Neuroscience: Action Potentials, Synaptic Transmission, and Ion Channels
1/100
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
101 Terms
What causes the membrane to become permeable to Na+ during depolarization?
The opening of Na+ sensitive channels.
What is the role of the Na+/K+ pump in neuronal signaling?
It maintains a higher concentration of sodium outside the cell than inside.
What is a passive electrical response?
An electrical response that occurs without unique neuronal properties in response to a stimulus.
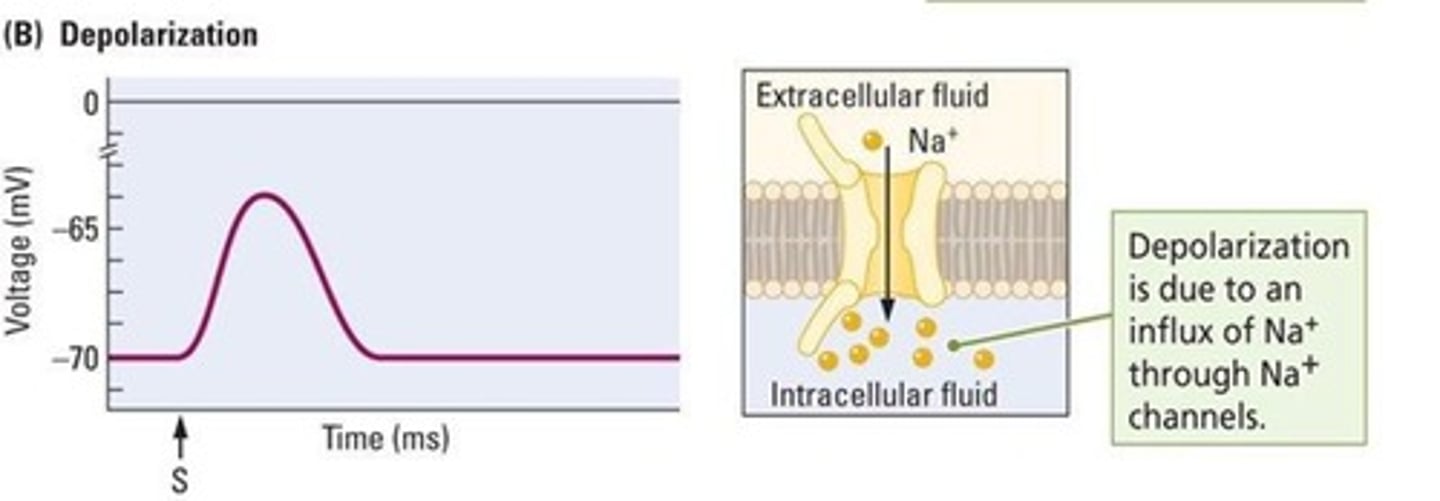
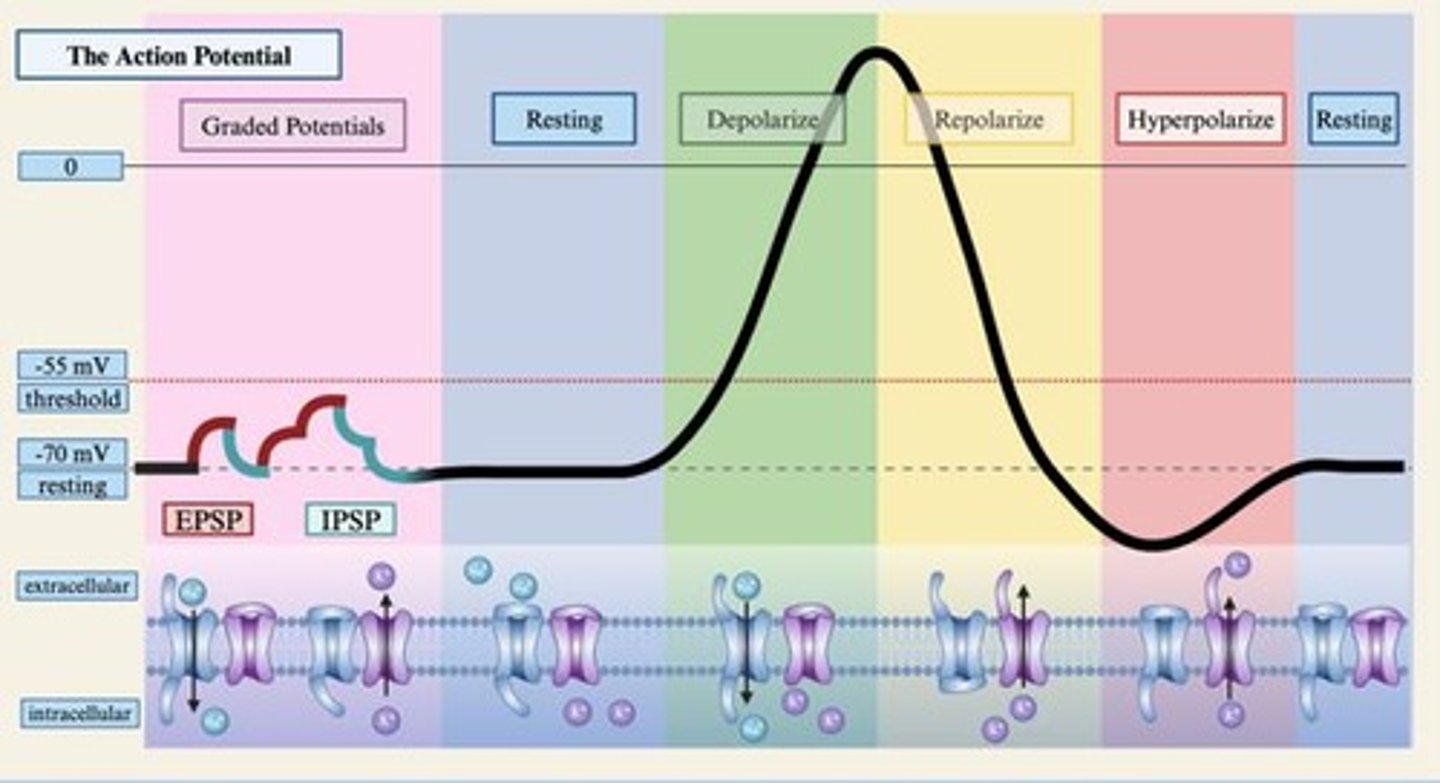
What happens during depolarization?
The membrane potential becomes more positive due to an inward flow of sodium ions.
What is an action potential?
A brief reversal in polarity of an axon that occurs when the membrane potential exceeds the threshold.
What is the threshold potential for initiating an action potential?
Approximately -50 mV to -40 mV relative to the extracellular environment.
What are graded potentials?
Small voltage fluctuations across the cell membrane caused by changes in ion concentration.
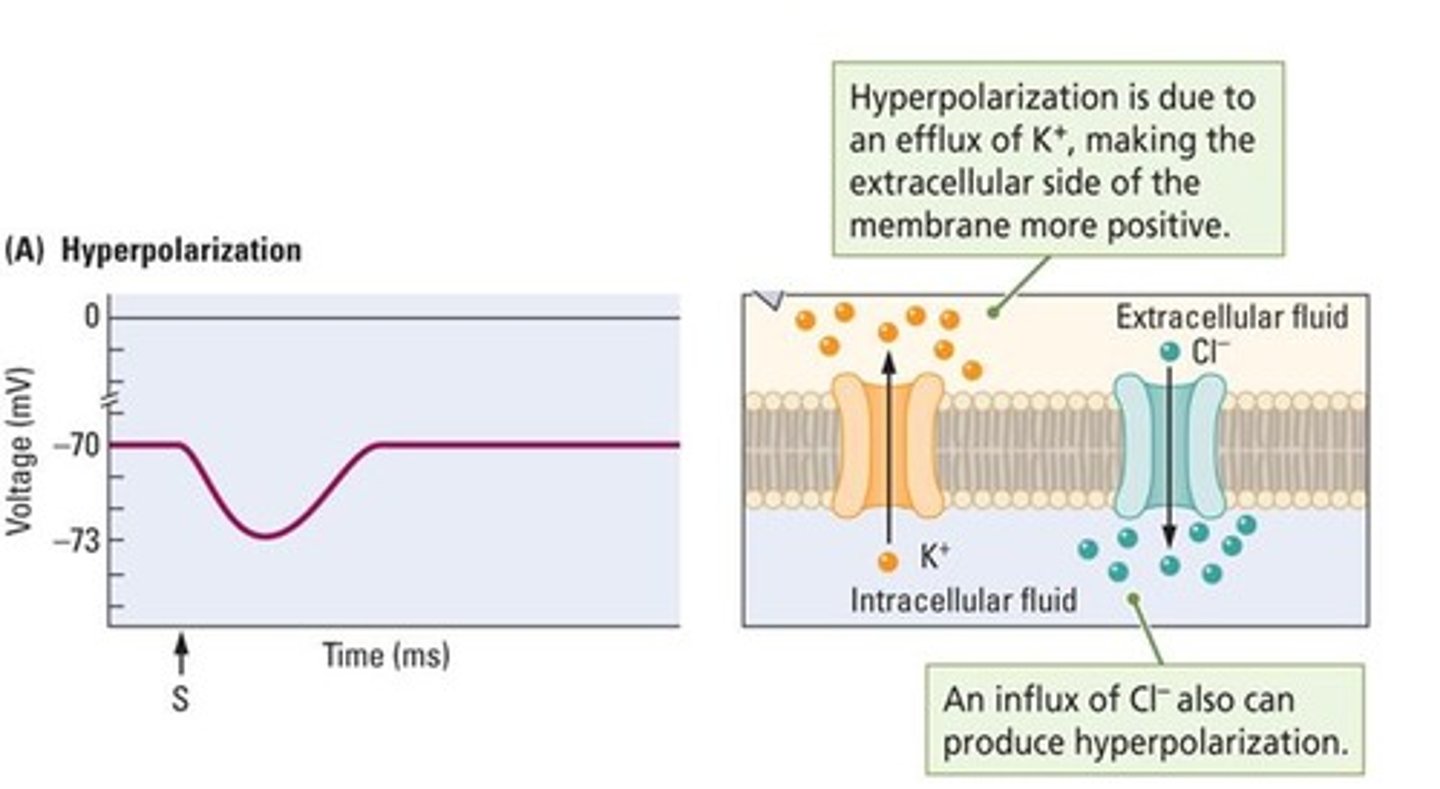
What occurs during hyperpolarization?
The membrane potential becomes more negative due to inward flow of chloride ions or outward flow of potassium ions.
What is the difference between EPSPs and IPSPs?
EPSPs cause brief depolarization making the neuron more likely to fire, while IPSPs cause brief hyperpolarization making it less likely to fire.
What is temporal summation?
The summing of postsynaptic potentials that occur at approximately the same time on a membrane.
What is spatial summation?
The summing of postsynaptic potentials that occur at approximately the same location on a membrane.
What is the axon hillock?
The junction of the cell body and axon where EPSPs and IPSPs are integrated and action potentials are initiated.
What are voltage-sensitive ion channels?
Gated protein channels that open or close at specific membrane voltages, such as sodium (Na+) and potassium (K+) channels.
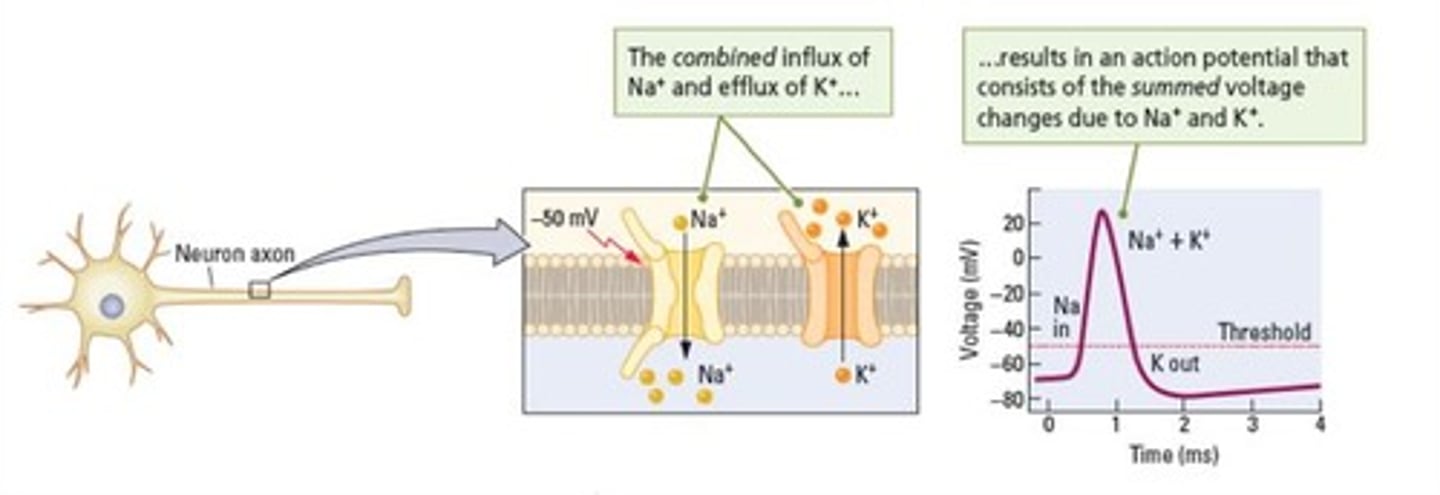
What is the role of sodium (Na+) channels during an action potential?
They are more sensitive and open sooner than potassium (K+) channels, allowing for depolarization.
What is the significance of membrane conductance in action potentials?
Changes in sodium and potassium conductance are time and voltage-dependent, influencing action potential generation.
What triggers the depolarization of the neuronal membrane?
Activation of sodium (gNa+) and potassium (gK+) conductances.
What is the duration of an action potential?
Approximately 1 millisecond.
What happens to EPSPs and IPSPs after they occur?
They last only a few milliseconds before decaying back to the resting potential.
What is the net flow of current during depolarization?
The net flow is inward, creating a current sink detected as negativity by nearby electrodes.
How does ligand binding affect membrane potential?
It can cause depolarization or hyperpolarization depending on the type of ion channels activated.
What is the relationship between stimulus intensity and action potential frequency?
Stimulus intensity is encoded in the frequency of action potentials generated.
What is the role of feedback cycles during an action potential?
They are responsible for membrane potential changes throughout the action potential process.
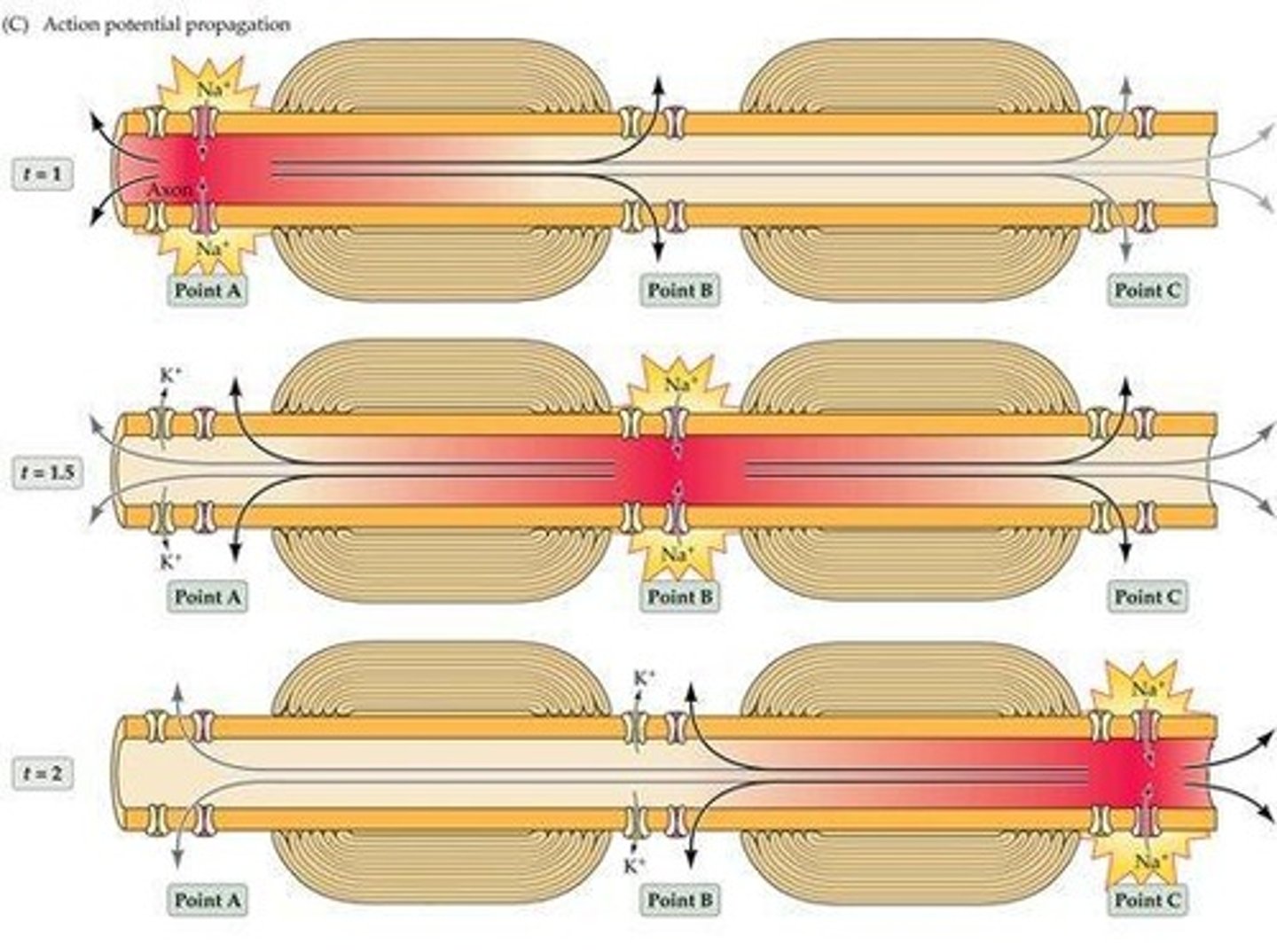
What is required for the propagation of an action potential?
Both active and passive ionic movement.
What is the role of Na+ during the propagation of an action potential?
Local inward movement of Na+ causes depolarization.
What is the role of K+ during the propagation of an action potential?
Local outward movement of K+ causes hyperpolarization.
How does passive current flow contribute to action potential propagation?
It involves local shuttling of charge to the adjacent segment of the membrane.
What is the Absolute Refractory Period?
The state of an axon during repolarization when a new action potential cannot be elicited due to closed sodium channel gates.
What is the Relative Refractory Period?
The state of an axon during the later phase of an action potential when increased electrical current is needed to produce another action potential.
What prevents an action potential from reversing direction?
Refractory periods ensure that the impulse travels away from the initial point of stimulation.
What is the function of the myelin sheath?
It speeds up neural impulse conduction.
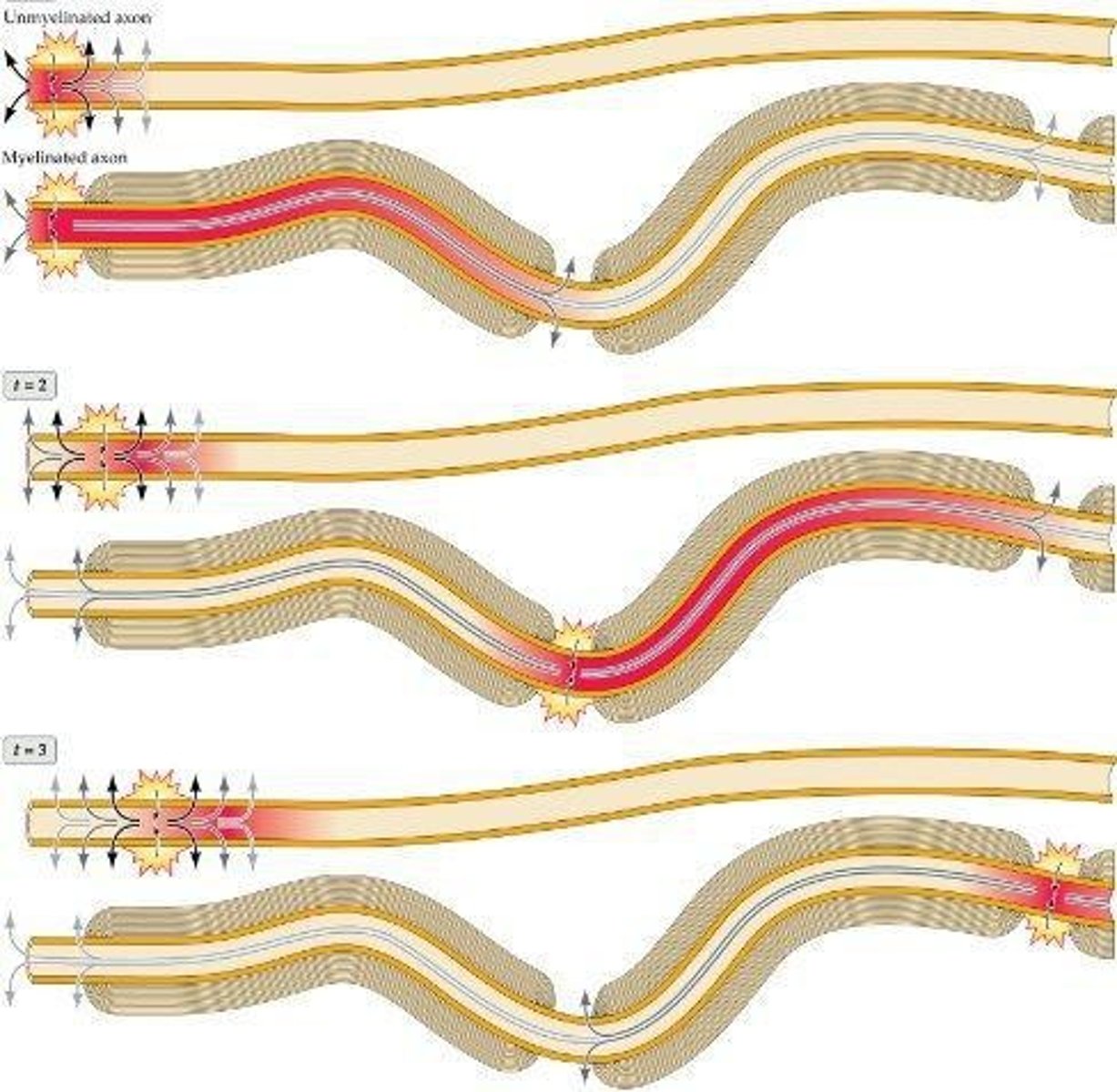
What are Nodes of Ranvier?
Tiny gaps in the myelin sheath that contain voltage-sensitive sodium and potassium channels.
How does myelin affect action potential conduction speed?
Myelin increases the speed of action potential conduction.
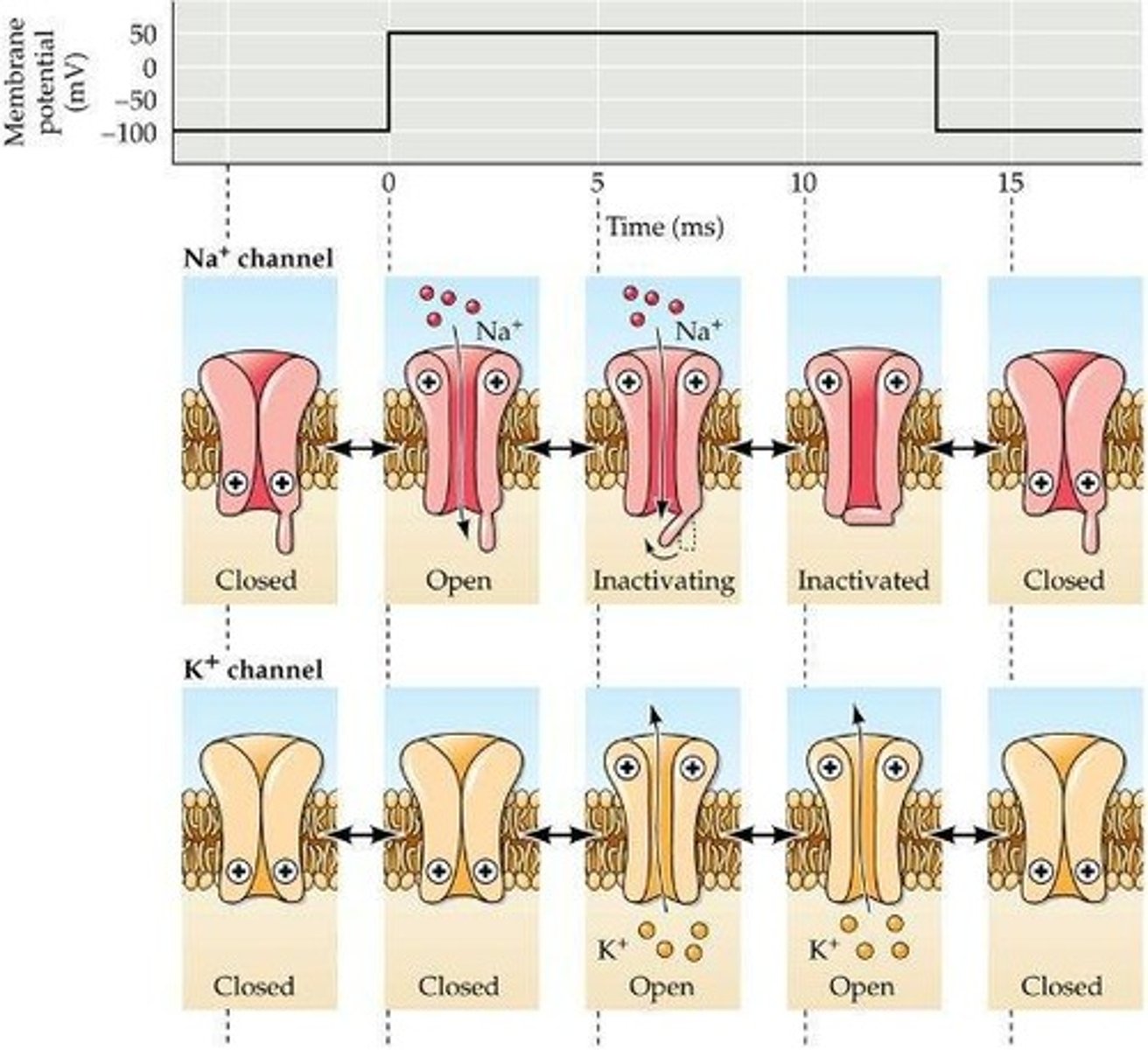
What are the properties of voltage-gated Na+ and K+ channels?
They open during depolarization and close during hyperpolarization.
What is the role of the voltage sensor in ion channels?
It detects the potential across the membrane and regulates the opening and closing of the channels.
What happens to Na+ channels during reverse polarity?
They become inactivated and enter a non-conducting state.
What is the structure of ion channel pores?
They are formed by the arrangement of loops and helices of the subunits that make up the channels.
What differentiates cation channels from anion channels?
Cation channels (Na+, K+, Ca++) and anion channels (Cl-) differ slightly in structure and the number of subunits.
What forms the selectivity filter in ion channels?
A ring of negative/positive charges within the membrane.
What are the transmembrane helices in ion channel subunits?
Each subunit has six transmembrane helices, with S1-S4 forming the voltage sensor and S5-S6 forming the pore domain.
How does a change in membrane voltage affect ion channels?
It moves the positively charged S4 in an outward direction, leading to the opening of the ion channel.
What is a selectivity filter in ion channels?
A specific structure that allows particular ions to enter while excluding others, including those with the same valence.
What factors influence the selectivity of ion channels?
The diameter of the pore, the atomic radius of the ion (both hydrated and unhydrated), and the electronegativity of the ion.
What is the role of the S4 segment in voltage-gated sodium channels?
It contains positively charged amino acids responsible for voltage sensing.
What happens during the closed state of voltage-gated sodium channels?
The frequency of openings decreases, and the channels remain closed.
What occurs when voltage-gated sodium channels are activated?
An appropriate stimulus increases the probability of openings, allowing sodium ions to flow through.
What is the inactivated state of voltage-gated sodium channels?
A state where Na+ entry no longer occurs even with an activating stimulus, indicating absolute refractory period.
What is the structure of voltage-gated potassium channels?
They consist of four similar alpha subunits, each with six transmembrane domains, forming a pore.
How do potassium channels return the membrane potential to resting state?
By closing potassium channels, which prevents hyperpolarization.
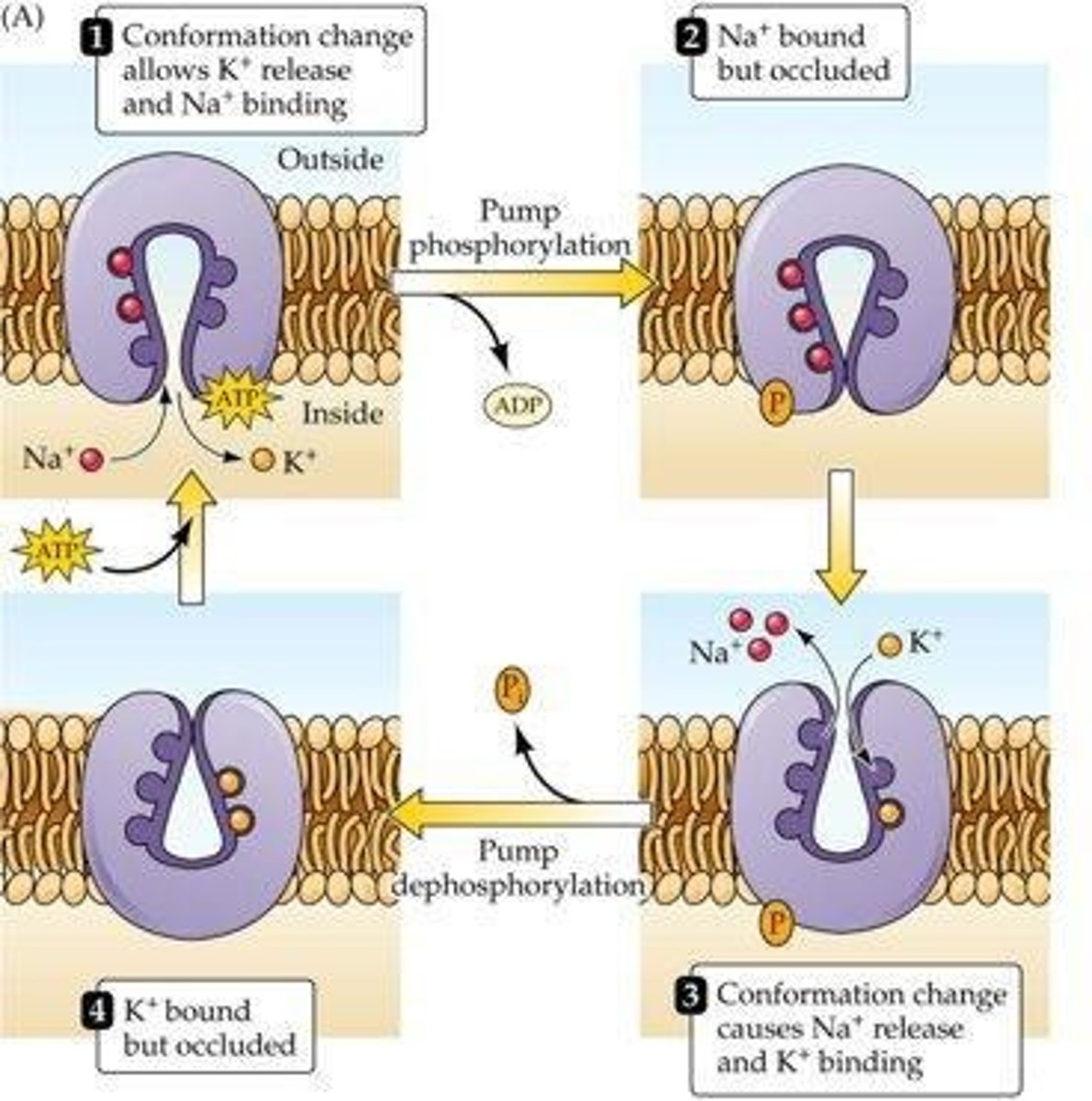
What is the function of active transporters in ion channels?
They maintain concentration gradients for physiologically relevant ions, requiring energy to function.
What is the role of the Na+/K+ ATPase pump?
It maintains the gradient for Na+ and K+ by removing 3 Na+ ions and bringing in 2 K+ ions using ATP hydrolysis.
What are calcium channels characterized by?
They are voltage-sensitive, consist of four subunits, and have S4 as the voltage sensor.
What is the primary function of synaptic transmission?
To transmit signals between neurons using neurotransmitters at chemical synapses.
How do chemical synapses differ from electrical synapses?
Chemical synapses use neurotransmitters and are unidirectional, while electrical synapses use gap junctions and are bidirectional.
What triggers neurotransmitter release at chemical synapses?
Calcium ion (Ca2+) influx into the presynaptic neuron.
What is the significance of gap junctions in electrical synapses?
They allow for rapid, bidirectional transmission of signals between neurons.
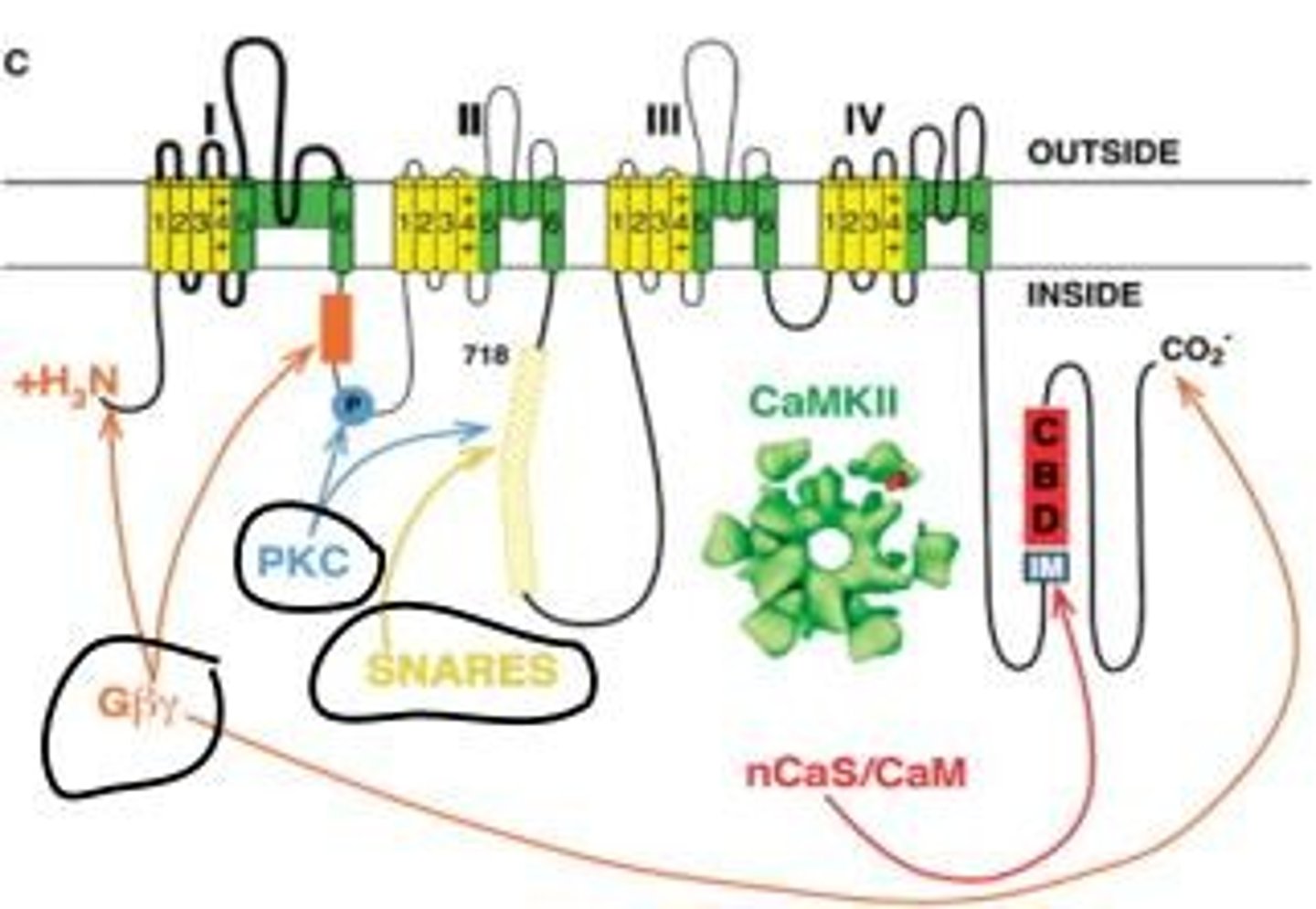
What is the role of SNARE proteins in synaptic transmission?
They link calcium to vesicles for neurotransmitter release.
What is the difference between depolarization and hyperpolarization in neurons?
Depolarization makes the membrane potential more positive, while hyperpolarization makes it more negative.
What is the function of the inactivation lid in sodium channels?
It prevents Na+ entry during the inactivated state, contributing to the absolute refractory period.
What is the role of accessory beta subunits in potassium channels?
They affect the voltage sensitivity and inactivation properties of the channels.
What happens during the depolarization of the membrane in relation to S4?
The rotation of S4 interacts with S6 segments to open the gate of potassium channels.
What is the primary function of voltage-gated calcium channels?
To allow calcium ions to enter the cell in response to membrane depolarization, facilitating neurotransmitter release.
What are the presynaptic structures in a chemical synapse?
Filamentous structures that help guide vesicles to the active zone and several pools of vesicles, with only those at the active zone ready for exocytosis.
What is the role of the postsynaptic density (PSD) in a chemical synapse?
The PSD helps anchor postsynaptic receptors in the postsynaptic membrane, preventing their movement and containing proteins involved in plasticity-dependent processes.
What happens during vesicular release of neurotransmitters?
Neurotransmitters (NTs) are packaged into vesicles, transported to the membrane, and released into the synaptic cleft after vesicle fusion.
What is the active zone in a chemical synapse?
The area at the presynaptic terminal where synaptic vesicles from the readily releasable pool are docked and primed for exocytosis.
How does depolarization affect neurotransmitter release?
Depolarization opens voltage-sensitive calcium channels, allowing calcium to enter the cell, which triggers the release of neurotransmitters.
What is the synaptic delay in neurotransmitter release?
The time required for calcium channels to open and for calcium to enter the cell, triggering transmitter release.
How do synapses with larger active zones differ from those with smaller active zones?
Larger active zones accommodate more calcium channels and vesicles, increasing the probability of neurotransmitter release.
What are SNARE proteins and their role in neurotransmitter release?
SNARE proteins, including synaptobrevin, syntaxin, and SNAP-25, facilitate the docking and fusion of synaptic vesicles with the plasma membrane.
What is the function of synaptotagmin in neurotransmitter release?
Synaptotagmin binds calcium ions, triggering a conformational change that promotes vesicle fusion with the plasma membrane.
What is the structure of voltage-sensitive calcium channels?
The a1 subunit is the largest and includes the conduction pore, voltage sensors, and gating apparatus, regulating channel activity.
What is the effect of Botox on neurotransmitter release?
Botox inhibits neurotransmitter release by preventing the priming and fusion of synaptic vesicles.
What are the two main types of neurotransmitter receptors?
Ionotropic receptors (ligand-gated ion channels) that produce fast responses and metabotropic receptors (G-protein-coupled receptors) that produce slower responses.
How are neurotransmitters synthesized in the axon terminal?
Building blocks from food are pumped into the cell and altered by enzymes translated from the cell body.
Where are neurotransmitters synthesized in the neuron?
Neurotransmitters can be synthesized in the axon terminal or in the cell body and transported to axon terminals in vesicles.
What is the difference between ionotropic and metabotropic receptors?
Ionotropic receptors are fast and directly open ion channels, while metabotropic receptors are slow and involve G-protein activation and second-messenger cascades.
What is the role of calcium in neurotransmitter release?
Calcium entry into the presynaptic terminal triggers the release of neurotransmitters by facilitating vesicle fusion with the plasma membrane.
What is the readily releasable pool (RRP) of vesicles?
The pool of synaptic vesicles that are immediately available for release upon stimulation.
What occurs during the docking of a synaptic vesicle?
SNARE proteins on the vesicle and plasma membrane form a complex that brings the two membranes close together for fusion.
What happens to neurotransmitters after they are released into the synaptic cleft?
Neurotransmitters diffuse out of the synaptic cleft and can bind to postsynaptic receptors to produce a response.
What is the significance of the postsynaptic response time in chemical synapses?
The postsynaptic response time can range from 1-2 milliseconds for ionotropic receptors to hundreds of milliseconds for metabotropic receptors.
What is the role of tethering proteins in synaptic vesicle exocytosis?
Tethering proteins help anchor vesicles in the active zone of the synapse, facilitating their readiness for release.
What is the role of acetylcholine in the nervous system?
Acetylcholine serves as a prototype neurotransmitter, part of the parasympathetic division, and reduces heart rate.
What is the source of choline in the body?
Choline comes from the diet and is transported into nerve terminals.
How is acetylcholine synthesized?
Acetylcholine is synthesized by combining choline with acetyl-CoA via choline acetyltransferase (ChAT).
What are vesicular neurotransmitter transporters (VNTs)?
VNTs are small proteins responsible for packing synaptic vesicles with neurotransmitters, determining the amount released per vesicle.
What activates the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor?
The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is activated by the binding of acetylcholine, forming a channel for cations to move.
What is the significance of nicotine in relation to nicotinic receptors?
Nicotine mimics the actions of acetylcholine on nicotinic receptors, acting as an agonist.
What are the structural properties of ligand-activated receptors?
Non-polar sequences form alpha-helices to span the lipid bilayer, while hydrophilic amino acids line the pore to allow water passage.
What types of receptors are involved in excitatory neurotransmission?
Ionotropic glutamate receptors, including AMPA, NMDA, and Kainate receptors, are involved in excitatory neurotransmission.
What distinguishes NMDA receptors from AMPA receptors?
NMDA receptors generate slower excitatory post-synaptic currents (EPSCs) and require a co-agonist (glycine) for activation.
What is the function of GABA in the brain?
GABA acts as an inhibitory neurotransmitter, found in about one-third of synapses, primarily in local circuit interneurons.
How is GABA synthesized?
GABA is synthesized from glucose through a series of steps: glucose → glu → GABA.
What type of channel does the GABAA receptor form?
The GABAA receptor forms a GABA-gated ion channel for Cl- ions, which enter the neuron upon activation.
What happens to intracellular chloride concentration in developing neurons?
In young cortical neurons, high intracellular chloride concentration ([Cl-]i) causes GABA to depolarize these neurons.
What is the significance of postsynaptic potential summation?
Summation of excitatory (EPSPs) and inhibitory (IPSPs) postsynaptic potentials determines whether an action potential (AP) will fire.
What factors influence the summation of postsynaptic potentials?
The distance from the axon hillock (space) and the timing of each postsynaptic potential (time) influence the summation.
What is the role of Mg2+ in NMDA receptor function?
Mg2+ blocks the NMDA channel, and depolarization pushes it out, allowing Ca2+ and other ions to enter.
What are the characteristics of ionotropic GABA receptors?
Ionotropic GABA receptors, such as GABAA, are pentameric and can have various subunit combinations, typically including 2α and 2β subunits.
What is the effect of GABA on young cortical neurons?
GABA can depolarize young cortical neurons due to high intracellular chloride concentrations.