Passive transport across cell membranes
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What level of permeability is the cell membrane (3 names)?
Selectively permeable, semi permeable, or differentially permeable
What can pass through a permeable, semi permeable, and impermeable membrane?
Permeable = All substances can go through
Semi permeable = Some substances can go through, while others can’t
Impermeable = No substances can go through
What is passive transport?
The movement of materials across a cell membrane without the use of energy from the cell
What is diffusion?
The movement of molecules from an area of high concentration to an area of low concentration along a concentration gradient to a state of equilibrium
What is the kinetic molecular theory (KMT)?
All matter consists of many, very small particles which are constantly moving or in a continual state of motion (brownian motion)
What happens in diffusion?
Particles collide, bounce off each other, and spread out from high to low concentration
What are three factors that increase the rate of molecules colliding, which in turn increases the rate of diffusion?
Concentration, temperature, pressure
How does concentration affect diffusion?
Increased number of molecules per volume = more collisions
How does temperature affect diffusion?
Increased kinetic energy = increased motion = more collisions
How does pressure affect diffusion?
Increased pressure causes a smaller volume for the same number of molecules = molecules are close = more collisions
What are other factors that affect diffusion across cell membranes and how do they affect diffusion?
Size and type of molecule (smaller cell = higher diffusion rates, larger cell = lower diffusion rates)
Membrane surface area (eg. microvilli are folds along a cells membrane used to absorb more nutrients, as the folds make more surface area)
What are the two types of passive transport in cells?
Simple diffusion
Facilitated diffusion and osmosis
When does simple diffusion happen?
When small and uncharged or small and non polar molecules can freely diffuse across the cell membrane
What molecules does simple diffusion include?
Water (it is polar, but some are small enough to pass through)
Oxygen
Carbon dioxide
Small fatty acids
Small alcohols
When does facilitated diffusion happen?
When transport proteins help move molecules across the cell membrane
What particles do channel proteins move?
Small polar molecules (like water) and charged ions
What particles do carrier proteins move?
Larger polar molecules like glucose and animo acids (both are monomers of biomolecules)
How does a carrier protein carry the molecule across the cell membrane?
The molecule and protein bind and the protein passes it to the other side
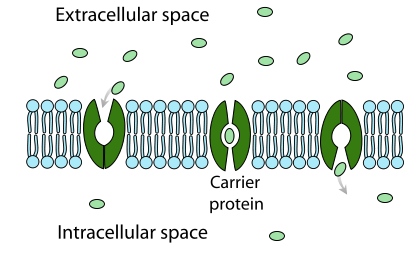
Do carrier proteins and channel proteins carry all types of molecules or only certain molecules?
They are both specific, so they generally only carry one type of molecule
What is osmosis?
The net movement of water molecules by diffusion from a solution of high water concentration to a solution of low water concentration through a semi permeable membrane
If there is a high concentration of water, is there a high or low concentration of solute?
Low
What is a solution made of?
Solute + solvent
What is a solute?
Something (usually a solid) that dissolves into the solvent (liquid)
What does [] around a word mean
eg. [sucrose]
Concentration of
[sucrose] = concentration of sucrose
What is osmoregulation?
The control of water inside a cell or organism
What are the three types of osmoregulation?
Hypertonic, hypotonic, and isotonic
What happens in a hypertonic solution?
A solution surrounding the cell has a higher concentration of a solute and a lower concentration of water than inside the cell
Solution = higher [solute], lower [water]
Cell = lower [solute], higher [water]
Where is the net movement of water in a hypertonic solution?
The net movement of water is out of the cell
What does a hypertonic solution generally cause?
The cell to lose water and shrivel up
What is an example of a hypertonic solution?
A cell in salty water
What is crenation, what type of cell does it happen in, and when does it happen?
The shrivelling of an animal cell in a hypertonic solution
What is plasmolysis, what type of cell does it happen in, and when does it happen?
Plasmolysis is the shrinking of the cell away from the cell wall in a hypertonic solution
Water diffuses out of the cells of the plant and loses its turgor pressure and becomes flaccid/wilted
What happens in a hypotonic solution?
The solution has a lower concentration of solute and a higher concentration of water than inside the cell
Solution = lower [solute], higher [water]
Cell = higher [solute], lower [water]
Where is the net movement of water in a hypotonic solution?
The net movement of water is into the cell
What does a hypotonic solution cause for a cell?
Causes the cell to swell or burst/lyse
What is cytolysis/lysing, what type of cell does it happen in, and when does it happen?
In animal cells, the cell swells and may even burst
What does turgid mean, what type of cell does it happen in, and when does it happen?
When plant cells take up water but cannot burst due to the cell wall, which makes the plant upright
What is turgor pressure?
The pressure of the cell contents against the cell wall when the central vacuole is full
Why can’t a plant cell burst?
The cell wall is strong and does not give away
Why is turgor pressure in plants important?
In order to maintain the plant’s upright and erect position
What happens in an isotonic solution?
The solute concentration and water concentration both inside and outside the cell are equal
Where is the net movement of water in an isotonic solution?
There is no net movement, only equal movement into and out of the cell
What happens to animal cells in an isotonic solution?
They are stable
What happens to plant cells in an isotonic solution?
They are in a state between turgidity and flaccidity
What organ in humans works to keep the body fluids isotonic compared to our cells?
Our kidneys