✂️ Lecture 8: Post-transcriptional Gene Control
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
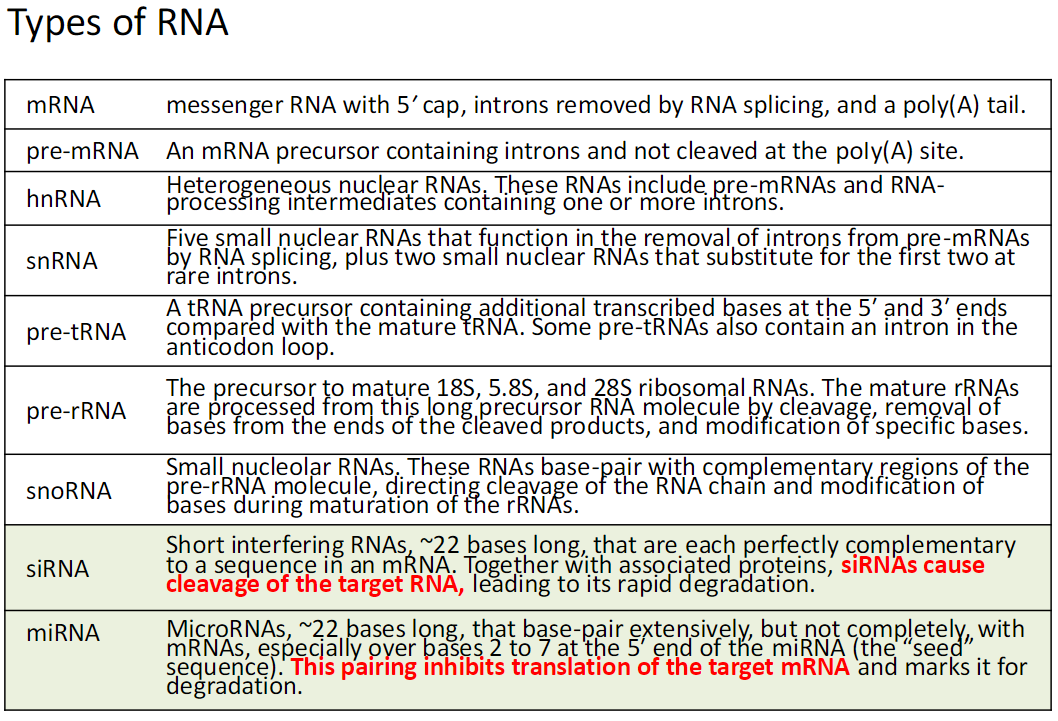
Types of RNA *Probably just know siRNA and miRNA
mRNA (Messenger RNA)
Contains a 5′ cap, introns removed by RNA splicing, and a poly(A) tail
pre-mRNA
Precursor mRNA containing introns
Not yet cleaved at the poly(A) site
hnRNA (Heterogeneous Nuclear RNA)
Includes pre-mRNAs and RNA-processing intermediates containing one or more introns
snRNA (Small Nuclear RNA)
Five small nuclear RNAs that remove introns from pre-mRNAs by splicing
Two additional snRNAs act at rare introns
pre-tRNA
tRNA precursor with extra bases at the 5′ and 3′ ends
Some contain an intron in the anticodon loop
pre-rRNA
Precursor to mature 18S, 5.8S, and 28S rRNAs
Processed by cleavage, trimming, and base modification
snoRNA (Small Nucleolar RNA)
Base-pairs with pre-rRNA
Directs cleavage and modification of rRNA during maturation
siRNA (Short Interfering RNA)
~22 bases long
Perfectly complementary to an mRNA sequence
Causes cleavage and rapid degradation of the target RNA
miRNA (MicroRNA)
~22 bases long
Partially base-pairs with target mRNAs, especially bases 2–7 (“seed” sequence)
Inhibits translation and marks mRNA for degradation
Pre-mRNA Processing and Splicing
Pre-mRNA Processing
The primary transcript is capped, spliced, and polyadenylated before export to the cytoplasm
Splicing
A large ribonucleoprotein spliceosome joins two exons and removes introns
Exon Recognition
SR proteins, snRNPs, and splicing factors form a cross-exon recognition complex
Specifies correct splice sites
SR Proteins
RNA-binding proteins with an RNA Recognition Motif (RRM) and an RS domain (arginine-serine repeats)
Involved in mRNA splicing, gene expression, mRNA export, stability, and translation
Alternative Splicing of mRNA
Function
Alternative splicing and alternative cleavage at different poly(A) sites generate diverse mRNAs from the same gene
Occurs in different cell types or developmental stages
Some resulting proteins have drastically different activities
Examples
1) Neurons – affects perception of sound and neuron connectivity
2) Drosophila – controls sex determination
Alternative Splicing in Sound Perception *Don’t memorize specifics
Function
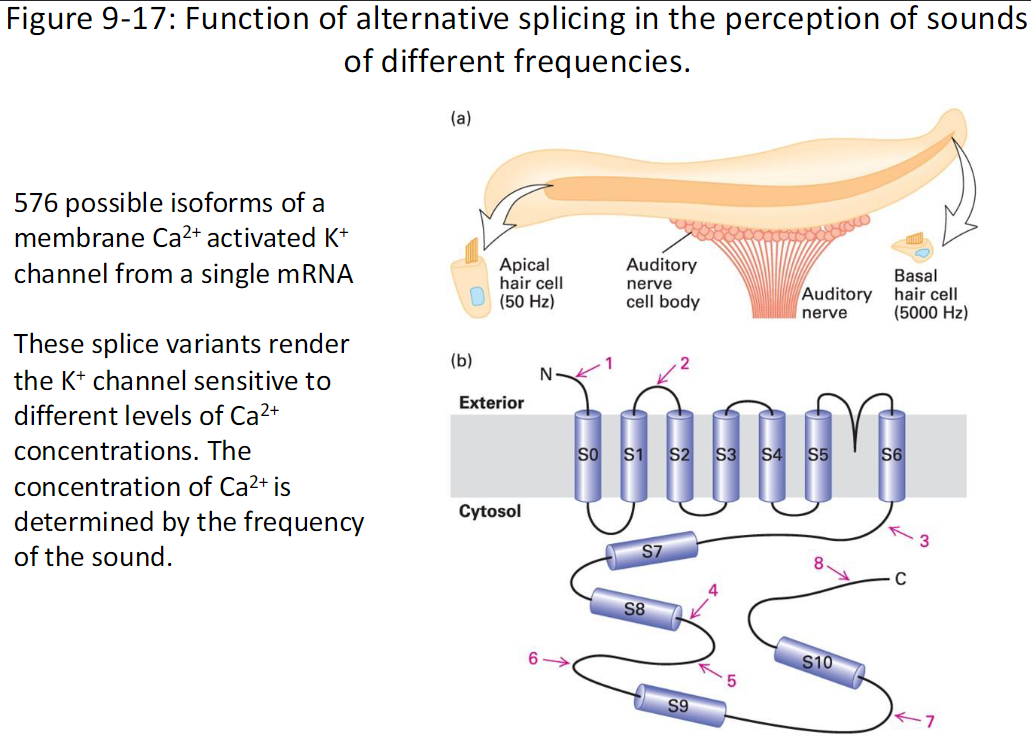
A single mRNA can produce 576 possible isoforms of a membrane Ca²⁺-activated K⁺ channel
Effect
Different splice variants make the K⁺ channel sensitive to varying Ca²⁺ concentrations
Ca²⁺ levels are determined by the frequency of the sound
Figure Reference
Fig. 9-17
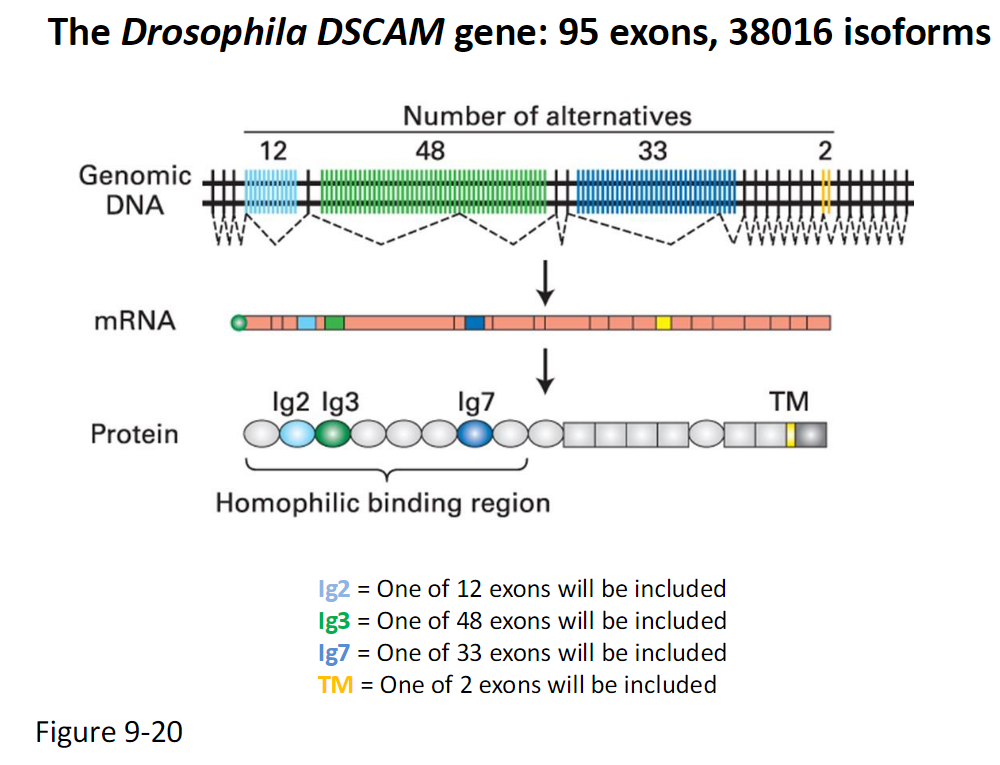
Drosophila DSCAM Gene and Alternative Splicing *Just know that splicing is important
Gene Structure
95 exons total
Produces 38,016 possible isoforms
Variable Exons
Ig2 – one of 12 exons included
Ig3 – one of 48 exons included
Ig7 – one of 33 exons included
TM – one of 2 exons included
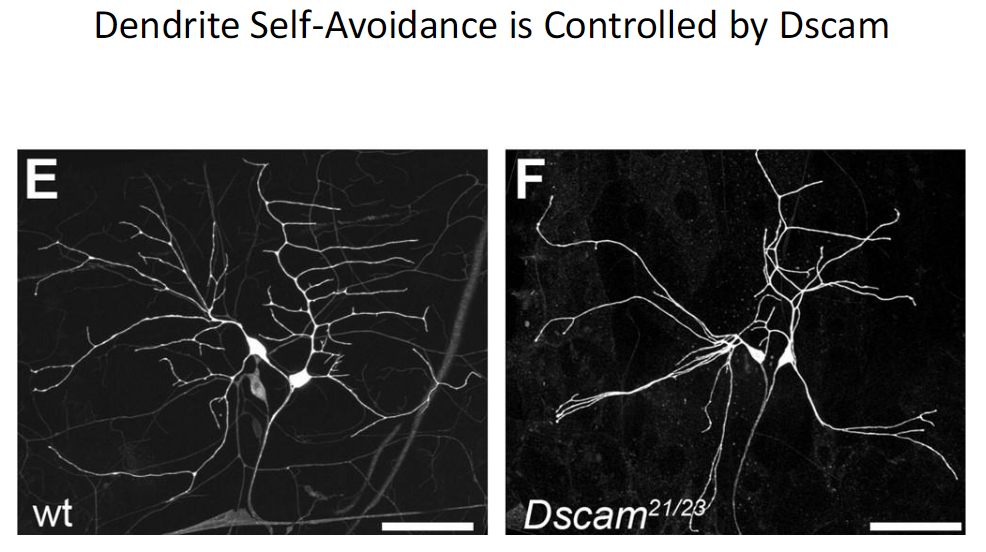
Dendrite Self-Avoidance and Dscam
Function
Dscam controls dendrite self-avoidance
Ensures that branches from the same neuron do not overlap
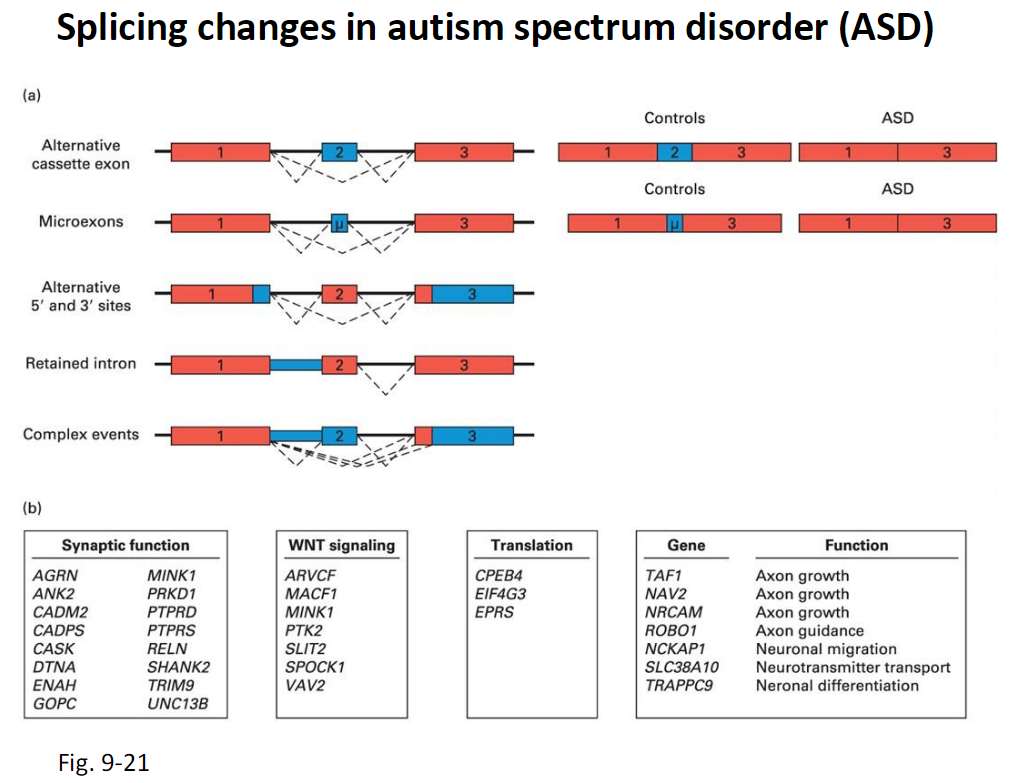
Splicing Changes in Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
Types of Splicing Changes
Alternative cassette exons
Microexons
Alternative 5′ and 3′ splice sites
Retained introns
Complex splicing events
Observation
These splicing changes differ between ASD patients and controls
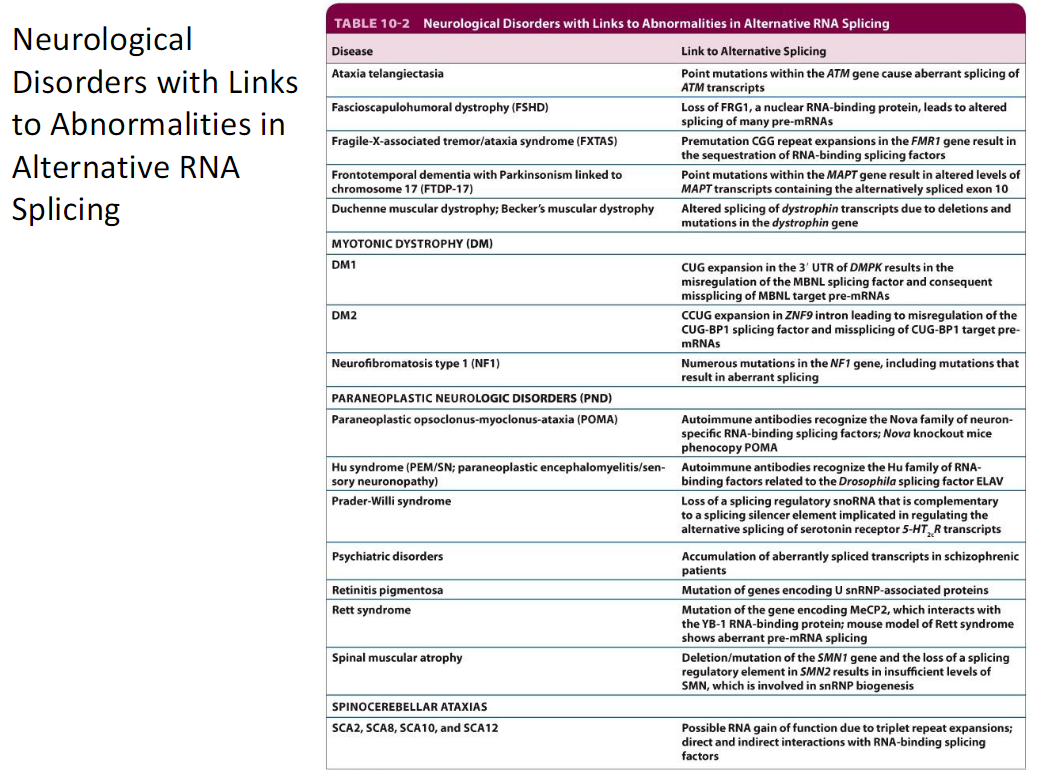
Neurological Disorders Linked to Abnormal Alternative RNA Splicing *Probably don’t need to know names
Diseases
Ataxia telangiectasia
Facioscapulohumeral dystrophy (FSHD)
Fragile-X-associated tremor/ataxia syndrome (FXTAS)
Frontotemporal dementia with Parkinsonism linked to chromosome 17 (FTDP-17)
Duchenne muscular dystrophy; Becker's muscular dystrophy
Myotonic dystrophy (DM1, DM2)
Neurofibromatosis type 1 (NF1)
Paraneoplastic neurologic disorders (PND)
Paraneoplastic opsoclonus-myoclonus-ataxia (POMA)
Hu syndrome (paraneoplastic encephalomyelitis/sensory neuronopathy)
Prader-Willi syndrome
Psychiatric disorders
Retinitis pigmentosa
Rett syndrome
Spinal muscular atrophy
Spinocerebellar ataxias (SCA2, SCA8, SCA10, SCA12)
Sex Determination in Drosophila
Sxl (Sex Lethal)
Controls female development by regulating splicing of downstream genes
Tra (Transformer)
Acts downstream of Sxl to control splicing of other genes
Dsx (Double Sex)
Final gene in the pathway that determines sexual characteristics
Figure Reference
Fig. 9-18
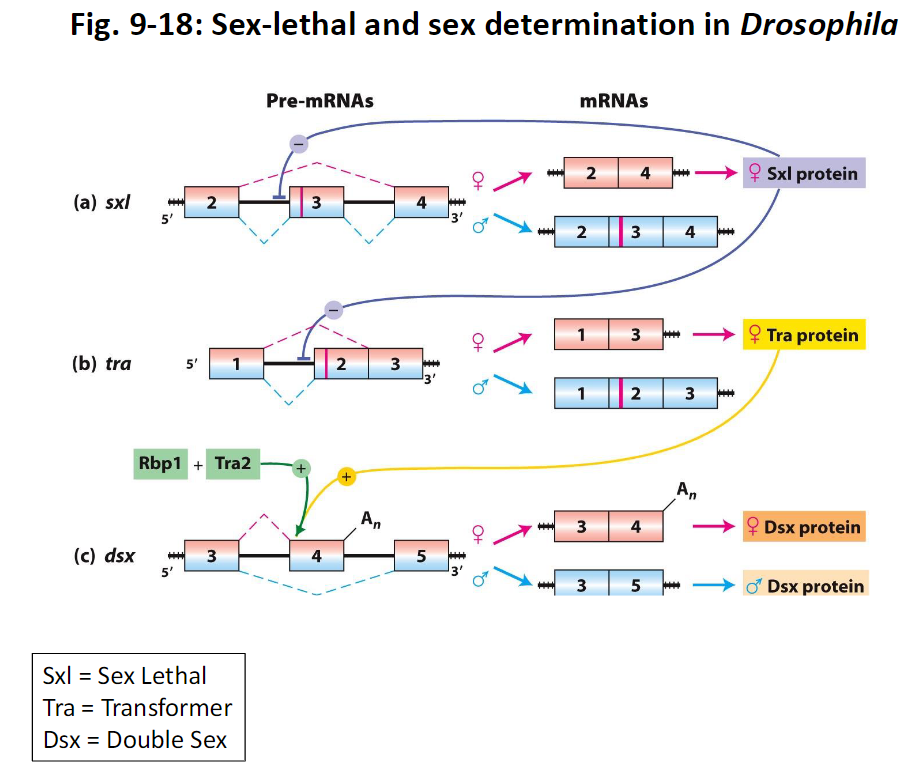
Alternative Splicing and Sex Determination in Drosophila
Key Regulators
Sxl, Tra, and Dsx control sexual differentiation
Mechanism
RNA-binding proteins recognize specific sequences near splice sites to regulate alternative splicing
Roles of Proteins
Sxl – RNA-binding protein, acts as a suppressor of splicing
Tra – RNA-binding protein, acts as an activator of splicing
Dsx – transcription activator or repressor

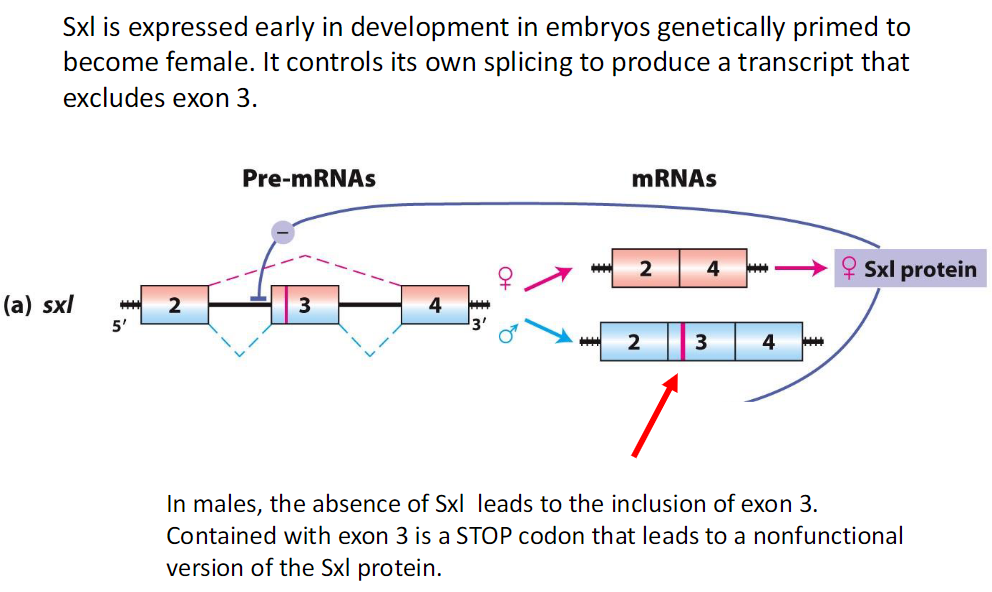
Sex-Lethal (Sxl) and Exon 3 Splicing
In Males
Sxl is absent
Exon 3 is included in the transcript
Exon 3 contains a STOP codon
Leads to a nonfunctional Sxl protein
In Females
Sxl is expressed early in development
Controls its own splicing to exclude exon 3
This produces a functional Sxl protein
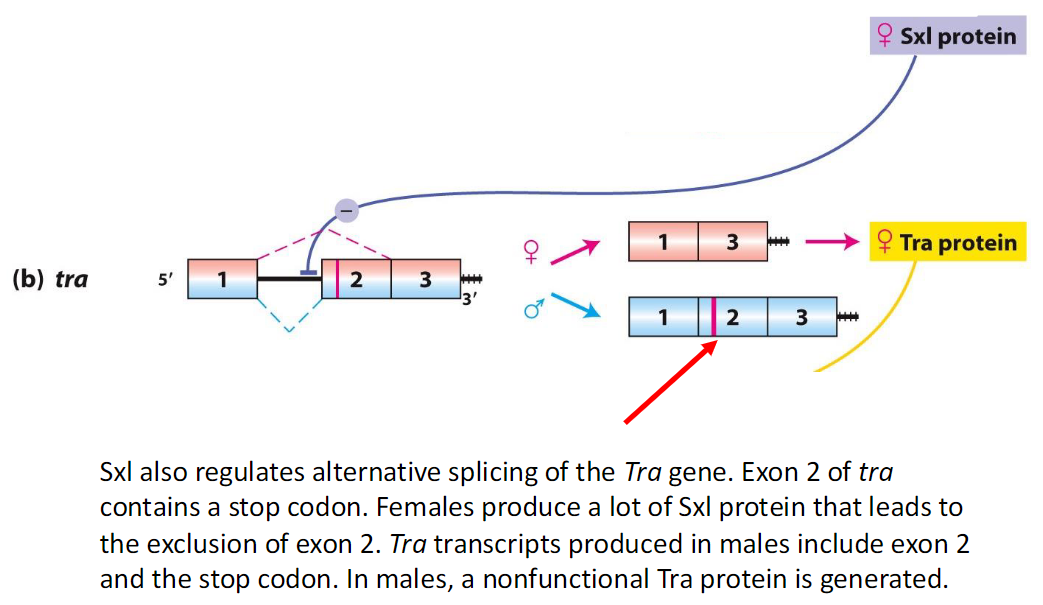
Sxl Regulation of Tra Splicing
In Females
High levels of Sxl protein
Exon 2 of Tra is excluded
Produces functional Tra protein
In Males
Sxl is absent
Exon 2 of Tra is included, containing a stop codon
Generates a nonfunctional Tra protein
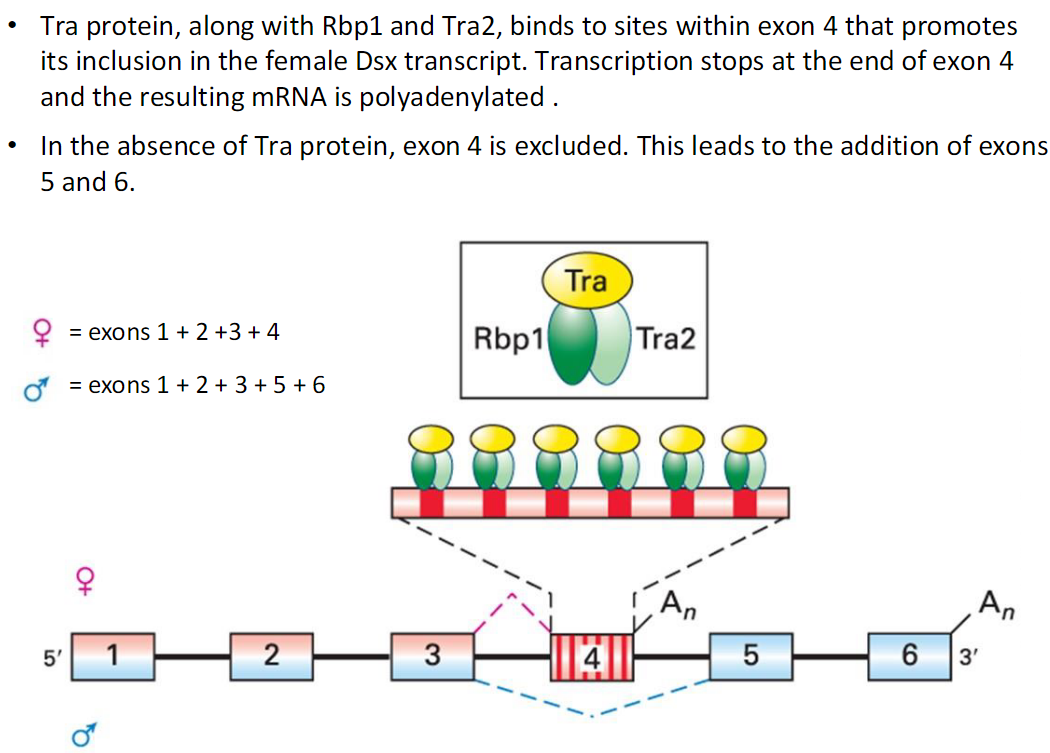
Tra Regulation of Dsx Splicing
In Females
Tra protein, with Rbp1 and Tra2, binds sites in exon 4
Promotes inclusion of exon 4 in the Dsx transcript
Transcription stops at exon 4
mRNA is polyadenylated
Resulting Dsx transcript = exons 1 + 2 + 3 + 4
In Males
Tra protein is absent
Exon 4 is excluded
Exons 5 and 6 are added instead
Resulting Dsx transcript = exons 1 + 2 + 3 + 5 + 6
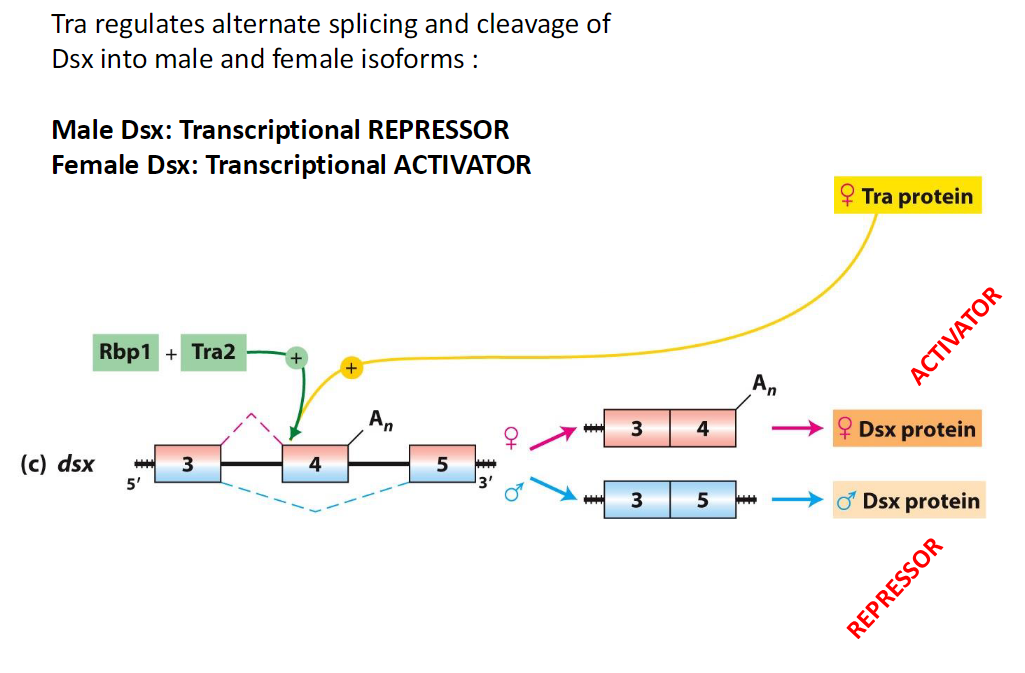
Tra and Dsx Isoforms
Function
Tra regulates alternative splicing and cleavage of Dsx
Dsx Isoforms
Male Dsx – acts as a transcriptional repressor
Female Dsx – acts as a transcriptional activator
miRNA and siRNA
Function
Regulate mRNA stability and translation
miRNA (microRNA)
Causes translational repression
Effect is reversible
siRNA (small interfering RNA)
Causes RNA degradation
Effect is permanent
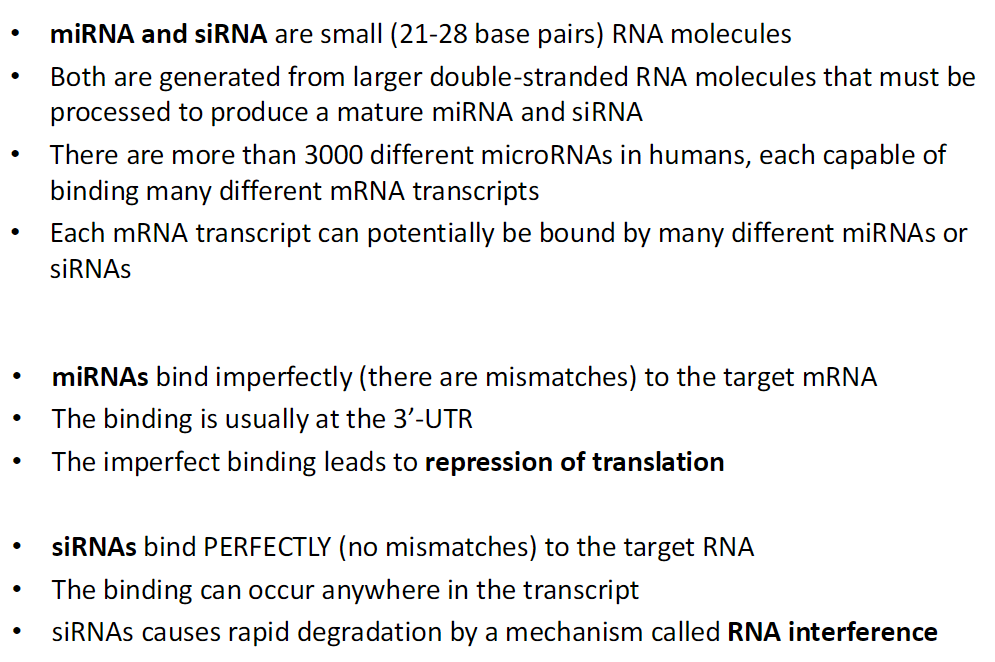
miRNA and siRNA: Small RNA Regulators
Size and Origin
Both are small RNA molecules (21–28 base pairs)
Generated from larger double-stranded RNAs that are processed into mature miRNA or siRNA
Diversity
Humans have over 3000 different miRNAs
Each miRNA can bind many different mRNA transcripts
Each mRNA can be targeted by many different miRNAs or siRNAs
Binding and Function
miRNAs – bind imperfectly (with mismatches), usually at the 3′-UTR, leading to translational repression (reversible)
siRNAs – bind perfectly (no mismatches), can bind anywhere on the transcript, cause rapid RNA degradation via RNA interference (permanent)
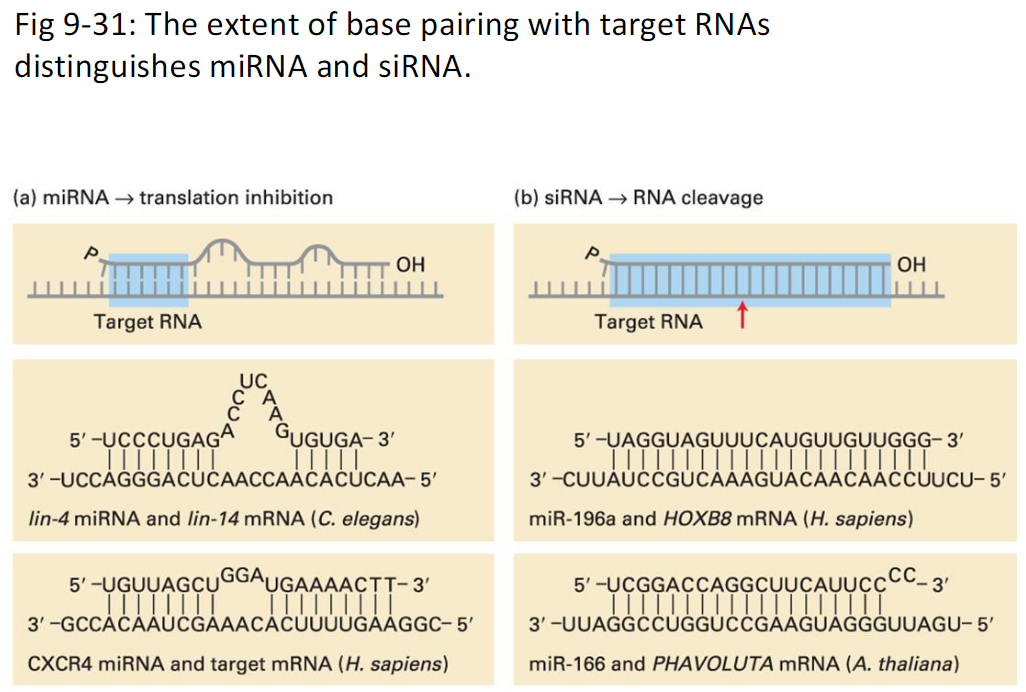
miRNA vs siRNA
Difference in Base Pairing and Effect
miRNA – binds imperfectly to target RNA, usually at the 3′-UTR → blocks the ribosome from translating the mRNA, so protein is not made (reversible repression)
siRNA – binds perfectly to target RNA anywhere in the transcript → recruits RNA cleavage machinery, causing the mRNA to be cut and degraded (permanent silencing)
Figure Reference
Fig. 9-31
miRNA and siRNA in Biological Regulation
Function
Regulate nearly every biological process
Example
Animals lacking Dicer, the enzyme that processes miRNAs/siRNAs, fail to develop beyond gastrulation
Knock-out strains are created by deleting or silencing a target gene
Disease Relevance
Abnormal miRNA/siRNA levels contribute to many diseases, including cancer
Dicer
An RNase that cleaves double-stranded RNA into miRNAs or siRNAs

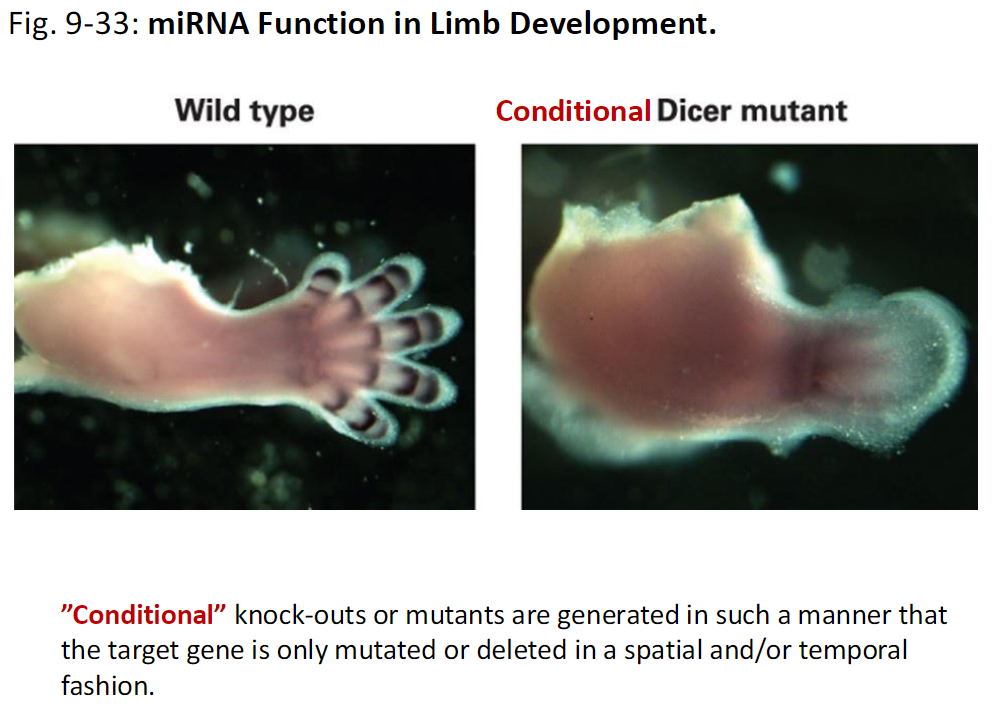
miRNA Function in Limb Development
Observation
Wild type – normal limb development
Conditional Dicer mutant – limb development is disrupted
Conditional Knock-Outs
Target gene is mutated only in specific tissues or at specific times, not throughout the whole organism
Figure Reference
Fig. 9-33
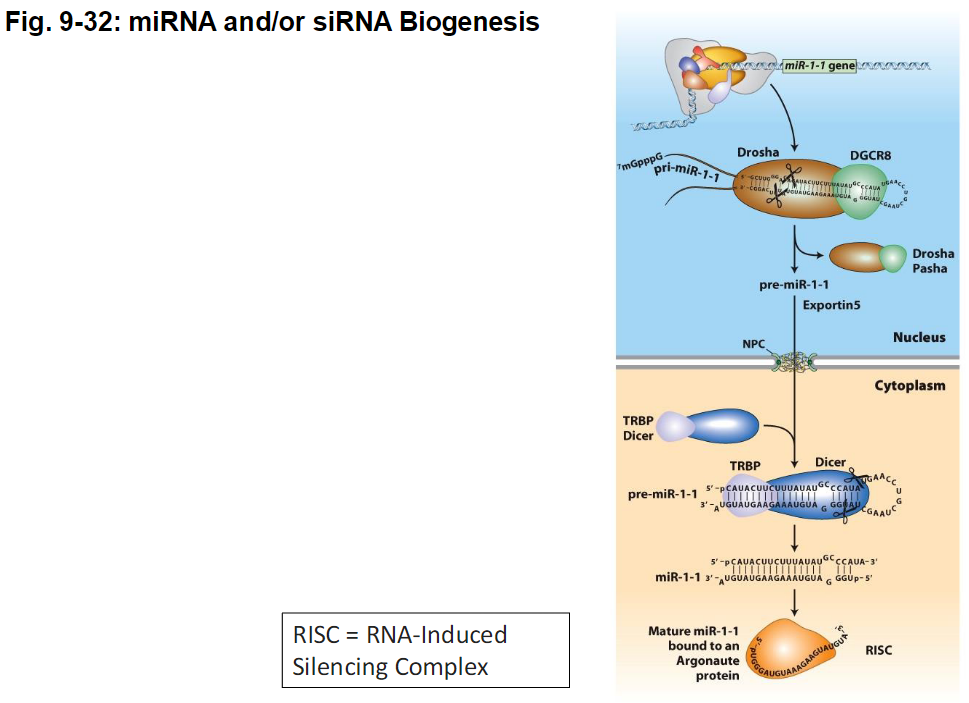
RISC and Small RNA Function
RISC (RNA-Induced Silencing Complex)
A protein complex that incorporates miRNA or siRNA
Guides the small RNA to its target mRNA
Function
miRNA in RISC – binds imperfectly to mRNA → blocks translation
siRNA in RISC – binds perfectly to mRNA → directs RNA cleavage
Figure Reference
Fig. 9-32: miRNA and siRNA biogenesis
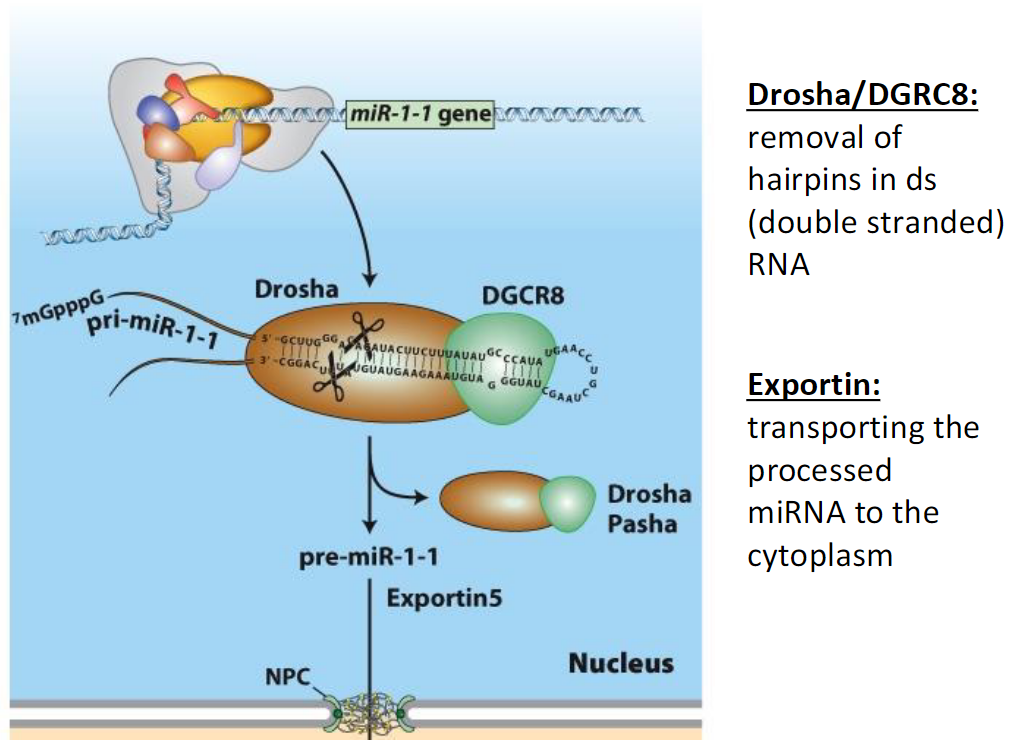
miRNA Processing and Export
Drosha/DGCR8
Removes hairpin structures from double-stranded RNA in the nucleus
Exportin
Transports the processed miRNA from the nucleus to the cytoplasm
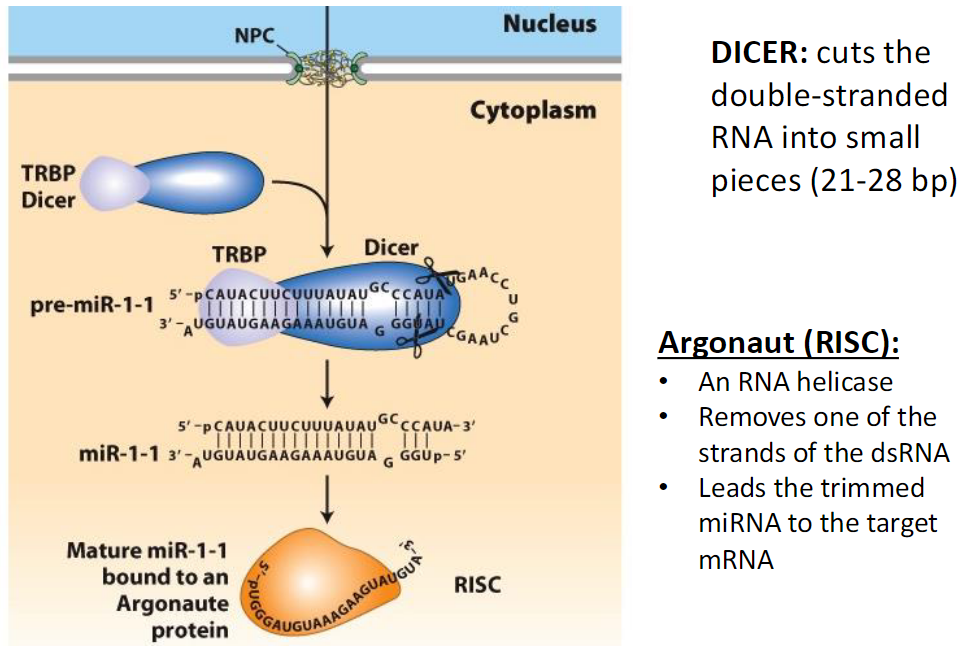
Dicer and RISC in miRNA/siRNA Processing
Dicer
Cuts double-stranded RNA into small fragments (21–28 bp)
Argonaute (RISC)
An RNA helicase
Removes one strand of the double-stranded RNA
Guides the remaining miRNA/siRNA to its target mRNA
miRNA vs siRNA: Similarities and Differences
Similarities
Both are short RNAs (21–28 bases)
Both are generated from double-stranded RNA by Drosha, Pasha, Dicer, and RISC
Differences
miRNA – binds imperfectly to target mRNA → suppresses translation (reversible)
siRNA – binds perfectly to target mRNA → causes rapid degradation (permanent), quickly stopping gene expression