Fructose
1/10
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
11 Terms
Describe the Oxidation of Fructose ?
2 main routes:
conversion to fructose 6-P in small intestine
conversion to fructose 1-P, primarily in liver
What enzyme converts fructose to fructose 6-P ?
hexokinase
What does Aldolase B do ?
Fructose 1-P is split into two 3-carbon molecules
Where is the main site of metabolism of free fructose ?
Liver-Transport Fructose into hepatocytes through GLUT2
Why is fructose metabolism faster than glucose metabolism ?
because it bypasses PFK1, the main rate limiting step in glycolysis
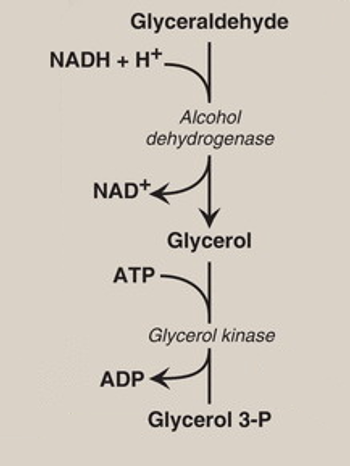
How does glyceraldehyde turn into glycerol3-P ?
Glyceraldehyde is a precursor for glycerol
Due to the lack of regulation in this pathway, high pyruvate levels are formed from fructose. Why is this an issue?
leads to high levels of acetyl CoA
High levels of triglyceride production
So fructose can lead to triglyceride production all on its own increasing lipids in the body
Also increasing the reparatory process
Leading to its association with obesity, diabetes, NAFLD
How is Fructose 6-P can be converted into glucosamine 6-P ?
amine transfer with addition of glutamine
What is the precursor for all nitrogen-containing sugars in the body ?
Glucosamine 6-P
How is fructose metabolized at low levels ?
At low levels it can be metabolized directly via glycolysis following conversion to fructose 6-P in the small intestine
How is fructose metabolized at high levels ?
At high levels (e.g., from sucrose or HFCS) an alternative pathway is followed in the liver that joins the glycolytic pathway at the three-carbon stage