Electron Configurations and Quantum Numbers
1/19
Earn XP
Description and Tags
These flashcards cover key concepts related to electron configurations and quantum numbers, aiding in the understanding of atomic structure.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
20 Terms
Principal Quantum Number (n)
A positive integer that indicates the shell and relative size of orbital(s).
Orbital Quantum Number (l)
An integer from 0 to n-1 that defines the shape of the orbital and sub-shell.
0 (s) 1 (p) 2 (d) 3 (f) 4 (g)
Magnetic Quantum Number (ml)
An integer with a value from -l to +l that defines the orientation of an orbital in space.
Spin Quantum Number (ms)
Accounts for the two possible spin states with values +1/2 and -1/2.
Quantum Numbers

P orbitals
three 2p orbitals
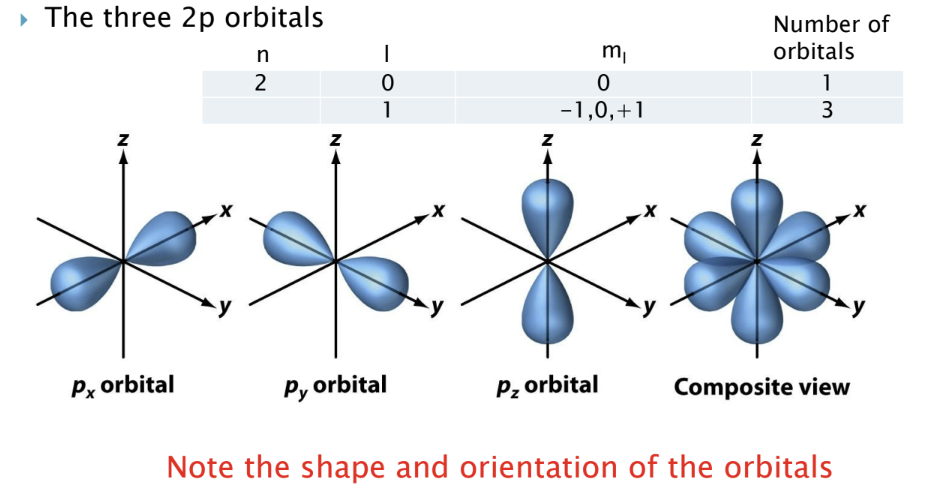
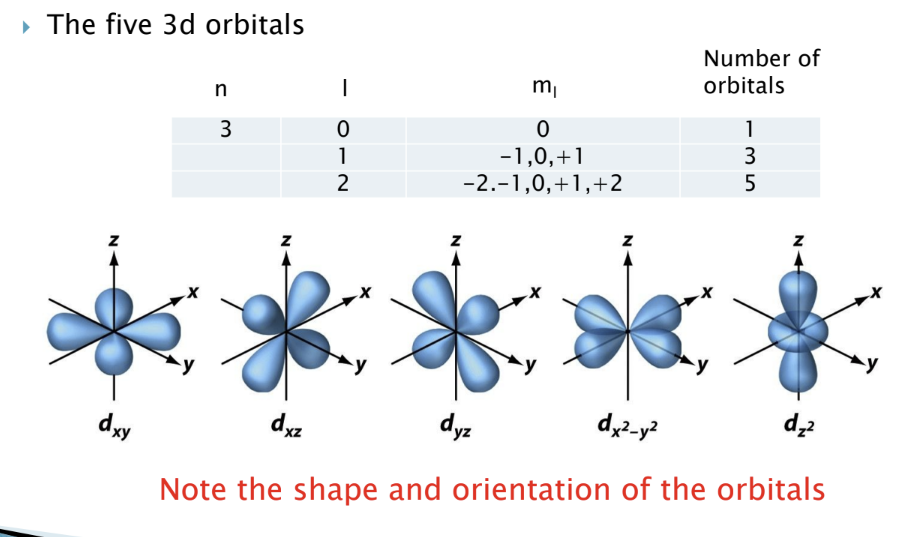
D orbitals
five 3d orbitals
Pauli Exclusion Principle
Orbitals can contain a maximum of two electrons which must be of opposite spin.
Aufbau Principle
Electrons enter and fill lower energy orbitals before higher energy orbitals.
Hund's Rule
Electrons will enter the orbitals one-at-a-time to maximize degeneracy.
Madelung's Rule
Orbitals fill with electrons as n + l
Degenerate Orbitals
Orbitals that have the same energy level.
Valence Electrons
Electrons in the outermost shell that influence an atom's chemical behavior.
Core Electrons
Electrons in the filled, inner shells that are not involved in chemical reactions.
Radial Distribution Plot
A graphical representation of the probability of finding an electron in a thin spherical layer near the nucleus.
Electromagnetic Character
Refers to the behavior of atoms with unpaired electrons when exposed to a magnetic field.
Anomalous Electron Configurations
Configurations that deviate from expected patterns to achieve lower energy states.
Isoelectronic
Atoms or ions that have identical numbers and configurations of electrons.
Electron Configuration
The arrangement of electrons in an atom's orbitals.
Compactness of d Orbitals
3d orbitals are more compact than 4s orbitals, leading to greater electron-electron repulsion.