Fundamental Neuroscience: Understanding Ourselves
1/33
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key vocabulary and concepts from the lecture on fundamental neuroscience, including definitions of important terms related to cell structure and function, neuronal types, and aspects of the nervous system.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
34 Terms
Cell
The structural, functional, and biological unit of an organism.
Plasma Membrane
Outer boundary of the cell.
Cytoplasm
Interior of the cell.
Mitochondria
Powerhouses of the cell that produce energy.
Microtubules and filaments
From the cytoskeleton of the cell
Endoplasmic reticulum (ER)
Network of membranes involved in synthesis and storage. Smooth ER; Rough ER: with ribosomes attached
Nucleus
Organelle that contains genetic material DNA
Golgi Apparatus
Organelle that processes, modifies, and packages proteins and lipids
Secretory vesicles
Contains materials(proteins, neurotransmitters or hormones) to be released from the cell.
Neurons
Elementary cellular unit of information processing in the nervous system.
Astrocytes
Glial cells providing structural support and metabolic support in the nervous system. No axon meaning no polarization (structure) . Have soma and tiny branches called processes.
Oligodendrocytes
Glial cells that form myelin in the central nervous system.
Schwann cells
Gilal cells that from myelin in the PNS
Myelin
A fatty substance that dramatically increases the speed of electrical signal conduction down the axon.
NG2+ cells
Primarily responsible for remyelinoation (heals tissue myelin)
Cell body or soma
Houses the organelles and nucleus responsible for producing proteins and energy acting as the neurons control for life, growth and energy.
Neural Stem Cell
A type of cell that can differentiate into various types of neurons and glial cells.
Microglia
Immune cells of the CNS involved in debris clearance and immune defense.
The human brain contains
80 billion glial cells (non-neuronal cells), 1000 synapses per neuron = 80 trillion synapses
The reticular theory (Camillo Golgi)
The nervous system was considered to be formed by a continuous reticulum or network of cells fused together
The Neuron Doctrine Theory
The nervous system is composed of discrete, individual cells called neurons which communicates at synapses
Synapse
The junction between neurons where communication occurs. (Transmits information)
Extracellular Space
The space outside of cells.
Gray Matter
Regions of the brain and spinal cord containing nerve cell bodies (somas).
White Matter
Regions of the brain and spinal cord mainly composed of axons.
Functional Architecture of the Brain
The arrangement of interconnected neurons that form networks, circuits, and systems in the brain.
Meninges
Membranes that cover the brain and spinal cord, providing protection.
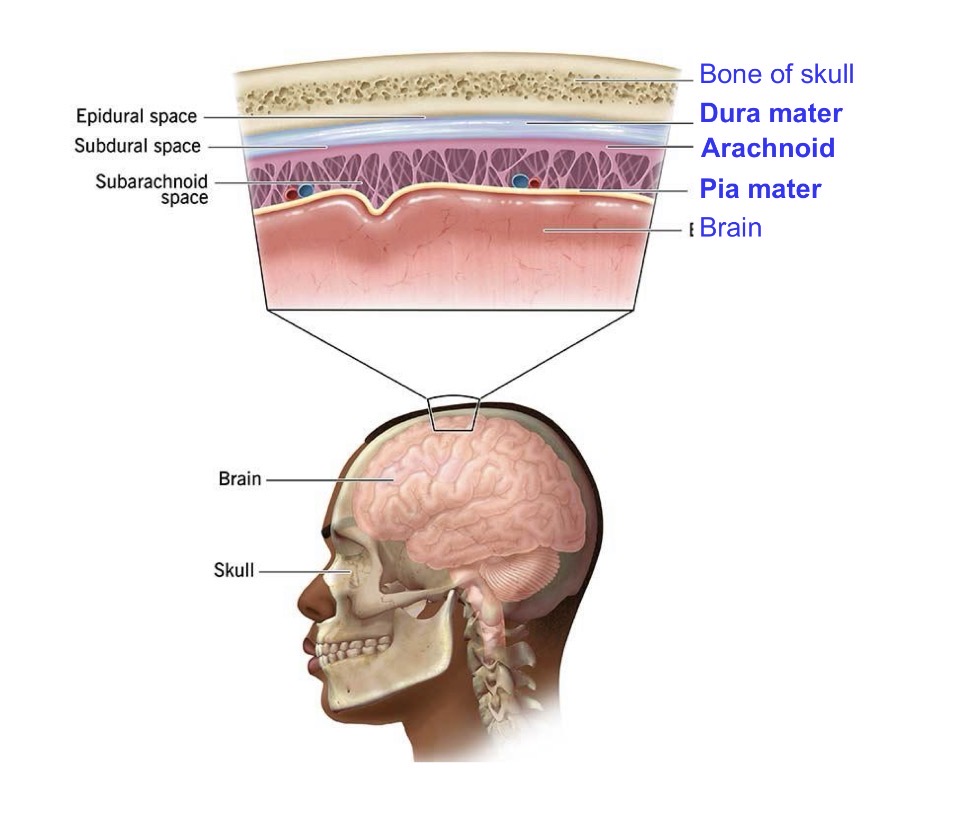
Cerebrospinal Fluid (CSF)
Fluid filling brain ventricles and the spinal cord canal, providing buoyancy and waste product removal.
Dendrites
Protrusions on neurons that receive messages (chemical signals or neurotransmitters) from other neurons and then transmits the, as electrics; impulses towards the soma or cell body.
Axon
The long projection of a neuron that conducts electrical impulses away from the cell body.
Golgi Apparatus
Organelle that processes, modifies, and packages proteins and lipids.
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
Network of membranes involved in synthesis and storage, with smooth and rough types.
Ribosomes
Organelles responsible for protein synthesis.
Ependimocytes
Circles around the central canal, plays a role in CSF homeostasis