BIOL 4100 - exam 1
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
Cells vary enormously in ____ and _____
appearance and function
Living cells all have a similar basic chemistry (T/F)
true
living cells are self-replicating collections of __________
catalysts
instructions for the form, function, and behavior of cells and organisms are stored in _______
genes
In all living cells, genetic information flows from ______ to ______
DNA to RNA
All living cells have apparently evolved from different ancestral cells (T/F)
FALSE
The invention of the _______ microscope led to the discovery of cells
light microscope
The fine structure of a cell is revealed by ________ microscopy
electron microscopy
____________ are the most diverse and numerous cells on earth
Prokaryotes
Prokaryotes are divided into two domains:
Bacteria and Archaea
***some bacteria are photosynthetic
Eukaryotic cells possess ______ and _______
nucleus and organelles
Mitochondria generate usable energy from ________ ________.
food molecules
Chloroplasts capture energy from ________
sunlight
The _____________ is responsible for directed cell movements
cytoskeleton
Mitochondria are thought to have evolved from engulfed _______
bacteria
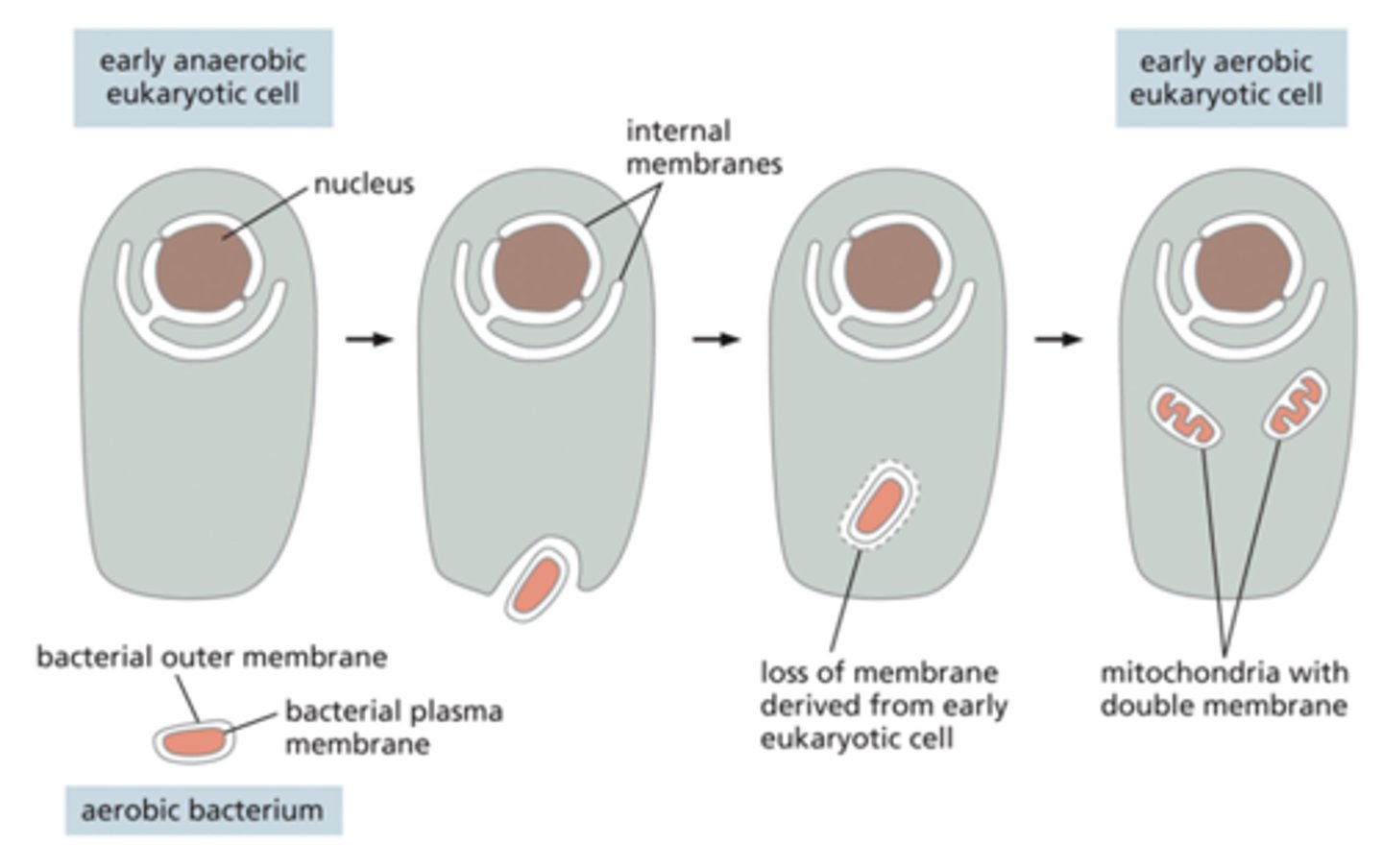
Chloroplasts almost certainly evolved from engulfed _____________ _____________.
photosynthetic bacteria.
____________ __________ create intracellular compartments with different functions
Internal membranes
Eukaryotic cells engage in continual ___________ and __________ across their plasma membrane.
endocytosis and exocytosis
import extracellular materials by _______
endocytosis
secrete intracellular materials by ________
exocytosis
endocytosed material is first delivered to membrane-enclosed organelles called __________
endosomes
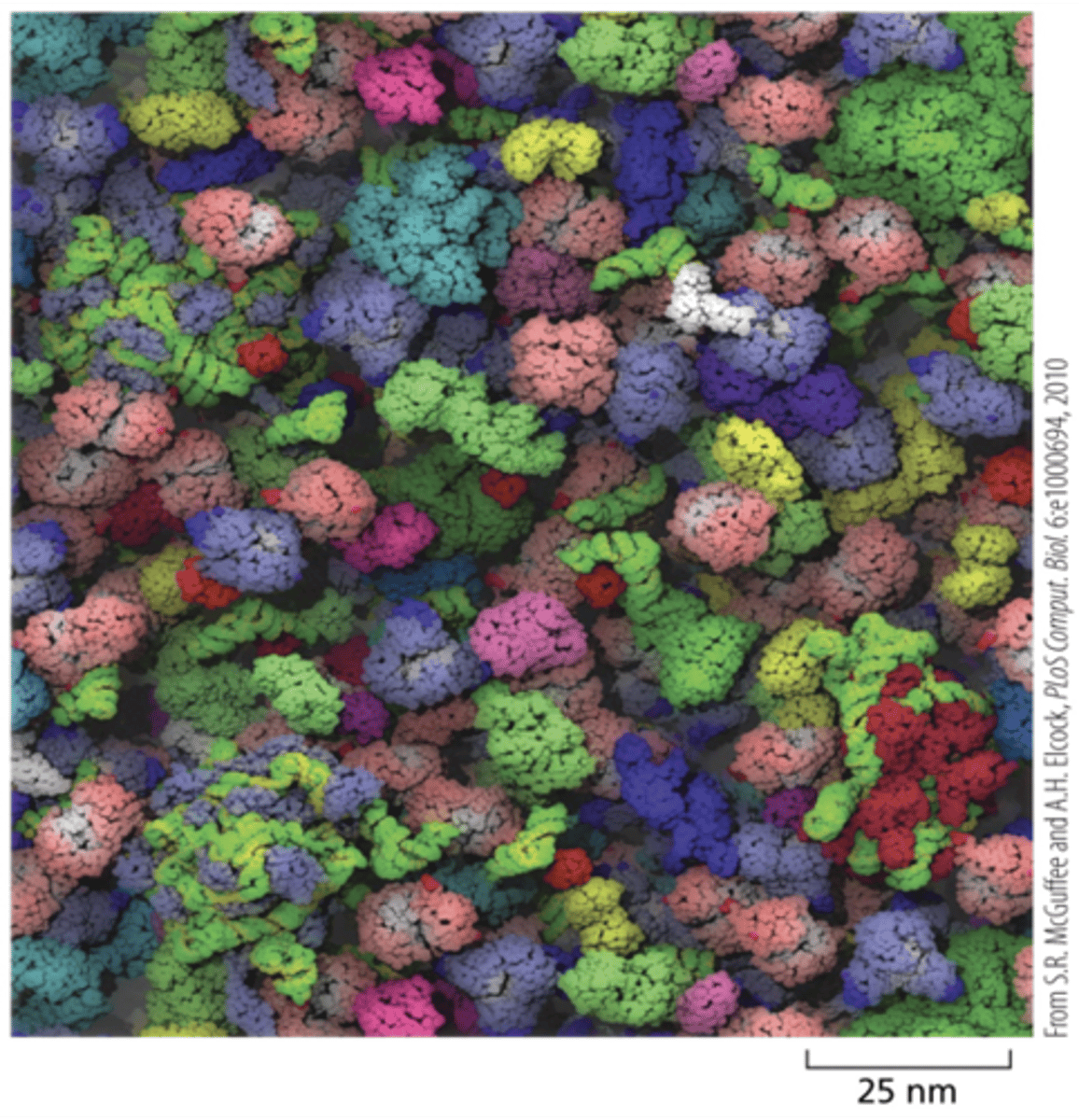
The ________ Is a Concentrated Aqueous Gel of Large and Small Molecules
Cytosol
This atomically detailed model of the cytosol of E. coli is based on the sizes and concentrations of 50 of the most abundant large molecules present in the bacterium.
RNAs, proteins, and ribosomes are shown in different colors
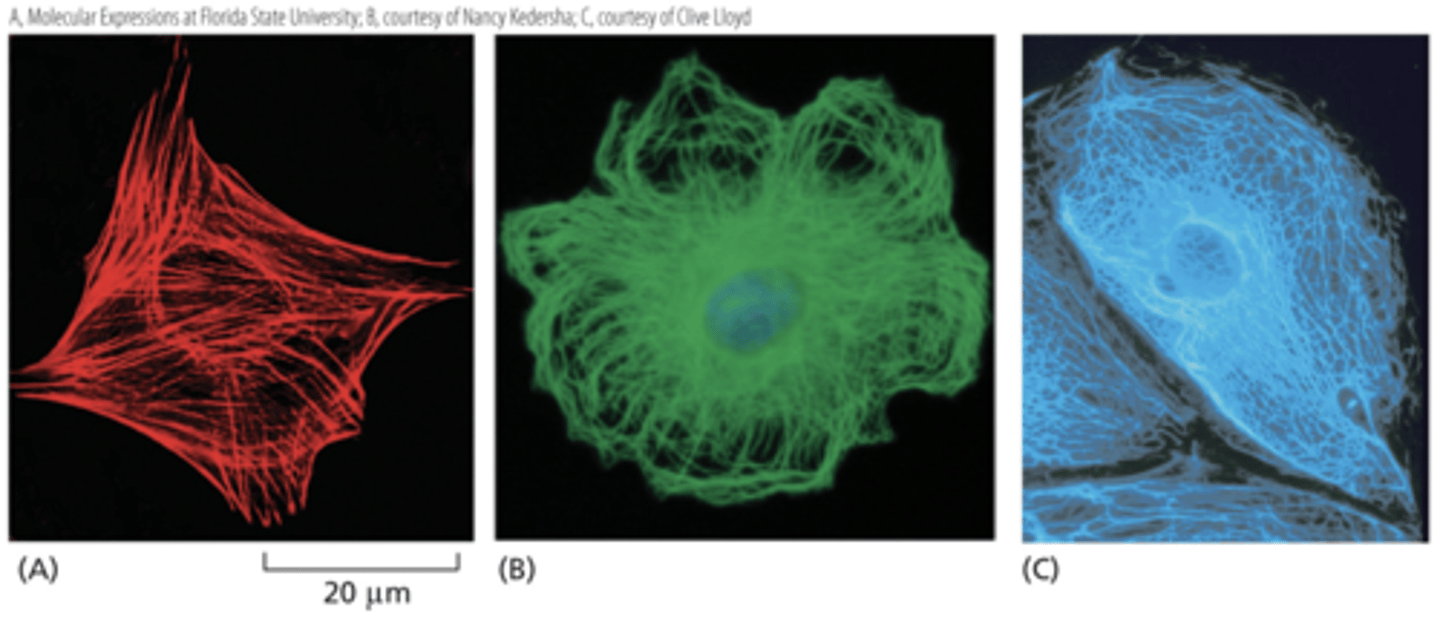
The three major types of filaments can be detected using different fluorescent stains.
(A)actin filaments,
(B) microtubules, and
(C) intermediate filaments.
Intermediate filaments are not found in the cytoplasm of cells with cell walls, such as plant cells. (T/F)
true
The ___________ is a network of protein filaments that can be seen crisscrossing the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells
The cytoskeleton
__________ help segregate the chromosomes in a dividing animal cell
Microtubules
When a cell divides, its _________ ________ breaks down and
Its DNA condenses into visible chromosomes, each of which has duplicated to form a pair of conjoined chromosomes
Chromosomes are pulled apart into separate daughter cells by the spindle ____________.
nuclear envelope
microtubules.
Why don't all cells act and look the same?
gene expression
phase contrast microscope
brightfield microscope w/ stained cells
chronological order of mitochondria evolving (4 steps)
1. bacteria and archaea diverged
2. eukaryote and archaea diverge
3. eukaryotes acquired mitochondria
4. eukaryotes acquired chloroplast
All biological systems are composed of cells containing the same types of chemical molecules and employing similar principles of organization at the cellular level. (T/F)
T
Eukaryotic cells may have originated as ___________
predators
What model organism have molecular biologists focused on?
E. coli
Brewer's yeast is a ______ eukaryote
simple eukaryote
____________ has been chosen as a model plant
Arabidopsis
Model animals include ______, ______, _______, and _____
flies, worms, fish, and mice
Comparing genome sequences reveals life's ________ ________
common heritage
genomes only become genes (T/F)
False
Why have molecular biologists focus on E. coli as their model organism?
easy to grow, grows fast, contains most bacterial structures, easy to manipulate, can accept foreign DNA (singular circular chromosomes, may have some plasmids); pathogenic, non-pathogenic, or a commensal; grows with oxygen or without
Brewer’s yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) is a _________ ________
simple eukaryote
main activities studied through Brewer's yeast (S. cerevisiae)
cell cycle and secretion
Brewer's yeast (S. cerevisiae) model organism benefits
- Exist as both Diploid and Haploid.
- They share many of the more than 6000 proteins with most eukaryotic cells
•Cell cycle
•Protein secretion
Mutations in _________ _________ led to the identification of key cell cycle proteins
Brewer's yeast
uncontrolled cell growth in yeast is similar to what
human cancers
The cell-division-cycle proteins from yeasts and human are very similar in their ________ ________ _________.
amino acid sequences.
Why are Zerbrafish ideal for development studies?
as their transparent embryos develop outside the mother, making it easy to observe cells moving and changing their characters in the living organism as it develop
Confocal microscope, a ________ fluorescent protein marks the developing lymphatic vessels and a ______ fluorescent protein marks developing blood vessels
green
red
Are human cells a model organism?
yes
the first immortal human cell
Hela cells
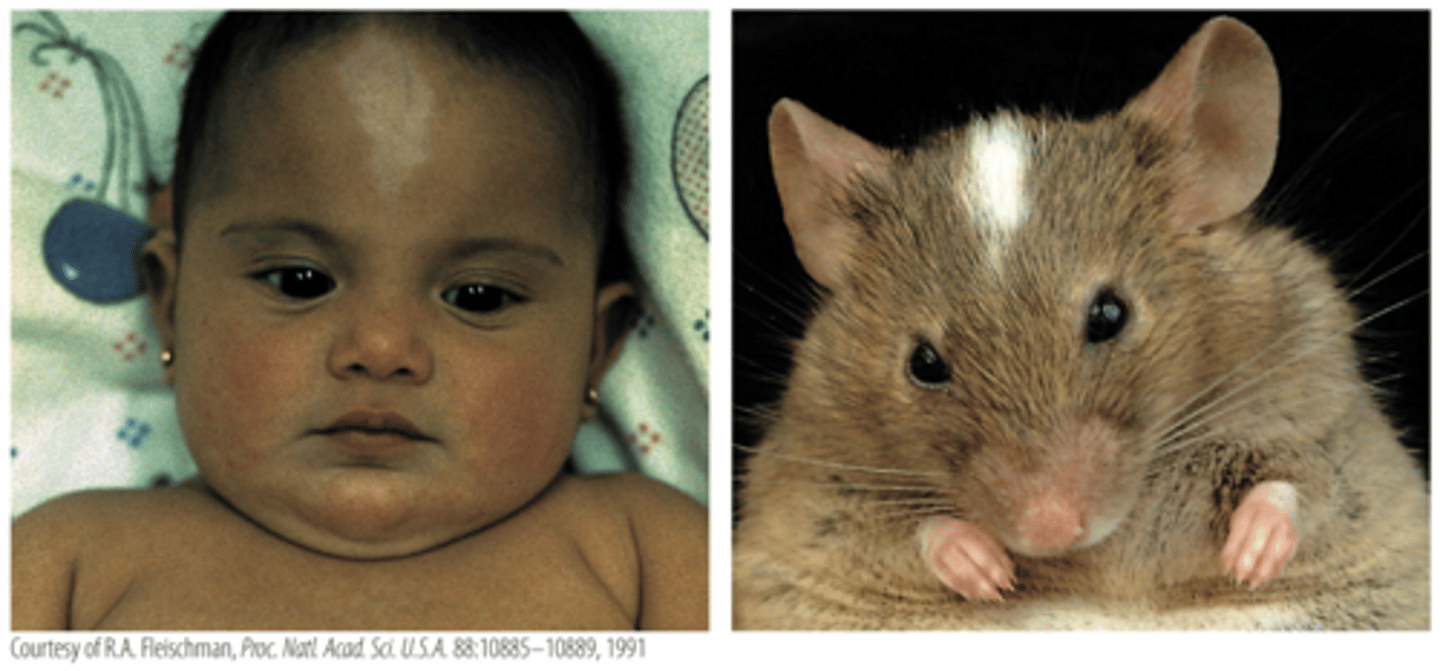
what is Kit?
both have defects in the same gene (called Kit), which is required for the normal development, migration, and maintenance of some skin pigment cells
Arabidopsis has been chosen as a model _______
model plant
What makes Arabidopsis thaliana a good model organism?
•short generation time and
•the ability to self-fertilize (selfing)
•has a small genome ~114.5 Mb and
•is genetically well characterized due to the volume of work being focused on this plant.
Comparing ________ _________ reveals life's common heritage
genome sequences
cell wall in animal vs. plant vs. bacterial cells
animal cells - no cell wall
plant cells - some have cell wall
bacterial cell wall - has cell wall
eukaryotes share a lot of genetic similarities with humans (T/F)
true
most important characteristics
eye color
what model organism led to the discovery that genes are linked to chromosomes and a specific location on each chromosome?
Drosophila melanogaster - fruit fly
are humans owner of their own cells? common rule
cells detached from the body can be used
The __________ electrons determine how atoms interact
The outermost electrons determine how atoms interact
__________ bonds form by the sharing of electrons
Covalent bonds
*****Covalent bonds are strong enough to survive the conditions inside cells
_________ bonds form by the gain and loss of electrons
Ionic bonds
____________ bonds are important noncovalent bonds for many biological molecules
Hydrogen bonds
_____________ van der Waals attraction bonds for many biological molecules
noncovalent
Cells are made of relatively few types of ________
atoms
Cells contain four major families of small organic molecules, what are they?
sugars, fatty acids, amino acids, nucleotides
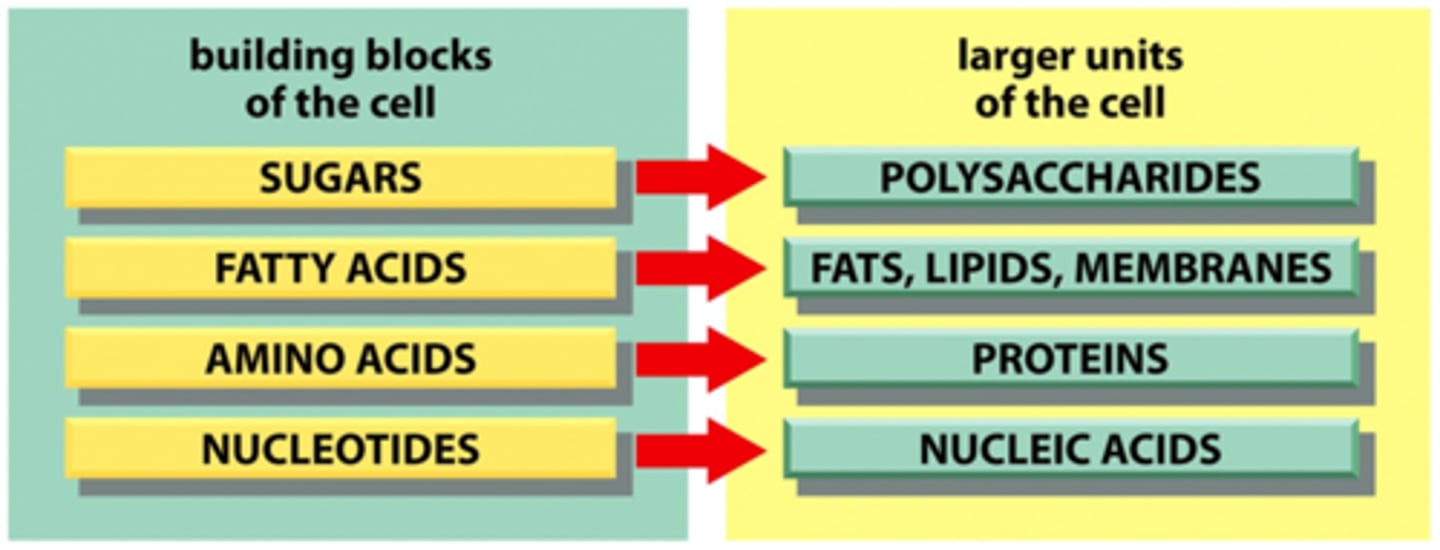
_________ are both energy sources and subunits of polysaccharides
Sugars
_______ ________ chains are components of cell membranes
Fatty acid
________ ________ are the subunits of proteins
Amino acids are the subunits of proteins
____________ are the subunits of DNA and RNA
Nucleotides
Two monosaccharides can be linked by a _________ __________ bond to form a disaccharide.
covalent glycosidic bond
In _______________ reaction, two molecules join as a result of loss of water molecule. • Requires an input of energy
Condensation reaction
____________ reaction, water is added and bring the molecules together • Release of energy
Hydrolysis reaction,
In the lipid bilayer is made of __________ phospholipids
• the ______________ heads of the phospholipid molecules are on the outside, facing the aqueous environment, and
• the _______________ tails are on the inside, where water is excluded
amphipathic phospholipids
hydrophilic
hydrophobic
______________, a typical phospholipid, glycerol is covalently linked via a phosphate group to choline.
Phosphatidylcholine,
Phospholipid bilayer is formed by fatty acids linked to glycerol-3-phosphate (G3P) via ______ bonds
via ester bonds
__________ have the most extreme variations in phospholipid sidechain structures.
Archaea
__________ links between glycerol and fatty acids
- Help to grow at high temperature
Ether
Hydrocarbon chains are branched ___________
terpenoids
_________ __________ are the subunits of proteins
Amino acids
Amino acids in a protein are held together by _________ bonds
peptide bonds
_____________ are the subunits of DNA and RNA
Nucleotides
A chain of a deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) molecule is formed by linking nucleotides with a _______________ bonds
phosphodiester bonds
ATP is synthesized from ADP and inorganic phosphate, and it releases energy when it is hydrolyzed back to ADP and inorganic phosphate.
ATP cycle
_______ is the most common molecule used by cells to capture, store, and transfer energy
ATP
____________ bonds specify the precise shape of a macromolecule and allow a macromolecule to bind other selected molecules
Noncovalent
The _________________ helped to settle the debate about the nature of macromolecules
ultracentrifuge
Both _________ bonds and ______________ bonds are needed to form a macromolecular assembly such as a ribosome.
covalent bonds and noncovalent bonds
A major portion of the energy stored in the chemical bonds of food molecules is dissipated as _______
heat