eukaryotic transcription 2
1/44
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
45 Terms
What is the main role of transcription factors (TFs)?
They decide whether transcription happens, which genes are expressed, and when (e.g. in response to signals) 🎛️.
Why are transcription factors hard to study experimentally?
They are low-abundance proteins present in very small amounts 🧪.
What determines a transcription factor’s function?
Its amino acid sequence and 3D structure 🧠.
How can transcription factors be identified using bioinformatics?
By finding conserved DNA sequences near genes that suggest TF binding sites 💻.
How can we use mutations to analysis and help identify transcription factors?
By mutating promoter or USE sequences and observing changes in transcription 🔧.
How were transcription factors classically isolated?
Using DNA affinity chromatography to purify proteins that bind specific DNA sequences 🧲.
What classic experiment identified Sp1?
Tjian (1986) used GC-box DNA to isolate Sp1 from HeLa cells 🧬.
What does it mean that transcription factors are modular proteins?
They have separate DNA-binding and regulatory domains that work independently 🧩.
Why does DNA binding alone not activate transcription?
Because activation requires a separate activation domain to interact with transcription machinery ⚠️.
What are the three major types of DNA-binding domains in transcription factors?
Zinc fingers ✋,
helix–turn–helix 🌀,
and basic (positively charged) domains ➕.
What is a zinc finger DNA-binding domain?
A ~23 amino acid loop stabilised by Zn²⁺ that uses an α-helix to bind DNA, usually in the major groove 🧷.
Does zinc bind DNA directly in zinc finger proteins?
No — Zn²⁺ stabilises protein folding, not DNA binding ❌.
Which transcription factor is a classic zinc finger protein?
Sp1 🧬.
What is a helix–turn–helix (HTH) DNA-binding domain?
Two α-helices where one “recognition helix” binds the major groove of DNA 🔍.
How do HelixTturnHelix proteins bind DNA?
As dimers, with recognition helices spaced one DNA turn apart 🔗.
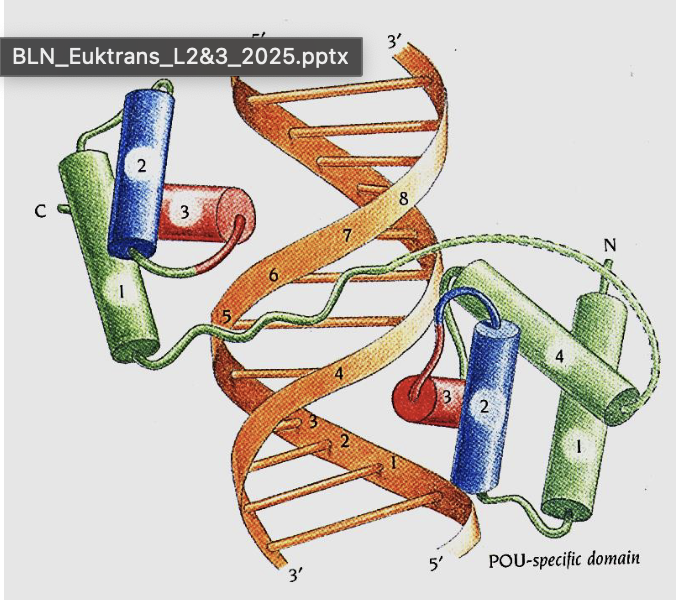
What are homeodomains?
A type of HTH domain (~60 aa, 3 α-helices) important for developmental gene regulation 🧠.
What is a basic DNA-binding domain?
A positively charged domain in the TF that cannot bind DNA alone and must dimerise ➕.
What are the two main types of basic DNA-binding domains?
Leucine zipper 🤐 and helix–loop–helix 🔁.
Which transcription factor is an example of a basic zipper protein?
C/EBP 🧬.
How are ligand-dependent transcription factors regulated?
They are inactive without ligand and become active after ligand binding 🎯.
Where are steroid hormone receptors located before activation?
In the cytoplasm or nucleus, but inactive 🚫.
What structural feature do steroid hormone receptors contain?
Cys₂–Cys₂ zinc fingers ✋.
What happens when a ligand binds a steroid hormone receptor?
Conformational change 🔄, dimerisation 🤝, nuclear localisation 🚪, DNA binding.
Give examples of ligand-dependent transcription factors.
VDR, GR, ER, AR 🧪.
What is an activation domain?
A region of a TF that stimulates transcription but does not bind DNA ⚡.
Do activation domains have a fixed 3D structure?
No — they are flexible and defined by amino acid composition 🧠.
What are the three common types of activation domains?
Acidic ⚡, glutamine-rich 🧬, and proline-rich 🧱.
How do activation domains stimulate transcription?
By interacting directly with the PIC or recruiting co-activators 🤝.
Which PIC components can activation domains interact with?
TBP and TAFs 🧩.
What are co-activators?
Proteins that do not bind DNA but link TFs to transcription machinery and modify chromatin 🔗.
Why is chromatin structure important for transcription?
Tightly packed chromatin blocks access to DNA and represses transcription 🧶.
How do histone acetyltransferases (HATs) activate transcription?
They acetylate lysines, reduce histone positive charge, and loosen chromatin 🔓.
Why does histone acetylation loosen chromatin?
It weakens histone–DNA interactions by neutralising charge ⚖️.
What is p300/CBP?
A major co-activator with HistonAcetylTransferase activity recruited by steroid hormone receptors 🏗.
Which histones are acetylated by p300/CBP?
H3, H4, H2A, and H2B 🧬.
What is an inhibitory (repressor) domain?
A TF domain that reduces or shuts down transcription 🚫.
List three mechanisms of transcriptional repression.
Blocking activator binding ✋, blocking the PIC 🧱, or recruiting co-repressors 🧲.
What do histone deacetylases (HDACs) do?
Remove acetyl groups, tighten chromatin, and repress transcription 🔒.
What is SMRT?
A co-repressor that works with HDAC1/2 to repress transcription 🧩.
How does SMRT repress transcription?
It recruits HDACs and stabilises interactions that block transcription ❌.
Why is tamoxifen clinically important?
It is an oestrogen receptor antagonist used in breast cancer treatment 💊.
How does tamoxifen inhibit transcription?
It forces ER into a conformation that recruits co-repressors instead of co-activators 🚫.
Why can tamoxifen resistance occur in some cancers?
Some cancers recruit co-activators even when tamoxifen is present ⚠️.
What is the key takeaway about transcription factor regulation?
Transcription depends on TF structure, chromatin state, and co-activator or co-repressor recruitment 🧠.