Acute inflammation
1/36
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
What is inflammation
What is the goal?
Defense mechanism to injurious stimuli
Aims to dilute,isolate,and eliminate stimulus
What is acute inflammation
occurs within hours to days
hallmarks of acute inflammation
short duration,exudates (especially fibrinous)Neutrophilic inflammation due to innate immunity
What are the three phases of acute inflammation
fluidic-leakage of fluid,protein,cells resulting in exudate to dilute stimulus and bring in inflammatory mediator
cellular-neutrophil exit vessels to isolate and eliminate offending agent
reparative-if solved in timely manner inflammation ceases and tissue will regenerate without permanent damage
What are the exogenous causes of acute inflammation
microbes, foreign body, mechanical/physical, chemical toxins, nutrition
What are the endogenous causes of acute inflammation
Degenerative or neoplastic cells, hypersensitivity reaction(I&IV)
what are the effector cells of Acute inflammation
Vascular endothelial cell(main in fluid response), Neutrophil, mast cell, basophil, eosinophil, macrophage/monocytes, NK cells
What is the role of vascular endothelial cells
allows for exudates to form and for paracellular passage of water/cells
Isolates the response and expresses adhesion
What is role of neutrophils in acute inflammation
kill microbes and remove foreign material via phagocytosis
Neutrophils in intracellular microbial destruction
Respiratory burst, form phagolysosome, facilitate myeloperoxidase to kill microbes
Neutrophil mechanism of extracellular microbial destruction
release neutrophil granule contents. myeloperoxidase—>pus formation
Which species do not have neutrophils
Birds and reptiles-heterophils. Exudate=caseous
Role of mast cells/basophils in acute inflammation
degranulation and release preformed histamine
Role of eosinophils in acute inflammation
recruited from blood sites of allergic reaction/parasite infection
Bridge chronic´
Role of macrophage/monocyte in acute inflammation
first responder-survelliance and phagocytic role
Role of NK cells in acute inflammation
Trigger cell death without previous antigen exposure
What is the fluidic phase of acute inflammation characterized by
Vasodilation- hyperemia + heat increased vascular permeability and exudation—>swelling(edema)
What is key difference in edema vs exudate? Increased interendothelial gaps in…
inflammation(edema)
What are some gross manifestation of fluidic phase of acute inflammation
effusion,fibrin,hyperemia
What is the purpose of the cellular phase of acute inflammation
Bring leukocytes to site of injury to eliminate the cause
What are the 4 steps of cellular phase of acute inflammation
Margination-vasodilation= slower flow=leukocyte settle
Rolling=selectins=initial attachment of leukocytes
Tight binding=inflammatory mediators express integrin=stable adhesion
Diapedesis& migration=leukocytes pass through the endothelium to reach the tissue
Functions of Histamine and Serotonin as cell derived mediators
Vasodilation, increase vascular permeability, eosinophil chemotaxis
Function of cytokines and interferons as cell derived mediators
Regulate immune response
Function of free radicals as cell derived mediators
Increase vascular permeability, activate endothelium, promote chemokine production, inactivate protease
Role of fibrin in acute inflammation
Attempts to wall off site of inflammation
Role of MAC
insert on bacterial wall create a pore and lead to lysis of cell
What are the four outcomes in reparative phase of acute inflammation
Resolution (ultimate goal), healing by fibrosis, abscess formation, progress to chronic inflammation
For resolution to occur in acute inflammation what must occur
Macrophages and lymphatics remove exudate, incite cause eliminated, stroma intact for regeneration, epithelial cells regenerate along basement membrane
5 cardinal sign of inflammation
Calor, rubor, tumor, dolor
Serous exudate characteristics
watery, clear fluid
Characterized by low protein, low cellularity
Causes: thermal injury, allergies, viral infection
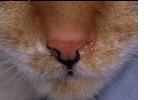
Catarrhal exudate characteristics
Mucoid discharge-cloudy tan to light yellow
Abundant mucus and neutrophils
Causes: chronic allergies and viral infections

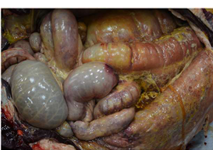
Fibrinous inflammatory exudate characteristics
Tan to yellow stringy often lining serosal surface
Caused by bacterial infections, viral infections that injure endothelium
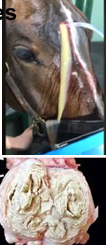
Suppurative/purulent exudate characteristics
Tan to yellow, thick liquid to semi solid caseous material
Pus
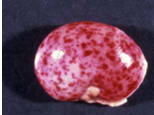
Hemorrhagic exudate characteristics
Red foci
#erythrocytes caused by trauma, coagulopathies
Morphologic diagnosis-duration What is acute?
Necoris,fibrin,hemorrhagic,suppurative inflammation
For morphologic diagnosis duration-what is chronic?
Fibrosis, granulomatous inflammation, altered size
When we name a morphologic diagnosis what do we use?
Duration, severity, distribution, modifier, process