Intro to Cardiovascular System
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/216
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 3:40 AM on 11/8/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
217 Terms
1
New cards
-transportation of O2 to tissues
-transportation of nutrients
-transportation of CO2 and metabolites to lungs and kidneys
-distribution of hormones
-thermoregulation
-urine formation
-transportation of nutrients
-transportation of CO2 and metabolites to lungs and kidneys
-distribution of hormones
-thermoregulation
-urine formation
Functions of the cardiovascular system
2
New cards
-activation of sympathetic nervous system
-increased cardiac output
-increased skin blood flow
-decreased blood flow to kidney
-decreased visceral blood flow
-maintenance of blood flow to the brain
-increased cardiac output
-increased skin blood flow
-decreased blood flow to kidney
-decreased visceral blood flow
-maintenance of blood flow to the brain
cardiovascular responses to exercise
3
New cards
1. FiO2 and air quality
2. airways
3. lungs and chest wall mechanics
4. diffusion/transit time
5. perfusion
6. myocardial function
7. peripheral circulation
8. tissue extraction and use of O2
9. return of CO2 and partially desaturated blood to lungs
2. airways
3. lungs and chest wall mechanics
4. diffusion/transit time
5. perfusion
6. myocardial function
7. peripheral circulation
8. tissue extraction and use of O2
9. return of CO2 and partially desaturated blood to lungs
steps in O2 transport pathway
4
New cards
O2 levels less than 300mL
(low oxygen)
(low oxygen)
when is anaerobic metabolism triggered?
5
New cards
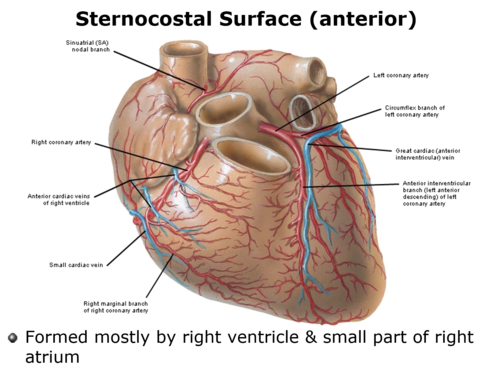
-anterior surface
-right atrium and ventricle
-right atrium and ventricle
sternocostal surface of heart
6
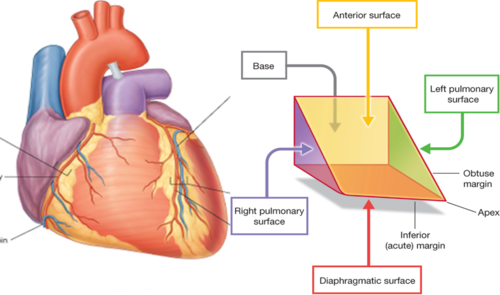
New cards
-inferior surface
-right and left ventricles
-right and left ventricles
diaphragmatic surface of heart
7
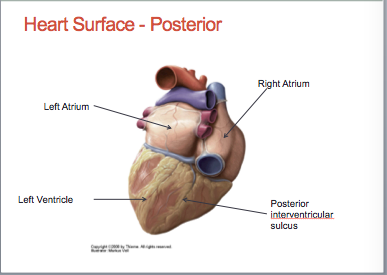
New cards
-base
-left atrium and some right atrium
-left atrium and some right atrium
posterior surface of heart
8
New cards
the posterior surface (base)
which surface of the heart do the great vessels enter at?
9
New cards
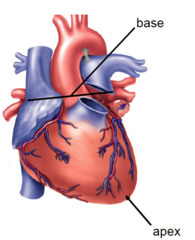
3rd rib
rib level of base of the heart
10
New cards
5th rib at midclavicular line
rib level of apex of heart
11
New cards
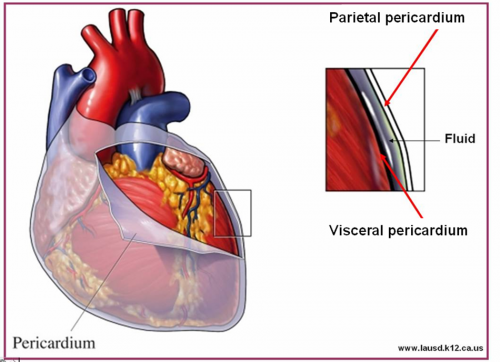
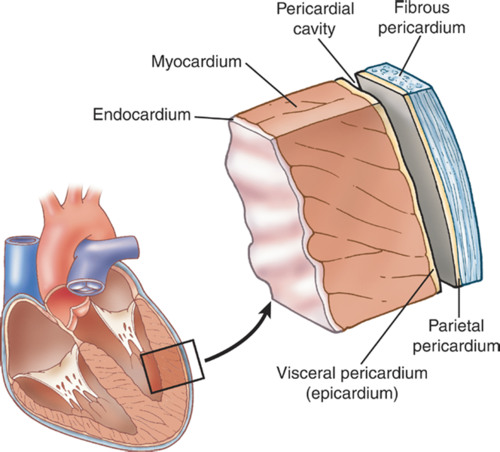
Double-layered membrane surrounding the heart.
pericardium
12
New cards
-fibrous pericardium (outer)
-serous pericardium (inner)
---parietal pericardium
---visceral pericardium (on heart)
-serous pericardium (inner)
---parietal pericardium
---visceral pericardium (on heart)
parts of pericardium
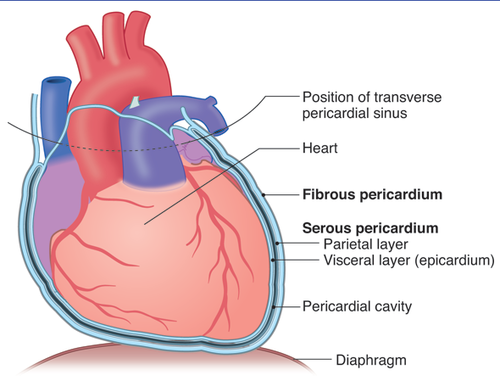
13
New cards
-epicardium
-myocardium
-endocardium
-myocardium
-endocardium
layers of cardiac tissue
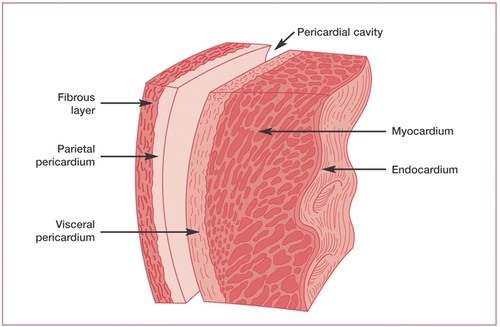
14
New cards
outer layer of the heart
-surrounded by visceral pericardium
-surrounded by visceral pericardium
epicardium
15
New cards
muscular
-middle layer of the heart
-middle layer of the heart
myocardium
16
New cards
inner lining of the heart
endocardium
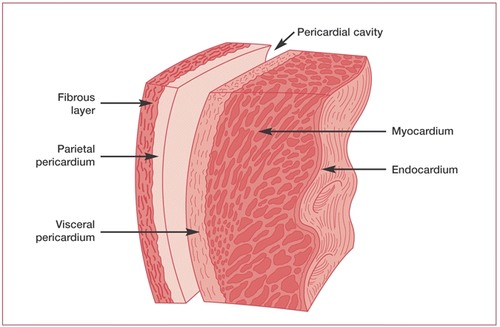
17
New cards
-functional syncytium
-inherent spontaneous rhythmicity
-polarized irritability
-all or none law
-inherent spontaneous rhythmicity
-polarized irritability
-all or none law
4 properties of cardiac muscle
18
New cards
-heart acts as one cell
-due to branching fibers and intercalated discs
-due to branching fibers and intercalated discs
functional syncytium
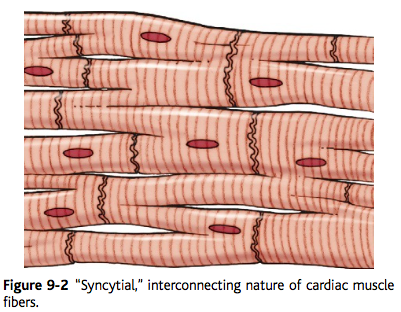
19
New cards
-heart can depolarize on its own without CNS input
-reason why dysrhythmia can occur
-reason why dysrhythmia can occur
Inherent spontaneous rhythmicity
20
New cards
-some parts of the heart are more likely to depolarize than others
-SA is most irritable due to decreased refractory time
-SA is most irritable due to decreased refractory time
polarized irritability
21
New cards
all cardiac fibers depolarize or none do
-no recruitment
-no recruitment
all or none law
22
New cards
easily depolarized
-60 to 100 bpm
-60 to 100 bpm
polarize irritability of SA node
23
New cards
-takes a little longer to be ready for another depolarization
-40 to 60 bpm
-40 to 60 bpm
polarize irritability of AV node
24
New cards
-takes a very long time to be ready for deploarization
-20-30 bpm
-20-30 bpm
polarize irritability of ventricular muscle
25
New cards
less likely that SA node is in charge
a lower HR indicates ____ is in charge
26
New cards
-inferior and superior vena cava
-right atrium
-> tricuspid valve
-right ventricle
-> pulmonic valve
-pulmonary artery
-lungs
-right atrium
-> tricuspid valve
-right ventricle
-> pulmonic valve
-pulmonary artery
-lungs
deoxygenated blood flow through heart
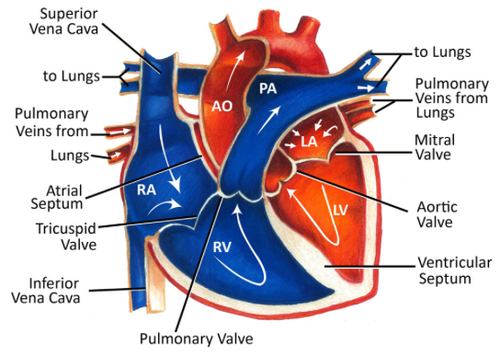
27
New cards
-lungs
-pulmonary vein
-mitral valve
-left ventricle
-aortic valve
-aorta
-pulmonary vein
-mitral valve
-left ventricle
-aortic valve
-aorta
oxygenated blood flow through heart
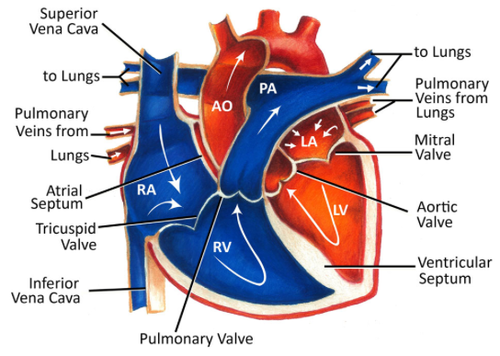
28
New cards
70-80%
-no passive muscle contraction
-no passive muscle contraction
How much of ventricular filling is passive?
29
New cards
we can survive without atria
-a fib is the most common arrhythmia with no active atrial output
-a fib is the most common arrhythmia with no active atrial output
impact of passive ventricular filling
30
New cards
Relaxation of the heart
-tricuspid and mitral open
-aortic and pulmonary valve closed
-tricuspid and mitral open
-aortic and pulmonary valve closed
diastole
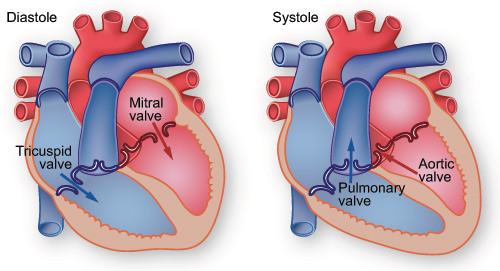
31
New cards
in response to pressure changes
Why do valves open and close?
32
New cards
Contraction of the heart
-mitral and tricuspid valves closed
-pulmonary and aortic valve open
-mitral and tricuspid valves closed
-pulmonary and aortic valve open
systole
33
New cards
inversely proportional
resistance and radius
34
New cards
-elastic fibers
-more smooth muscles
-more smooth muscles
artery structures
35
New cards
venous
more blood is in ____ system
36
New cards
_____ stimulates collateral channels (anastamoses)
tissue hypoxia
37
New cards
side depends on which coronary artery supplies posterior descending artery
-90% right
-10% left
-90% right
-10% left
R vs L dominant heart
38
New cards
-Right atrium
-right ventricle
-Left ventricular inferior wall
_left ventricular posterior wall (90%)
-posterior 1/3 oc interventricular septum
-right ventricle
-Left ventricular inferior wall
_left ventricular posterior wall (90%)
-posterior 1/3 oc interventricular septum
myocardium supplied by RIGHT coronary artery
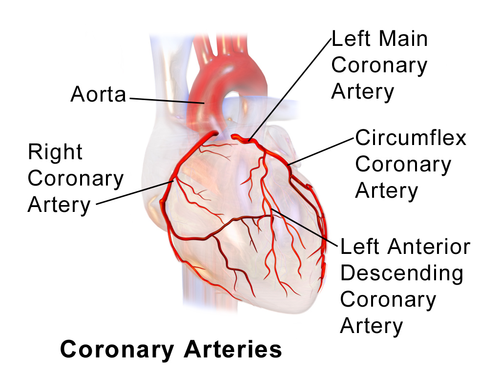
39
New cards
-SA node (55%)
-AV node and Bundle of His (90%)
-posterior fascicle of L bundle branch
-AV node and Bundle of His (90%)
-posterior fascicle of L bundle branch
conducting system supplied by RIGHT coronary artery
40
New cards
-left ventricular anterolateral wall
-anterior 2/3 of septum
-anterior 2/3 of septum
myocardium supplied by LEFT coronary artery circulation: ANTERIOR DESCENDING BRANCH
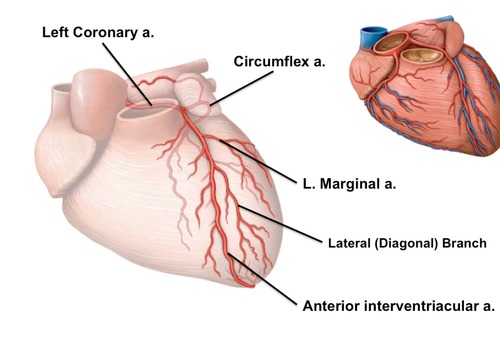
41
New cards
-most of right bundle branch
-anterior fascicle of L bundle branch
-part of posterior fascicle of L bundle branch
-anterior fascicle of L bundle branch
-part of posterior fascicle of L bundle branch
conduction system supplied by LEFT coronary artery circulation: ANTERIOR DESCENDING BRANCH
42
New cards
-left atrium
-left ventricular anterolateral wall
-left ventricular posterolateral wall
-left ventricular posterior wall (10%)
-left ventricular anterolateral wall
-left ventricular posterolateral wall
-left ventricular posterior wall (10%)
myocardium supplied by LEFT coronary artery circulation: CIRCUMFLEX BRANCH
43
New cards
-SA node (45%)
-AV node and bundle of His (10%)
-AV node and bundle of His (10%)
conduction system supplied by LEFT coronary artery circulation: CIRCUMFLEX BRANCH
44
New cards
-left anterior descending
-circumflex artery
-circumflex artery
branches of LEFT coronary artery
45
New cards
1 cm long
how long is the left coronary artery before it divides?
46
New cards
branches of the circumflex artery
-obtuse marginal 1 and obtuse marginal 2
47
New cards
branch of left anterior descending artery
first diagonal branch
48
New cards
-55% right coronary artery
-45% circumflex branch of the LCA
-45% circumflex branch of the LCA
what provides blood supply for SA node
49
New cards
what provides blood supply for AV node
-90% right coronary artery
-10% circumflex branch of the LCA
-10% circumflex branch of the LCA
50
New cards
what is involved in cardiac metabolism
-glucose
-fatty acids (rest)
-lactate (prevents lactate accumulation) (heavy exercise)
-amino acids
-fatty acids (rest)
-lactate (prevents lactate accumulation) (heavy exercise)
-amino acids
51
New cards
components of oxygen consumption and where they occur?
-oxygen exchange-> respiratory function
-oxygen transport-> cardiovascular
-oxygen extraction-> circulation to muscle
-oxygen transport-> cardiovascular
-oxygen extraction-> circulation to muscle
52
New cards
-cardiac output (CO)
-arterial venous difference (A-VO2)
-arterial venous difference (A-VO2)
oxygen required for any activity is determined by ____
53
New cards
VO2= CO x A-VO2
-cardiac output
-arterial venous difference
-cardiac output
-arterial venous difference
VO2 formula (oxygen consumption)
54
New cards
the heart's ability to pump blood
cardiac output measures ____
55
New cards
CO = HR x SV (heart rate x stroke volume)
Cardiac output equation
56
New cards
the peripheral tissue's ability to extract O2
A-VO2 difference measures ____
57
New cards
decreases
-intrinsic rate of SA node
-not related to fitness
-intrinsic rate of SA node
-not related to fitness
maximum HR ____ with age and why
58
New cards
increased
increased HR means _____ oxygen demand by the heart
59
New cards
decreased
increased HR leads to ____ diastolic filling time
60
New cards
-vagus nerve
-sympathetic nerves (Beta 1 receptors)
-sympathetic nerves (Beta 1 receptors)
nervous control of the heart
61
New cards
-decreases HR
-decreases contractility
-slows conduction through AV node
-decreases contractility
-slows conduction through AV node
vagus nerve effect on heart
62
New cards
AV node
vagus nerve slows HR through ____ (structure)
63
New cards
-increase HR
-increase contractility
-increase speed of conduction through AV node
-increase contractility
-increase speed of conduction through AV node
sympathetic nerve (beta 1) effect on heart
64
New cards
coronary arteries and some peripheral vessels
-vasodilation of coronary arteries
-vasodilation of coronary arteries
Beta 2 receptors
-where and function
-where and function
65
New cards
mainly in peripheral arteries
-vasoconstriction of peripheral arteries
-vasoconstriction of peripheral arteries
alpha receptors
-location
-function
-location
-function
66
New cards
-resting HR increased because there is no vagus nerve control (based on SA node intrinsic rate)
-catecholamines released from adrenal gland (epinephrine) increase HR slowly with exercise
-catecholamines released from adrenal gland (epinephrine) increase HR slowly with exercise
how does HR increase with a denervated heart due to transplant?
67
New cards
-baroreceptors (control BP)
-chemoreceptors (hypoxemia-> increase HR)
-body temperature
-concentration of potassium and calcium
-hormones (epinephrine, norepinephrine)
-chemoreceptors (hypoxemia-> increase HR)
-body temperature
-concentration of potassium and calcium
-hormones (epinephrine, norepinephrine)
additional controls of HR
68
New cards
-heat: increase
-cold: decreases
-cold: decreases
heat and cold control of heart control
69
New cards
3.5-5.0 mEq/L
normal potassium range
70
New cards
-ECG changes
-ausea
-diarrhea
-numbness/tingling
-trouble breathing
-chest pain
-palpitations/irregular heart beats
-ausea
-diarrhea
-numbness/tingling
-trouble breathing
-chest pain
-palpitations/irregular heart beats
hyperkalemia can cause
71
New cards
-dangerous ventricular arrhtyhmias
-prolonged QT
-cardiac irritability
-ST segment depression
-dizziness
-HYPOTENSION
-decreased contractility
-prolonged QT
-cardiac irritability
-ST segment depression
-dizziness
-HYPOTENSION
-decreased contractility
hypokalemia can cause
72
New cards
call physician ASAP
what to do with hypokalemia
73
New cards
-CHF
-renal insufficiency
-hypovolemia
-renal insufficiency
-hypovolemia
causes of hypernatremia (increased sodium)
74
New cards
-irritability
-agitation
-seizure
-coma
-hypotension
-tachycardia
-weak pulse
-decreased urine output
-agitation
-seizure
-coma
-hypotension
-tachycardia
-weak pulse
-decreased urine output
symptoms of hypernatremia
75
New cards
-diuretics
-drinking excessive water
-drinking excessive water
causes of hyponatremia (low sodium)
76
New cards
-nausea
-vomiting
-headache
-confusion
-loss of energy
-drowsiness
-restlessness
-irritability
-muscle weakness, spasm, cramps
-seizures
-coma
-vomiting
-headache
-confusion
-loss of energy
-drowsiness
-restlessness
-irritability
-muscle weakness, spasm, cramps
-seizures
-coma
signs of hyponatremia
77
New cards
effectiveness of the heart as a pump
stroke volume reflects the ____
78
New cards
preload, afterload, contractility
stroke volume is dependent on
79
New cards
venous return and distensibility
-how much blood is in the ventricle by end of diastole (relaxation)
-how much blood is in the ventricle by end of diastole (relaxation)
what is preload
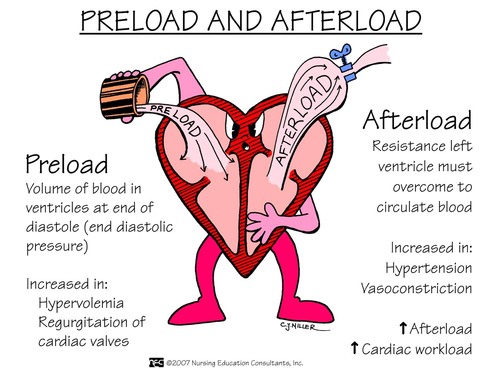
80
New cards
supine
what position is preload greatest?
81
New cards
1. vasodilation
2. diuresis (dehydration)
2. diuresis (dehydration)
What can decrease preload?
82
New cards
strength of ventricular contraction
what is contractility?
83
New cards
-increase end diastolic volume increases heart contraction (force dependent on length)
-increase ejection fracture due to sympathetics (force independent of length)
-increase ejection fracture due to sympathetics (force independent of length)
what effects contractility?
84
New cards
aortic distensibility to accept blood from aorta
what is afterload?
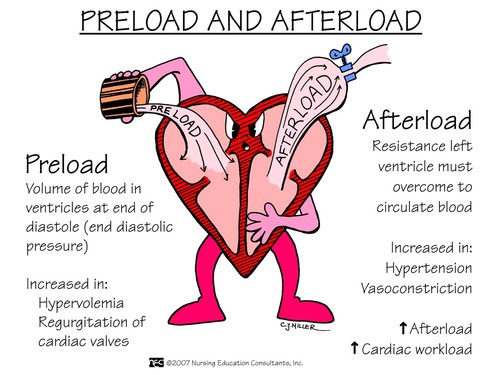
85
New cards
-aortic distensibility
-vascular resistance
-patency of aortic valve
-blood viscosity
-vascular resistance
-patency of aortic valve
-blood viscosity
what impacts afterload>
86
New cards
decreases
increase in afterload, ___ Stroke volume
87
New cards
decreases
peripheral resistance ____ with exercise
88
New cards
EF= SV/EDV
-stroke volume
-end diastolic volume
-stroke volume
-end diastolic volume
ejection fraction forumla
89
New cards
-normal: 50-70%
-slightly below normal: 40-54%
-reduced:
-slightly below normal: 40-54%
-reduced:
resting Ejection fraction
-normal:
-slightly below normal:
-reduced:
-normal:
-slightly below normal:
-reduced:
90
New cards
-rapidly rises initially with aerobic exercise
-usually levels off at 40-50% VO2 max (HR increase leads to less diastolic filling time)
-usually levels off at 40-50% VO2 max (HR increase leads to less diastolic filling time)
stroke volume levels with exercise
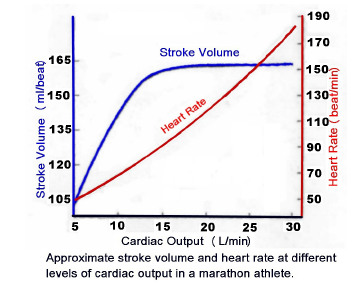
91
New cards
-main mechanism at low level exercise is stroke volume
-as exercise intensity increases, HR is main mechanism
-as exercise intensity increases, HR is main mechanism
what causes increased cardiac output?
92
New cards
-70% veins
-10% systemic arteries
-15% pulmonary circulation
5% capillaries
-10% systemic arteries
-15% pulmonary circulation
5% capillaries
location of blood volume
93
New cards
-increased blood flow
-increased oxygen extraction
-increased oxygen extraction
A-VO2 difference increased due to
94
New cards
25% at rest
-3X greater O2 extraction during exercise
-3X greater O2 extraction during exercise
A-VO2 difference in skeletal muscle
95
New cards
70-80% at rest
-less wiggle room for O2 extraction with exercise so coronary blood flow is critical
-less wiggle room for O2 extraction with exercise so coronary blood flow is critical
A-VO2 difference in cardiac muscle
96
New cards
nitric oxide
-vasodilation
-vasodilation
endothelial derived relaxing factor
-what and function
-what and function
97
New cards
-decreased pH
-increased PCO2
-increased Ca (vasoconstriction)
-increased ADP
-decreased O2
-increased Magnesium (vasoconstriction)
-increased temperature
-increased PCO2
-increased Ca (vasoconstriction)
-increased ADP
-decreased O2
-increased Magnesium (vasoconstriction)
-increased temperature
local metabolite conditions leading to vasodilation during exercise
-___ pH
-___PCO2
-___ Ca (function)
-____ ADP
-____ O2
-_____ Mg (function)
-_____ temperature
-___ pH
-___PCO2
-___ Ca (function)
-____ ADP
-____ O2
-_____ Mg (function)
-_____ temperature
98
New cards
congestive heart failure
local metabolite conditions are impaired with ____
99
New cards
-vasodilation
-occurs with autonomic neurons, synthesized by vascular endothelium, drugs, or when pressure builds on epithelium
-occurs with autonomic neurons, synthesized by vascular endothelium, drugs, or when pressure builds on epithelium
role of nitric oxide
100
New cards
-liver: 27%
-kidney: 22%
-muscle: 20%
-kidney: 22%
-muscle: 20%
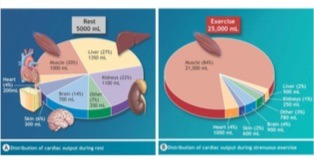
cardiac output distribution at rest