Psychology VCE
1/298
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
299 Terms
Accuracy
The precision with which a person completes a task
Acquisition
When a response or behaviour is first learned
Action potential
The neural message, in the form of an electrical impulse, sent down the axon of a neuron when certain conditions met
Acronyms (Mnemonics)
Pronouncable words formed from first letters to aid memor.
Eg. NAB, ANZAC, BODMAS.
Acrostics (Mnemonics)
First letters of items to create a phrase/rhyme/poe.
May be useful when words must be remembered in a certain order.
Eg. Never Eat Soggy Weetbix (North, East, South, West)
Advanced Sleep Phase Disorder (ASPD)
Melatonin is secreted earlier than normal, causing the individual to sleep and wake earlier than normal.
Agonist
A type of drug that imitates neurotransmitters and works to initiate a neural response (excitatory or inhibitory) when it binds to the receptor sites of the neuron
Aim
A statement outlining the purpose of the study
Alarm reaction
The first stage of the General Adaptation Syndrome which involves the body's initial decline (shock) and then rise in arousal to a stressor (counter-shock)
Allocation
The process of assigning participants to conditions in the experiment for the research
altered state of consciousness (ASC)
A state of consciousness that is characterised by different levels of awareness as compared to normal waking consciousness.
Alzheimer's disease
A neurodegenerative disease that involves the progressive loss of neurons in the brain and is characterised by memory decline
Caused by amyloid plaques and build up of neurofibrillary tangles.
Amygdala
Encodes and consolidates emotional info in explicit episodic memory, and implicit emotional memory, such as classically conditioned memories
Amyloid plaques
Fragments of the protein beta-amyloid that accumulate into insoluble plaques that inhibit communication between neurons
Antagonist
A type of drug that works to prevent a neural response (excitatory or inhibitory) by blocking the receptor sites of a neuron
Antecedant stage
a stimulus that causes a voluntary behaviour to occur
Anxiety
A state of uneasiness, usually associated with a future uncertainty.
Aphantasia
a phenomenon in which individuals lack the capacity to generate mental imagery
Appraisal
an assessment or evaluation
Approach stratergies
Coping strategies which confront the source of the stressors
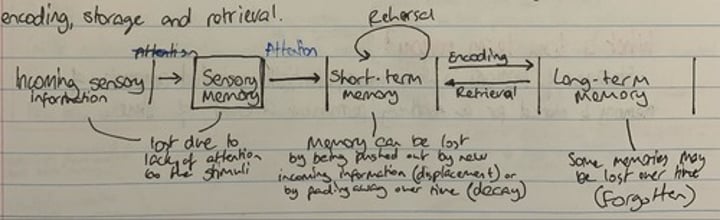
Atkinson-Shiffrin multi store model of memory
a model of memory which outlines the flow of information in memory formation and retrieval through three separate stores of memory (sensory, short-term and long-term) each of which have a different function, capacity and duration
Attention stage
the first stage of the observational learning where learners must actively focus on the model in order to learn.
ATSI multimodal system of knowledge
....

Autonomic nervous system
the branch of the PNS responsible for connecting the CNS and the body's visceral (non-skeletal) organs, muscles and glands like the heart and liver
Avoidance strategies
coping strategies that evade the stressor, seeking to reduce stress by indirectly dealing with it
Axon
the long strand-like part of a neuron that transmits a message from one end of the neuron to the other.
Axon terminals
The ends of the neuron that releases a message into the synapse
Basal ganglia
Encodes and stores procedural and classically conditioned memories associated with habits, behaviours and procedures
Behaviour
a voluntary action in response to an antecedent.
Benign-positive
an initial appraisal of a stimulus as neutral or good, and not causing stress for an individual
Benzodiazapines
a type of short-acting anti-anxiety medication that works to reduce anxiety
Biological protective factors
factors that increase resilience by supporting healthy physiological functioning
- Adequate nutritional intake and hydration + sleep
Biological determinants of phobias
- GABA Dysfunction
- Long term Potentiation
Biological interventions of phobia
Anti-anxiety benzodiazepine agents (GABA agonists)
Relaxation techniques: Breathing retraining and exercise
Blood alcohol concentration (BAC)
a measure of how much alcohol is in a person's blood
Brain
The body's information centre, responsible for initiating and processing actions, thoughts and behaviour
Brain waves in sleep
•higher frequency and lower amplitude in REM sleep.
•high frequency and low amplitude in NREM sleep stage 1 (transitioning from wakefulness to sleep)
•medium frequency and medium amplitude in NREM sleep stage 2 (light sleep).
•lower frequency and higher amplitude in NREM sleep stage 3 (deep sleep).
Brain surgery
The treatment of brain injury or disease with the use of medical instruments
Breathing retraining
a method used to teach someone breathing control techniques that they can apply when facing their phobic stimulus
Bright light therapy
a method used to adjust a person's circadian rhythm through exposure to a high-intensity light source.
Factors of B.L.T include appropriate timing of exposure, the right amount of light and safe exposure

Case study
an in-depth study of an individual or a group of individuals
Catastrophic thinking
a kind of cognitive bias in which a stimulus or event is predicted to be far worse than it is likely to be in reality, and overestimate the dangers of the situation
Central nervous system
the brain and the spinal chord, responsible for transmitting neural messages to and receiving neural messages from the peripheral nervous system
Cerebellum
a brain structure which encodes and stores implicit procedural memories
Cerebral cortex
a brain structure where long-term memories are stored
Chunking (STM)
The grouping of smaller separate bits of information into a larger single unit or 'chunk' of information.
Circadian phase disorder
a sleep disorder which interferes with the normal regulation of the circadian rhythm of sleep, leading to a change in the sleep-wake cycle
Circadian rhythm
changes to physiological function or activity that occur as part of a cycle that lasts around 24 hours
Classical conditioning
a model of learning in which organisms learn through the involuntary association of two or more stimuli
Classical conditioning as a precipitating factor for phobia
Phobias are precipitated by classical conditioning as repeated pairings of a neutral stimulus with pain or fear can create a phobia.
Classically conditioned memory
a type of implicit memory which involves an involuntary response, such as fear, to a stimulus which has repeatedly been associated with an emotionally arousing stimulus
Cognition
the mental processes an individual performs in order to understand and process information
Cognitive and behavioural strategies
the techniques of cognitive behavioural therapy used to promote an individual's psychological resilience
Cognitive behavioural therapy (CBT)
a form of psychotherapy which encourages individuals to substitute unhealthy cognitions and behaviours with more healthy ones.
Cognitive bias
a predisposition to think about and process information in a certain way
Cognitive tasks
a form of assessment that measures some aspects of a person's thought processes
Cognitive model of phobias
involves distorted thinking involved in the development and maintenance of the phobia.
- Memory bias
- Catastrophic thinking
Concentration
the ability to focus on certain stimuli or tasks
Conclusion
a statement regarding the results of an investigation as to whether the hypothesis was supported or not
Conditioned emotional response
an emotional response to a stimulus that doesn't naturally produce that response, learned through the process of classical conditioning
Conditioned response (CR)
a response caused by a conditioned stimulus
Conditioned stimulus (CS)
a stimulus that elicits a response due to it being paired with an unconditioned stimulus (presented at the same time)
Confidentiality
the right of the participant for their personal details to remain private
Confounding variables
Variables other than the independent variable that have directly and systematically had an effect on the independent variable
Consciousness
The awareness of internal and external stimuli
Consciousness continuum
A progression of states of consciousness ranging from least aware to most aware
Consequence
an event following an action that makes it either more or less likely to occur again
Consolidation (memory)
The physical process whereby memories become permanent.
Requires three factors:
LTP, no interruptions, and 30 minutes of time.
Context-specific effectiveness
when the coping strategy or mechanism used is appropriate for the demands of the stressor
Control group
a group that is used as a basis for comparison (they are not exposed to the experimental conditions or independent variable)
Convenience sampling
when a sample is selected using the quickest and easiest means possible, selecting people who are readily available from the population
Coping
the process of dealing with stress
Coping flexability
an individuals ability to adjust or change their coping strategies depending on the unique and changing demands of a stressor
Cortisol
a hormone released into the body in times of stress by the hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis
Counterbalancing
a method used in repeated-measures experimental designs to reduce order effects
Cross-sectional study
when data is collected from participants from different segments of the population to represent a "snapshot" in time
Cultural determinants
Cultural continuity
Self determination
Debriefing
occurs at the conclusion of an experiment and involves the researcher outlining the nature of the experiment to participants and includes ensuring that participants do not leave the experiment with lasting harm
Deception
When the participant is unaware of the true nature of the experiment
Dendrites
the bushy spines of a neuron that receive a message
Dependent variable
the variable that is being measured in an experiment for changes it experience due to the independent variable
Depressants
a class of drugs that reduce central nervous system and body activity, reducing levels of alertness compared to NWC
Distress
a form of stress characterised by a negative psychological state
Dopamine
a neurotransmitter primarily responsible for the coordination of voluntary movement and experiences of pleasure and pain
Double-blind procedure
a procedure in which both the participant and the person conducting the experiment are unaware of which condition participants have been allocated to, in order to reduce experimenter bias
Echoic memory
- A type of sensory memory which temporarily stores auditory information
- Lasting 3-4 seconds, with an unlimited capacity
Elaborative rehearsal
encoding new information by meaningfully linking it to information already stored in long-term memory to enhance its storage and later retrieval
Electro-oculograph (EOG)
a device that detects, amplifies and records the electrical activity of the muscles surrounding the eyes
Electroencephalograph (EEG)
a device that detects, amplifies and records the electrical activity of the brain
Electromyograph (EMG)
a device that detects, amplifies and records the electrical activity of the body's muscles
Emotion-focussed coping
the use of coping strategies that target the emotional components of a stressor, dealing with it indirectly rather than confronting its source
Emotional awareness
the understanding and control people have over their feelings , as well as the ability to accurately perceive the emotions of others
Emotional wellbeing
the ability for an individual to appropriately control and express their own emotions in an adaptive way, aswell as understand the emotions of others
Encoding
the process of converting raw information from stimuli into a useable form which can be stored in the brain
Episodic memory
a type of explicit memory which involves a personal experience or event
Ethics comittee
a group of people who review research proposals, consider the potential risks, benefits and implications in order to either approve or disapprove them for research
Eustress
a form of stress characterised by a positive psychological state
excitatory effect
when a neurotransmitter causes the postsynaptic neuron to become more likely to fire an action potential
Exhaustion stage
The final stage of the general adaptation syndrome which involves the body's defences and energy levels depleting, leading to a greatly reduced ability to cope with current and future stressors
Experiment
a study conducted in a carefully controlled environment to measure the cause and effect between variables