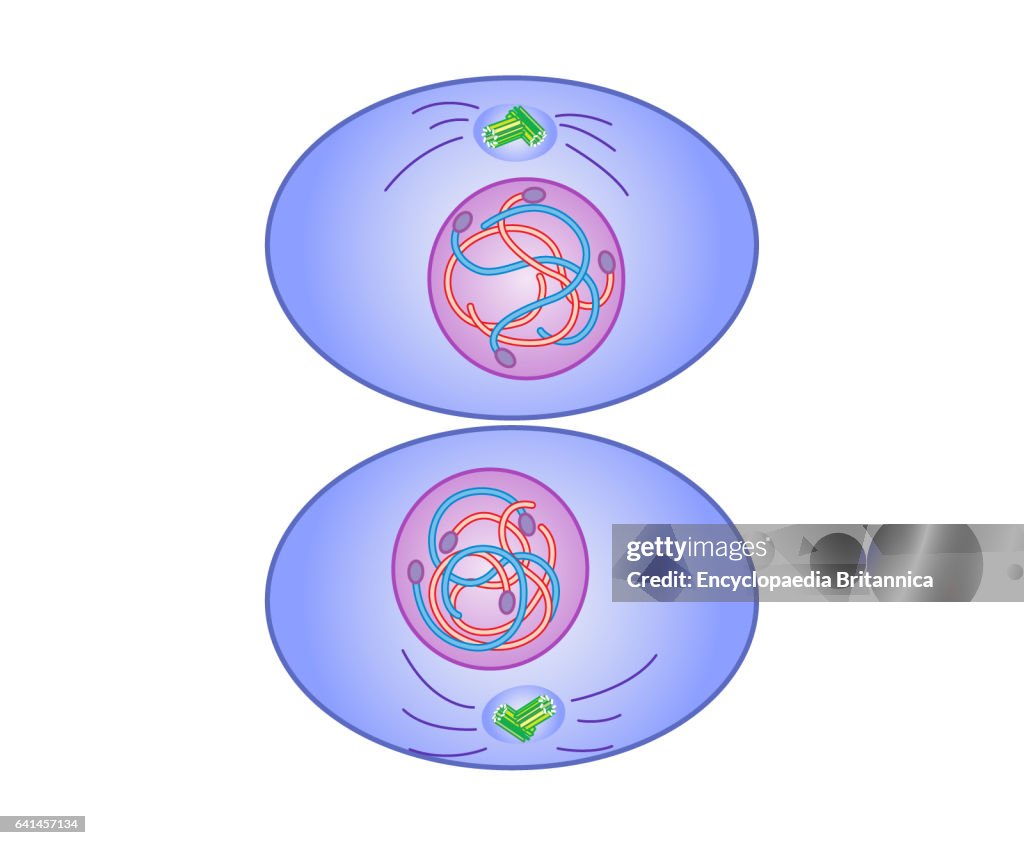
Phases of Cell Division (Mitosis)
1/7
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
8 Terms
G1 Interphase
Cell is metabolically active
Organelles duplicate
Centrosome replication begins
G2 Interphase
Cell growth continues
Enzymes & other proteins are synthesized
Centrosome replication is completed
Begins to reorganize its contents in preparation for mitosis
S phase
The cell synthesizes a complete copy of DNA in the nucleus
Duplicates a microtubule organizing structure called the centrosome
→ centrosomes help to separate DNA during the M (mitotic phase)
Prophase
Chromatin condenses into chromosomes
Nuclear membrane breaks down and disappears
Centrosomes move to opposite poles
Mitotic spindles (microtubules) begin to form
→ Spindles connect to each chromosome’s centromere via the kinectochore (a complex of proteins on the centromere that act as an attachment point)
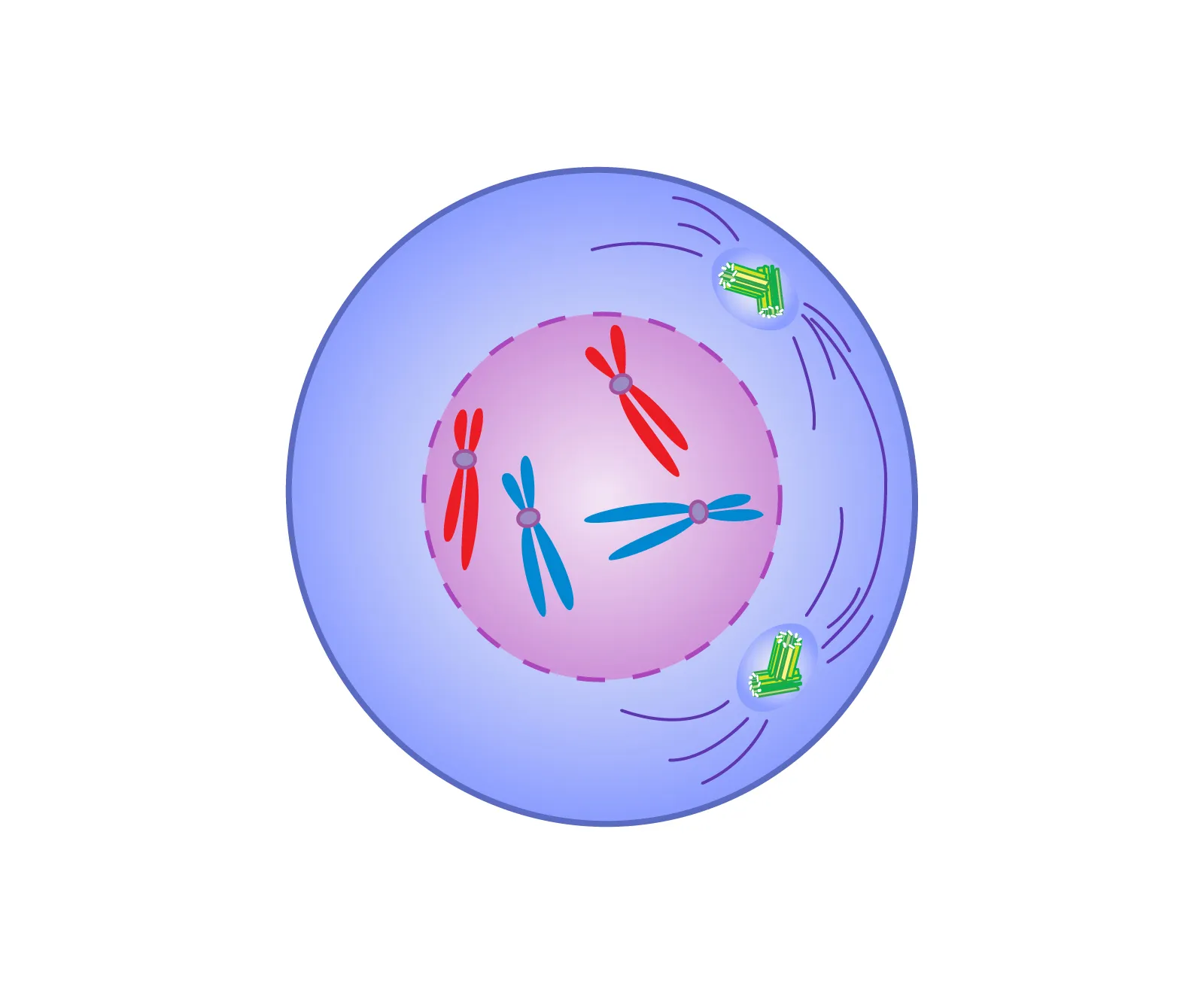
Metaphase
Centromeres of chromosomes line up along the middle of the cell & attach to the spindle fibers from opposite cell poles
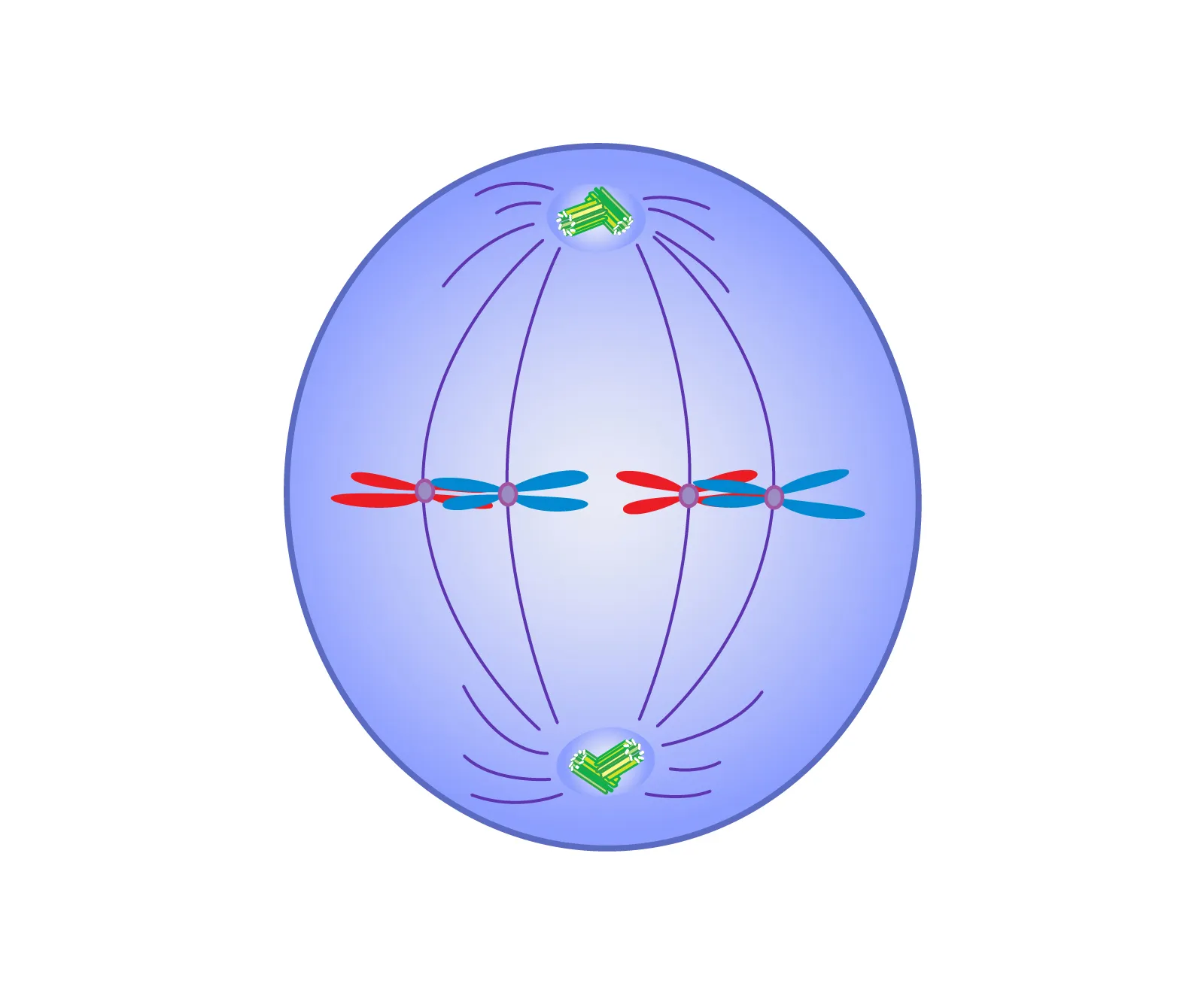
Anaphase
Centromeres of chromosomes break apart
Spindle fibers pull sister chromatids toward opposite poles of the cell
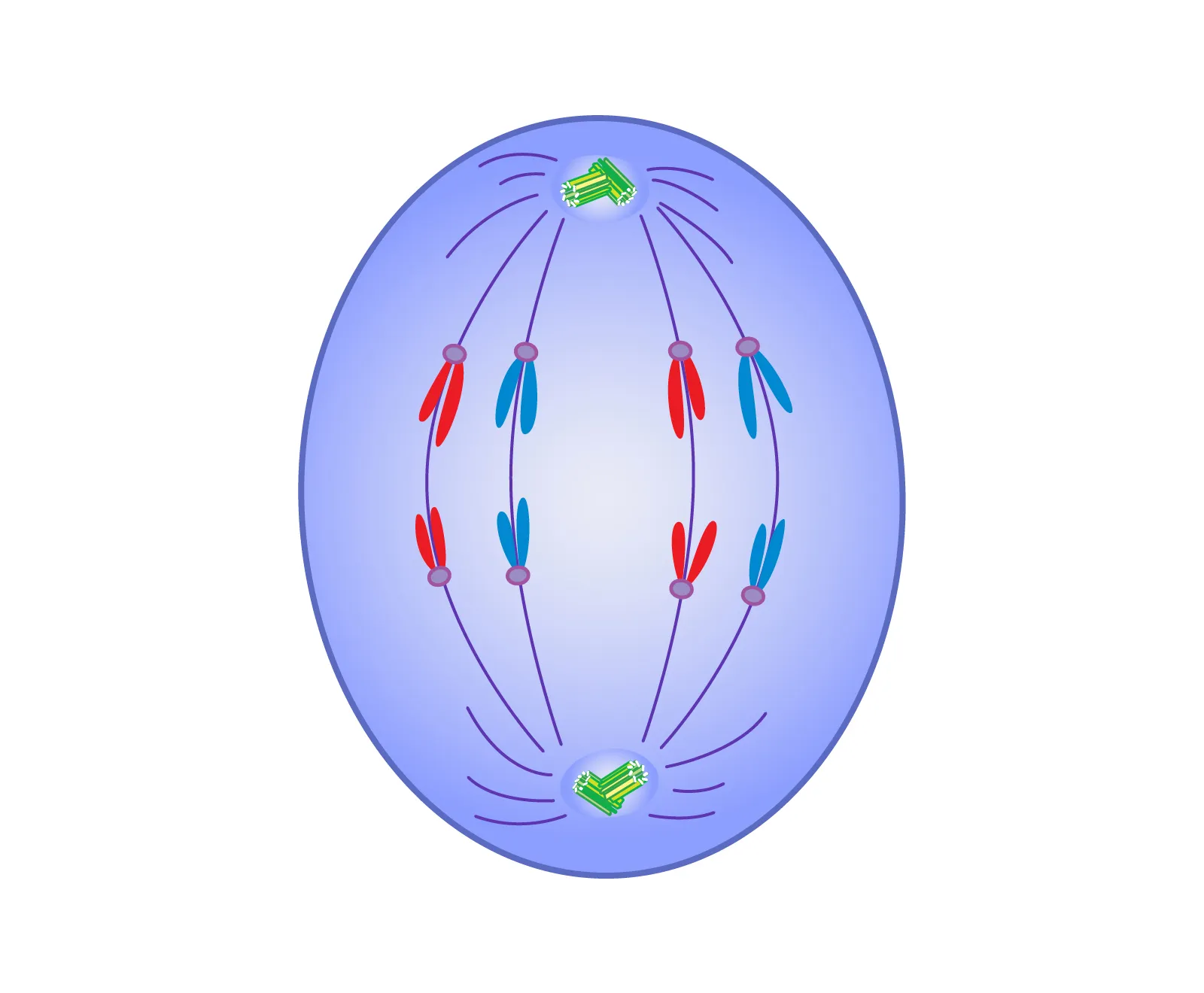
Telophase
The mitotic spindles dissolve
Chromosomes regain their chromatin appearance
A new nuclear membrane forms
A cleavage furrow forms & deepens
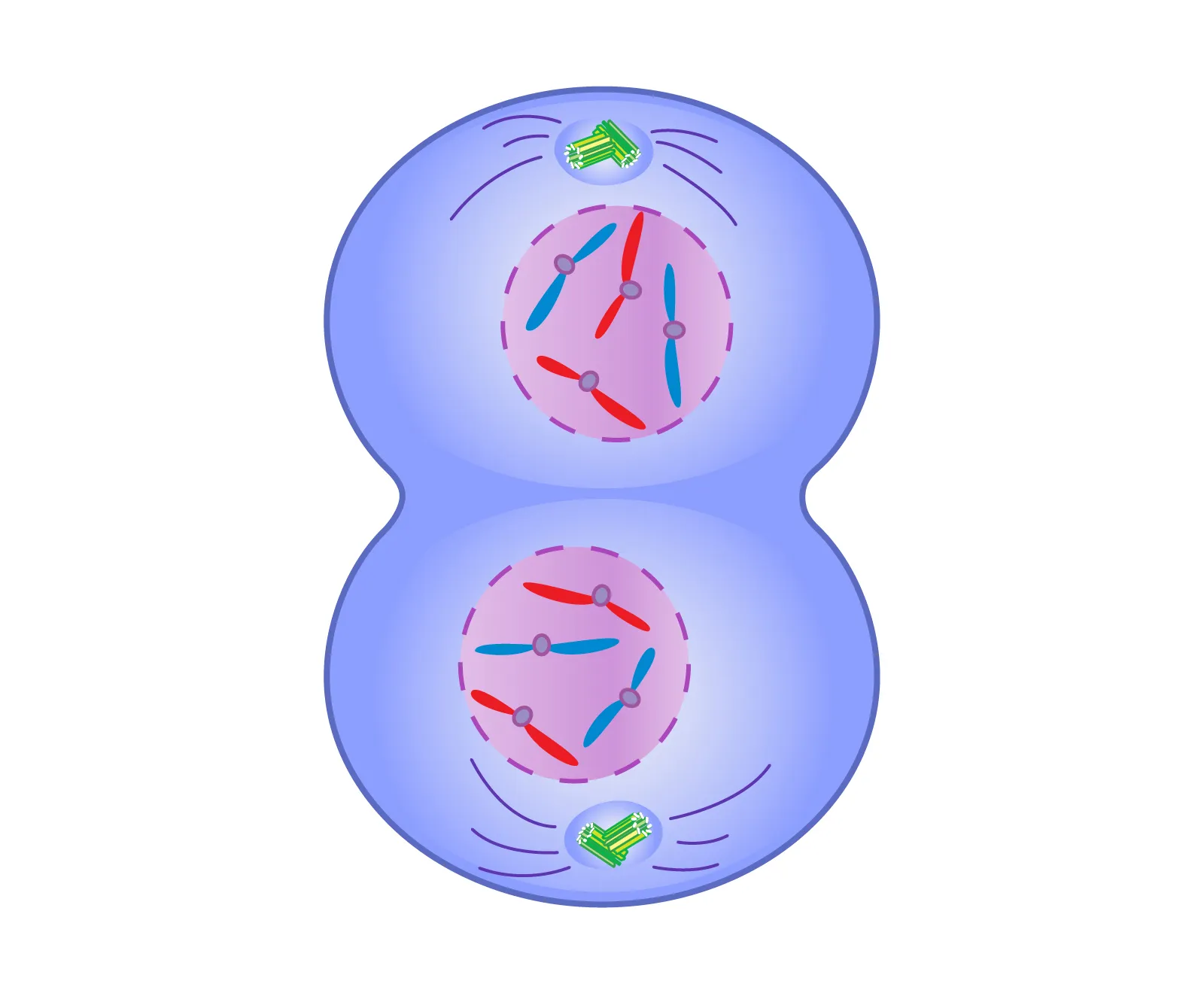
Cytokinesis
Parent cell splits, dividing the cytoplasm and nuclei into 2 identical cells