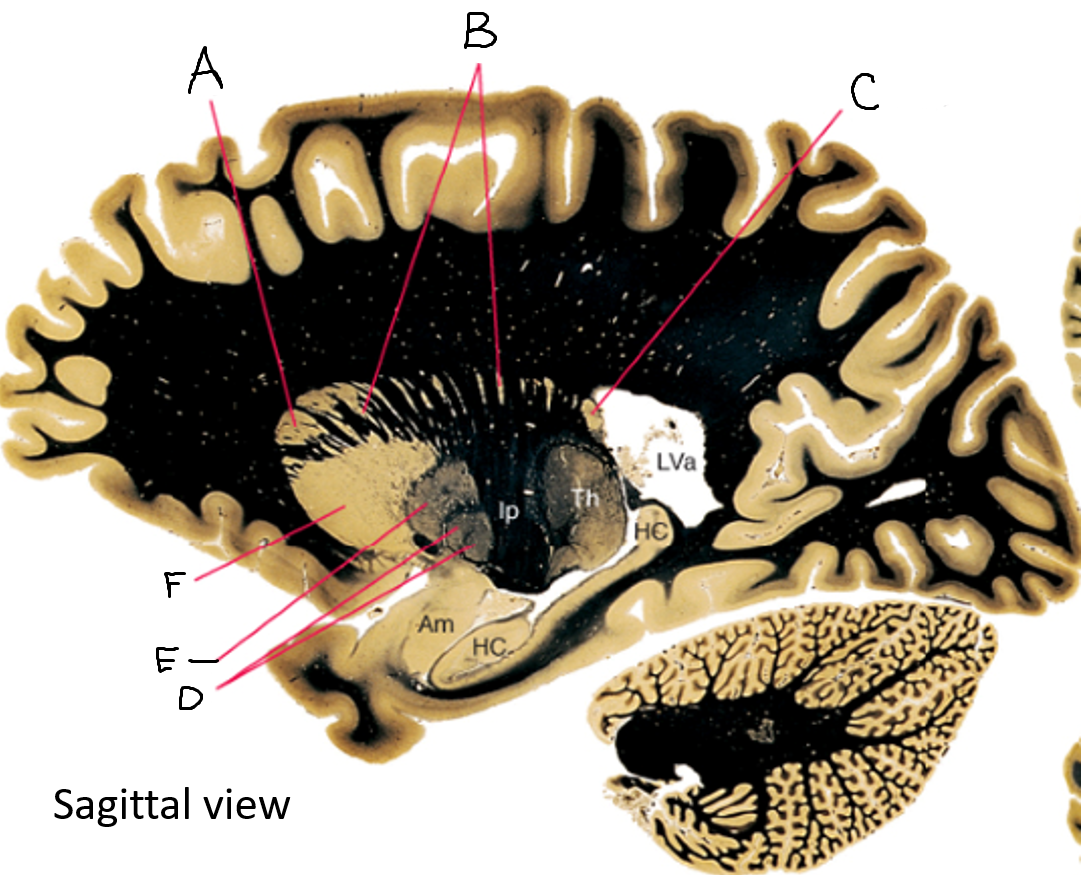
E
globus pallidus (external segment)
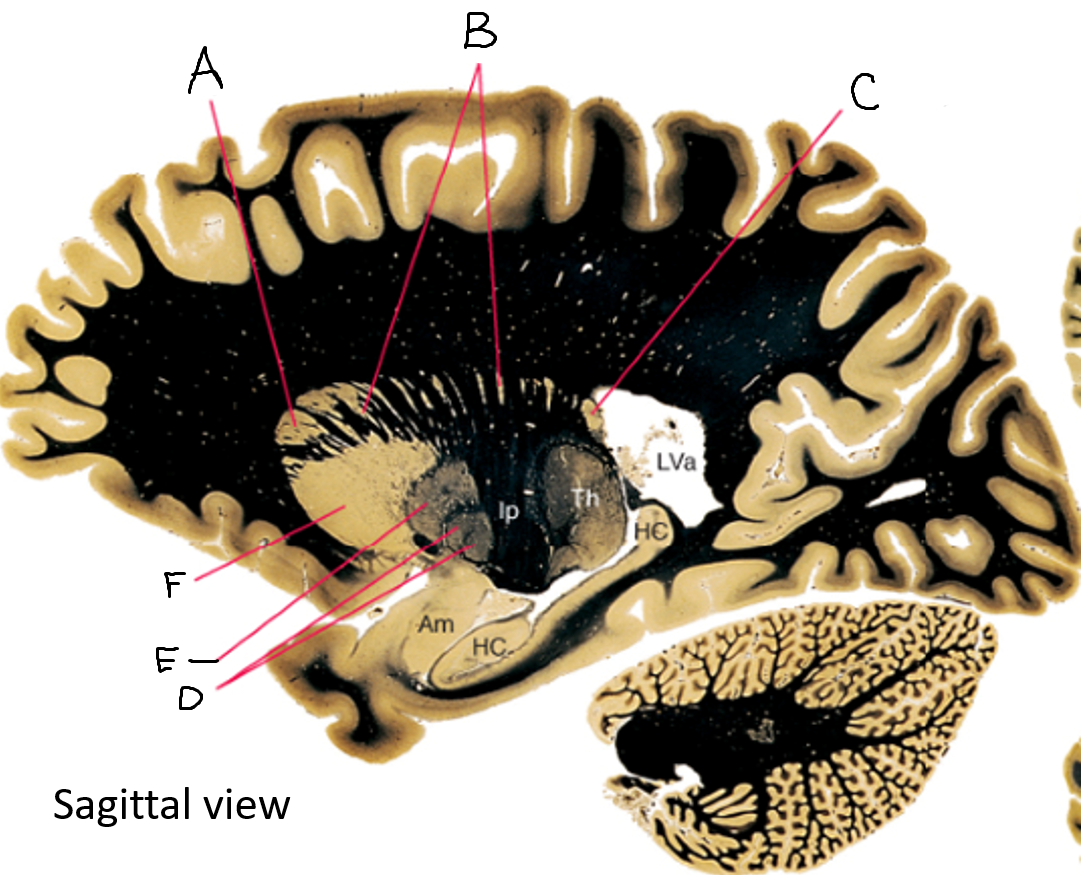
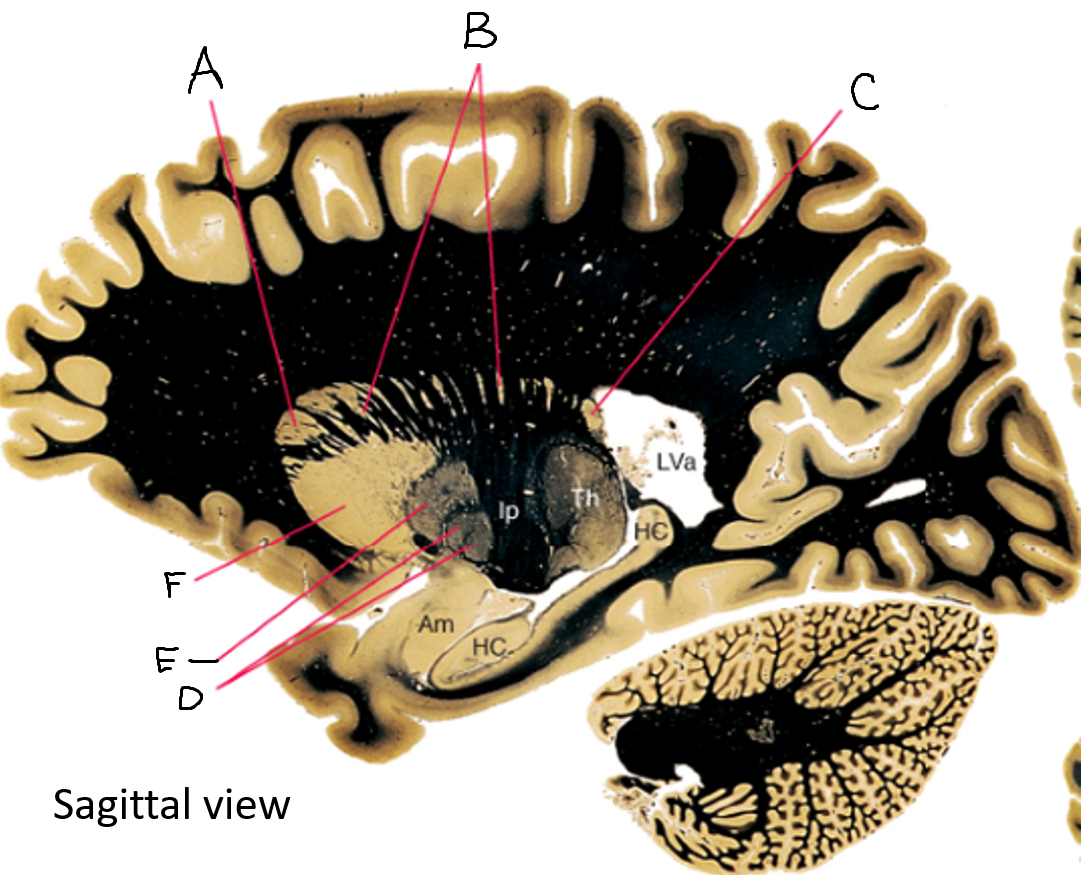
F
putamen
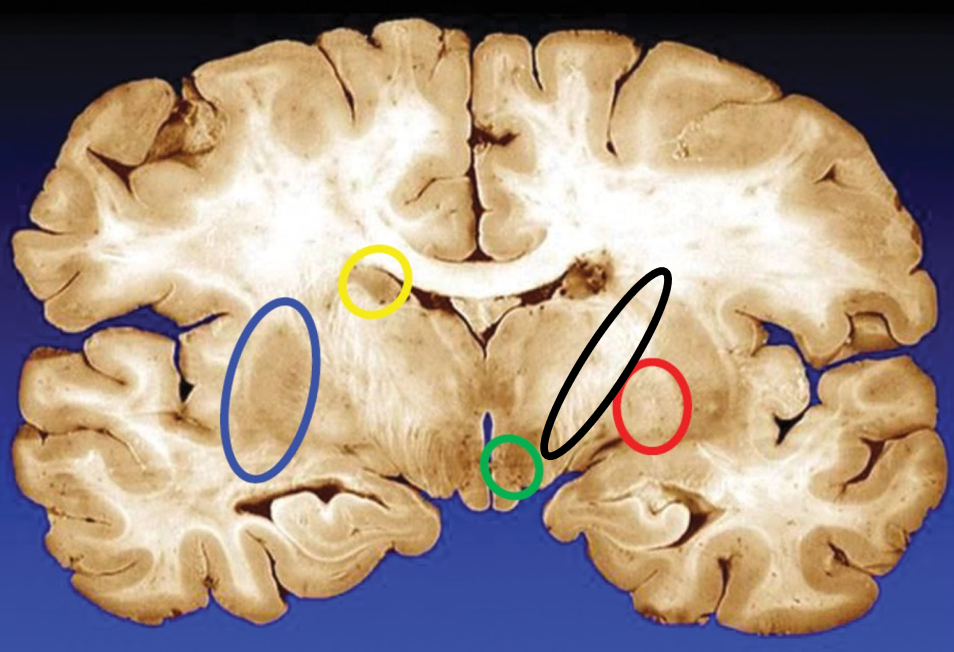
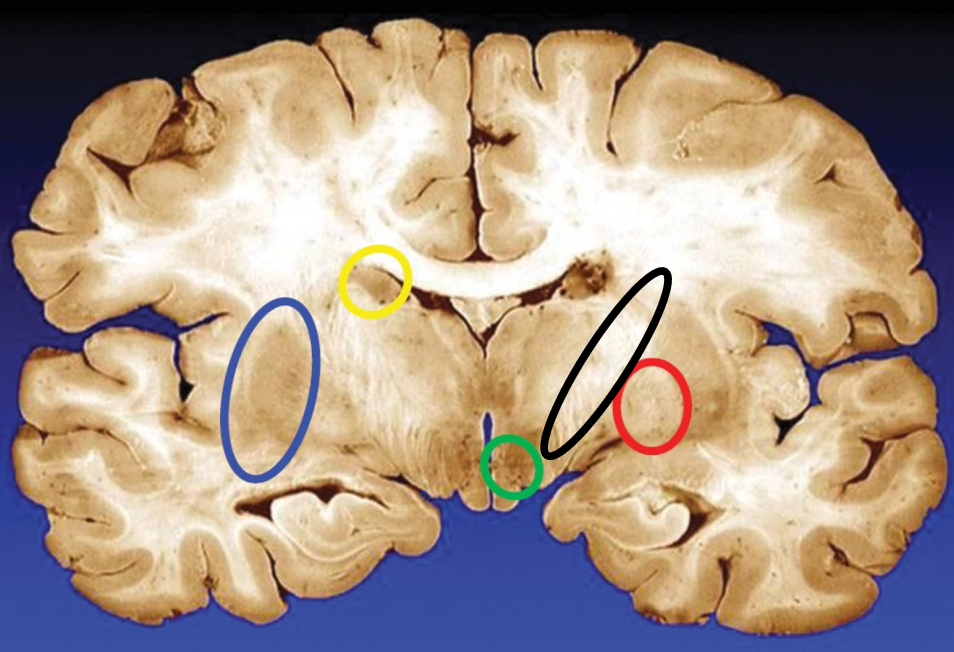
blue
putamen
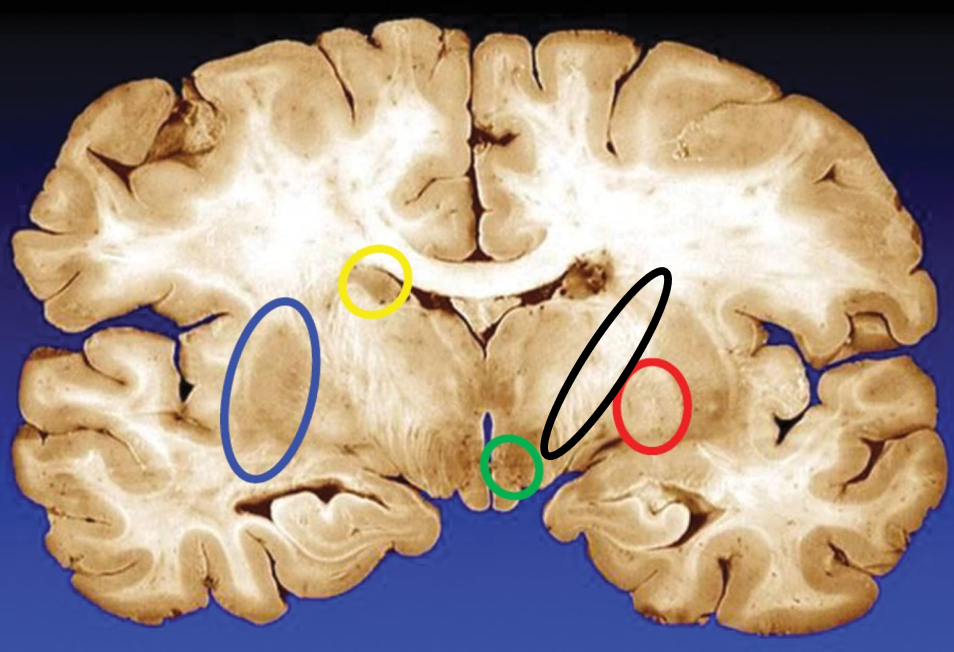
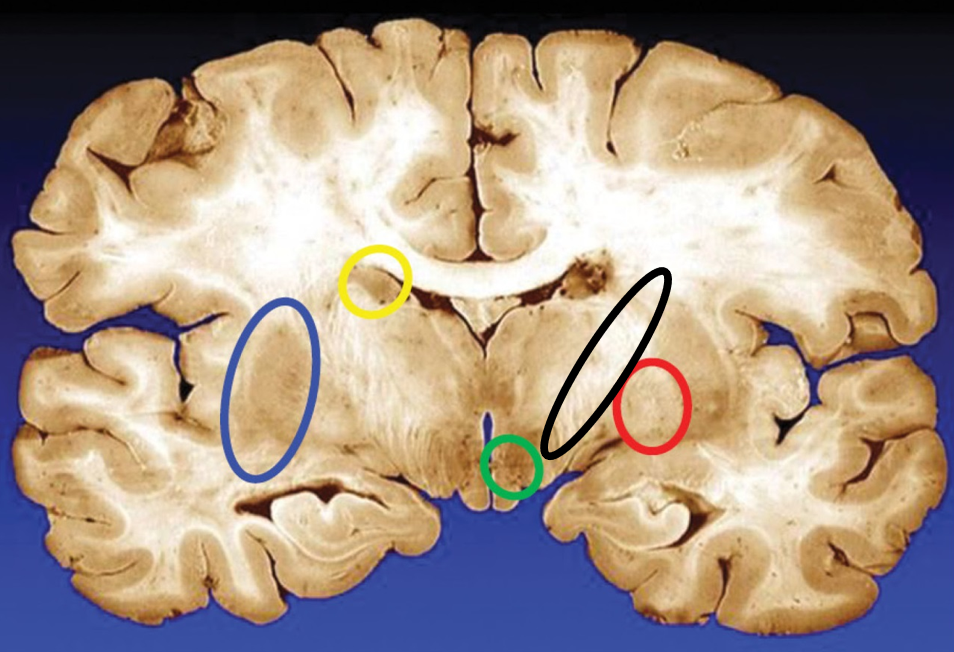
yellow
caudate
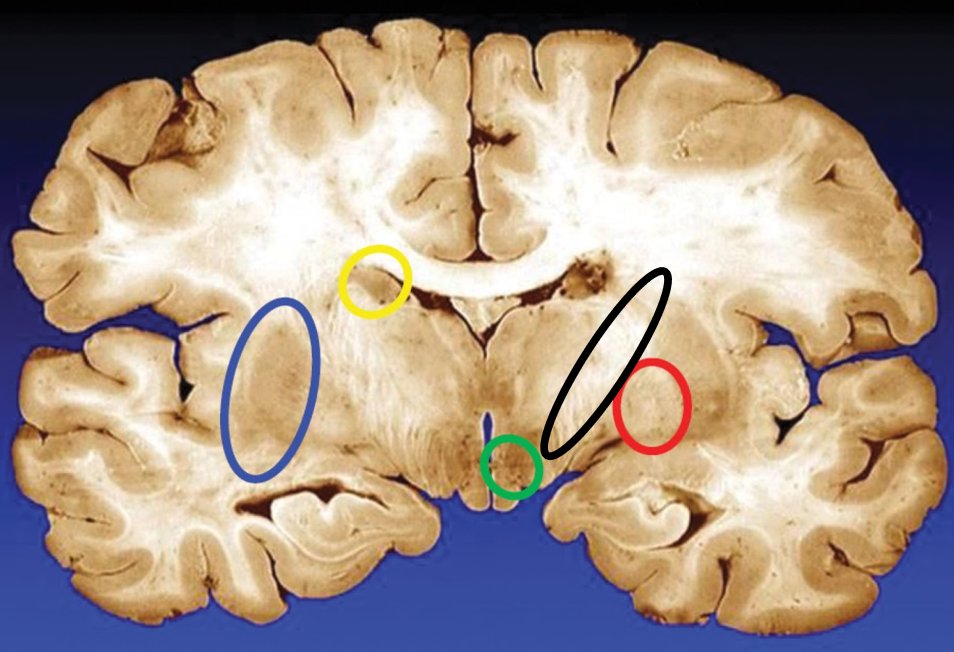
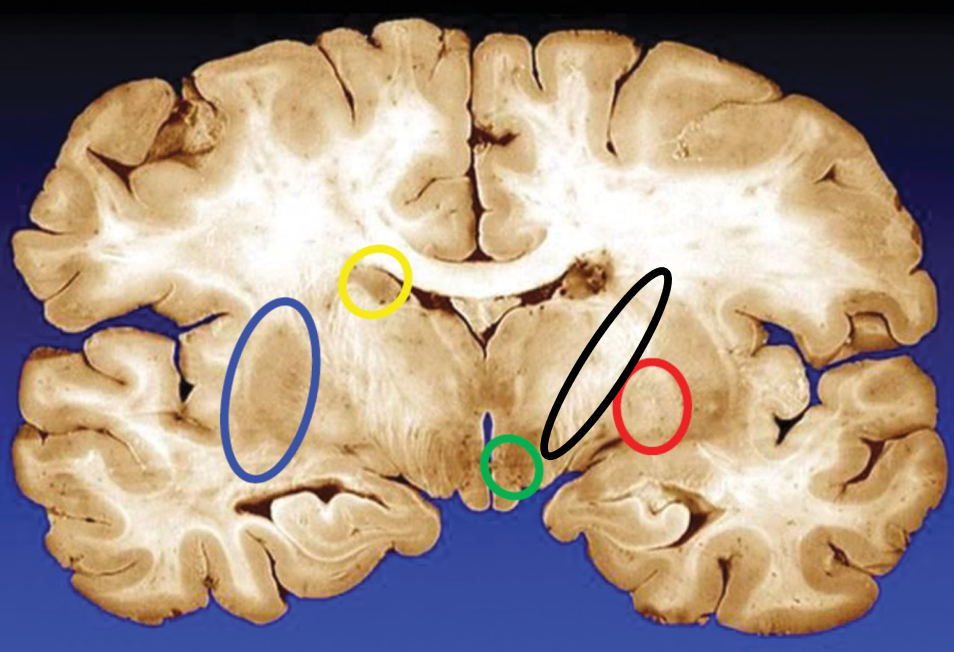
green
subthalamic nuclei
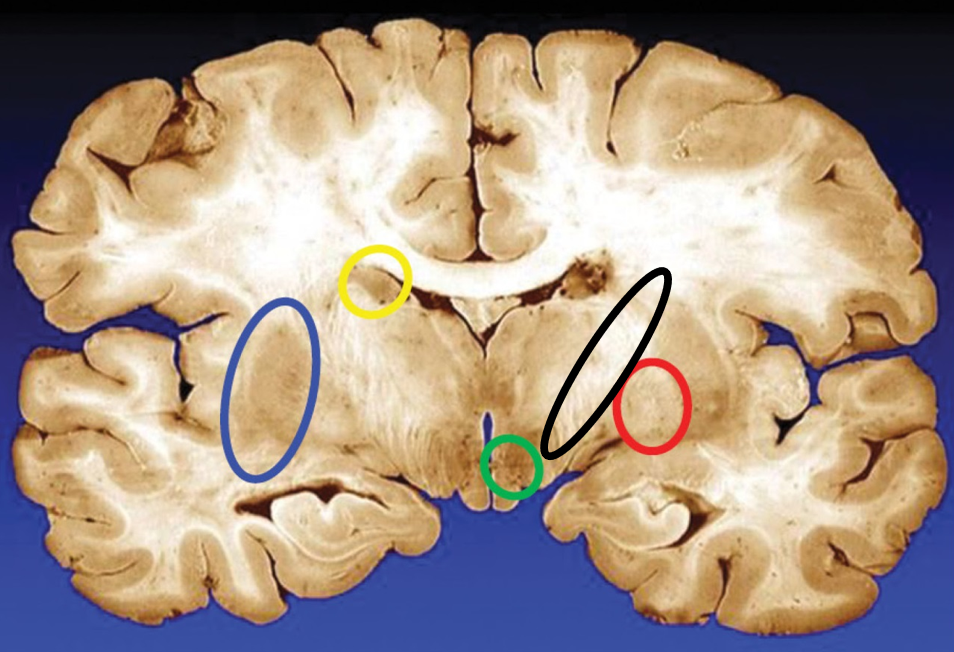
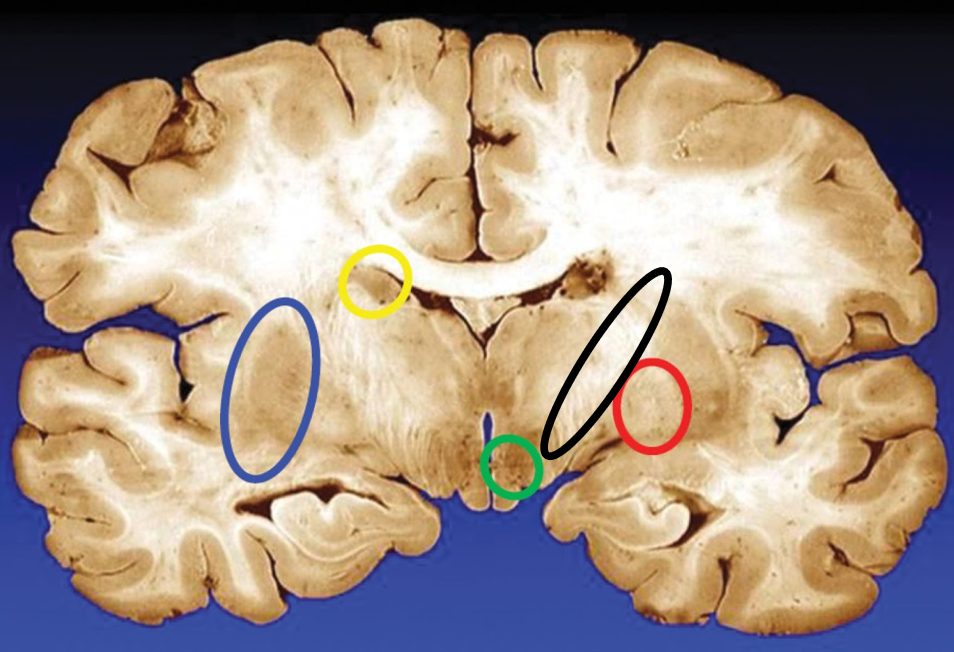
black
internal capsule
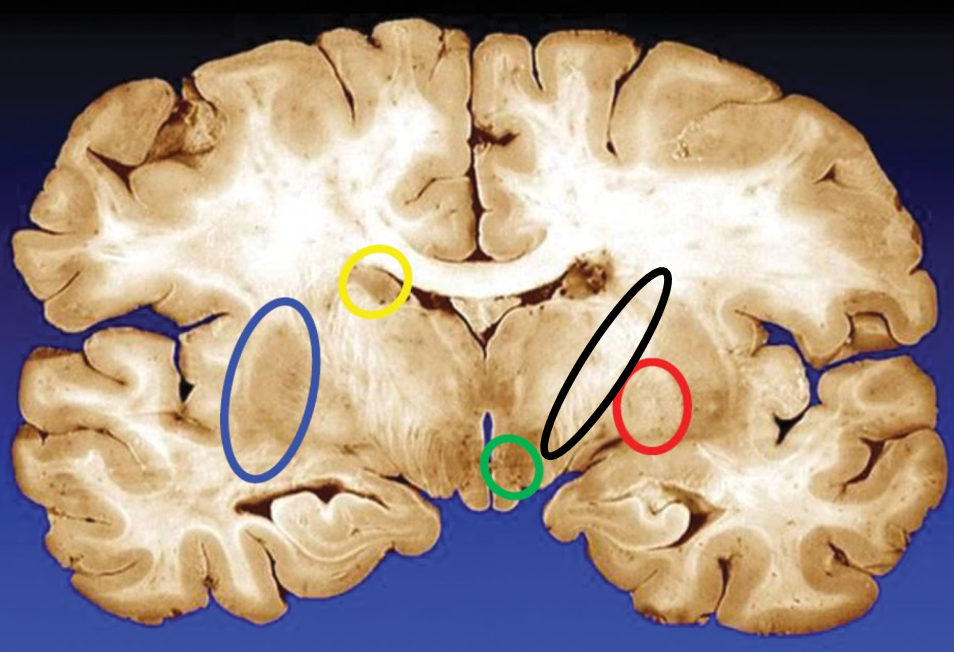
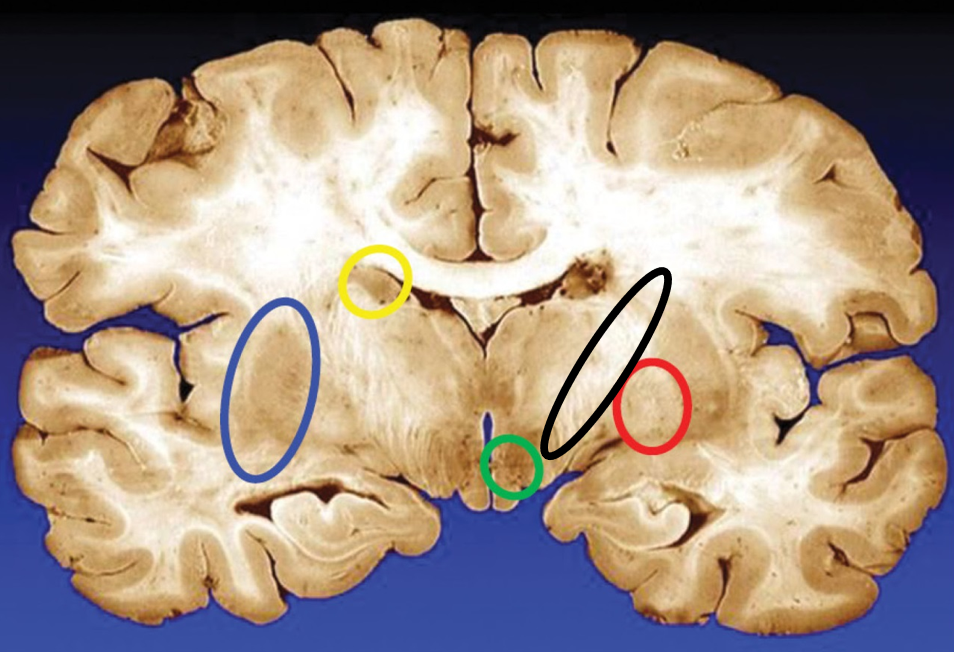
red
globus pallidus
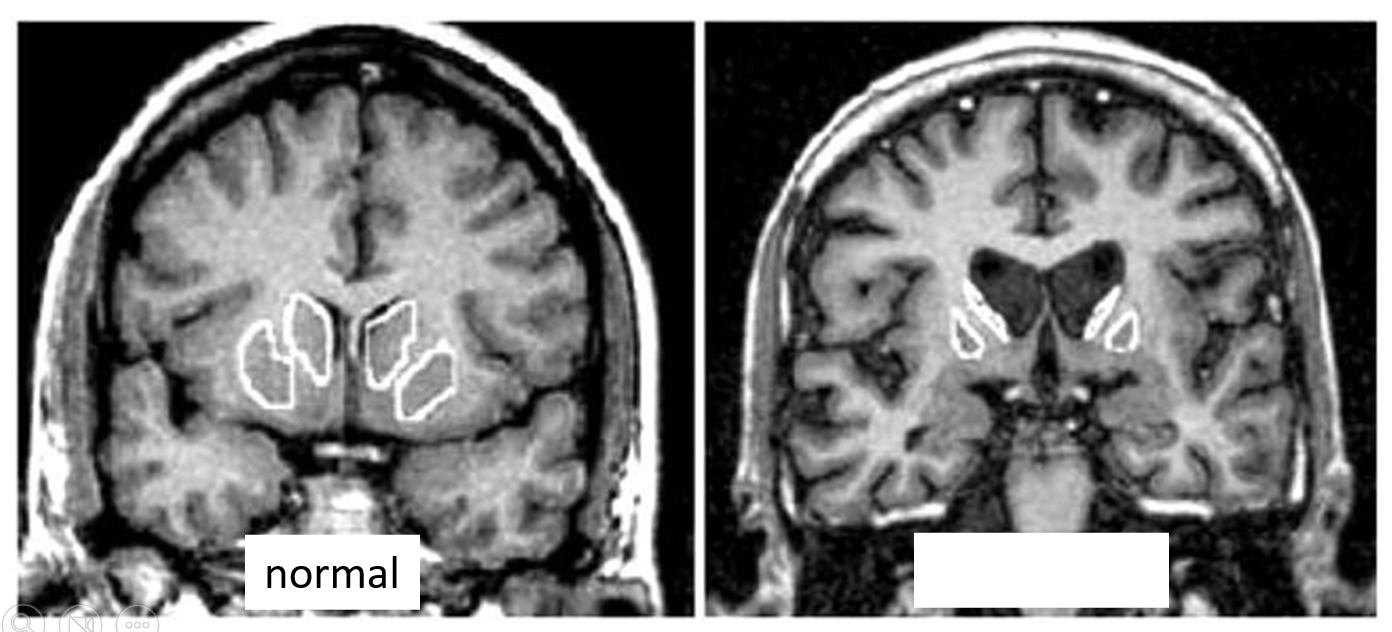
name the condition
Huntington’s (reduced caudate)
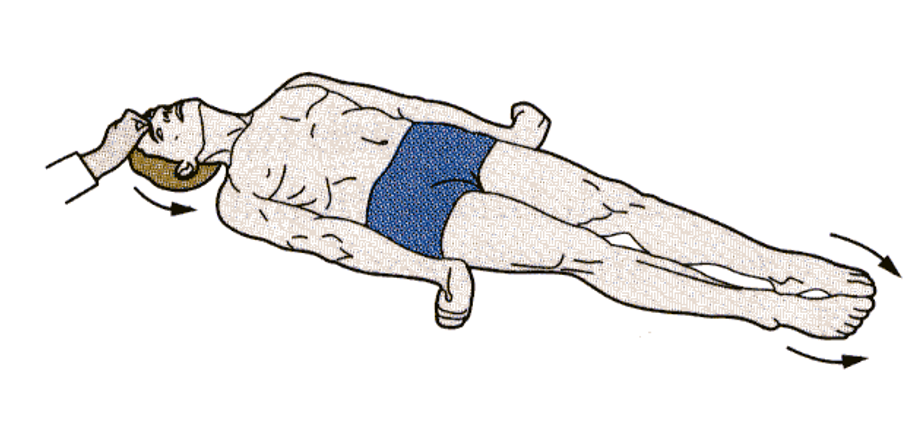
what posturing? which tracts are impaired?
decerebrate posturing. damage to cortex, rubrospinal (midbrain) lost, reticulo intact
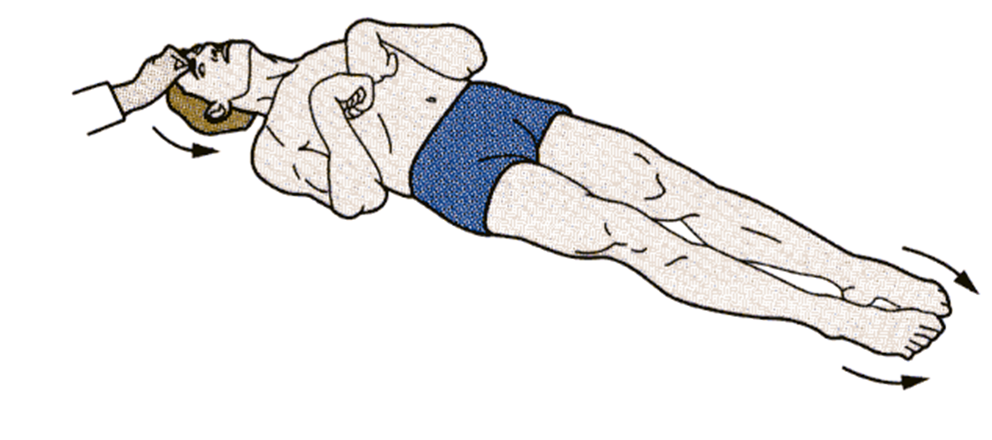
what posturing? which tracks are impaired
decorticate posturing. rubrospinal intact