BIOL 4004 UMN Exam 2
1/111
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
112 Terms
A neuron cell and a liver cell share the same _____, but they have different _____
share the same genome, have different morphology
function by presumably expressing different sets of RNAs and proteins
Transcription regulators account for about ______ of all protein-coding genes.
10%
How do transcription regulators work
the transcription regulators recognize DNA cis-regulatory sequences and make their contacts with the major grooves.
The protein also contacts the minor groove and phosphates in the backbone
Dimerization of Transcription Regulators Increases Their
affinity and specificity for DNA
dimer (transcription regulators) finds Nanog cis-regulatory sequence in genome, specific for dimer types
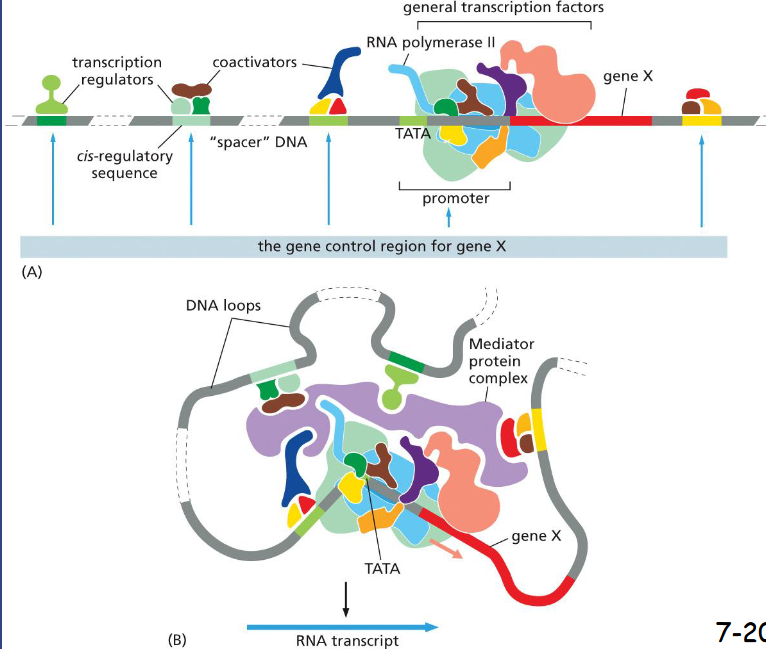
A Eukaryotic Gene Control Region Consists of a ______ Plus Many ________ sequences, and functions to regulate..
Consists of a Promoter Plus Many cis-Regulatory Sequences
has co-activators, DNA looping, and transcription regulators
All of these ultimately regulate the recruitment of RNA polymerase II by the general transcription factors to the promoter
co-activators
proteins that do not bind DNA themselves but assemble on other DNA binding transcription regulators
Gene Expression regulated at steps in the pathway from DNA to RNA to protein
1: transcriptional control
2: RNA-processing control
4: translational control
5: mRNA degradation control
dont worry about others for now
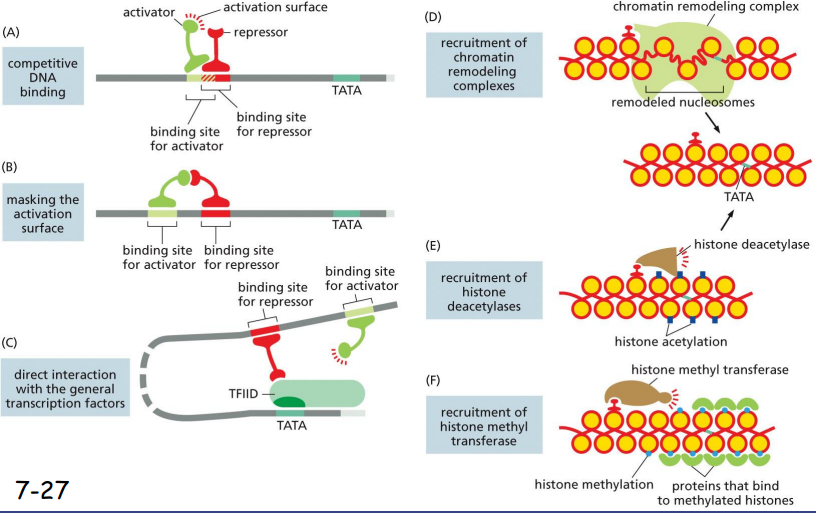
Eukaryotic Transcription Repressors Can Inhibit Transcription in Several Ways (6)
1: competitive DNA binding
(repressor binding site overlapping w/ activator binding site)
2: masking the activation surface
(repressor binding site too close to activator binding site, represses)
3: direct interaction with the general transcription factors
(repressor binding site in place where repressor directly interacts w/ TFIID)
4: recruitment of chromatin remodeling complexes
(remodels chromatin into heterochromatin)
5: recruitment of histone deacetylases- histone deacetylation
6: recruitment of histone methyl transferase - histone methylation, protein bind to methylated histones
3-6: Chromatin remodeling and histone de-acetylation or methylation decrease the accessibility of TATA box to the general transcription factors and RNA polymerases
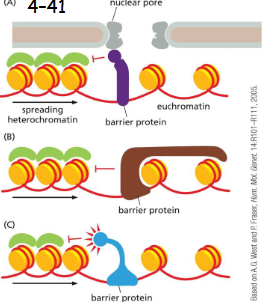
Insulator DNA Sequences Prevent Eukaryotic Transcription Regulators from Influencing _____ Genes
Insulator DNA Sequences Prevent Eukaryotic Transcription Regulators from Influencing Distant Genes
barrier sequences
Barrier sequences prevent the spread of heterochromatin The tethering to a fixed site stops the spread of heterochromatin.
By recruiting histone-modifying enzymes, barriers erase the histone marks that are required for heterochromatin to spread
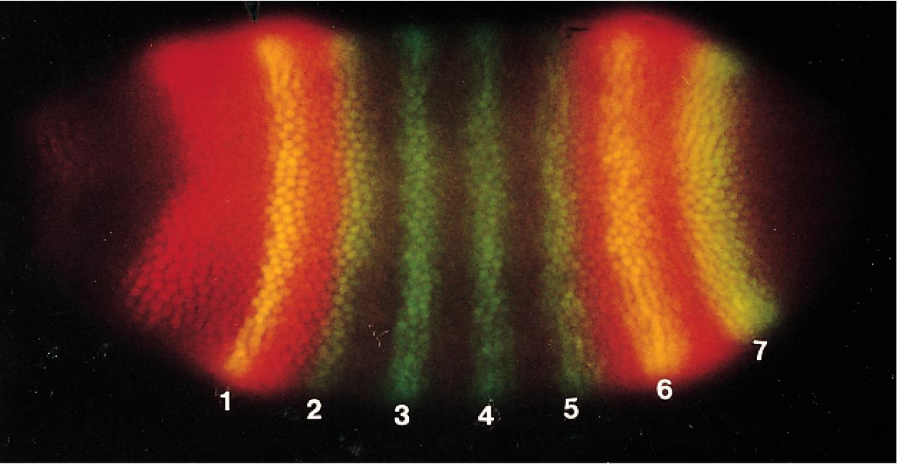
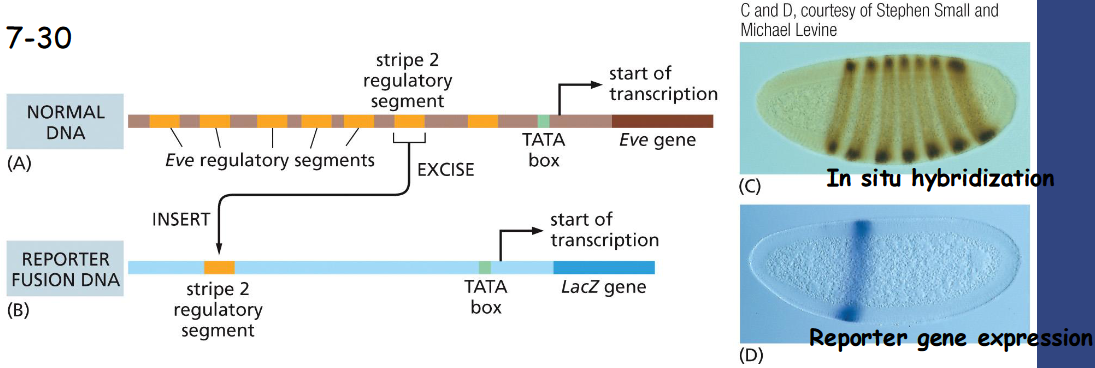
Complex Genetic Switches That Regulate Drosophila Development Are Built Up from _________
Complex Genetic Switches That Regulate Drosophila Development Are Built Up from Smaller Molecules
The Drosophila Even-skipped gene (eve) is expressed in seven precisely positioned stripes as shown in green. Giant gene is expressed in the head and tail as shown in red, whereas yellow indicates the presence of both.
A 20 kb region upstream of the eve gene contains multiple cis-regulatory sequences, each specifies its specific expression in one stripe
The Drosophila Eve Gene Is Regulated by __________
Combinatorial Controls
Combinatorial Gene Control Creates Many Different Cell Types
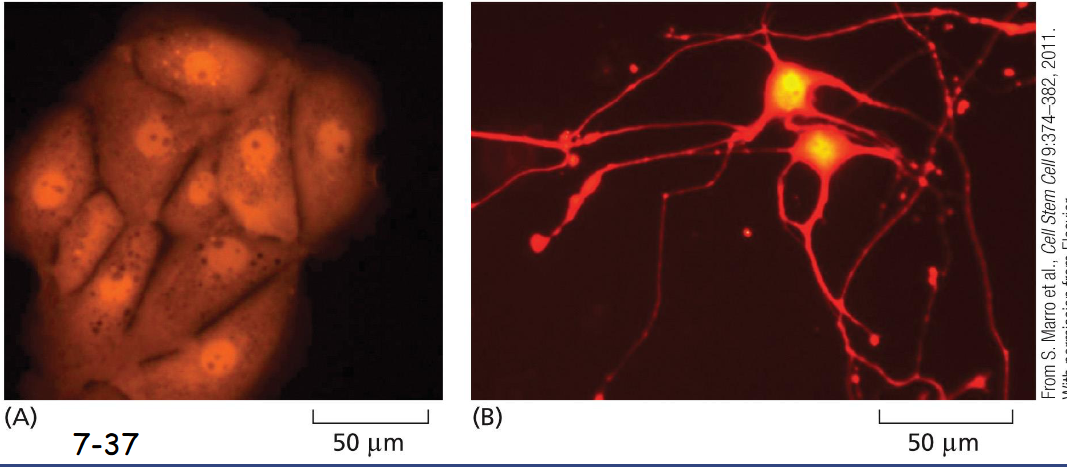
Combinatorial Gene Control Creates ________
many different cell types
Liver cells (A) were converted into neuronal cells (B) via the artificial expression of three nerve-specific transcription factors that activate many nerve-specific genes and repress many liver-specific genes.
In drosophila, the expression of the Eyeless gene in precursor cells of the leg triggers the development of ________
an eye on the leg
Specialized Cell Types Can Be Experimentally Reprogrammed to Become:
Pluripotent Stem Cells
Stem cells: undifferentiated cells that can perpetuate themselves and give rise to other daughter cells capable of differentiating into specialized cells
a differentiated fibroblast cell can be induced to a ____
induced pluripotent stem cells iPS
genes encoding three transcription regulators introduced to and expressed in fibroblast nucleus
cells induced by further transcription regulators to differentiate in culture
fibroblast —> iPS cell —> muscle cell, neuron, fat cell, etc.
_____ leads to the depletion of a stem-cell population in the hair follicles of mice nervous system
stress
This discovery sheds light on why stress turns hair grey
Patterns of DNA Methylation Can Be ______ When Vertebrate Cells ______
Patterns of DNA Methylation Can Be Inherited When Vertebrate Cells Divide
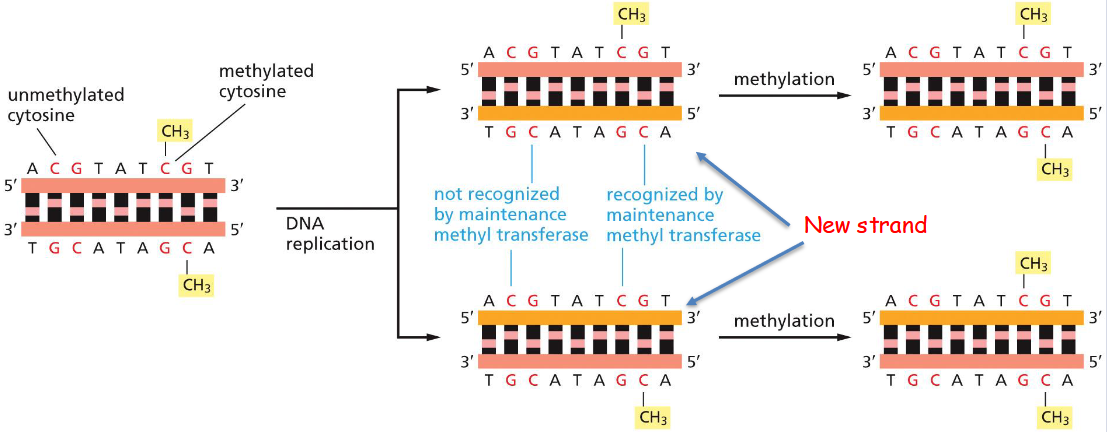
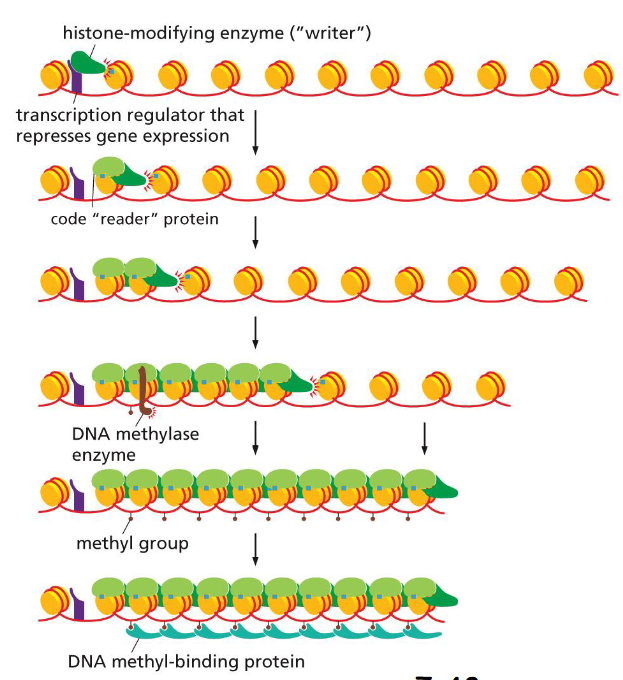
DNA methylation steps
transcription regulator brings in a writer for histone modification, which is then read by code reader
the reader relays the writer to perform similar modification
at some moments the reader also brings in a de novo (new) DNA methylase
The methylated cytosine lies in the major groove and interferes with the binding of proteins
The binding of additional proteins to the methylated DNA adds further insulation
Genomic Imprinting Is Based on ________
DNA Methylation
Genomic imprinting: when the maternally inherited gene is active, its paternally inherited gene copy is silent or vice versa
The silence is due to DNA methlyation
If mutated only one gene copy matters
genomic imprinting steps
both parents express the same allele of gene A (from chromosome inherited from father)
removal of imprinting in germ cells, followed by meiosis
Female/male imprints established
Grow into mature individuals
Offspring differ in the allele of gene A that is expressed
basically when maternally inherited gene is active, paternally inherited gene copy is silent or vice versa
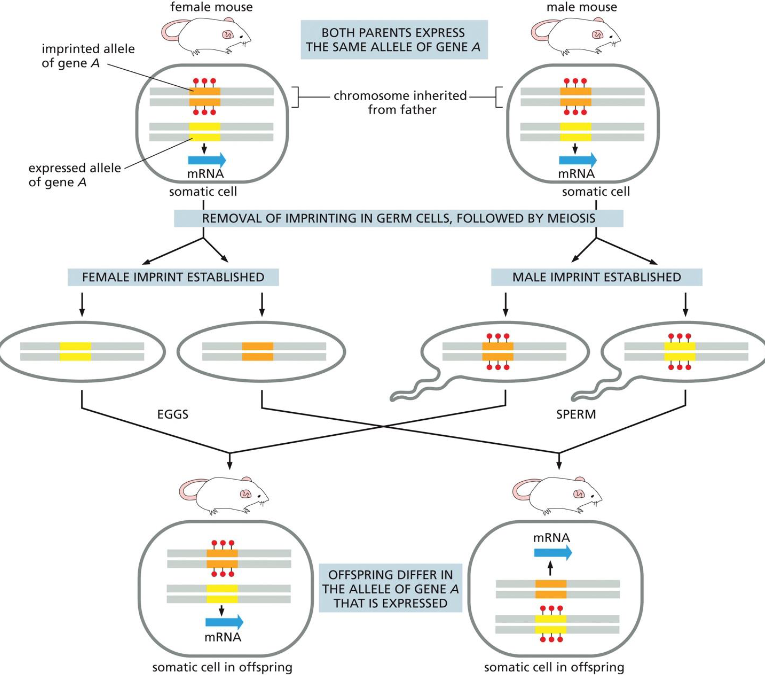
genomic imprinting silencing vs expression
methylation of insulator element leads to no CTCF binding, communication between cis-regulatory sequence and lgf2 gene established, gene expressed
if not methylated, CTCF binds insulator and blocks communication
synthesis of lncRNA can be blocked by methylation on Kcnq1 gene, leads to gene expression
if no methylatio on Kcnq1 gene lncRNA synthesized, alters chromatin, Kcnq1 silenced
Introduction and Alternative RNA Splicing Can Produce Different Forms of a Protein from the ____
same gene
alternative RNA splicing occurs for about 90% genes in human and may be critically regulated
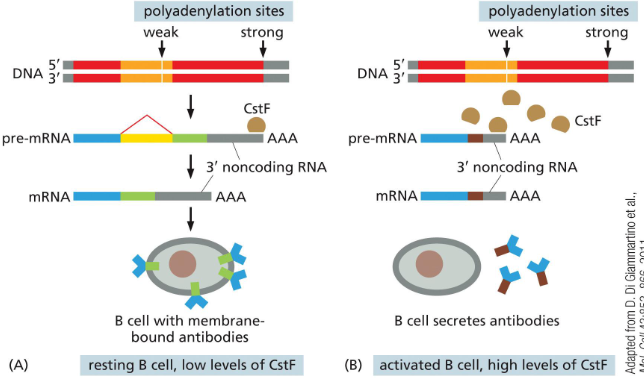
A Change in the Site of RNA Transcript Cleavage and Poly-A Addition Can Change the ________ of a Protein
C-terminus
When the level of Cleavage stimulation factor (CstF) is low, it skips the first weak polyadenylation signal to produce a longer transcript.
A longer string of hydrophobic amino acids is retained as the membrane-bound domain.
When activated to produce antibodies, CstF level increases to cleavage the weak site
microRNAs (miRNAs) Regulate ____ and ____
Translation and Stability
There are about ____ 23-nt miRNAs in humans
1000
RNA Interference Can Direct ________ Formation
Heterochromatin formation
Many transposable elements and viruses produce double-strand RNA in their life cycles, triggering RNAi to against the invaders in plants, worms,and insects
steps in heterochromatin formation by RNA interference
protein complex (dicer) cleaves double stranded RNAs to siRNAs
siRNAs trigger the inhibition of translation and destruction of mRNAs as other miRNAs do
siRNAs also cause transcriptional silence. The short siRNAs interact with a group of proteins including argonaute to form RNA induced transcriptional silence (RITS) complex
The RITS complex directs the formation of heterochromatin
Long Noncoding RNAs Functions in the Cell
lncRNA does not code for proteins
lncRNAs carry proteins to specific RNA or DNA sequences through complementary base-pairing
Some lncRNAs regulate transcription in cis
Other lncRNAs diffuse from their sites of synthesis and act in trans
major lipids in cell membranes
Phosphoglycerides, Sphingolipids, and Sterols
Phosphoglycerides or phospholipids are derived from ______, whereas sphingomyelin is derived from _______ as _____
Phosphoglycerides or phospholipids are derived from glycerol
sphingomyelin is derived from sphingosine as a sphingolipid
__________ is the most abundant phospholipid
phosphatidylcholine
______ has a net negative charge
phosphotidylserine
cholesterol formula, model, and schematic drawing
C27H46O
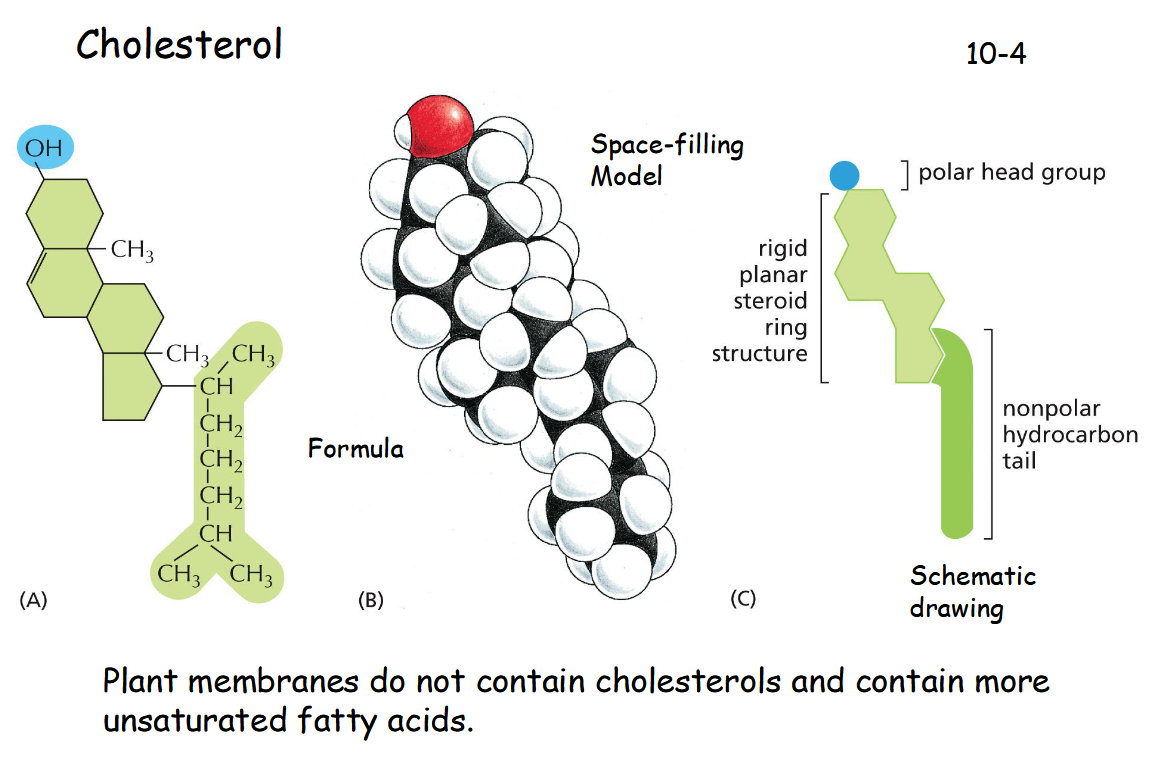
plant membranes do not contain cholesterols and contain more __________
unsaturated fatty acids
The Lipid Bilayer Is a _________ fluid
two-dimensional
fatty acid tails, lipid head groups on either side
water molecules stay on both sides of the membrane
_______ channels allow the bulk flow of water molecules across the lipid bilayer
aquaporin channels
raft domain lipid bilayer
specialized domains or membrane regions involving protein-protein, protein-lipid and lipid-lipid interactions.
Raft domains have an increased membrane thickness.
GPI: glycosylphosphatidylinositol
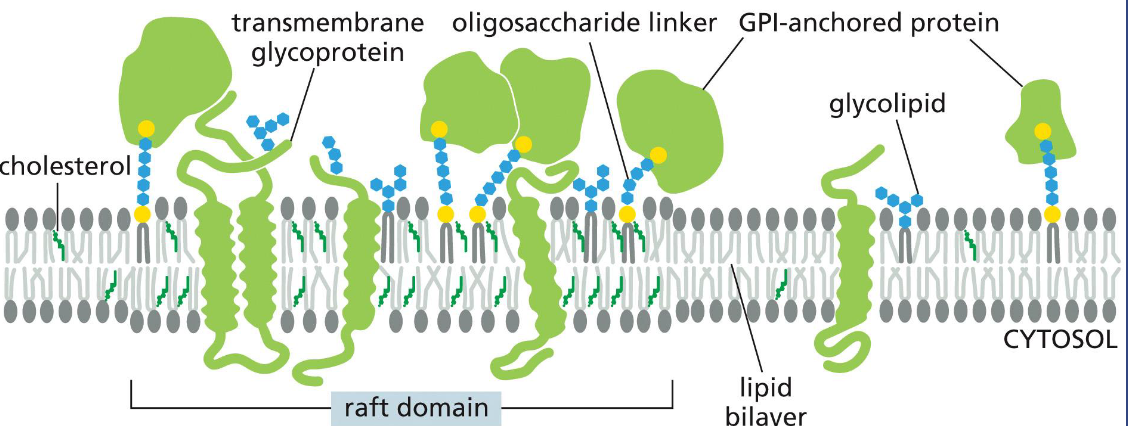
lipid bilayer asymmetry
Outer layer: phosphatidylcholine, sphingomyelin
Inner layer: ethanolamine (terminal amino group), serine
The cytosolic (inner) side carries negative charges
Some lipid kinases phosphorylate its head group to form a binding site that recruits other proteins to the cell surface or cytosolic face
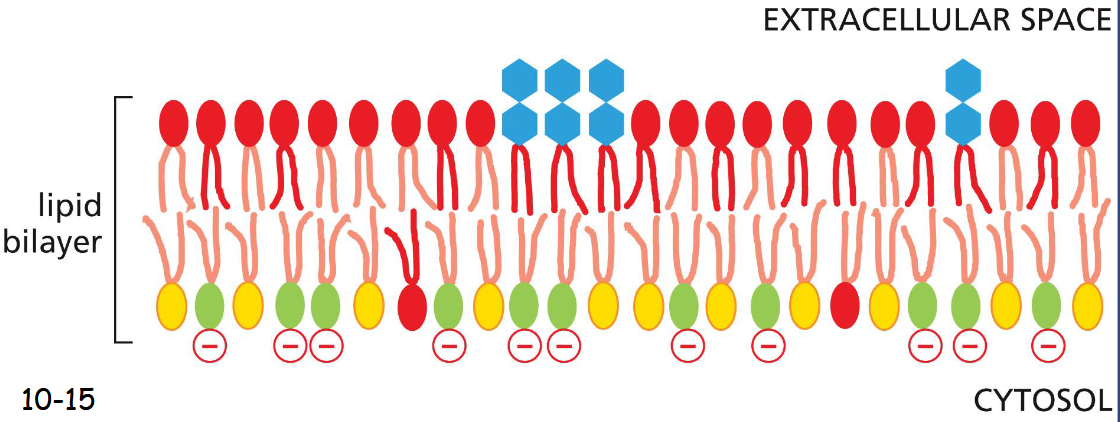
Membrane Proteins Can Be Associated with the Lipid Bilayer in Various Ways
Transmembrane proteins covalently attached to a fatty acid chain in the cytosolic side, multiple alpha-helices or a rolled-up beta-sheet
Protein can be anchored to the cytosolic surface by an amphilic alpha-helix
Protein can be attached to the bilayer by a lipid chain
Protein can associate with the membrane via GPI-anchor (glycosylphosphatidylinositol)
Peripheral proteins associate with other membrane proteins
how to determine membrane protein topology
make cell not permeable, treat with trypsin, it digests extracellular parts of proteins, do SDS-PAGE, find which proteins had most taken off them = probably extracellular facing
Lipid Anchors Control the _______ of Some Signaling Proteins
membrane localization
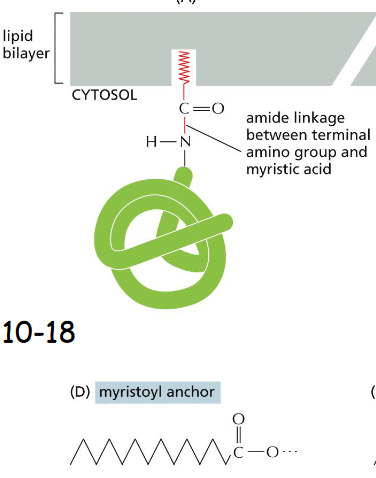
Myristoyl anchor lipid anchor
Myristic acid is 14-C unsaturated fatty acid and recruits Src family tyrosine kinase in the cytosolic face
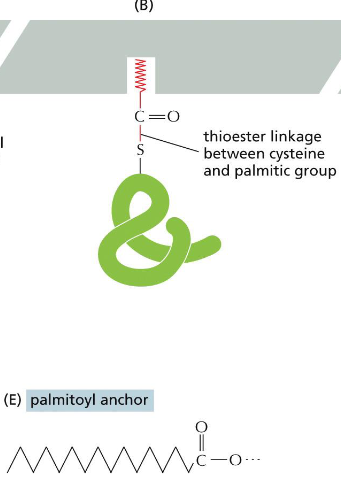
Palmitoyl anchor lipid anchor
Palmitic acid is 16-C unsaturated fatty acid as the second anchor to recruit Src, and Src returns to cytosol when the signal is off
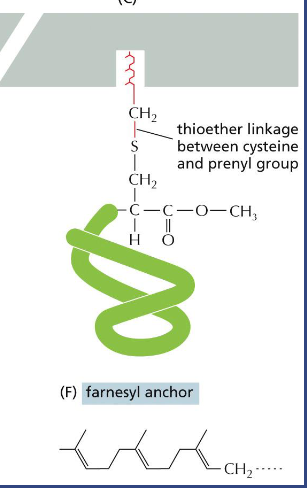
Farnesyl anchor lipid anchor
Farnesyl is a tri-prenyl group as a 15-carbon unsaturated hydrocarbon chain
in Most Transmembrane Proteins, the Polypeptide Chain Crosses the Lipid Bilayer in an ________ conformation
alpha-helical
Hydrophobic Amino acids with non-polar side chain align with hydrophobic core
Intra-molecular hydrogen bonds between adjacent peptide bonds stabilize the alpha-helical structure
Some β-Strands Form Large _________
channels
Multipass beta-strands form antiparallel beta-barrels normally in the outer membrane of bacteria, mitochondria and chloroplasts.
OmpA is a receptor for a bacterial virus
OMPLA is a lipase
Porin and FepA are transporters
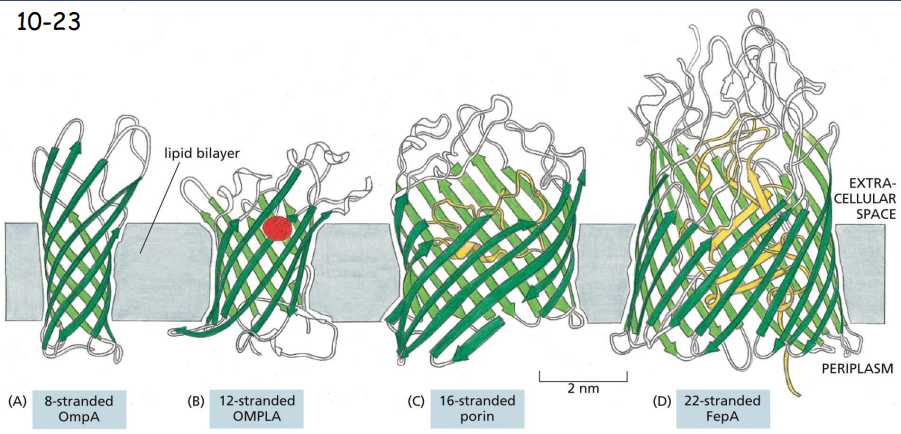
many Membrane Proteins Are _______-ated
purpose of this modification?
glycosylated
Purpose primarily to help during protein folding, attachment onto membrane
Membrane Proteins Can Be Solubilized and Purified in _______
detergents
Three commonly used detergents are
sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS), an anionic detergent (negatively charged), and Triton X-100 and β-octylglucoside, two nonionic detergents
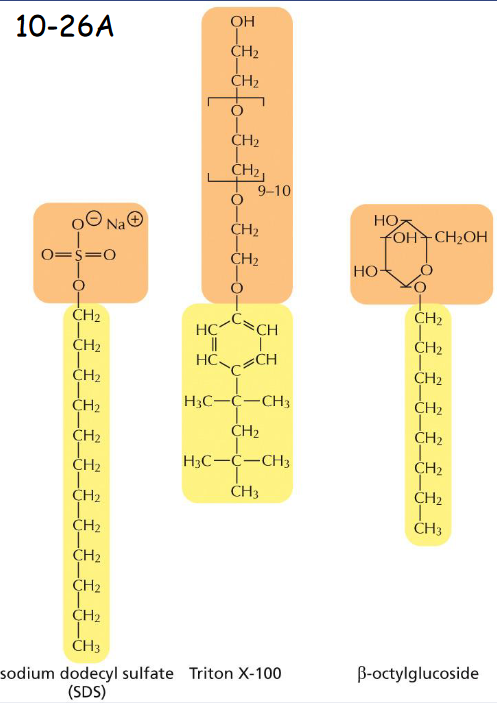
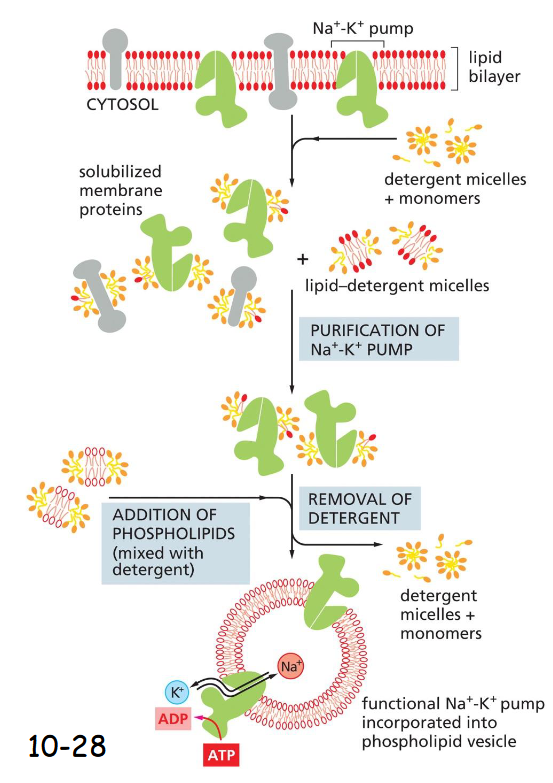
______ detergents are used for solubilizing membrane proteins such as Na+/ K+ pump
steps for solubilizing Na+/K+ pump
mild non-ionic detergents
add detergent, membrane protein solubilized
add lipid-detergent to purify
removal of detergent
addition of phospholipids (mixed with detergent)
functional pump incorporated into phospholipid vesicle
Many Membrane Proteins _____ throughout the Plane of the Membrane
diffuse
Many membrane proteins rotate and move laterally. When mouse cells are fused with human cells, the two sets of proteins diffuse and mix in about half an hour
Cells Can Confine Proteins and Lipids to Specific _____ Within a _________
can confine proteins and lipids to specific domains within a membrane
In epithelial cells that line the gut or the tubules of the kidney, proteins are confined to the apical or lateral and basal surfaces due to tight junction
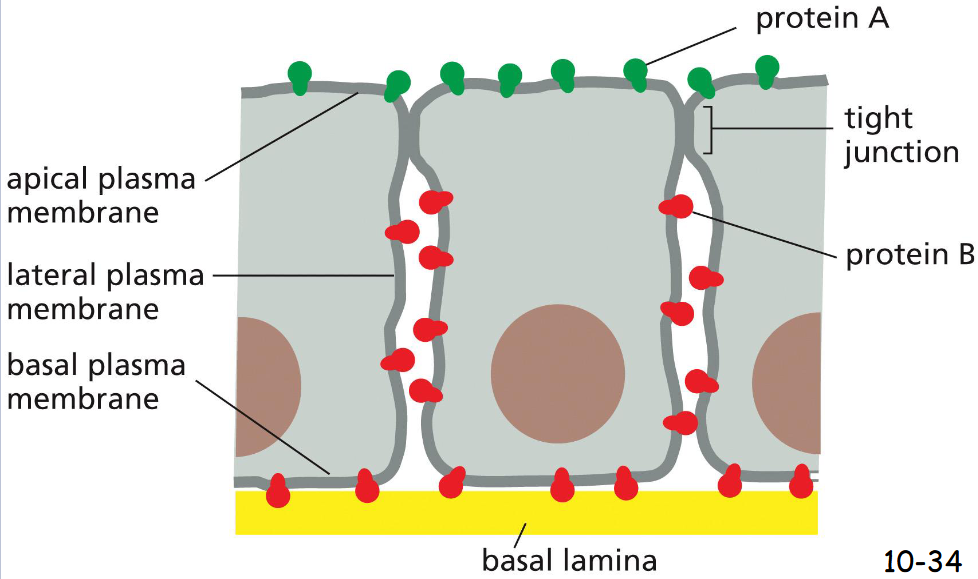
Four ways of restricting the lateral mobility of specific plasma membrane proteins
(A) The proteins can self-assemble into large aggregates.
(B) They can be tethered by interactions with assemblies of macromolecules outside the cell.
(C) They can be tethered by interactions with assemblies of macromolecules inside the cell.
(D) they can interact with proteins on the surface of another cell.
Protein-Free Lipid Bilayers permeability
hydrophobic molecules very permeable
small uncharged polar molecules somewhat permeable
large uncharged polar molecules not very permeable
impermeable to ions
intra vs extracellular concentrations of common ions
GREATER OUTSIDE CELL:
Na+, big margin
Mg2+, small margin
H+, small margin
Ca2+, big margin (low concentration both)
GREATER INSIDE CELL:
K+, big margin
two main classes of membrane transport proteins
transporters and channels
Transporters bind the specific solutes and undergo a series of conformational changes
Channels form a pore across the bilayer through which specific solutes can diffuse through
Active Transport Is Mediated by ________ Coupled to an _________
Active Transport Is Mediated by transporters, Coupled to an energy source
Concentration gradient drives passive transport.
Active Transport is against its concentration gradient and coupled to a source of energy such as ATP hydrolysis or ion gradient.
For a charged molecule, the electrical potential or membrane potential is also considered. It is defined as electrochemical potential (inside is normally negative).
Coupled transporters
use energy stored in concentration gradients to couple the downhill transport of one solute to the uphill transport of another
Glucose transport fueled by
a Na+ gradient as symport
Alternates between outward-open and inward-open, and the binding of Na+ and glucose is cooperative
Light and ATP driven pumps
Light-driven pumps couple energy from light to the uphill transport
ATP-driven pumps couple the hydrolysis of ATP to the uphill transport
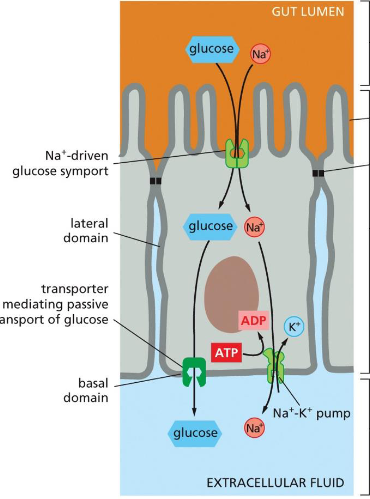
An _______ Distribution of Transporters in Epithelial Cells Underlies the ___________
Asymmetric Distribution of Transporters in Epithelial Cells Underlies the Transcellular Transport of Solutes
asymmetric distribution of transporters in epithelial cells underlies what process
what is the distribution of transporters in epithelial cells and why do they need a K+/Na+ pump?
uneven distribution underlies transcellular transport of solutes
Na+-linked symporters are located in the apical domains, whereas glucose transporters in the basal or lateral (basolateral) domains passively allow glucose to leave the cells down their concentration gradients.
Why do we need a Na+/ K+ pump?
The Na+ gradient is maintained by an ATP- driven Na+/ K+ pump in the basolateral domains, which keeps the internal concentration of Na+ low —> Na+ symporter uses the gradient to pump in glucose
Three Classes of ATP-Driven Pumps
P-type pumps phosphorylate themselves and maintain gradients of the four ions.
ABC (ATP Binding Cassette) transporters primarily pump small molecules across cell membranes, but also pump large molecules.
V-type proton pumps transfer H+ into organelles such as synaptic vesicles, lysosomes, and plant and yeast vacuoles to acidify their interiors
The Plasma Membrane Na+-K+ Pump Establishes Na+ and K+ Gradients Across__________
The process is _____-genic
across the plasma membrane
A Na+-K+ ATPase antiporter pump acts against their steep electrochemical gradients
The process is electrogenic as it pumps three positively charged ions out for every two it pumps in. However, it contributes less than 10% for the inside negative membrane potential
ABC Transporters Constitute the __________ Family of Membrane Transport Proteins
largest
● Antimalarial drug chloroquine is pumped out of cell by an acquired ABC transporter of the protist
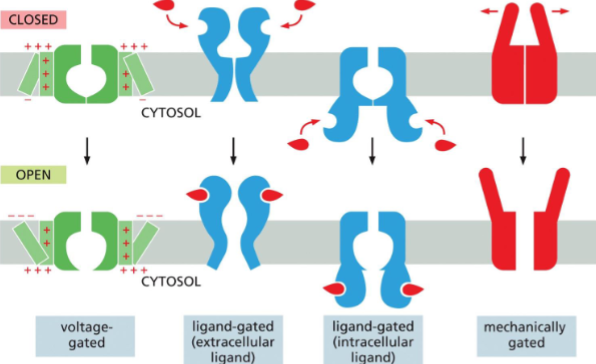
Ion Channels Are _____ and Fluctuate Between ____ and____ States
Ion channels general characteristics
Types of ion channels
Ion Channels Are Ion-Selective and Fluctuate Between Open and Closed States
Ions diffuse down their electrochemical gradients through channels
Ion channels allow 105 times faster rate of transport.
Ion selectivity is dependent on pore size to atomic dimensions in one particular region.
The gate is not always open but gated by voltage, ligand, and mechanical forces (hair cells)
Ligand-gated includes transmitter- gated, ion-gated, or nucleotide-gated
The Function of a Neuron Depends on ________
Neuron structure
its elongated structure
Dendrites branch from the cell body like antennae to receive signals from the axons of other neurons.
One long axon conduct signals away from the cell body. An electrical excitation known as an action potential or nerve impulse can travel without attenuation at speeds of 100 meters per second or more.
Axon branches pass messages to dendrites of other neurons or many target cells such as muscle or gland cells
Voltage-Gated Cation Channels Generate Action Potentials in __________ cells
electrically excitable
Voltage-gated Na+ channels open following membrane depolarization from its resting value of -65 mV to about +50 mV in half of a millisecond.
Na+ channels then automatically inactivate and voltage-gated K+ channels open to restore the normal membrane potential
Transmitter-Gated Ion Channels Convert _________ Signals into _________ Ones at Chemical ______
Chemical. Electrical, at synapses
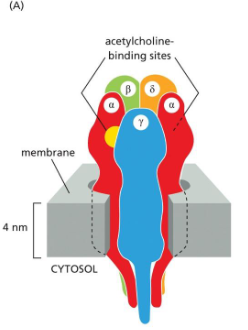
The _________ Receptors at the Neuromuscular Junction Are __________ Channels
AChR has two __ subunits and three other subunits
Two acetylcholine bind to alpha-subunits, causes:
acetylcholine, excitatory transmitter-gated cation channels
The acetylcholine Receptor has two alpha and three other subunits. The gate is made by the hydrophobic side chains of five leucine amino acids
When two acetylcholines bind the two alpha-subunits, a conformational change opens the channels for the through-traffic of Na+ and K+, together with some Ca2+
Neuromuscular Transmission Involves the Sequential Activation of _____ Different Sets of Ion Channels
FIVE different sets
All Eukaryotic Cells Have the Same Basic Set of Membrane-enclosed Organelles:
Rough ERs synthesize proteins and lipids, and send them to Golgi apparatus.
Golgi apparatus modifies the proteins and lipids, and dispatches them to various destinations.
Lysosomes contain digestive enzymes to degrade intracellular organelles, and macromolecules and particles from outside through endocytosis. On the way to lysosomes, the materials must pass endosomes.
Peroxisomes are small vesicular compartments that contain enzymes used in various oxidative reactions
Evolutionary Origins Explain the Topological Relationships of Organelles
enclosure of bacterial symbiont by archaeal membrane fusion —> escape of endosymbiont into cytosol —> elaboration of internal compartments
The organelles in the secretory and endocytic pathways have an interior or lumen that is topologically equivalent to the exterior of the cell, including ER, Golgi, endosomes, lysosomes, and peroxisomes
The nuclear membrane may originate from
an invagination of the plasma membrane and pinch off with a double membrane.
The lumen of the ER is _________ with the space between the inner and outer nuclear membranes, and the space is topologically ________ to the extracellular space.
The lumen of the ER is continuous with the space between the inner and outer nuclear membranes, and the space is topologically equivalent to the extracellular space
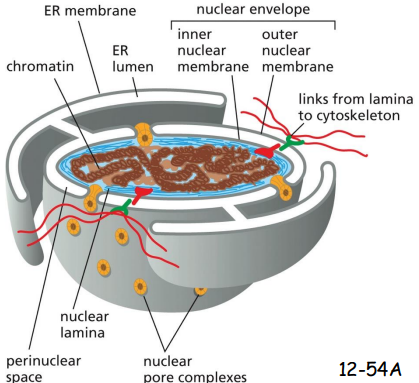
The nucleus and the cytosol communicate through_______ and topologically __________
The nucleus and the cytosol communicate through nuclear pore complexes and topologically continuous.
4 different ways proteins can move between compartments
Gated transport involves nuclear pore complexes
Protein translocation uses transmembrane protein translocators
Vesicles loaded with a cargo of molecules bud or pinch off, travel, and fuse to a second compartment of topological equivalence
Engulfment refers to moving proteins from the cytosol into the lysosome in autophagy or enclosing chromosomes inside the nucleus during nuclear envelope re-formation after mitosis
protein translocations
nucleus to cytosol: gated transport and engulfment
out of cytosol: protein translocation
everything else pretty much: vesicular transport
Sorting Signals and Sorting Receptors Direct Proteins to the correct _______ __________
cell address
common sorting signals
import into nucleus: positively charged AA
Export from nucleus, Import into ER: hydrophobic AA
import into mitochondria: hydrophobic AA alternating with + charged AA
import into plastid: uncharged polar or hydroxylated AA
Import into peroxisomes: uncharged polar/pos charged/hydrophobic AA at C-terminus
Return to ER: some negatively charged AA
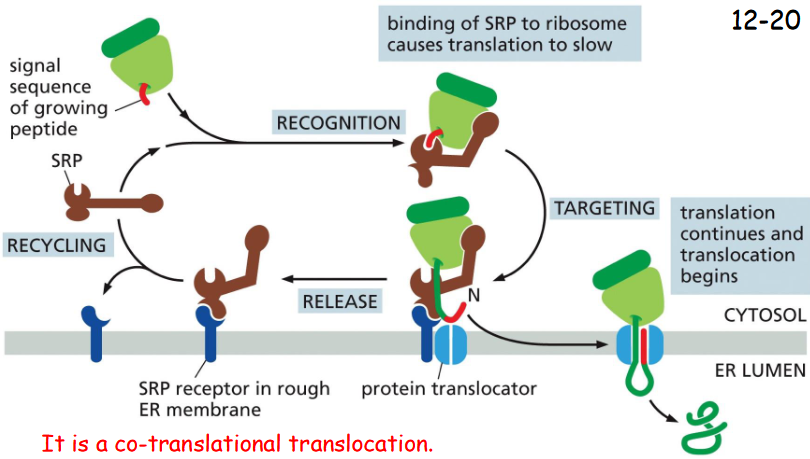
A __________ Directs the ER Signal Sequence to a __________ in the Rough ER Membrane
A Signal-Recognition Particle (SRP) Directs the ER Signal Sequence to a Specific Receptor in the Rough ER Membrane
The hydrophobic ER signal sequences are usually recognized by SRP. SRP receptor binds to SRP-ribosome complex and brings it to the translocator.
The translocator then binds ribosome, inserts the polypeptide chain into the membrane, and transfers it across the lipid bilayer to lumen
is a co-translational translocation
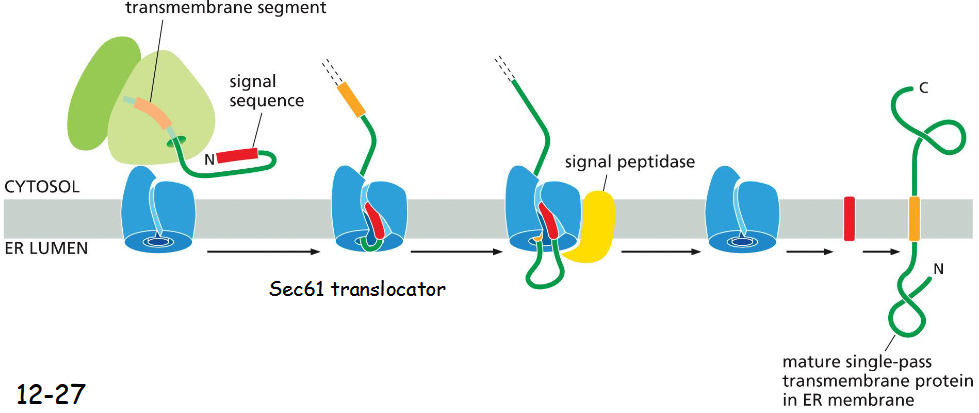
Transmembrane Proteins Contain __________ Segments That Are Recognized Like _____
hydrophobic segments recognized like signal sequences
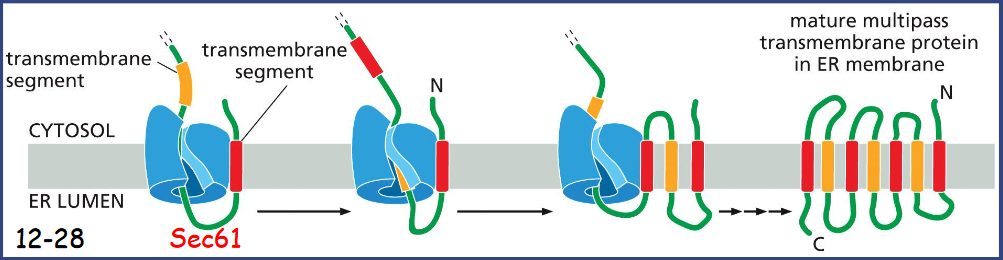
orientation of hydrophobic segments of multipass transmembrane proteins
interpret context to find orientation
When the next transmembrane segment emerges from ribosome, it inserts into lateral gate of Sec61 in orientation opposite to that of first transmembrane segment
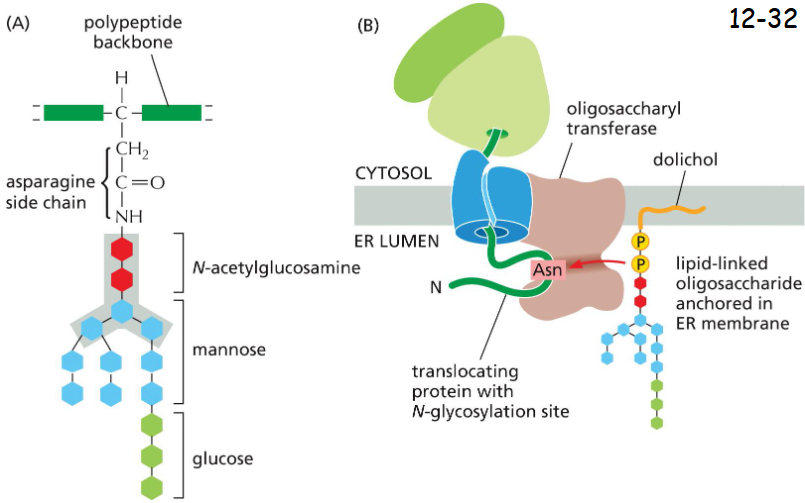
Most Proteins Synthesized in the Rough ER Are Glycosylated by the Addition of a____________
Common N-Linked Oligosaccharide
A) An oligosaccharide is attached to asparagines in the sequences Asn-X-Ser or Asn-X-Thr (where X is any amino acid except proline). The five sugars in gray box form the core region that survive extensive trimming in the Golgi apparatus.
B) A lipid molecule anchors the precursor oligosaccharide in ER lumen membrane, which is then transferred to Asn by the enzyme
Sorting Signal Sequences for import into peroxisomes
import receptor recognizes the Ser-lys-leu signal in C-terminus of proteins made in cytosolic ribosomes
Needs ATP
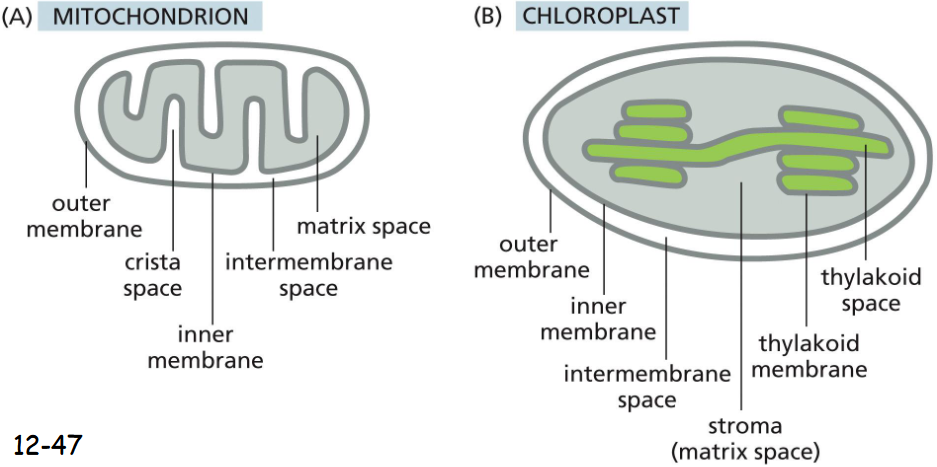
mitochondrion v chloroplast image
Thylakoid membrane is not connected to the inner membrane.
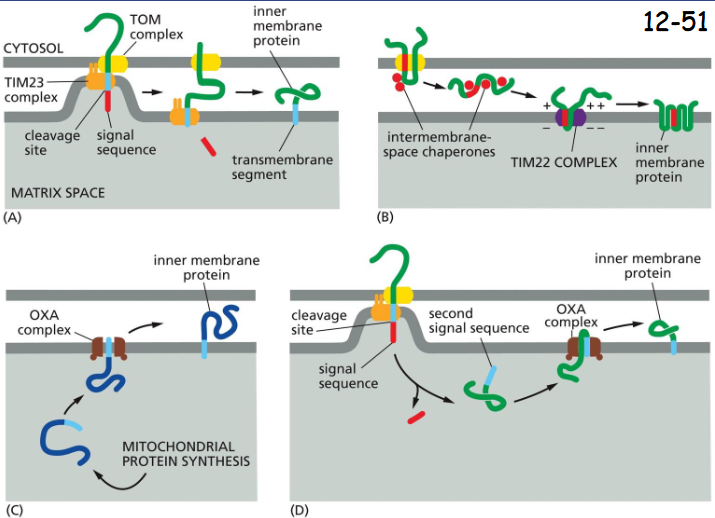
Transport Into the Inner Mitochondrial Membrane Occurs Via Several (4) Routes:
(A) A hydrophobic transmembrane segment binds to TOM and then TIM23 which puts it across the membrane
(B) Binding of the proteins to the chaperones guides to TIM22 complex, which then insert the multipass inner membrane proteins.
(C) The protein is first made in the matrix space, and a signal then directs it to the inner membrane through OXA complex.
(D) Nuclear-encoded proteins translocate into the matrix space via the TOM and TIM23 complexes. Cleavage of the signal sequence unmasks an adjacent hydrophobic signal sequence at the new N- terminus. It is inserted to the inner membrane visa OXA complex
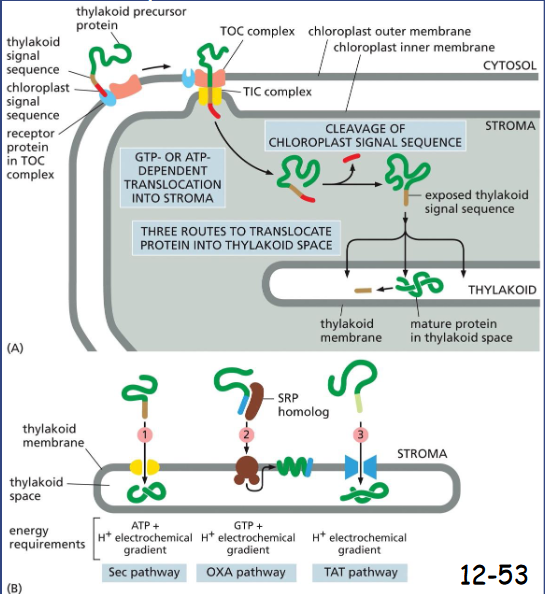
Two Signal Sequences Direct Proteins to the ___________ in Chloroplasts
Two Signal Sequences Direct Proteins to the Thylakoid Membrane in Chloroplasts
A. Chloroplast signal sequence initiates the translocation through TOC then TIC (GTP or ATP dependent) then peptide is in stroma. Cleavage unmasks the thylakoid signal sequence that initiates the translocation across the thylakoid membrane.
B. Translocation to the thylakoid space or membrane by using:
1) homolog of Sec61 (multipass proteins) that mediates protein translocation across the bacterial plasma membrane
2) homolog of OXA pathway (also using SRP homolog)
3) a TAT (twin arginine translocation) pathway, arginines important for directions
protein import into chloroplast organelles evolved from
a bacterial protein-export system
Plant cells: TIC/TOC
Bacterium: Bam/Tam
TIC —> TamB
TOC → TamA/BamA
nuclear envelope structure
Nuclear Envelope (inner + outer nuclear membrane) perforated by nuclear pore complexes (NPCs)
Nuclear Localization Signals Direct Nuclear Proteins to the
____
nucleus
mutation of nuclear import signal can lead to greater localization
Nuclear Import Receptors Bind to Both _______ _____ _________ and ______
also sometimes can bind ___ repeats in unstructured domains of _______ ____________
Nuclear Import Receptors Bind to Both Nuclear Localization Signals and NPC Proteins
Nuclear import receptors also bind the phenylalanine-glycine (FG) repeats in the unstructured domains of the channel nucleoporins
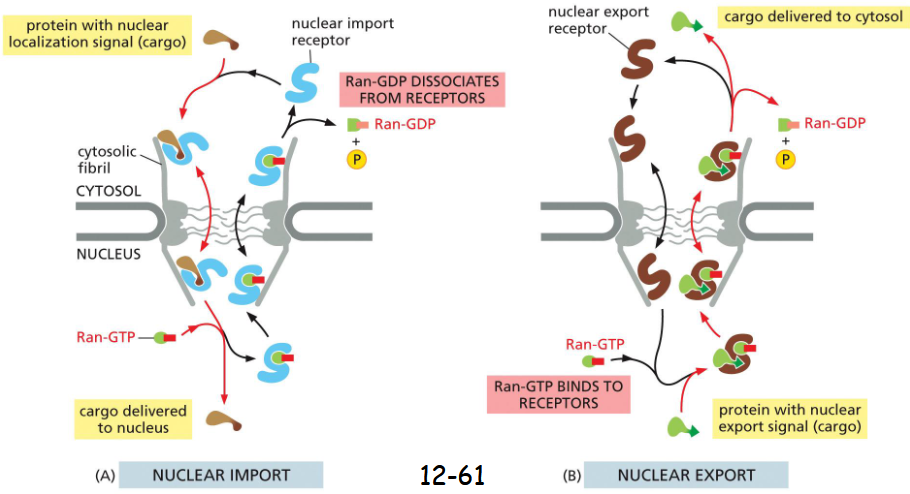
The Ran GTPase Imposes _________ on Transport Through NPCs
directionality
Ran-GDP is in the cytosol and Ran-GTP is in the nucleus. It is due to the activity of GTPase activating protein (GAP) in the cytosol and guanine exchange factor (GEF) in the nucleus
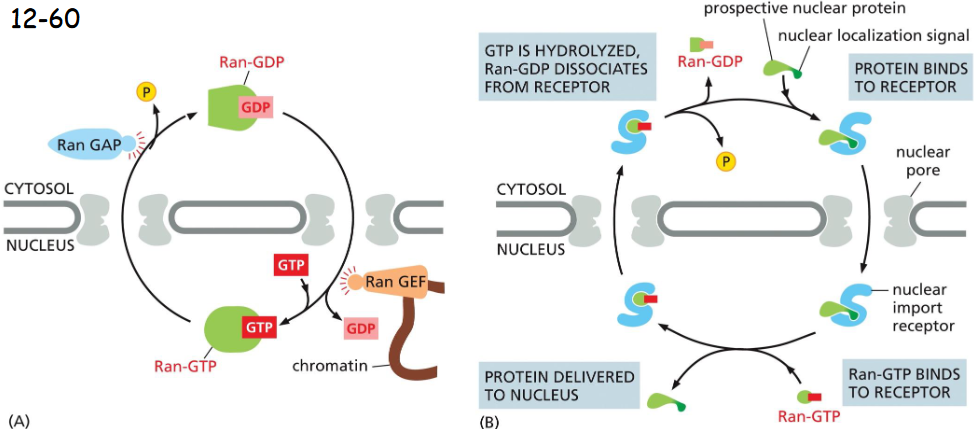
nuclear export vs import
export works just like import but in reverse
For nuclear import, Ran-GTP binding causes the receptor to release the cargo in the nuclear side, critical for the directionality of the nuclear transport.
For nuclear export, Ran-GTP binding promotes the loading of cargo. GAP in the cytosol triggers GTP hydrolysis and its dissociation from the receptor
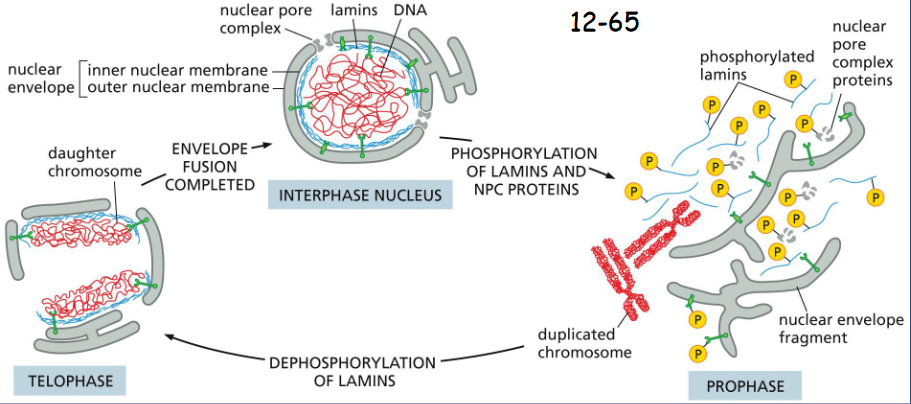
During Mitosis the Nuclear Envelope _________
disassembles
Nuclear lamina is a meshwork made by protein complex of lamins and gives shape and stability of the nuclear envelope.
During mitosis, the NPCs and lamina disassemble and the nuclear envelope fragments
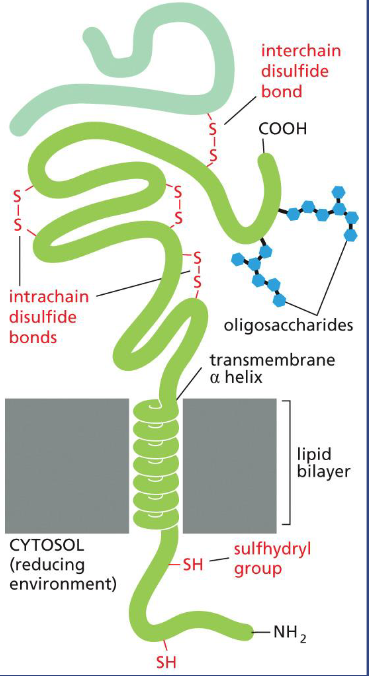
Two different structural features for inside and outside membrane protein domains:
Most membrane proteins in animal cells are glycosylated on the cell surface, or the oligosaccharides are only found on non-cytosolic surface
The intrachain or interchain disulfide bonds are only found on non-cytosolic surface. The sulfhydryl group is not forming disulfide bond in the cytosolic side due to a reducing environment.
Channels always mediate _____ transport, whereas transporters mediate either ____ or ____ transport.
channels = always passive
transporters = active or passive
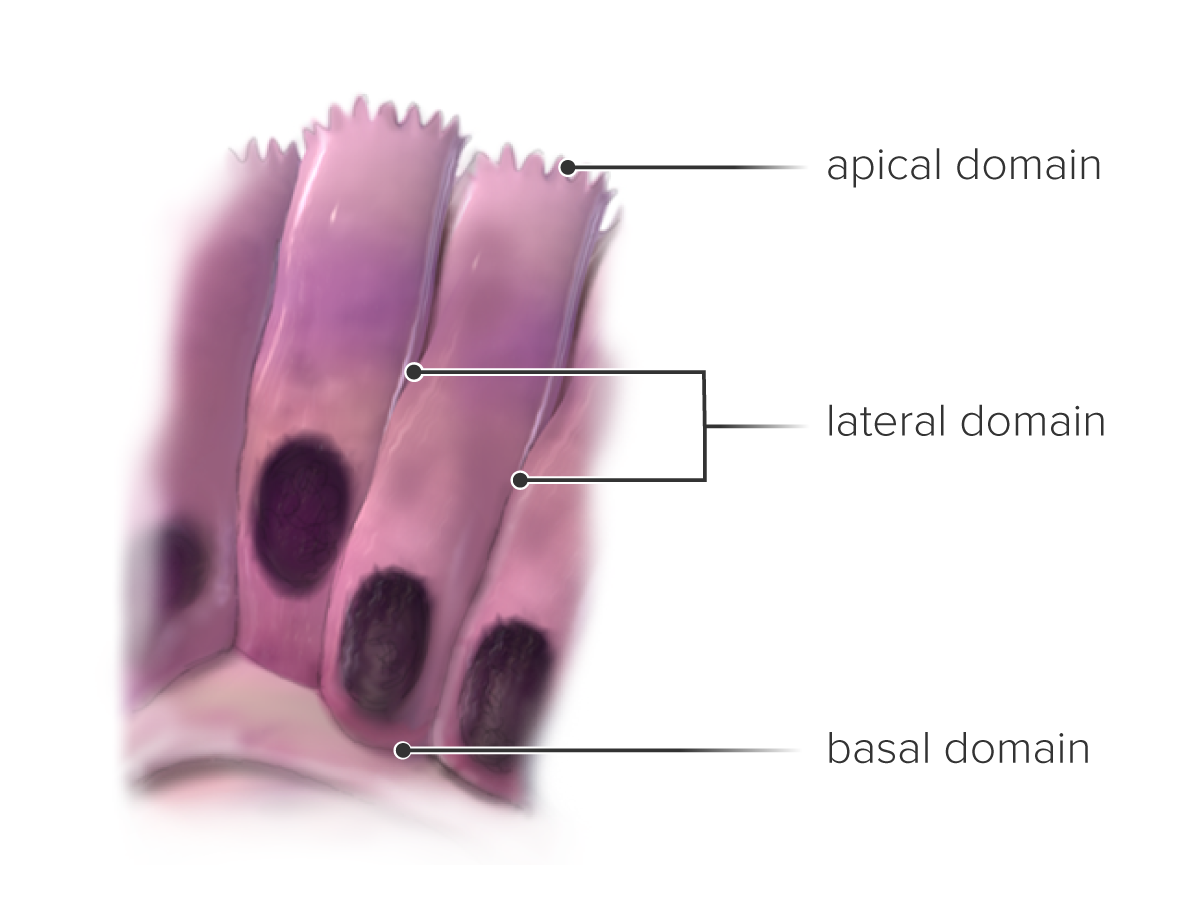
epithelial cell domains
basal domain = at base
lateral domain = middle of cell
apical domain = end of cell, tip
ABC transporters in bacteria vs eukaryotes
Both importers and exporters are found in bacteria.
In eukaryotes, most ABC transporters are exporters for ions, amino acids, polysaccharides, lipids, drugs, and peptides from cytosol to the extracellular space or into ER (similar topology as outside), or from the mitochondrial matrix to the cytosol (much like bacteria).