L2-4 Psychoactive Drugs & Addiction
1/31
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards provide terminology and definitions related to psychoactive drugs and addiction, aimed to facilitate understanding and retention of key concepts from the lecture.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
32 Terms
CT (Computed Tomography)
An imaging technique used to create detailed images of internal structures, often used in diagnosing neuropsychiatric disorders.
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
An imaging technique that uses magnetic fields and radio waves to produce detailed images of the body's tissues and structures.
fMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging)
A type of MRI that measures brain activity by detecting changes associated with blood flow.
PET (Positron Emission Tomography)
An imaging technique that uses small amounts of radioactive material to identify active brain regions.
SPECT (Single Photon Emission Computed Tomography)
A nuclear medicine imaging technique that provides information about blood flow and metabolism of brain tissues.
Serotonin (5-HT)
A neurotransmitter that affects mood, anxiety, and cognition, and is commonly associated with feelings of well-being.
Psychotomimetic Drugs
Substances that can induce symptoms similar to psychosis, including altered perceptions and hallucinations.
drugs that mimic psychosis (hallucinogens + cocaine)
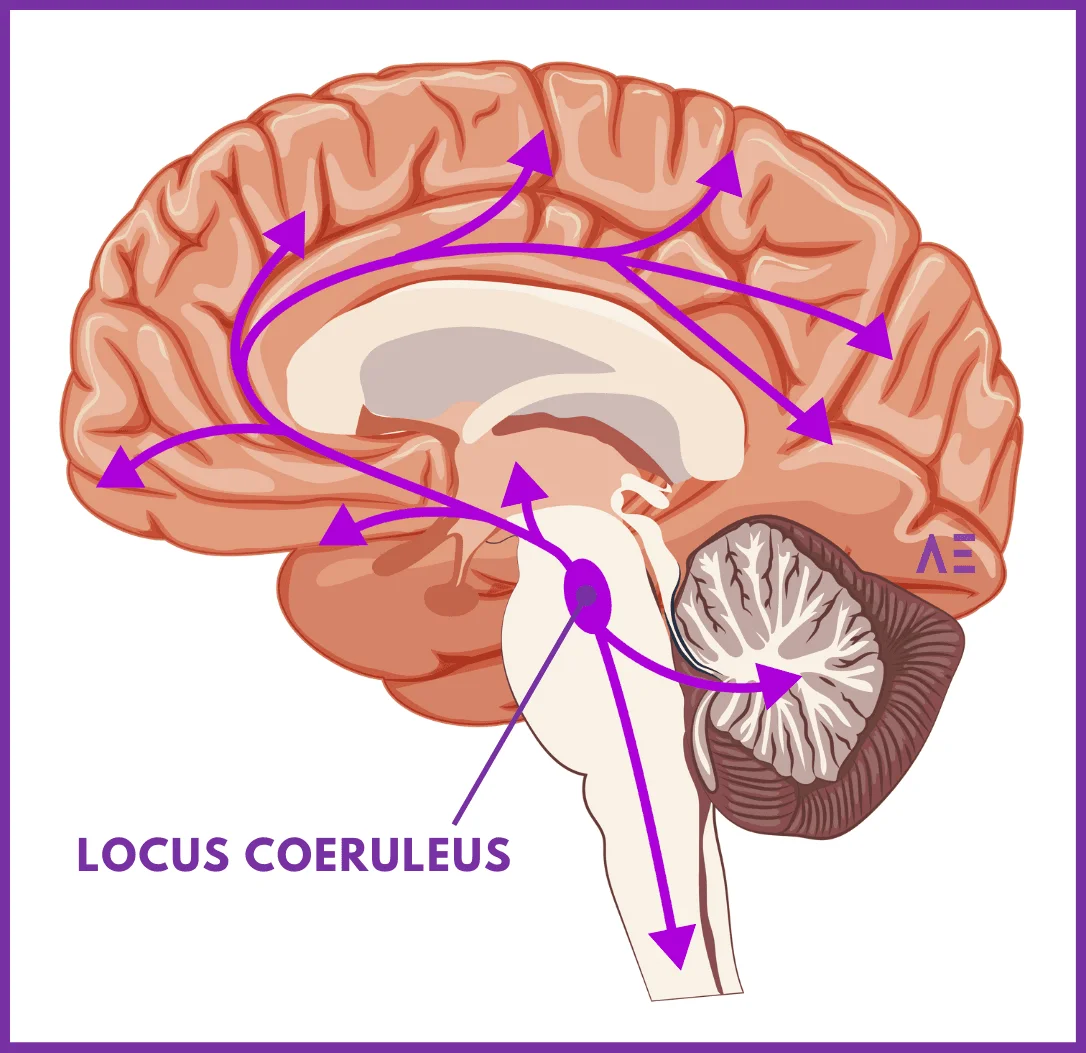
Locus Coeruleus
A small cluster of nuclei in the brainstem
main source of noradrenaline in CNS
involved in physiological responses to stress and panic, arousal and memory
Cocaine
A potent stimulant drug that can lead to increased levels of catecholamines in the synaptic space, contributing to addiction.
Amphetamines
Stimulant drugs that can increase dopamine levels and are often used to treat ADHD and narcolepsy.
Epigenetic Therapy
Treatments that aim to modify gene expression through external factors (diet, behaviour) without changing the DNA sequence, potentially useful in addiction treatment.
Neuroadaptive Changes
Alterations in the brain's structure and function that occur as a response to chronic drug use, contributing to addiction. eg. tolerance
Reward Pathway
A brain circuit that reinforces behaviors through the release of neurotransmitters like dopamine, often involved in addiction.
Longitudinal Studies
Research studies that follow the same subjects over a period of time to assess changes and long-term effects.
Genetic Analysis
The examination of genetic changes that may increase the risk of developing certain diseases or conditions.
ayahuasca active ingredient
harmaline
peyote active ingredient
mescaline
magic mushroom active ingredient
psilocybin → psilocyn
LSD
vasoconstricting agent by ergot alkaloids
acts as agonist of brain 5-HT receptors
how LSD affects dorsal raphe neurons
LSD DECREASES firing rate of raphe neurons (5-HT1A receptors)
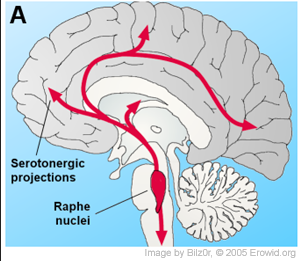
dorsal raphe
serotonergic neurons that send extensive projections to the forebrain
how LSD affects locus coeruleus
LSD INCREASES activity in locus coeruleus neurons
what layer of pyramidal neurons does LSD increase the activity of?
layer V
reward pathway (circuit)
involves dompaine axons in VTA of medial forebrain bundle with axons that project to nucleus accumbens in cortical forebrain
spiroperidol
antipsychotic that blocks reinforcement system
dopamine receptor antagonist
medial forebrain bundle
A collection of axons that connect VTA in midbrain to NAC in forebrain cortex
reinforcement system and reward pathways
includes:
5-HT axons from raphe neurons
noradrenergic axons from locus coeruleus neurons
dopaminergic axons from VTA
how does cocaine work
blocks voltage-gated sodium channels
binds to monoamine transporter on presynaptic terminal
prevents recycling of catecholamines (dopamine)
therefore increased levels of catecholamines in synaptic space
lisdexamfetamine
prodrug. blocks reuptake of dopamine and norepinephrine, increasing their release
Dorsal Raphe Nucleus vs Locus Coeruleus
DRN → serotonin
LC → noradrenaline
Alterations in the DRN are implicated in depression.
limits of researching on humans
brain is inaccessible
diverse patient group
varying neuropsychiatric disorders
genetics, environment, life experiences, risks etc affect patient group that is difficult to control
paired pulse inhibition
dampening of response to second stimulus
less PPI in Scz patients
cross tolerance
tolerance towards LSD also leads to tolerance to mescaline
they target same receptor
LSD decreases raphe firing rate
mescaline does not affect dorsal raphe neuron firing