The Global Economy
1/128
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
129 Terms
International trade
The transnational exchange of goods and services. It involves the sale of exports (goods and services sol to overseas buyers) and imports (foreign goods and services bought by domestic households and firms).
Factor endowment
Refers to the quantity and quality of factors of production available in a country such as natural resources and human capital. Countries well endowed with natural resources tend to have a cost advantage in the production of products using these resources.
Comparative Advantage
Exists when a country can produce a given amount of output at a lower opportunity cost than another country, that is, the country gives up fewer resources than other nations in order to produce that good or service.
Trade protection
The use of barriers to trade to safeguard an economy from excessive international trade and foreign competition.
Barriers to trade
Obstacles to international trade, imposed by a government to safeguard national interests by reducing the competitiveness of foreign firms.
Types of trade protection
Tariffs
Quotas
Subsidy (export subsidy)
Administrative barriers)
Tarrifs
Specific tax on imported goods and services
Non-tariff barriers
Restrictions to international trade that do not involve a tax or duty (tariff), such as quotas, export subsidies and administrative barriers.
Quotas
Quantitative limits on the importation of a good into a country.
Subsidies
A form of financial assistance to domestic firms by lowering their costs of production in order to help them compete against foreign imports.
Administrative barriers
The application of bureaucratic standards and regulations imposed on foreign firms in order to protect domestic firms and consumers.
Embargoes
A form of administrative barrier that involves the use of bans on trade with a certain country, often due to political and/or economic disputes
Exchange controls
A form of administrative barrier involving restrictions on the quantity of foreign exchange that can be bought or sold by domestic residents.
Infant industries
Often new or unestablished industries that have the potential to achieve a comparative advantage but are too underdeveloped to compete with foreign firms.
Dumping
The sale of goods and services by foreign firms at a price lower than the cost of production.
The balance of payments
A financial record of a country’s transactions with the rest of the world, usually over one year. It includes the country’s trade in goods and services with other countries.
Economically least developed countries (ELDCs)
Low-income countries facing severe structural barriers to sustainable economic development. They have low levels of human capital and are highly vulnerable to economic and environmental shocks.
Retaliation
Refers to the actions taken by a country in response to trade restrictions being imposed on it from other countries.
Trade war
An economic conflict that results from extreme measures of trade protection between two or more countries, by imposing reciprocal restrictions to international trade.
X-inefficiency
Occurs when firms lack the incentive to control costs of production. It represents the difference between the behavior of rational firms in competitive markets and those in the absence of competition.
Export competitiveness
Refers to the ability of domestic firms to export products successfully to foreign markets owing to their ability to compete in overseas markets.
Arguments for trade controls
Protection of infant industries
National security
Health and safety
Environmental standards
Anti-dumpting
Unfair competition
Balance of payments correction
Generating government revenue
Protection of jobs
Economically least developed country (ELDC) diversification
Arguments against trade controls
PC CRIME
Misallocation of resources
Retaliation
Increased costs
Higher prices
Less choice
Domestic firms lack incentive to become more efficient
Reduced export competitiveness
Economic integration
The process of countries becoming more interdependent and economically unified
Preferential trade agreement (PTA)
A trade treaty between two or more countries, giving special or favourable terms and conditions of trade to member countires.
Bilateral trade agreement
A preferential trade agreement between two countries, usually by mutual agreement to reduce or remove barriers to trade
Multilateral trade agreement
A legally binding preferential trade agreement between more than two countries and/or trade blocs, under the guidelines of the WTO.
Trading bloc
A group of countries that agree to economic integration and freer international trade by reducing or removing trade barriers with one other.
Free trade are (FTA)
A type of trading bloc between member states that agree to trade freely with each other but can impose separate trade restrictions with non-member countries.
Customs union
Consists of member countries in a trading bloc that engage in free trade with each other but impose a common external tariff when trading with non-member sttaes/
Common external tarrif
All members of a customs union impose the same (common) trade barriers to non-member countries.
Common market
The most integrated trading bloc, consisting of a customs union that allows the free movement of factors of production between member countries.
Advantages of trading blocs
Access to larger markets and the potential for economies of scale
Greater employment opportunities
Stronger bargaining power in multilateral negotioations
Greater political stability and co-operation
Disadvantages of trading blocks
Loss of sovereignty
Challenges to multilateral trading negotiations
Monetary union
Refers to the monetary system in a common market that requires the convergence of monetary policy that is governed by a common bank.
The World Trade Organization (WTO)
A global organization that exists to promote trade liberalization, to oversee multilateral trade agreements and to resolve trade disputes between member states.
The objectives of the WTO
Non-discrimination
More open
Predictable and transparent
More competitive
More beneficial for eocnomically less developed countries
Protect the environment
Non-discrimination
Means a WTO country cannot discriminate between its trading partners in terms of their goods, services or people.
The functions of the WTO
Trade negotiations
Implementation and monitoring
Dispute settlement
Building trade capacity
Outreach
Factors affecting the influence of the WTO
Difficulties of reaching an agreement on services/primary products
Unequal bargaining power of members
Exchange rates
The value of one currency expressed in terms of another currency.
Floating exchange rate
Where the value of a currency is determined by the demand for and supply of the currency in the foreign exchange market.
Appreciation
A sustained increase in the value of one currency in terms of another under a floating exchange rate system.
Depreciation
A sustained decrease in the value of one currency in terms of another under a floating exchange rate system.
Inward foreign direct investment
Refers to foreign multinational companies expanding their operations in the domestic economy.
Outward foreign direct investment
Refers to multinational companies from the domestic economy expanding their operations in overseas markets.
Portfolio investment
The purchase of financial investments abroad, such as the purchase of stocks, shares and bonds of overseas firms and governments.
Reminttances
Refer to the movement of money when nationals working abroad send money back to their home country.
Speculation
Occurs when a financial asset such as the domestic currency or a foreign currency, is purchased in the hope or anticipation that the resale value will be higher.
Net exports
The value of exports minus the value of imports, are part of the aggregate demand equation (and GDP)
The current account
A record of all trade flows (exports and imports of goods and services), income flows and income trasnfers between countries by individuals, firms and governments).
Fixed exchange rate system
Exists when the central bank or monetary authority buys and sells foreign currencies to ensure the value of its currency stays at a single, predetermined rate.
Foreign currency reserves (or reserve assets)
Stocks of foreign currencies held by a central bank, usually to influence the value of its currency.
Devaluation
Occurs when the price of a currency operating in a fixed exchange rate system is officially and deliberately lowered.
Revaluation
Occurs when the price of a currency operating in a fixed exchange rate system is officially and deliberately increased.
Managed exchange rate
A system where the government or central monetary authority intervenes periodically in the foreign exchange market to influence the exchange rate, when deemed necessary to maintain certainty and confidence in the economy.
Crawling peg
A form of fixed exchange rate system in which a currency is permitted to fluctuate within predetermined bands of exchange rates.
Overvalued currency
Occurs when the value of a currency is above its equilibrium value in the long run
Undervalued currency
Occurs when the value of a currency is below its equilibrium value in the long run.
Balance of payments
A financial record of a country’s transactions with the rest of the world, usually over one year. It includes the country’s trade in goods and services with other countries.
Credit items
Payments received from consumers, firms and institutions or governments located outside of the economy.
Debit items
Payments made to consumers, firms and institutions or governments located outside of the economy.
Surplus
Exists when the total value of credit items exceeds the total value of debit items over a given period of time.
Deficit
Exists when the total value of debit items exceeds the total value of credit items, over a given period of time.
Current account
balance of trade in goods and services
income
current transfers
Capital account
capital transfers
transactions in non-produced, non-financial assets
Financial account
Foreign direct investment
Portfolio investment
Reserve assets
Official borrowing
Current transfers
The inflows and outflows of money that are not made in exchange for trade or any corresponding output. For example, foreign aid, government grants, concessionary loans, donations, remittances.
Current account deficit
Occurs when the sum of money flowing out of a country’s current account exceeds the money flowing into its current account, per time period.
Current account surplus
Occurs when the sum of money flowing into a country’s current account exceeds the money flowing out of its current account, per time period.
Capital account
Records the different forms of capital inflows and outflows of a country during a given time period, namely capital transfers and transactions in non-produced financial assets.
Capital transfers
The different forms of capital inflows and outflows of a country, such as debt aid, debt forgiveness and the flow of money by emigrants and immigrants.
Transactions in non-produced, non-financial assets
The legal property rights to natural resources (such as land rights, mineral rights and fishing rights) and intellectual property rights (such as trademarks, copyrights, brands and patents).
Capital account balance equation
capital account balance (or net capital transfers) = capital transfers received from abroad - capital transfers sent abroad.
Financial account
A record of the transactions that relate to the change in ownership of assets, that is, cross-border investments. These include foreign direct investment, portfolio investment, reserve assets and official borrowing.
Foreign direct investment (FDI)
Spending by multinational corporations (MNCs) in economies that they are not headquartered in.
Portfolio investment
Refers to the stock of investment assets which can include equities (stocks and shares), government debt (bonds, treasury bills and securities) and debentures (corporate debts).
Reserve assets
Stocks of foreign currencies and liquid assets such as gold reserves held by central banks used to balance international transactions and payments.
Official borrowing
Refers to government borrowing rather than borrowing of private indivdiuals, households and firms.
Interdependence between the accounts
zero balance in the overall balance of payments
credit items are matched by debit items
deficits are matched by surpluses
Current account = capital account + financial account
Current account = capital account + financial account + errors and omissions
Sustainable development
The economic development that meets the needs of the present generations without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs.
Social sustainability
Refers to the ability of an economy to develop social processes and structures that enable its current population to live optimally and to support the ability of future populations to do the same.
Economic sustainability
Refers to the optimal use of scarce resources in such a way to ensure future generations are not disadvantaged in favour of today’s generation.
Environmental sustainability
Refers to the responsible use of the planet’s natural resources so that future generations are not comprised on their use of these natural resources.
Single indicator
Refers to a statistical measure of economic development that uses on particular gauge such as literacy rates, income per capita or life expectancy.
Health indicators
A category of single indicators of measuring economic development by using health-related determinants of the quality of life, such as life expectancy and the under-five mortality rate.
Education indicators
A category of single indicators of measuring economic development by using education related determinants of the quality of life, such as literacy rates and mean years of schooling.
Economic indicators
real GNI per capita, real GDP per capita, etc.
Social indicators
Used to determine the extent to which societal factors contribute to development. Include shelter and housing, crime rates, homicide rates, safety and degree of trust in a neighbourhood or community. Income inequality and wealth inequality such as the Gini coefficient.
Energy indicators
A category of single indicators of measuring economic development by using factors that create affordable, reliable, sustainable and modern energy for all citizens.
Proportion of population with access to functioning electricity.
proportion of population with primary reliance on clean fuels and technology.
renewable energy usage as a proportion of total energy consumption.
energy use as a proportion of GDP.
Enviornmental indicators
global warming and climate change
desertification
deforestation
waste disposal and management systems
loss of biodiversity and ecosystems.
Composite indicator
A statistical method that combines single indicators of economic development into a combined index such as the human development index.
The human development index (HDI)
A composite indicator as a measure of economic development, comprising real income, life expectancy and educational attainment.
Limitations of the human development index (HDI)
ignores qualitative measures affecting standards of living such as gender inequalities and human rights
does not take into account inequitable income distribution
ignores the impact of environmental and resource depletion on development
ignores cultural differences in the interpretation of the meaning standards of living and quality of life
ignores the concept of sustainable development
Gender inequality index (GII)
A composite measure of development by calculating gender disparities through three dimensions, namely reproductive health, empowerment (share of parliamentary seats held by each gender and higher education attainment levels)and labour market participation.
Inequality adjusted human development index (IHDI)
A composite measure of the average level of human development by accounting for inequalities in society.
Happy Planet Index (HPI)
A measure of sustainable human well-being, that is, how individuals and countries are able to achieve long, happy and sustainable lives.
Well-being
Life expectancy
Inequality of outcomes
Ecological footprint
Economic growth vs development
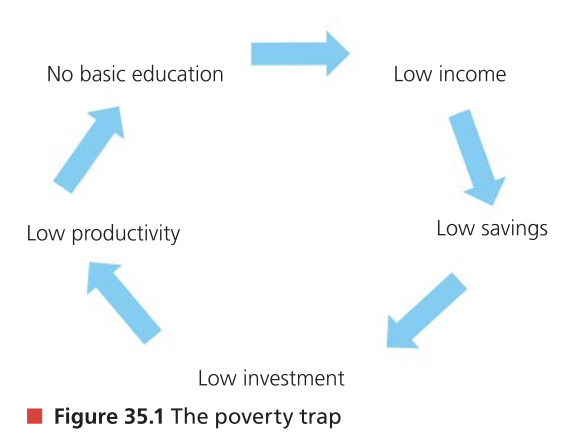
Poverty trap (or poverty cycle)
A vicious cycle of poverty and deprivation causing even greater poverty, from one generation to the next. Low-income earners spend most, if not all, of their income in order to meet their essential needs but this also means they have insufficient funds to invest in their future so are trapped in poverty. Additionally, banks are unlikely to lend money to poor people as there is a high risk of them failing to repay the money borrowed. Government intervention or foreign aid is therefore required to bring people out of extreme poverty.
Savings ratio
The amount of savings expressed as a proportion of total disposable income in an economy. Having low income also means. alow savings ratio.