ARTH 205 Maddox Midterm (ID's and Vocab)
1/81
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
82 Terms
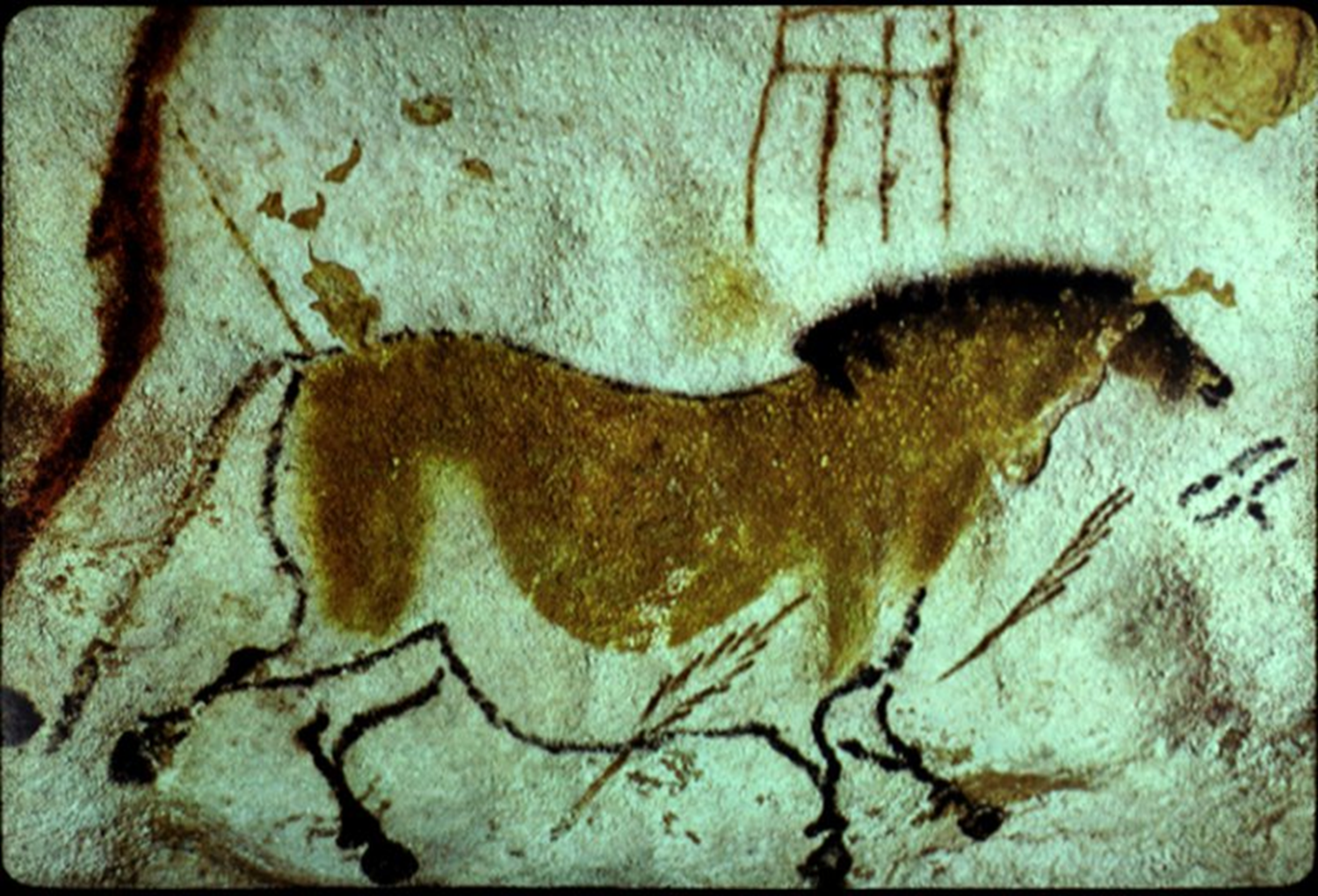

Chinese horse in Lascaux Caves, Upper Paleolithic, 15,000 BCE in Dordogne, France
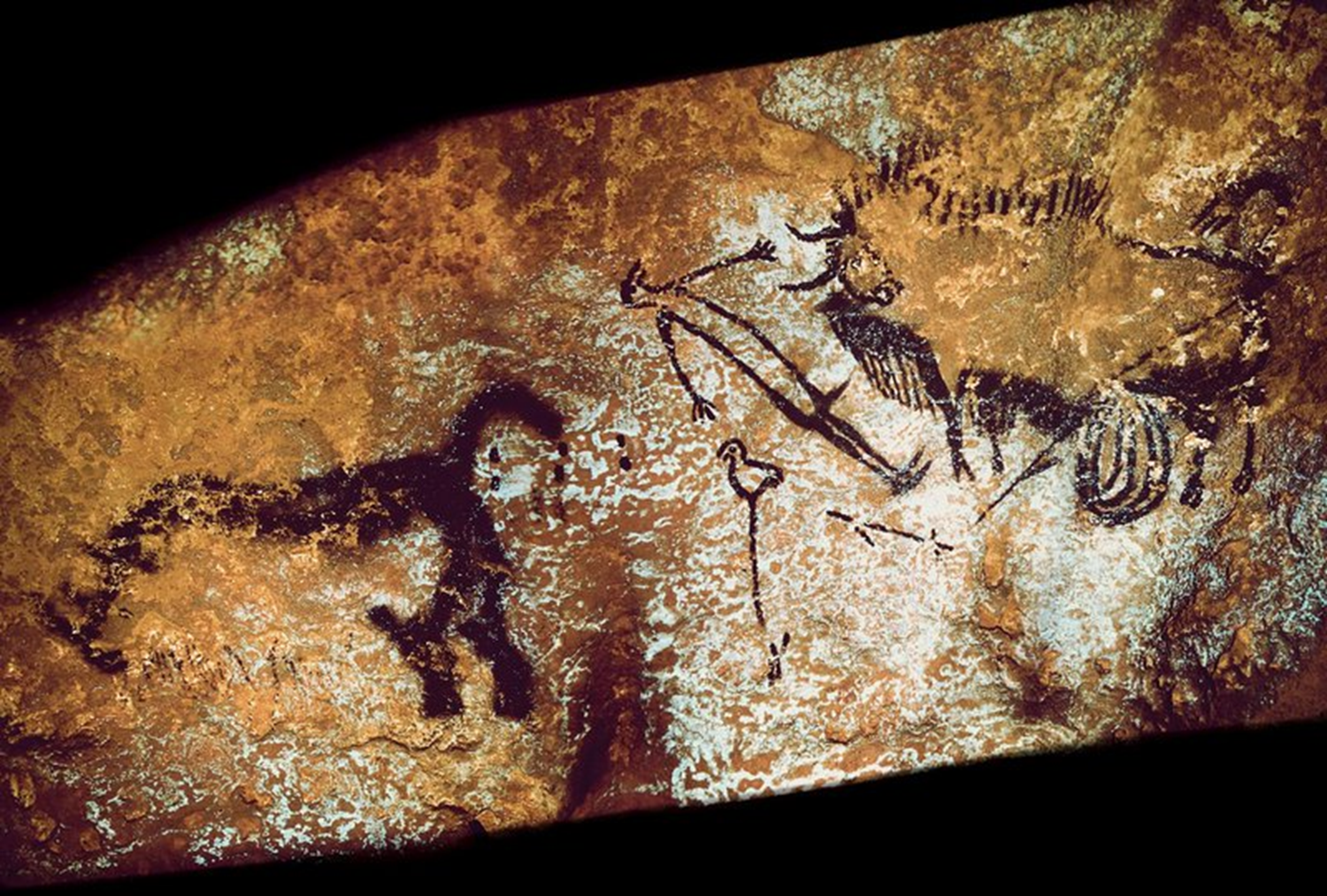

Bird-headed man with bison in Lascaux Caves, Upper Paleolithic, 15,000 BCE in Dordogne, France
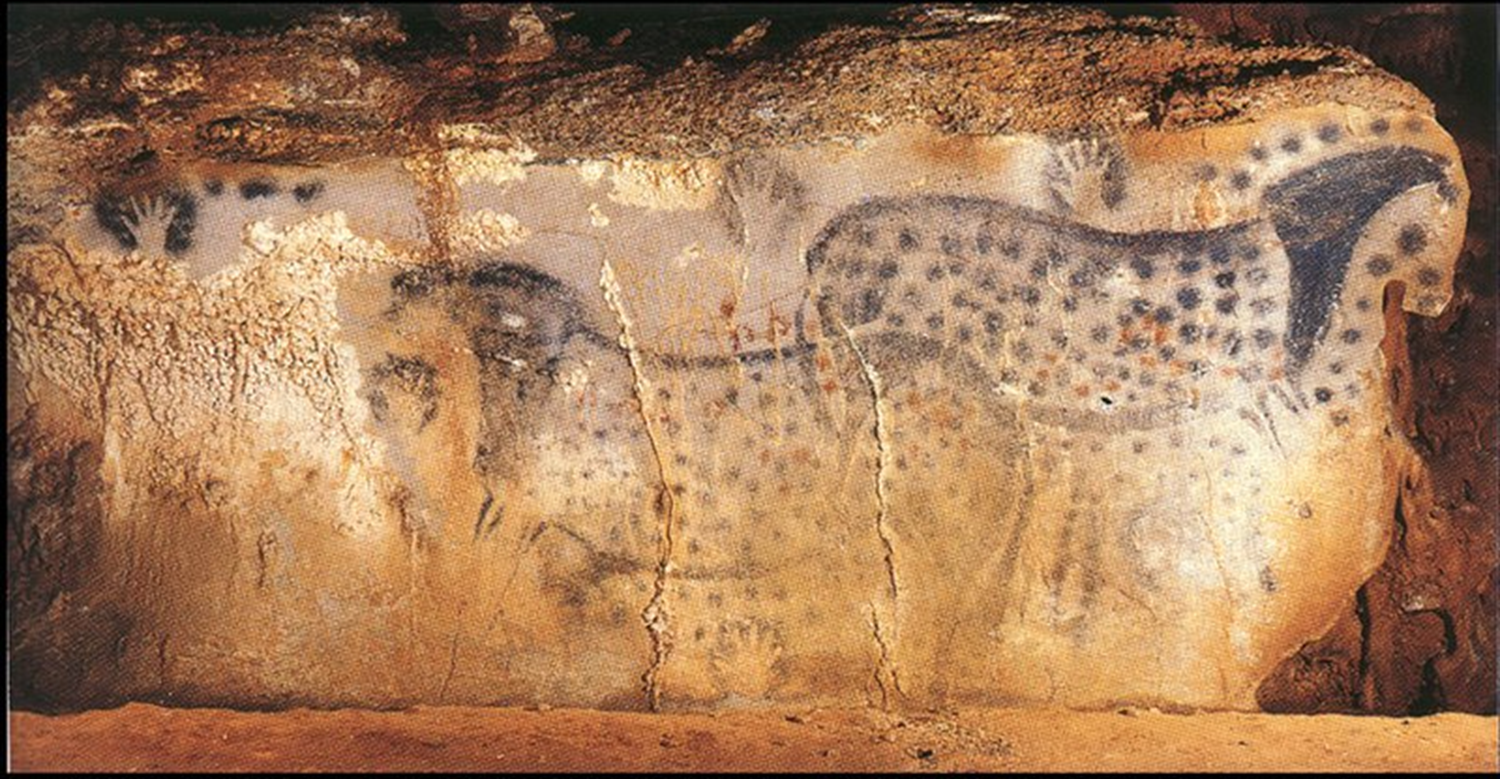

Spotted Horses and Human Hands in Pech-Merle Cave, Upper Paleolithic, 16,000 BCE in Dordogne, France

Woman from Willendorf, Upper Paleolithic, 24,000 BCE in Austria
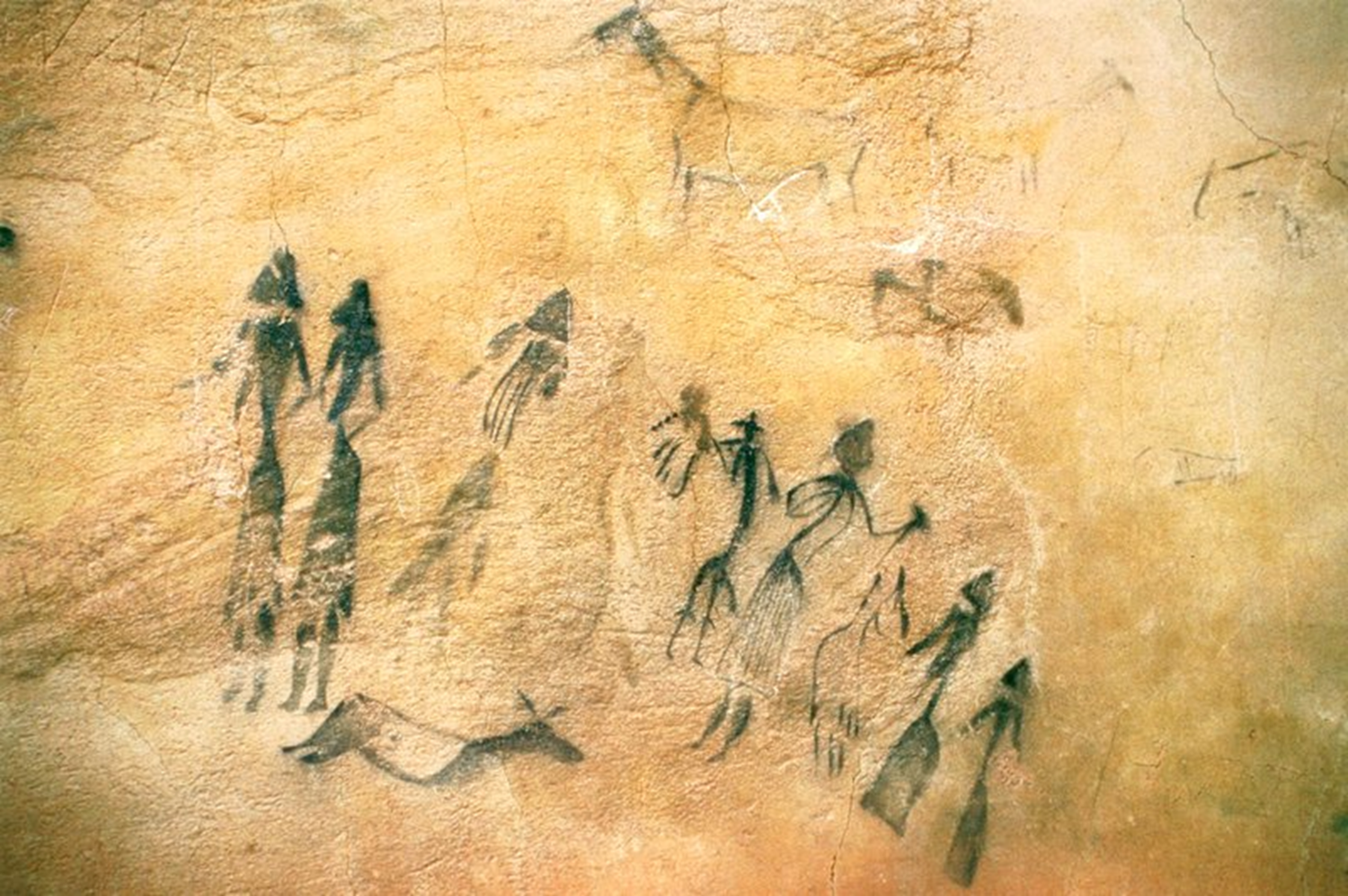

People and Animals, Mesolithic, 4000 BCE in Spain

Gobleki Tepe, Mesolithic, 9600 BCE in Turkey

Catalhoyuk (reconstruction drawing), Neoithic, 7400 BCE in Turkey
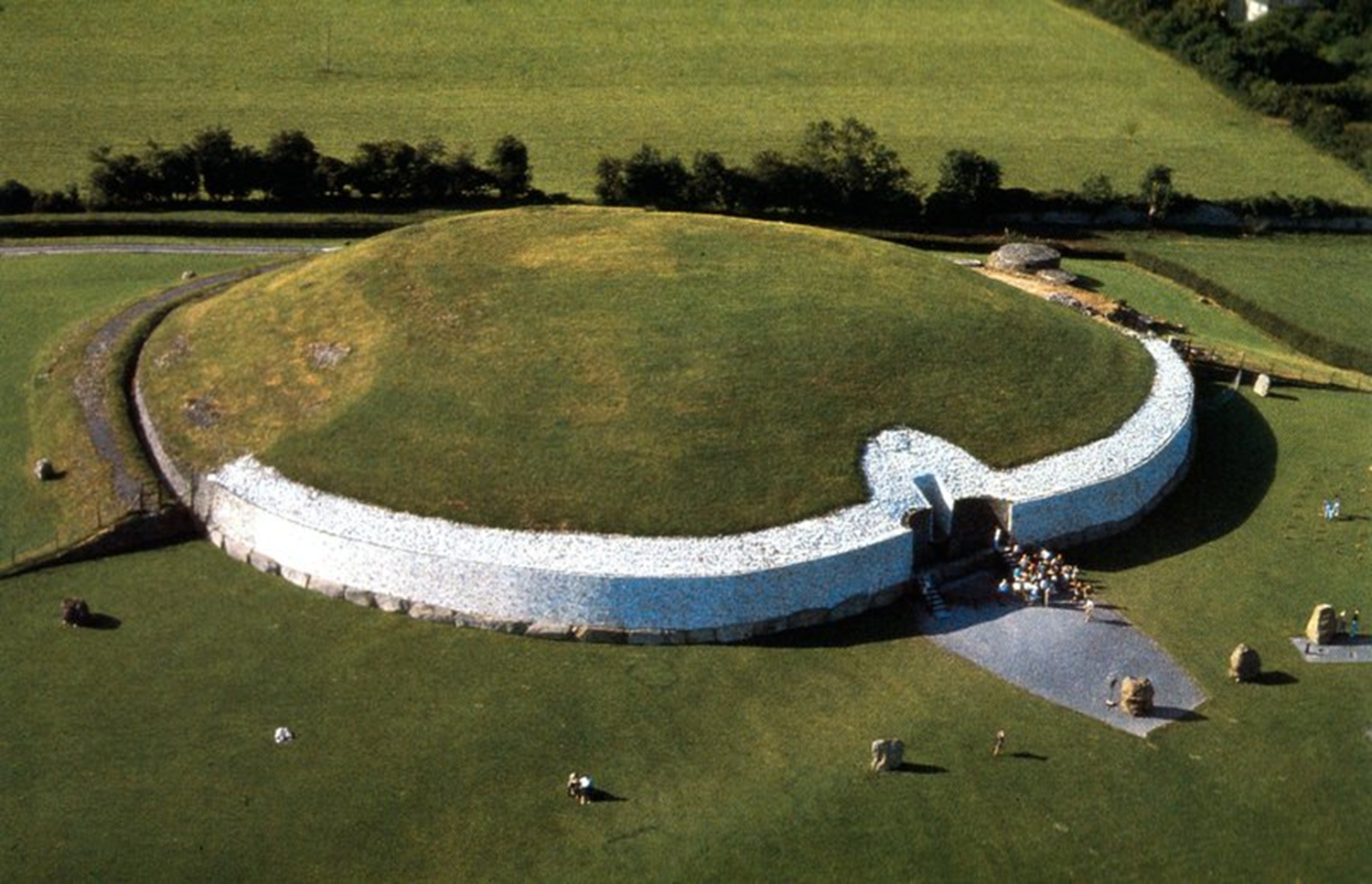
Newgrange, Neolithic, 3000 BCE in Ireland
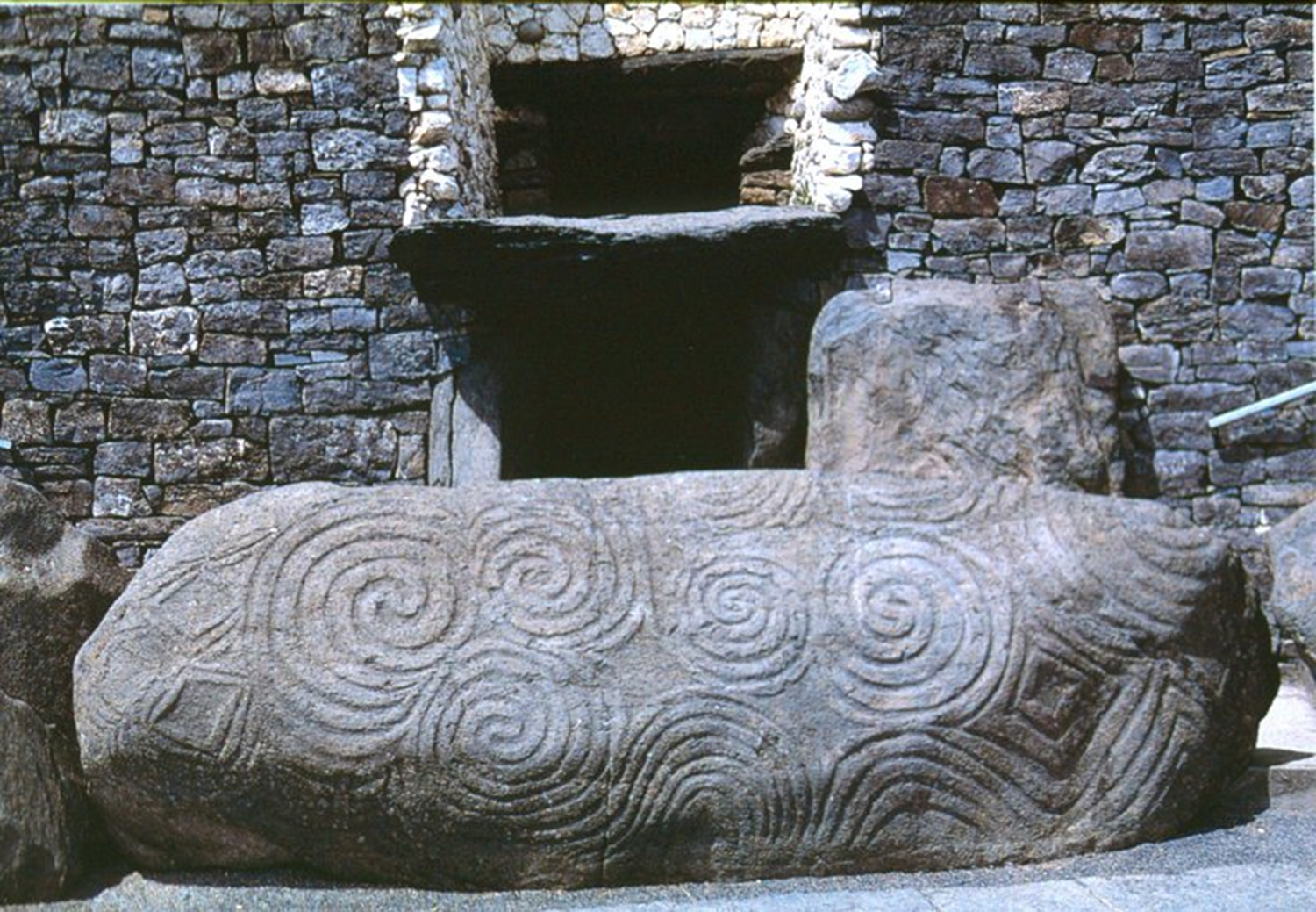

Newgrange, Neolithic, 3000 BCE in Ireland
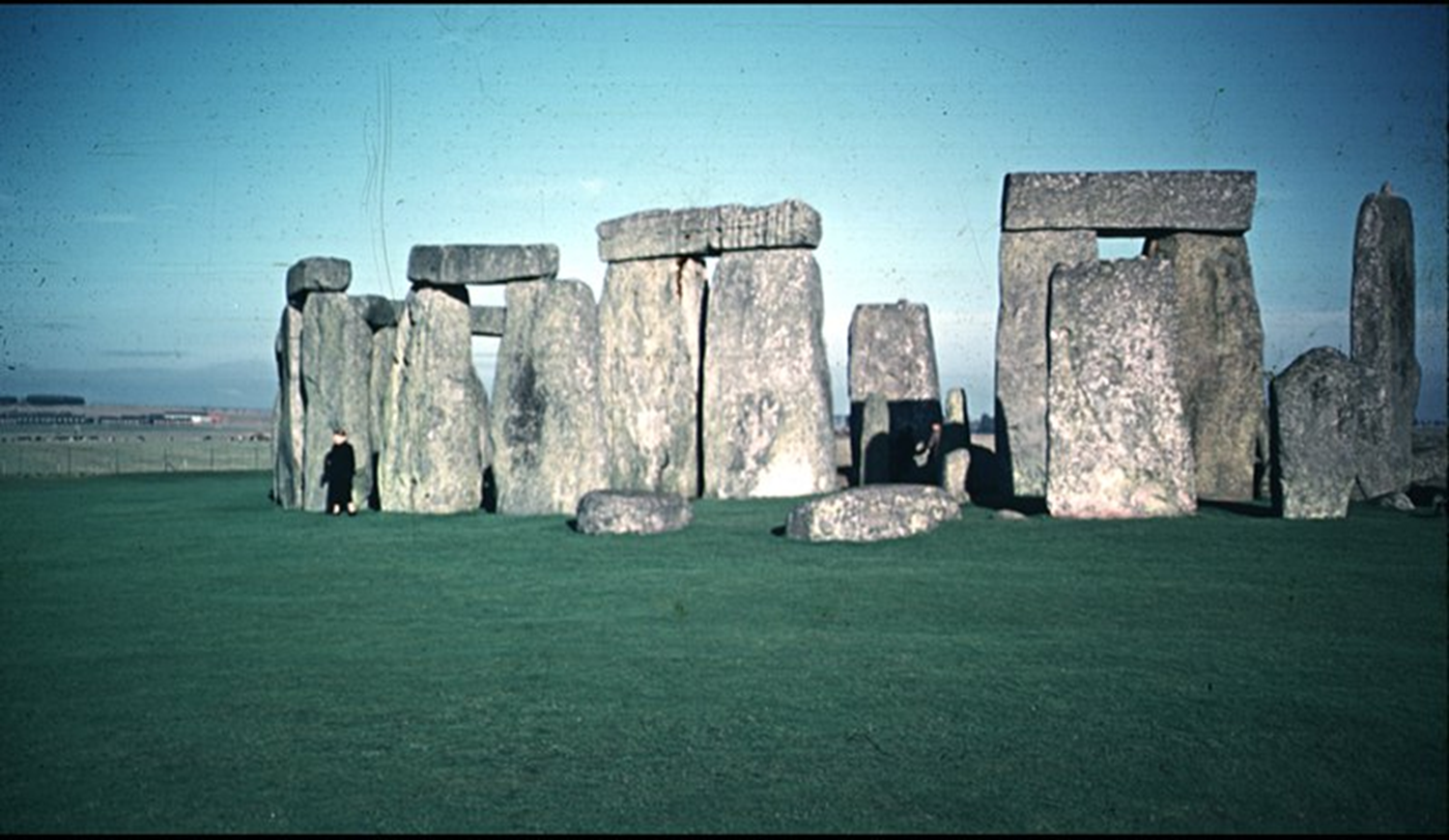

Stonehenge, Neolithic, 2900 BCE in England
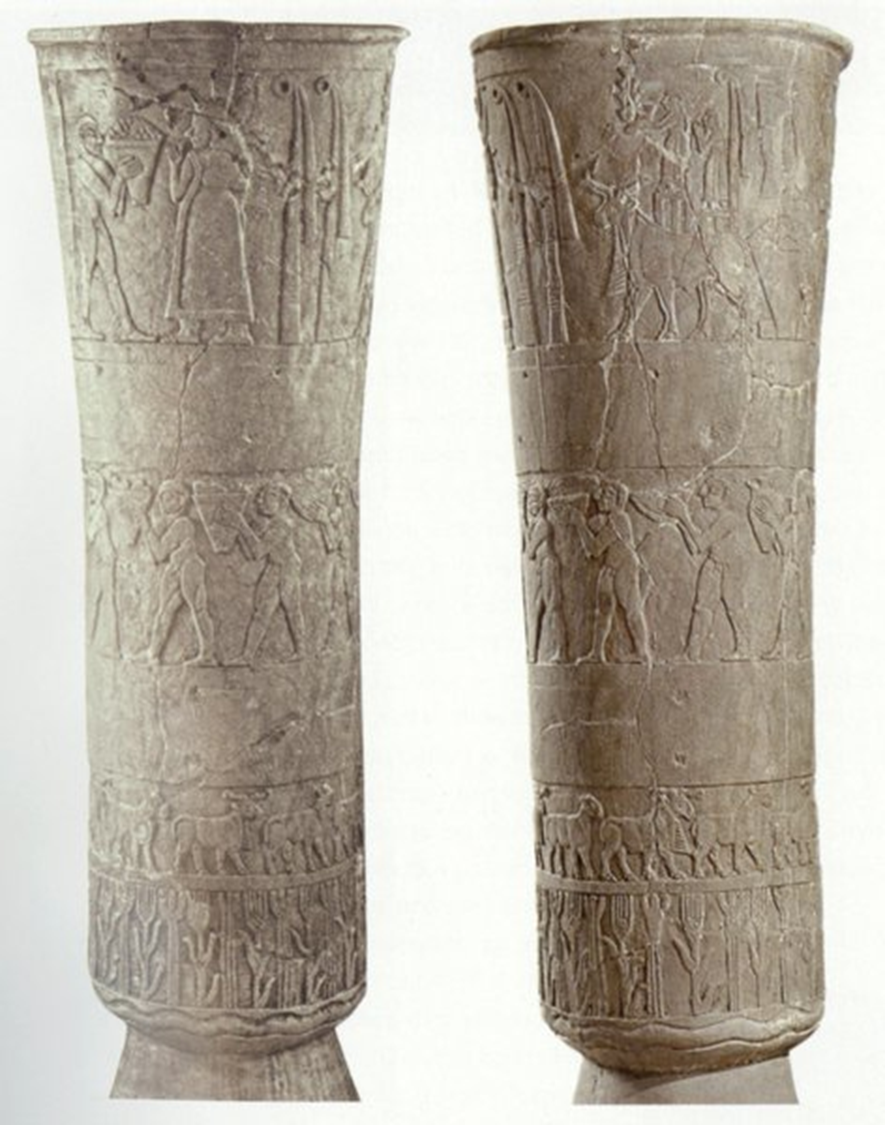

Carved Vessel, Sumerian, 3300 BCE in Iraq

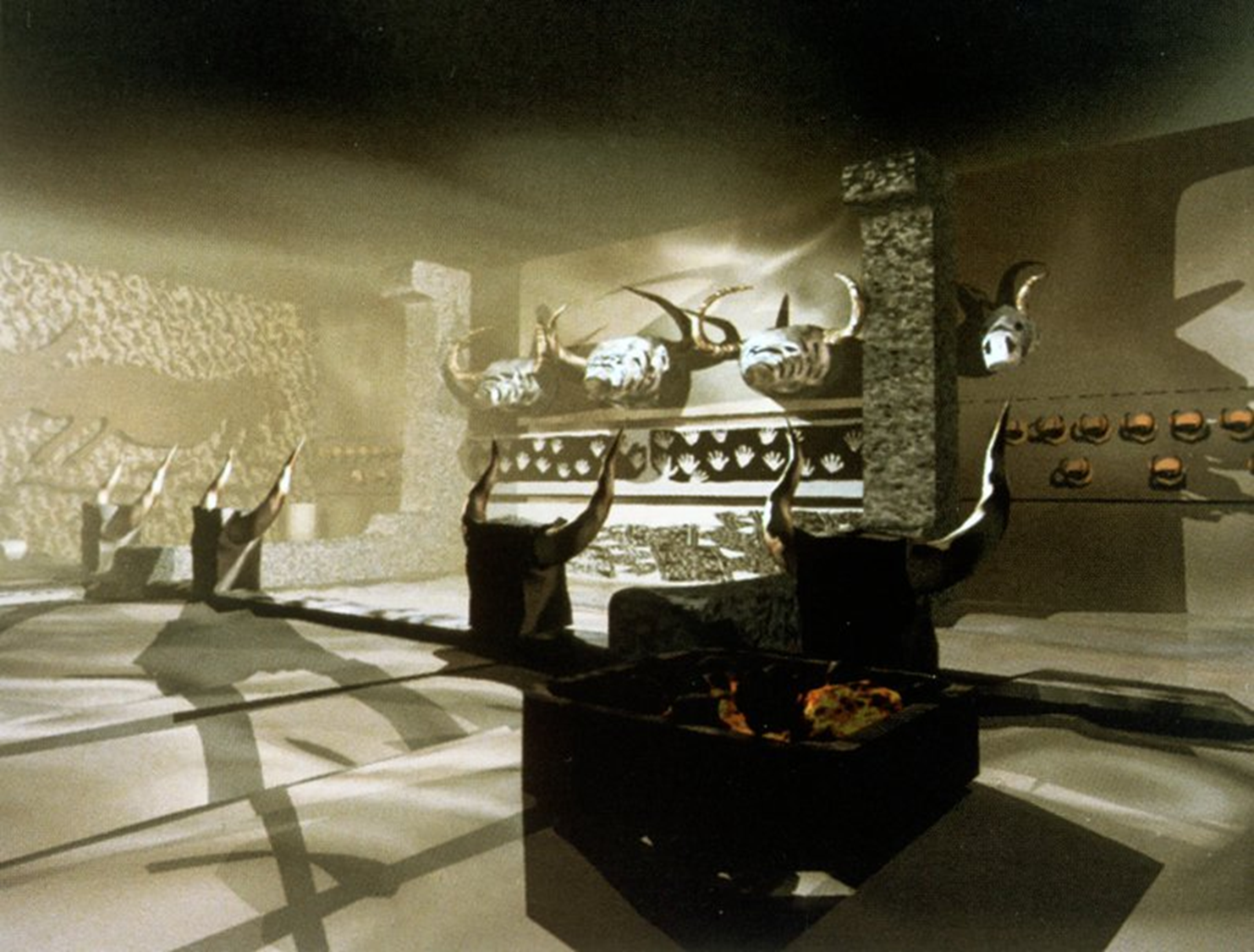
Front Panel of the Great Bull-Headed Lyre, Sumerian, 2600 BCE in Iraq

Stele of Hammurabi, Babylonian, 1792 BCE in Iran
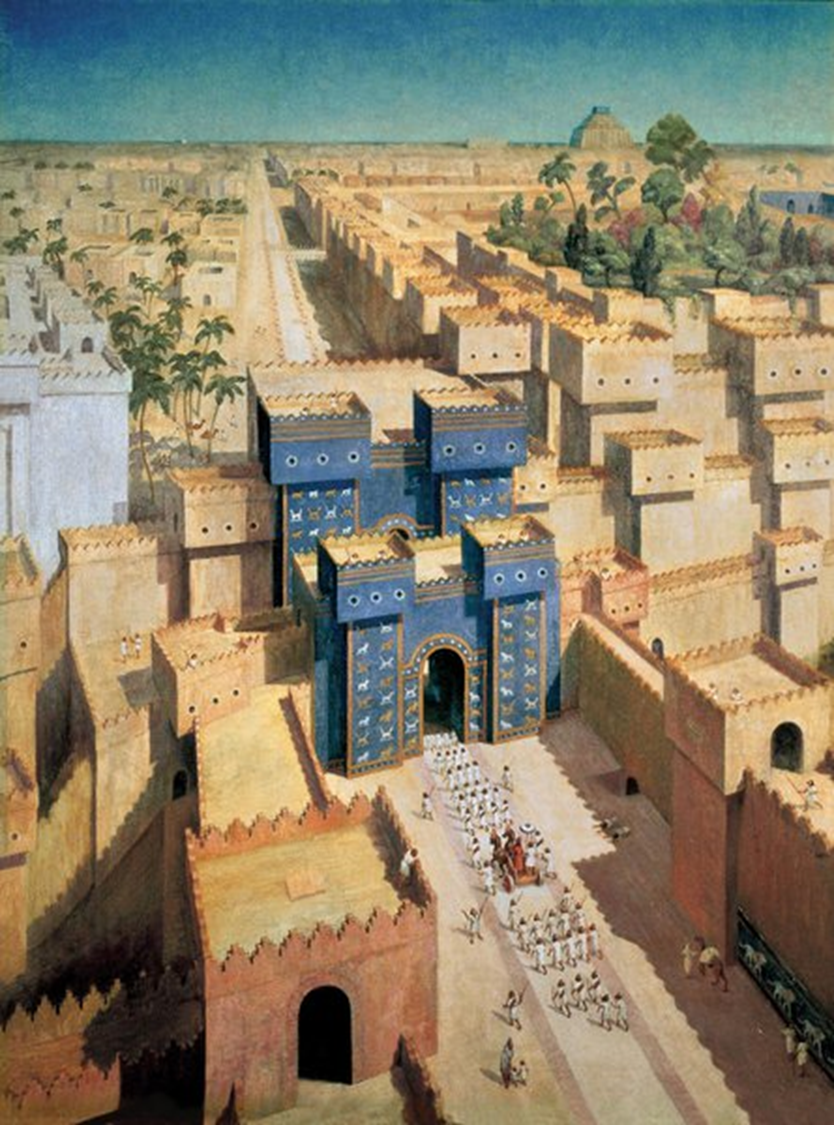

Babylon (reconstruction drawing), Neo-Babylonian, 6thc. BCE in Iraq
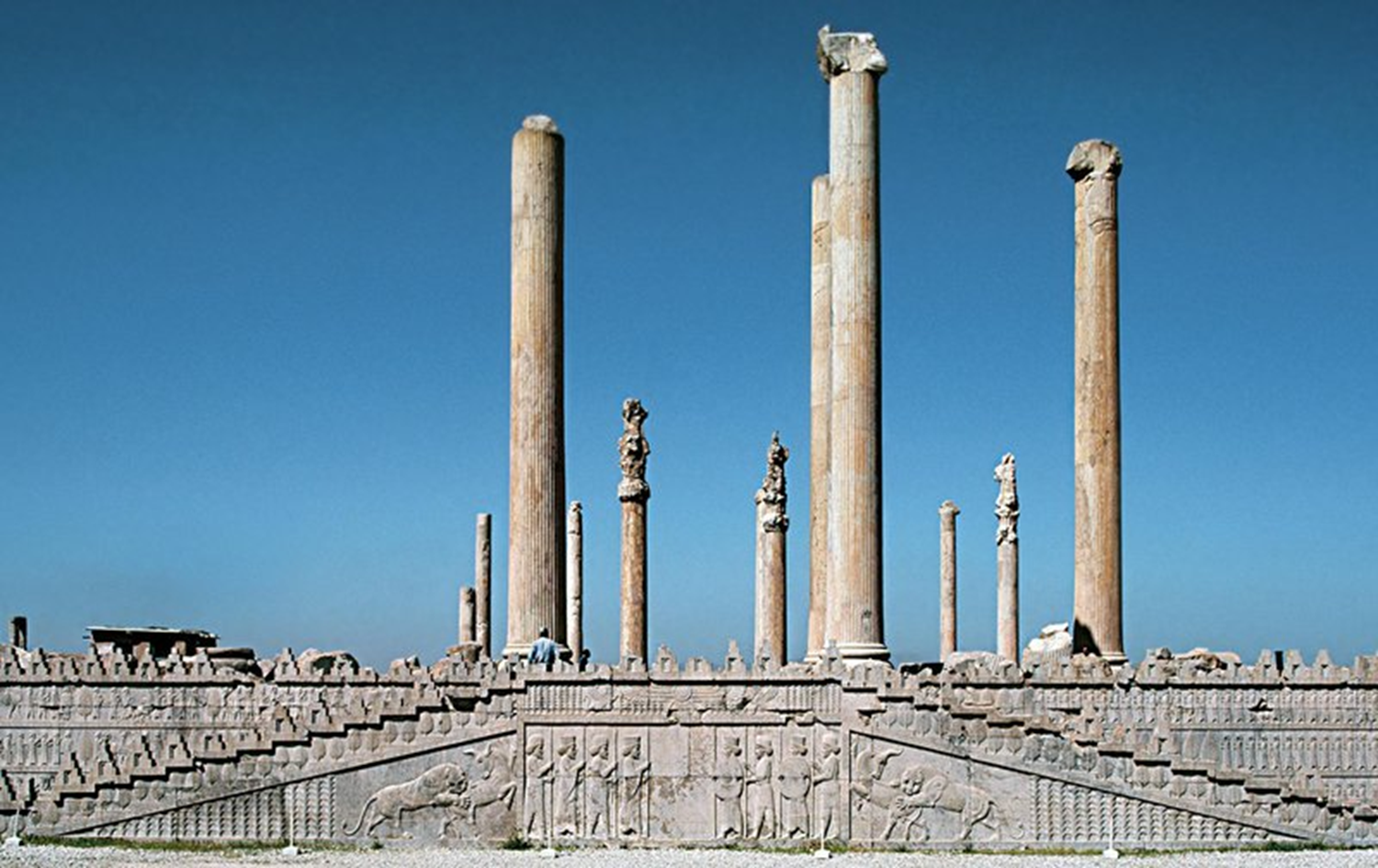

Persepolis Apadana of Darius and Xerxes, Persian, 518 BCE in Persepolis, Iran
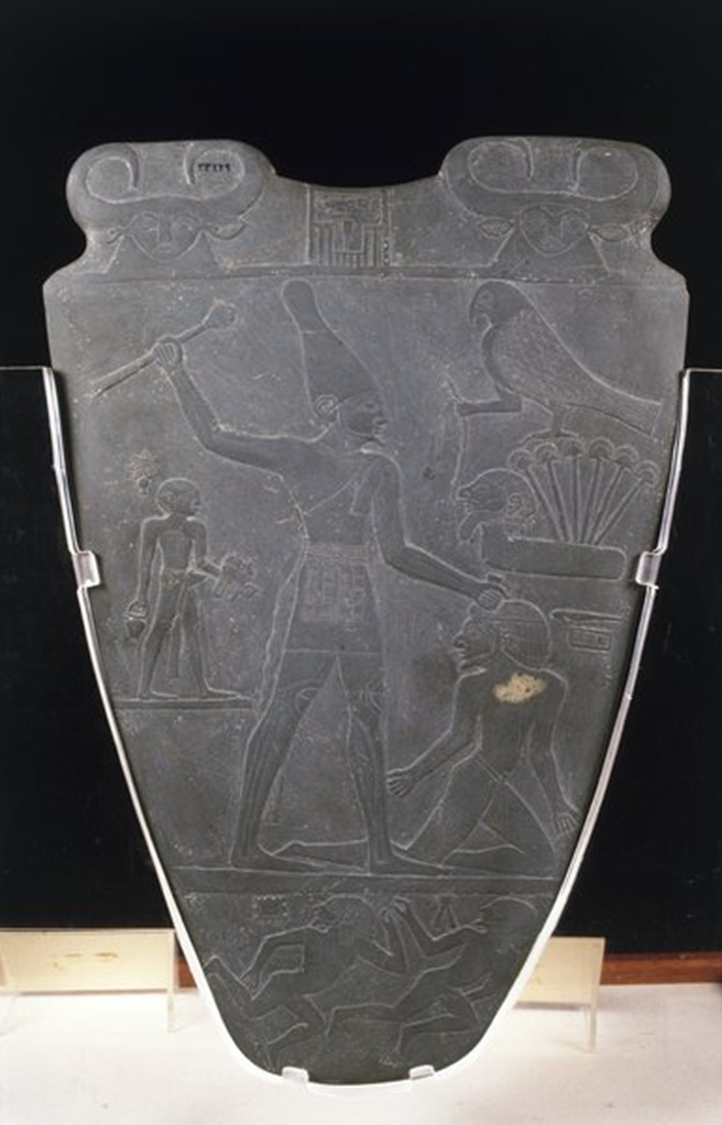

Palette of Narmer, Early Dynastic, 2950 BCE in Egypt
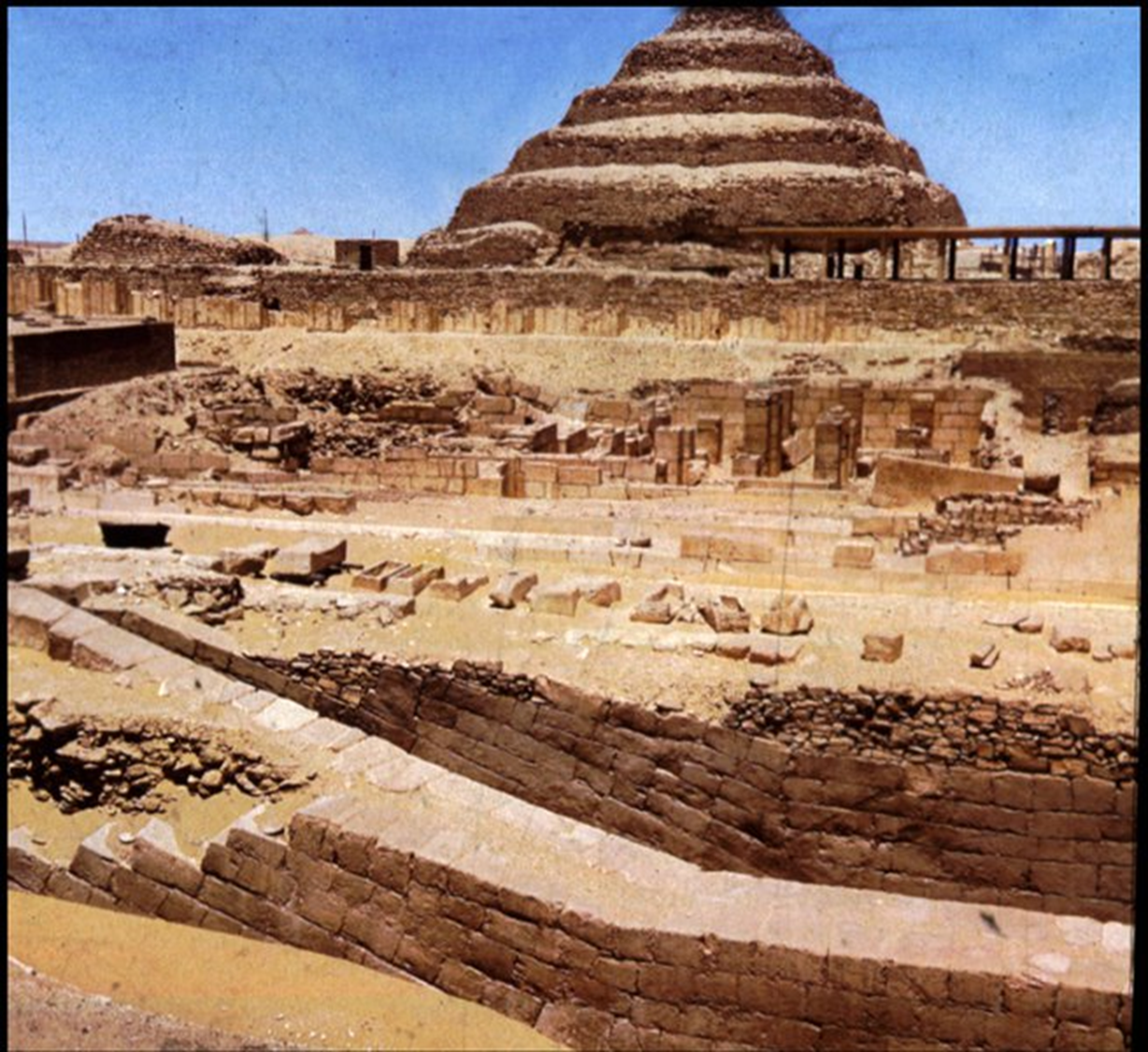

Stepped Pyramid of Djoser, Imhotep, 2630 BCE in Egypt
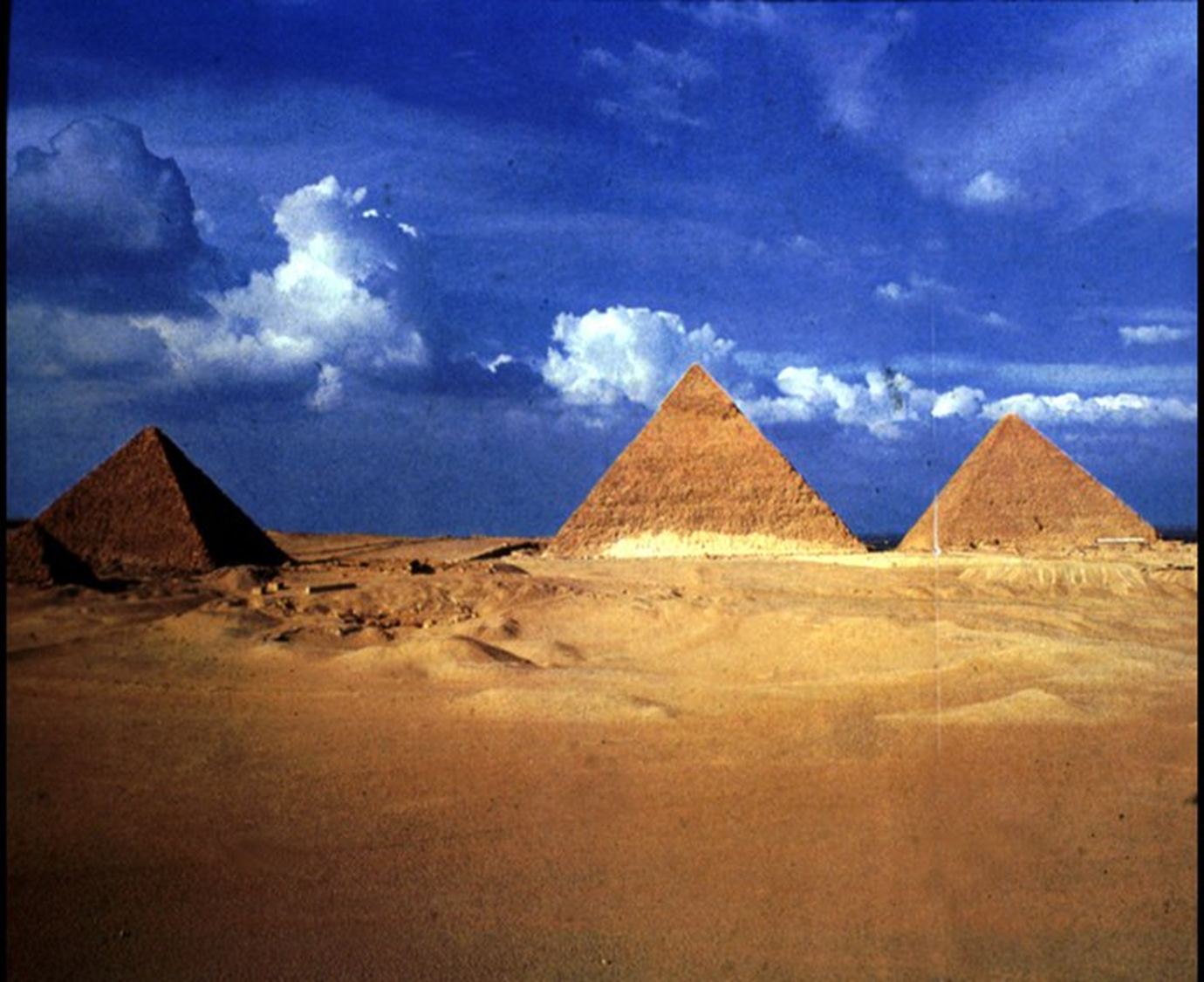

Great Pyramids of Giza, Old Kingdom, 2575 BCE in Egypt
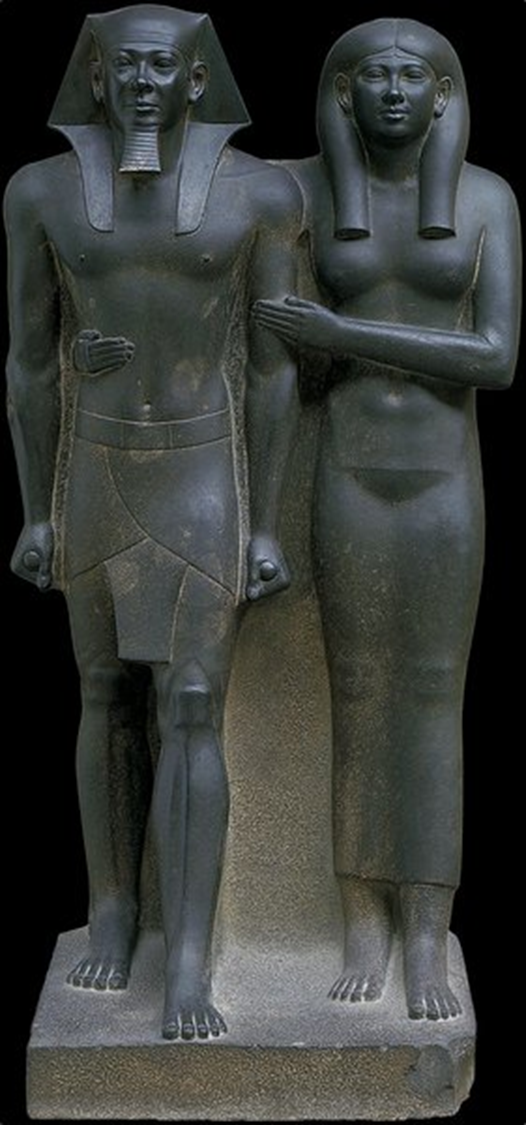

Menkaure and a Queen, Old Kingdom, 2490 BCE in Egypt
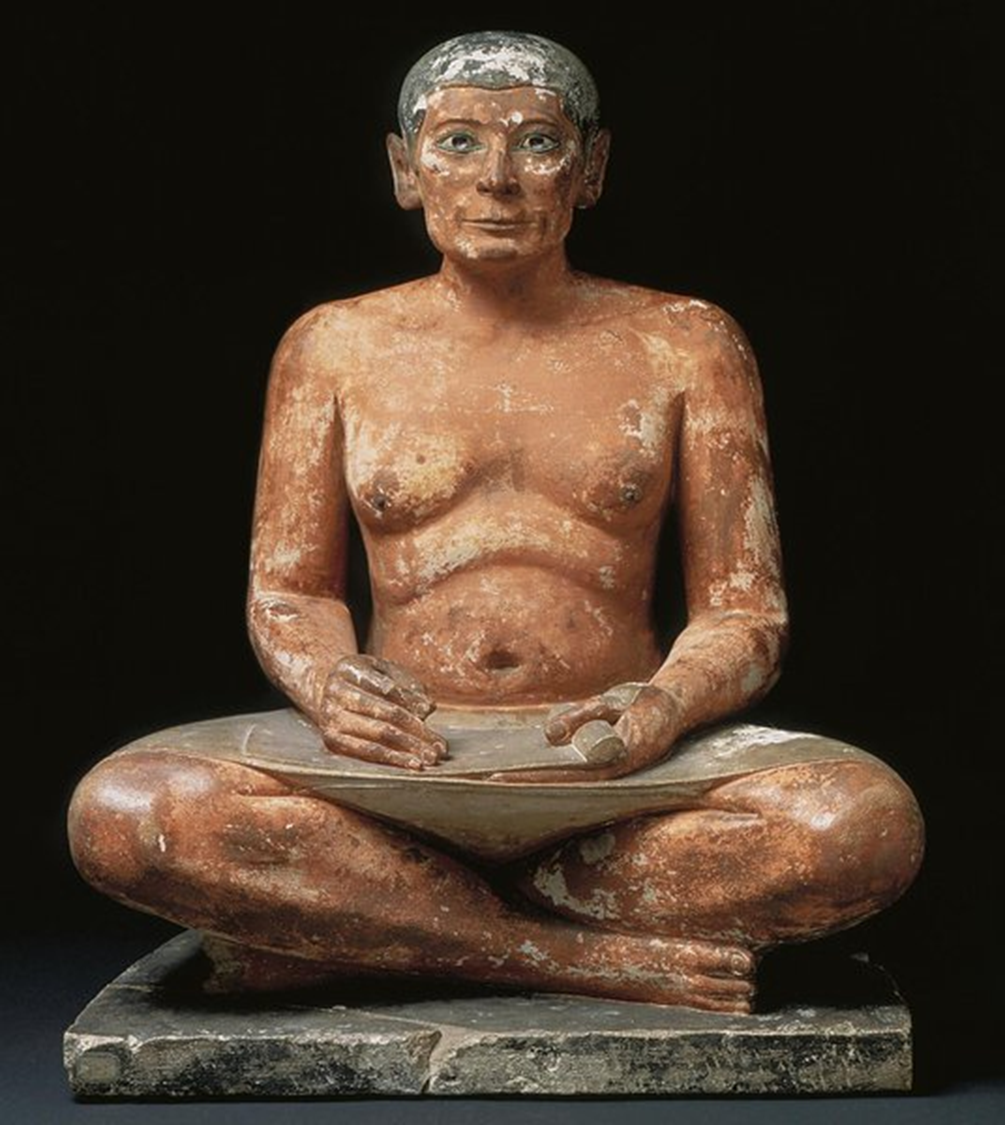

Seated Scribe Kai, Old Kingdom, 2450 BCE in Egypt
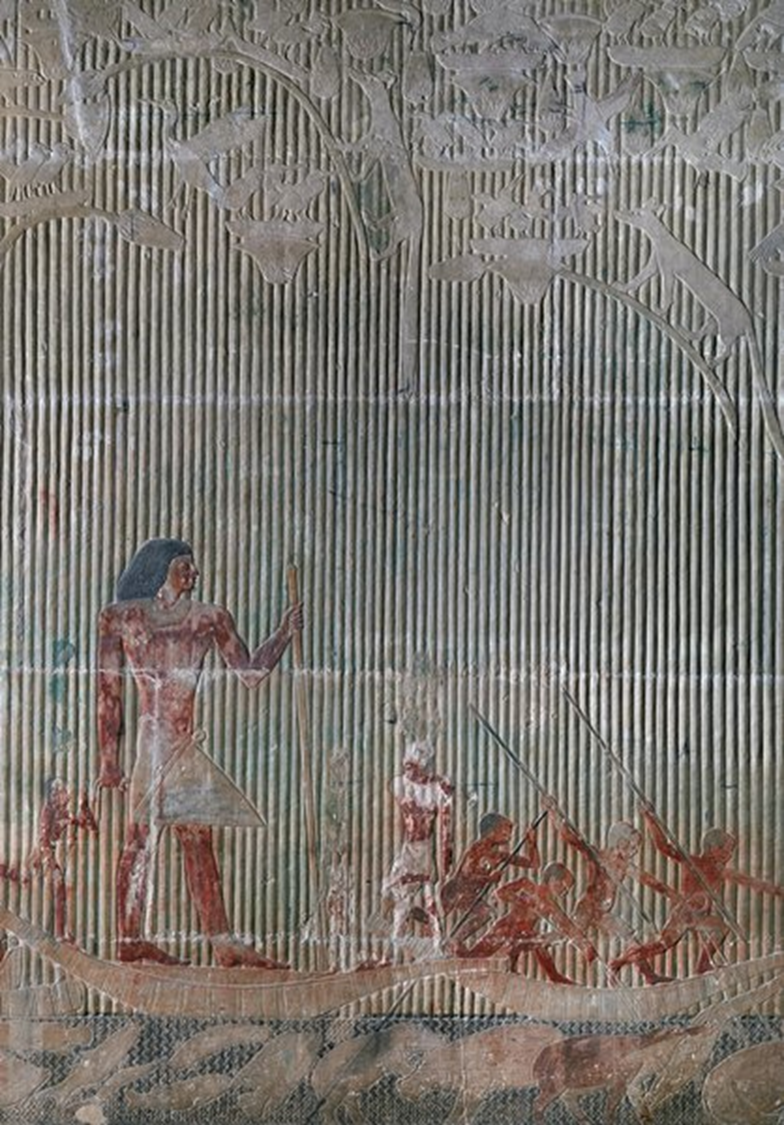

Ti Watching A Hippopotamus Hunt, Old Kingdom, 2450 BCE in Egypt
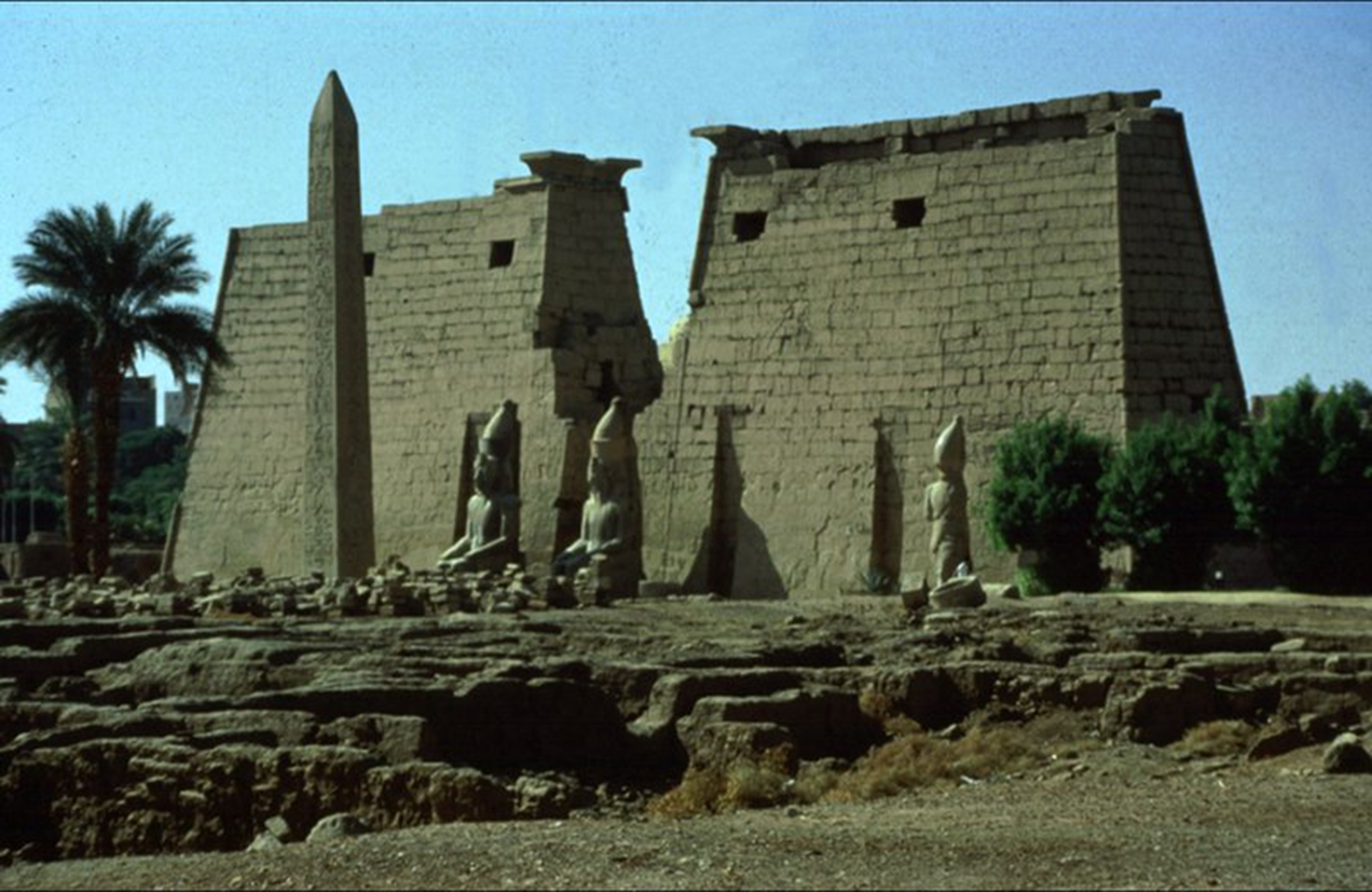

Temple of Amun-Mut-Khons at Luxor, New Kingdom, 1279 BCE in Egypt

Akhenaten and His Family, New Kingdom, 1353 BCE in Egypt
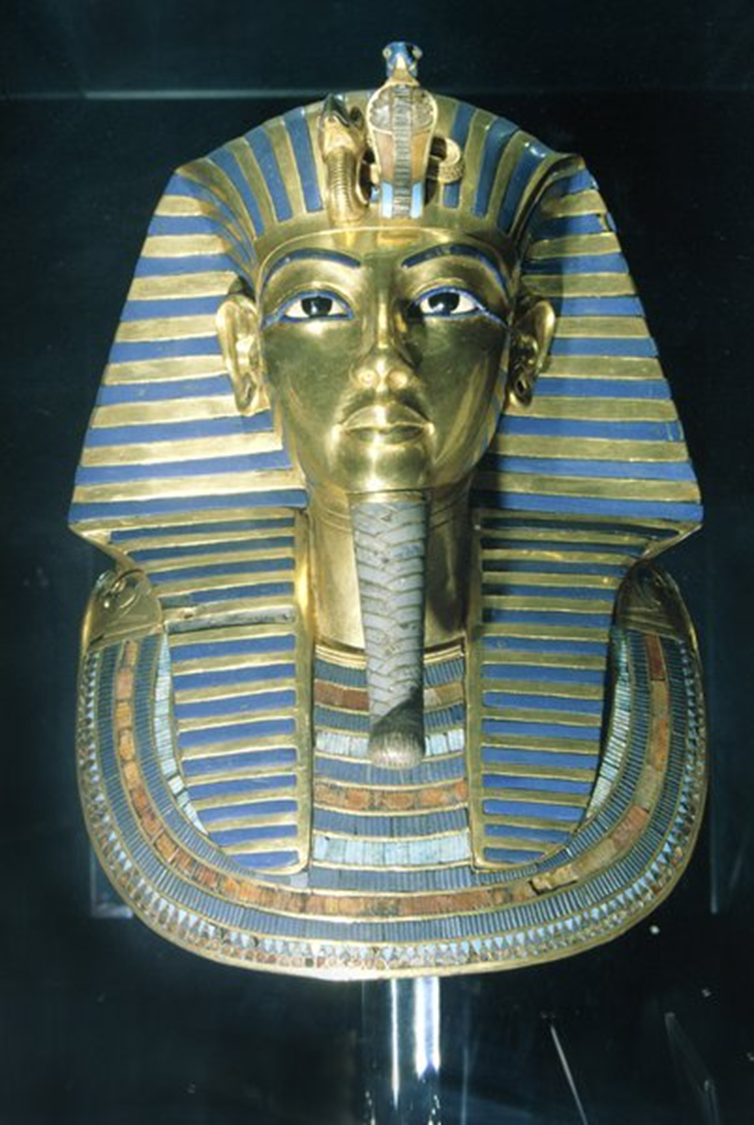

Funerary Mask of Tutankhamun, New Kingdom, 1327 BCE in Egypt
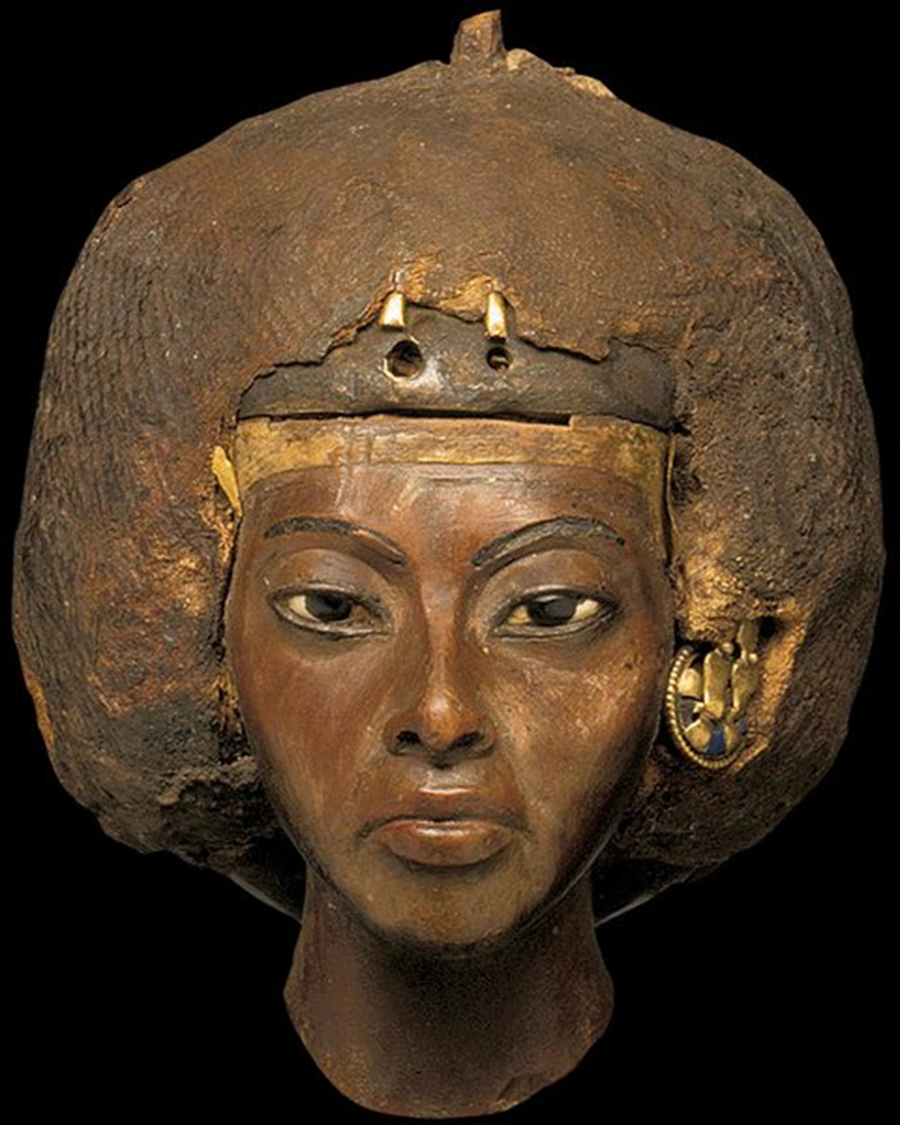

Queen Tiy, New Kingdom, 1352 BCE in Egypt
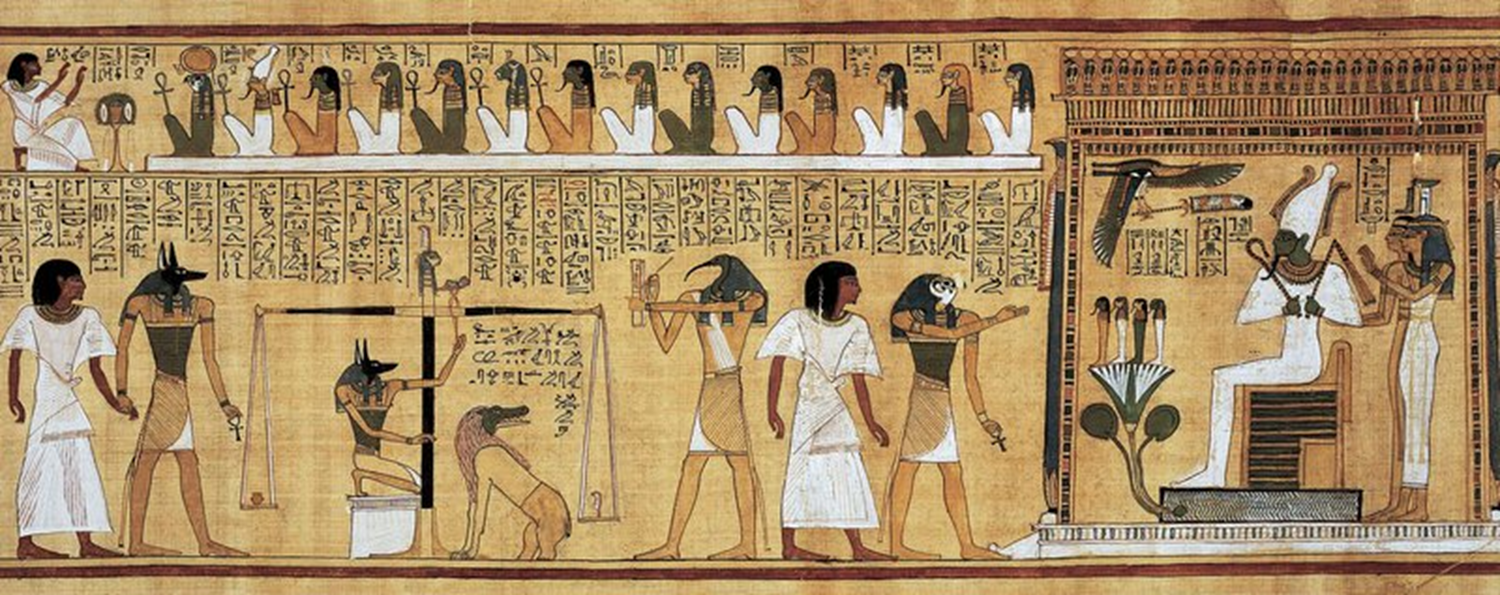
Judgment of Hunefer before Osiris, New Kingdom, 1285 BCE, Egypt
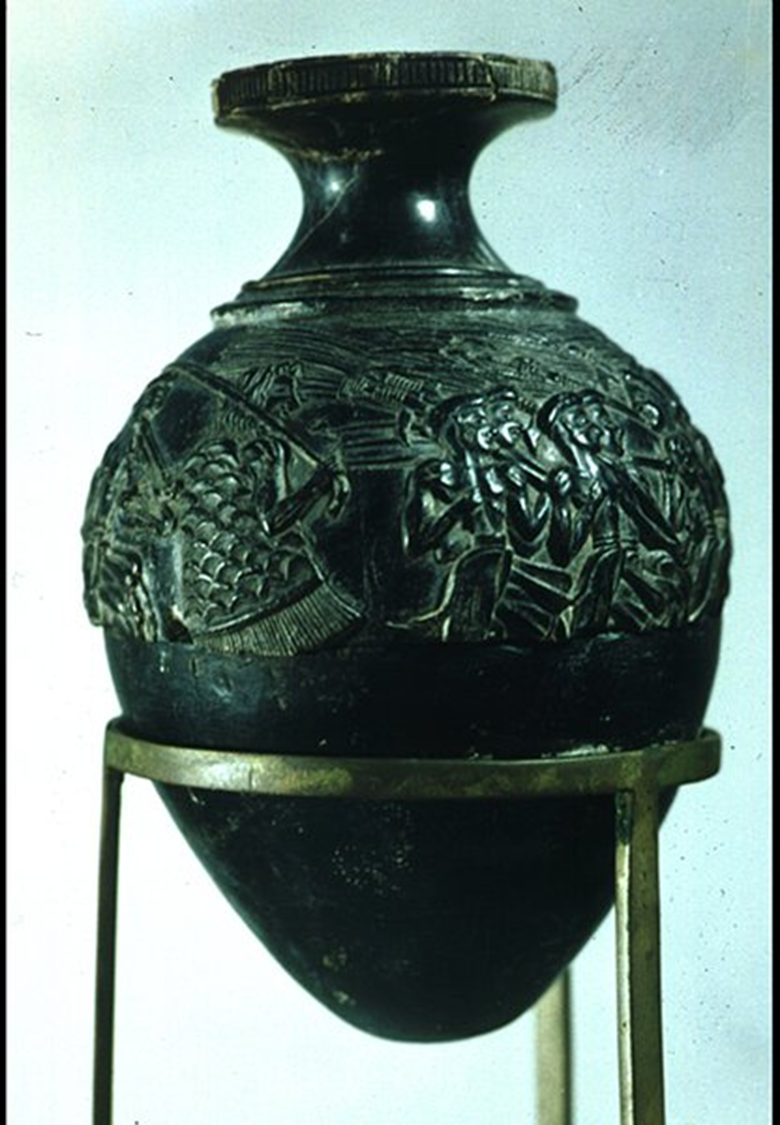

Harvester Rhyton, New Palace Period, 1650 BCE in Greece
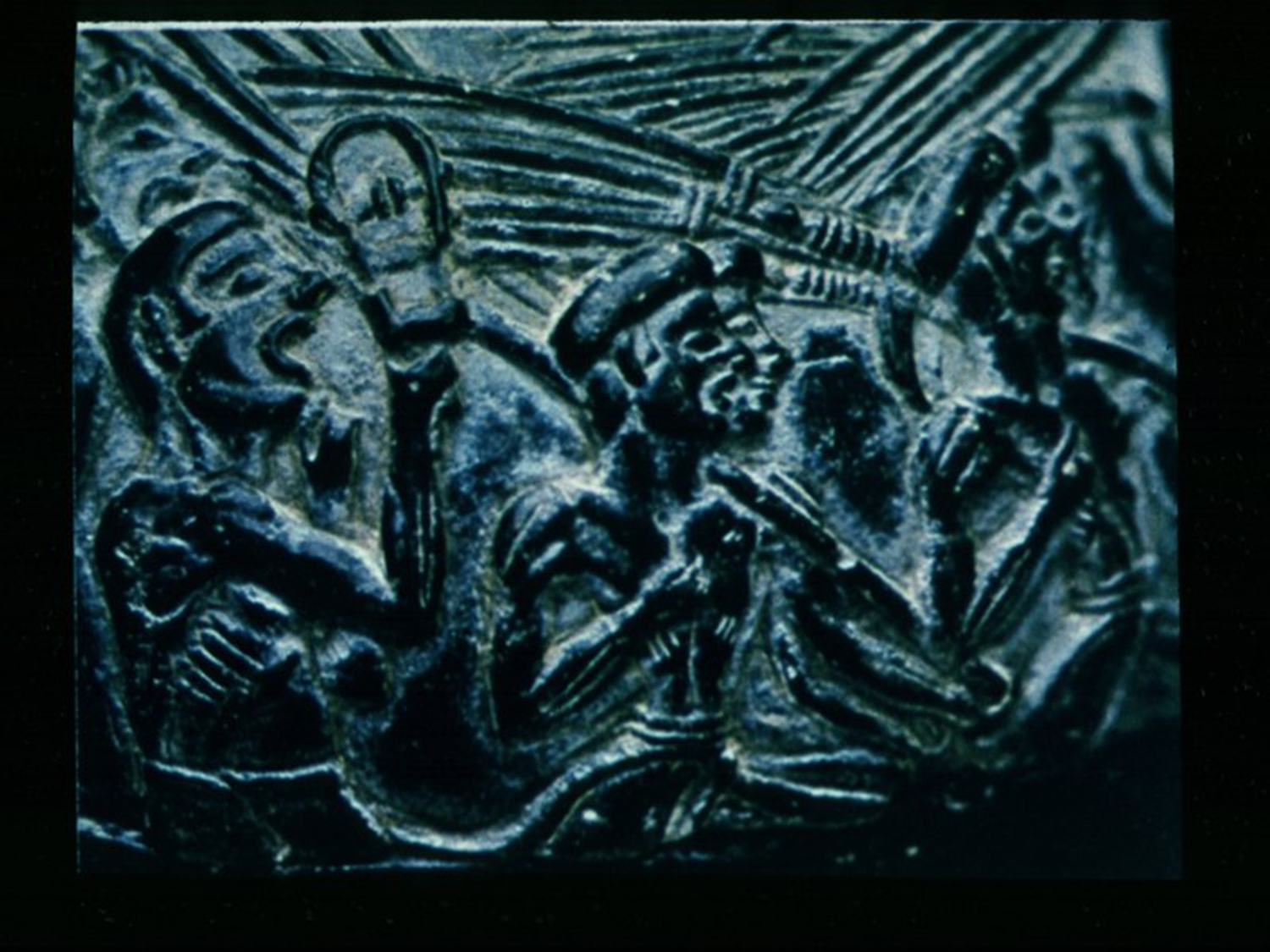

Harvester Rhyton, Minoan New Palace Period,1650 BCE in Greece
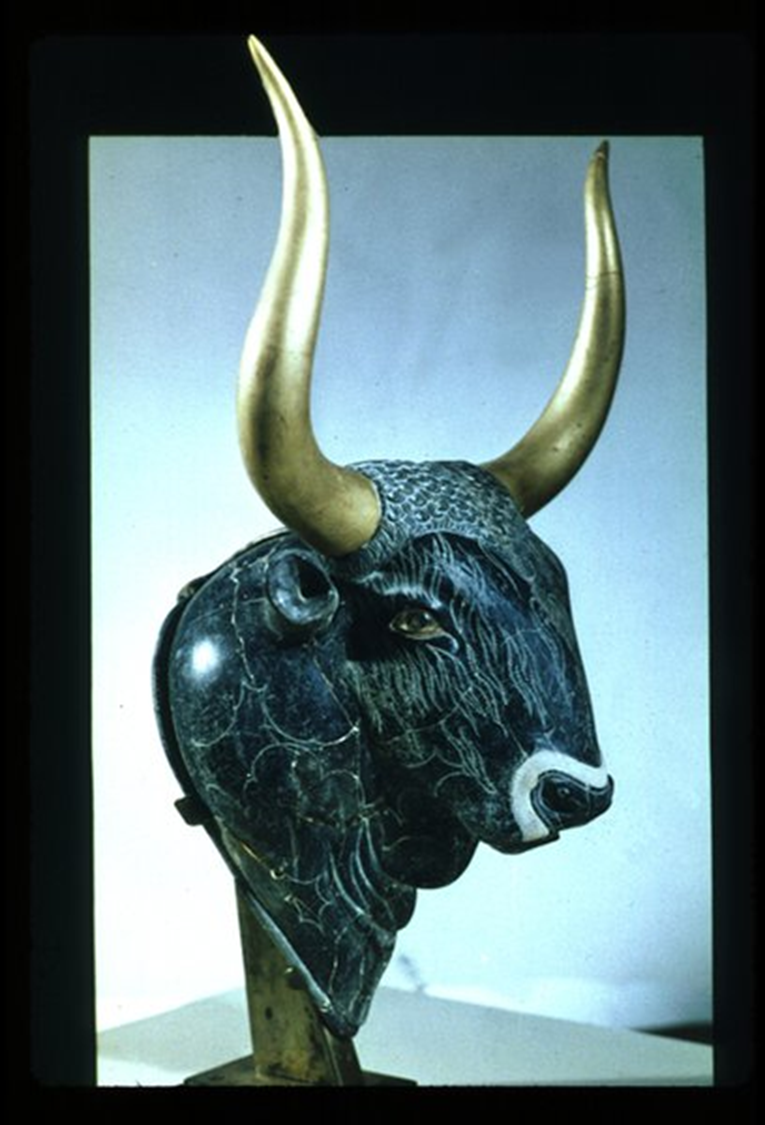

Bull's-head Rhyton, Minoan New Palace Period,1550 BCE in Crete
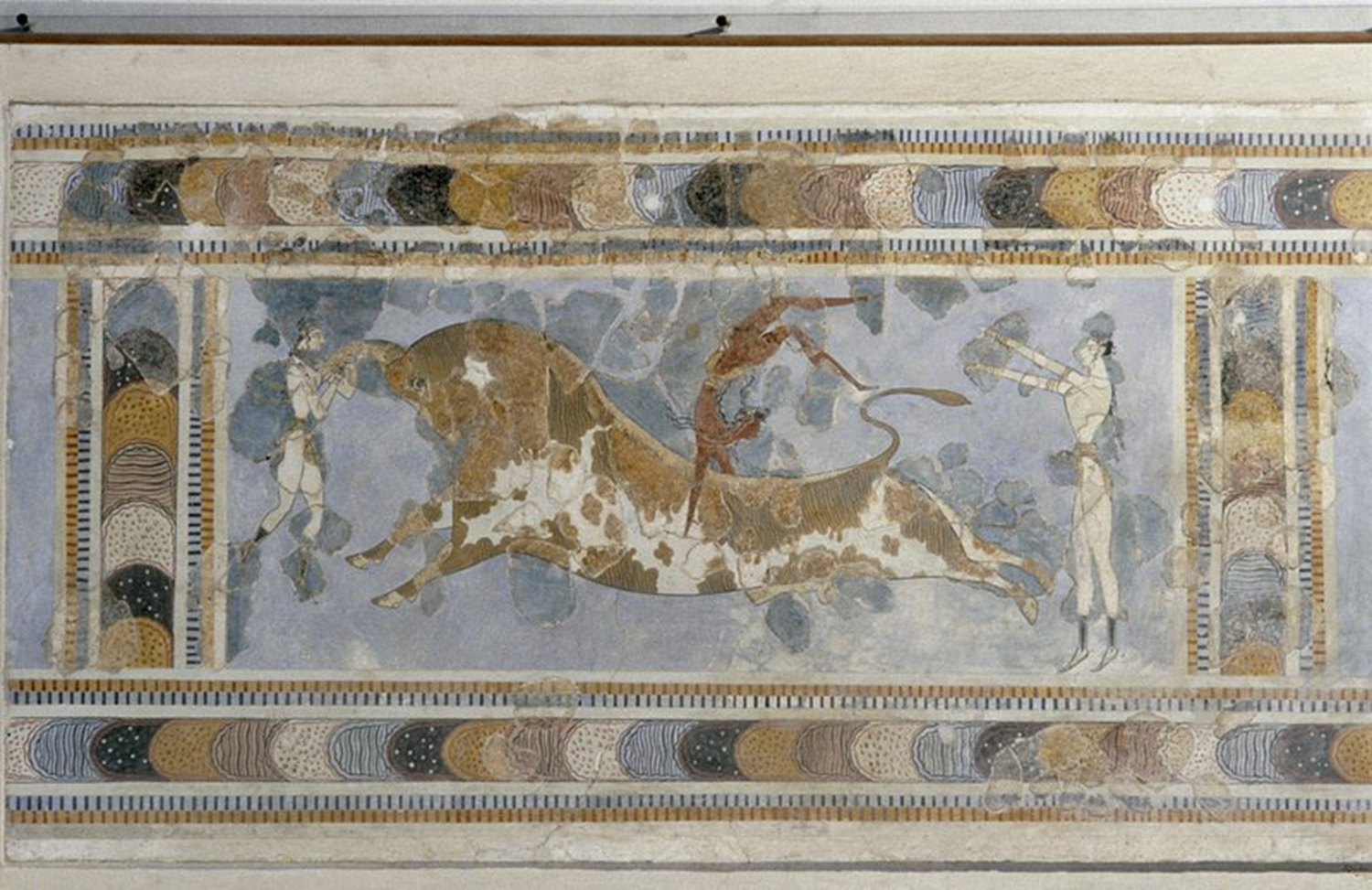

Bull Leaping from the palace complex, Knossos, Crete, Late Minoan Period, 1550 BCE in Crete
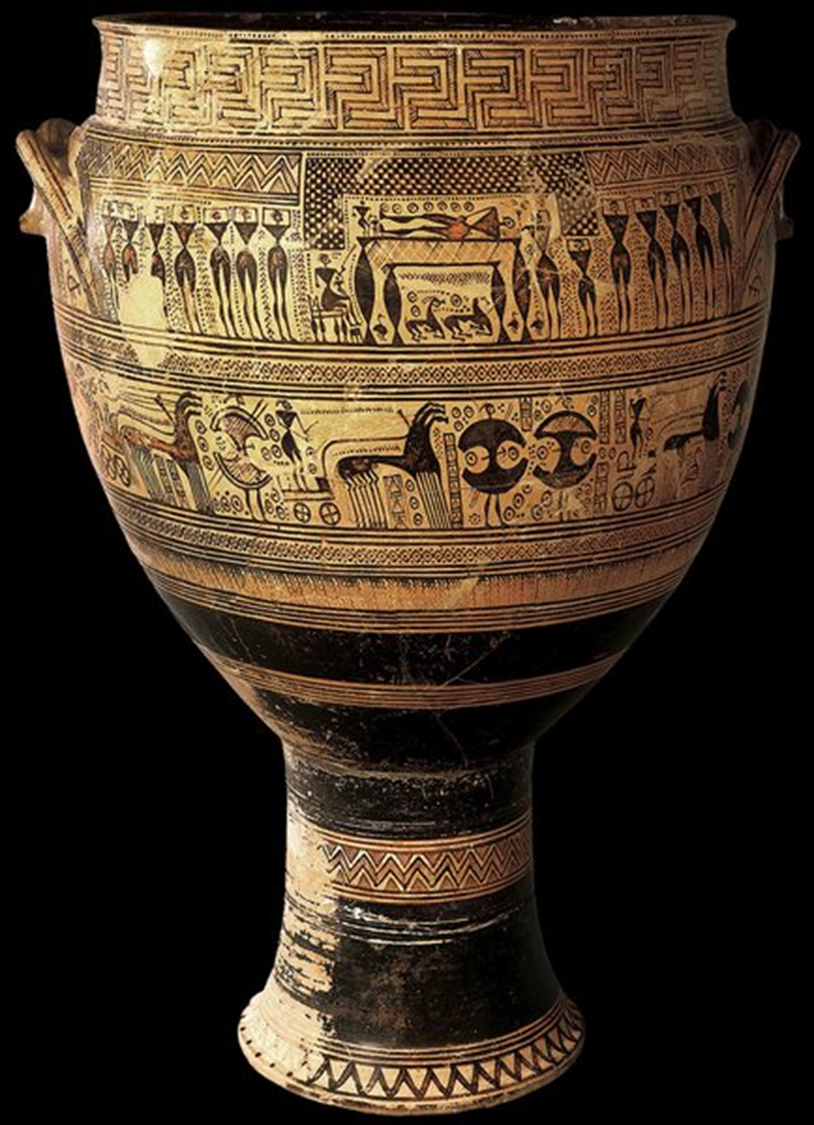

Funerary Krater, Hirschfeld Workshop, 750 BCE in Greece
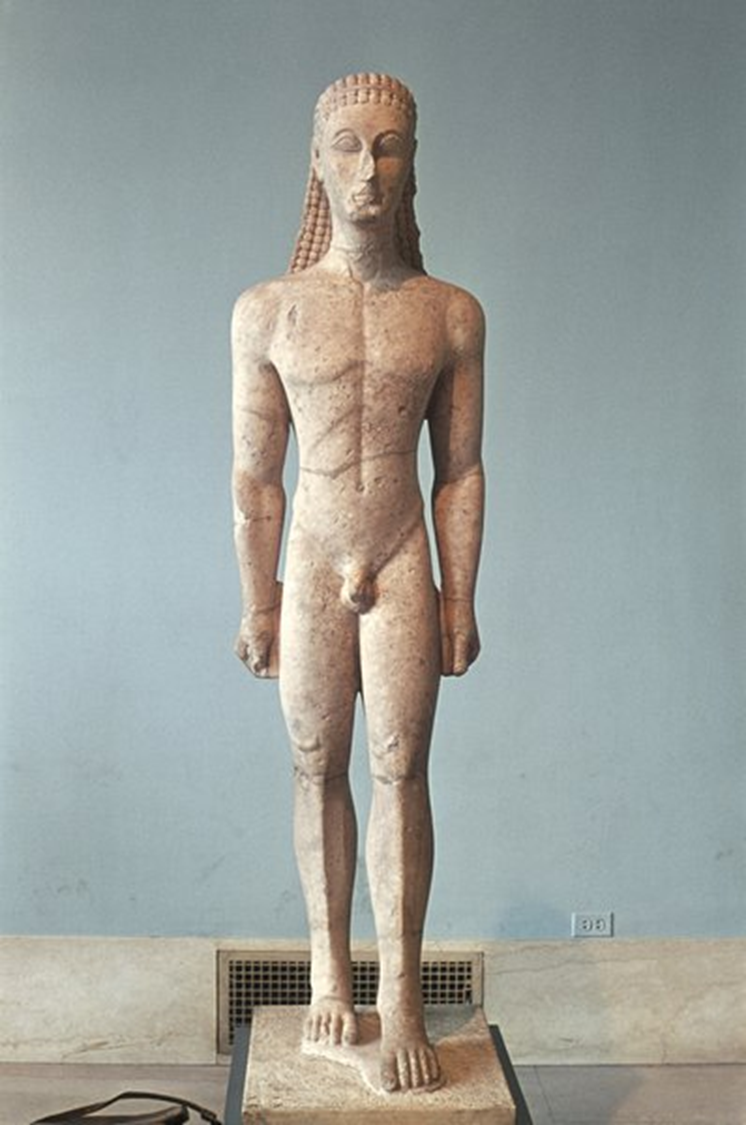

Metropolitan Kouros, Archaic, 600 BCE in Greece
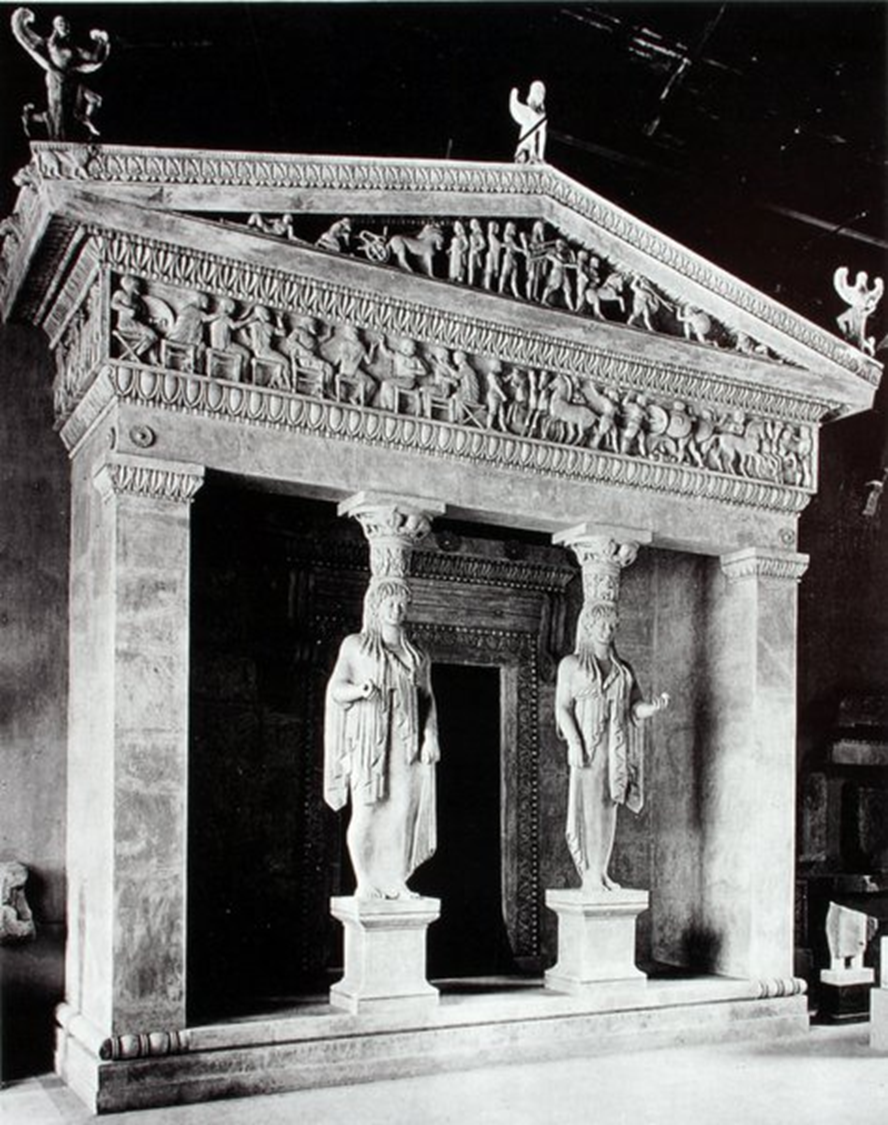

Treasury of the Siphnians, Archaic, 530 BCE in Greece
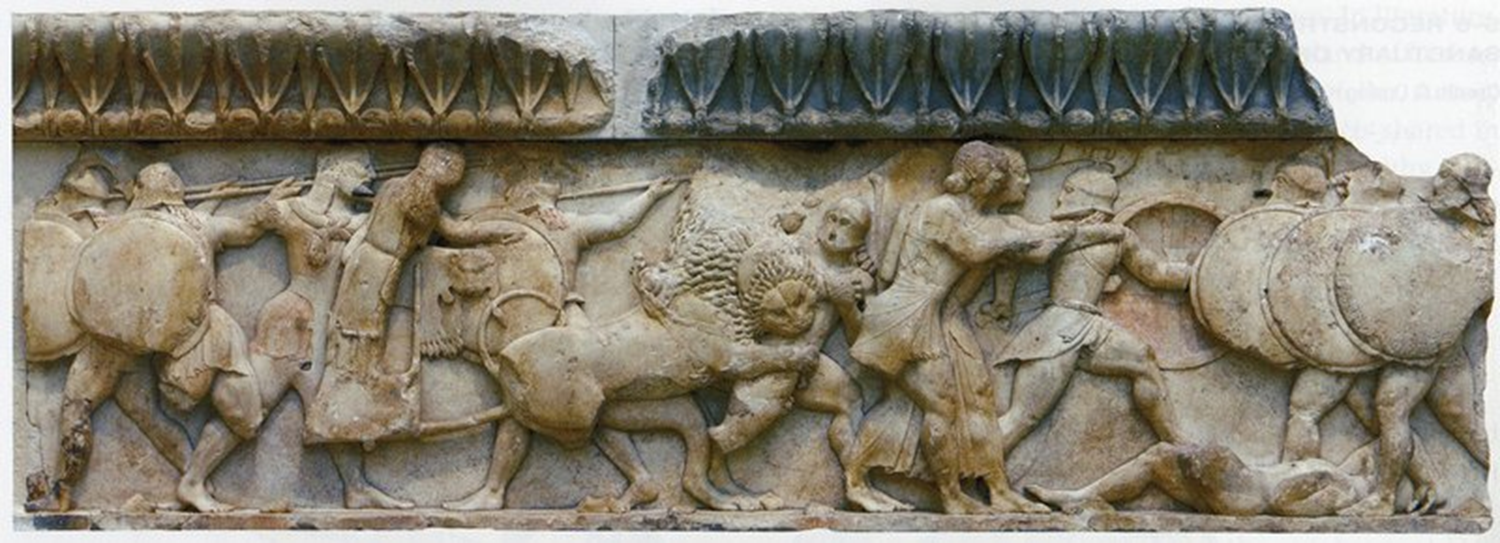

Battle Between the Gods and the Giants, Archaic, 530 BCE in Greece
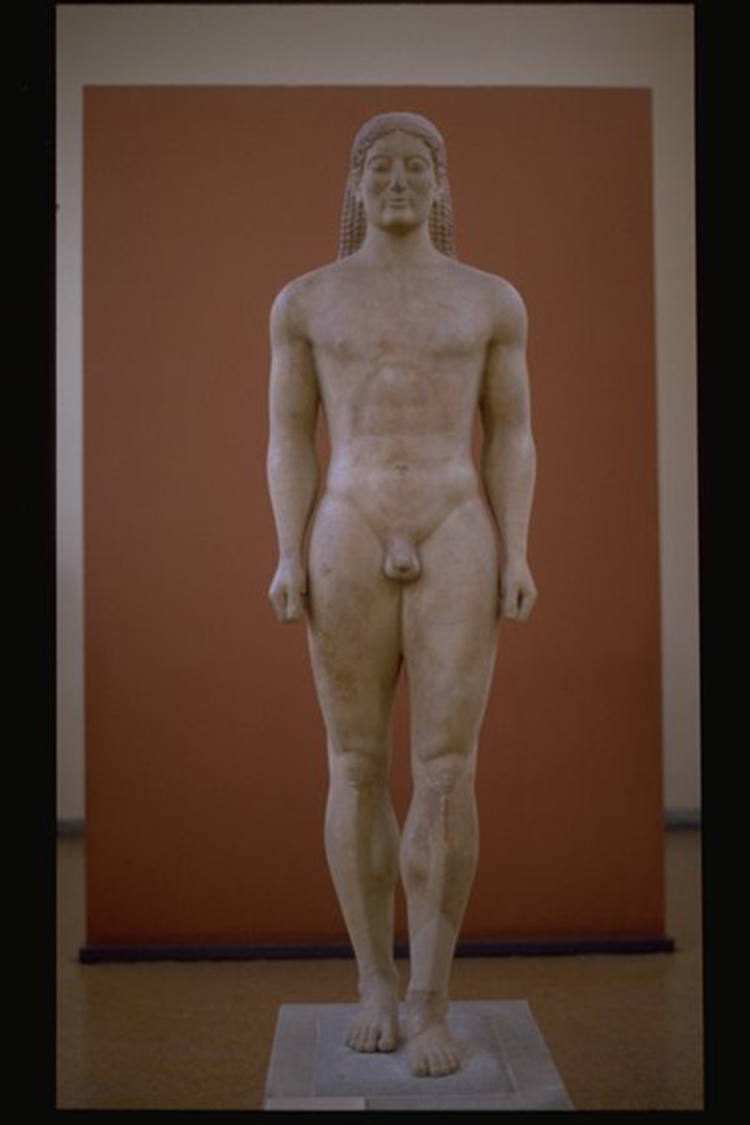

Anavysos Kouros, Archaic, 530 BCE in Greece
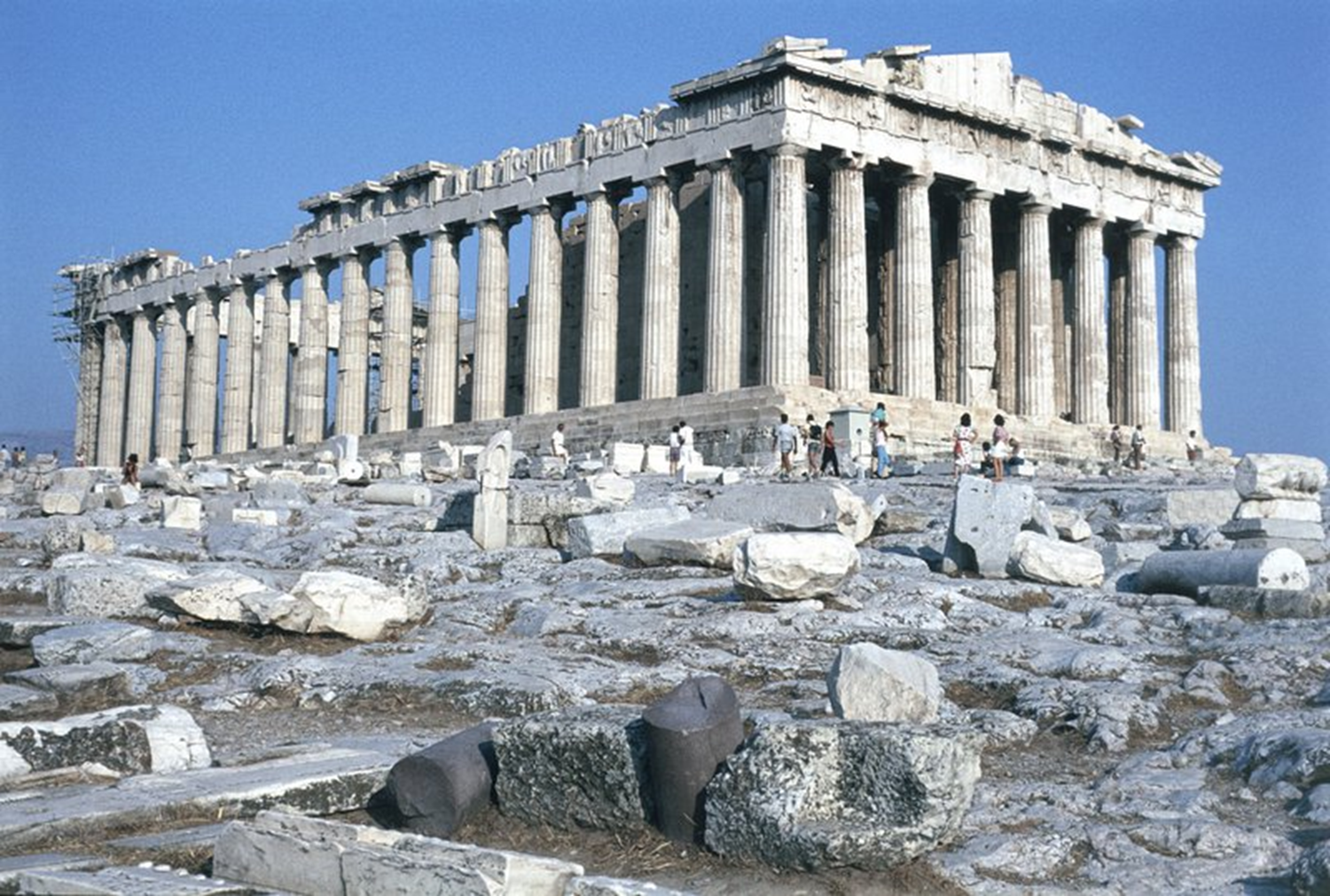

Parthenon, Acropolis, Kallikrates and Iktinos, 447 BCE in Athens
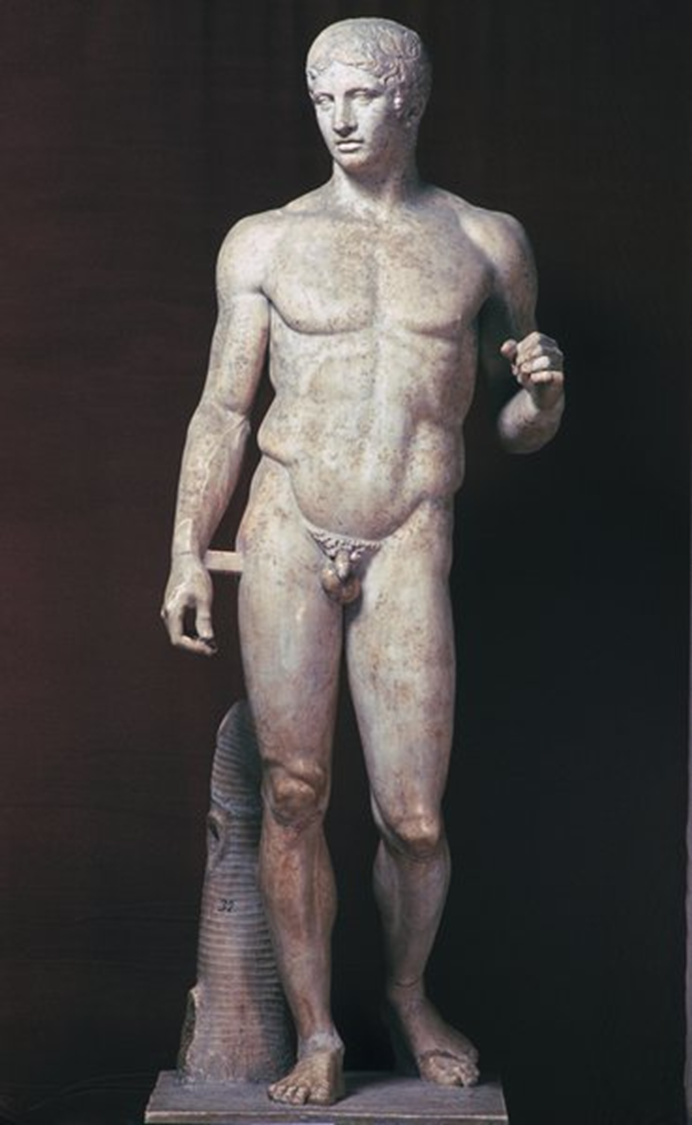

Spear Bearer, Polykleitos, 450 BCE in Greece
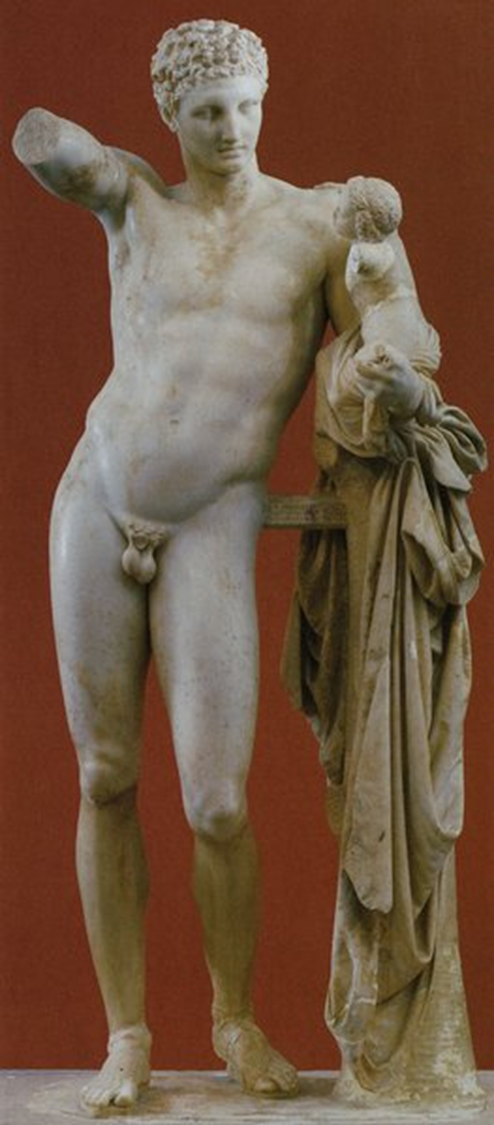

Hermes and the Infant Dionysus, Praxiteles or his followers, 4thc. BCE in Greece
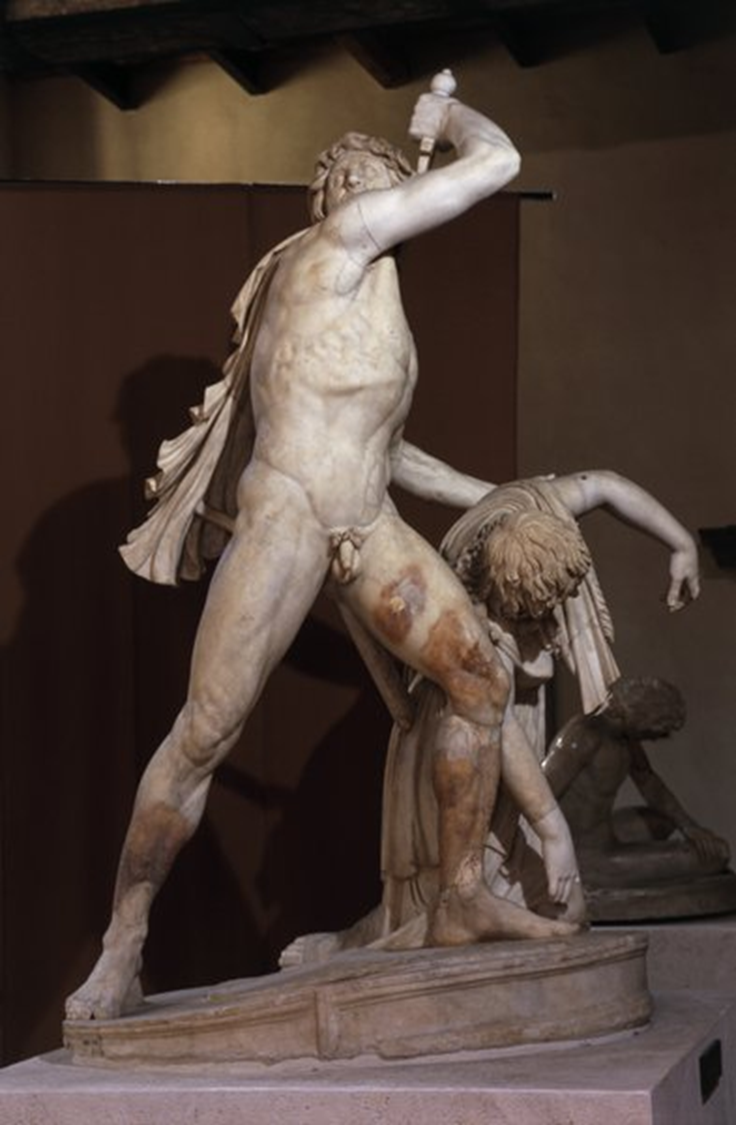

Gallic Chieftain Killing Himself and his Wife from Pergamon, Epigonos, 230 BCE in Greece
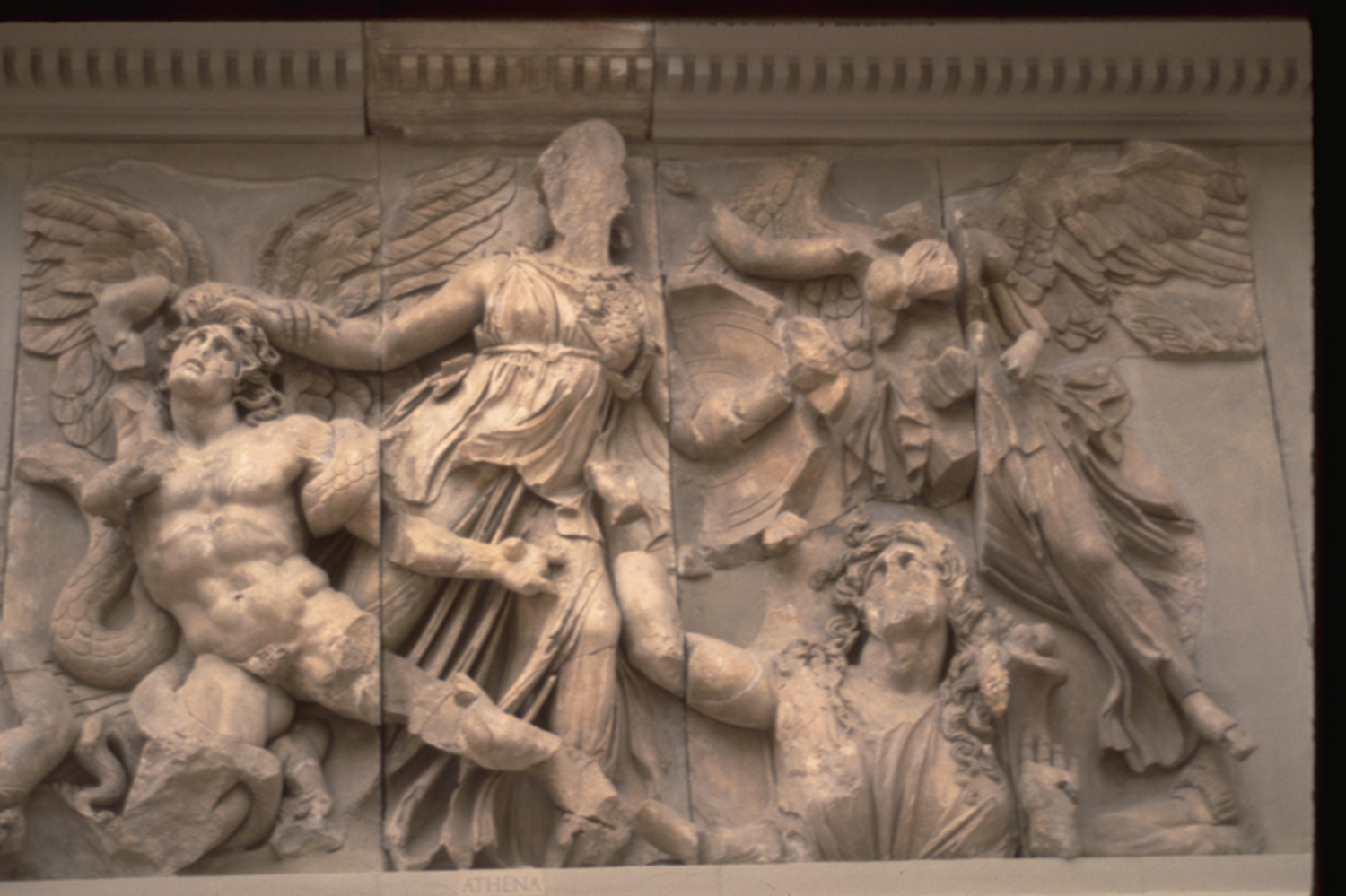

Athena Attacking the Giants on the Altar from Pergamon, Hellenistic, 175 BCE in Ancient Greece
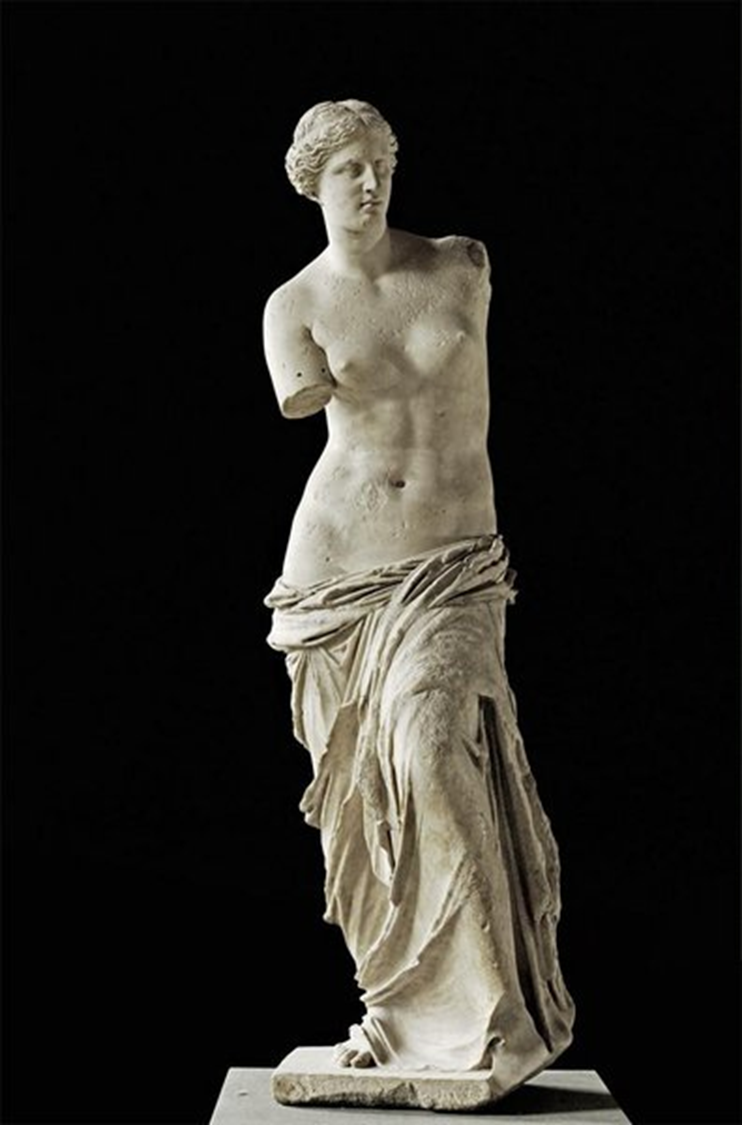

Aphrodite of Melos, 150 BCE, Hellenistic in Greece
iconography
Identifying and studying the subject matter and conventional symbols in works of art.
iconology
Interpreting artworks by relating them to the social, political, religious, and intellectual context of their time
parietal art
wall paintings
therianthrop
half animal and half human figure
modeling
the process of creating the illusion of three-dimensionality on a two-dimensional surface by use of light and shade.
post-and-lintel construction
An architectural system of construction with two or more vertical elements supporting a horizontal element
corbel, corbelling, corbelled arch and vault
An early roofing and arching technique in which each course of stone projects slightly beyond the previous layer until the uppermost corbels meet
megalith
A large stone used in some prehistoric architecture
menhir
a single, upright megalith
alignment
an alignment of menhirs
ziggurat
In ancient Mesopotamia, a tall stepped tower of earthen materials, often supporting a shrine.
registers
A device used in systems of spatial definition
hieratic scale
The use of differences in size to indicate relative importance
composite view
a way of representing a figure so that part of it is seen in profile and part of it is seen frontally.
votive figure
An image created as a devotional offering to a deity.
ba
that aspect of the Egyptian individual that marks him or her as an individual. It refers to those non-physical properties that make a person unique.
ka
the creative life-force of each individual, human or divine. It marks the difference between the living and the dead, and comes into being at birth. It must be united with the ba in order for the akh to come into being.
akh
The enduring and unchanging form of the deceased in the afterlife created by the reunion of the ba and the ka.
ankh
A looped cross signifying life, used by ancient Egyptians.
necropolis
A large cemetery or burial area; literally a “city of the dead.”
sed festival
an ancient Egyptian festival theoretically held every 30th year of the reign of a king that reestablishes the power and authority of the king over Egypt
relief sculpture
A 3D image or design whose flat background surface is carved away to a certain depth, setting off the figure
high relief
the extent of projection of the image from the background
sunken relief
when the image is carved below the original surface of the background
buon fresco
Murals painted onto wet plastered surfaces
fresco secco
Murals painted onto dry plastered surfaces
rhyton
A vessel in the shape of a figure or an animal, used for drinking or pouring liquids on special occasions
repoussé
A technique of pushing or hammering metal from the back to create a protruding image
megaron
The main hall of a Mycenaean palace or grand house
humanism
the idea that human beings are the primary measure of all things.
rationalism
the belief that human reasoning is the source for understanding the world.
idealism
a belief in and the pursuit of perfect forms. These forms may be political, social, economic, religious or artistic.
expressionism
Artistic styles in which aspects of works of art are exaggerated to evoke subjective emotions
Doric Order
the column shaft of the Doric order can be fluted or smooth-surfaced and has no base
Ionic Order
the column of the Ionic order has a base, a fluted shaft, and a capital decorated with volutes
Corinthian order
the most ornate of the orders
Kouros
An Archaic Greek statue of a young man or boy.
black-figure vase
A technique of ancient Greek ceramic decoration in which black figures are painted on a red clay ground
red-figure vase
A technique of ancient Greek ceramic decoration characterized by red claycolored figures on a black background
contrapposto
the Classical convention of representing human figures with opposing alternations of tension and relaxation
syncretism (syncretic, adj.form)
A process whereby artists assimilate and combine images and ideas from different cultural traditions, beliefs, and practices, giving them new meanings.