Energy & Enzymes (AP Bio Topics 3.1-3.4)
1/55
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
56 Terms
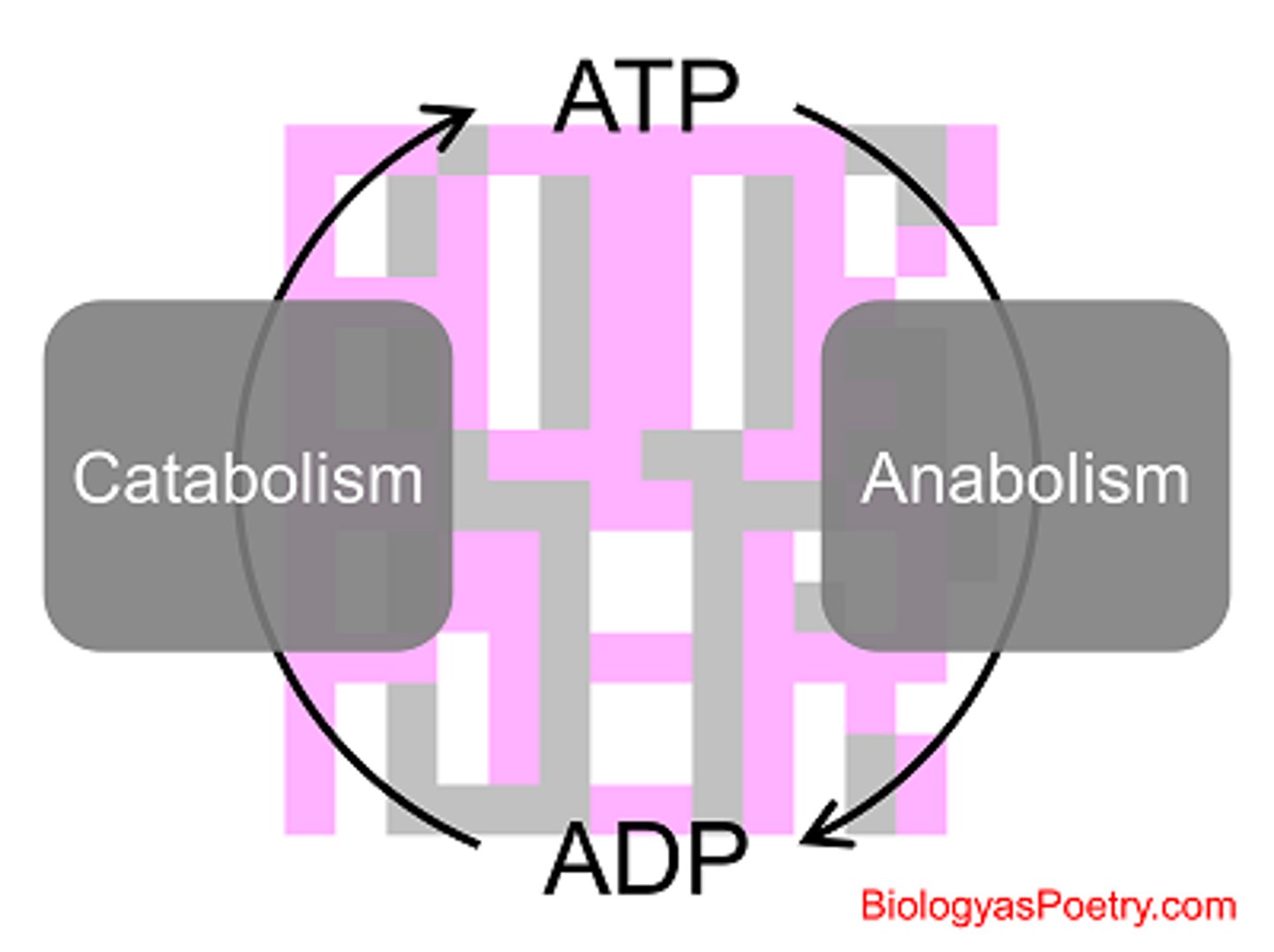
metabolism
The sum of the building & breaking reactions occurring in cells
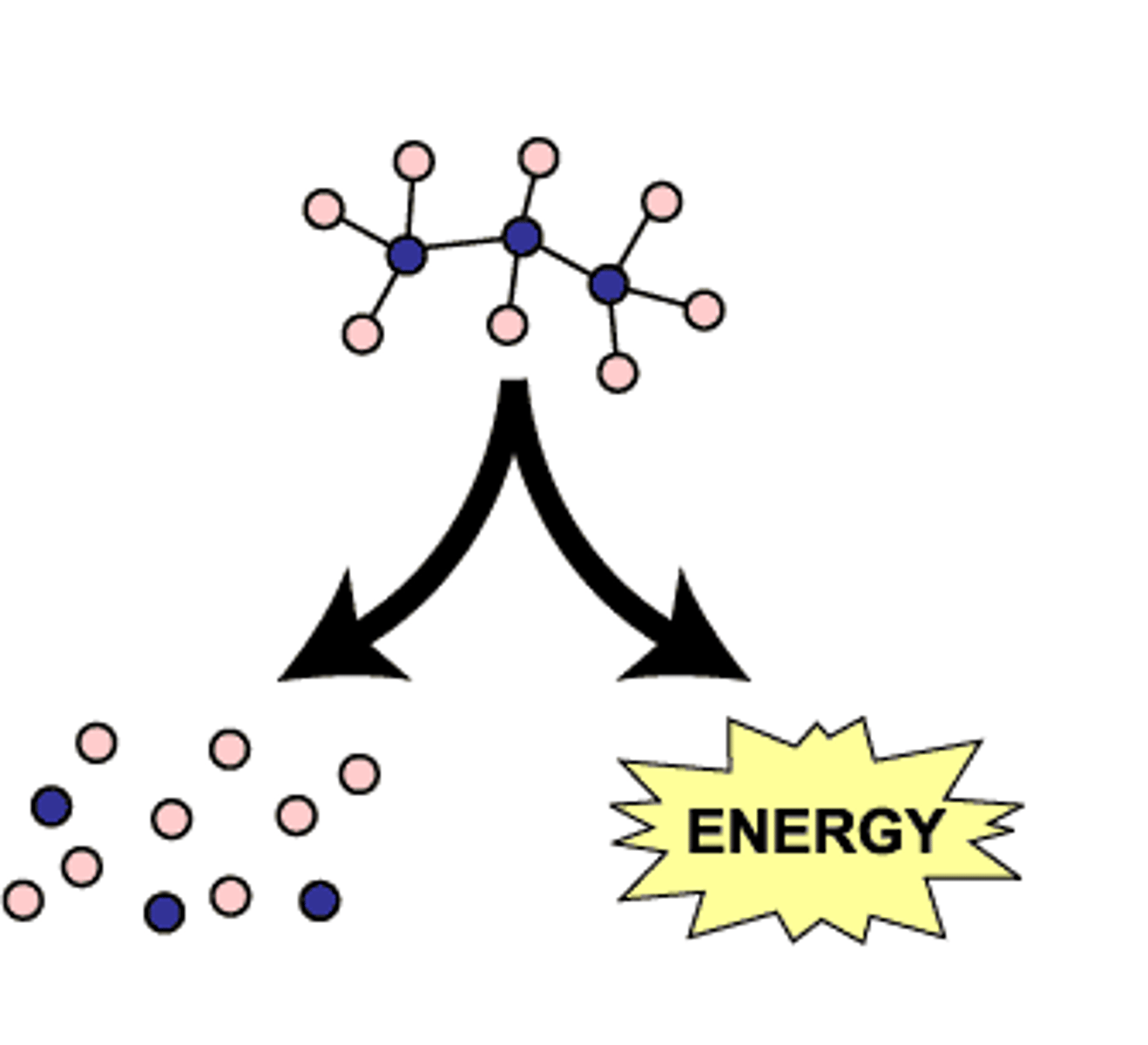
catabolic pathways
Series of reactions that release energy by breaking down complex molecules into simpler compounds; Negative ΔG
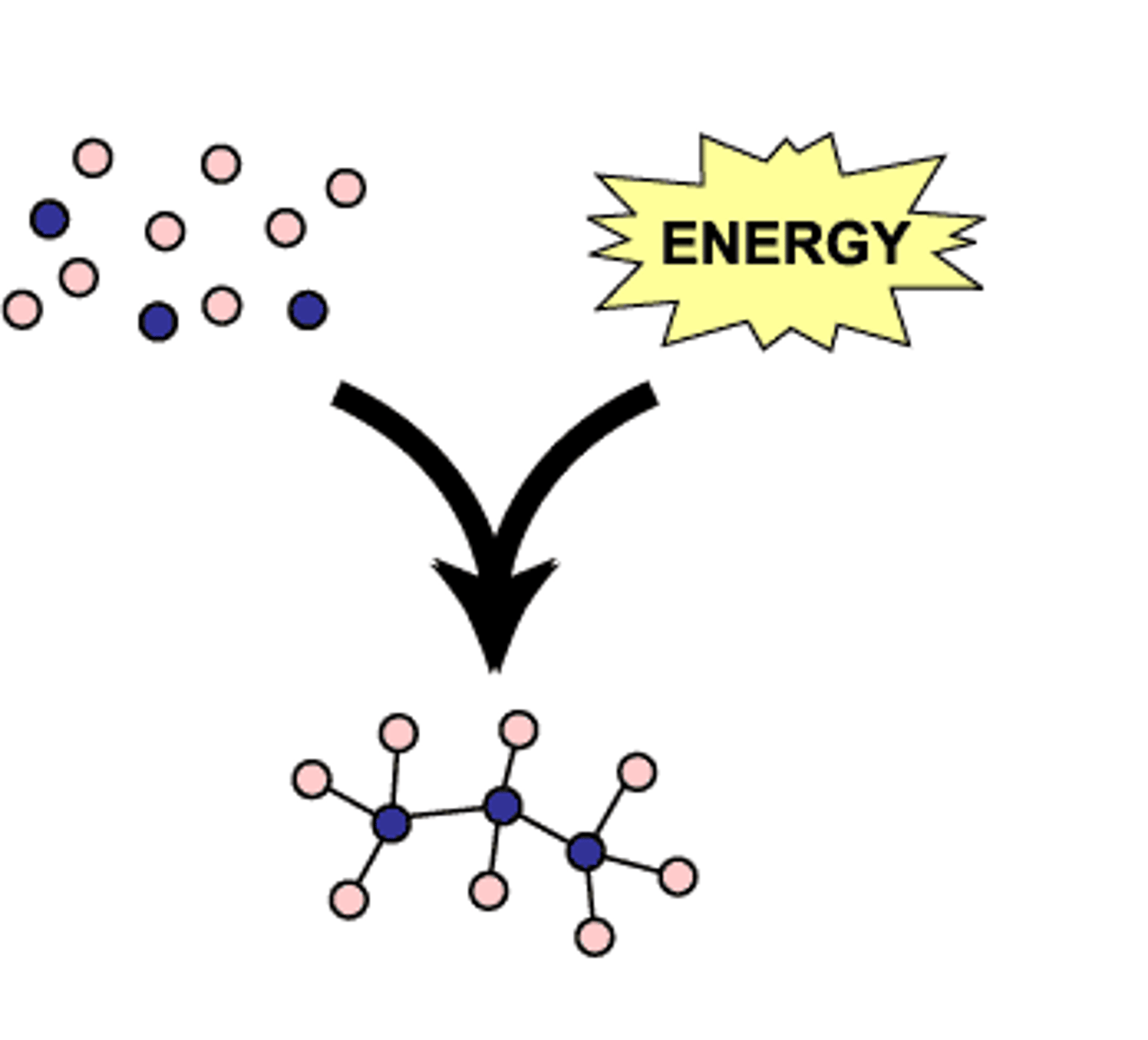
anabolic pathways
Series of reactions that consume energy to build complicated molecules from simpler ones; Positive ΔG
kinetic energy
Energy associated with relative motion of objects.

thermal energy
Kinetic energy associated with the random movement of molecules or atoms. (heat)

potential energy
Stored energy.

entropy
A measure of disorder or randomness. Tends to increase in the universe.

free energy
Measures the portion of a system's energy that can perform work when temperature and pressure are uniform throughout the system, as in a living cell.
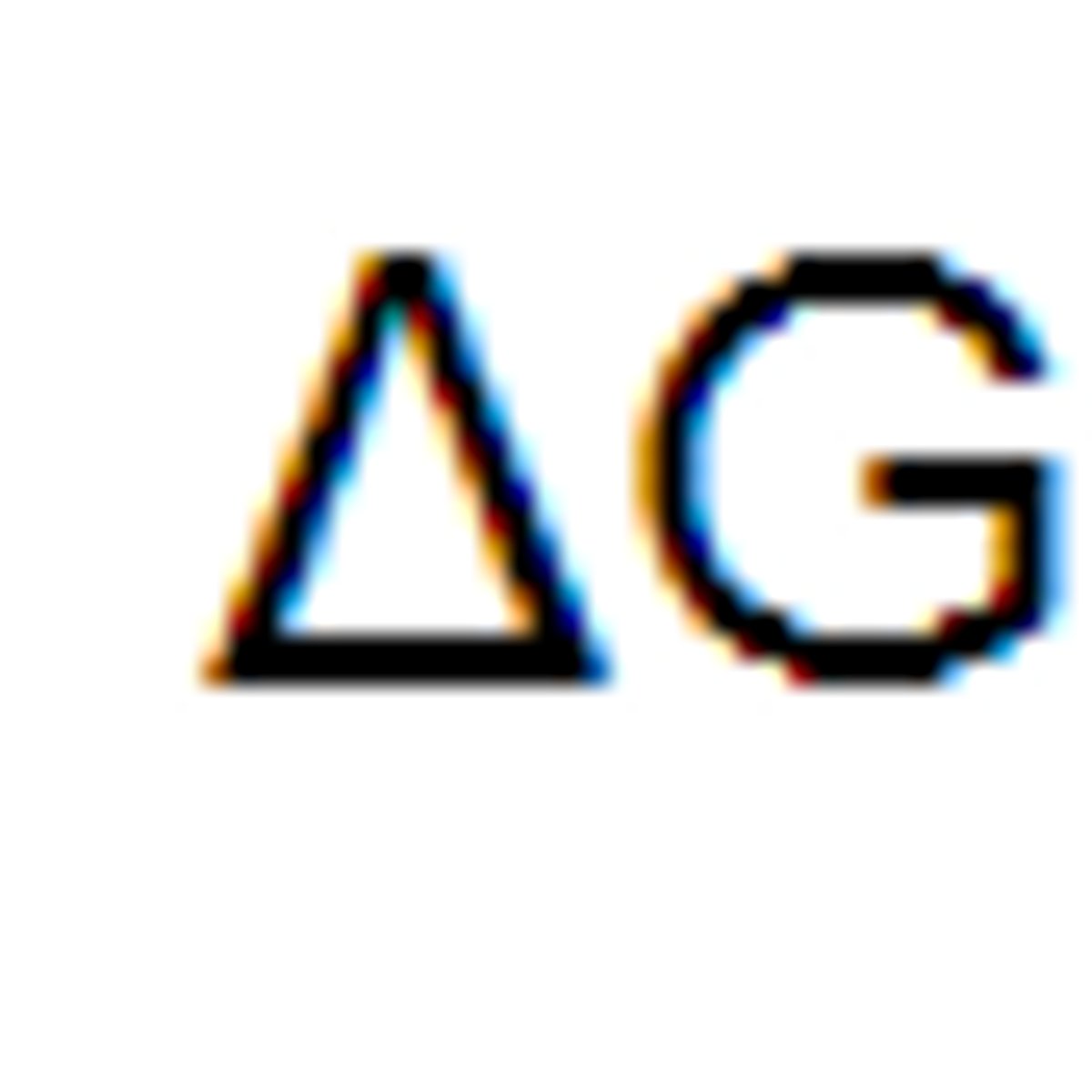
endergonic reaction
Reaction that absorbs free energy from its surroundings.
exergonic reaction
Reaction that proceeds with a net release of free energy.
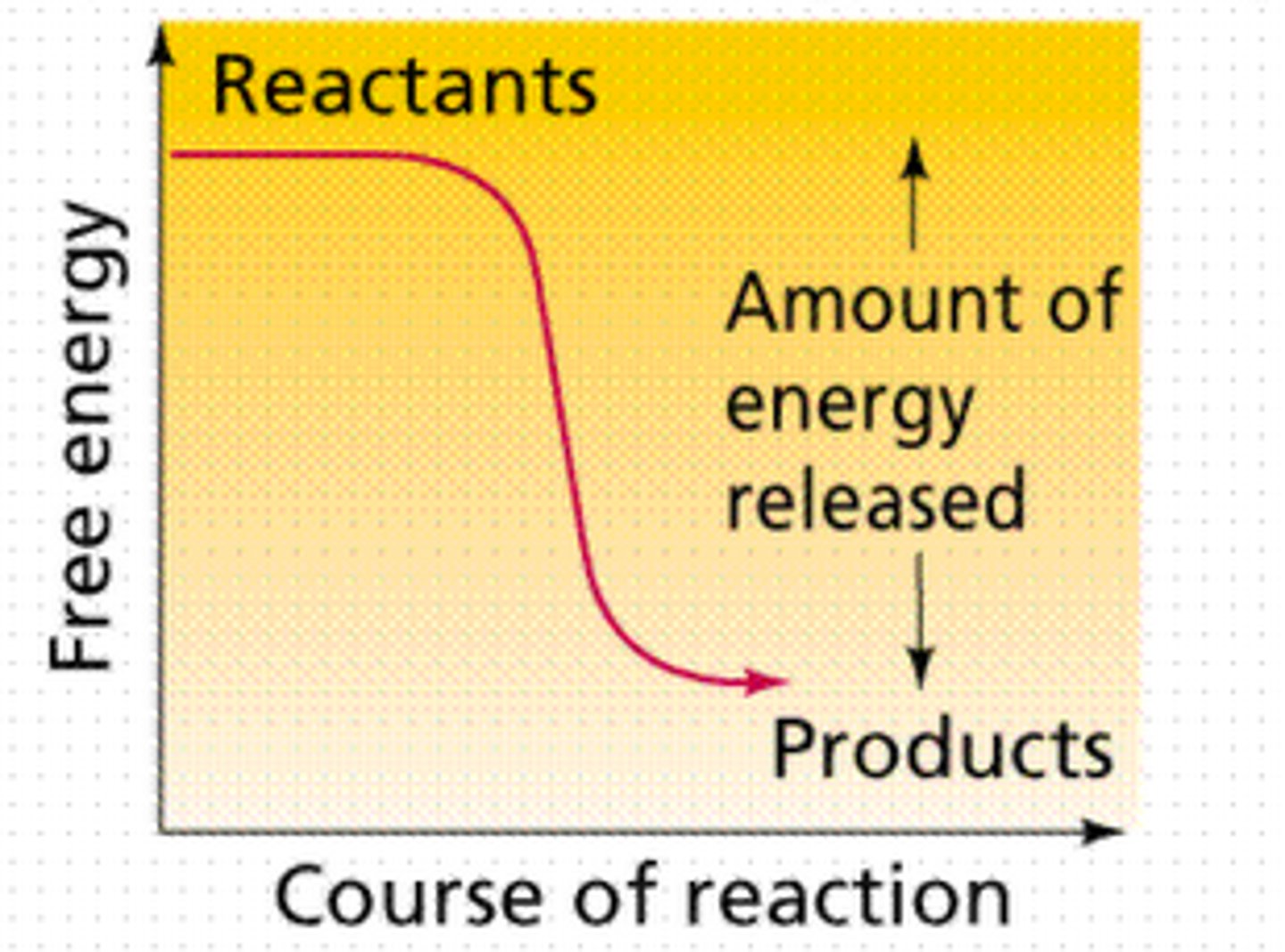
energy coupling
The use of an exergonic process to drive an endergonic one.
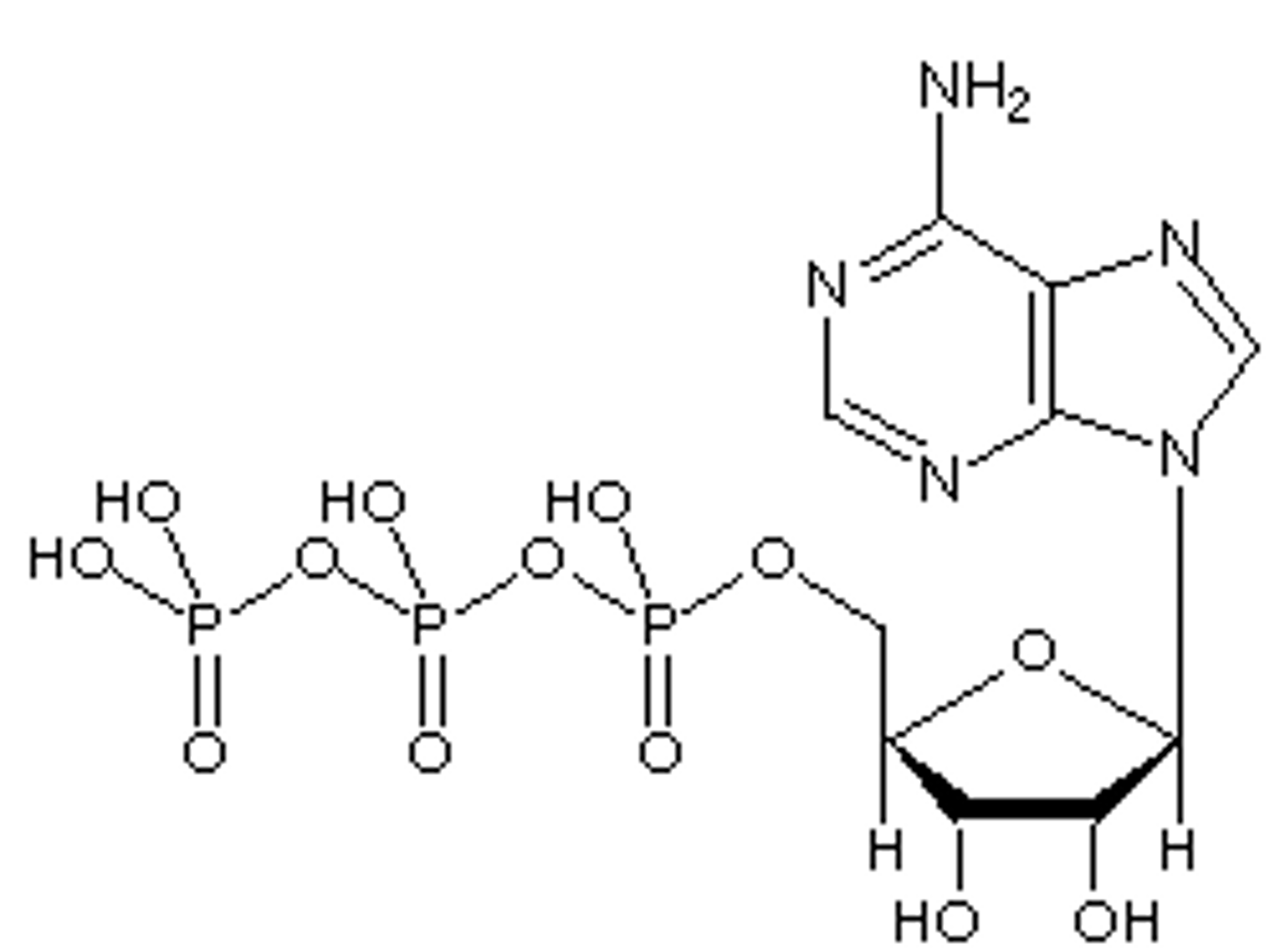
ATP (adenosine triphosphate)
Composed of a sugar ribose, nitrogenous base adenine, and a chain of three phosphate groups bonded to it.
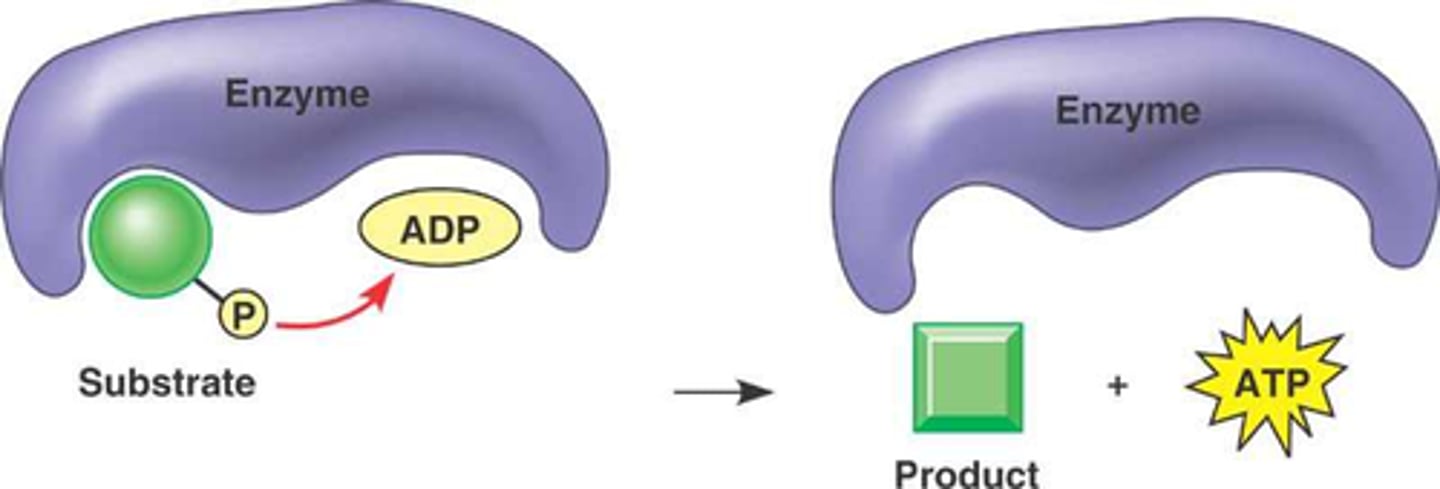
phosphorylation
The metabolic process of introducing a phosphate group into an organic molecule.
catalyst
A chemical agent that speeds up a reaction without being consumed by the reaction.
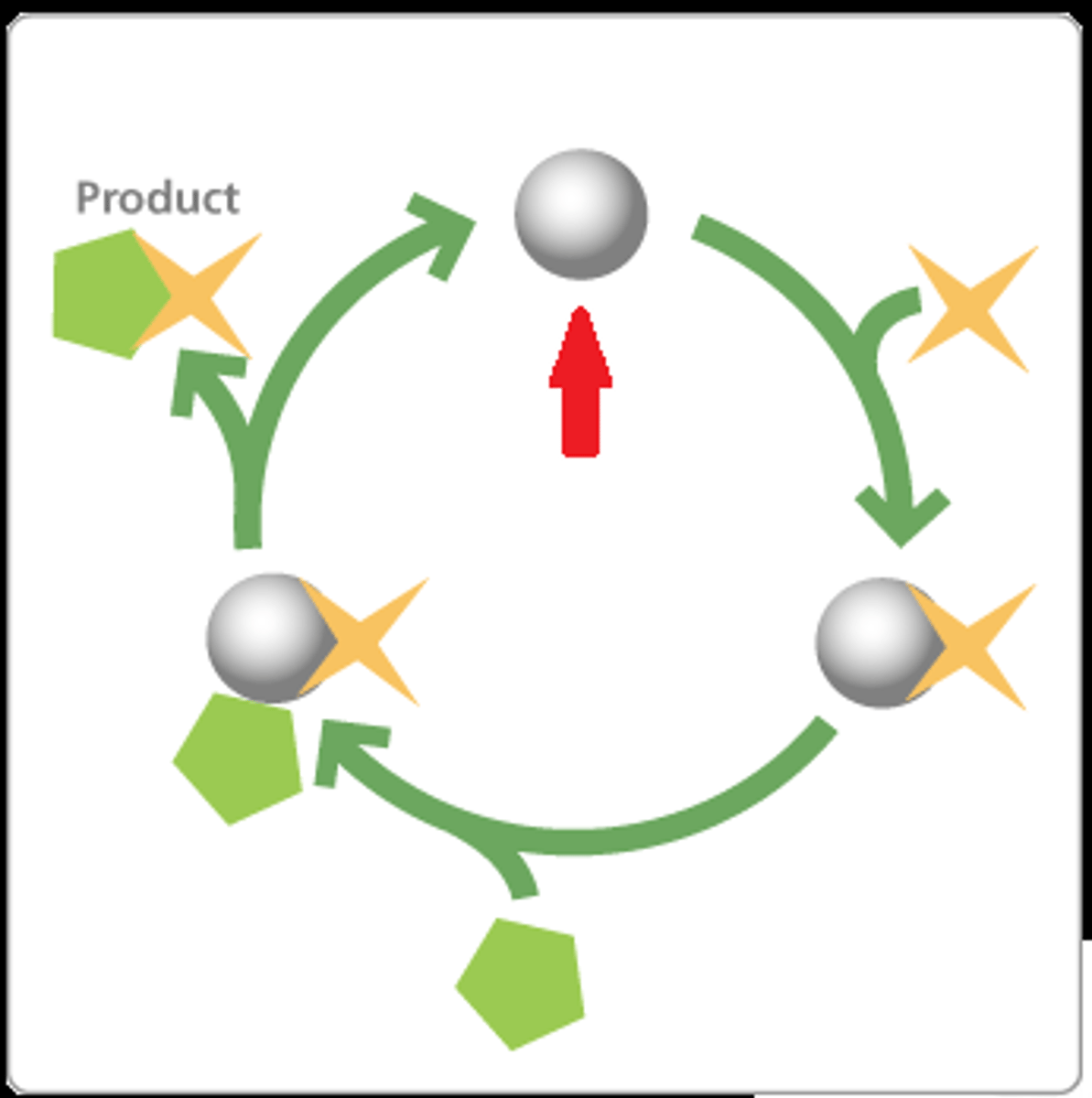
enzyme
Protein that speeds up reactions. Typically end in "ase" (ex. Peroxidase, Lipase)

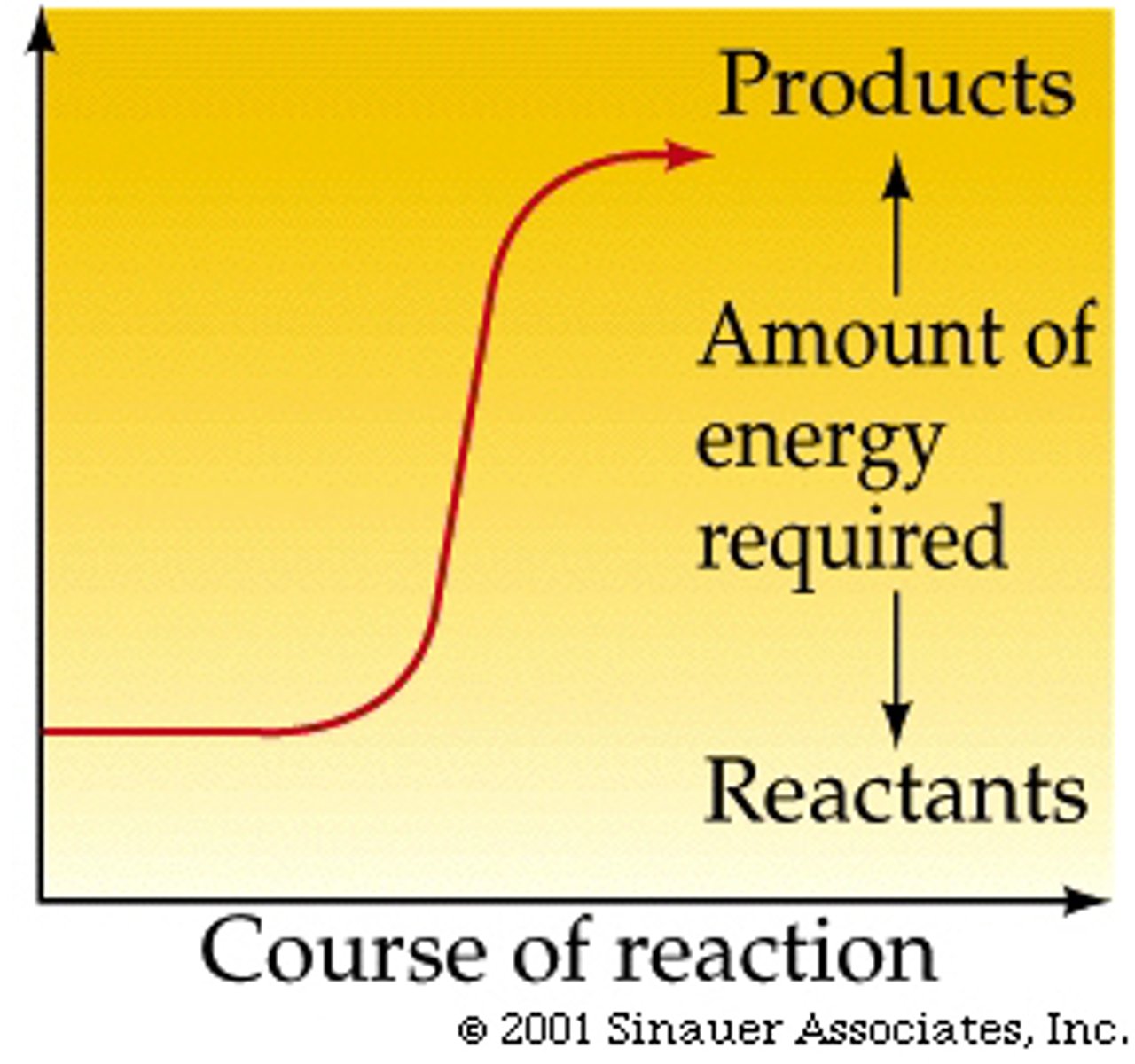
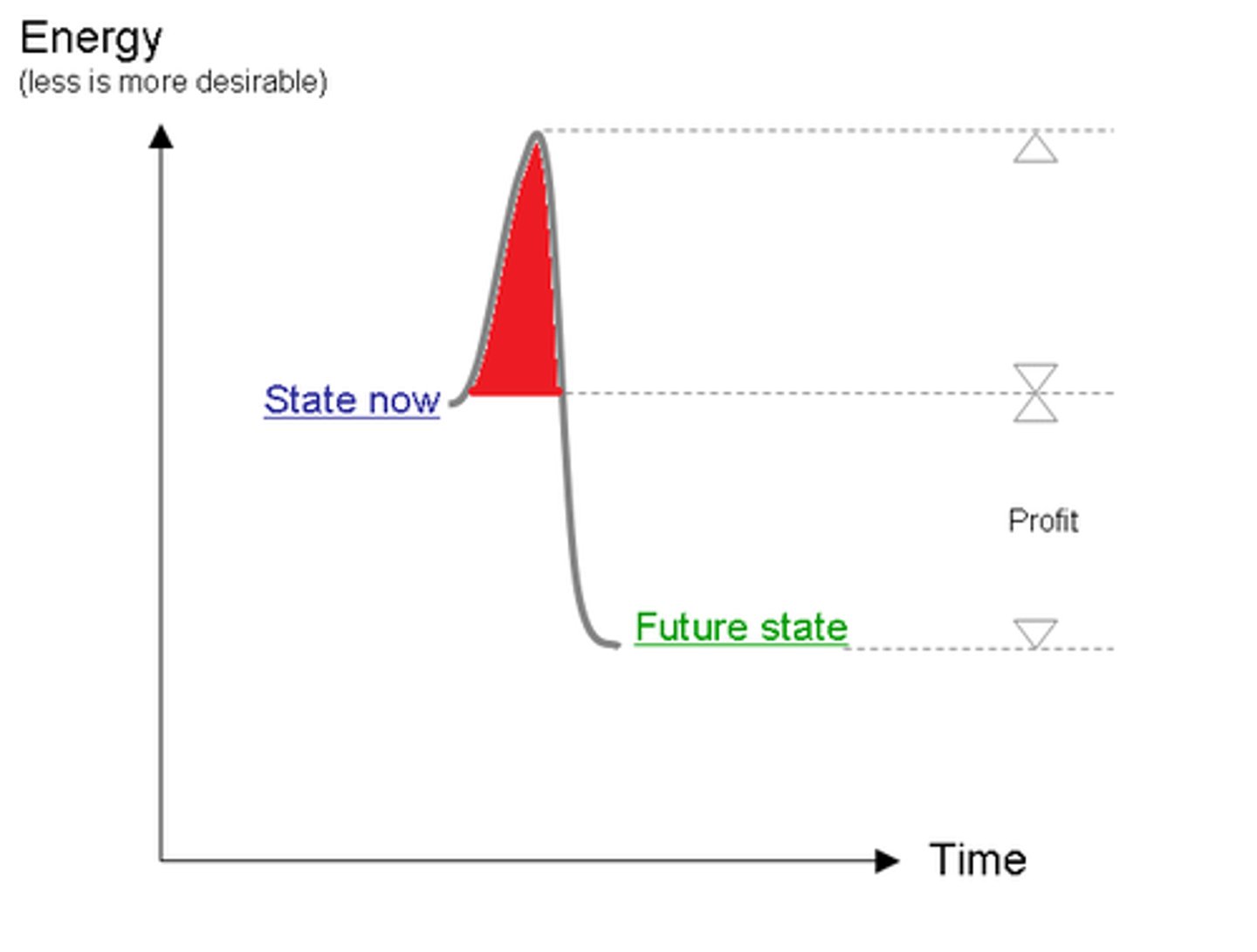
activation energy
The amount of energy needed to push the reactants over an energy barrier.
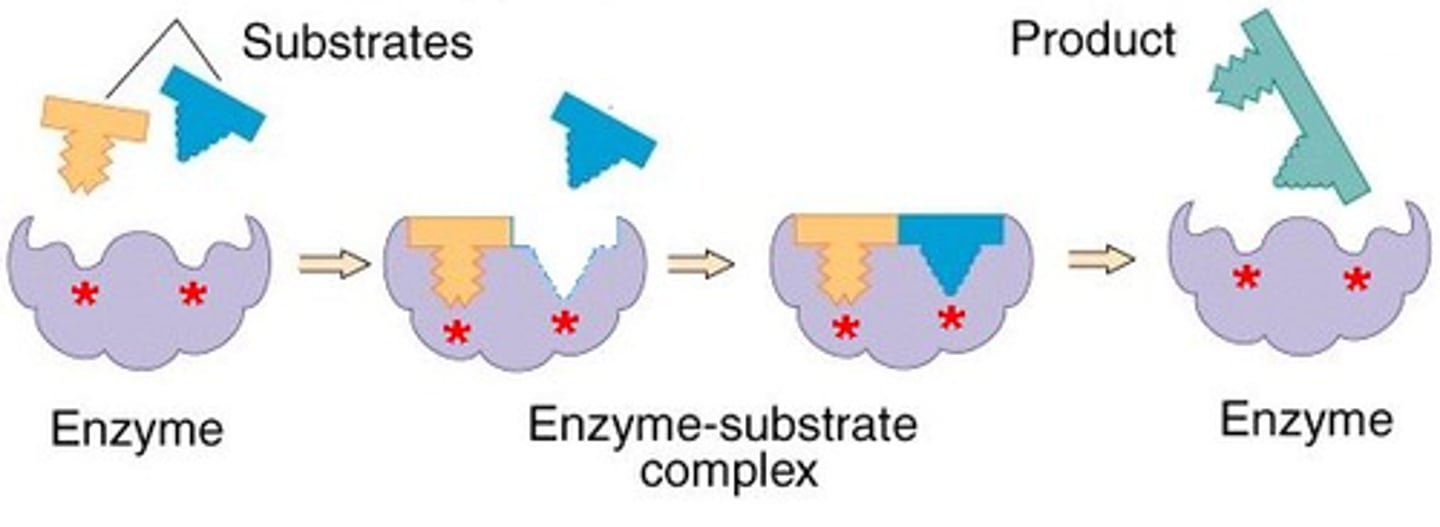
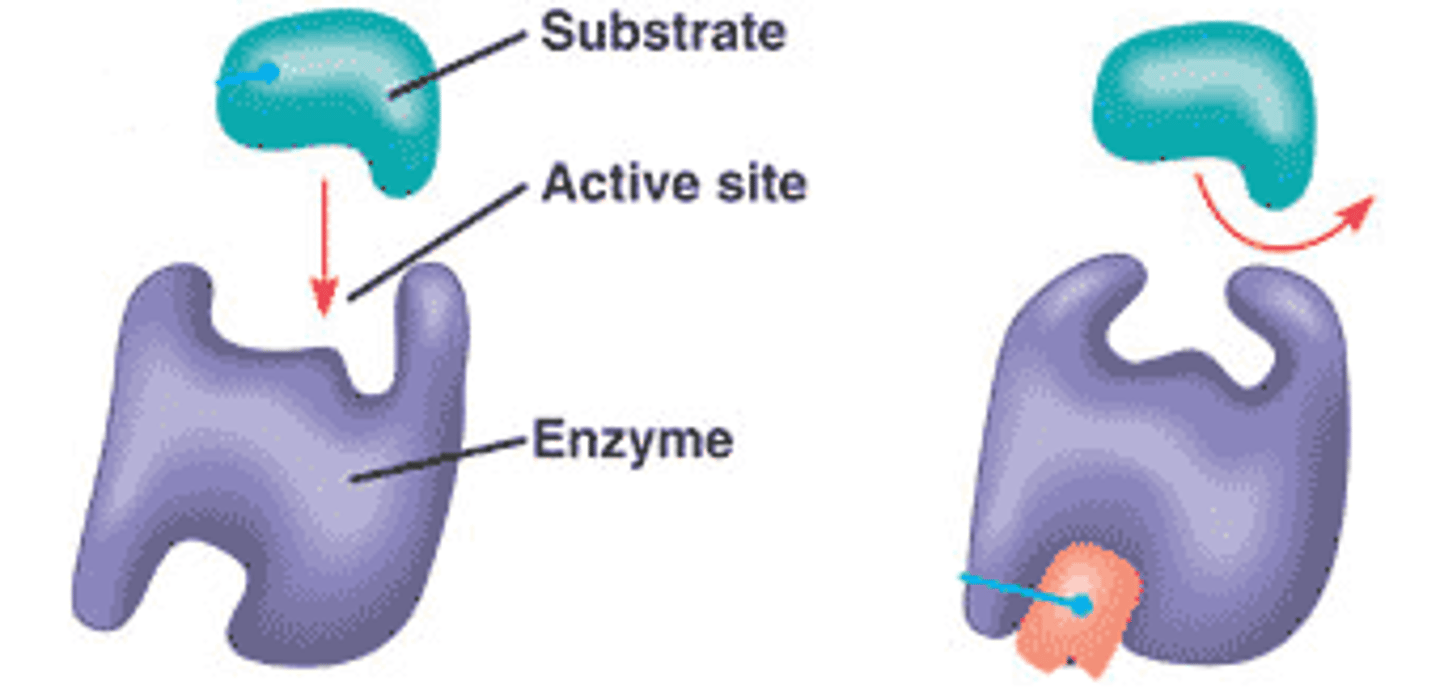
enzyme-substrate complex
When an enzyme binds to its substrate, it forms:

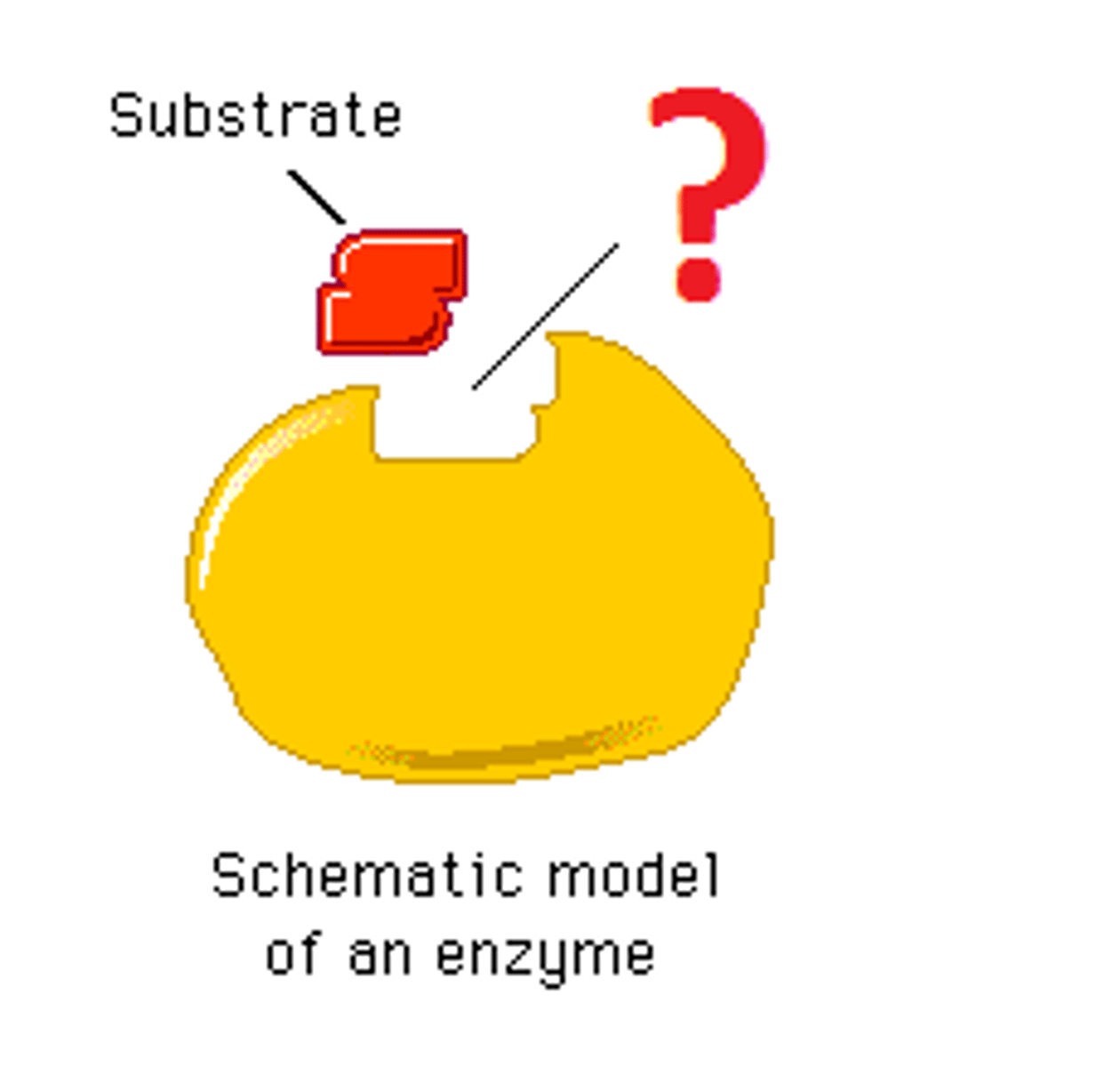
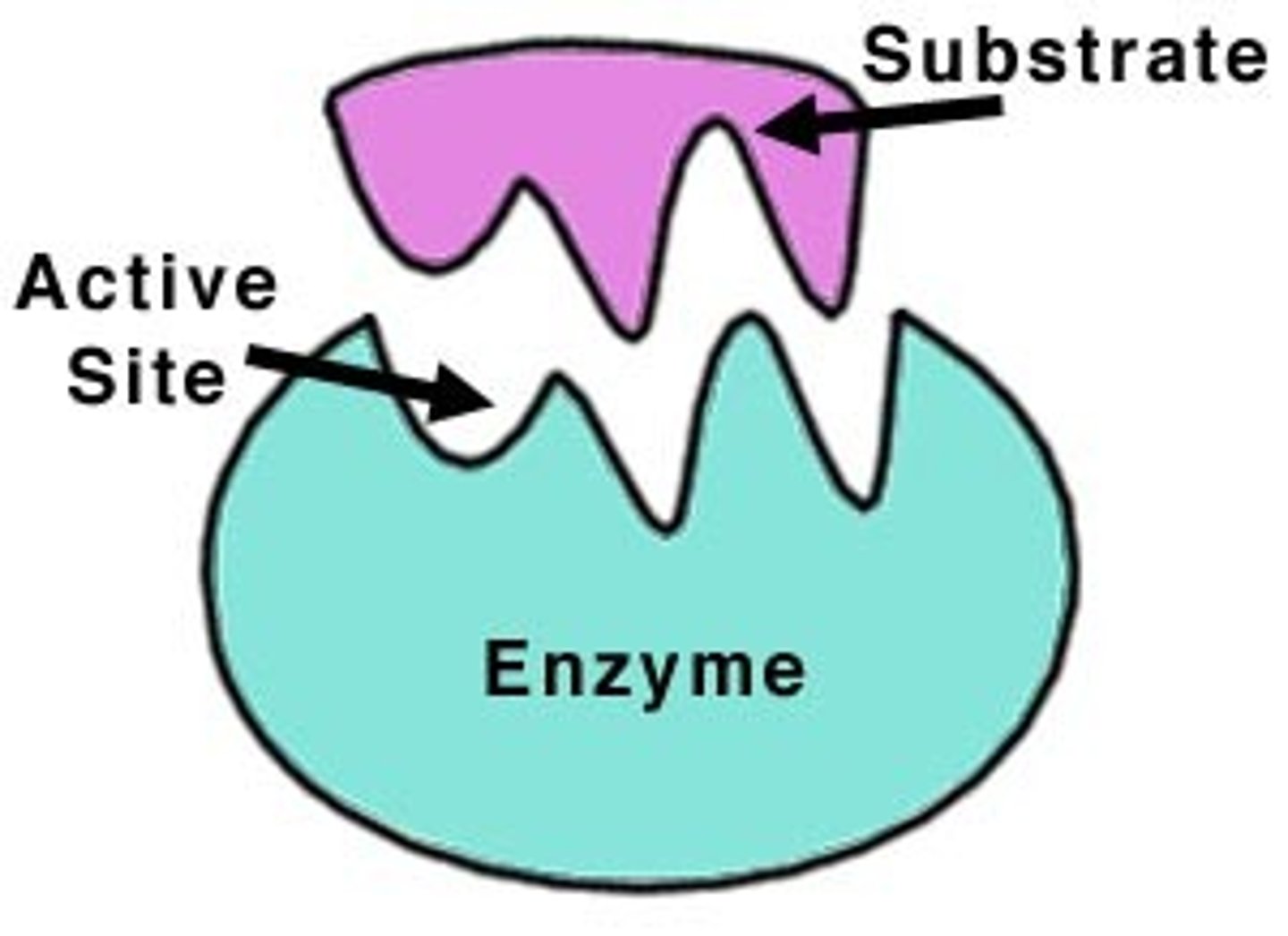
active site
A pocket or groove on the surface of the enzyme where a substrate can bind.
induced fit model
States that the enzyme and substrate undergo conformational changes to interact fully with one another (as opposed to "Lock & Key"
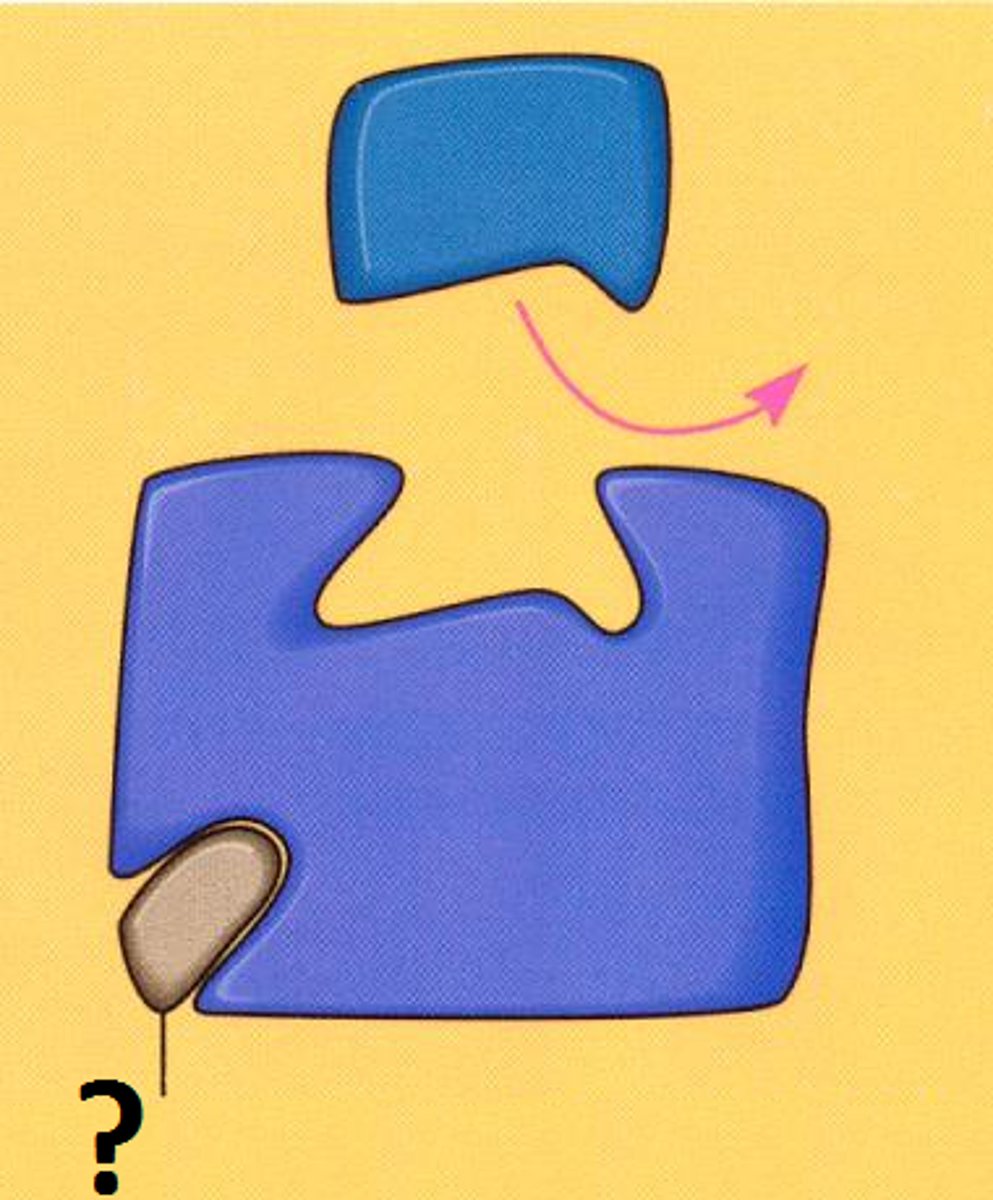
competitive inhibitors
Reduce the productivity of enzymes by blocking substrates from entering active sites.
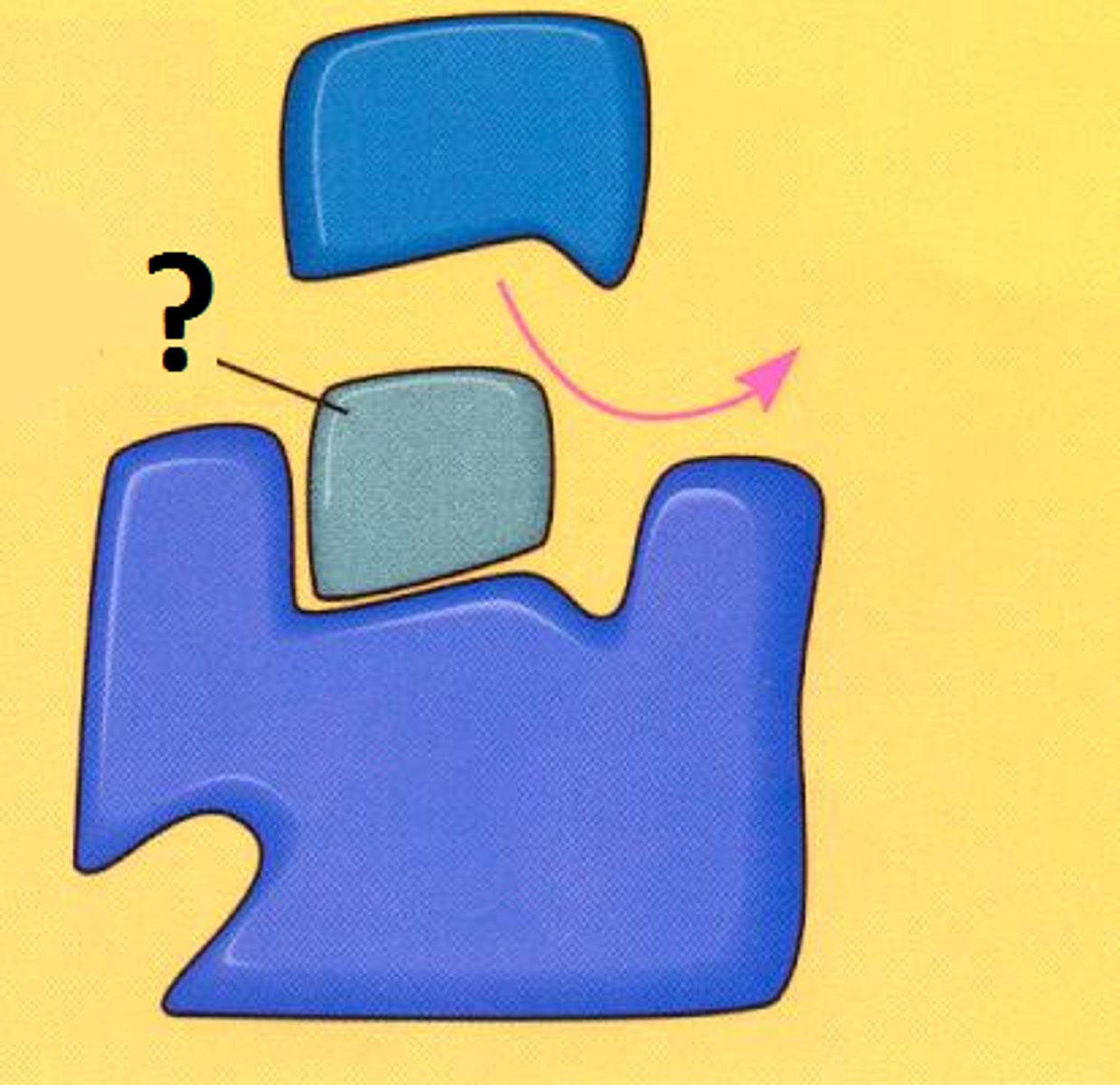
noncompetitive inhibitors
Impede enzymatic reactions by binding to another part of the enzyme (other than the active site).
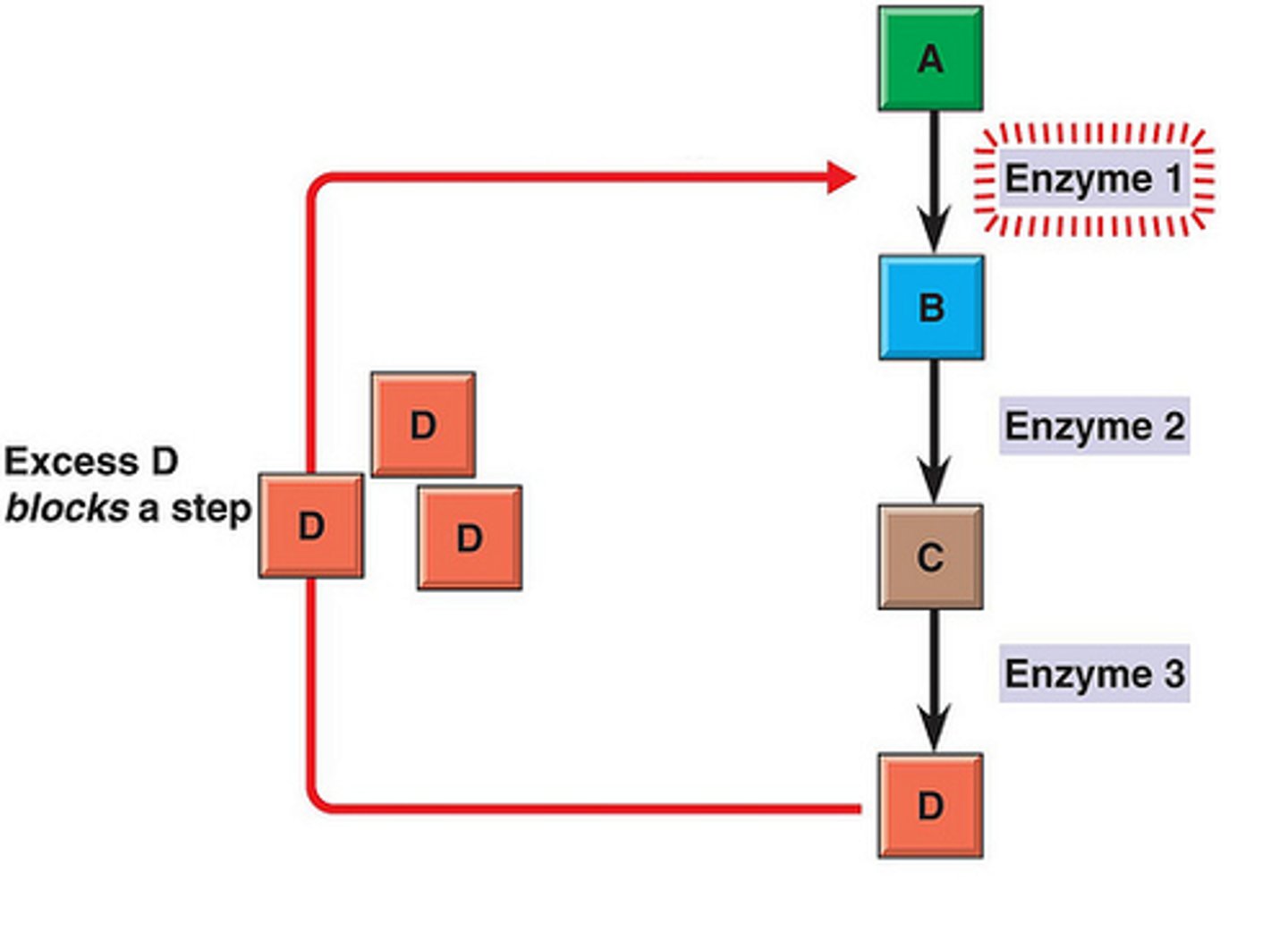
feedback inhibition/negative feedback
A metabolic pathway is switched off by the inhibitory binding of its end product to an enzyme that acts early in the pathway.
saturated enzyme
Describes an enzyme's maximum activity when every active site is being used.
Chemical Energy
Potential energy trapped in molecular bonds.

Spontaneous Reaction
When a reaction doesn't require energy to proceed it is said to be this - doesn't mean it will be FAST.
chemical reaction
A process that changes one set of chemicals into another set of chemicals.
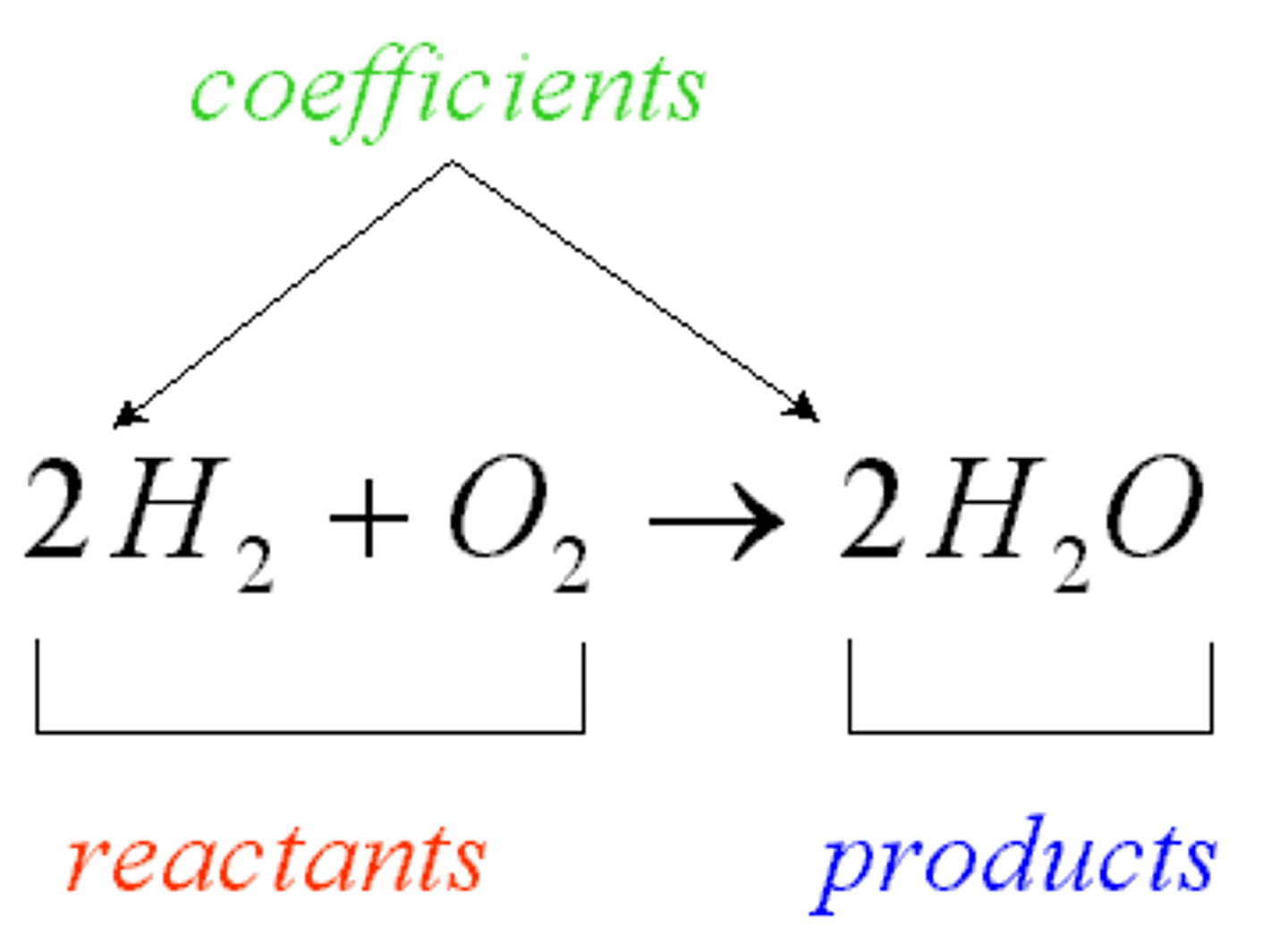
reactants
compounds that enter into a chemical reaction
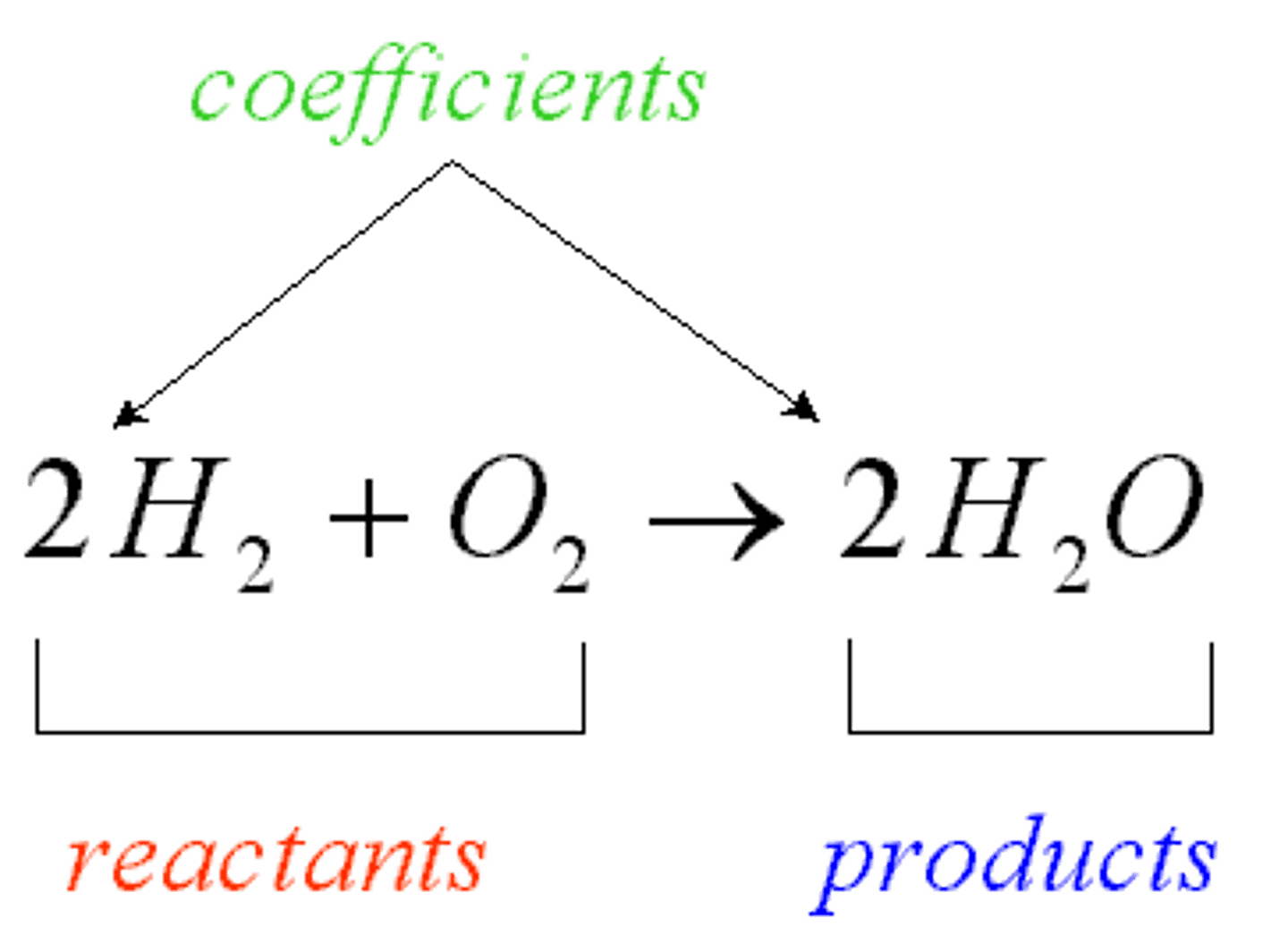
product
compounds produced by a chemical reaction.
Competitive inhibition
substance that resembles the normal substrate competes with the substrate for the active site
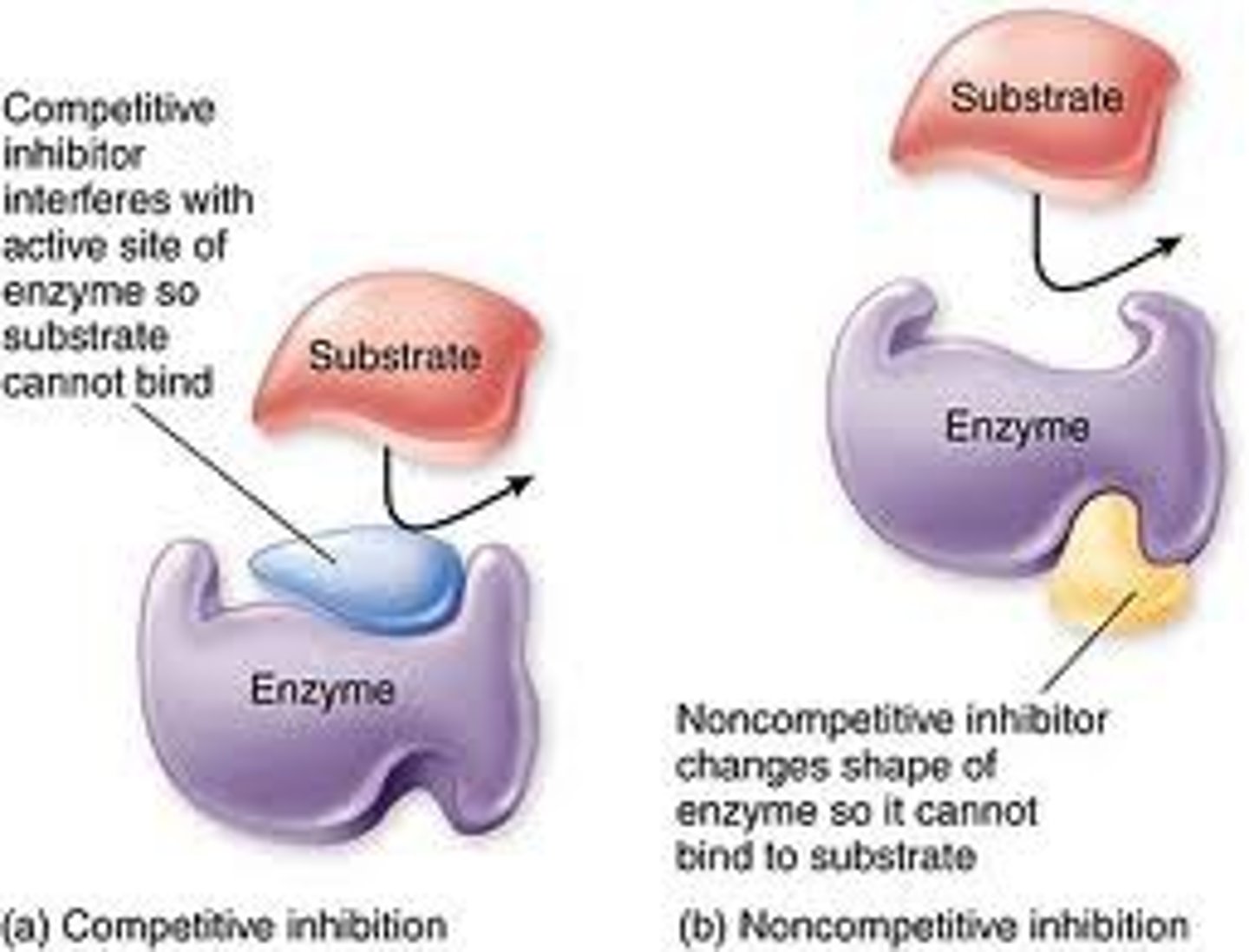
Noncompetitive inhibitor
a chemical that binds to an enzyme but not in the active site. This chemical will change the shape of the enzyme (reversible)
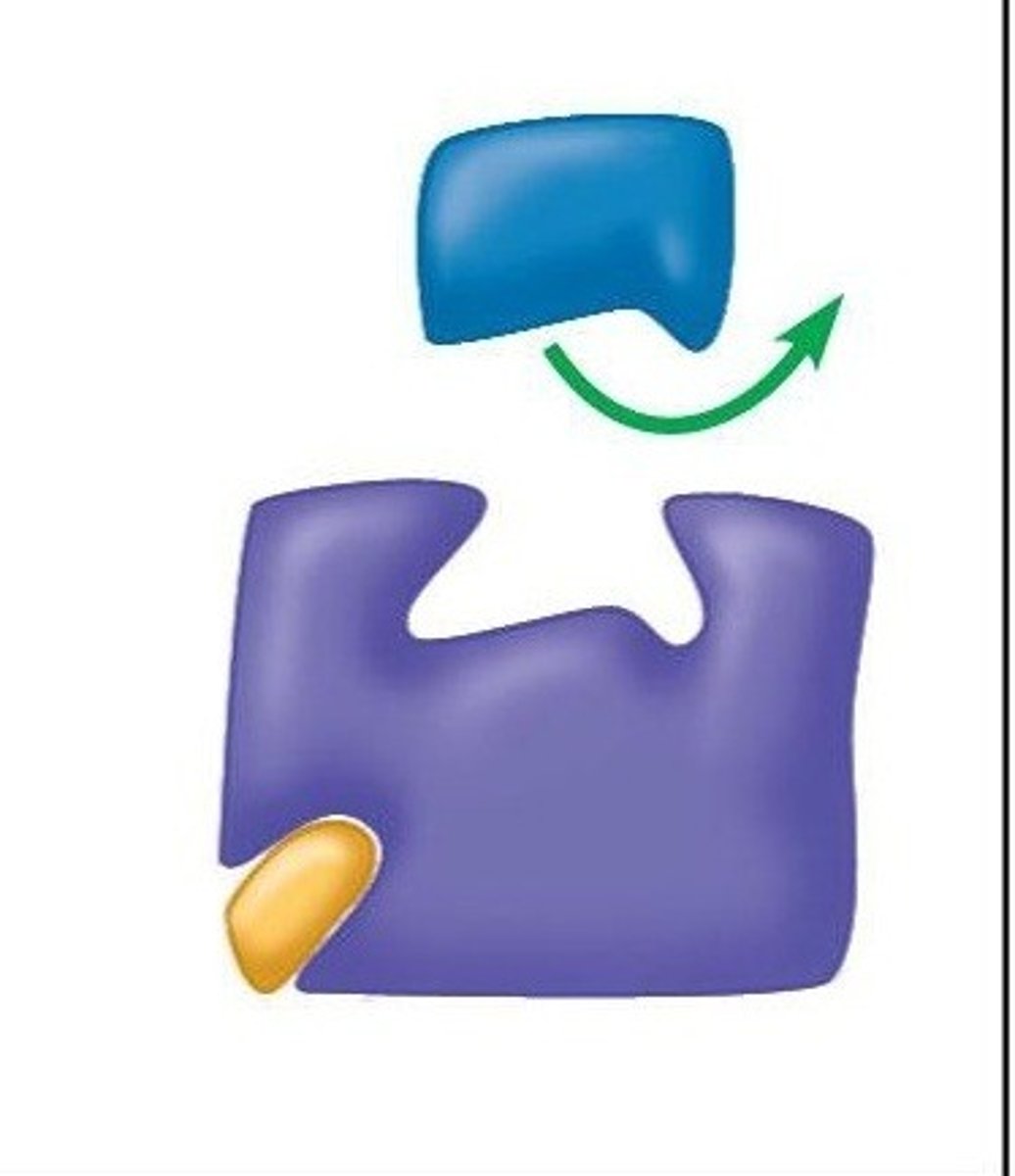

substrate
A specific reactant acted upon by an enzyme
exothermic reaction
a chemical reaction where energy is given off, so that the products have less energy than the reactants.
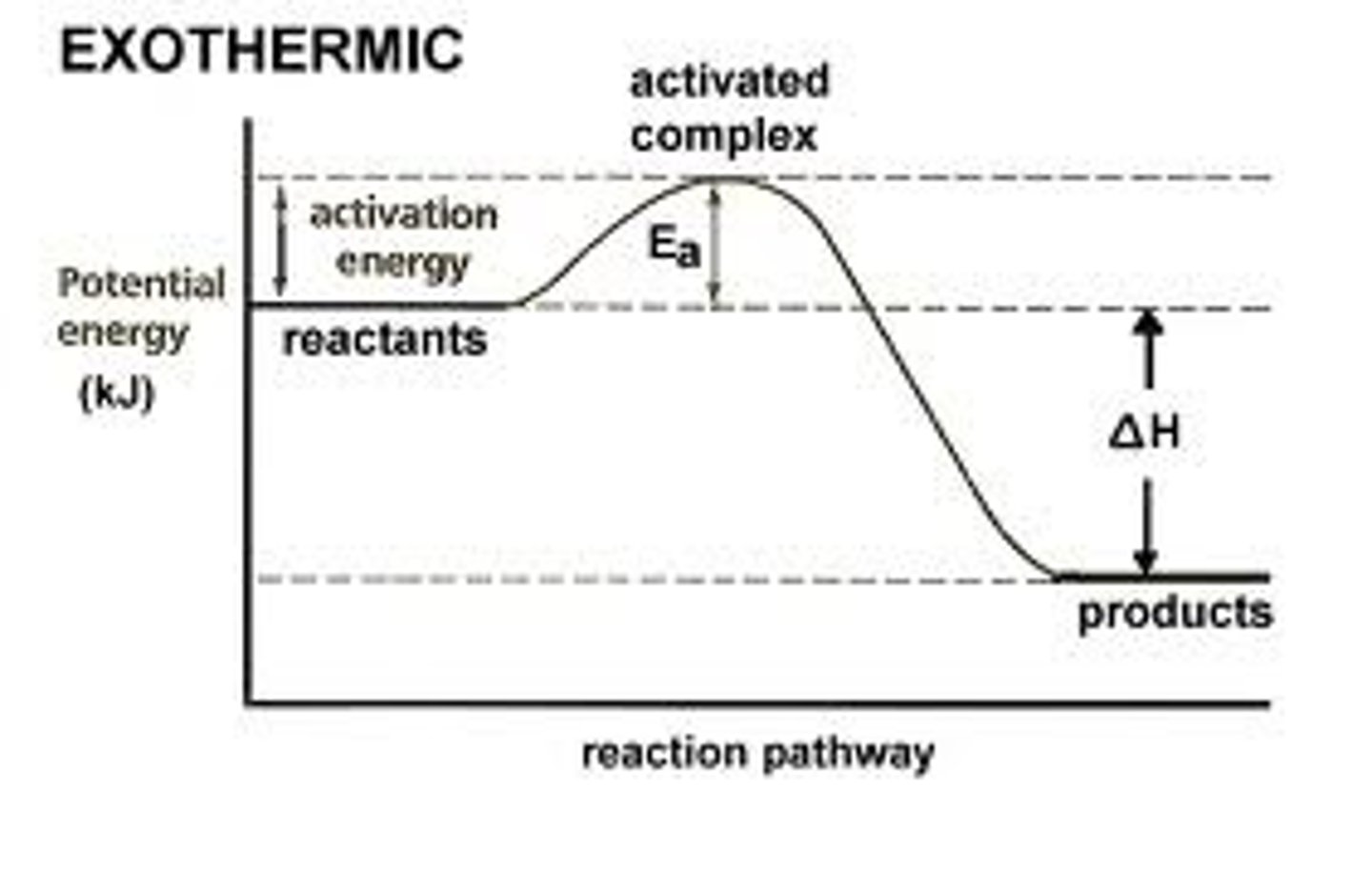
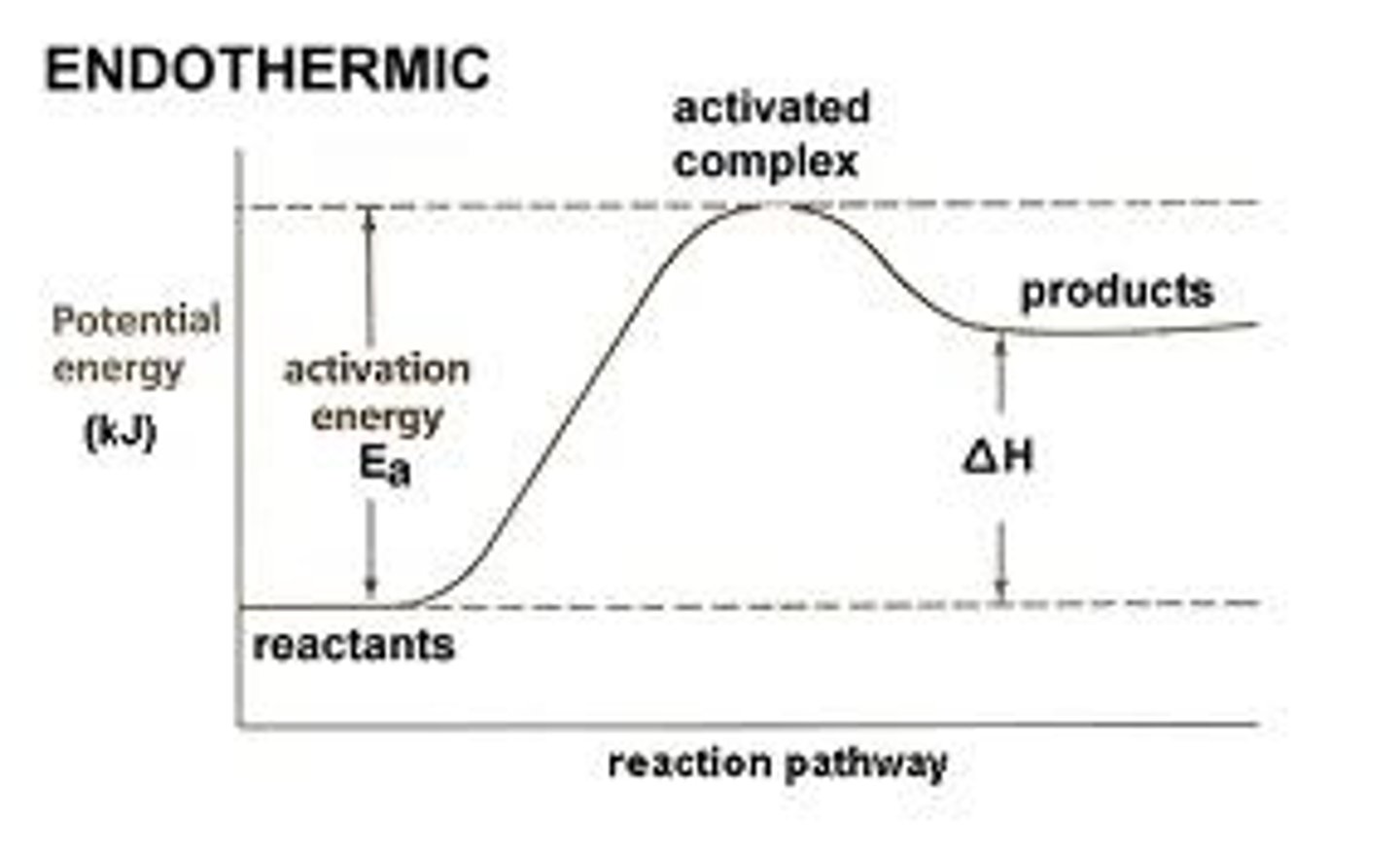
endothermic reaction
a chemical reaction where energy is taken in, so that the products have more energy than the reactants.
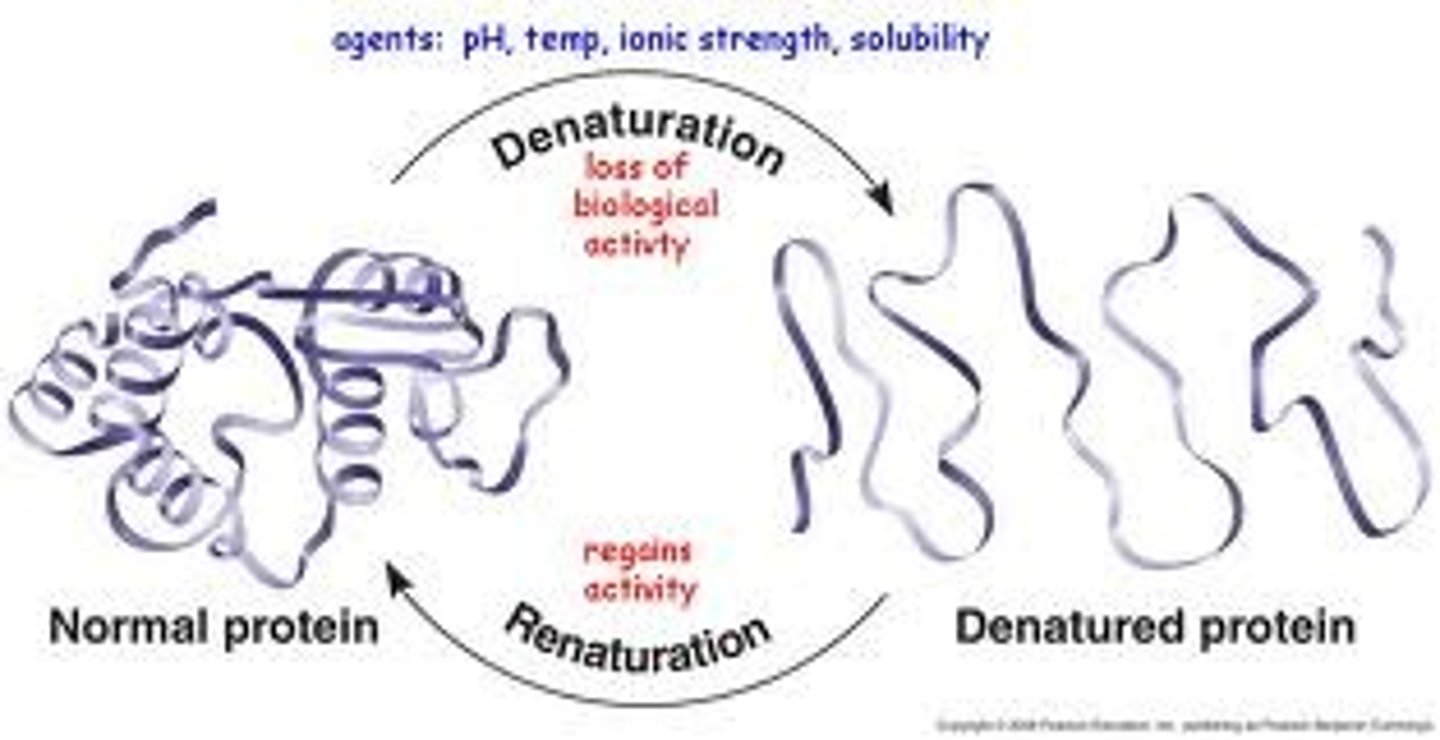
Denature
A change in the shape of a protein (such as an enzyme) that can be caused by changes in temperature or pH (among other things).
Allosteric
__________ regulation of enzyme occurs when a molecule binds to an enzyme changing the protein's shape
Catalyst
______ an agent that speeds up a chemical reaction without itself being permanently altered
Transition State
The less stable state that occurs and is usually a high-energy state between reactants and products in a chemical reaction
Substrate orientation
When Enzyme bring together specific atoms into a correct position that are otherwise rotating and tumbling so that bonds can form
Protein Kinases
enzymes that reversibly activate or inactivate other proteins by adding phosphate groups to (phosphorylating) them
pH
After looking at the graph the enzyme activity of the the three different enzymes is being regulated by what variable
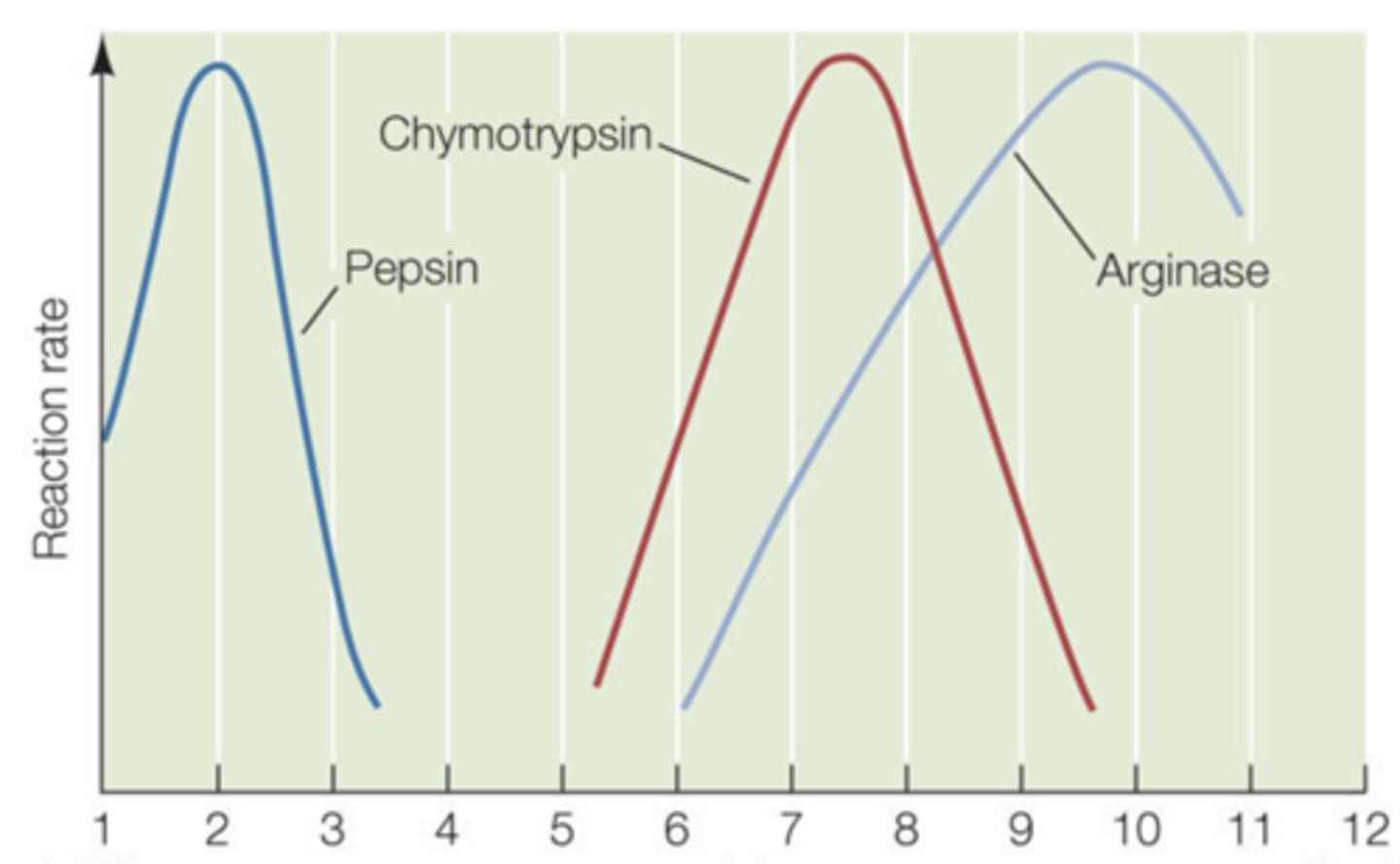
Temperature (variable affecting enzyme activity)
After looking at the shape of this graph, the enzyme activity of this enzyme is being regulated by what variable?
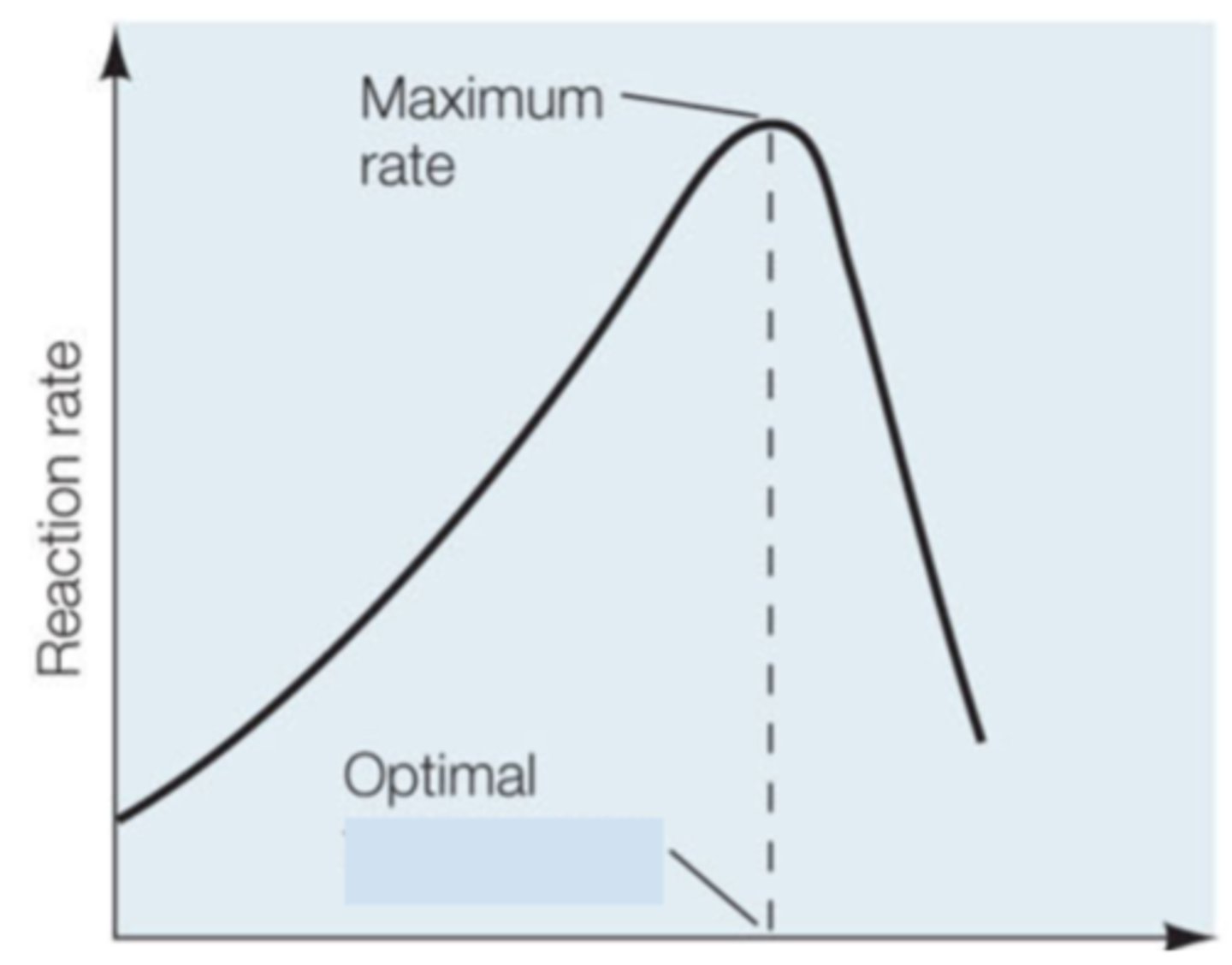
Substrate Concentration (variable affecting enzyme activity)
After looking at the shape of this graph, the enzyme activity of this enzyme is being regulated by what variable?
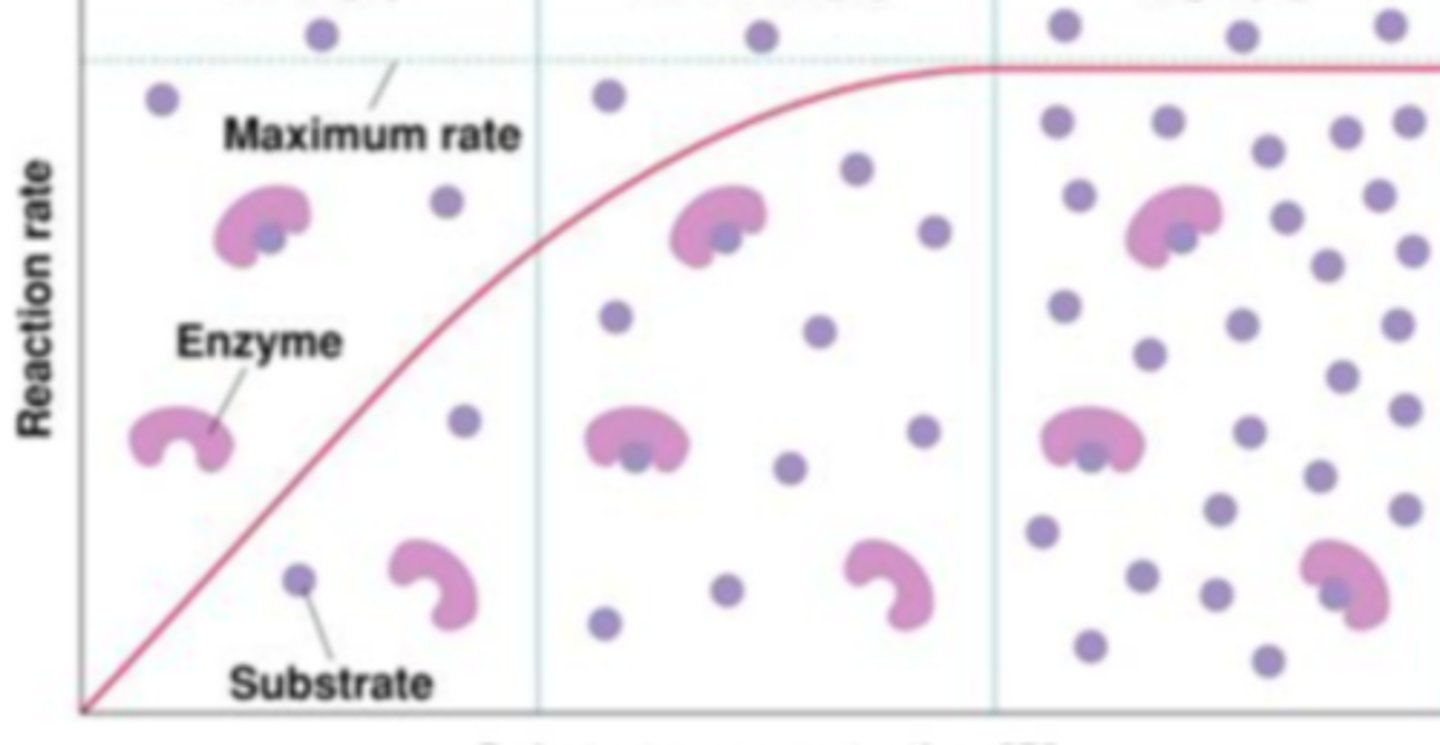
Metabolism
The totality of an organism's chemical reaction
Entropy
Disorder
Free energy
Energy that can do work
Negative ΔG - effect on spontaneity
Spontaneous
Energy releasing, Negative ΔG
Exergonic
Energy storing, Positive ΔG
Endergonic
Positive - effect of spontaneity
Not spontaneous
ΔG = ΔH - TΔS
Equation for ΔG
symbol G
Free energy
Symbol H
Enthalpy aka system's total energy
symbol T
Temperature
symbol S
Systems total entropy (disorder)
Adenine, ribose, phosphate group
ATP is composed of
Homeostasis
Maintaining a stable internal environment