Midterms: Biotechnology
1/149
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
150 Terms
Fermentation
Anaerobic process that involves breakdown of organic compounds to generate energy.
Fermentation
Any process that produces yeast and bacteria biomass.
Biotransformation
Transformation by cells of a compound added to the medium of a commercially valuable compound.
Bioreactor
Large Chambers where fermentation takes places.
Enzymes
The most common product produced by microbes.
Detergent
Largest application of industrial enzymes.
Mannanase
Enzyme that remove stains containing guar gum
Subtilisin
Enzyme secreted in large amount of bacillus amyloiquefaciens.
Nucleic Acid Isolation
separation of the DNA or RNA from the other components of the cell.
Guanidine isothiocyanate
Potent protein denaturant that isolates RNase activity.
Spectrophotometry
Determination of DNA Concentration and Purity technique that uses DNA standards (different concentrations) and UV-VIS/Nanodrop.
Fluorometer
Determination of DNA Concentration and Purity technique that utilizes fluorescent dyes that are specific to the target molecule. It accurately quantifies DNA, RNA, and protein even at low concentration and minimizes effect of contaminants.
Microfluidics
This provides sizing, quantitation and quality check of DNA, RNA, Protein and cells. It employs microchannel-based elecrophoretic cell technology.
Maxam-Gilbert method
It involves labeling the 5"‘ end of DNA fragments followed by chemical cleaving at random sites.
Sanger chain termination method
This technique involves enzymatic termination of DNA synthesis at random sites using dideoxynucleotide.
Pyrosequencing
Sequencing technique that uses in vitro DNA amplification method known as emulsion PCR. This requires no cloning.
Chemiluminescence
Sequencing by synthesis measures the release of inorganic phosphate by __.
Illumina (Solexa) sequencing
Sequencing technique in which DNA stranded molecules are attached to single molecule arrays or flow cell.
Shotgun sequencing
Sequencing Technique in which genomic DNA is cut into small fragments (~1Kb or less) and inserted into a universal cloning vector to create small insert libraries, random clones are sequenced.
Shotgun
it means random or redundant.
GEL ELECTROPHORESIS
Biotech technique that involves the movement of electrically charged molecules in an electrical field. Allows molecular separation based on: size and net charge.
GEL ELECTROPHORESIS
most common method for separation & visualization of DNA.
Inversely
DNA migrates towards the anode (+) at a rate _____ proportional to its molecular weight.
EtBr (Ethidium Bromide)
the stain used in gel electrophoris.
red-orange
EtBr in UV light emits this color (flourescence) at 590 nm detected by he naked eye.
Buffer
It provides ions that carry a current through the gel, and to maintain a constant pH.
Tris-Acetate EDTA
common running buffer for agarose.
Tris-Borate EDTA
stronger buffering capacity vs. TAE; can be used for agarose or PAGE.
microwave
Agarose solution is cooked in ___.
Snaking or Reptation
Refers to the end-on movement of DNA through the agarose gel.
Southern or Norther Blotting
includes the transfer of DNA/RNA fragments from an elecrophoresis gel to a membrane support
DNA
Target molecule of Southern Blot technique
RNA
Target molecule of Northern Blot Technique
Protein
Target molecule of Western Blot technique
electroblotting
most reliable method for polyacrylamide
Radiolabels
detection is by autoradiography; less popular because of safety considerations but the most sensitive; 32P can detect single copy genes in only 0.5 μg of DNA; high sensitivity means detection of low concentrations of probe-target hybrid.
Non-radioactive labels
safer than radiolabels; does not require dedicated rooms, glasswares, and equipment but not as sensitive.
Hybridization
ssDNA (probe) can base pair to a second (DNA or RNA) molecule that contains a complementary sequence (target).
BIOTECHNOLOGY
any biology-based technology that makes use of an organism or any of its parts to make or modify a product, or improve plants, animals, microorganisms.
1979
The year of establishment of the UPLB Biotech (National Institute of microbiology and Biotechnology)
2011
Completion of Golden Rice Confined Field Testing/Establisment of the Philippine Genome Center
2021
Year of commercial release of Golden Rice
2022
Year of commercial release of BT talong
1944
Discovery of DNA as hereditary material
1953
The year when Watson and Crick discovered the Double Helix Structure of DNA
1973
The year when Cohen and Boyer discovered the DNA-Recombiinant technology
1994
Year of release of FlavrSavr Tomato
1997
Dolly the Sheep was born(?)
2000
The 1st draft of the Human Genome.
1996
First Greenhouse trial of BT Corn and Congressional hearing for GM Rice.
1998
Papaya Biotechnology Network Established to developed a PRSV resistant and delayed ripening Papaya.
1999-2001
Field Testing of BT Corn
2002
Release of BT Corn/Issuance of AO no. 8
2006
HErbicite-Tolerannt GM Corn/ National Biosafety Framework
2009
BT eggplant limited Trial Completion
2010
BT cotton confined Field testing completion
2011
Completion of Golden Rice COnfine Field Testing/Establishment of the Ph Genome Center.
2012
Lawsuit was filed against the Commercialization of BT eggplant.
Nucleic Acids
Chemical repositories of genetic information
Nucleic Acids
Biopolymers of nucleotides linked together by phospodiester bonds,
DNA
RNA
Two forms of Nucleic Acid
Phosphate
Purine or Pyramidine Base
Pentose
Three components of Nucleotide Structure
Phosphate Groups
Form the backbone of the polynucleotide together with the pentose
Phosphate Groups
Imparts (–) charge to the DNA hence enabling DNA to associate with the positively charged histones.
Phosphodiester bonds
sugar and phosphate groups are linked together by
Hydrogen Bonds
Two complimentary strands of DNA are held together by __
Chargaff’s Rule
This rule states that #A = #T ; #C = #G
hydrophobic interactions
Base pair stacking maximizes ___ to stabilize the DNA structure
DNA
1
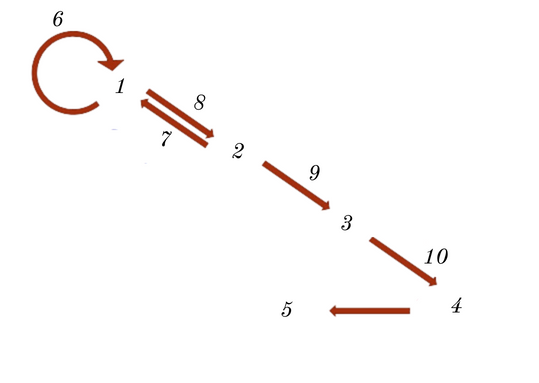
RNA
2
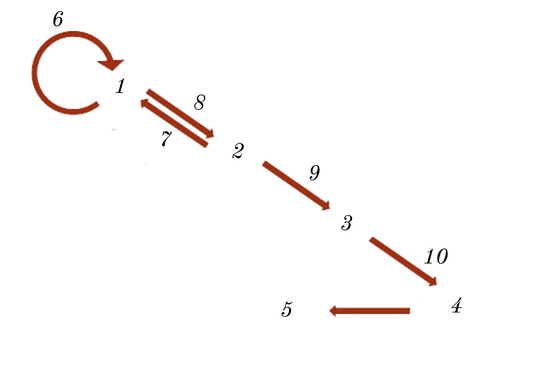
POLYPETIDES
3
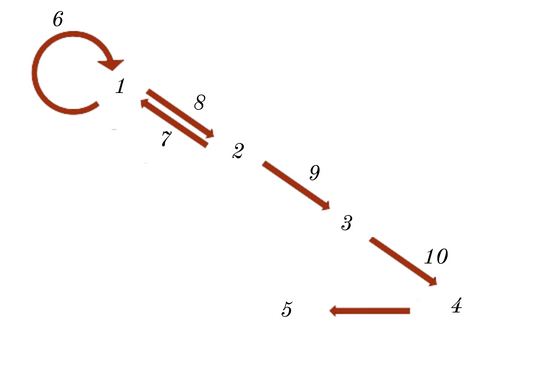
Proteins
4
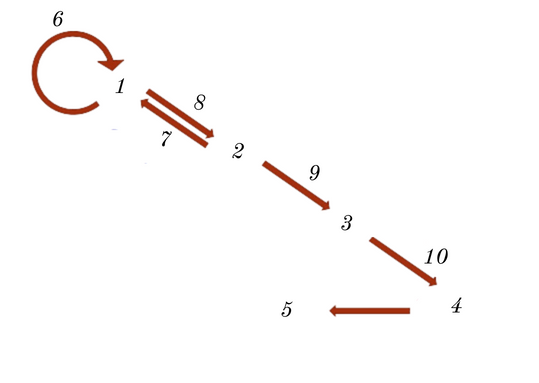
Phenotype
5
Replication
6
Reverse Transcription
7
Transcription
8
Translation
9
Replication
Process by which DNA makes identical copies of itself; the Synthesis of DNA.
S-phase
Replication occurs during what phase of the cell cycle in preparation for cell division.
DnaA Protein
The protein responsible for opening duplex at specific sites in origin.
DnaB Protein (DNA helicase)
The protein that unwinds the DNA double helix.
SSBP (Sing strand DNA-binding proteins)
The protein that binds to ssDNA and keeps them separated.
DNA Topoisomerase (DNA gyrase)
The protein that relieves torsional strain brought about by DNA unwinding.
RNA Primer
Responsible for providing the free 3’ —OH group where deoxyribonucleotides will be added.
RNA Primer
It is need because the major DNA replicating enzyme can only extend a pre-existing DNA strand and cannot initiate a nucleotide DNA.
DnaA Protein
DnaB Protein (DNA helicase)
SSBP (Single strand DNA-binding proteins)
DNA Topoisomerase (DNA gyrase)
RNA Primers
RNA Primase
Proteins required during the initiation stage of DNA replication.
RNA Primase
The enzyme responsible for the catalyzation of the synthesis of the RNA.
DNA Polymerase III
This protein catalyzes chain elongation from 5’ to 3’ direction with respect to the daughter DNA strand.
dATP
dGTP
dCTP
dTTP
the deoxyribonucleoside triphosphates.
DNA Polymerase I
This protein proofreads the daughter DNA for mismatches.
DNA Polymerase I
This protein exercises RNA primers and fills in gaps with deoxyribonucleotides until only one phosphodiester bond remains to be formed.
DNA ligase
This enzyme catalyzes formation of phospodiester bond to seal nich in the sugar phoesphate backbone.
DNA Polymerase III
DNA Polymerase I
DNA ligase
The proteins required during the elongation stage of DNA Replication.
Termination
The stage of DNA Replication in which the entire length of the DNA molecule has been duplicated already.
two daughter strands
Products of termination stage of DNA Replication.
Semi-conservative
The characteristic of DNA replication that refers to the daughter DNA molecules containing one strand from the parent and one newly synthesized strand.
Bidirectional
The characteristic of DNA replication that refers to the occurrence of DNA replication in two opposite directions about the origin of replication.
Semidiscontinuous
The characteristic of DNA Replication that refers to the synthesis of new DNA strand always occurs from the 5’ to 3’ direction with respect to the DNA strand being synthesized.
Leading strand
that stand that elongates continuously.
Lagging strand
the strand that elongates discontinuously.