Leopold's Maneuver
1/92
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
93 Terms
Leopold's Maneuver
are a systematic method of observation and palpation to estimate fetal size, locate parts, and determine presentation, position, lie, engagement and attitude
estimate fetal size
locate parts
determine (PPLEA)
presentation
position
lie
engagement
attitude
what will you observe and palpate during leopold maneuver
gravidity
means pregnancy
gravida
woman who is pregnant
primigravida
woman who is pregnant for the first time
multigravida
woman who has had 2 or more pregnancies
nulligravida
woman who has never been pregnant
parity
refers to number of pregnancies in which the fetus or fetuses have reached 20 wks of gestation when they are born, not the number of fetuses, whether it is born alive or is stillborn
primipara
woman who have complete one pregnancy who have reached 20 wks of gestation
multipara
woman who have completed 2 or more pregnancies to gestation of 20 wks or more
nullipara
woman who has not completed a pregnancy with a fetus or fetuses who have reached 20 wks of gestation
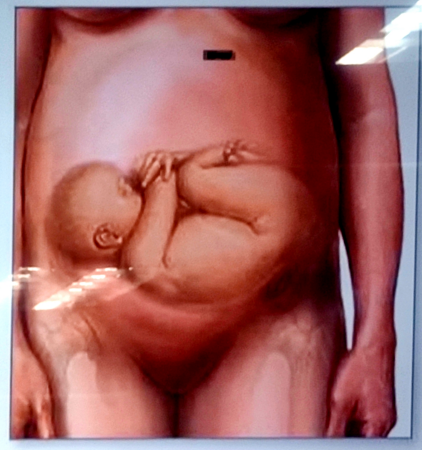
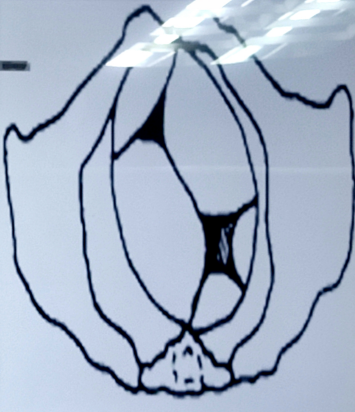
fetal attitude
describes the relationship of fetal parts to one another
fetal attitude
used to designate the characteristic posture assumed by the fetus inside the utero
habitus
other term for fetal attitude
consistency of abdominal wall and uterine wall
amount of amniotic fluid
movements of extremities of mother
fetal attitude is often modified by
presentation
means the portion of fetus which engages at pelvic inlet and is felt through the cervix on vaginal examination
cephalic presentation
breech
shoulder
3 types of presentation
occiput or vertex presentation
face
sinsiput
brow
4 types of cephalic presentation
full or complete breech
frank
footling / incomplete
3 types of breech presentation
sinciput presentation
military attitude with anterior fontanelle presenting
brow presentation
cephalic presentation
partial extension
face presentation
cephalic presentation
poor flexion, complete extension
vertex presentation
cephalic presentation
full flexion
sinciput
cephalic presentation
moderate flexion, military attitude
vertex
cephalic presentation
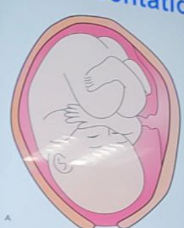
sinciput
cephalic presentation
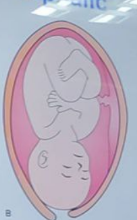
brow
cephalic presentation

face
cephalic presentation
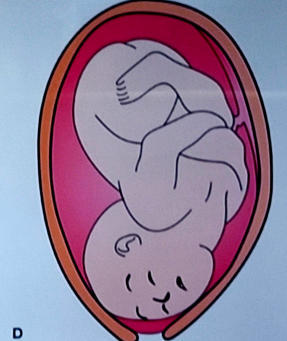
chin anterior
cephalic presentation
chin posterior
cephalic presentation
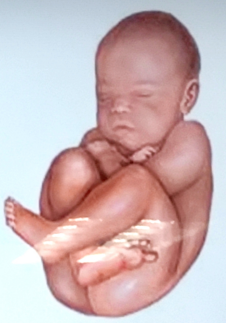
complete breech
breech presentation
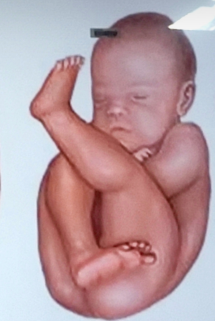
incomplete breech
breech presentation
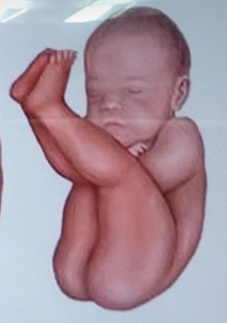
frank breech
breech presentation
transverse lie presentation / shoulder
type of presentation
head first facing backwards
normal delivery presentation
breech
face
shoulder
abnormal deliveries
fetal lie
means the relationship which the long axis of the fetus to the long axis of the mother
longitudinal lie
normal fetal lie
longitudinal
transverse
oblique
3 types of fetal lie
longitudinal lie
one wherein the long axis of the fetus is parallel to the long axis of the mother
cephalic
breech
2 types of presentation for longitudinal lie
transverse lie
when the fetal axis crosses the maternal axis such that they are perpendicular to one another
shoulder presentation
type of presnetation for transverse lie
oblique lie
when the fetal axis crosses the maternal axis at an angle but not at right angles
oblique lie
this type of lie is only temporary and maybe converted into a longitudinal or transverse lie under the influence of uterine contractions
position
defined as the relationship of an arbitrarily chosen portion of fetus to the left or right of the mother’s pelvis anterior or posterior
cephalic
breech
face
shoulder
4 types of position
small fontanelle or occiput
position of cephalic
tip of the sacrum
position of breech
chin or mentum
position of face
acromion process of the scapula
position of shoulder
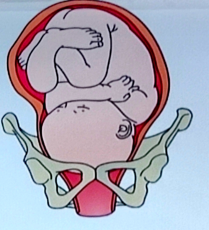
LOP (left occiput posterior)
position
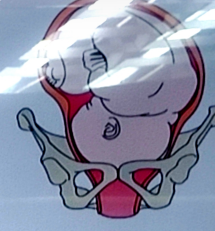
LOT (left occiput transverse)
position
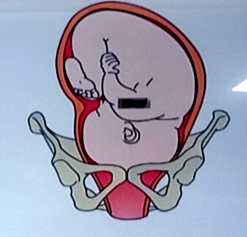
LOA (left occiput anterior)
position
ROP (right occiput posterior)
position
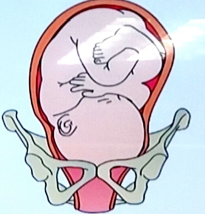
ROT (right occiput transverse)
position
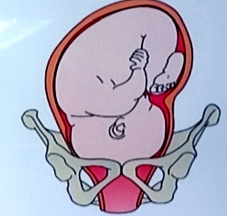
ROA (Right occiput anterior)
position
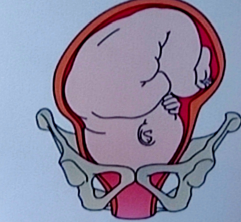
left occiput anterior
position
right occiput anterior
position
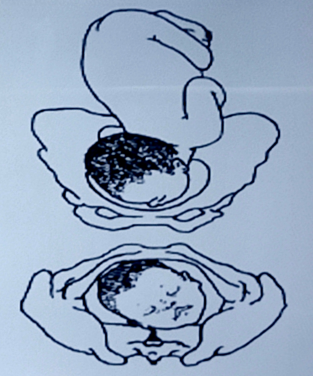
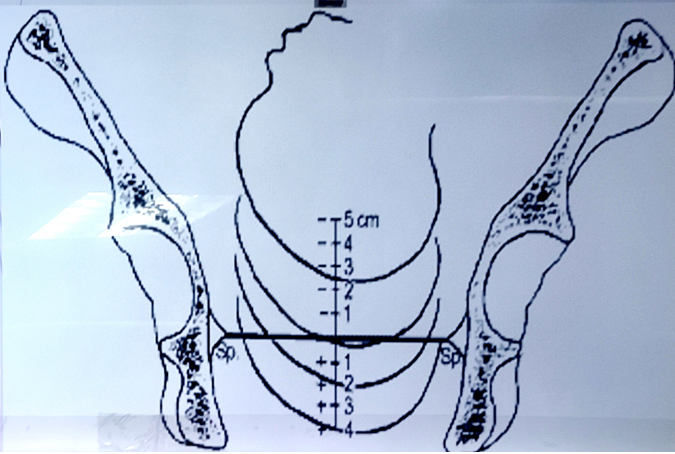
station
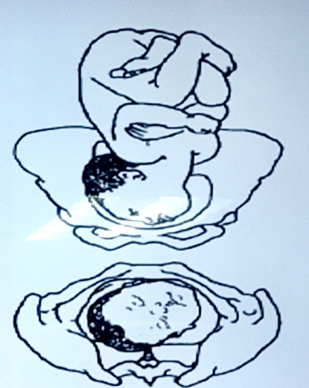
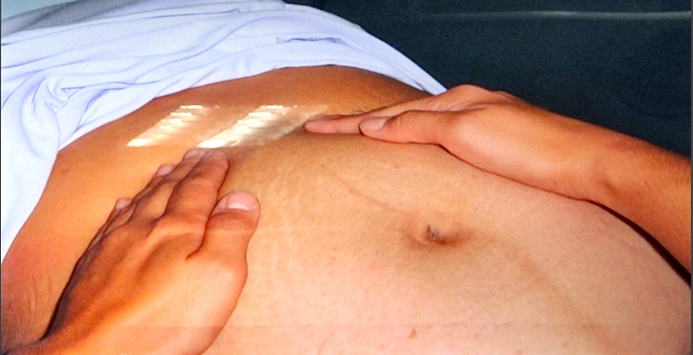
dorsal recumbent
position of client during leopold maneuver
fundal grip
lateral grip
pawlik’s grip
pelvic grip
4 types of maneuvers
fundal grip
examiner stands at side of bed facing women’s head and palpate uterine fundus
uterine fundus
what will you palpate during fundal grip
fetal part
in fundal grip, what will you determine at the uterine fundus
relative consistency
shape
mobility
in fundal grip, what will you observe at the uterine fundus
fundal grip
this type of maneuver determines the presentation
first maneuver
determine what occupies at the fundus
1st maneuver - fundal grip
type of maneuver
lateral grip
examiner face woman’s head and palpate with one hand on each side of abdomen
lateral grip
assess which side is the fetal back and which extremities
fetal back
lateral grip
smooth curve, hard, resistant part
knees and elbows
lateral grip
number of angular nodulations
small parts of the fetus
2nd maneuver
type of maneuver
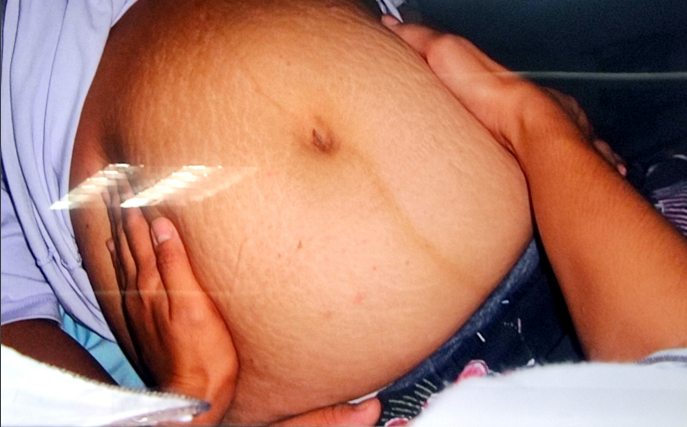
lateral grip
determine location of fetal heart tones
bell
after identifying back of fetus, the ____ of stethoscope is placed to determine FHT
120 to 160 bpm
normal FHT
pawlik’s grip
examiner stands at side and facing the client and grasp lower portion of abdomen, just above the symphysis pubis using thumb and 2 fingers of one hand and pressing together
pawlik’s grip
assess for presenting part and if it is engaged or still floating
pawlik’s grip or 3rd maneuver
determine position and mobility of presenting part
pawlik’s grip or 3rd maneuver
type of maneuver
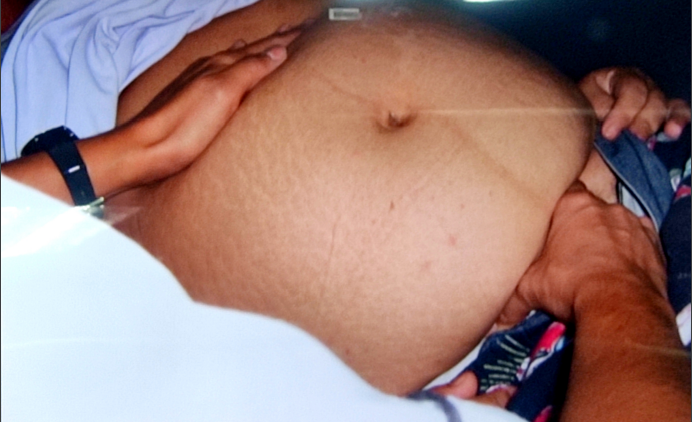
pelvic grip
examiner face woman’s feet and determines fetal attitude and fetal position
pelvic grip
examiner place tips of 3 fingers on either side of symphysis pubis, just above inguinal ligament and press fingers downward and inward
brow
in pelvic grip, if one hand will meet an obstruction above ligament what is it
nape
in pelvic grip, if one hand have none what is it
pelvic grip or 4th maneuver
type of maneuver
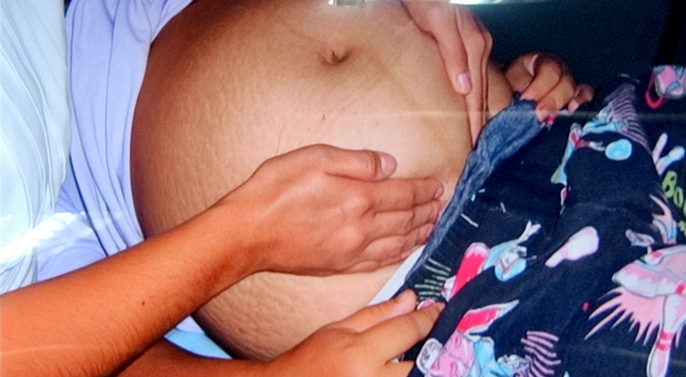
good attitude and full flexion
in pelvic grip,
when the brow is on the same side as small parts
chin is touching the chest and vertex presenting
poor flexion
in pelvic grip,
when brow is on same side with the back
fetal head is hyperextended