Last OSCE Study Guide Set
1/98
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
99 Terms
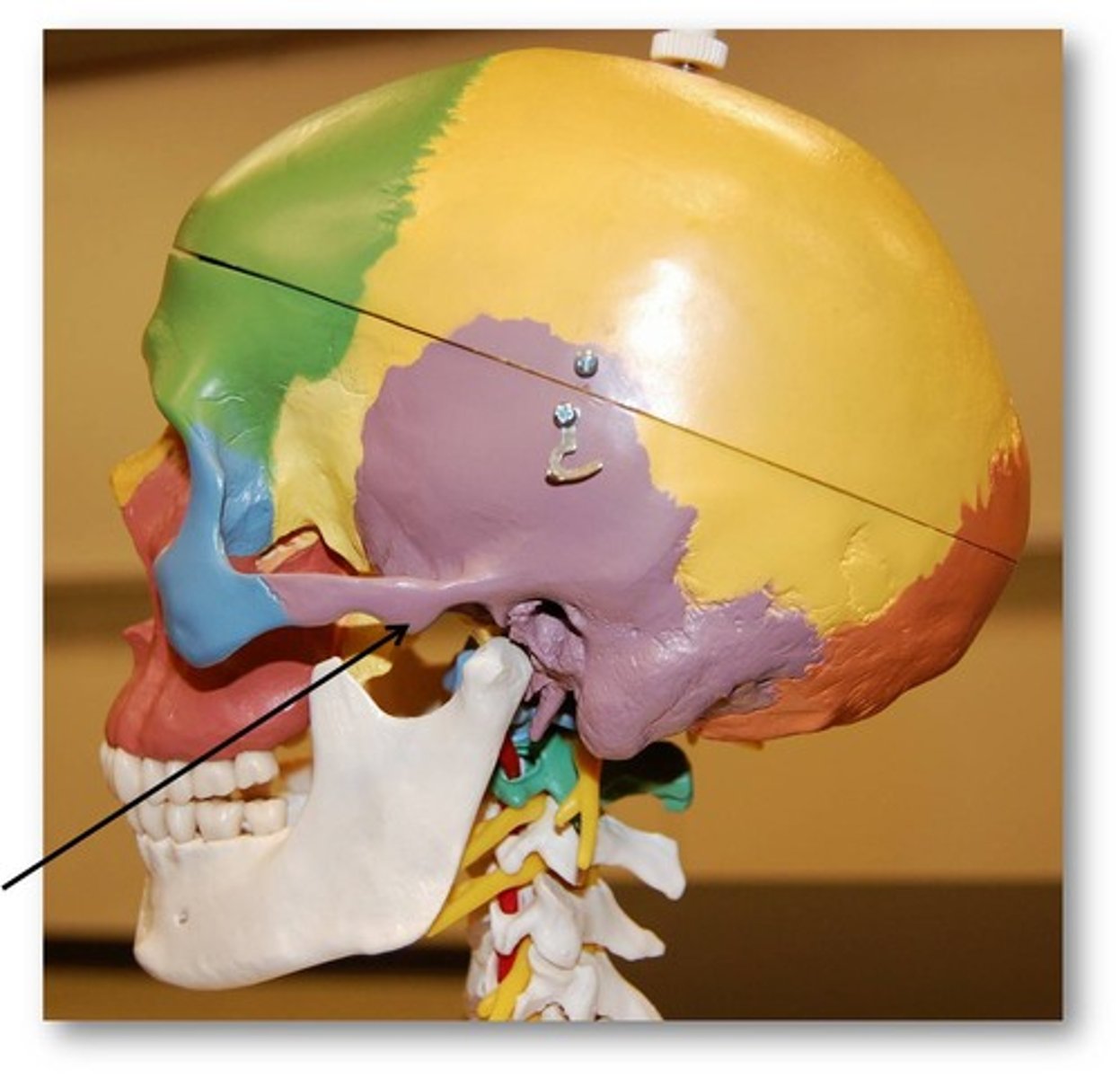
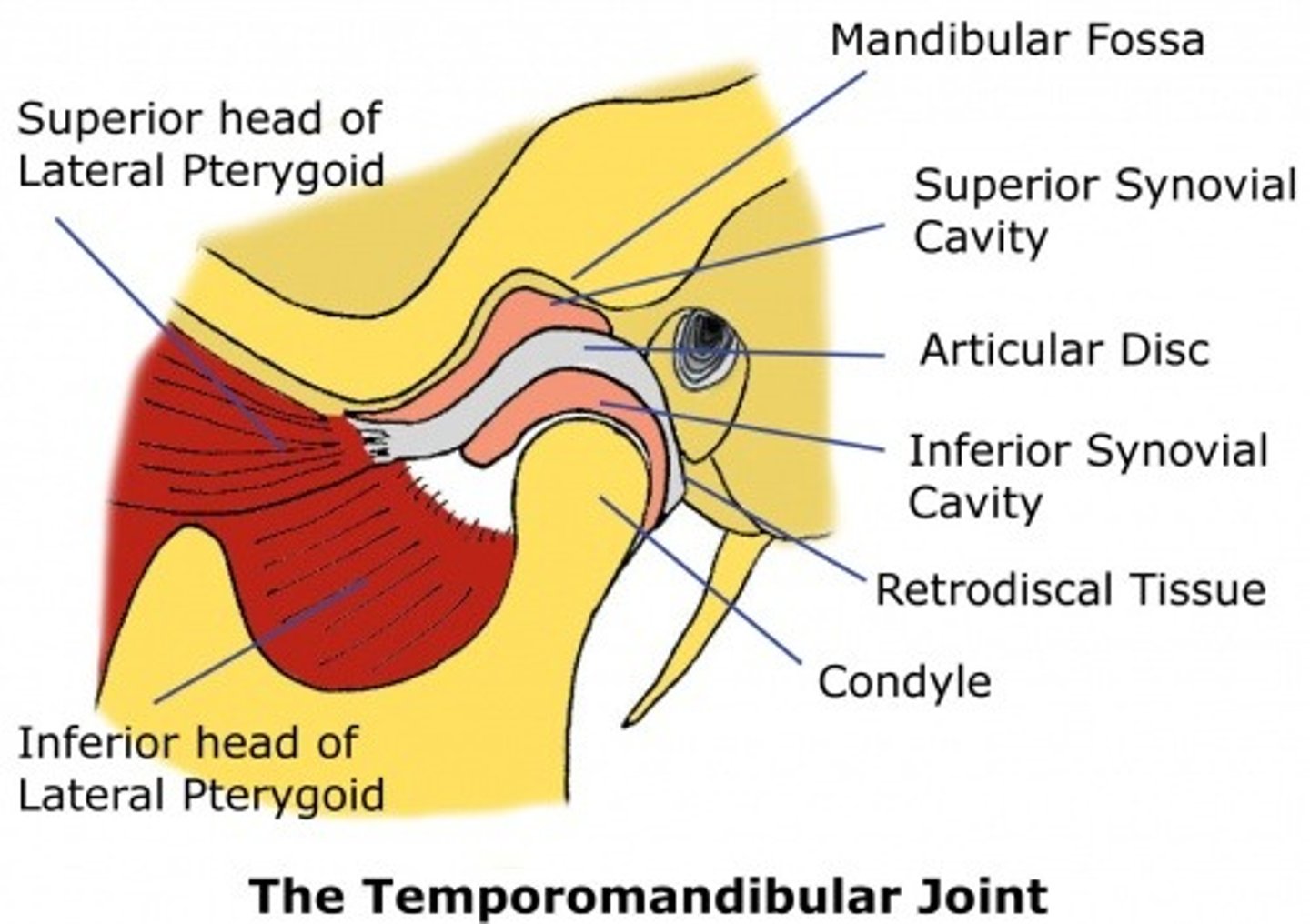
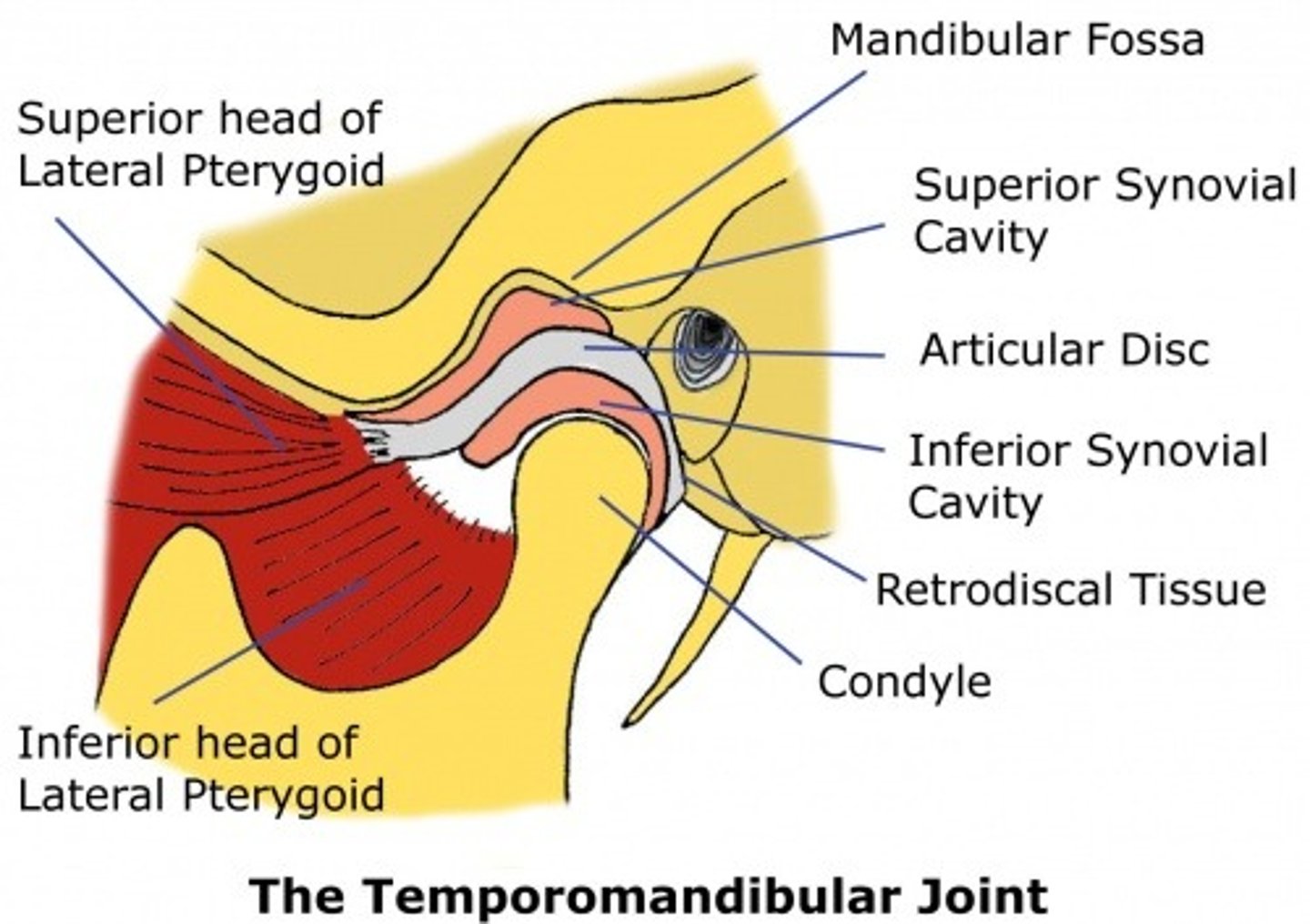
Articular disk of TMJ
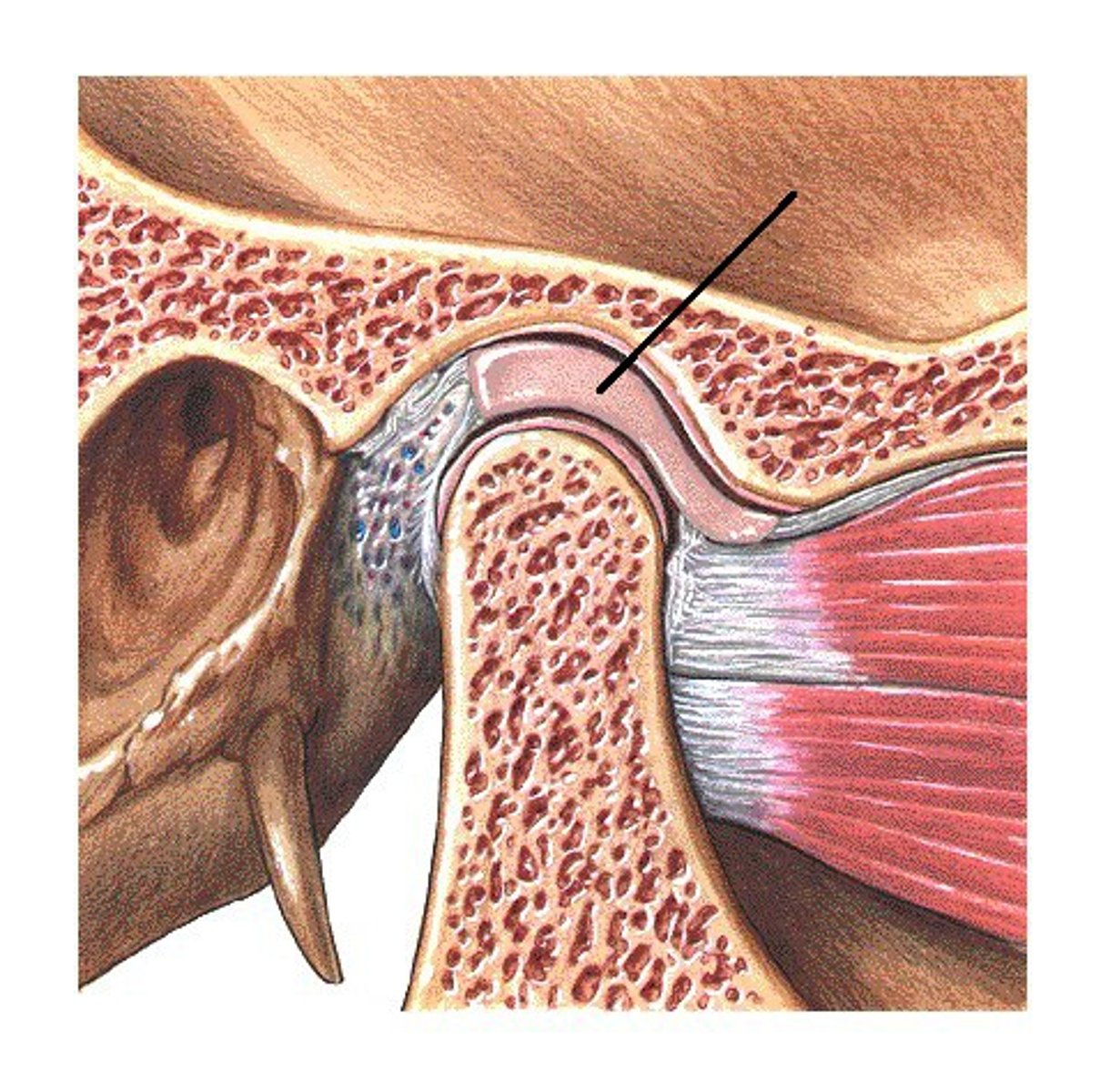
Temporomandibular joint
a joint one each side of the head that allows for movement of the mandible for mastication, speech, and respiratory movements
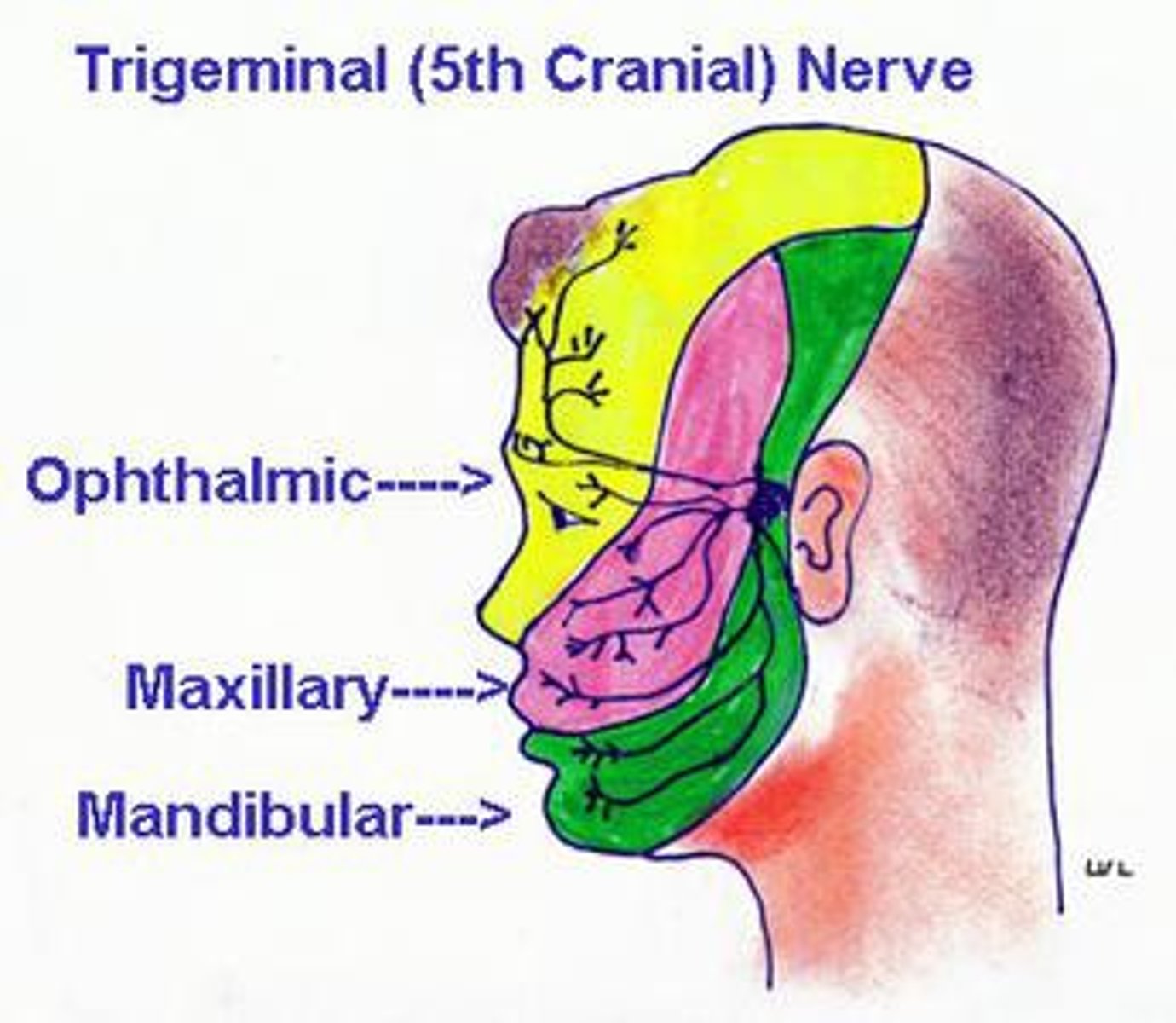
TMJ is innervated by
Innervated by cranial nerve V (Trigeminal)
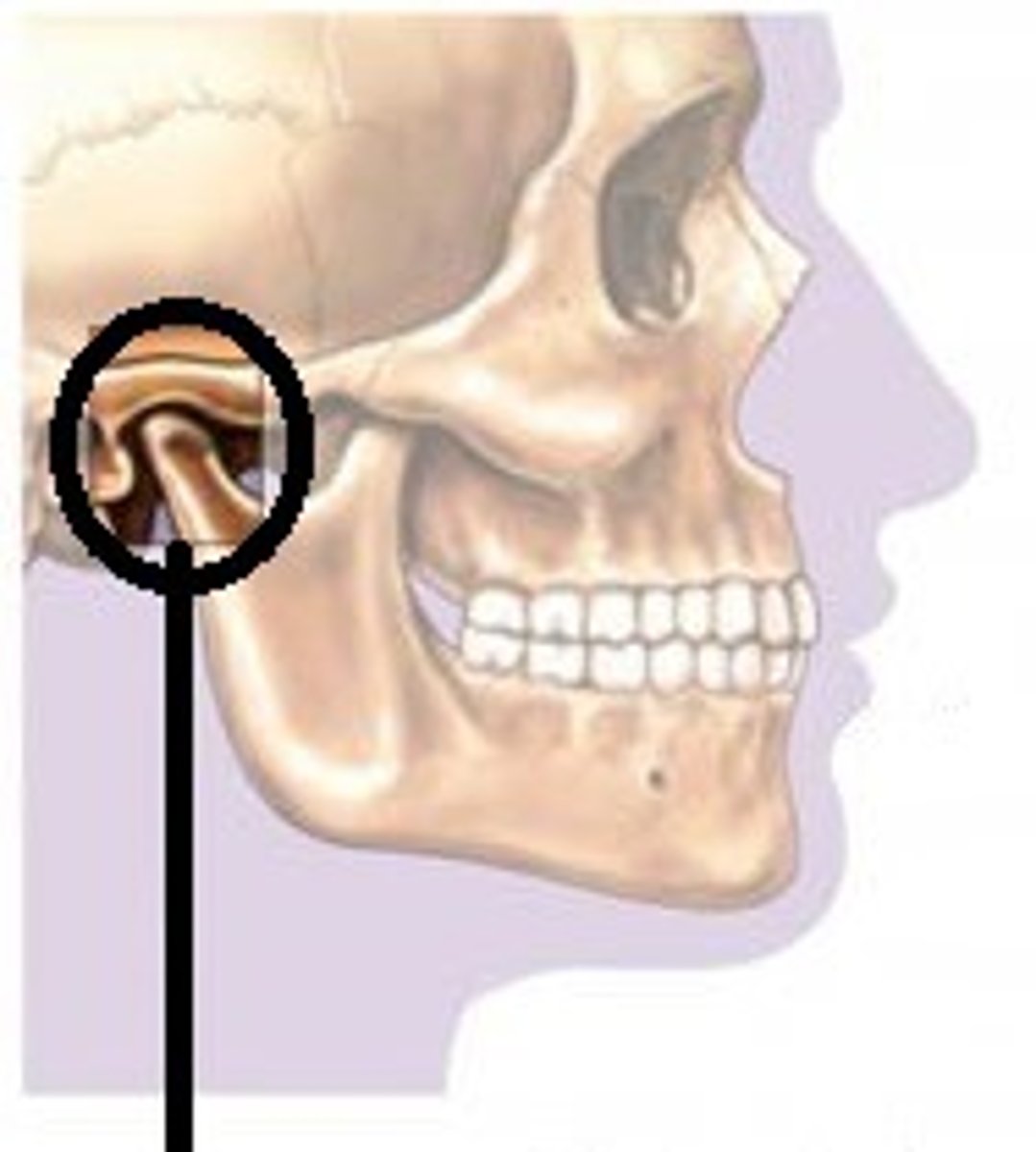
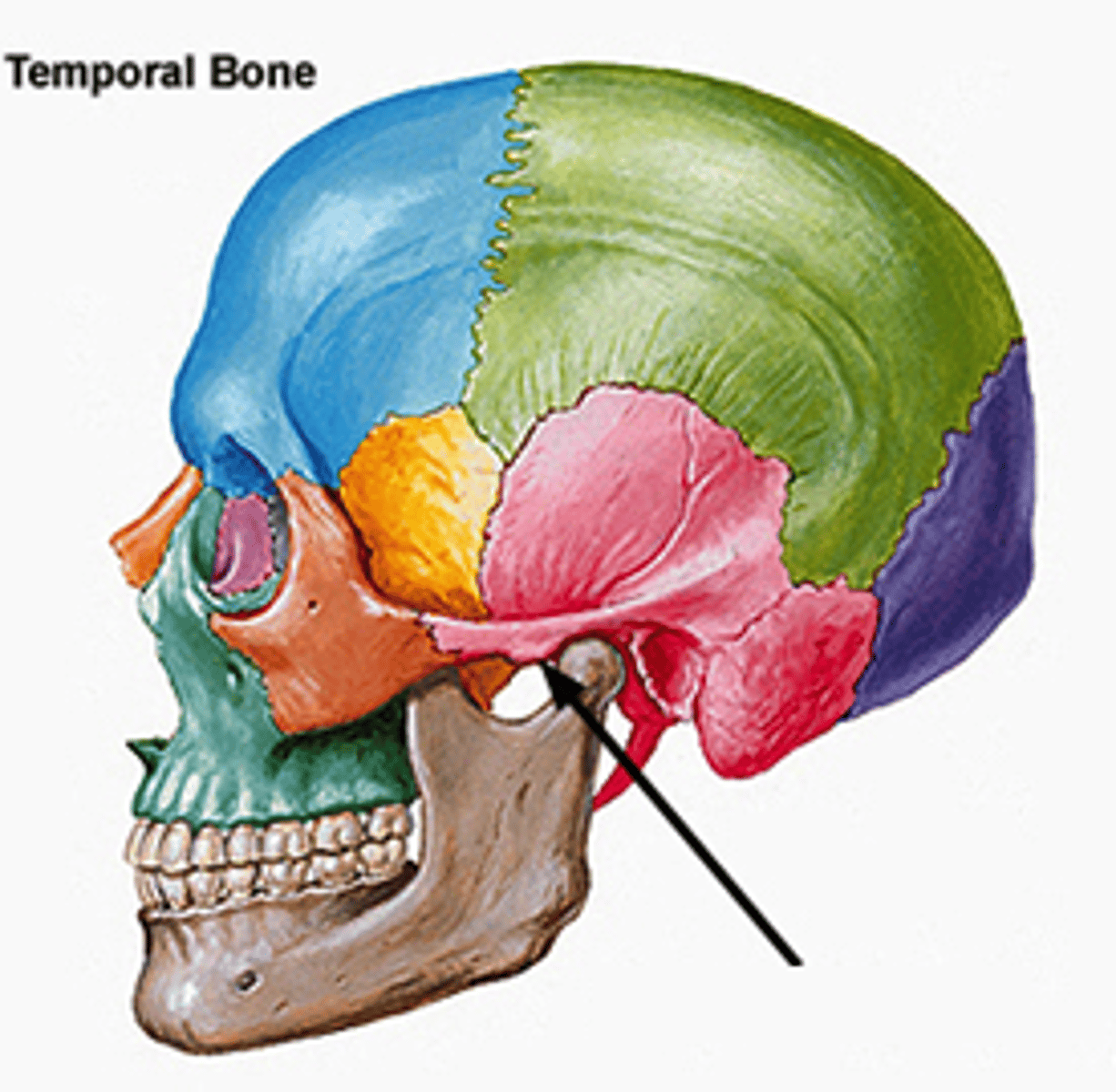
articular eminence
Raised portion of the temporal bone just anterior to the glenoid fossa.
What is this?
Articulating disc or meniscus is comprised of
dense fibrous connective tissue
articular fossa
depression on the inferior aspect of the temporal bone
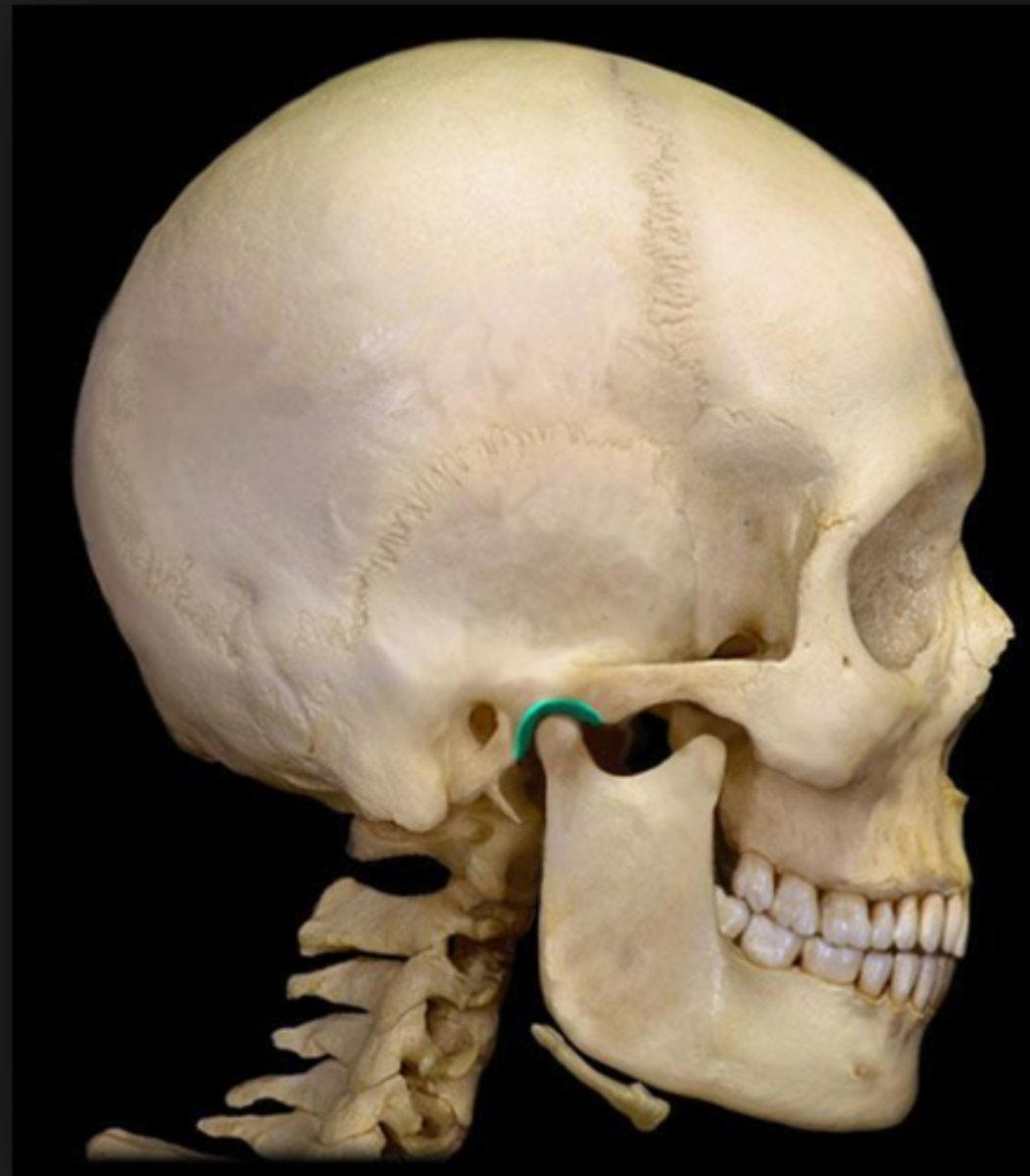
what is this?
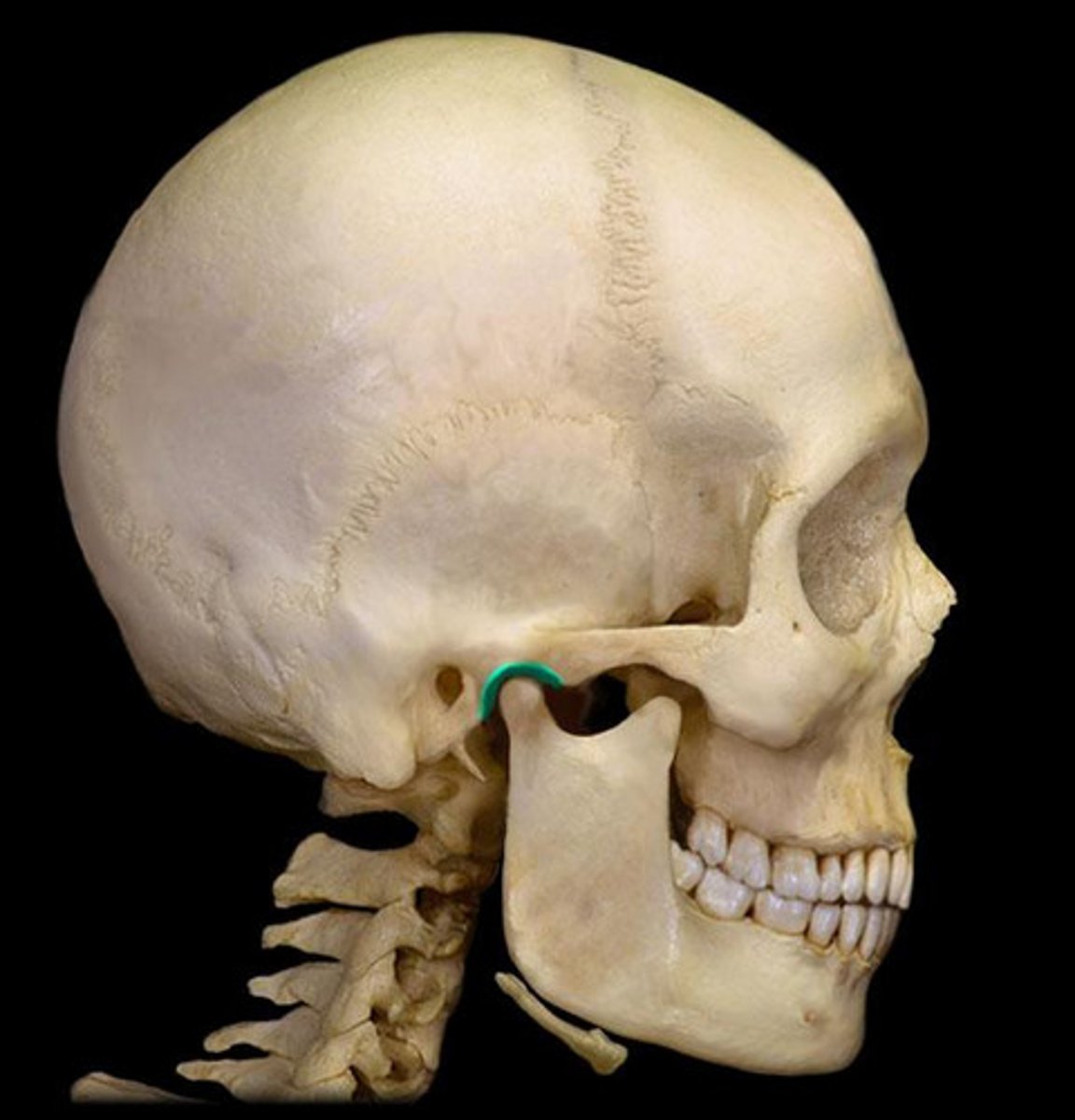
Completely closes the TMJ
joint capsule
Movements of the TMJ:
depression, elevation, protraction, retraction, lateral deviation
Temporomandibular disorder (TMD)
a group of conditions affecting the (TMJ) and the muscles controlling jaw movement.
Patients with TMD may experience
chronic joint tenderness, swelling, difficulties in moving the joint, and painful muscle pains.
TMJ pain comes from
originates from one of the surrounding soft tissues, pain causes a reflex to limit the mandible's movement
TMD Acute Episode
can occur when a patient opens too wide which causes subluxation
Subluxation of TMJ
partial dislocation of both joints, occurs when the head of each condyle moves too far anteriorly past the articular eminence
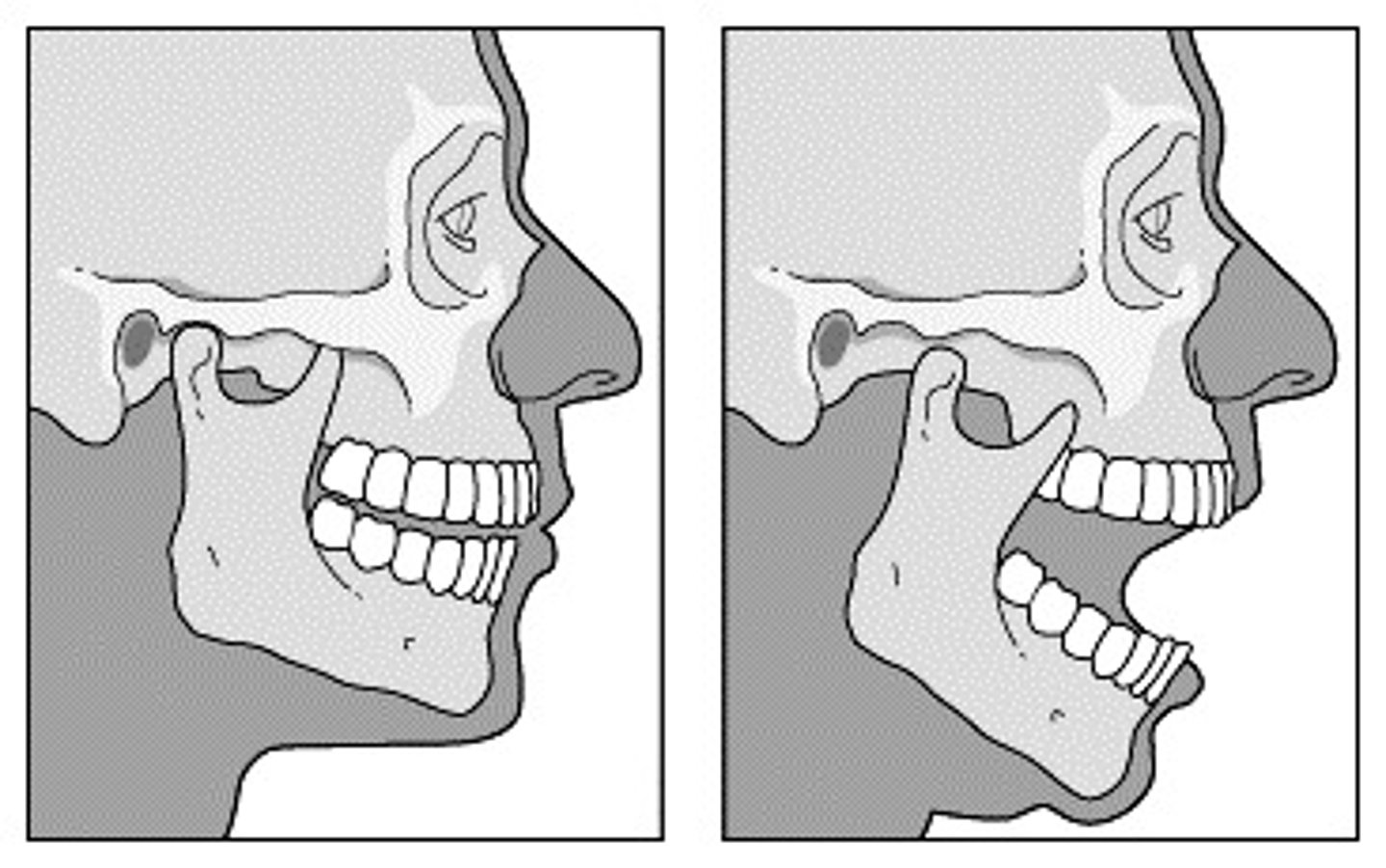
Crepitus of TMJ
joint noise, generally indicates joint damage (disc tear, and/or bone to bone contact)
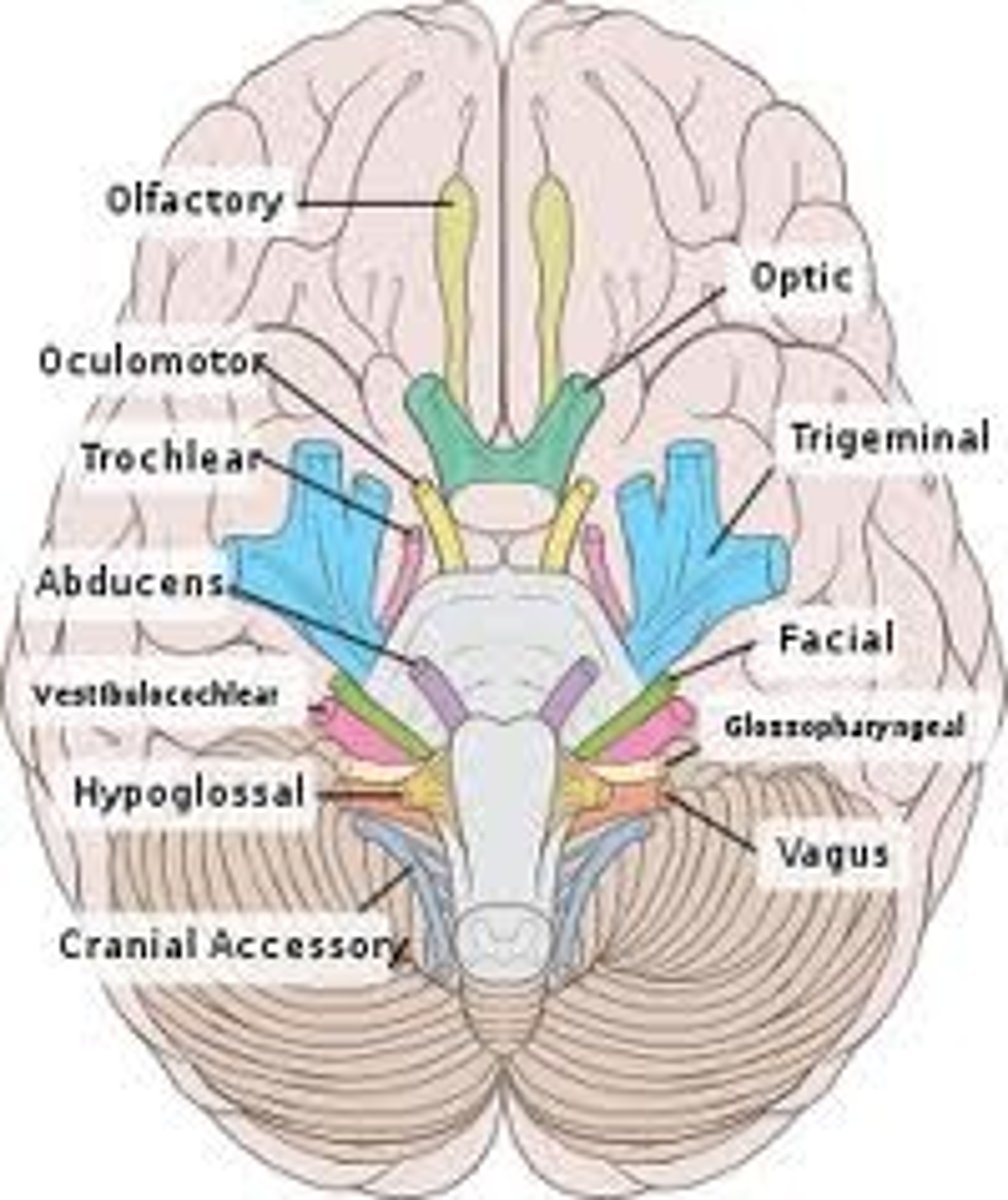
cranial nerve I
Olfactory, sense of smell, sensory
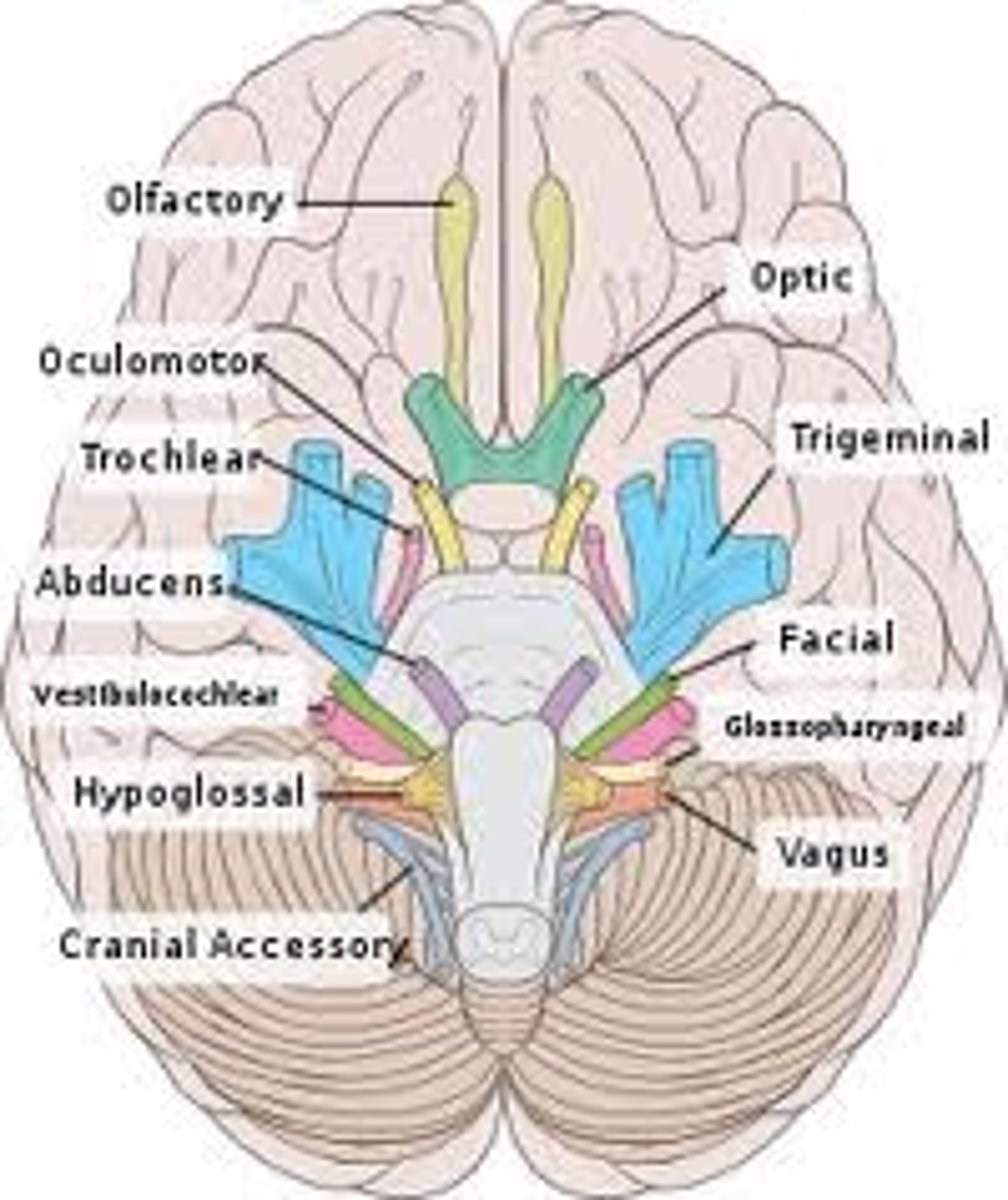
Cranial nerve II
Optic - vision, sensory
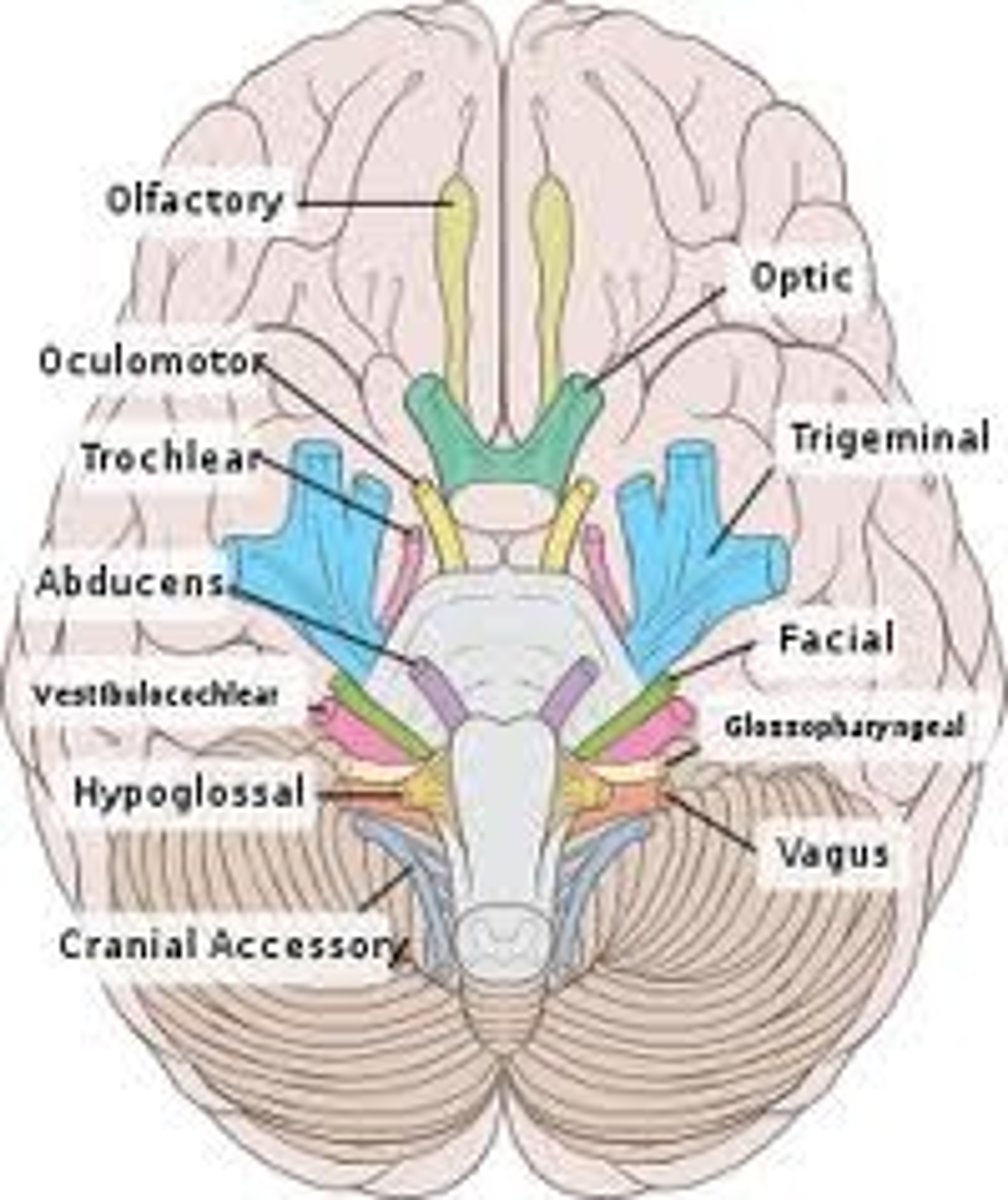
Cranial nerve III
oculomotor, moves eye muscles, motor
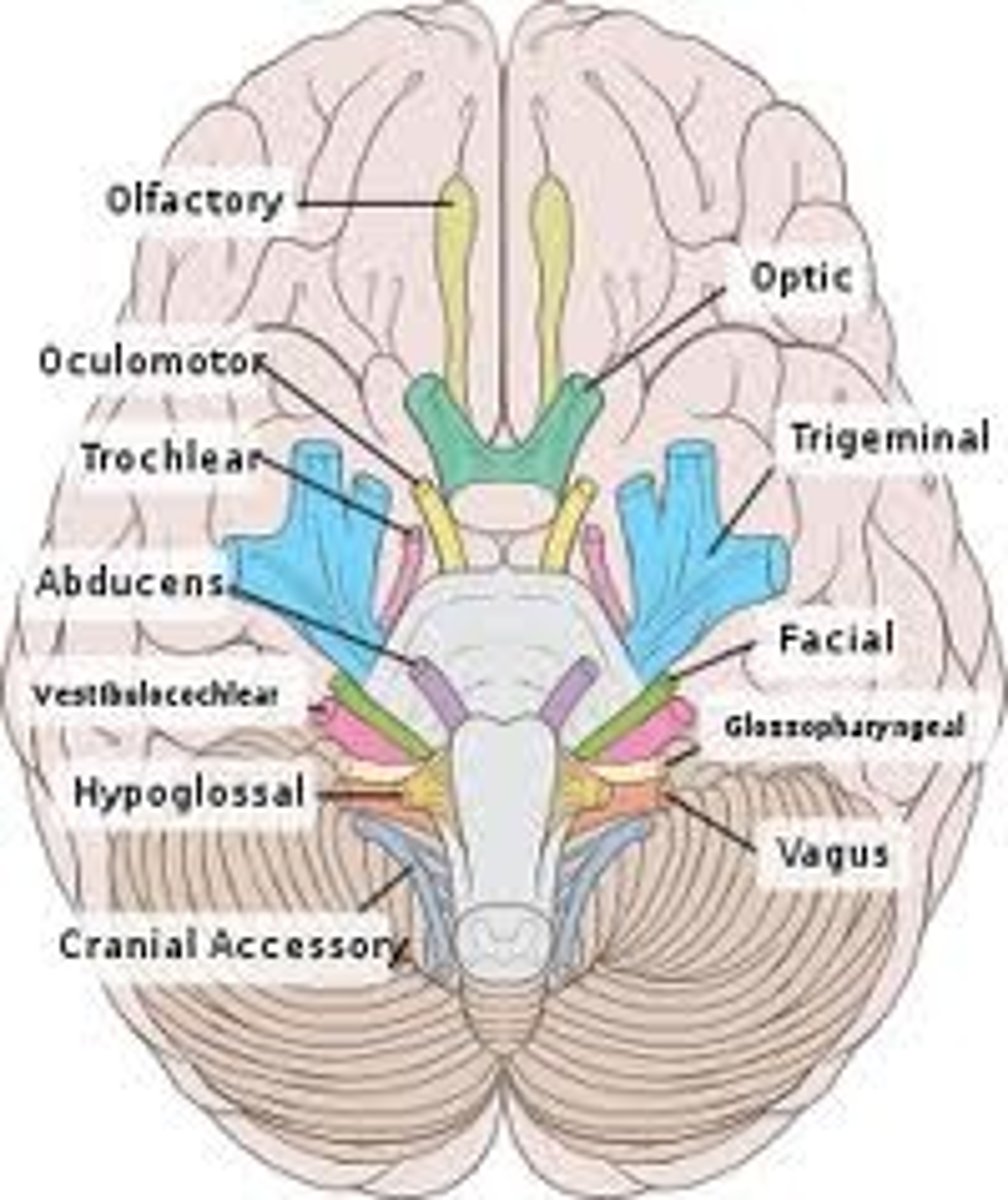
Cranial nerve IV
Trochlear - motor: eye movement
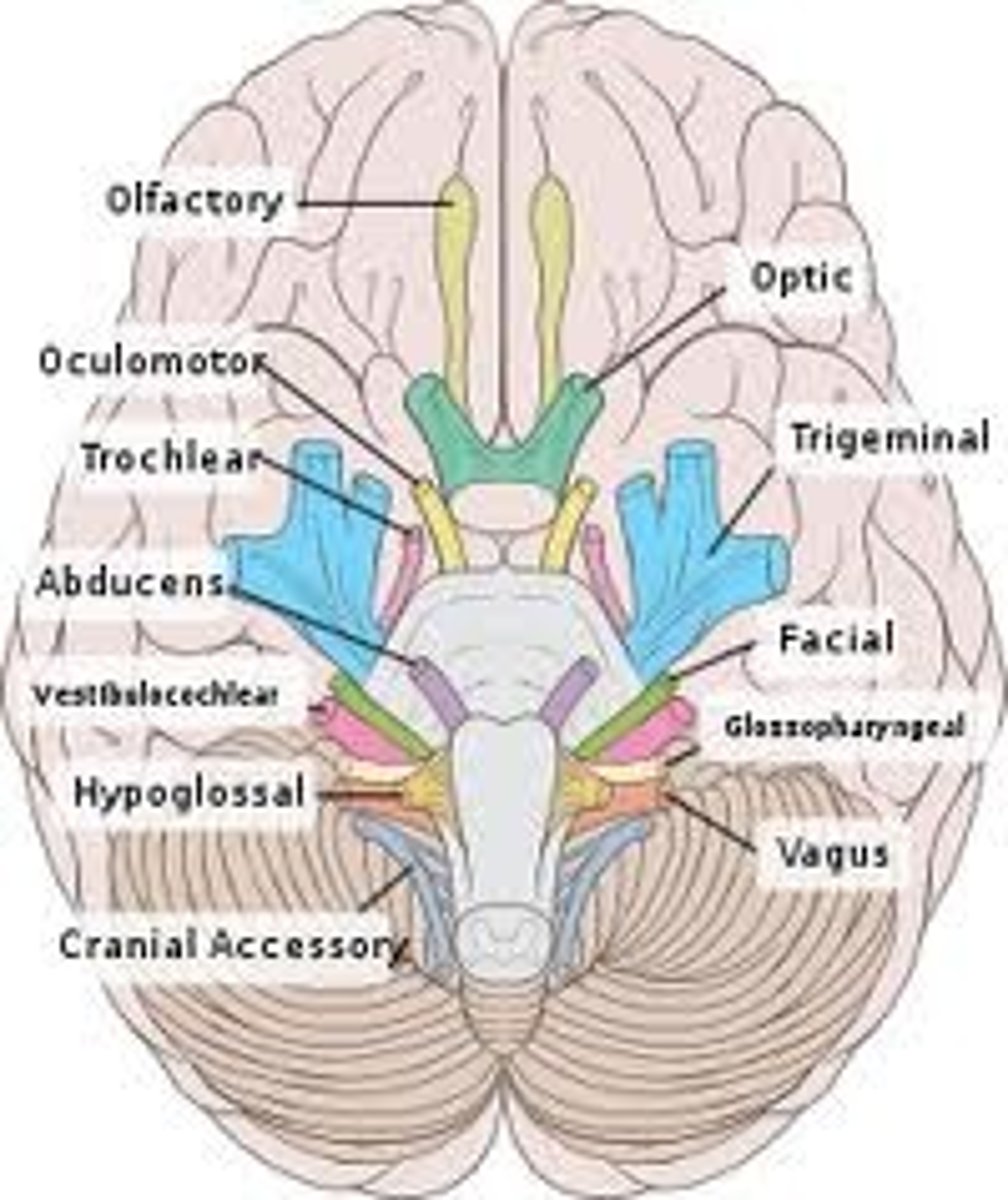
Cranial nerve V
Trigeminal, mixed, facial/teeth sensation and muscles of mastication
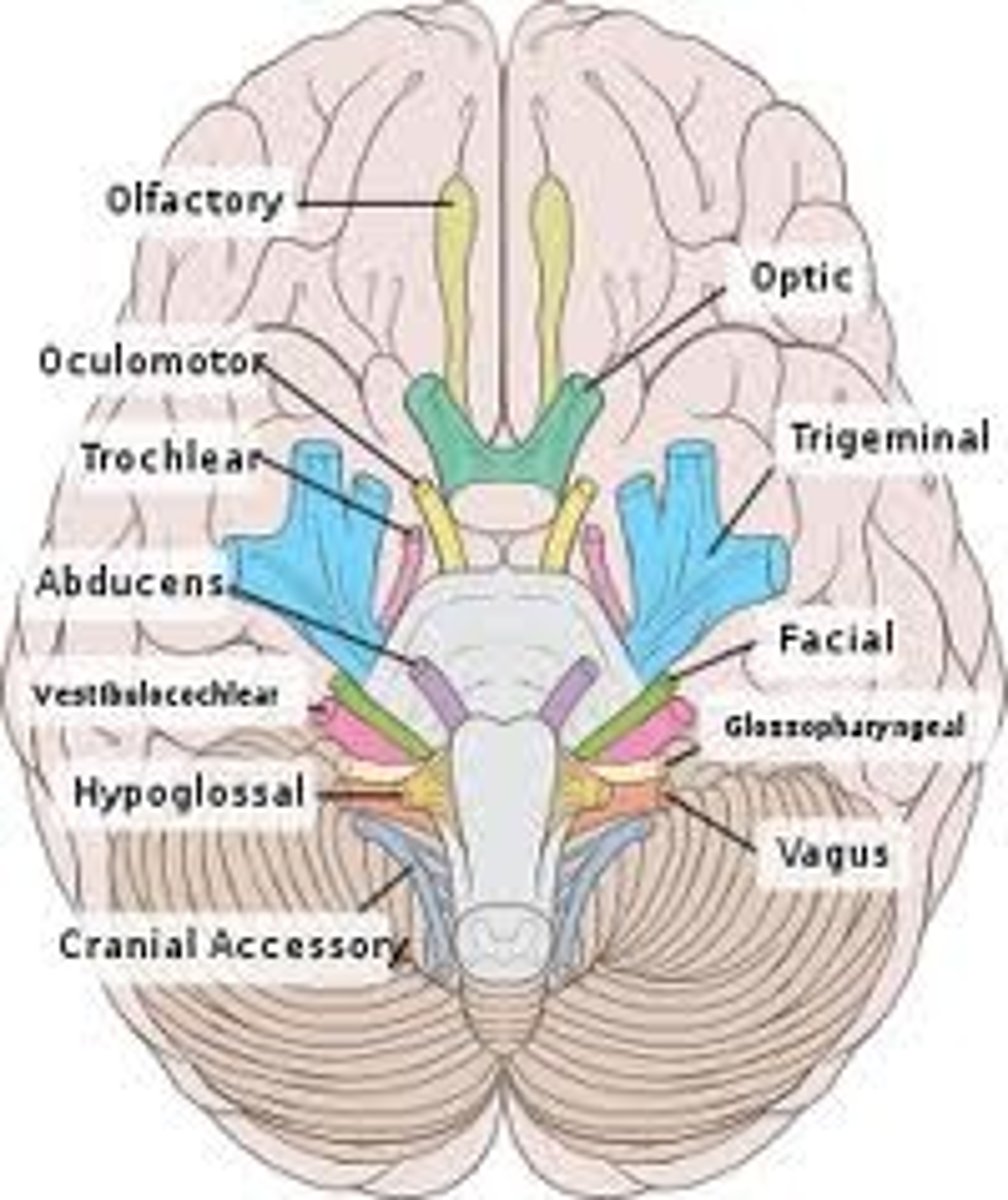
Cranial nerve VI
Abducens, Motor, Lateral movement of the eye
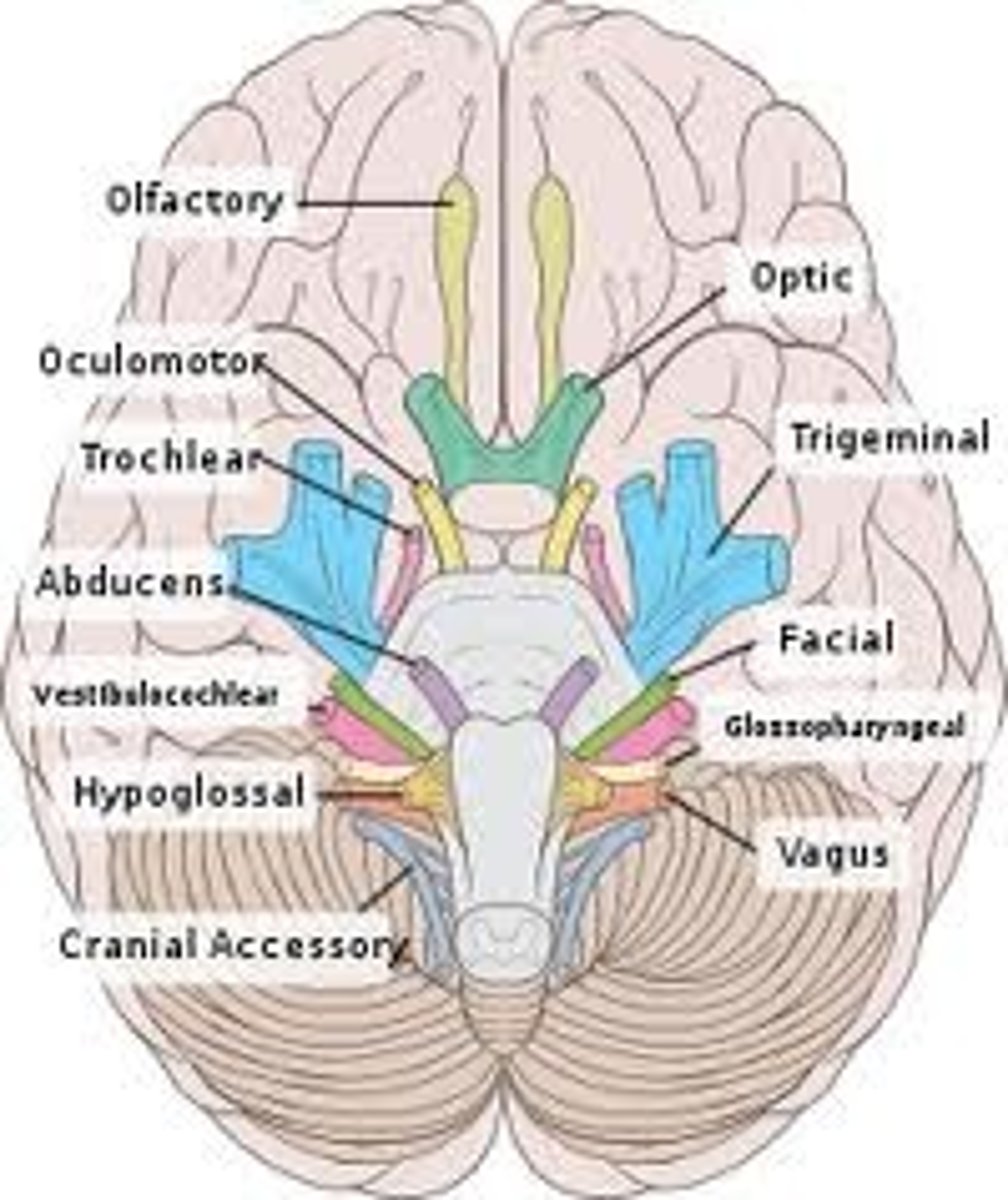
Cranial nerve VII
Facial, mixed, facial expressions and taste
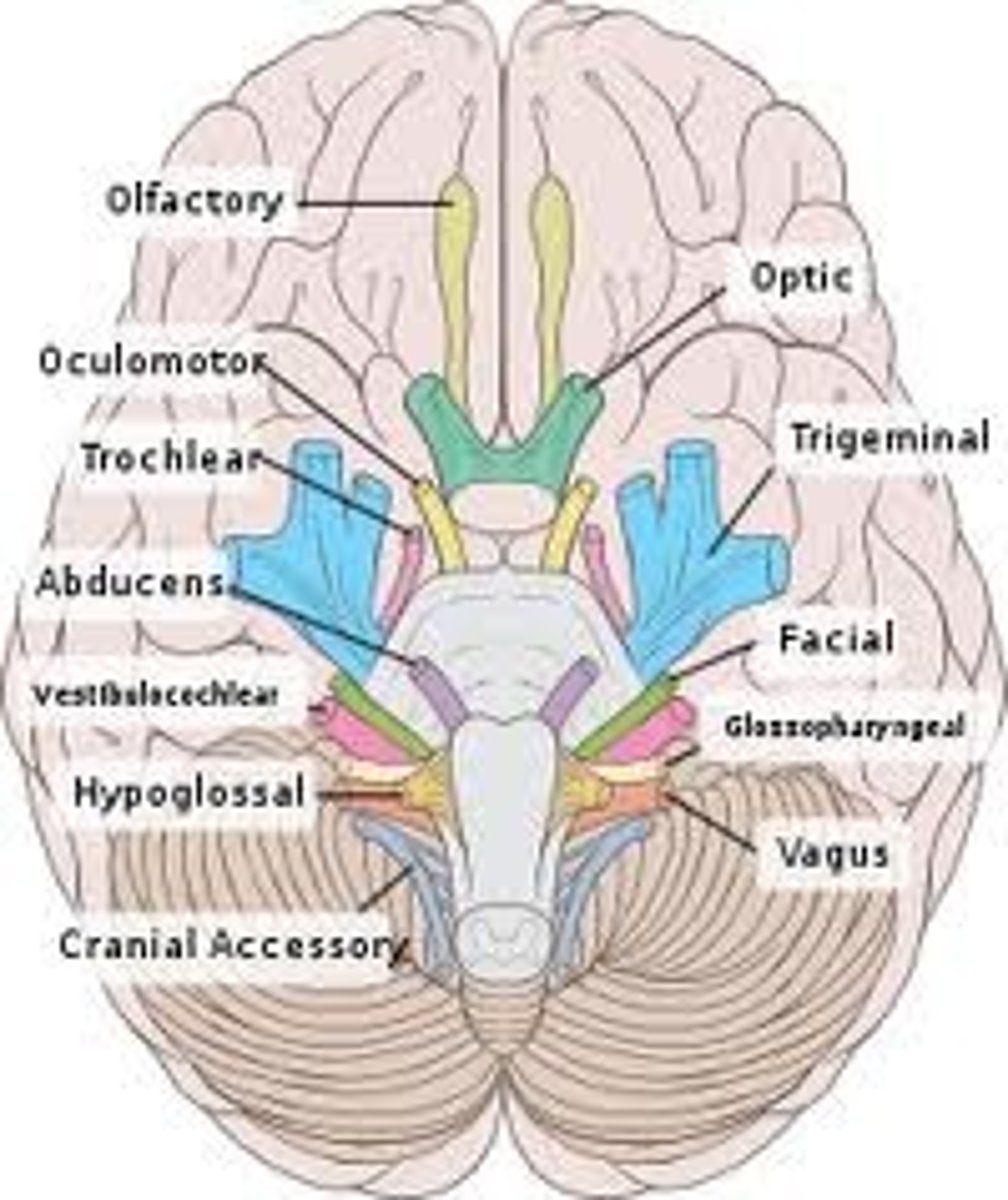
Cranial nerve VIII
Vestibulocochlear, sensory, hearing and balance
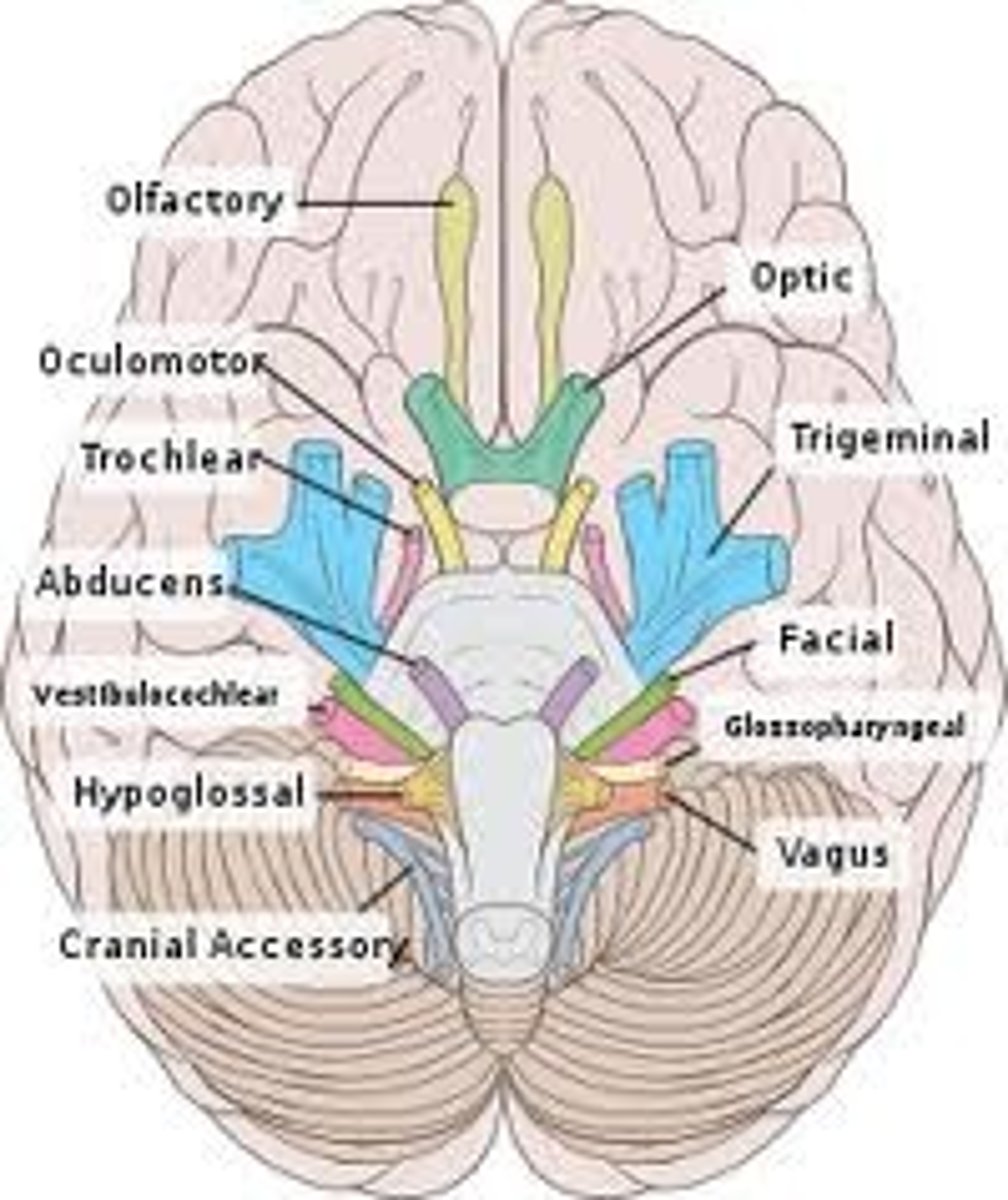
Cranial nerve IX
Glossopharyngeal, mixed, controls pharynx muscles, taste
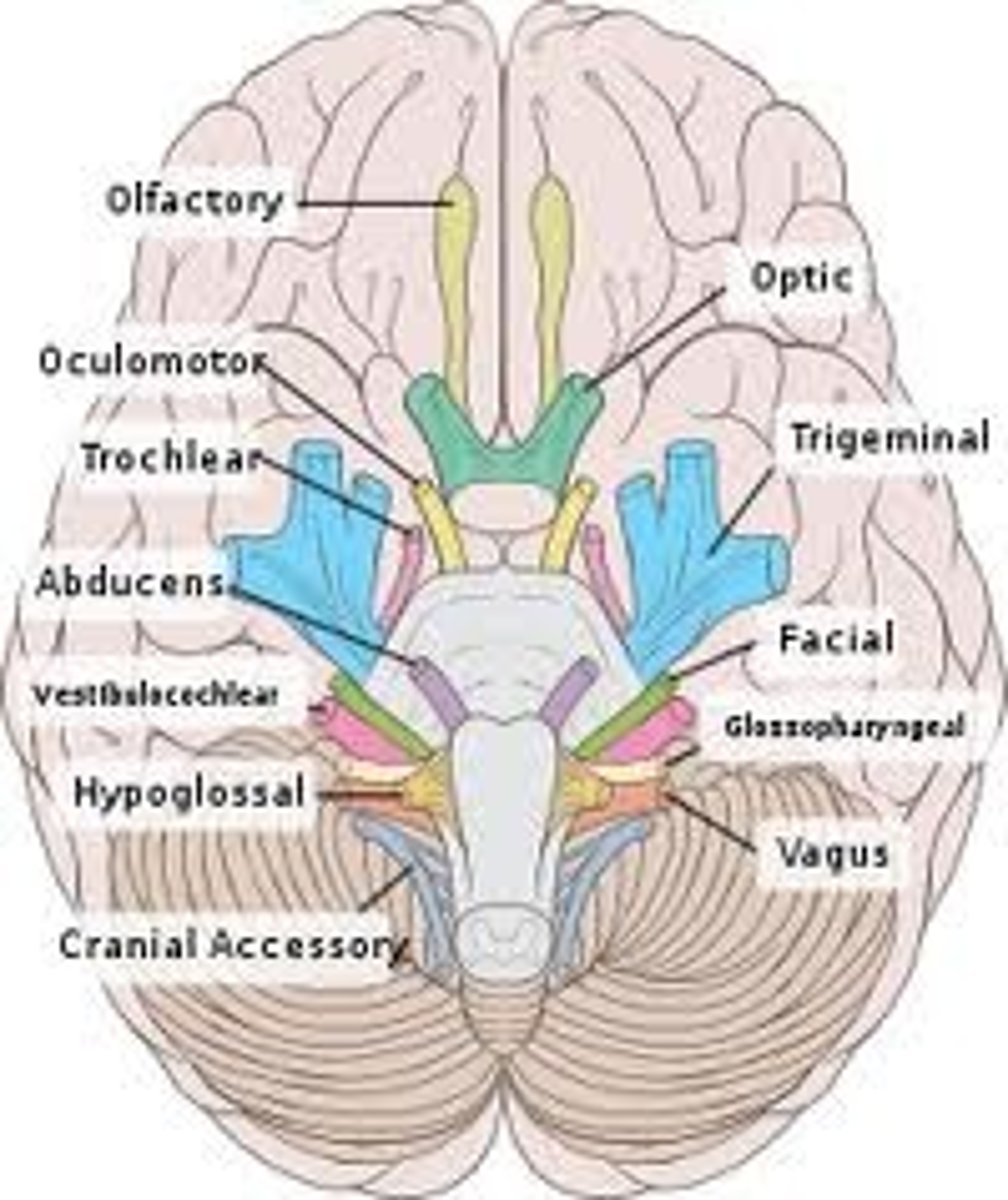
Cranial nerve X
the vagus nerve, both, muscles of the soft palate and abdominal organs
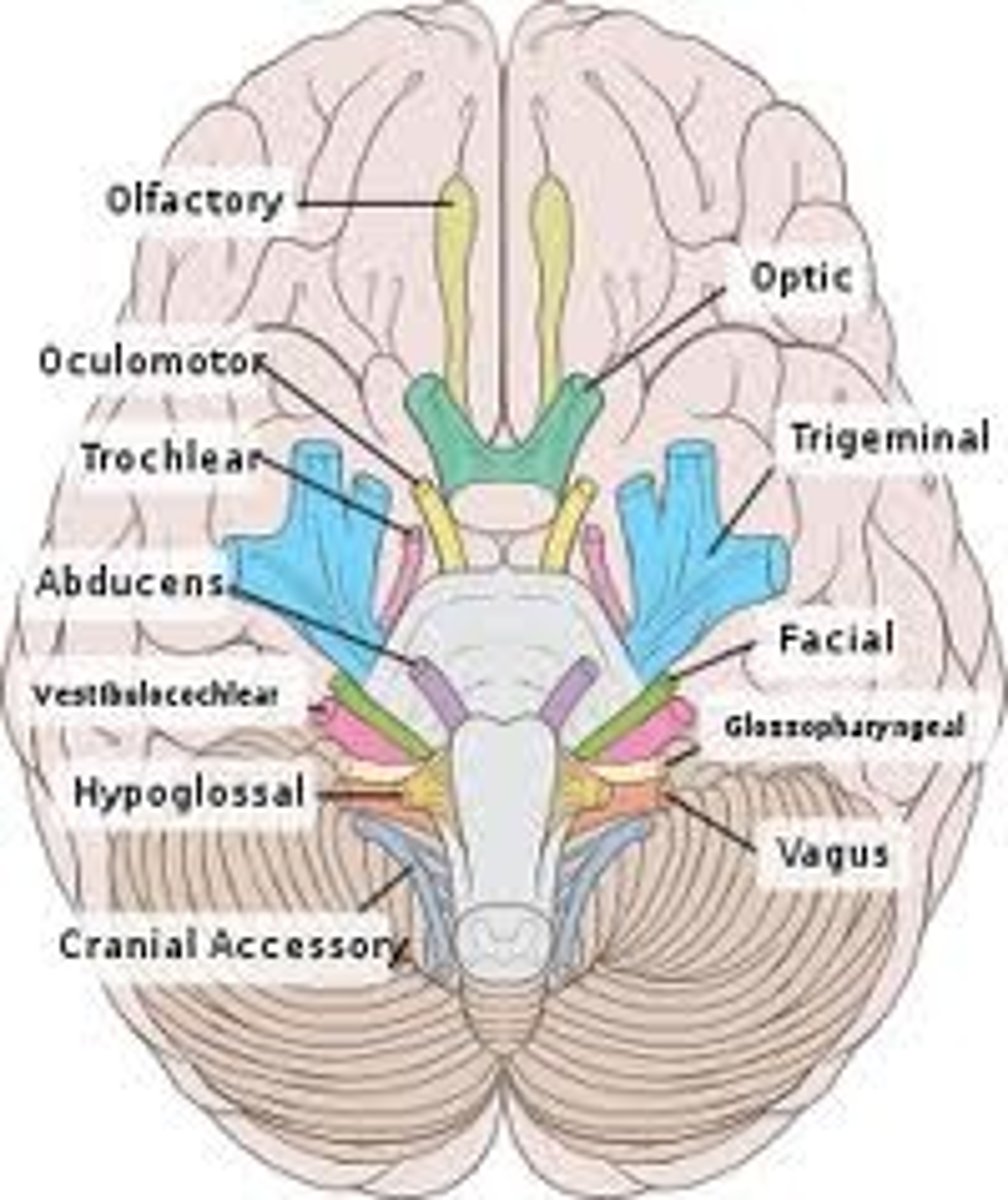
Cranial nerve XI
accessory, motor, moves neck muscles
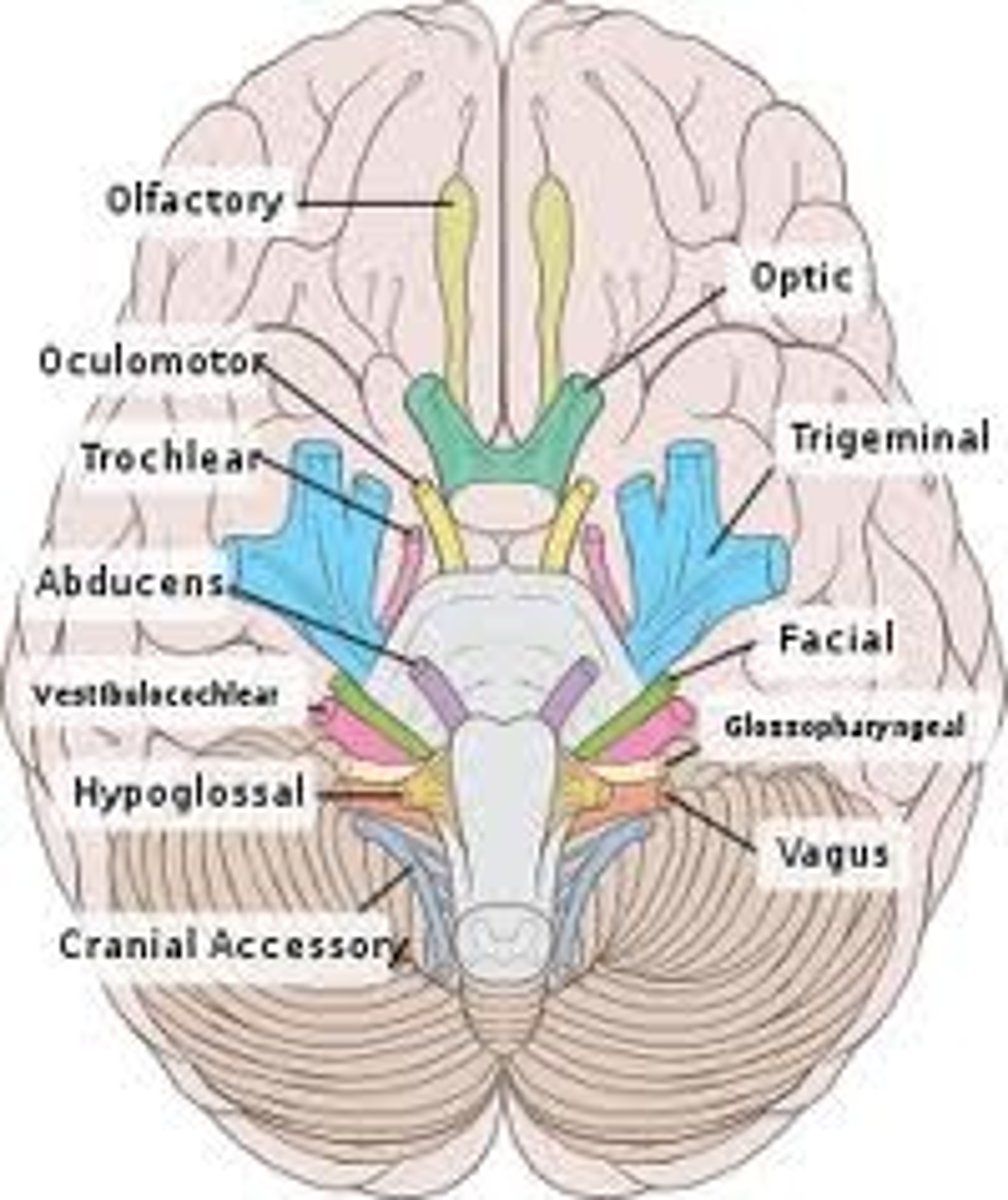
Cranial nerve XII
Hypoglossal, motor, tongue movement
trigeminal neuralgia
inflammation of the 5th cranial nerve characterized by sudden, intense, brief attacks of sharp pain on one side of the face
NO KNOWN ETIOLOGY
Bell's Palsy
Unilateral facial paralysis with no known cause.• A loss of excitability of the facial nerve, is idiopathic
local infiltration anesthesia
anesthetizes a small area
nerve block anesthesia
affects a larger area than local infiltration
Area does anesthesia tend to be more successful in
maxilla due to it being less dense and having less variation
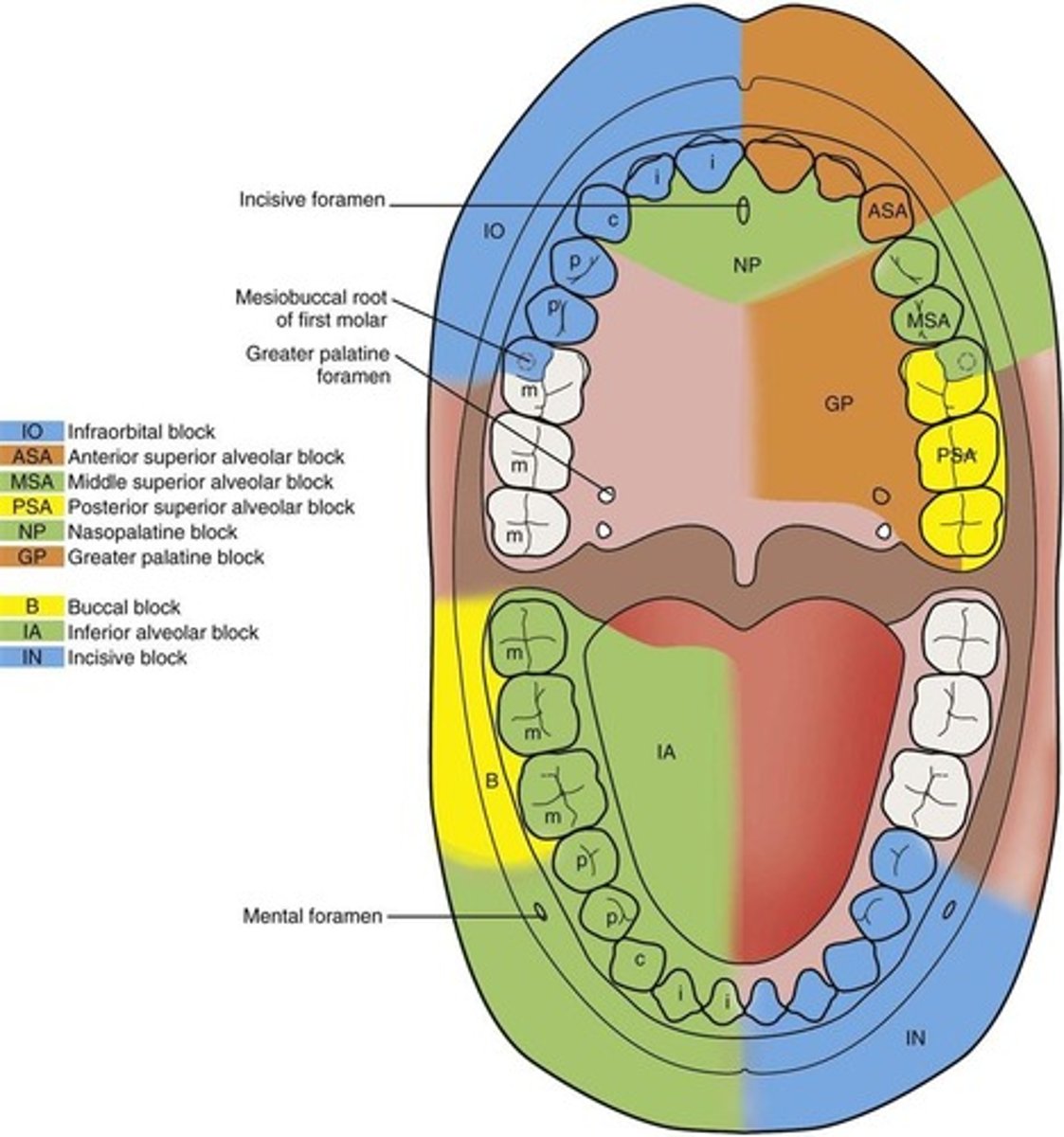
PSA Maxillary Block
posterior superior alveolar block
completed to anesthetize the maxillary molars on one side of the mouth, but the mesial buccal cusp of first molar may need a MSA block
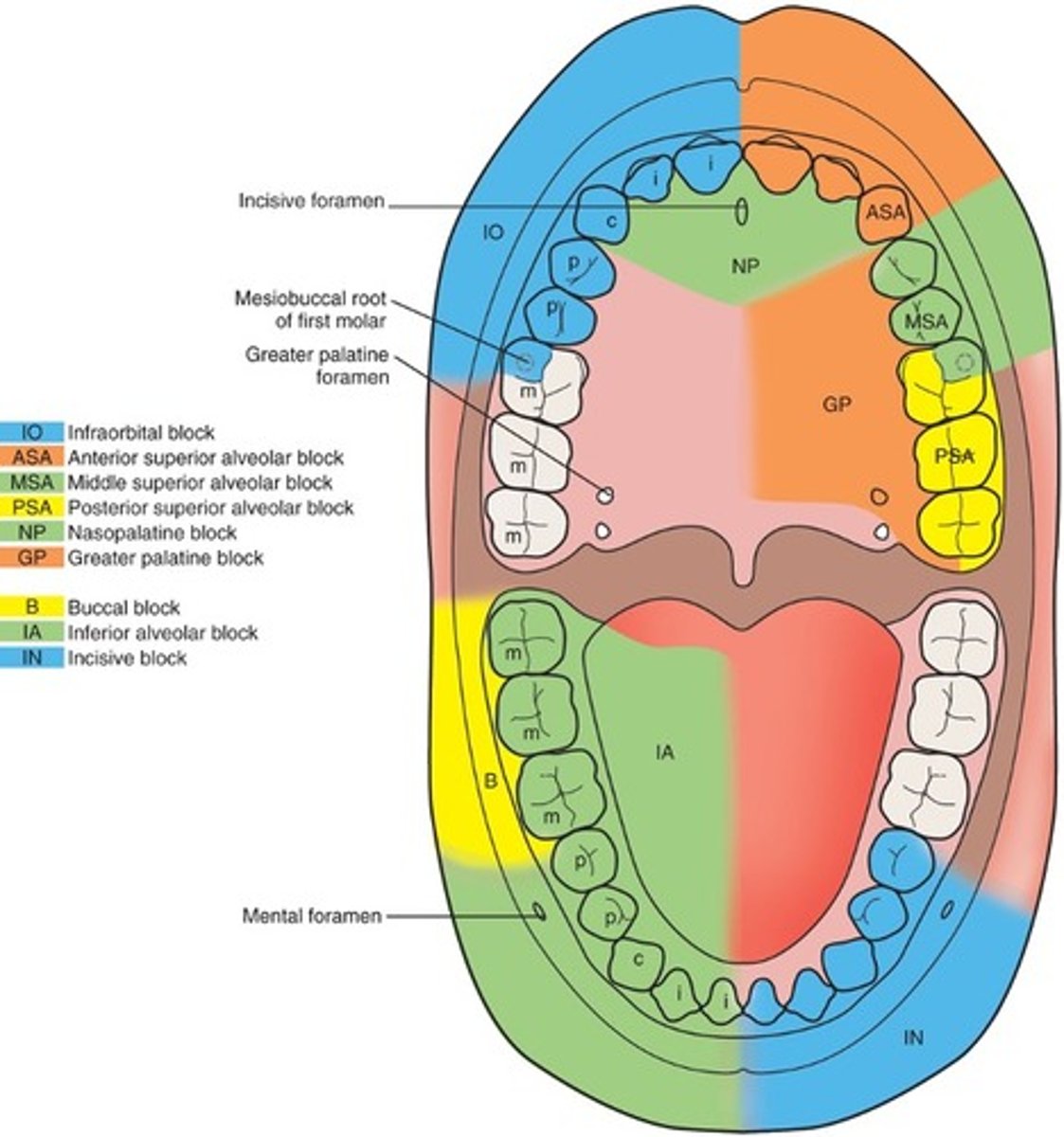
MSA Maxillary Block
Middle superior alveolar block
anesthetizes the pre-molars on one side and buccal side of the mesial cusp of the first molar
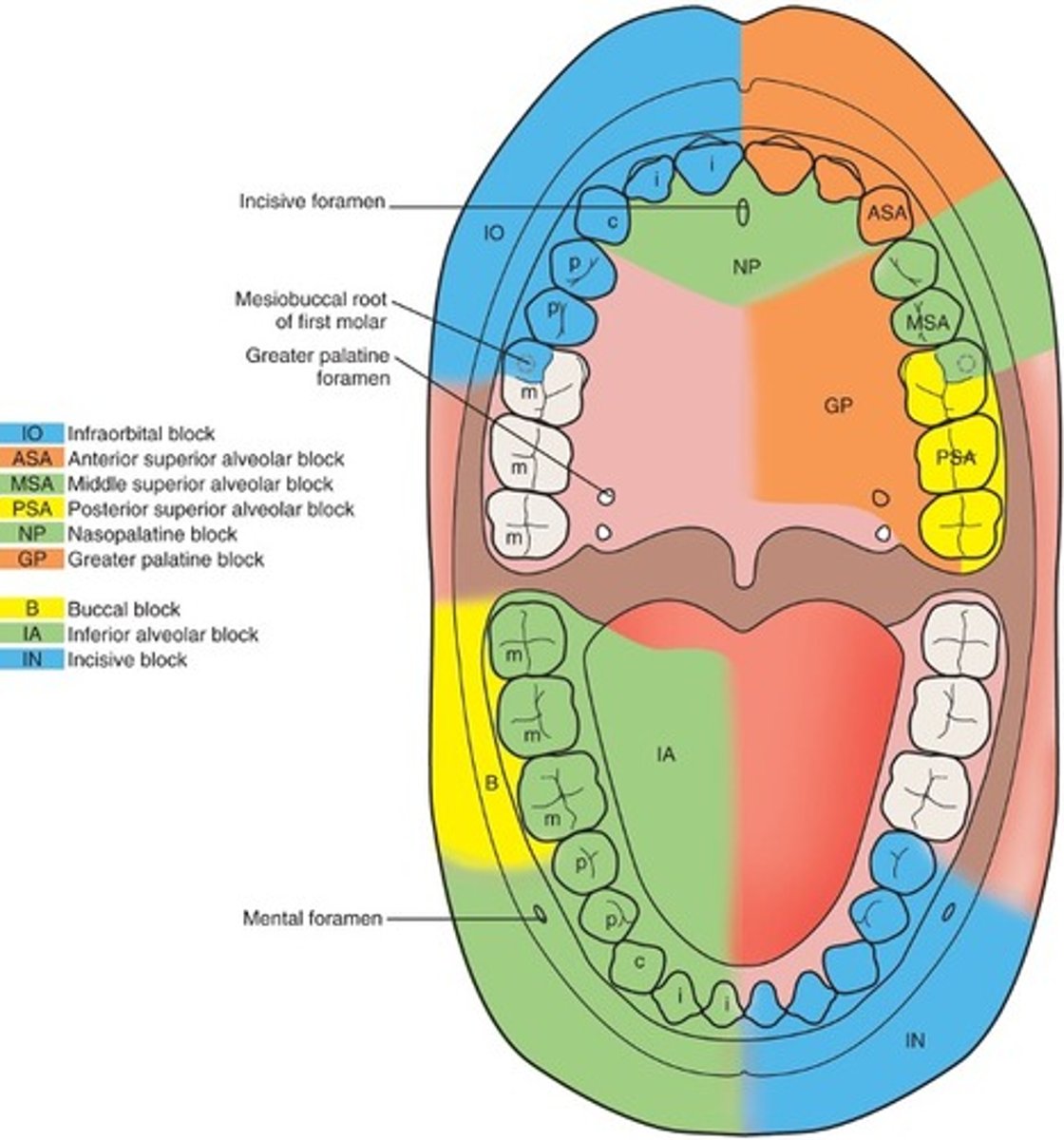
NP Maxillary block
Nasal Palatine Block
anesthetize the anterior hard palate from canine to canine
GP Maxillary block
Greater Palatine Block
anesthetize the posterior portion of the hard palate from the premolar through the molars on one side
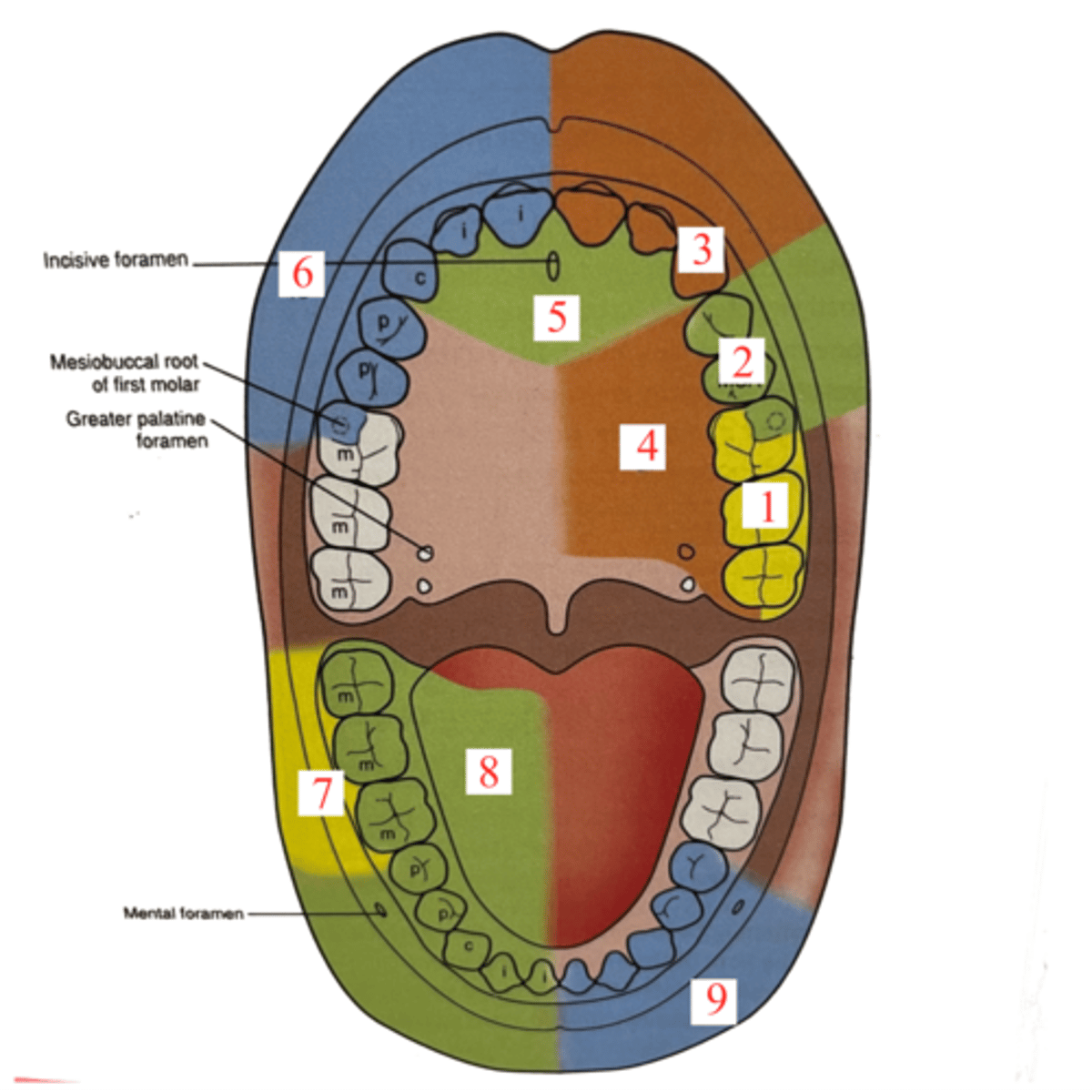
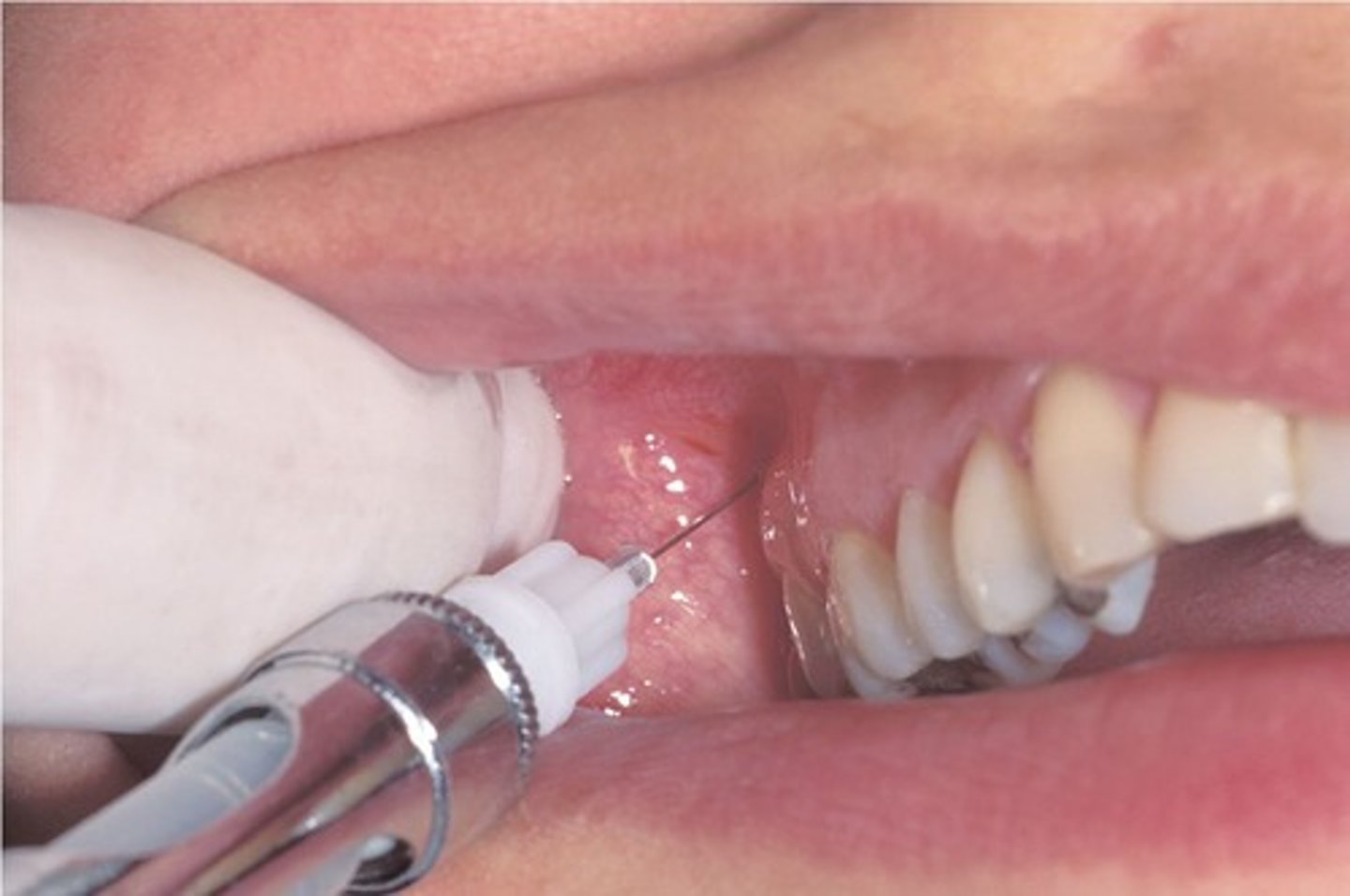
PSA injection site
muccobuccal fold at the apex of MX 2nd Molar
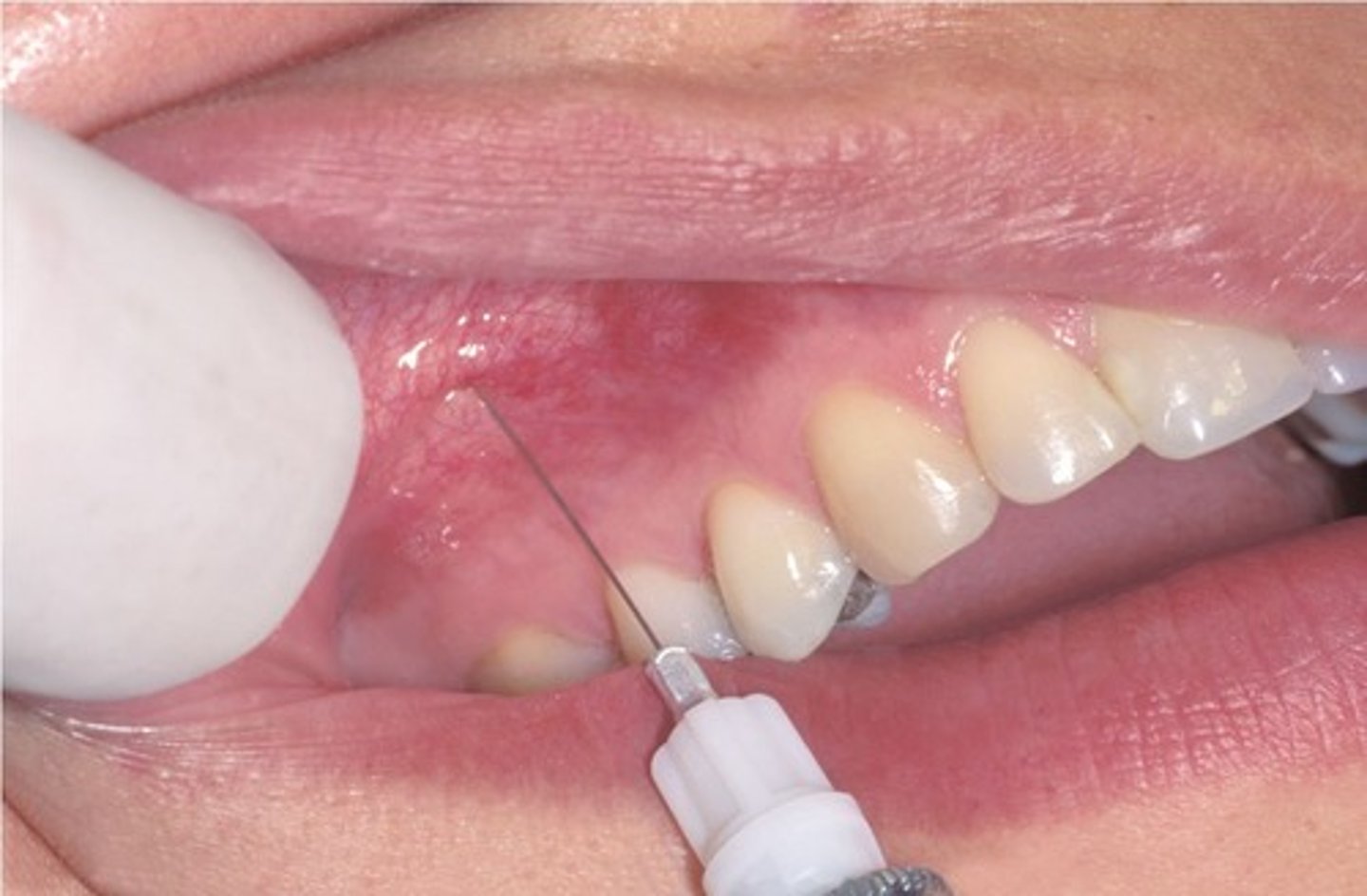
MSA injection site
height of mesiobuccal fold at the apex of the maxillary second pre-molar
ASA Maxillary Block
anterior superior alveolar block
anesthetizes anterior teeth on one side
ASA Maxillary injection site
apex of the canine, parallel with the canine emine
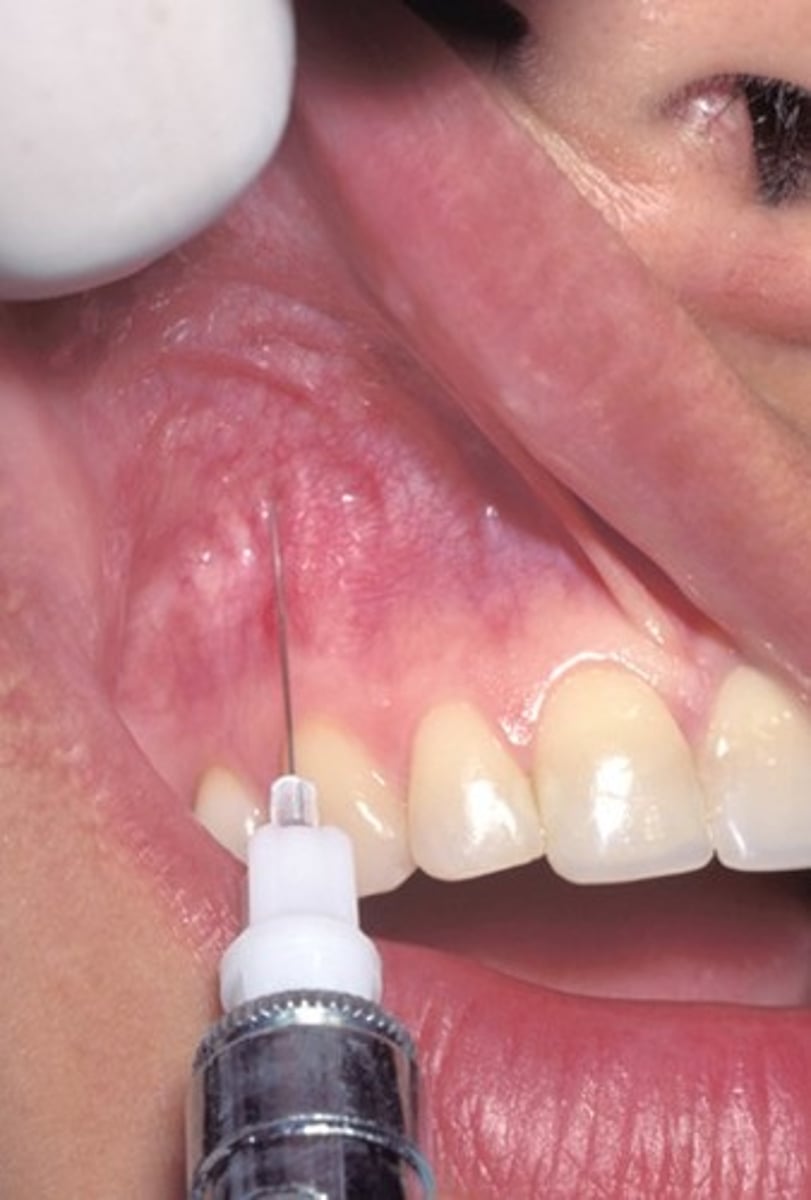
GP Maxillary injection site
palatal tissue anterior to the greater palatine foramen, use pressure anesthesia to cause blanching.
Blanching in the tissue in a GP site
helps a little bit with the discomfort of the palatal injection and to feel the depression of the greater Palatine foramen
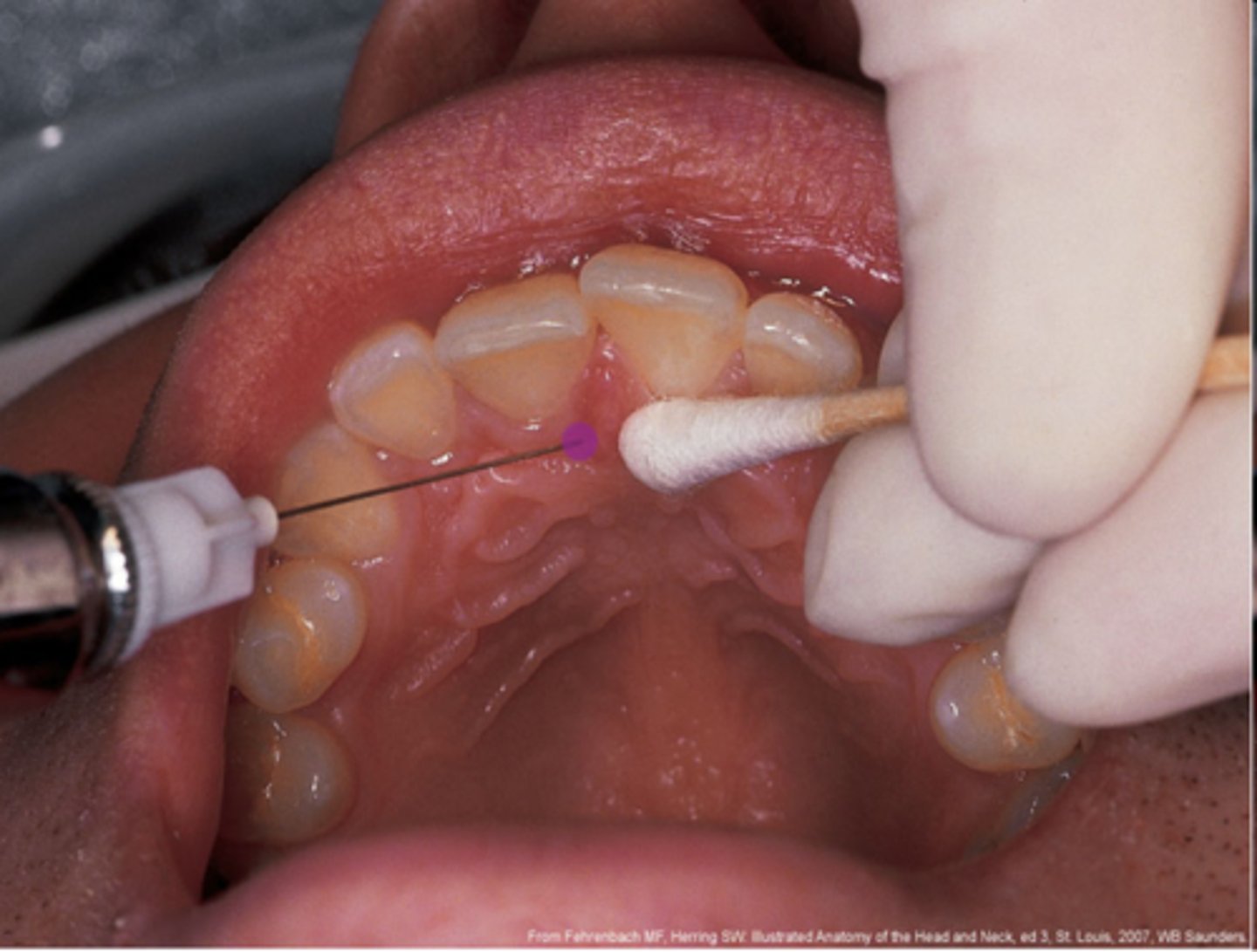
NP Maxillary injection site
palatal tissue lateral to the incisive papilla
IA Mandibular Block
used to anesthetize almost all of the tissue and teeth on one side of the mandible. Except for the buccal mucosa of the mandibular molars
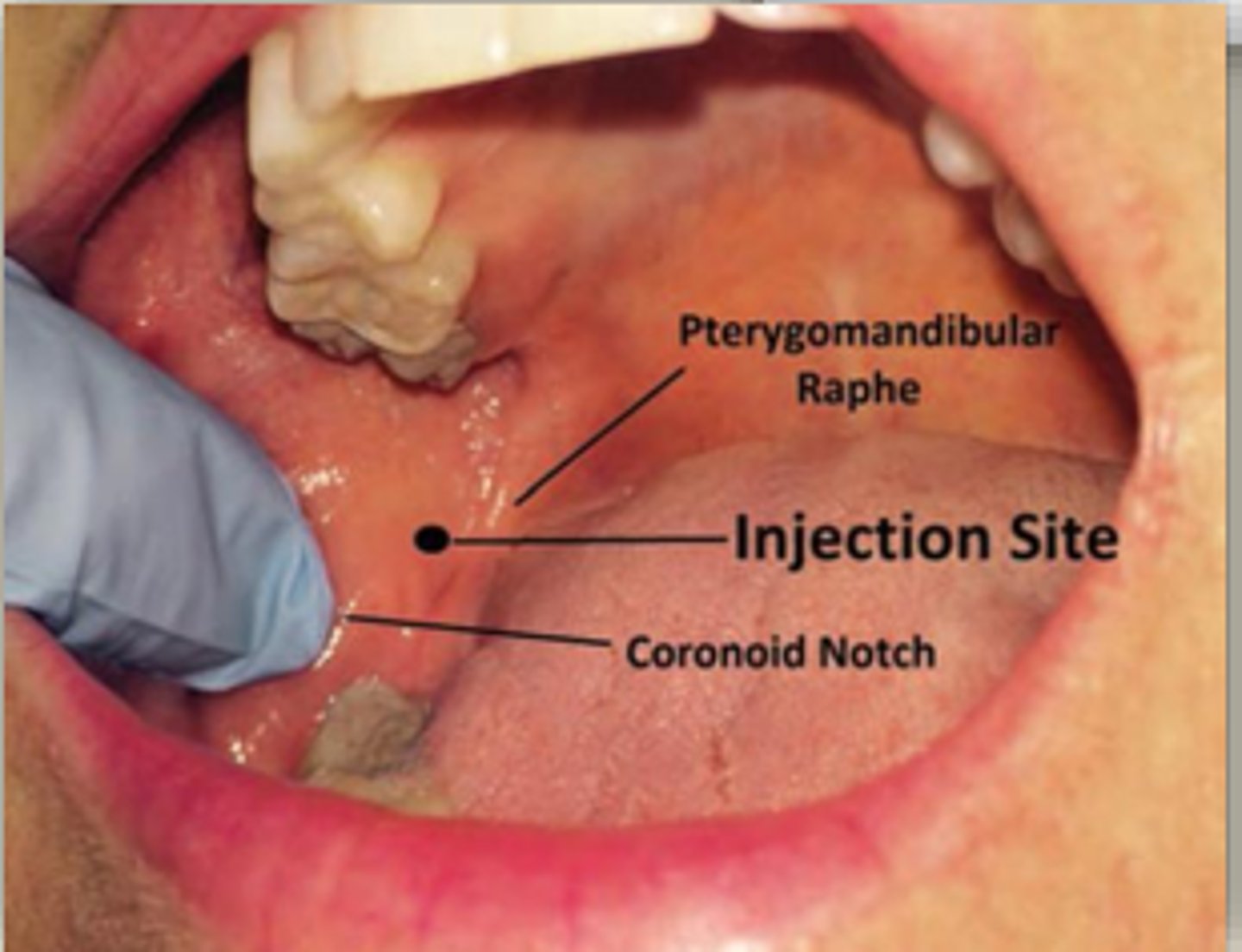
IA injection site
3 quarters of the way between the coronoid notch and the pterygomandibular fold, and you're going to be coming across from the opposite premolar
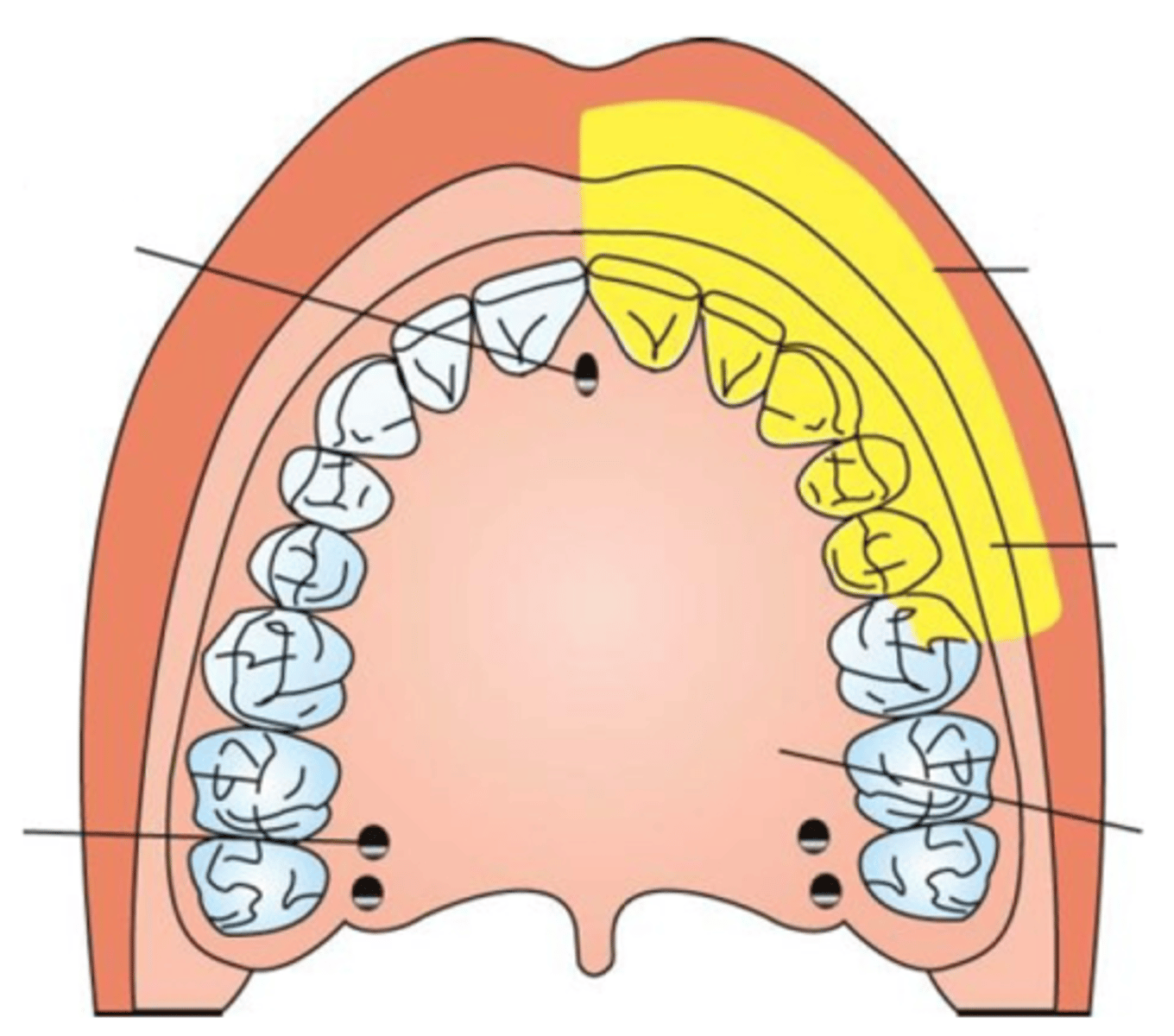
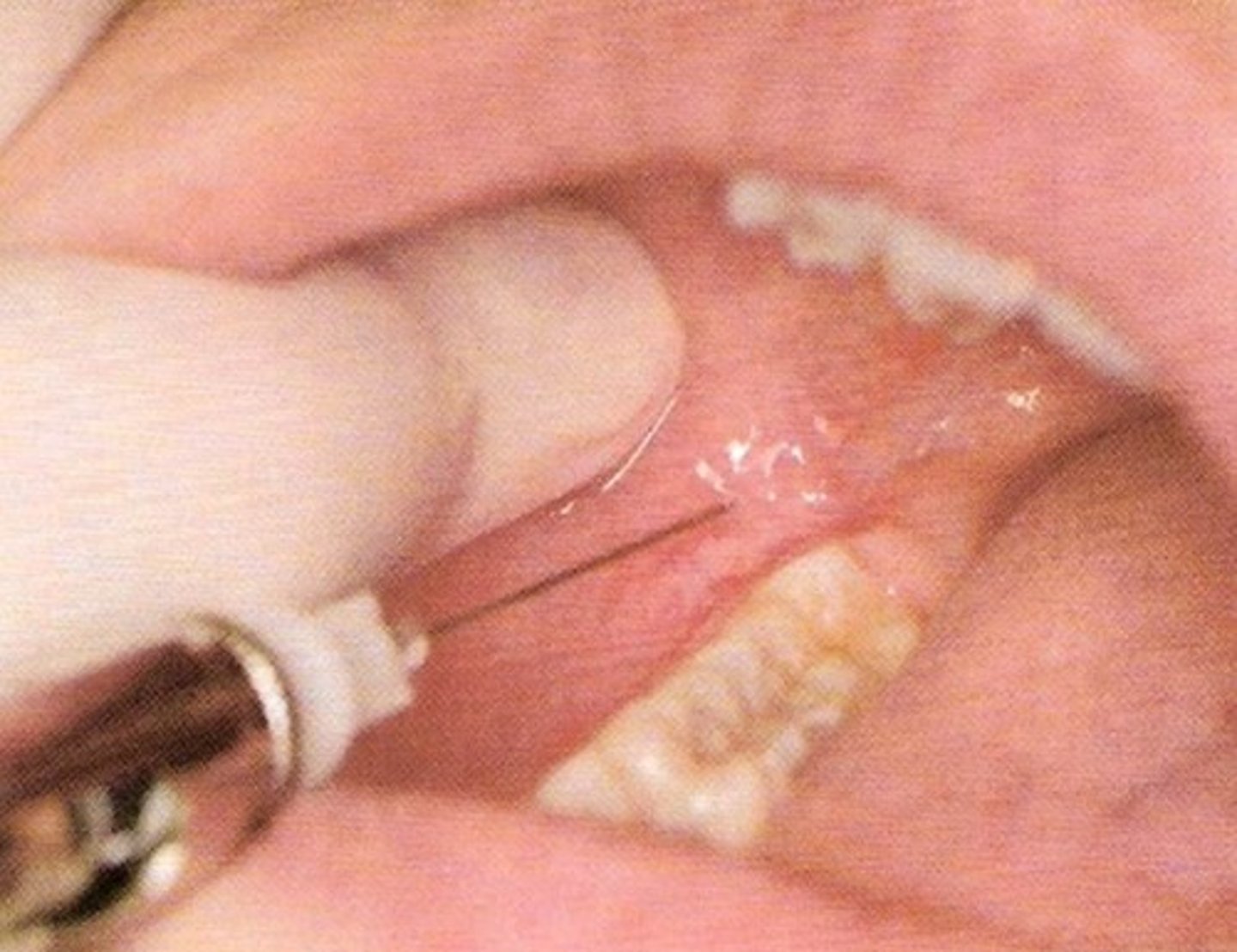
Buccal Block
Mandibular Molars buccal
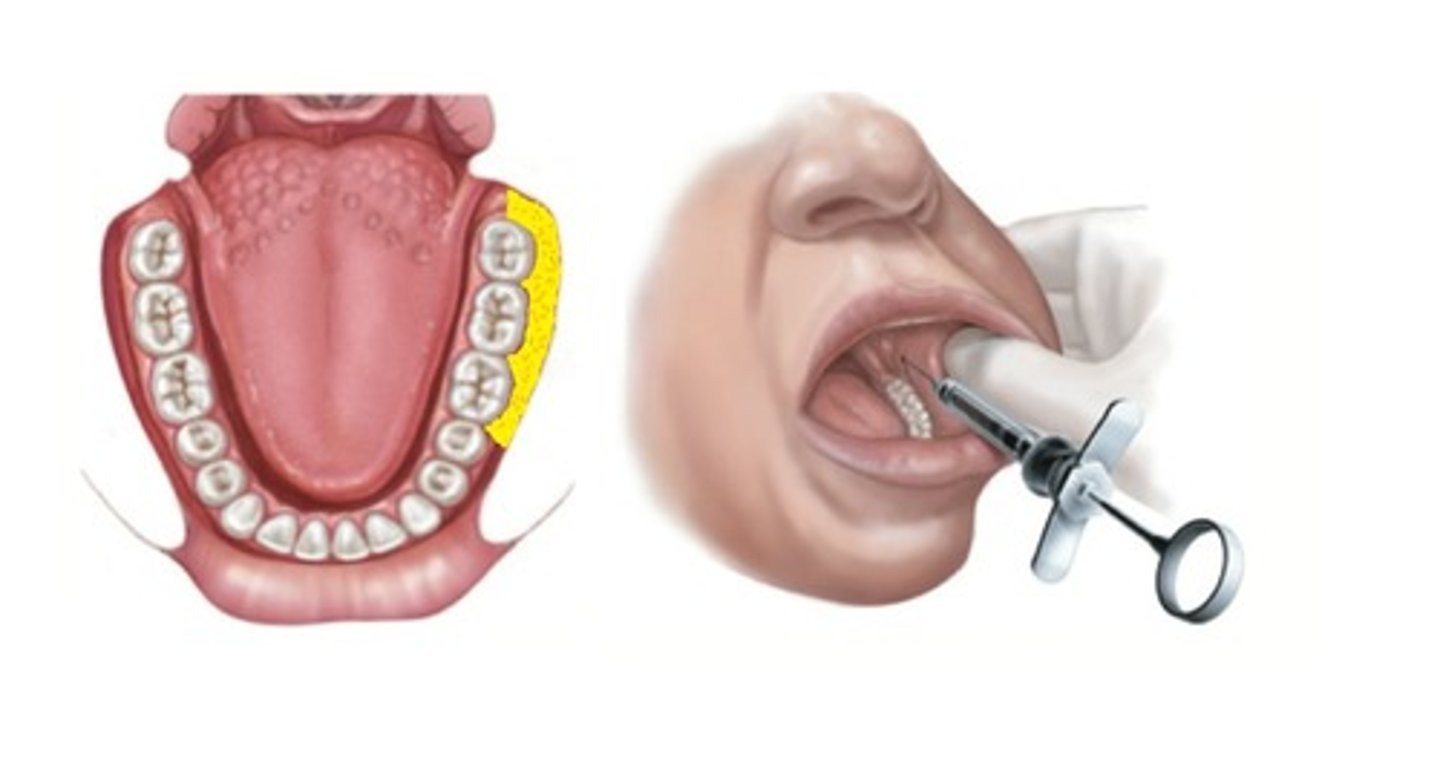
buccal block injection site
the buccal fat pad, just distal and buckle to the terminal molar
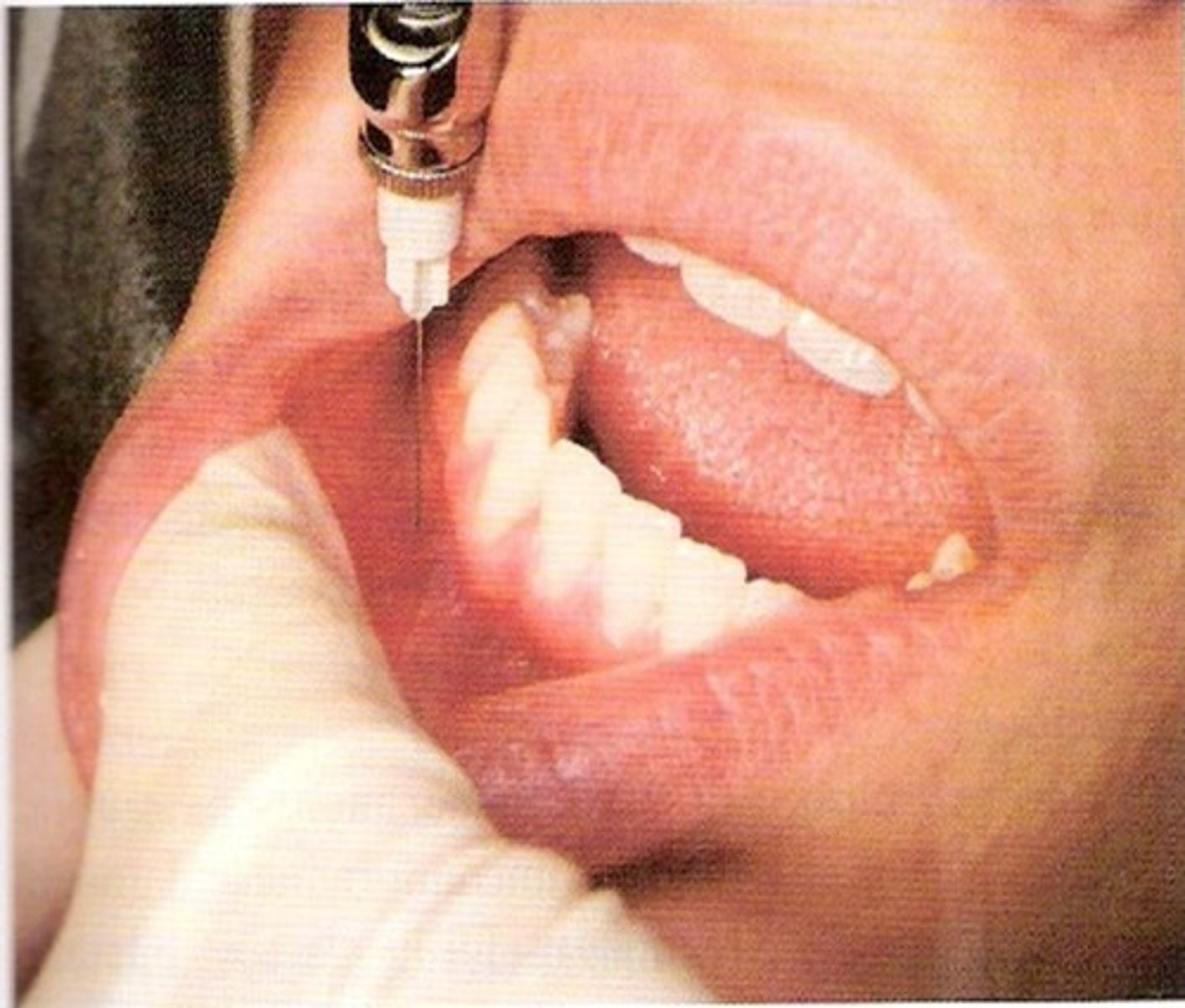
mental block
anesthetize the mandibular premolars and anterior teeth and associated buccal tissue
Mental Block Injection Site
anterior to mental foramen at depth of mandibular mucobuccal fold
lympatic vessels
A network of vessels that carry lymph throughout the body
Lymph
colorless fluid that is part of the body's immune system
lymph nodes
Small, bean-shaped structures distributed throughout the body that filter lymph and house immune cells (like lymphocytes) to fight infection
Afferent Lymphatic Vessel
Lymphatic vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node
efferent lymphatic vessels
Lymphatic vessels that carry filtered lymph away from the lymph node
palatine tonsils
tonsils that are located on either side of the throat
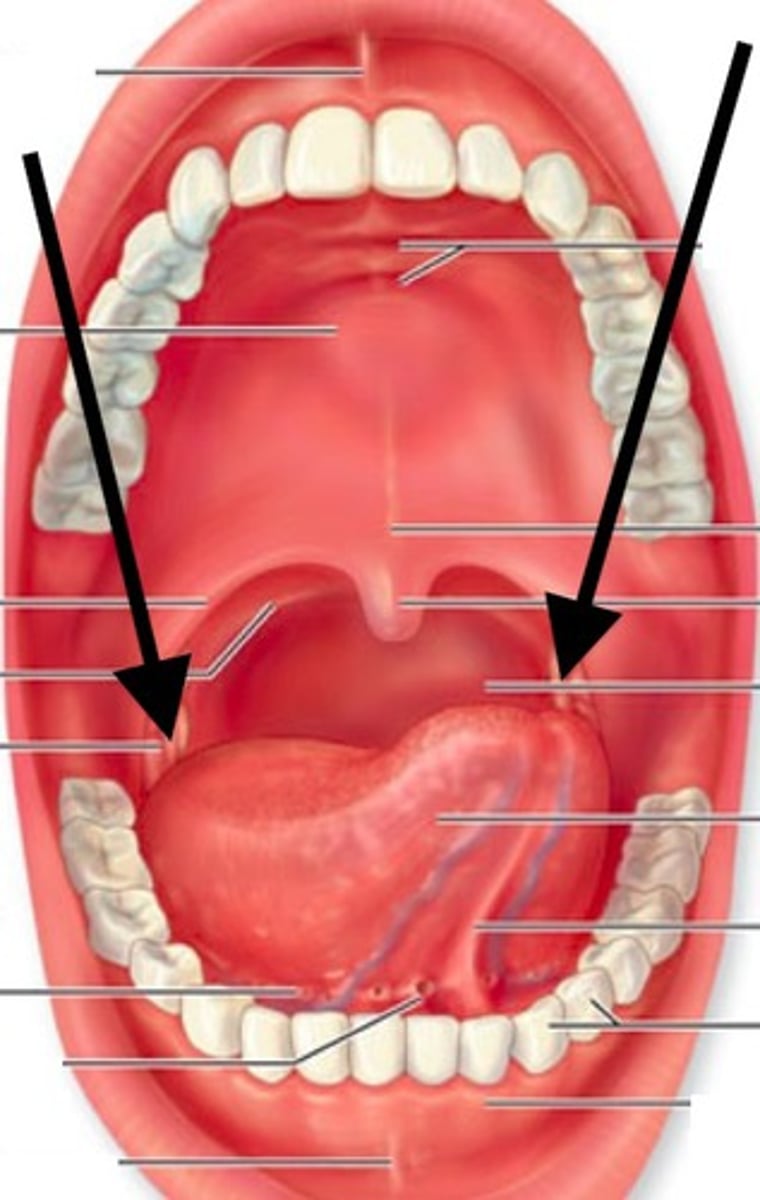
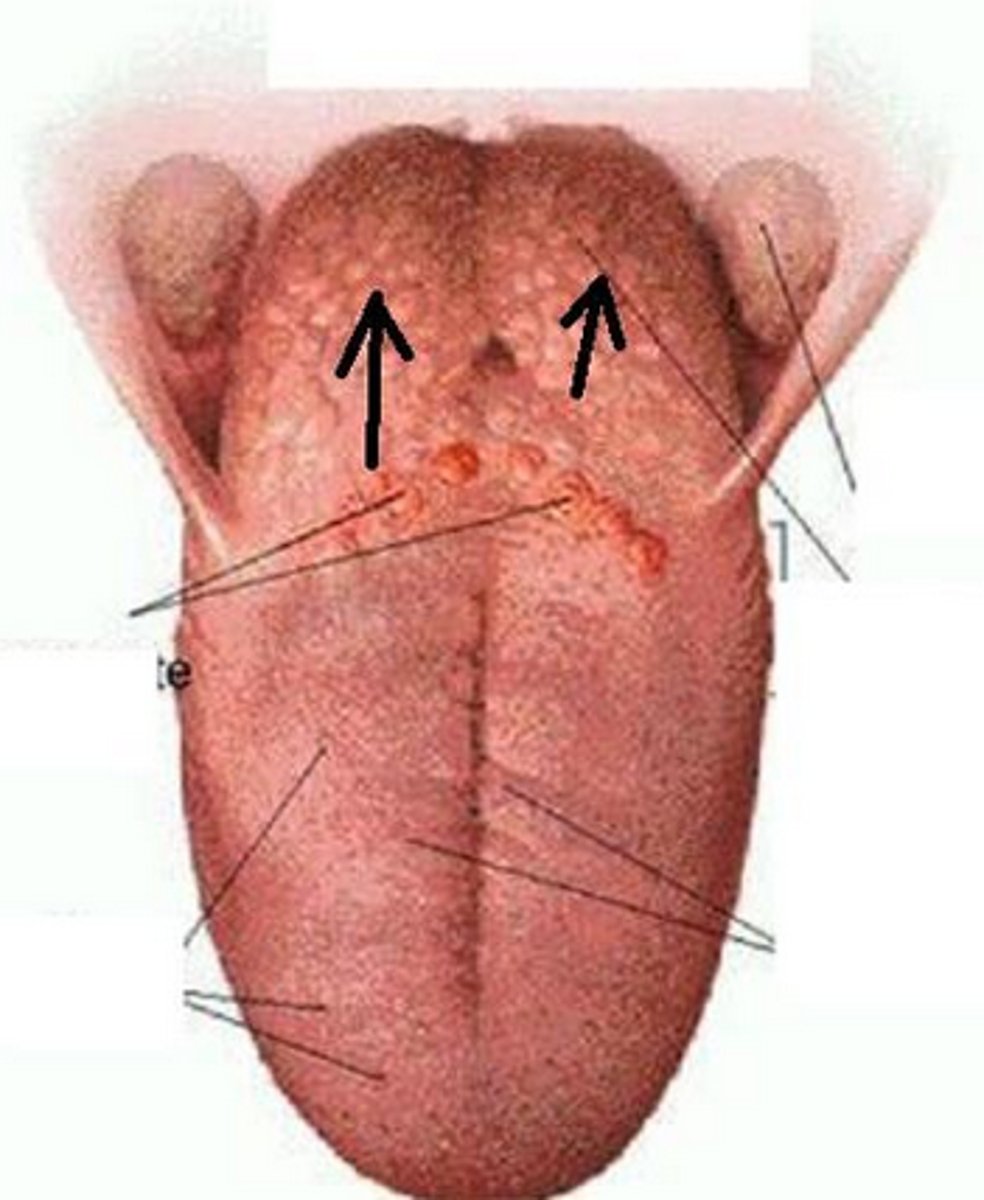
lingual tonsils
located at the base of the tongue
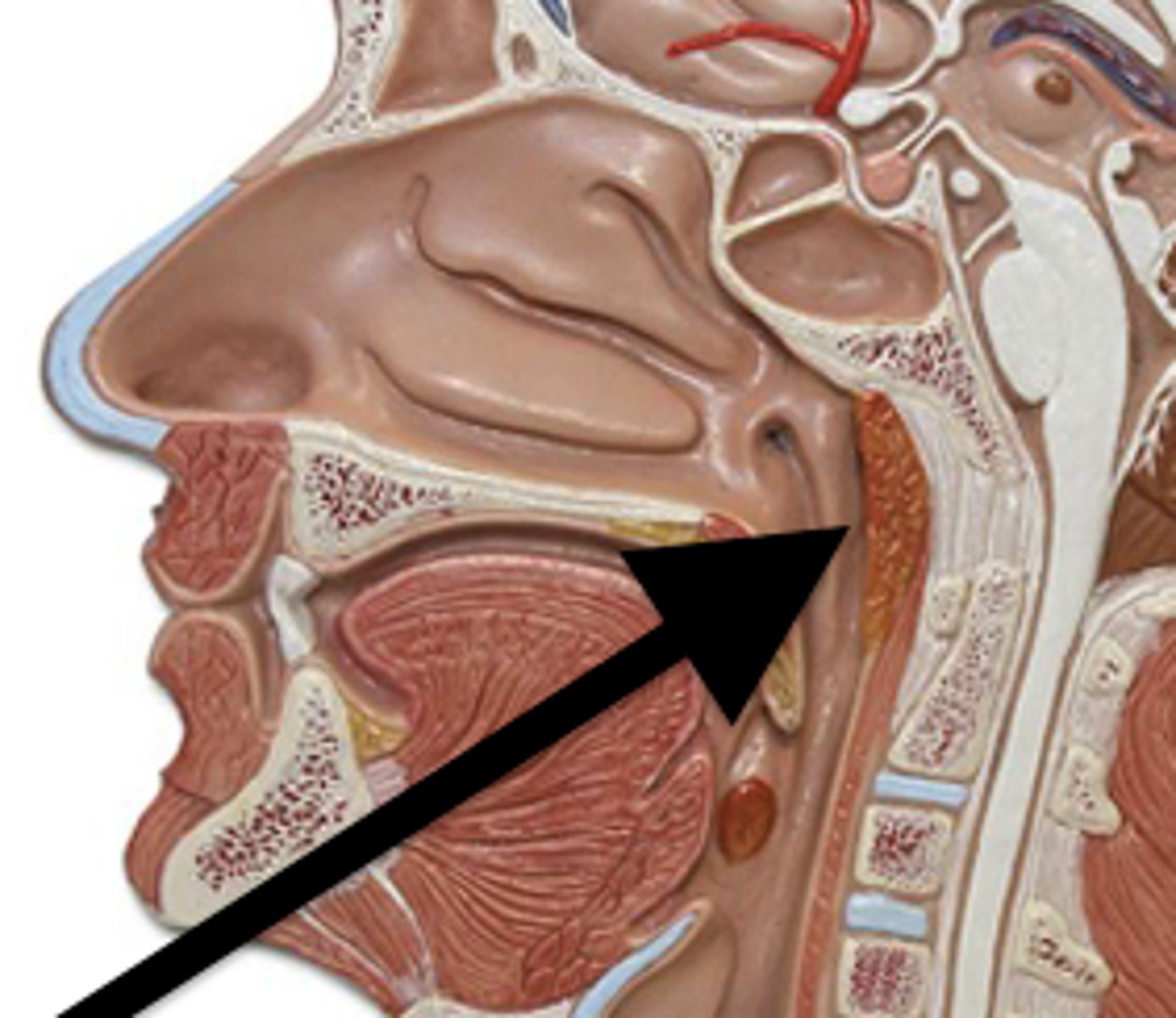
Pharyngeal Tonsil (Adenoids)
Located in the upper part of the throat, behind the nose
Odontogenic Infection
infection that originates in the teeth or jawbone
abscess
localized collection of pus caused by infection
Fistula
abnormal passage
stoma
an opening
Cellulitis
diffuse inflammation of soft tissue spaces
supperation
pus
Odontogenic infection can spread to
to the paranasal sinuses or can be spread by the vascular system, lymphatic system, or spaces in the head and neck
bacteremia
Bacteria traveling in the vascular system
Ludwig angina
is cellulitis of the submandibular space, with a risk of spreading to the parapharyngeal space and then onto the retropharyngeal space of the neck
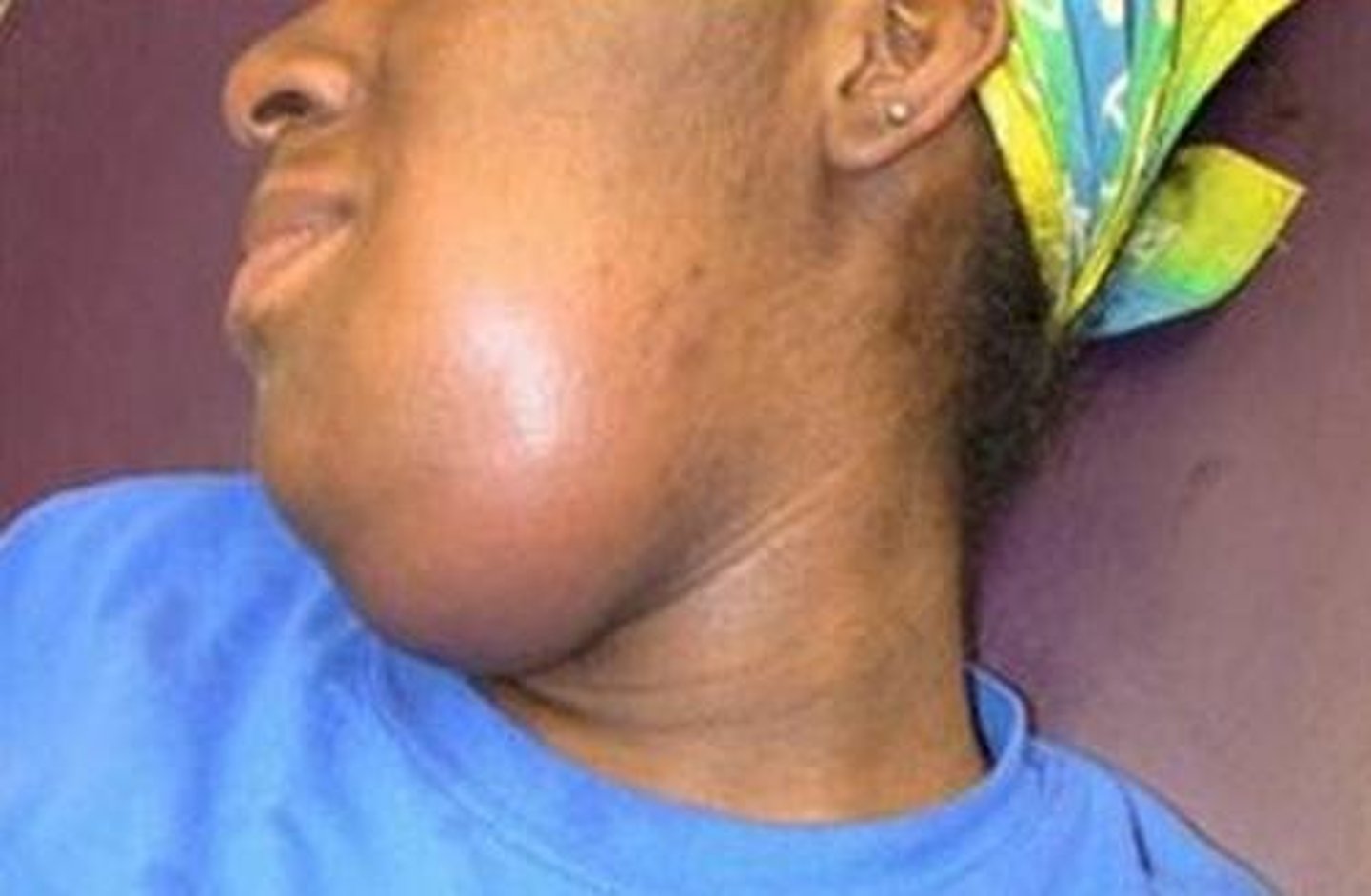
"Danger space" of the neck
the retropharyngeal space, becomes involved with edema of the larynx there can be complete respiratory obstruction,asphyxiation, and death
Thus, Ludwig angina is ____ medical emergency
acute
Piercing causing possible infection
tongue piercing
hilus of lymph nodes
depression where vessels and nerves enter an organ
lymphatic ducts
drain tissues of body and move lymph into major veins
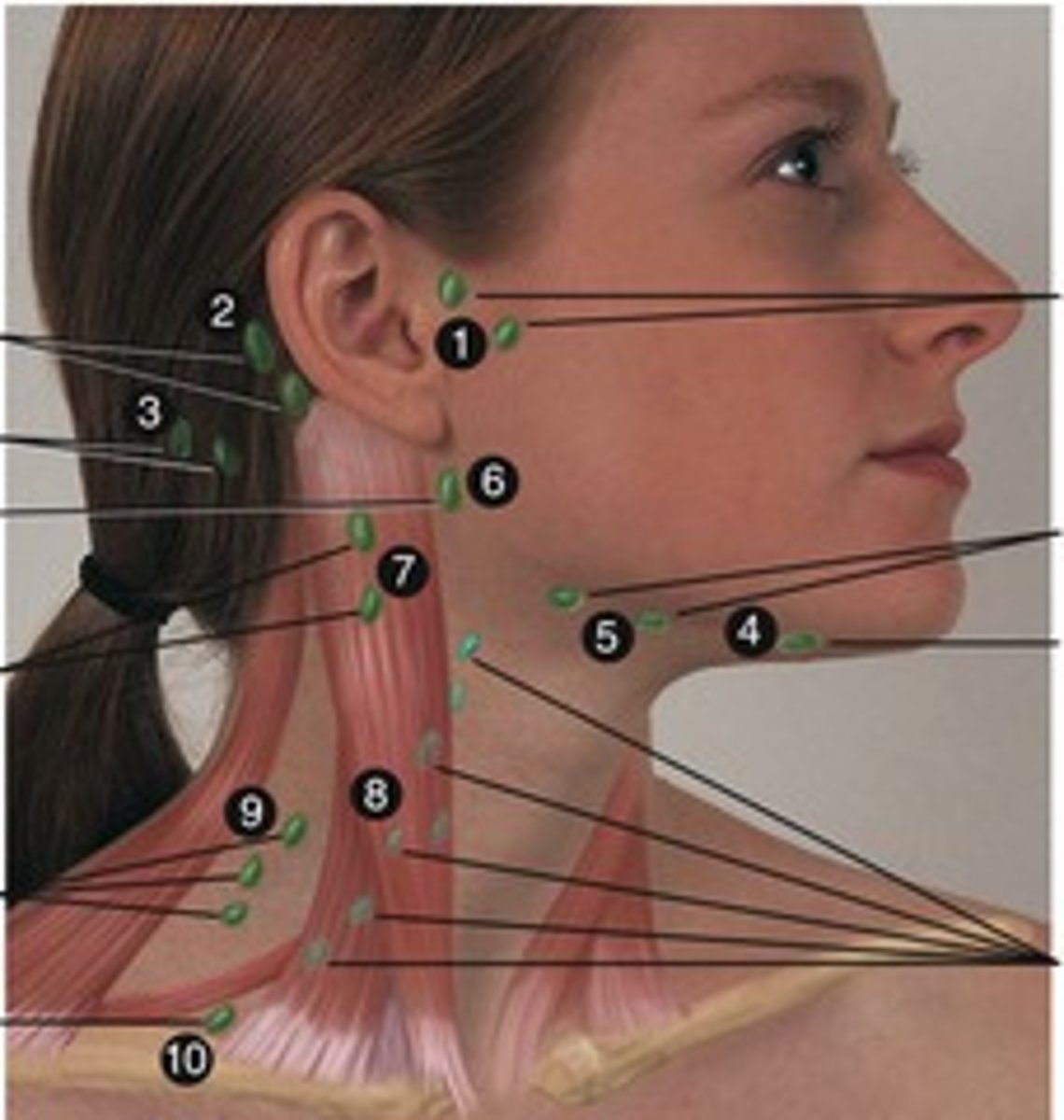
5 groups of paired superficial lymph nodes in the head:
the occipital, retroauricular, anteriorauricular, superficial parotid, and facial
occipital lymph node location
posterior base of the head
retroarticular lymph node location
located posterior to each auricle
anterior auricular lymph node location
in front of the ear
superficial parotid lymph node location
located just superficial to each parotid salivary gland
facial lymph node location
located along the length of the facial vein
four facial node subgroups
malar, nasolabial, buccal, and mandibular
Deep parotid lymph node location
located deep within the parotid salivary gland
retropharyngeal lymph node location
posterior to the pharynx, palate,paranasal sinuses, and nasal cavity
4 groups of superficial cervical lymph nodes include:
submental, submandibular, external jugular, and anterior jugular.
AKA Adenoids
The pharyngeal tonsil
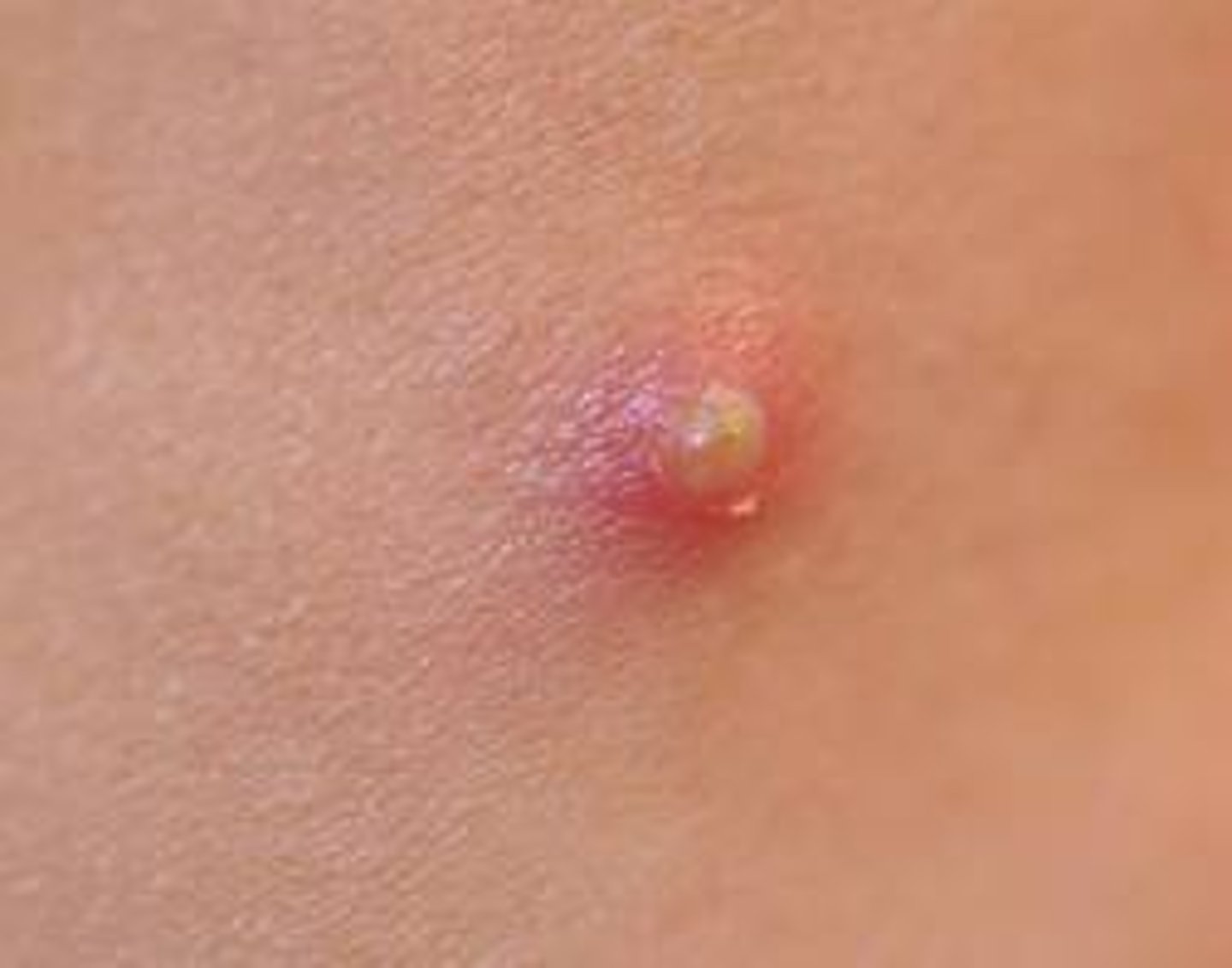
pustule
elevation of skin containing pus
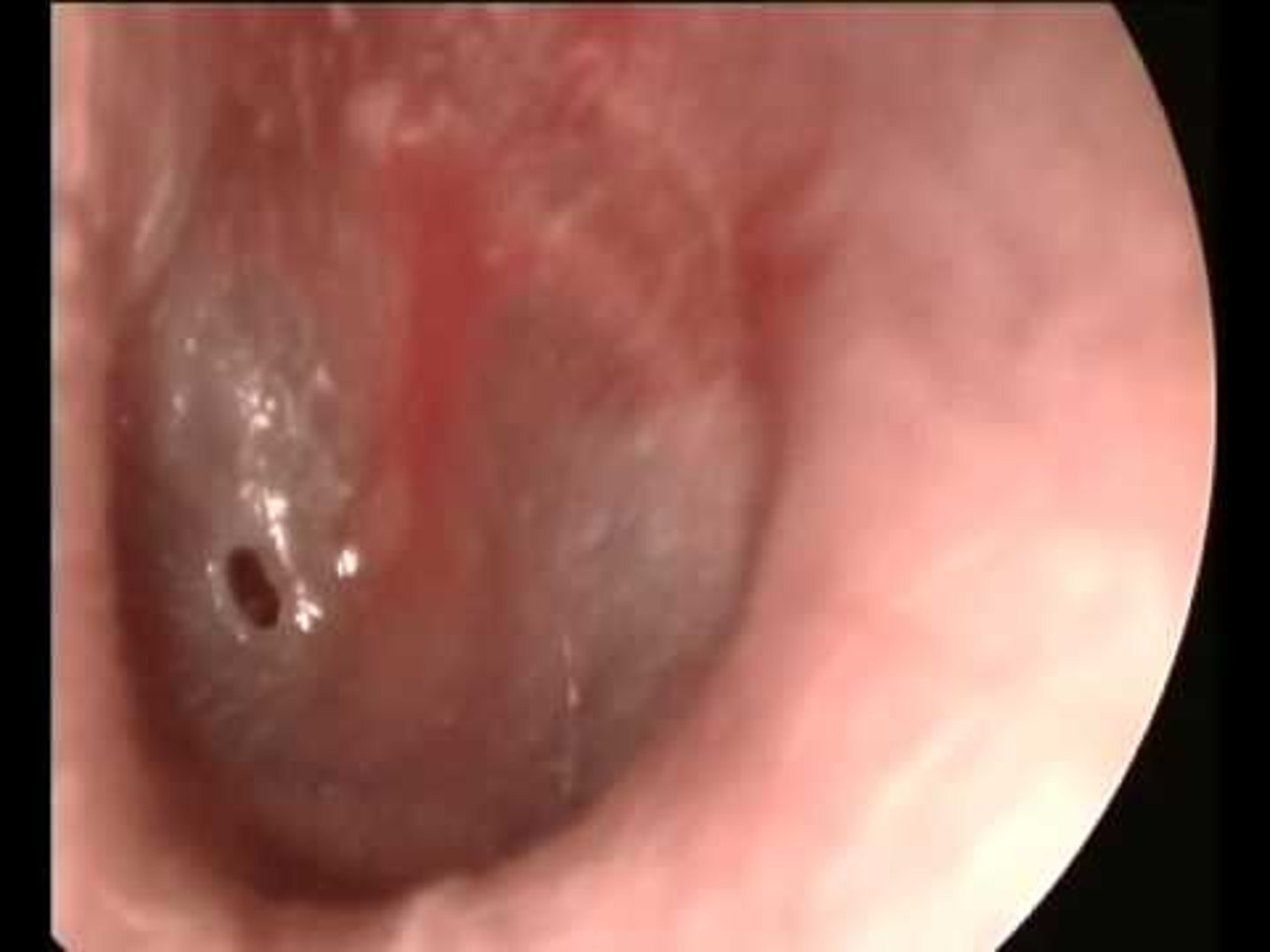
perforation
an abnormal hole in the wall of the sinus
Muscle that pulls the condyle of the mandible forward for opening
lateral pterygoid muscle
3 branches of the cranial nerve
Opthalmic (V1), Maxillary (V2), and Mandibular (V3)
Lymphadenopathy
Swelling of the lymph nodes, which can indicate infection
Management of Odontogenic Infections
Antibiotics, Incision and Drainage, and Surgical Intervention
inferior synovial cavity
under the articular disk
superior synovial cavity
above the articular disk
considered the tonsillar node
the jugulodigastric lymph node
Palpatable nodes
superficial ones
Unpalpatable nodes
deep ones
Acute symptoms
abscess plus draining, pain
chronic symptoms
no drainage, an abscess but no fistula
Health Implications of Bacteremia from Oral Sources
sepsis risk, infective endocarditis, Systemic Inflammation, and Chronic Conditions
Hinging motion of mandible provides
elevation and depression
Gliding motion of mandible provides
protrusion and restrusion