Infectious Disease Pharmacology
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/263
Earn XP
Description and Tags
This is still a work in progress!
Last updated 10:17 PM on 2/23/23
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
264 Terms
1
New cards
Define selective-toxicity
toxic to the micro-organism, but not harmful to the cells of the host
2
New cards
What do antimicrobial agents target?
Antimicrobial agents target
* metabolic channels
* metabolic pathways
* structures present in the micro-organism, but not in the host
* metabolic channels
* metabolic pathways
* structures present in the micro-organism, but not in the host
3
New cards
What is the difference between antibiotic and antimicrobial?
Antibiotic
* Substance produced by a micro-organism (natural origin)
\
Antimicrobial
* Substance of natural, synthetic or semi-synthetic origin
* Substance produced by a micro-organism (natural origin)
\
Antimicrobial
* Substance of natural, synthetic or semi-synthetic origin
4
New cards
What is a cytostatic / bacteristatic antimicrobial?
They inhibit the growth of the target organism/bacteria
5
New cards
What is a cytocidal / bactericidal antimicrobial?
They kill the target organism/bacteria
6
New cards
How are antimicrobial agents classified?
* Their target organism
* Cytostatic versus cytocidal
* Mechanism of action
* Spectrum of activity
* Cytostatic versus cytocidal
* Mechanism of action
* Spectrum of activity
7
New cards
What groups of organisms do antimicrobes target?
* Bacterias
* Fungi
* Viruses
* Protazoas
* Fungi
* Viruses
* Protazoas
8
New cards
What is the mechanism of action of antibiotics?
* Inhibition of cell wall synthesis
* Inhibition of protein synthesis (translation)
* Inhibition of nucleic acid replication and transcription
* Inhibition of synthesis of essential metabolites
* Injury to plasma membrane
* Inhibition of protein synthesis (translation)
* Inhibition of nucleic acid replication and transcription
* Inhibition of synthesis of essential metabolites
* Injury to plasma membrane
9
New cards
What are the two spectrums of antibacterial targets?
* Broad spectrum
* Narrow spectrum
* Narrow spectrum
10
New cards
What is a broad spectrum antibiotic + give examples?
Activity against a broad range of bacteria – Gram positive and Gram negative
* Carbapenems
* Fluoroquinolones
* 3rd and 4th generation cephalosporins
\
The broader the spectrum, the more chance of antibiotic resistance
* Carbapenems
* Fluoroquinolones
* 3rd and 4th generation cephalosporins
\
The broader the spectrum, the more chance of antibiotic resistance
11
New cards
What is a narrow spectrum antibiotic + give examples?
Limited activity
* ^^Nitroimidazoles^^ active only against anaerobic bacteria
* ^^Glycopeptides^^ active only against Gram positive bacteria
* ^^Nitroimidazoles^^ active only against anaerobic bacteria
* ^^Glycopeptides^^ active only against Gram positive bacteria
12
New cards
What are the benefits of antimicrobial therapies?
* Reduced mortality
* Reduced morbidity
* Safer surgery
* Safer transplants
* Reduced morbidity
* Safer surgery
* Safer transplants
13
New cards
What are the downsides of antimicrobial therapies?
* Resistance
* Toxicity (to host)
* Secondary infection
* Hypersensitivity / allergic reactions
* Toxicity (to host)
* Secondary infection
* Hypersensitivity / allergic reactions
14
New cards
What is the steps of antimicrobial treatments?
Empiric treatment:
* Initial treatment, before causative organism identified
* It is the ‘Best guess’
\
Definitive treatment:
* Targeted at identified organism
* Initial treatment, before causative organism identified
* It is the ‘Best guess’
\
Definitive treatment:
* Targeted at identified organism
15
New cards
How do you select the type of antimicrobial agent?
* Site of infection
* Likely causative organism(s)
* Oral or intravenous therapy → also dependent on where patient gets treatment e.g. oral in GP practice?
* Pharmacodynamic characteristics of agent
* Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM)
* Likely causative organism(s)
* Oral or intravenous therapy → also dependent on where patient gets treatment e.g. oral in GP practice?
* Pharmacodynamic characteristics of agent
* Therapeutic drug monitoring (TDM)
16
New cards
What is a minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC)?
Lowest concentration of the antimicrobial →
which results in inhibition of detectable growth of the organism
which results in inhibition of detectable growth of the organism
17
New cards
What are the 2 types of pharmacodynamics of antimicrobials?
* Time-dependent killing
* Concentration-dependent killing
* Concentration-dependent killing
18
New cards
What is a time-dependent killing pharmacodynamic + examples?
Bactericidal effect is dependent on the ^^length of time that the bacteria are \n exposed to concentrations of drug above the MIC^^
* Penicillins
* Cephalosporins
* Carbapenems
\
A property associated with cell wall synthesis inhibtors
Bactericidal activity continues as long as the plasma concentration is greater than the minimum bactericidal concentration (or MIC).
* Penicillins
* Cephalosporins
* Carbapenems
\
A property associated with cell wall synthesis inhibtors
Bactericidal activity continues as long as the plasma concentration is greater than the minimum bactericidal concentration (or MIC).
19
New cards
What is a conc.-dependent killing pharmacodynamic + examples?
Bactericidal effect ^^increases with the concentration of the drug^^
* Fluoroquinolones
* Aminoglycosides
\
The rate & extent of killing increases as the peak drug concentration increases
A property associate with drugs inhibiting protein or DNA synthesis
* Fluoroquinolones
* Aminoglycosides
\
The rate & extent of killing increases as the peak drug concentration increases
A property associate with drugs inhibiting protein or DNA synthesis
20
New cards
What are the host factors for antimicrobial therapies?
* Age
* Renal and hepatic function
* Underlying disease
* Antimicrobial allergy
* Genetic variation (e.g., G6PD deficiency)
* Pregnancy, breastfeeding
* Recent antimicrobial therapy
* Recent microbiology results
* Renal and hepatic function
* Underlying disease
* Antimicrobial allergy
* Genetic variation (e.g., G6PD deficiency)
* Pregnancy, breastfeeding
* Recent antimicrobial therapy
* Recent microbiology results
21
New cards
What are some complications of antimicrobial therapies?
* Development of antimicrobial resistance
* Drug toxicity
* Side effects (adverse reactions)
* Interactions with other medications
* Allergy (hypersensitivity reactions)
* Secondary infections
* Treatment failure
* Drug toxicity
* Side effects (adverse reactions)
* Interactions with other medications
* Allergy (hypersensitivity reactions)
* Secondary infections
* Treatment failure
22
New cards
What are the types of allergy/hypersensitivity reactions?
* Immediate, IgE mediated, type 1
* Delayed, non-IgE mediated, usually type 4
* Delayed, non-IgE mediated, usually type 4
23
New cards
What is a type-1 allergy reaction?
* It is immediate - Within 1 hour
* IgE mediated
* S/E: Urticarial rash, itch, flushing, wheeze, angioedema, hypotension, anxiety
* IgE mediated
* S/E: Urticarial rash, itch, flushing, wheeze, angioedema, hypotension, anxiety
24
New cards
What is a type 4 allergy reaction?
* Delayed - takes more than 1 hour
* Non-IgE mediated
* S/E: rash, fever, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
* Non-IgE mediated
* S/E: rash, fever, Stevens-Johnson syndrome
25
New cards
What is important to consider for allergic patients?
Detailed history important \n Need to distinguish:
* Nature of allergy
* Between allergy and side effect/intolerance (Type 1 or Type 4?)
* Groups of antibacterials that they had allergy / hypersensitivity / intolerance reactions to
* Nature of allergy
* Between allergy and side effect/intolerance (Type 1 or Type 4?)
* Groups of antibacterials that they had allergy / hypersensitivity / intolerance reactions to
26
New cards
Why can an antimicrobial treatment fail?
* Incorrect diagnosis
* Inappropriate choice of agent - e.g. doesn’t cross blood-brain barrier
* Suboptimal dose, frequency or duration
* Inadequate source control - e.g. if line is infected → remove the line as well as prescribing antibiotic!
* Drug resistance
* Inappropriate choice of agent - e.g. doesn’t cross blood-brain barrier
* Suboptimal dose, frequency or duration
* Inadequate source control - e.g. if line is infected → remove the line as well as prescribing antibiotic!
* Drug resistance
27
New cards
What are the principles in prescribing antimicrobes?
* Treat only if evidence of infection
* Use as narrow-spectrum as possible
* Send appropriate microbiology samples, ideally prior to treatment
* Follow antimicrobial prescribing guidelines
* Use local guidelines if available
* Document indication and review/stop date
* Review with results
* Modify treatment, de-escalate if possible
* Use as narrow-spectrum as possible
* Send appropriate microbiology samples, ideally prior to treatment
* Follow antimicrobial prescribing guidelines
* Use local guidelines if available
* Document indication and review/stop date
* Review with results
* Modify treatment, de-escalate if possible
28
New cards
What groups of drugs are inhibitors of bacterial cell wall synthesis + examples?
^^**Beta-lactam antimicorbials**^^
* Penicillins
* Cephalosporins
* Monobactams
* Carbapenems
\
^^**Glycopeptides:**^^
* Vancomycin
* Teicoplanin
\
**Bacitracin** \n
**Anti-**__**myco**__**bacterial agents:**
* Isoniazid
* Ethambutol
* Penicillins
* Cephalosporins
* Monobactams
* Carbapenems
\
^^**Glycopeptides:**^^
* Vancomycin
* Teicoplanin
\
**Bacitracin** \n
**Anti-**__**myco**__**bacterial agents:**
* Isoniazid
* Ethambutol
29
New cards
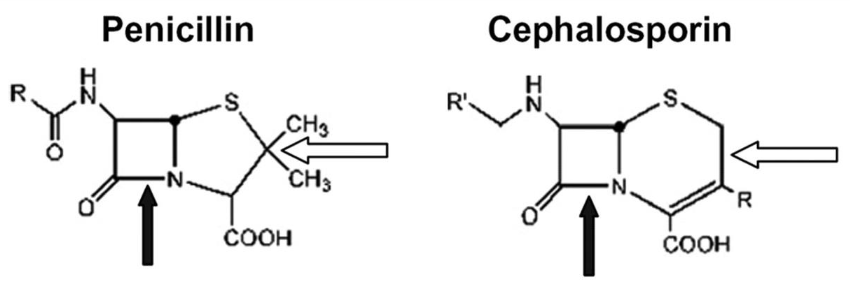
What is the structure of β-lactam antimicrobials + examples?
4-member core β-lactam ring + a side ring
* Penicillins have a 5 member side ring
* Cephalosporins have a 6 member side ring
* Penicillins have a 5 member side ring
* Cephalosporins have a 6 member side ring
30
New cards
Are β-lactams bactericidal or bacteristatic?
Bactericidal
31
New cards
How can β-lactams be modified?
By the modification of their side-rings
32
New cards
Why are β-lactams modified?
* To change antimicrobial activity
* To make resistance to β-lactamase enzymes
* Change their pharmacokinetics
* To make resistance to β-lactamase enzymes
* Change their pharmacokinetics
33
New cards
What is the mechanism of action of β-lactams?
Cross-linking of newly formed peptide to glycan backbone is catalysed by \n ^^transpeptidase^^ (aka penicillin binding protein, PBP) → β-lactam antimicrobials ^^bind to transpeptidase and prevent formation of cross links^^ \n
* Inhibition of cell wall synthesis activates autolytic enzymes which trigger cell death
* Production of β-lactamase by bacteria can inactivate drug and confer resistance
* Inhibition of cell wall synthesis activates autolytic enzymes which trigger cell death
* Production of β-lactamase by bacteria can inactivate drug and confer resistance
34
New cards
How can a bacteria become resistant to β-lactam drugs?
Production of β-lactamase by bacteria can inactivate drug and confer resistance
35
New cards
What are the different classifications of Penicillins?
* ^^Natural penicillins^^
* ^^β-lactamase resistant penicillins^^
* ^^Aminopenicillins^^
* ^^Carboyxypenicillins^^
* Ureidopenicillins (not used clinically)
* ^^Penicillin and β-lactamase inhibitor combinations^^
* ^^β-lactamase resistant penicillins^^
* ^^Aminopenicillins^^
* ^^Carboyxypenicillins^^
* Ureidopenicillins (not used clinically)
* ^^Penicillin and β-lactamase inhibitor combinations^^
36
New cards
What are the natural penicillin drug names?
* Penicillin G aka benzylpenicillin (IV)
* Penicllin V (oral)
* Penicllin V (oral)
37
New cards
What are the β-lactamase resistant penicillin drug names?
* ^^Flucloxacillin^^
* \[Methicillin\]
* \[Cloxacillin\]
* \[Nafcillin\]
\
\[brackets\] = either not used in Ireland/UK or not used clinically
* \[Methicillin\]
* \[Cloxacillin\]
* \[Nafcillin\]
\
\[brackets\] = either not used in Ireland/UK or not used clinically
38
New cards
What are the aminopenicillin drug names?
* Ampicillin
* Amoxicillin
* Amoxicillin
39
New cards
What are the carboxypenicillin drug names?
* ^^Temocillin^^
* \[Ticarcillin\]
* \[Ticarcillin\]
40
New cards
What are the penicillin and Β-lactamase inhibitor drug combinations?
* Amoxicillin/clavulanate (aka coamoxiclav)
* Piperacillin/tazobactam (aka piptazobactam)
* \[Ampicillin/sulbactam\] - not used in IE/UK
* \[Ticarcillin/clavulanate\] - not used in IE/UK
* Piperacillin/tazobactam (aka piptazobactam)
* \[Ampicillin/sulbactam\] - not used in IE/UK
* \[Ticarcillin/clavulanate\] - not used in IE/UK
41
New cards
What are the routes of administration for penicillins?
* Oral – penicillin V, amoxicillin, flucloxacillin
* IV – penicillin G, piperacillin, flucloxacillin
* IM – penicillin G
* IV – penicillin G, piperacillin, flucloxacillin
* IM – penicillin G
42
New cards
Which penicillin is has a higher bioavailability? Amoxicillin or Penicillin V?
Amoxicillin > Penicillin V
43
New cards
What reduces the absorption of penicillins?
* Food
* Acid pH
* Acid pH
44
New cards
What is the protein binding of penicillins?
Variable
45
New cards
What is the distribution of penicillins like?
* Distributes in most tissues and fluids
* Crosses placenta
* Crosses blood-brain barrier (BBB) if inflamed e.g. meningitis
* Crosses placenta
* Crosses blood-brain barrier (BBB) if inflamed e.g. meningitis
46
New cards
How is penicillin excreted?
* Predominantly renal excretion
* Tubular secretion >> glomerular filtration
* Dose reduction required in severe renal impairment (calc. eGFR)
* Tubular secretion >> glomerular filtration
* Dose reduction required in severe renal impairment (calc. eGFR)
47
New cards
What does the metabolism of penicillins look like?
Some hepatic metabolism
48
New cards
How much is nafcillin metabolised in the liver?
80% hepatic metabolism
49
New cards
What does probenecid do to penicillins? Why’s that useful?
* It inhibits the tubular secretion of penicillins
* Helps to lower daily intakes for patients (lower dosage, easier to manage/remember)
* Helps to lower daily intakes for patients (lower dosage, easier to manage/remember)
50
New cards
What are the side-effects of penicillins?
* GI - nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, C. difficile infection
* Skin – rash, phlebitis
* Haematological – neutropenia, platelet dysfunction
* CNS – seizures, encephalopathy
* Nephrotoxicity – acute interstitial nephritis
* Hepatic effects – hepatitis, cholestasis
* Hypokalaemia
* Hypersensitivity type 1 and 4 reactions
* Skin – rash, phlebitis
* Haematological – neutropenia, platelet dysfunction
* CNS – seizures, encephalopathy
* Nephrotoxicity – acute interstitial nephritis
* Hepatic effects – hepatitis, cholestasis
* Hypokalaemia
* Hypersensitivity type 1 and 4 reactions
51
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of Penicillin V/G?
Narrow spectrum:
* Streptococci
* Neisseria meningitidis
* Treponema pallidum
* Clostridia
* Streptococci
* Neisseria meningitidis
* Treponema pallidum
* Clostridia
52
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of Flucloxacillin?
Narrow spectrum:
*Staph. aureus*
*Staph. aureus*
53
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of Amoxicillin?
Narrow spectrum:
* Streptococci
* Enterococci
* E. Coli
* Listeria
* Streptococci
* Enterococci
* E. Coli
* Listeria
54
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity Amoxicillin/clavulanate (coamoxiclav)?
Broad spectrum:
* Gram negative bacilli
* streptococci
* Enterococci
* Staph. aureus
* Anaerobes
* Gram negative bacilli
* streptococci
* Enterococci
* Staph. aureus
* Anaerobes
55
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of Piperacillin/tazobactam (piptazobactam)?
Broad spectrum:
* Gram negative bacilli
* ^^**Pseudomonas aeruginosa - main use, in CF, burn patients, chemotherapy patients**^^
* Streptococci
* Enterococci,
* Staph. aureus
* Anaerobes
\
* Gram negative bacilli
* ^^**Pseudomonas aeruginosa - main use, in CF, burn patients, chemotherapy patients**^^
* Streptococci
* Enterococci,
* Staph. aureus
* Anaerobes
\
56
New cards
What is are the clinical uses of Penicillin V/G?
* Streptococcal infections (pharyngitis, skin, soft tissue, pneumonia, bone, joint, endocarditis)
* Meningococcal meningitis
* Syphilis
* Diphtheria
* Meningococcal meningitis
* Syphilis
* Diphtheria
57
New cards
What is are the clinical uses of Flucloxacillin?
Staph. aureus infections (skin, soft tissue, bone, joint, endocarditis)
58
New cards
What is are the clinical uses of Amoxicillin?
* Enterococcal infections (UTI, endocarditis)
* E. coli infections (UTI, intra-abdominal infections)
* Listeria infections
* E. coli infections (UTI, intra-abdominal infections)
* Listeria infections
59
New cards
What is are the clinical uses of Amoxicillin/clavulanate?
* Intra-abdominal infections (usually polybacterial)
* Anaerobic infections
* Pneumonia
* Anaerobic infections
* Pneumonia
60
New cards
What is are the clinical uses of Piperacillin/tazobactam?
* Intra-abdominal infections,
* Anaerobic infections
* Hospital-acquired pneumonia (Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
* Neutropenic sepsis
* Anaerobic infections
* Hospital-acquired pneumonia (Pseudomonas aeruginosa)
* Neutropenic sepsis
61
New cards
How many groups are Cephalosporins classified into?
1st-5th Generations
62
New cards
What are the 1st gen. Cephalosporins?
* Cephalexin
* Cefazolin
* Cefazolin
63
New cards
What are the 2nd gen. Cephalosporins?
* Cefuroxime
* Cefaclor
* Cefaclor
64
New cards
What are the 3rd gen. Cephalosporins?
* Cefotaxime
* Cetriaxone
* Ceftazidime
* Cetriaxone
* Ceftazidime
65
New cards
What is the 4th gen. Cephalosporin?
Cefepime
\*Not used in IE
\*Not used in IE
66
New cards
What is the 5th gen. Cephalosporin?
Ceftaroline
67
New cards
What are the routes of administration of Cephalosporins?
* Oral – cephalexin, cefaclor
* IV – cefuroxime, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone
* IM – ceftriaxone
* IV – cefuroxime, cefotaxime, ceftazidime, ceftriaxone
* IM – ceftriaxone
68
New cards
What is the bioavailability of Cephalosporins?
Cephalexin > cefaclor >> cefuroxime
69
New cards
What is the protein binding of cephalosporins?
Variable
70
New cards
What is the distribution of cephalosporins?
* Crosses most tissues and fluids
* Crosses the placenta
* ^^1st and 2nd generation do not cross BBB^^
* Crosses the placenta
* ^^1st and 2nd generation do not cross BBB^^
71
New cards
How are cephalosporins excreted?
Predominantly renal excretion
Dose reduction required in severe renal impairment (calc. eGFR)
Dose reduction required in severe renal impairment (calc. eGFR)
72
New cards
How are cephalosporins metabolised?
Some hepatic metabolism
73
New cards
What are the side effects of cephalosporins?
* GI – nausea, vomiting, diarrhoea, C. difficile infection
* Skin – rash, phlebitis
* Haematological – neutropenia, platelet dysfunction
* CNS – seizures, encephalopathy
* Nephrotoxicity – acute interstitial nephritis
* Hepatic effects – cholestasis
* Hypersensitivity type 1 and 4 reactions
* Estimated 10% cross reactivity with penicillins – likely \~1-2%
* Skin – rash, phlebitis
* Haematological – neutropenia, platelet dysfunction
* CNS – seizures, encephalopathy
* Nephrotoxicity – acute interstitial nephritis
* Hepatic effects – cholestasis
* Hypersensitivity type 1 and 4 reactions
* Estimated 10% cross reactivity with penicillins – likely \~1-2%
74
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of 1st gen. cephalosporins?
* Streptococci
* Staph. aureus
* Some Gram negative bacilli
* Staph. aureus
* Some Gram negative bacilli
75
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of 2nd gen. cephalosporins?
* Streptococci
* Staph. aureus
* Gram negative bacilli
* Haemophilus influenzae
* Staph. aureus
* Gram negative bacilli
* Haemophilus influenzae
76
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of 3rd gen. (cefotaxime, cetriaxone) +4th gen. cephalosporins?
* Streptococci
* Staph. aureus (less than 1st or 2nd)
* Neisseria meningitidis
* Gram negative bacilli
* Staph. aureus (less than 1st or 2nd)
* Neisseria meningitidis
* Gram negative bacilli
77
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of ceftazidime (also a 3rd gen., but has more activity)
* Streptococci
* Staph. aureus (less than cefotaxime, cetraixone)
* Neisseria meningitidis
* Gram negative bacilli
* ^^**Pseudomonas aeruginosa**^^
* Staph. aureus (less than cefotaxime, cetraixone)
* Neisseria meningitidis
* Gram negative bacilli
* ^^**Pseudomonas aeruginosa**^^
78
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of 5th gen. cephalosporins?
* Enhanced Gram positive cover, including MRSA and enterococci
* No anti-pseudomonal cover
* No anti-pseudomonal cover
79
New cards
What is the clinical use of 1st gen. cephalosporins?
* Streptococcal and Staph. aureus infections (pharyngitis, skin, soft tissue)
* Uncomplicated UTI
* Some Gram negative bacteria
* Uncomplicated UTI
* Some Gram negative bacteria
80
New cards
What is the clinical use of 2nd gen. cephalosporins?
* Intra-abdominal infections
* Surgical prophylaxis
* UTI
* Respiratory tract infection
* Surgical prophylaxis
* UTI
* Respiratory tract infection
81
New cards
What is the clinical use of 3rd gen. cephalosporins?
Broad spectrum
* Meningitis (N. meninigitidis, S, pneumoniae)
* Pneumonia
* Pyelonephritis
* Lyme disease
* Gonorrhoea
* Neutropenic sepsis
* Pseudomonal infections (^^ceftazidime^^ only)
* Meningitis (N. meninigitidis, S, pneumoniae)
* Pneumonia
* Pyelonephritis
* Lyme disease
* Gonorrhoea
* Neutropenic sepsis
* Pseudomonal infections (^^ceftazidime^^ only)
82
New cards
Name a monobactam
Aztreonam
83
New cards
What are the targeted organisms of monobactams?
Active only against:
* Aerobic Gram negative bacilli, including P. aeruginosa
* Aerobic Gram negative bacilli, including P. aeruginosa
84
New cards
What is the benefit of monobactams?
Resistant to many β-lactamases
85
New cards
How are monobactams administered?
IV only
86
New cards
How are monobactams excreted?
Renal excretion – reduce dose in severe renal impairment
87
New cards
What are the side effects of monbactams?
* Rash
* Pancytopenia
* Suprainfections, including C. difficile
* Convulsions
* Pancytopenia
* Suprainfections, including C. difficile
* Convulsions
88
New cards
What are the clinical uses of monobactams?
* Pyelonephritis
* Gram negative respiratory tract infections (cystic fibrosis)
* Intra-abdominal infections (in combination with other antimicrobials)
* Gram negative respiratory tract infections (cystic fibrosis)
* Intra-abdominal infections (in combination with other antimicrobials)
89
New cards
Give examples of cabapenems
* Ertapenem
* Meropenem
* Imipenem-cilastin
* Doripenem
* Meropenem
* Imipenem-cilastin
* Doripenem
90
New cards
What is the benefit of carbapenems>
Resistant to most β-lactamases (including extended-spectrum βlactamases, ESBL)
91
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of carbapenems?
**Extremely broad spectrum cover**
* Gram negative bacilli
* Streptococci
* Listeria,
* Anaerobes
* Pseudomonas aeruginosa (not ertapenem)
* Gram negative bacilli
* Streptococci
* Listeria,
* Anaerobes
* Pseudomonas aeruginosa (not ertapenem)
92
New cards
When are carbapenems clinically used?
**RESERVE drug**:
* Used only for infections due to bacteria caused by resistant organisms
* Severe sepsis
* Used only for infections due to bacteria caused by resistant organisms
* Severe sepsis
93
New cards
How are carbapenems administered?
IV only
94
New cards
How are carbapenems excreted?
Renal excretion
Reduce dose in sever renal impairment
Reduce dose in sever renal impairment
95
New cards
What are the side effects of carbapenems?
* Rash,
* Hepatic and haematological effects
* Seizures
* Hepatic and haematological effects
* Seizures
96
New cards
How do glycopeptide antimicrobials work?
* Inhibit bacterial cell wall synthesis
* Interact with the terminal amino acids of the side chain → thereby interfering with the formation of cross links between chains
* Interact with the terminal amino acids of the side chain → thereby interfering with the formation of cross links between chains
97
New cards
What are some examples of glycopeptide antimicrobials?
* Vancomycin
* Teicoplanin
* Oritavancin (single dose)
* Dalbavancin (weekly dosing)
* Teicoplanin
* Oritavancin (single dose)
* Dalbavancin (weekly dosing)
98
New cards
What is the spectrum of activity of glycopeptide antimicrobials?
Narrow spectrum of activity
\
**Gram positive organisms**
* Staph. aureus (including MRSA)
* Coagulase negative
* Staphylococci
* Enterococci
* Streptococci
\
**Gram positive organisms**
* Staph. aureus (including MRSA)
* Coagulase negative
* Staphylococci
* Enterococci
* Streptococci
99
New cards
Why can’t glycopeptide antimicrobials target gram negative bacteria?
Molecule too big to pass through the outer membrane of Gram negative bacteria
100
New cards
How are glycopeptide antimicrobials administered?
* IV use only as not absorbed orally
* Exception is the use of oral vancomycin for treatment of C. difficile infection (not absorbed, so available at intended site of action in bowel)
* IV dose based on weight and renal function
* Exception is the use of oral vancomycin for treatment of C. difficile infection (not absorbed, so available at intended site of action in bowel)
* IV dose based on weight and renal function