Connective Tissue Proper (draft)
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Coordinator: Tomislav Jelesijevic
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
Mesenchymal stem cell function
Embryonic source of all connective tissue cells
Fibroblast function
Structural support. Synthesize collage, reticular and elastin fibers, extracellular substance (glycoproteins and glycosaminoglycans)
Pericytes function
Angiogenesis, maintenance of blood-brain barrier, vascular integrity, inflammation response
Adipocytes function
Energy storage, thermal insulation
Plasma cells function
Antibody production
Mast cells function
Important in allergies, mediate inflammatory response
Macrophages function
Immune mediated inflammatory response
Granulocytes function
Immune mediated inflammatory response
Lymphocytes function
Immune mediated inflammatory response
Mesenchymal cells
The stem cells of connective tissue hence have the potential to differentiate into nearly all connective tissue cells.
True or False: Mesenchymal cells are abundant in adult tissues.
False: rare in adult tissues, abundant in embryonic tissues
Which of the following in NOT a mixed/immobile CT cell?
Fibroblasts/cytes
Pericytes
Adipocytes
Granulocytes
Mast cells
Undifferentiated mesenchymal cells
Granulocytes are transient/mobile CT cells along with lymphocytes, monocytes, and plasma cells.
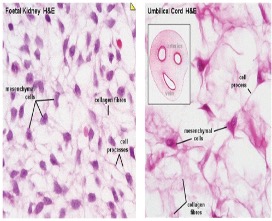
What is depicted in the photo?
Mesenchymal stem cells in between process of differentiating.
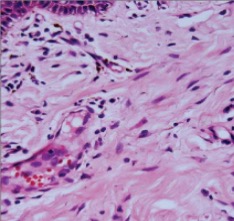
What is depicted in the photo?
Fibrocytes (darker, more condensed) and fibroblasts (lighter)
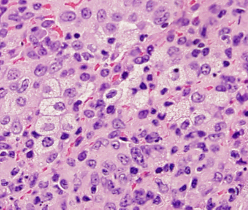
What is depicted in the photo?
Macrophages
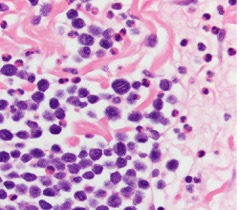
What is depicted in the photo?
Mastocytes
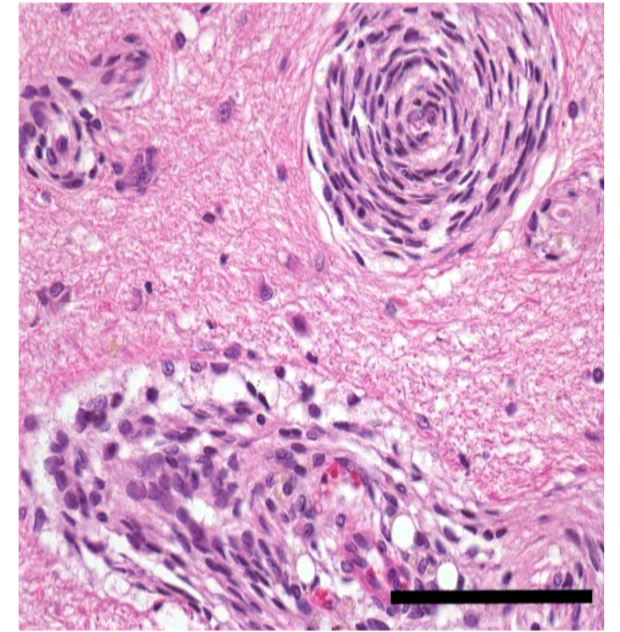
What is depicted in the photo?
Pericytes
What are the most important, abundant, long-living connective tissue cells?
fibroblast/cytes
What do fibroblast/cytes make?
Connective tissue fibers (collagen, reticular and elastic fibers) and ground substance
Difference between a fibroblast and fibrocyte?
smaller/larger nuclei and active/inactive cell
What identifies a pericyte?
associated with capillaries and endothelial cells
What are the two most common forms of adipocytes?
Unilocular and multilocular
Unilocular adipocytes
White fats cells (loose)
Single large fat lipid droplet like cytoplasm
Unilocular/White adipocytes function
Energy storage, insulation, protecting vital organs, secretion of adipokines
Multilocular
Brown fat cells (dense) in small mammals and newborns.
Multiple small fat lipid droplets in cytoplasm and high number of mitochondria.
Main functions of multilocular/brown adipocytes
thermogenisis and energy storage
What is the name for an inactive fibroblast?
Fibrocyte
What type of collagen is in white adipocytes?
type IV
What is special about white adipocytes outer layer?
Lipid droplets covered with phospholipid monolayer
Why are macrophages called glitter cells?
foamy cytoplasm
What are macrophages derived from?
Monocytes in the blood
Another name for macrophages
Histiocytes
Examples of macrophages
Kupffer cells in liver and microglial cells in the brain
Perivascular
Usually found around blood vessels
Metachromatic
stain a different color than dye used
Where are mastocytes usually found?
Found around blood vessels (perivascular)
What granules are metachromatic?
Mastocyte granules
What cells are transient/mobile?
leukocytes: ben, monocytes, lymphocytes
Plasma cells
activated B lymphocytes that secrete a large number of antibodies
What is the ground substance made of?
Glycosaminoglycans
What type of collagen do reticular fibers have?
type III
How many types are collagen fibers are there?
28
What cells/fibers are basophilic and which is acidophilic?
Mast cells and collagen fibers