2025 World History Midterm
1/303
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
304 Terms
“Humane” device used as a means of execution during the French Revolution
Guillotine
He seized power of the French government in 1799 with a military takeover
Napoleon
Louis XVI’s unpopular wife - her nickname was “Madame Deficit”
Maire Antoinette
The ruling family of France
Bourbon
King who bankrupted France by building Versailles and fighting lots of wars
Louis XIV
Following the Reign of Terror, this five-member board ruled France
The Directory
Term used to describe nobles who fled France and hoped to restore the Old Regime
Emigres
Jacobin leader who ruled during the most violent time of in which thousands of French citizens were executed
Robespierre
Author of The Declaration of the Rights of Woman and the Female Citizen
Olympe de Gouges
Radical group made up of Parisian wage earners and small shop keepers who wanted a greater voice in the government
Sans-Culottes
One of the most prominent members of the Jacobins, he edited a revolutionary newspaper that stirred up the violent mood in Paris
Marat
Well-known Jacobin and lawyer, eventually executed for being less radical than Robespierre
Danton
King during the French Revolution
Louis XVI
Made up from the French middle class and included merchants, bankers, industrialists
bourgeoisie
A sudden over throw/take-over of the government
coup de’teat
Accounted for about 97% of the French population but only received a one-third vote in the Estates-General
3rd estate
French revolution started this year
1789
Made up the First Estate in France
the Clergy
Supposedly represented all of the French people, although (prior to the French Revolution) it had not met in almost 175 years
the Estate-general
Made up majority of the Third Estate
peasants
Made up the Second Estate in France
nobles
The National Assembly was initially formed by this group
3rd Estate
This consisted of a series of peasant rebellions through out the French countryside which motivated the National Assembly to abolish class privileges
The Great Fear
What issue arose after the King called for the Estates General to meet
how many votes each Estate would get
In 1793, both the King and Queen of France were
beheaded
This was a popular slogan for members of the French Revolution
Liberty, Equality, Fraternity
Why did the National Assembly lose the support of many of the French peasants
It took away the Catholic Church’s lands and independance
What kind of government did the French Constitution of 1791 set up
limited monarchy
which of the following statements about the Reign of Terror is incorrect
It was stopped with the arrival of Napoleon and his army
which group imposed the Reign of Teroor
the Committee of Public Safety
Which of the following is an accurate description of the tax system in France in the years preceding the French Revolution
members of 3rd Estate paid almost all of the taxes
The Estates-General was convened in 1789 in order to deal with the
near bankruptcy of the French Treasury
Which of the following statements accurately depicts developments in the French Revolution
The National Assembly created a basic declaration of liberties and a new constitution to establish a limited monarchy
Louis XVI destroyed his public standing by attempting flee
Warfare broke out between France and Austria, which was endeavoring to restore the absolute French Monarchy
All of the above
Which group finally forced Robespierre from power
his fellow revolutionaries
Which group most strongly embraced the ideals and principles of the Enlightenment
the Bourgeoisie
His laws of motion and gravitation led to a whole new conception of the universe and his ideas served as the basis for the study of physics until the 20th century
Newton
He praised and analyzed the checks and balances of the British constitution
Montesquieu
He believed that all people possessed natural rights and that it was the government’s job to protect him
Locke
Brilliant French satirist and one of the most famous writers of the Enlightenment; he frequently targeted the clergy, the aristocracy and the government and he never stopped fighting for tolerance, reason, freedom of religion and freedom of speech
Voltaire
In A Vindication of the Rights of Women, this political thinker presented an argument for the education of women; she also declared that women should have the same political rights as men
Wollstonecraft
The Enlightenment was a movement of
intellectuals
Which of the following was not a core belief, or concept, of the philosophes
Faith
Happiness
Liberty
Progress
Reason
Which if the following did the Enlightenment promote
a belief in progress
a more secular outlook
faith in science
all of the above
Philosopher who believed that all people are born free and equal, with the rights to life, liberty and property was
John Locke
This philosophers ideas greatly influenced criminal law reformers in Europe and North America; he argued against the use of torture and other common abuses
Beccaria
French philosopher Jean Jacques Rousseau believed that the best form of government would be a:
direct democracy
Who took Montesquieu’s principles and worked them into their constitution
American philosophes
What did the word reason mean to Enlightenment intellectuals
understanding of all of life could be discovered through human mind & logical thinking
An influential French writer whose famous book, On the Spirit of the Laws, proposed that a separation of powers would keep any individual/group from gaining total control of the government
Baron de Montesquieu
The new intellectual movement that stressed reason and thought and the power of the individual to solve problems was the
Enlightenment
Monarchs who embraced new ideas and made reforms to improve the lives of their subjects
enlightened despotism
He supervised the publication of a huge encyclopedia that summarized human knowledge during Enlightenment
Denis Diderot
He believed that absolute power was needed to preserve order in society
Hobbes
This artistic style of the 1600s and early 1700s was characterized by grand, ornate designs
baroque
this artistic style of the late 1700s was characterized
neoclassical
in a history thesis paper where should you place your thesis statement
the last sentence of the intro paragraph
the theory that the sun was at the center of the universe with planets revolving around it
the heliocentric theory
for the medieval thinker this was the only sources of knowledge
the bible
the Roman Catholic church
the ancient Greek and Romans
this political thinker believed that all humans were naturally selfish and wicked and therefore argued that strong (authoritarian) governments were necessary to avoid chaos and maintain law and order
Thomas Hobbes
womans contributions to the Enlightenment included all of the following
urging women to enter male dominated fields
writing about inequalities between men and women
holding social gatherings for influential people to generate “enlightened” discussions
womans contributions to the Enlightenment included did not include
running for political offices
scottish orifesser who defended the idea of a free economy in his book the Wealth of Nations
Adam Smith
this swiss intellectual/writer, best known for his book on government, the Social Contract
Jean Jacques Rousseau
a major turning point in modern civilization as the Western world arrived at a new conception of the solar system/universe
the scientific revolution
learning that is based on a combination of the following three sources of knowledge: human reason/logic; experimentation and observation; and, math.
the scientific method
the willingness of people to hand over their rights to a ruler in exchange for law and order in society was called
a social contract
rights that belong to all humans at birth
natural rights
a movement in France that allowed ideas of Enlightenment to filter down to the larger population through discussions that took place at social gatherings of writers, musicians, painters, and philosophers
salons
the movement for woman’s rights is known as
feminism
the intellectuals/group of social critics of the Enlightenment were known by this French term:
Philosophes

Number 1 best represents
Portugal

Number two best represents
Spain

number 3 best represents
Great Britian

number 4 best represents
France

number 5 best represents
Belgium

number 6 is
Holland/Netherlands

number 7 best represents
Denmark

number 8 is
Germany

number 9 is
switzerland

number 10 is
Austria-Hungary

number 11 is
Serbia

number 12 is
Romania

number 13 is
Russia

number 14 is
Ottoman number 1Empire

number 15 is
Ottoman Empire

number 16 is
Greece

number 17 is
Italy
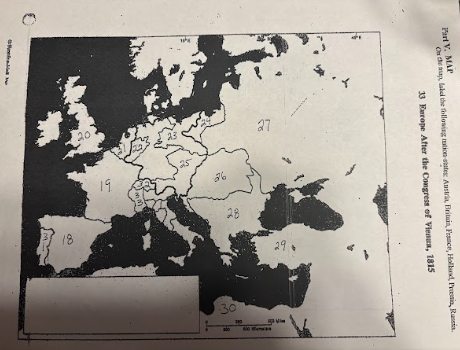
number 18 is
Spain
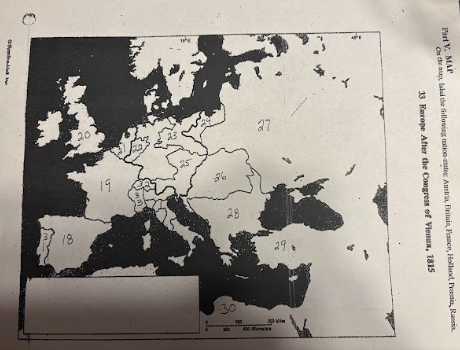
number 19 is
France
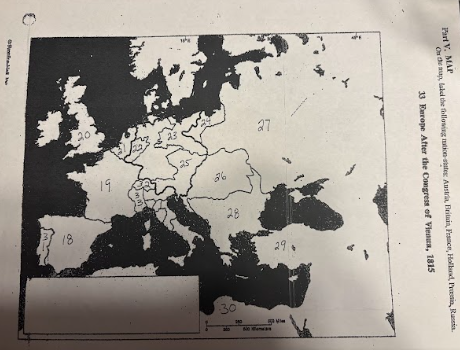
number 20 is
Great Britian
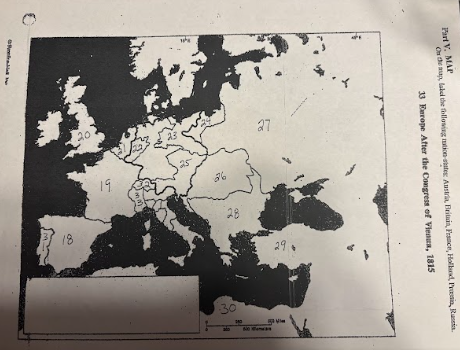
number 21 is
Netherlands
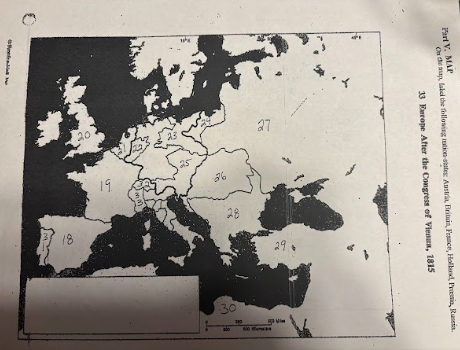
number 22 is
Prussia
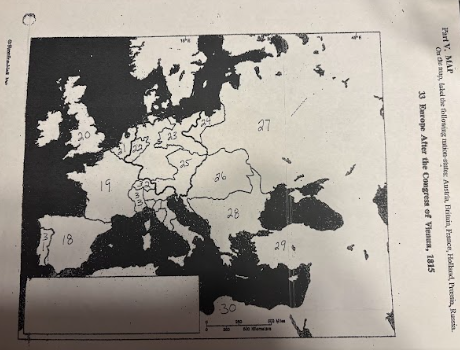
number 23 is
Prussia
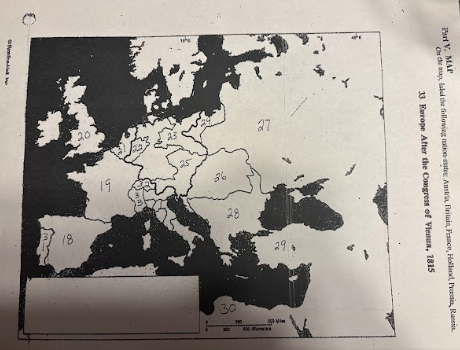
number 24 is
Prussia
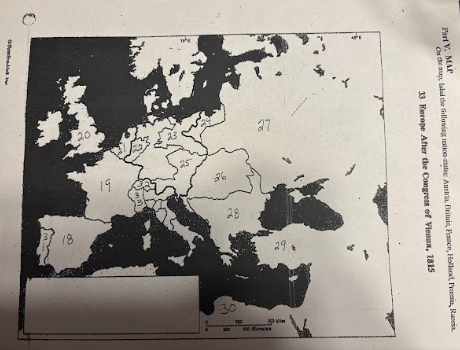
number 25 is
Austrian Empire
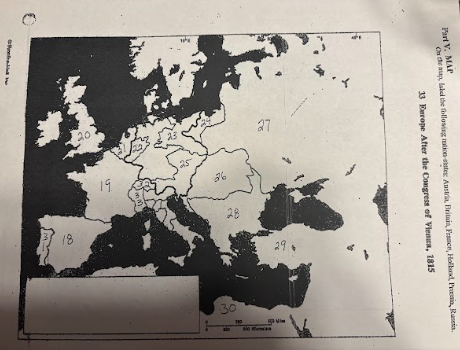
number 26 is
Austrian Empire
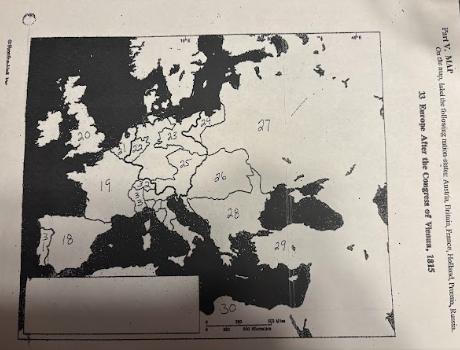
27 is
Russia
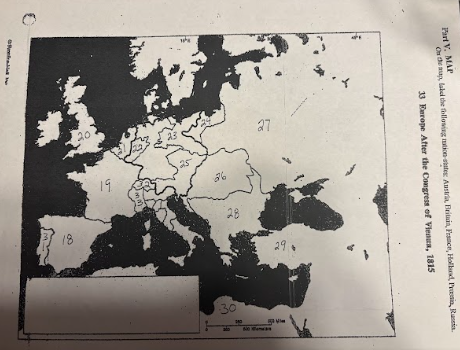
28 is
Ottoman Empire
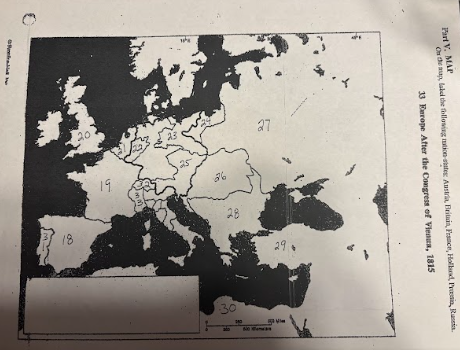
29 is
Ottoman Empire