Latches, Flip-flops, and Timers
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
What is a latch?
A type of bistable logic device or a multivibrator
How is an active-HIGH input S-R latch formed?
Two-cross coupled NOR gates
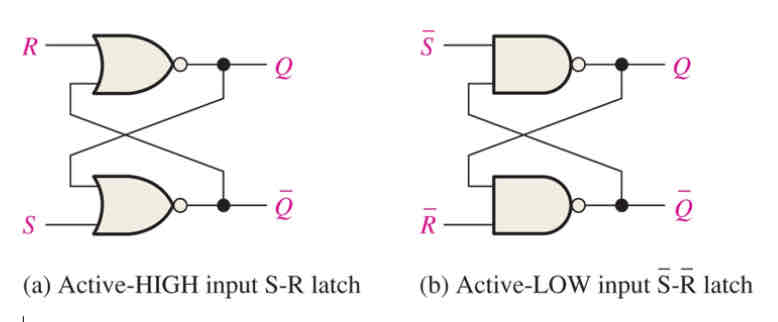
How is an active-LOW input S’-R’ latch formed?
Two cross-coupled NAND gates
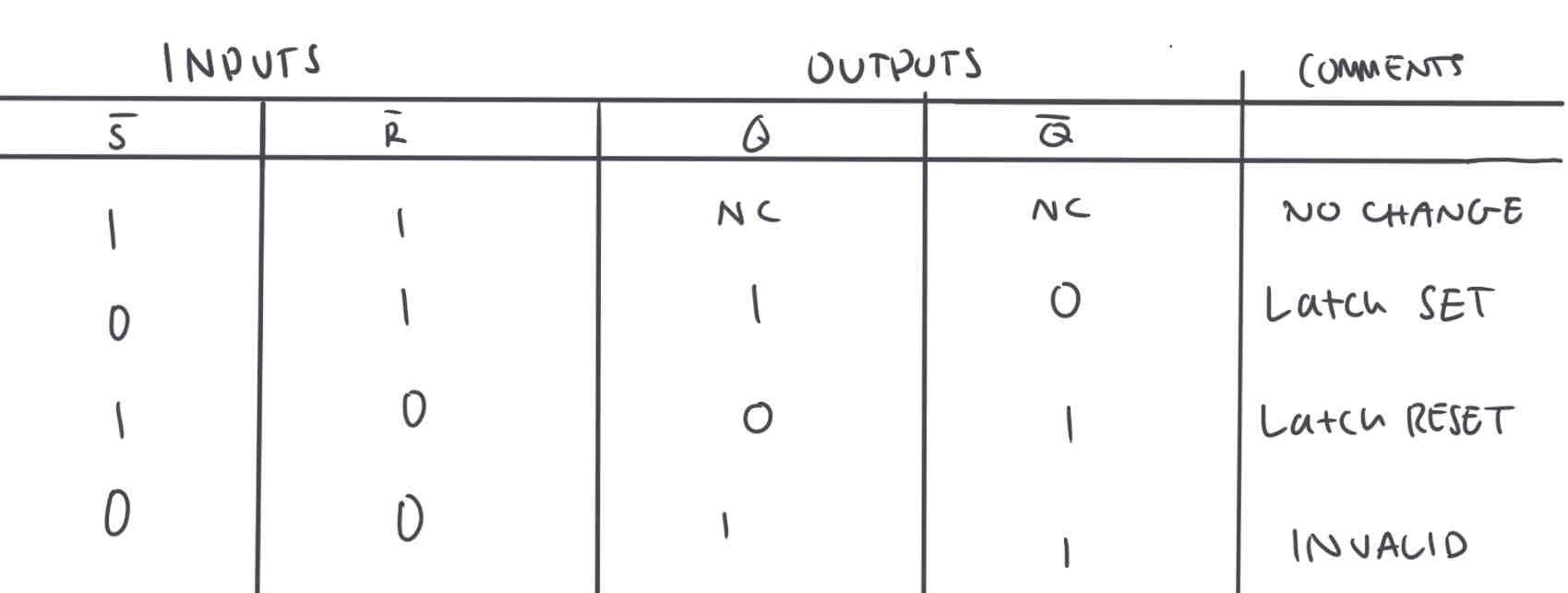
Draw an active-LOW S’-R’ latch truth table

The purpose of the clock input to a flip-flop is to…
Cause the output to assume a state dependent on the controlling inputs
What do S-R latches do?
Produce the regenerative feedback that is characteristic of all latches and flip-flops
When is the latch in a SET state?
When Q has a HIGH output
What happens when the latch is in SET state?
It will remain in this state indefinitely until a LOW is temporarily applied to R’ input.
What happens when a latch is in RESET state?
It will remain in this state indefinitely until a momentarily LOW is applied to the S’ input.
What is trie for the outputs of the latch?
The latch outputs are always complements of each other (when Q is high, Q’ is LOW, vice versa)
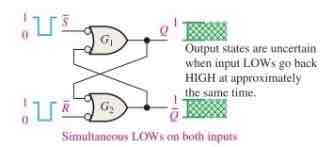
When is an active-LOW input S’-R’ latch in an invalid condition?
When LOWs are applied to both S’ and R’ at the same time
When can you not redact the next state of the latch?
When the LOWs are released simultaneously, both outputs attempt to go LOW. Due to some small difference in the propagation delay time of the gates, one of the gates will dominate in its transition to the LOW output state. So the slower gate remains HIGH.
What are two possibilities for SET operation?
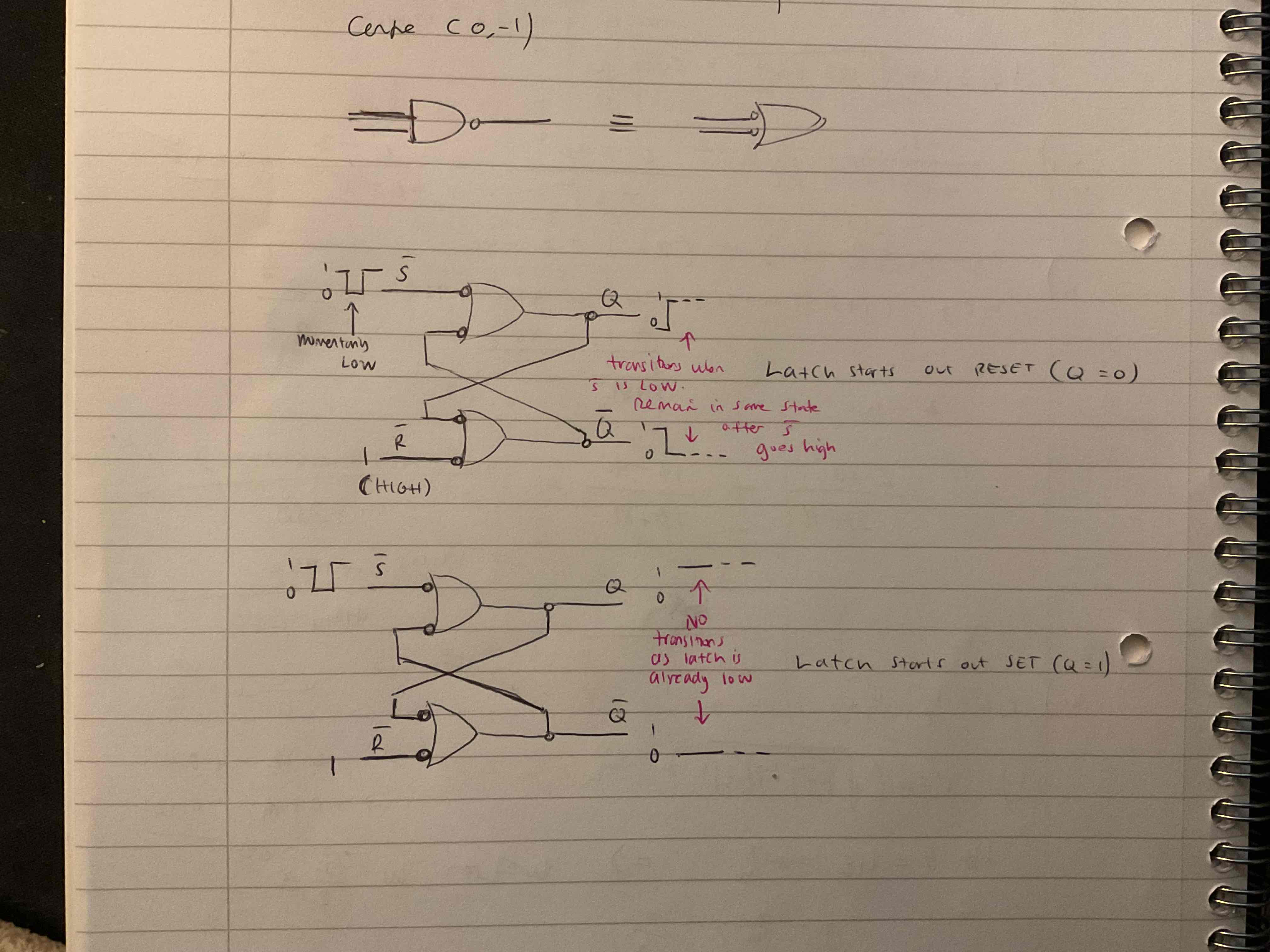
Two possibilities for the RESET operation
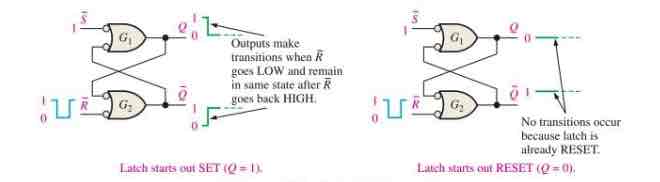
NO-Change Condition
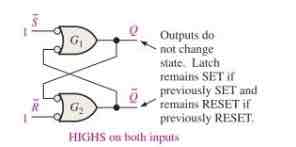
Invalid Condition
Complete a truth table for an active-LOW input S’—R’ Latch
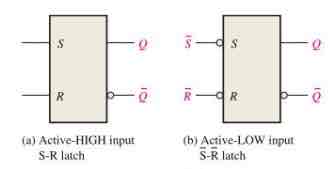
Draw the logic symbols for active-HIGH input and active-LOW input
Give one example where an S’-R’ latch is applied
Contact-bounce eliminator (smooths out erratic transition voltage)
Draw a gated S-R latch diagram and Logic symbols
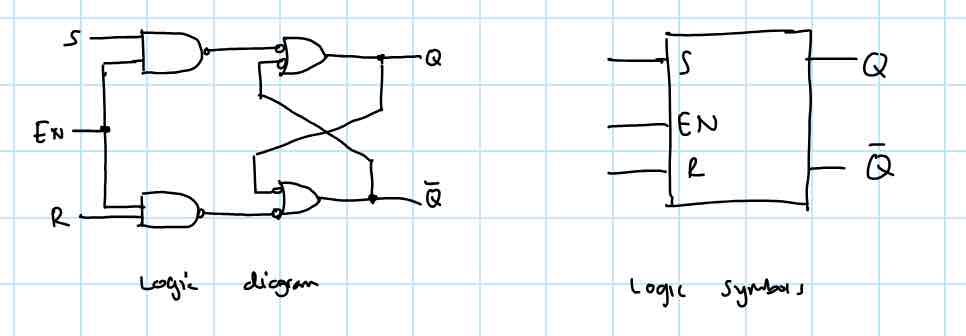
What is a gated S-R Latch?
Requires an enable input, EN. The S ad R inputs control the state to which the latch will go when a HIGH level is applied to the EN input. This device is level-sensitive.
How does a gated S-R latch change wave form?
S=1, R=0, EN=1 SETS last
S=0, R=1, En=1 RESETS Latch
S=0, R=0, NO CHANGE
How does a flip-flop differ from a latch
The way it changed states. Flip-flops are edge-triggered but gated latches are level-sensitive
What is a flip-flop?
A synchronous bistable device or multivibrator
Truth Table for a D flip-flop
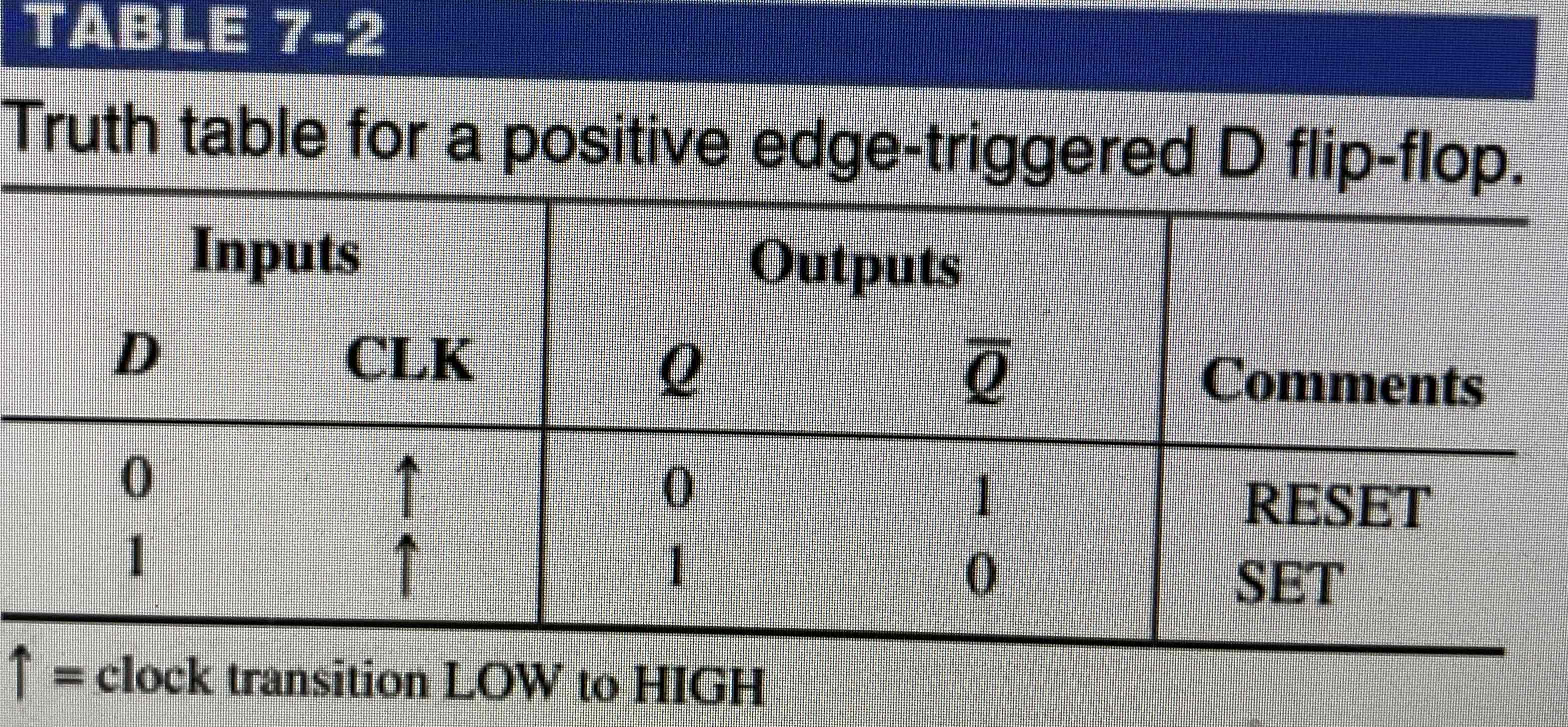
When does a flip-flop output change state?
Only at a specified point on the triggering input called the clock, CLK. Changes in output occur in synchronisation with the clock.
What is an edge-triggered flip-flop?
Changes state either at the positive (rising) edge or at the negative (falling) edge of the clock pulse
What are the two type of flip-flops?
D and J-K
Draw the logic symbols for each type of flip flop
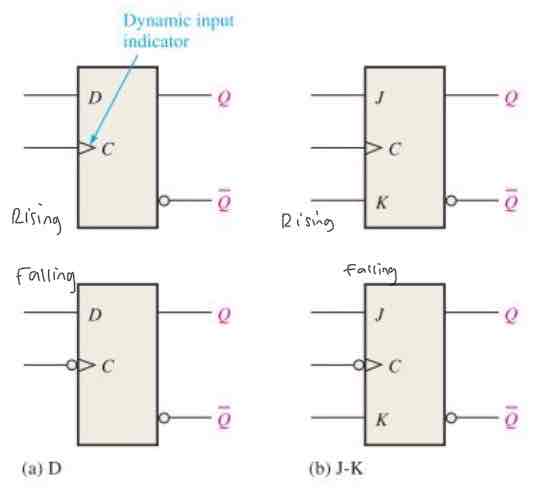
How does a J-K flip-flop differ to the D flip-flop
There is NO INVALIID STATE, instead it has a TOGGLE state
What happens when a J-K flip-flop is in toggle mode?
It changes state on every clock pulse
Draw a J-K flip-flop logic diagram
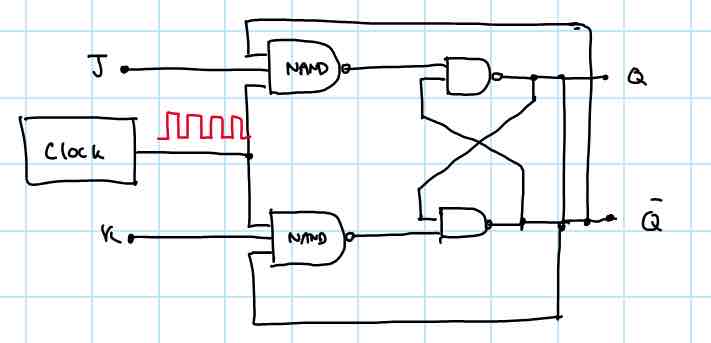
draw a J-K flip flop truth table

Name applications of flip-flops
Temporary data storage ( parallel data, shift registers), frequency dividers and counters
Parallel Data Storage
Storage of several bits of data form parallel lines. Multiple flip-flops are connected and triggered by the same clock pulse
Where is each parallel data line connected to?
The D input of the flip flop, data is simultaneously stored on the D inputs when the clock is triggered
What does a parallel data storage look like?
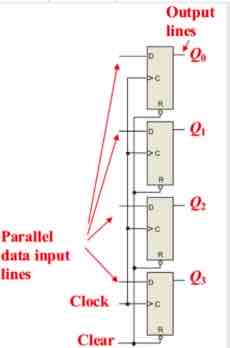
What is a shift register?
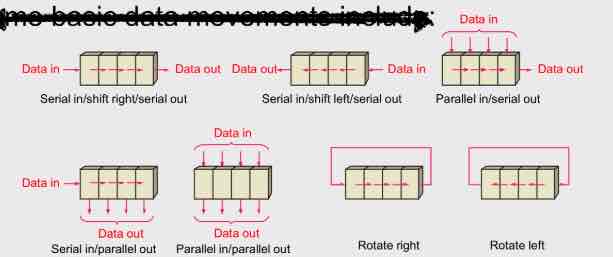
An arrangement of flip-flops that store and move data
What are some basic movements of shift registers?
What is a frequency dividers?
Reduces the frequency of a periodic waveform by half (the frequency of the CLK input)
Draw an example of a frequency divider
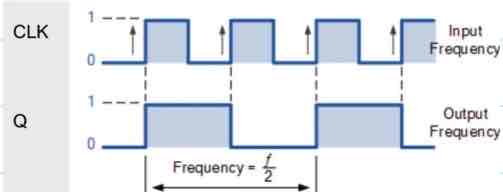
If there are n J-K flip-flops then the frequency can be divided by
2^n
What are digital counters?
2-edge triggered J-K flip-flops operating asynchronously (2-bit binary counter, flip-flop A triggers on the negative of each CLK pulse, QA becomes the CLK for flipflop B, each HIGH and LoW transition of QA forces flip—flop B to toggle
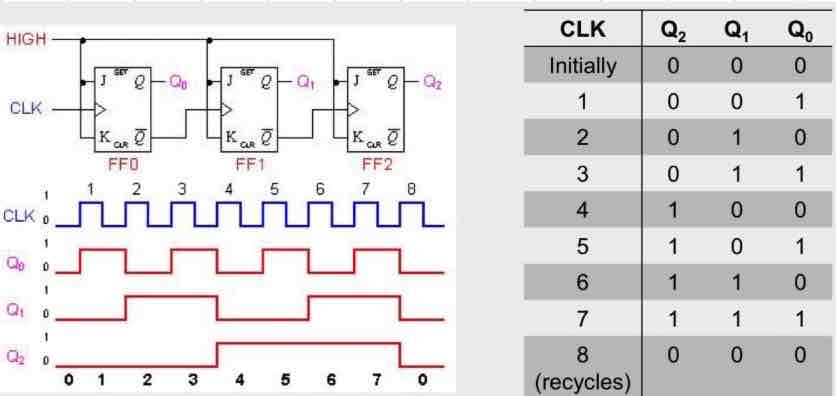
3-bit asynchrones counter
Extension to the 2-bit counter. There are 2³ possible states which enables counting 0-7 before recycling
What does a 3-bit counter look like and its truth table?
Propagation Delays
The effect of the CLK pulse is immediately ‘felt’ by the first FF but there is a short delay before the next is triggered and any subsequent FFs. This effect ‘ripples’ through the counter. The cumulative delay is a major disadvantage of asynchronous counters