Sociological Perspectives on Social Interaction: Key Concepts and Theories
1/50
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
51 Terms
Building blocks of social interaction
The five dimensions for a successful navigation of life: Height, Width, Depth, Time, Social.
Personality
A unique individual's distinctiveness captured in their personality.
Social environment
Composed of real or imagined others to whom a person is connected.
Organizations
Collectivities characterized by structure that encourages patterns in individual action.
Social interaction
Involves communication among people acting and reacting to one another, either face to face or via computer.
Medium of communication
Influences how we interact and the consequences of our interaction.
Status
A culturally defined position or social location.
Norms
Generally accepted ways of doing things.
Ascribed status
A social position imposed on a person at birth; related to a characteristic that is impossible or extremely difficult to change.
Achieved status
A social position that a person acquires through their efforts and choices.
Roles
Clusters of expectations about thoughts, feelings, and actions appropriate for occupants of a particular status.
Master status
A social position that a person considers central to their social identity.
Role-playing
Behaviour that involves conforming to existing performance expectations.
Role-making
The creative process by which individuals generate role expectations and performances.
Social Interaction (process)
The process by which role performers act in relation to others.
Mediated interaction
Communication that uses technologies to send and receive messages.
Instrumental communication
Involves sending messages that are a means to an end.
Expressive communication
Involves sending messages that are ends in themselves.
Technological determinism
Asserts that the adoption of technologies leads to inevitable and sometimes undesirable effects.
Displacement Hypothesis
Suggests that media use weakens in-person connections.
Emotion management
Involves people obeying 'feeling rules' and responding appropriately to the situations in which they find themselves.
Emotion labour
Emotion management that many people do as part of their job and for which they are paid.
Competitive interaction
Involves people seeking to gain the most—socially, emotionally, and economically—while paying the least.
Power
The capacity to carry out one's own will despite resistance.
Role Conflict
A situation where an individual faces competing demands from different roles.
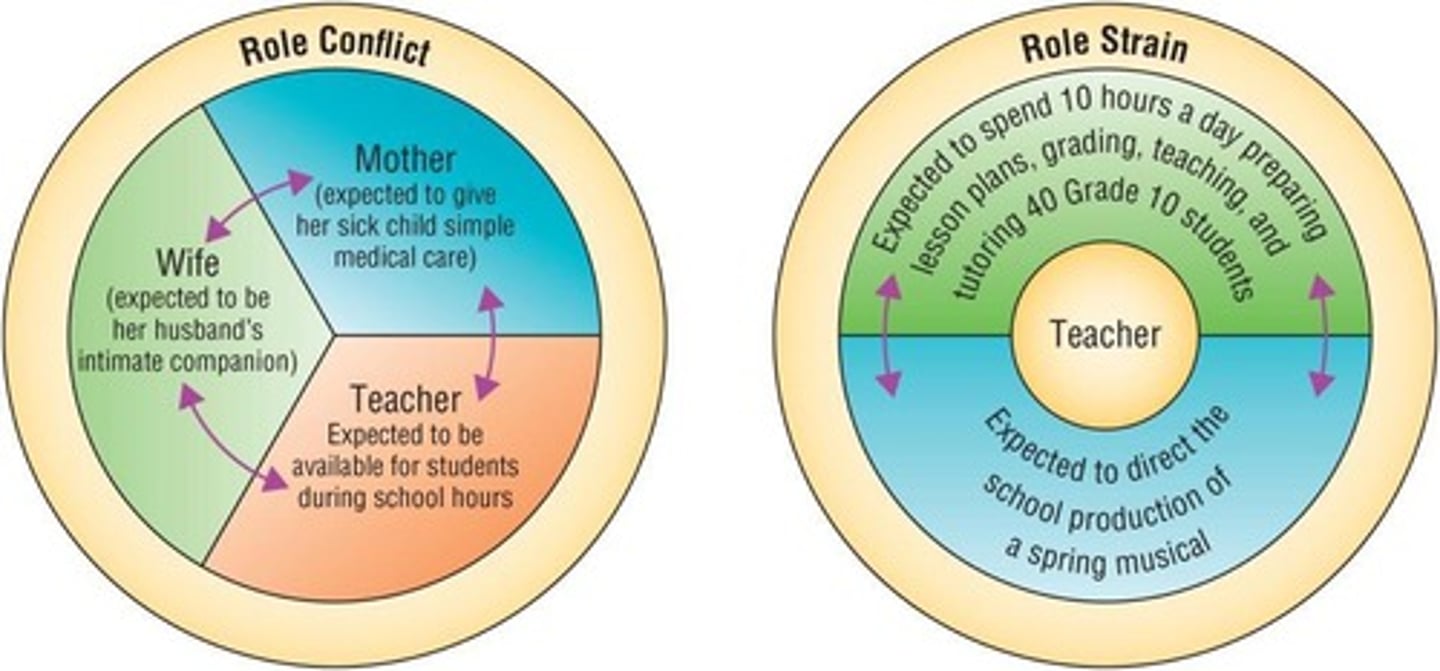
Role Strain
The stress experienced when the demands of a single role exceed an individual's capacity.
Gendered interaction patterns
Gender often structures interactions, with men more likely to engage in long monologues or interrupt others.
Social media effect on empathy
Research shows that social media affect empathy, with the direction of the effect depending on how people choose to use social media.
Routine social media use
Social media can positively affect mental health if it is routine and not disruptive of daily life.
Emotional connection to social media
Social media can positively affect mental health if there is no strong emotional connection to it.
Status hierarchy in interaction
When people interact, their statuses are often arranged in a hierarchy, with those on top enjoying more power.
Laughter in conversation
'Laughter' in a conversation often indicates who has higher or lower status.
Autonomous emotion management
Emotion management that allows actors to control their displays of emotion, fostering liberation.
Regulated emotion management
Emotion management that fosters alienation because others shape it.
Charles Derber's theory
Suggests that the typical conversation is a covert competition for attention.
Social media and offline socialization
National survey found that teens who report being online a lot are as likely to socialize with friends offline as teens who are online less often.
Social statuses
Typically ranked in terms of access to valuable financial, physical, social, or cultural resources.
Cultural scaffolding
The set of cultural values and beliefs that legitimate existing power arrangements, making them seem reasonable and giving them a natural, taken-for-granted quality.
Dramaturgical analysis
Views social interaction as a sort of play in which people present themselves so that they appear in the best possible light.
Role distancing
Involves giving the impression that we are just 'going through the motions' but actually lack serious commitment to a role.
Impression management
The effort to place oneself in the best possible light during social interactions.
Ethnomethodology
The study of how people make sense of what others do and say by adhering to pre-existing norms.
Breaching experiments
Illustrate the importance of everyday, ritualistic interactions by disrupting interaction patterns.
Status cues
Visual indicators of other people's social position.
Stereotypes
Rigid views of how members of various groups act, regardless of whether individual group members really behave that way.
Intimate zone
The physical space that separates individuals in close personal interactions.
Personal zone
The physical space that separates individuals in casual interactions.
Social zone
The physical space that separates individuals in social gatherings.
Public zone
The physical space that separates individuals in public speaking or large group interactions.
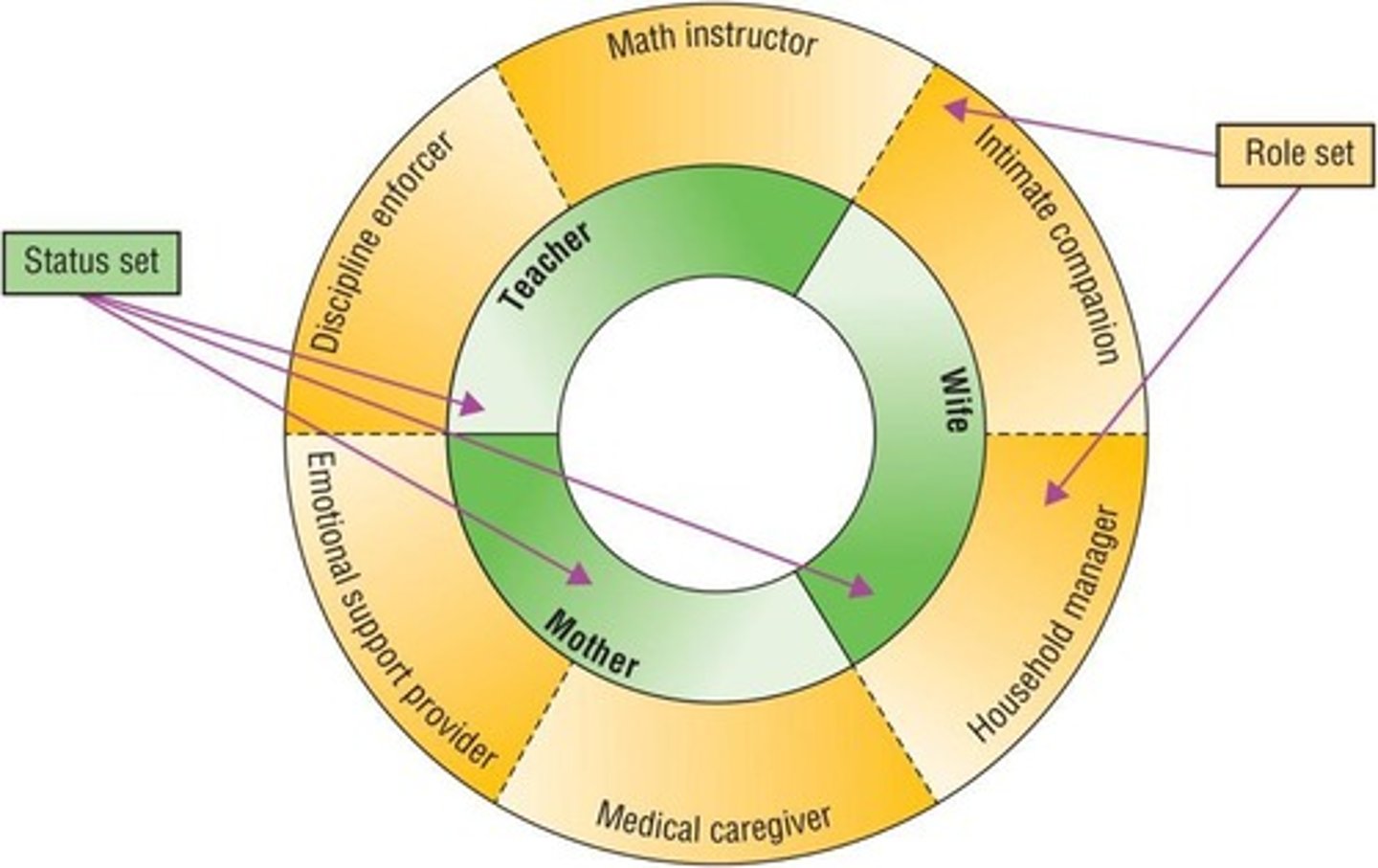
Statuses
Social positions that individuals occupy within a social structure.
Microstructures
The small-scale social interactions that form the basis of social life.