social studies test on ancient civilizations grade 8 ms sheahan
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
37 Terms
maya
the people of an important mesoamerican civilization that lasted from 2000 bce to 1500 ce - 3500 years
mesoamerica
the reigon extending from modern mexico throughout central america
ceremonial center
a large plaza in a city center, surrounded by temples and palaces, where religious rituals and other public ceremonies took place
hieroglyphic
writing that uses pictures as symbols
social pyramid
a social structure in the shape of a pyramid, with layers representing social classes of different rank
ritual
a set of actions that is always performed the same way as part of a religious ceremony
slash and burn agriculture
a farming technique in which vegetation is cut away and burned to clear land for growing crops
sacrifice
a gift of an animal for slaughter to honor the gods
compass rose
shows the orientation or direction of the map
map scale
helps the viewer convert the map to real life
longitude
longitude lines begin at the prime meridian and are spaced at equal distance to the east and west to the international date line
latitude
latitude lines begin at the equator and are equal distances to the north and south poles
cardinal directions
north, south, east, west
intermediate directions
northeast, southeast, southwest, northwest
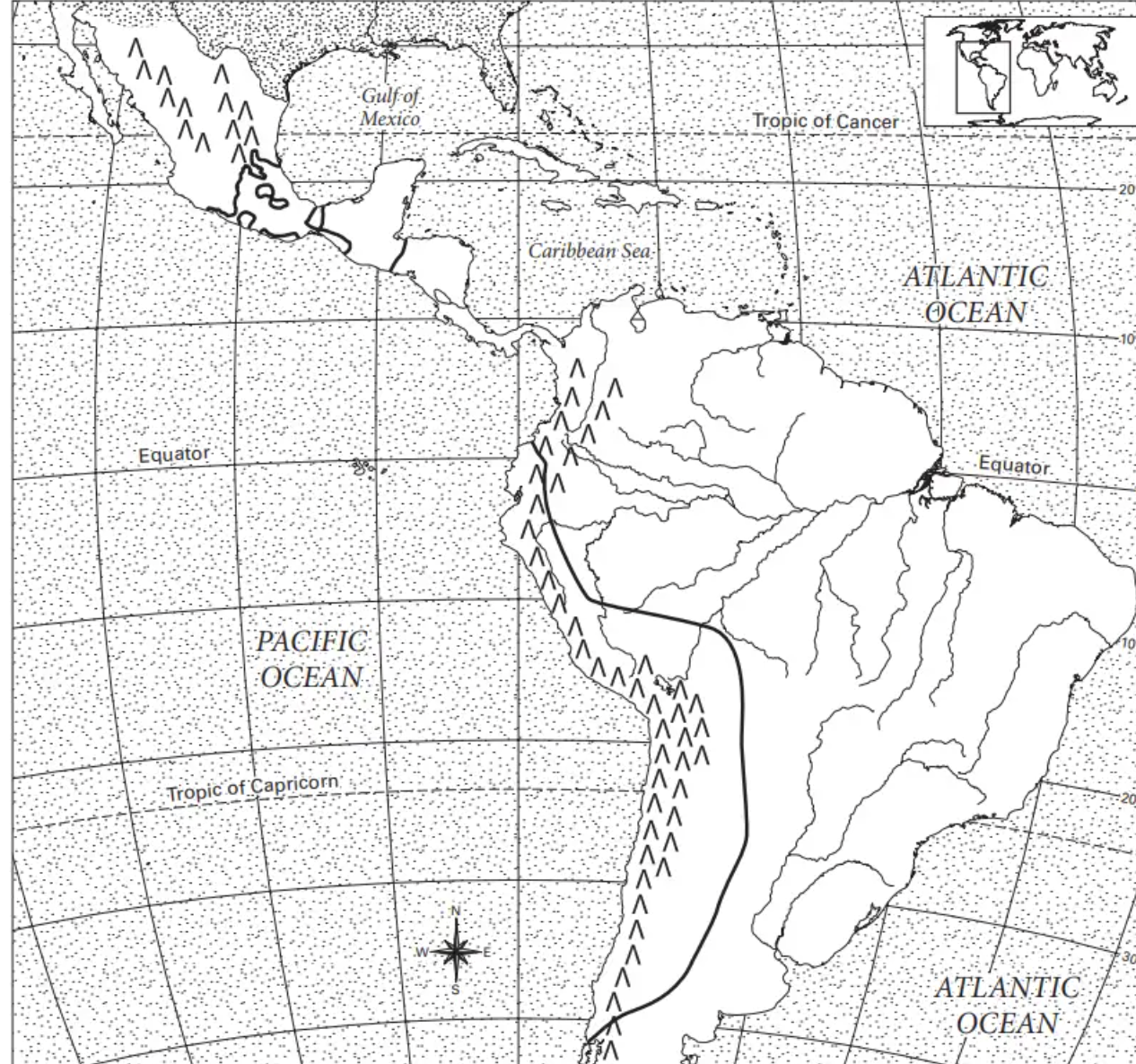
where are the andes mountains?
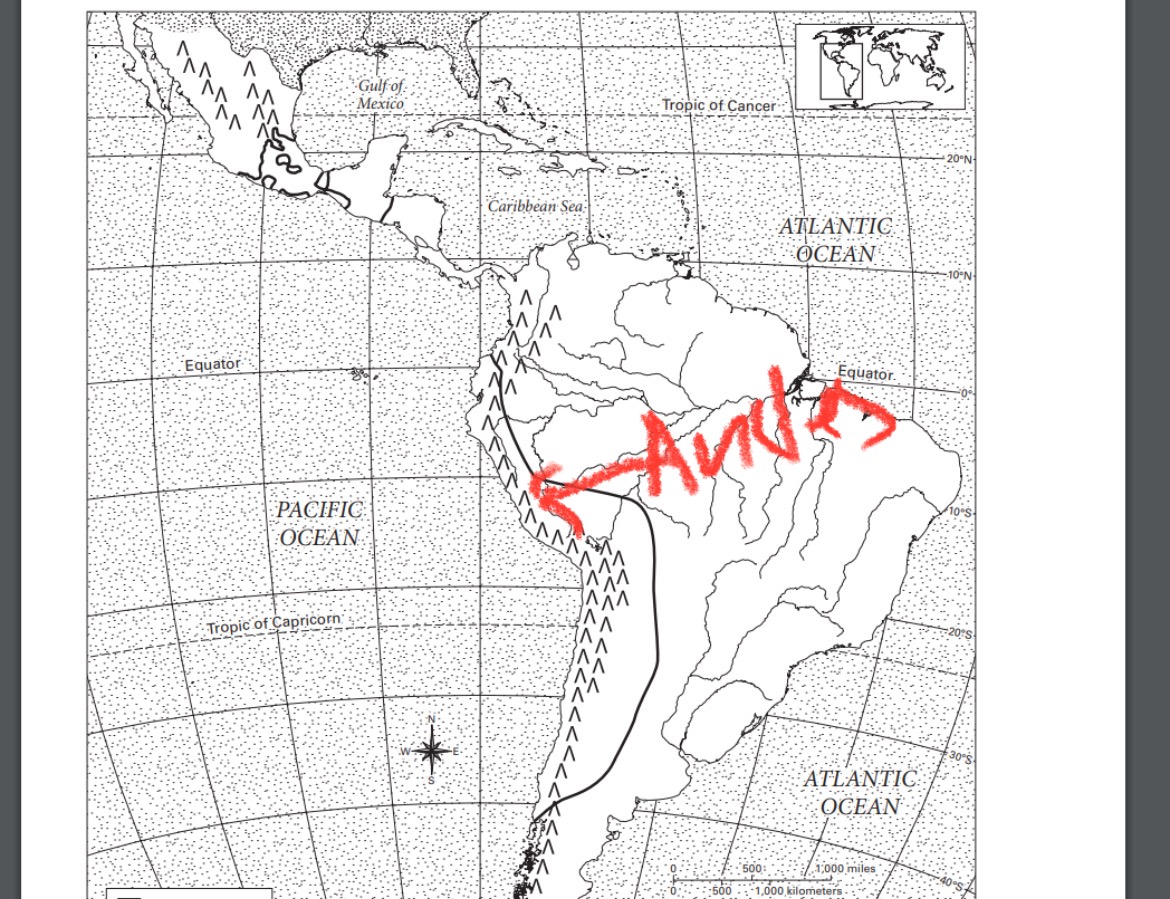
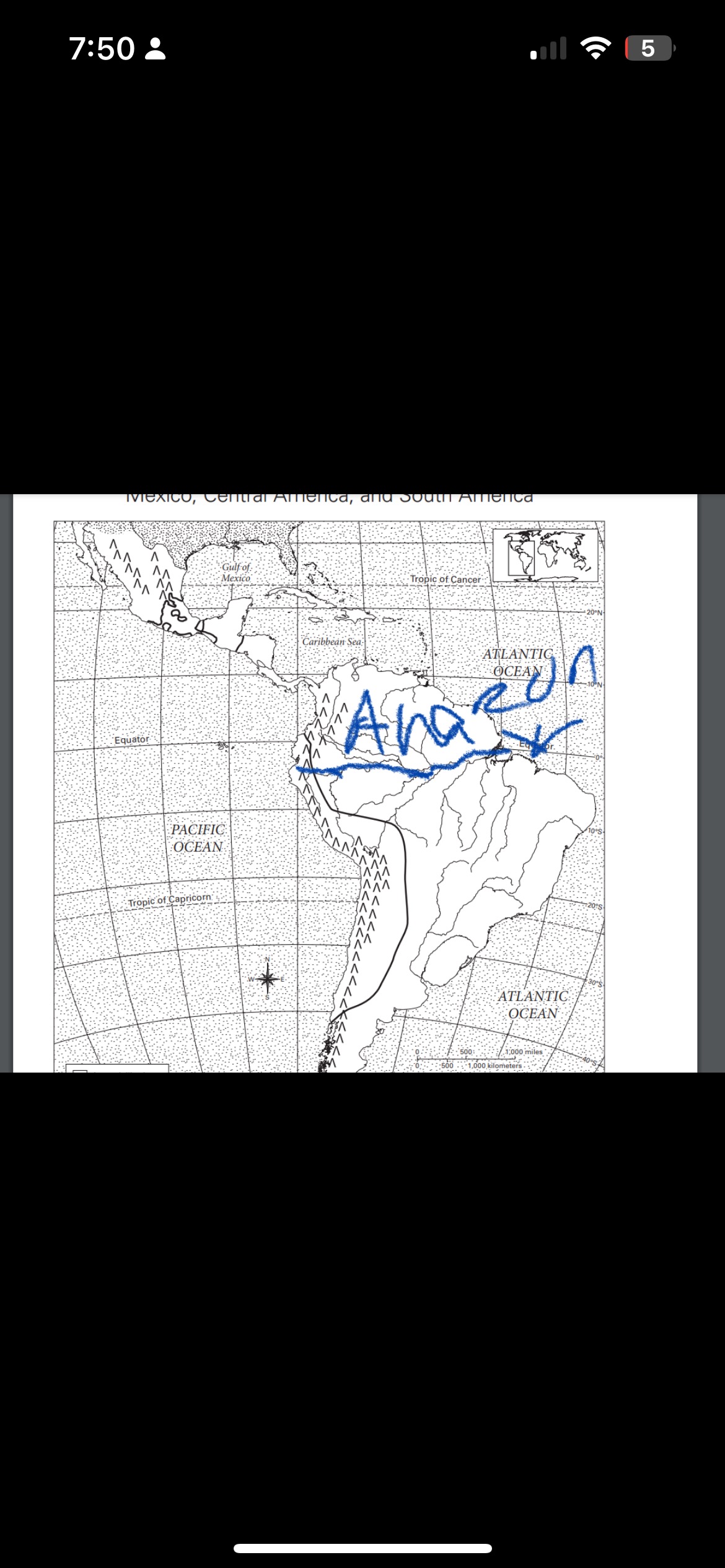
where is the amazon river?
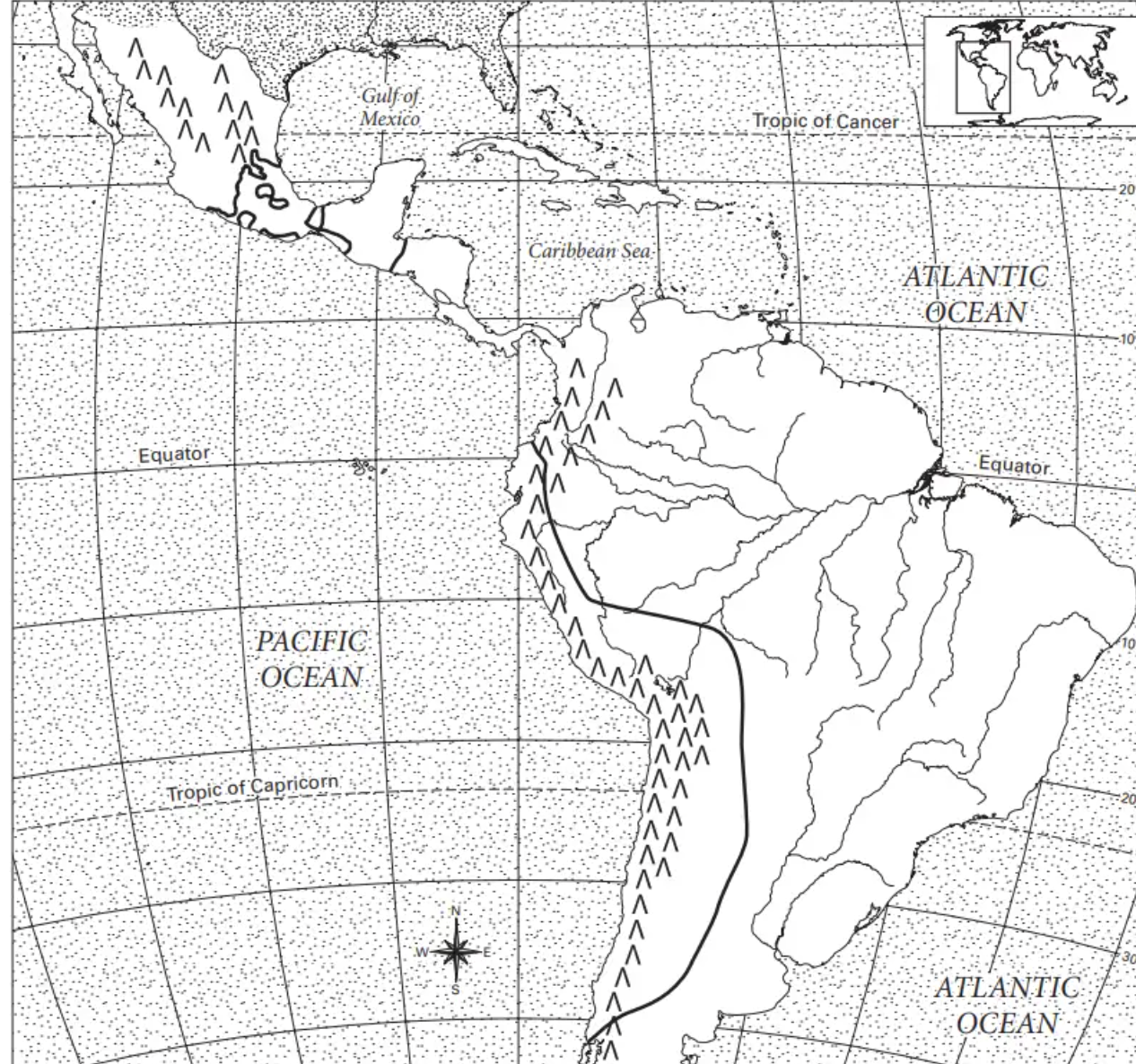
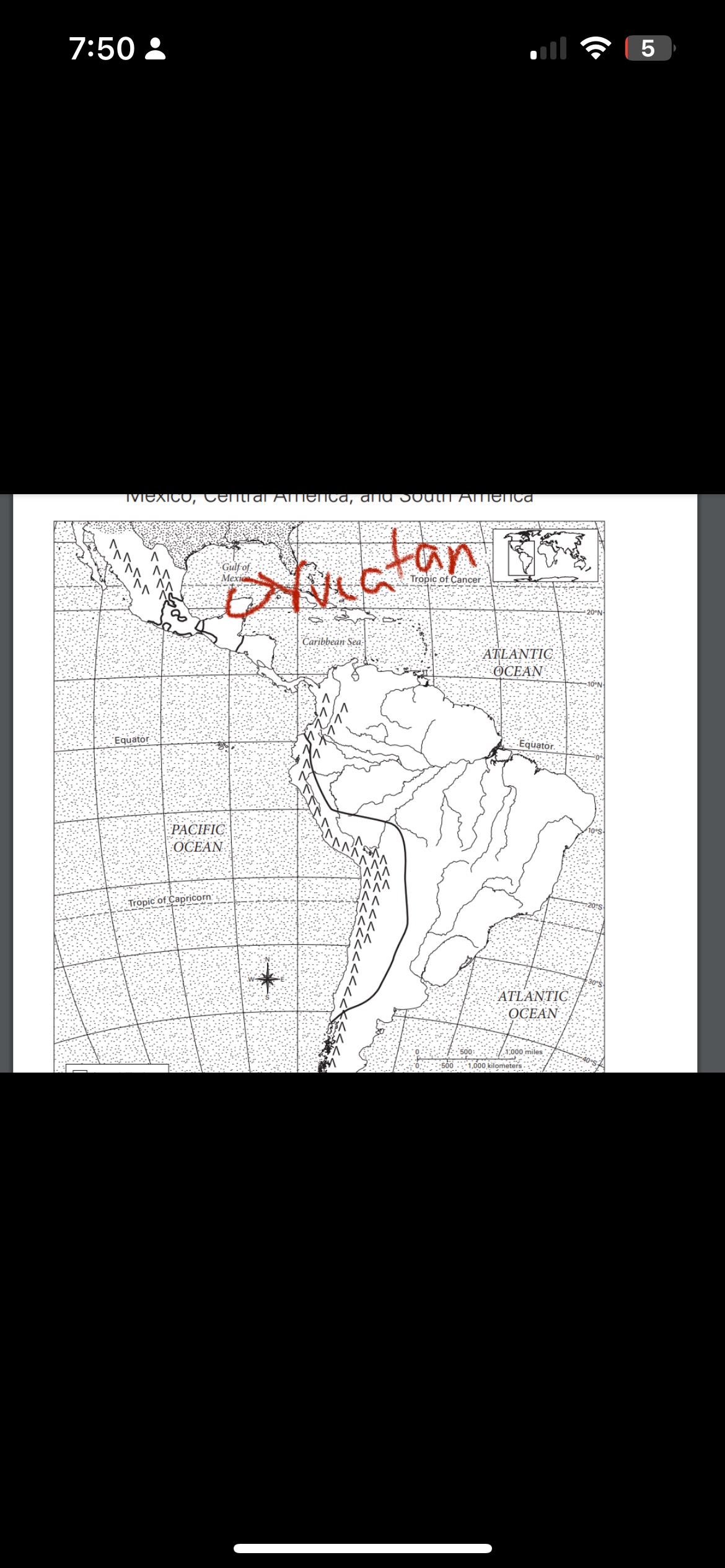
where is the yucatan peninsula?
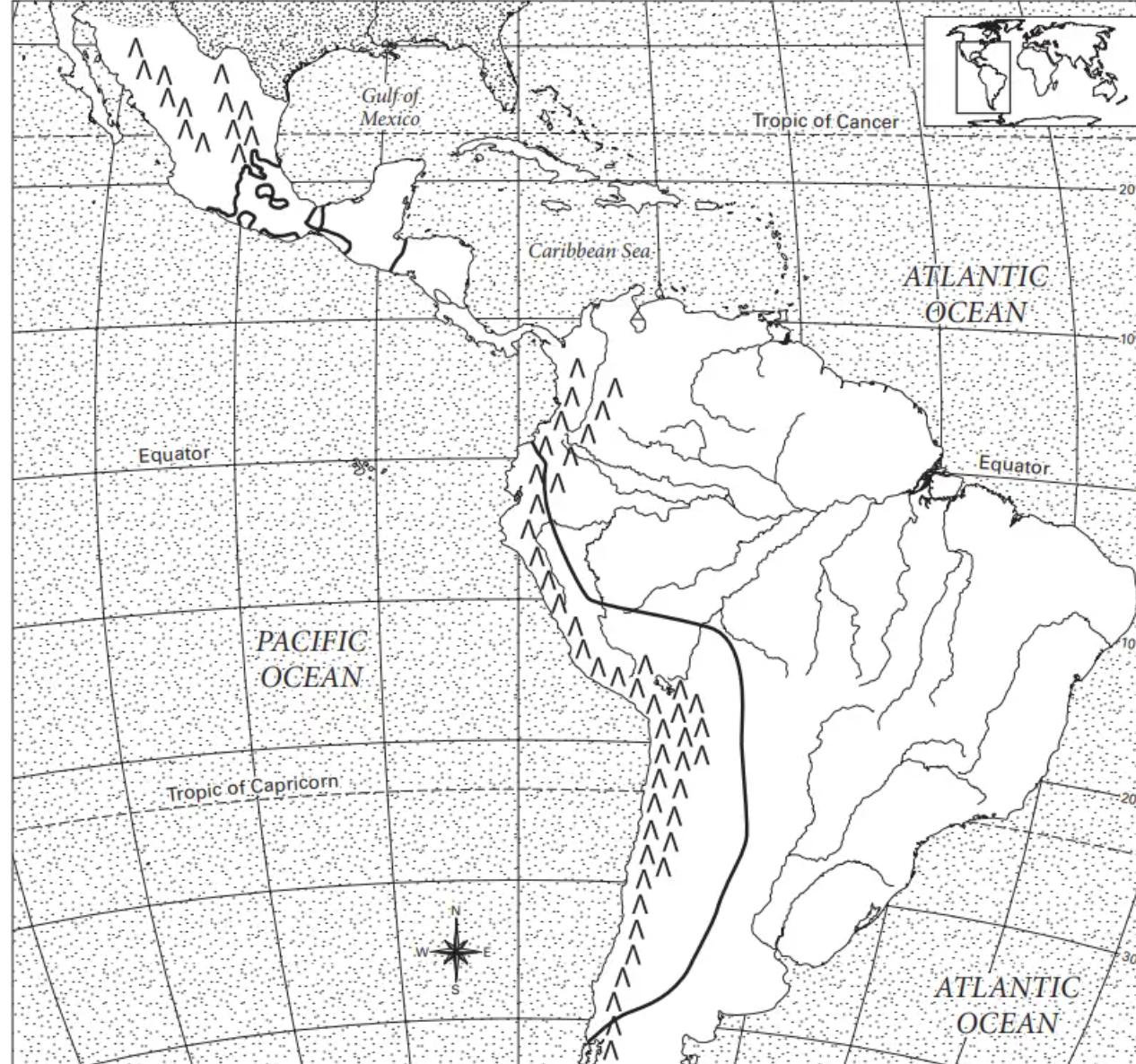
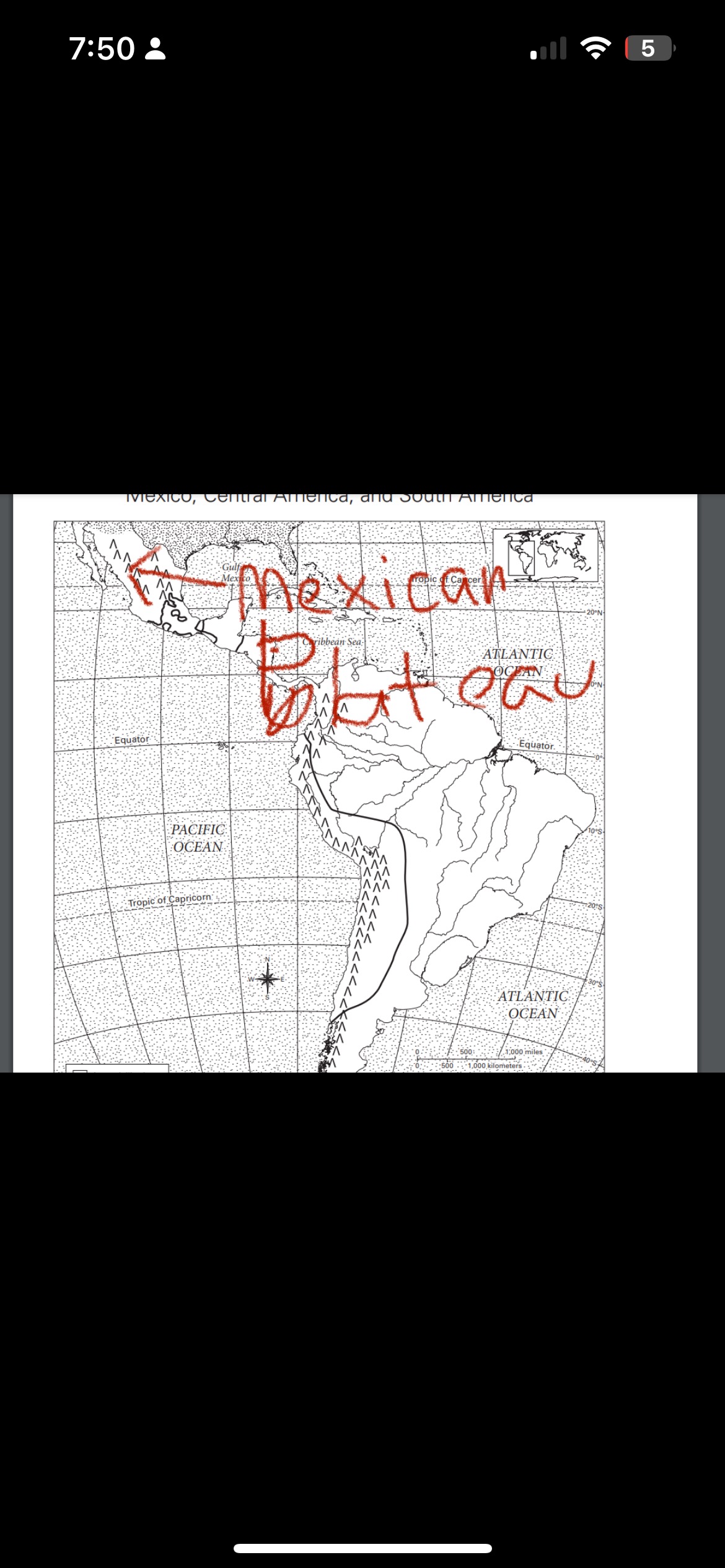
where is the mexican plateau
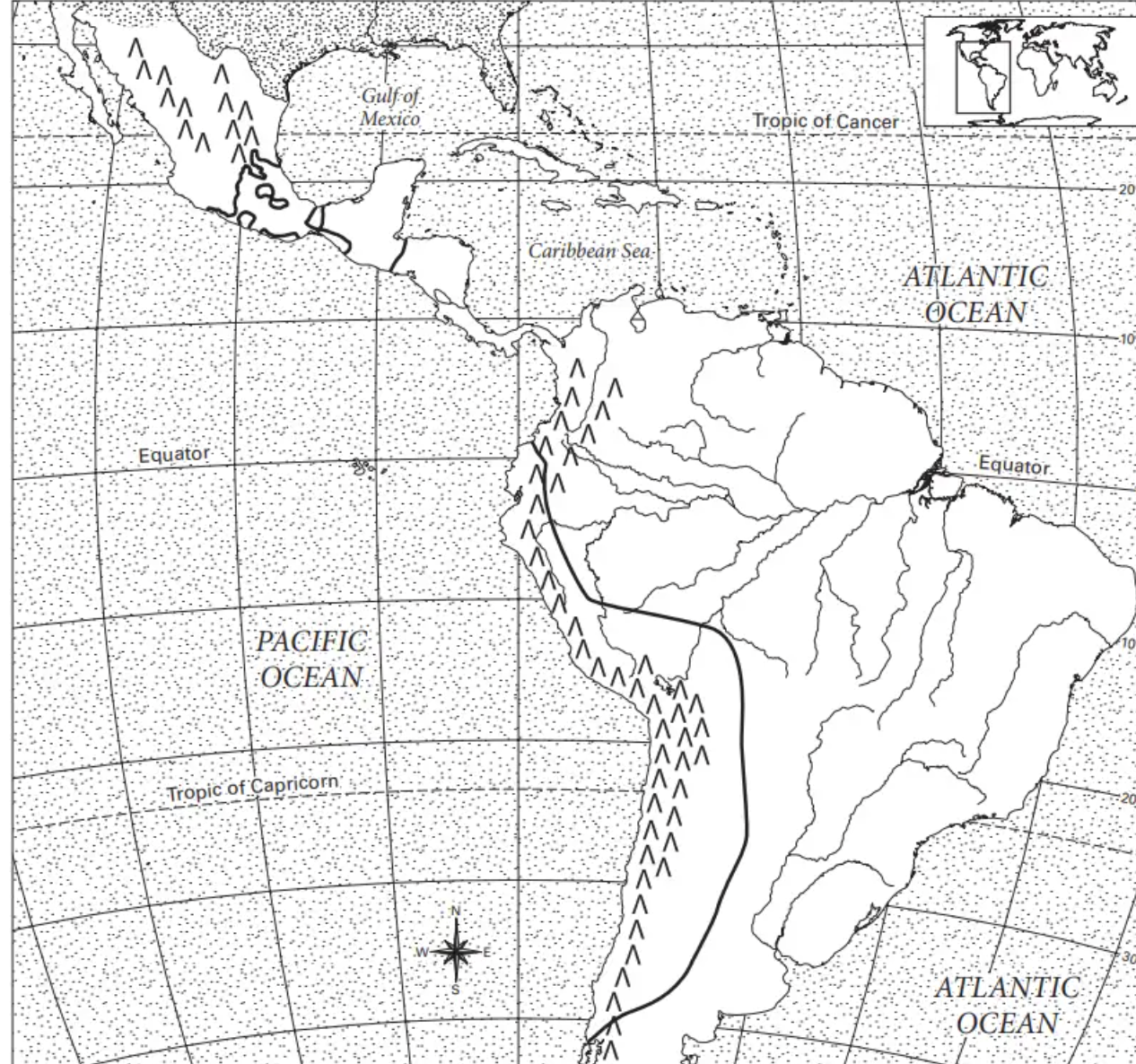
maya civilization
aztec civilization
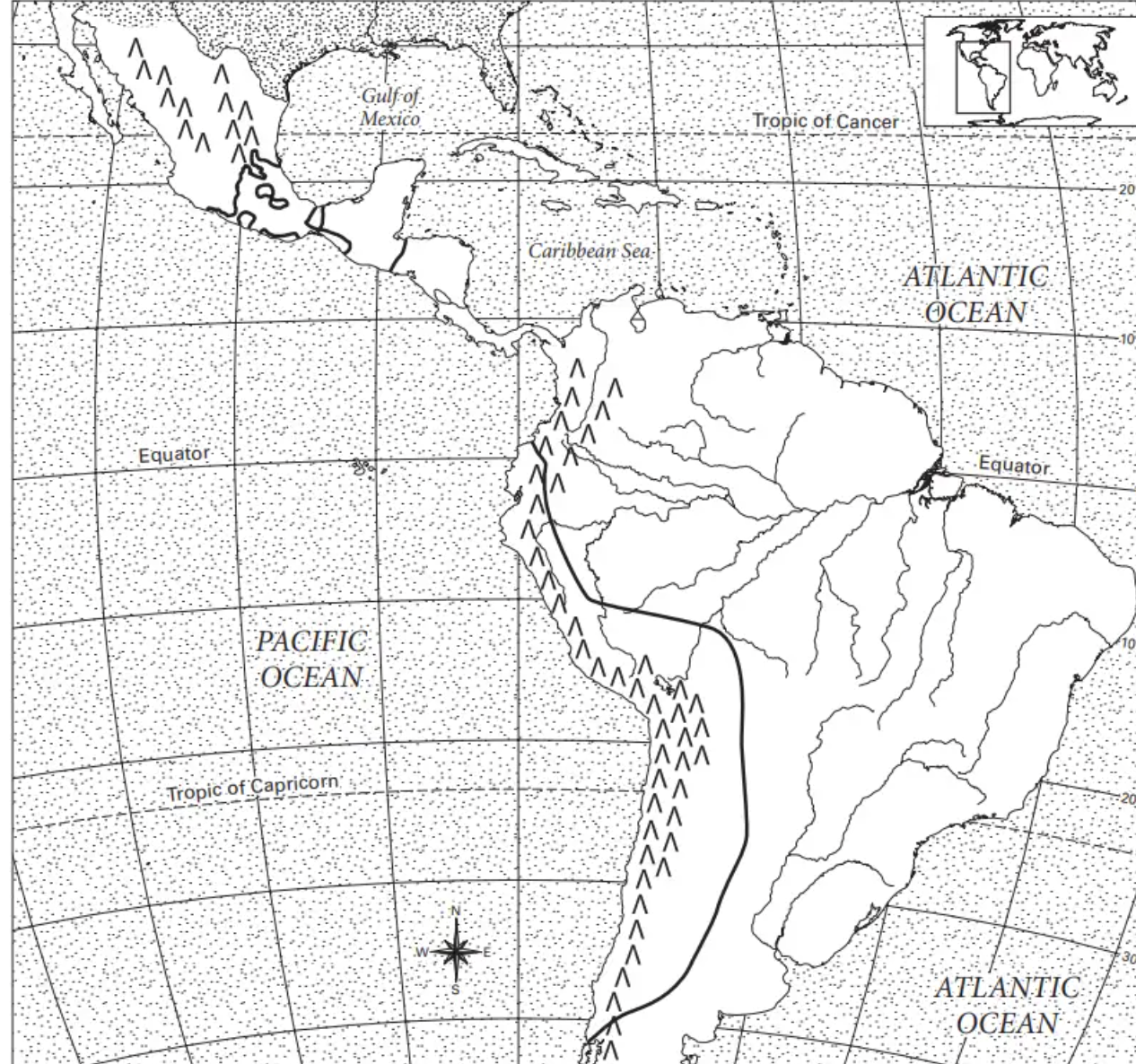
inca civilization
classic
golden age
city state
independent state that consists of a city and its surroundings
who was the highest authority in maya social structure
the ruler - halach uinic ‘true man’
second highest in social structure
nobles and priests
Only people (including ruler) who knew how to read
Priests performed sacrifices, led rituals, and foretold the future
Nobles gathered taxes and supplies
Nobles led peasant armies in war
3rd in social structure
Merchants and Artisans
Merchants imported valuable items used during religious ceremonies
Artisans painted books on paper from bark
Artisans painted murals
Were skilled weaves and potters
4th in social structure
Peasants
Grew crops
Farm with wooden hoes
Women worked at home preparing food, weaving, sewing, taking care of kids and animals
Built temples, pyramids, served as soldiers
lowest tier on social pyramid
Enslaved people
Did manual labor
Became enslaved if they committed a serious crime
Could become enslaved if they were war prisoners
Family could have sold them into slavery
Background information
Built homes, royal palaces, ball courts, and pyramids in ceremonial center
Calendar system
Based on 20, due to math
Had different types of calendars (Ritual, solar, and long count)
The Sacred Round (260 day calendar)
Calendars were used to determine the best days to plant, hunt, cure, do battle, and perform religious ceremonies
Had solar calendars (used astronomy to figure out weather) - DAILY CALENDAR - 365 days
Ritual calendar (Tzolkin - Sacred Round - only Priests could read this) - 260 days
Sacred Round
Had two cycles, one made up of the numbers 1-13 and one with 20 day names
Used to determine the best days to do activities, such as religious ceremonies
Only priests could read the Sacred Round
Offerings and Sacrifices
Made offering of plants, food, flowers, feathers, jade, and shells
Animals and sometimes humans were sacrificed
Mayan Gods
The Maya believed in more than 160 gods (polytheistic)
Primary gods were the the god of rain, the god of corn, and the god of death
The jaguar was an important animal in the Maya religion
Pok-a-tok
Ball games played by two teams of nobles
Players tried to hit a rubber ball through a stone hoop using anything but their hands
Members of the losing team MAY have been sacrificed
EVERYTHING MAYANS DID WERE TO HONOR THE GODS!
Number System
Based on the number 20
Had symbols representing values - dot (1), dash (5), shell (0)
Number system could not function without 0
Mayans DID NOT come up with 0, but incorporated it into their number system
What did peasant women usually work on
sewing and preparing food
How did maya peasant men work
worked in fields and built structures