Gr.9 Geography Unit 3 - Climate, Soils and Vegetation Test Review
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
7 vegetation regions of canada
Tundra
West Coast Forest
Cordilleran Vegetation
Boreal & Taiga Forest
Grassland
Mixedwood Forest
Deciduous Forest
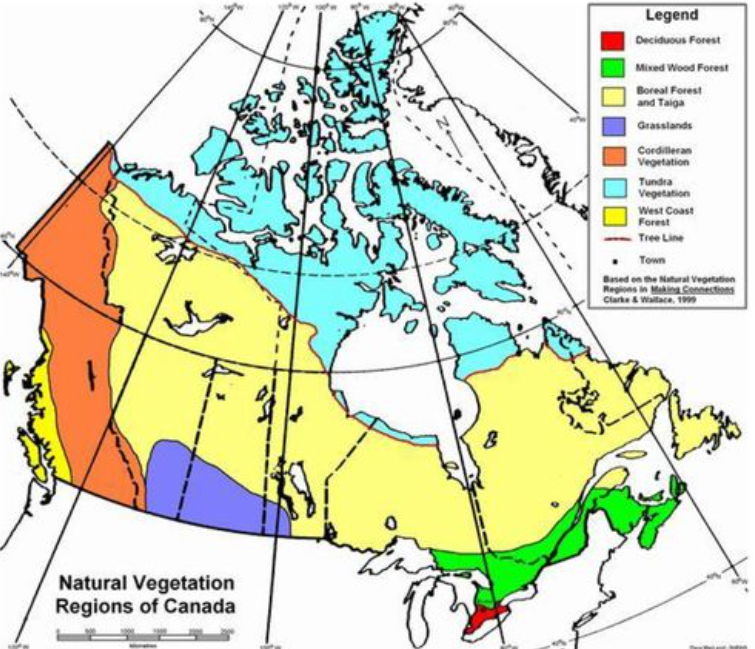
Tundra vegetation region
Climate: too cold, little precipitation
Vegetation: few small trees, shrubs, flowering plants, moss and lichens
Physiography: barren and somewhat rocky, permafrost soil
Location: Yukon, Northwest Territories, Nunavut, northeastern Manitoba, northern Ontario, northern Quebec and northern Labrador

West Coast Forest
Climate: large amounts of rainfall and warm climate
Vegetation: trees are lush and thick, trees here are important for the Lumber Industry
Physiography: forests are old, lush and thick fertile soil
Location: along the west coast of British Colombia

Cordilleran vegetation region
Climate: mild, wet and rarely has snow that stays
Vegetation: varies, many different trees
Physiography: alpine tundra to coastal rainforest to grasslands and savannah forests
Location: most of southern British Columbia and some of southwestern Alberta

Boreal & Taiga Forest
Climate: warm to cool summers and long, cold winters
Vegetation: thick forests, coniferous trees are more common than deciduous
Physiography: largest vegetation region, large and thick forests
Location: Newfoundland and Labrador on the Atlantic Coast to northeastern British Columbia and the Yukon Territory

Grasslands
Climate: very dry and are too dry for most trees
Vegetation: natural grasses grow taller in the wetter areas of the region than in the drier areas
Physiography: flat-to-gently rolling plain with a few major hill systems
Location: southern Manitoba into Alberta

Mixedwood Forest
Climate: cool winters and warm summers moderated by water bodies
Vegetation: deciduous (birch, aspen, maple, oak) and coniferous (spruce, pine) tree species
Physiography: large forests surrounded by bodies of water
Location: Southern Ontario and Quebec

Deciduous Forest
Climate: long and hot summers, mild winters and plenty precipitation
Vegetation: Many different kinds of deciduous trees
Physiography: Only small areas of trees are left as most of the area has been taken for human use
Location: southwestern Ontario

What is a soil horizon?
The different layers of soil parallel to its surface whose properties develop from the combined actions of living organisms and water
What is the structure of soil?
The way particles in soil are arranged and assembled.
Parts of soil?
Bacteria & Organic Minerals: Dead plants and animals are decomposed by bacteria releasing nutrients into soil
Air: Air spaces needed around plant roots, made by high humus levels or small animals
Moisture: water dissolves nutrients into soil and taken up by plants
Minerals: Comes from parent material and are weathered into soil
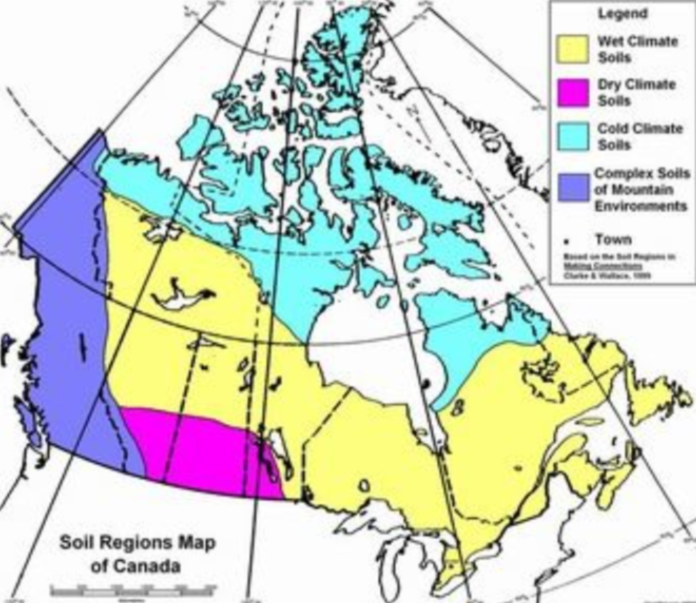
The soil regions of Canada and how to tell each one apart?
Soil can be told apart based on its fertility, texture, and moisture.
The Prairie provinces (Alberta, Saskatchewan and Manitoba) have the most fertile soil.
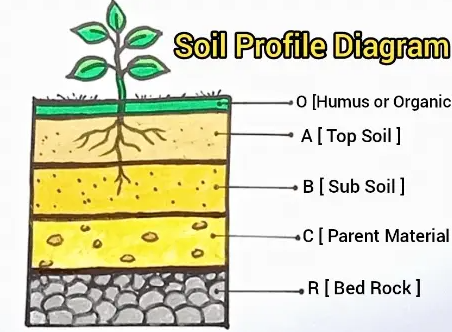
The layers of soil?
O Humus: dark, organic material that forms when plant and animal matter decays
A Top Soil: high concentration of organic matter and microorganisms
B Sub Soil: variable mixture of small particles, less organic matter and humus
C Parent Material: material forming soil horizons may be mineral rock and/or organic matter
R Bed Rock: solid rock beneath surface materials such as soil and gravel
What is natural vegetation?
Plants which grow without any human interference and grow in response to different climactic conditions
Define ecozone
an area with a particular type of natural environment
2 kinds of trees
Deciduous: leaves that fall off yearly
Coniferous: bear cones and have needles or scales that do not fall off and are acidic to the surrounding soil

Weather and climate?
Weather: short term atmospheric conditions
Climate: weather of a region averaged over a long period of time
What does LOWERN stand for? How does each factor affect weather?
Latitude: Closer to the equator means hotter temperatures
Ocean Currents: Flow of seawater in the ocean, affects temperature of air passing over
Wind & Air Masses: Carries weather conditions to different areas
Elevation: Higher elevation means lower temperatures
Relief: Causes less precipitation, creating dry climates
Near Water: Absences of large bodies of water cause less precipitation, hot summers, and cold winters
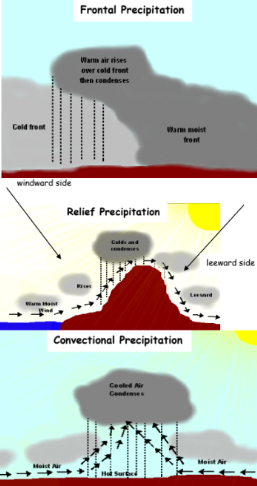
3 kinds of precipitation?
Relief/orographic: air is forced to cool when it rises over relief features. As it rises it cools, condenses and forms rain.
Convectional: heated air rises upwards with the water vapour and gets condensed when it reaches a higher altitude.
Frontal: colder air meets warmer air in a weather front. The warm air is then forced to rise over the cooler air
What is weathering?
Breaking down or dissolving of rocks and minerals on Earths surface through contact with water, atmospheric gases, sunlight, and biological organisms
What is leaching?
Process of water carrying soluble substances or small particles through soil or rock.
What is the tree line?
Point in a habitat above which trees can't grow
What is permafrost?
Permanently frozen layer on or under Earth's surface. Consisting of soil, gravel, and sand, usually bound together by ice.
What is calcification?
Deposition of calcium carbonate in a soil in low precipitation areas having high rates of evaporation and water deficit