CHEM 2070 Alkyl Halides: Nucleophilic Substitution and Elimination
1/13
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
14 Terms
Substitution reactions
Requires the loss of a leaving group and a nucleophilic attack
Concerted
Happens in one step
Stepwise
Happens in steps
SN2 Mechanism
Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular
The nucleophile always attacks opposite the leading group, “backside attack”
Results in the inversion of a chiral center
Concerted reaction
Rate = k[Nu][substrate]
Increasing the concentration or strength of either increases the rate
![<p>Substitution Nucleophilic Bimolecular</p><p>The nucleophile always attacks opposite the leading group, “backside attack”</p><p>Results in the inversion of a chiral center</p><p>Concerted reaction</p><p>Rate = k[Nu][substrate]</p><p>Increasing the concentration or strength of either increases the rate</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/eb91c500-d19e-4462-b6bd-f28f832ab75f.png)
Backside attack
Electron density repels the attacking nucleophile from the front-side
The nucleophile must approach the backside to allow electrons to flow from the HOMO of the nucleophile to the LUMO of the electrophile
Proper orbital overlap cannot occur with front-side attack because there is a node on the front-side of the LUMO
SN1 Reaction
Substitution Nucleophile Unimolecular
Products are a mix of R/S
Rate = k[substrate]
Carbocation formation is rate-determining step
Strength and concentration of Nu don’t matter
![<p>Substitution Nucleophile Unimolecular</p><p>Products are a mix of R/S</p><p>Rate = k[substrate]</p><p>Carbocation formation is rate-determining step</p><p>Strength and concentration of Nu don’t matter</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/e8c876d5-441d-451b-98ef-35a7bd9164b8.png)
What are the features of substitution reactions
Carbon attached to the leaving group must be sp³-hybridized
Nucleophile
Substrate
Leaving group
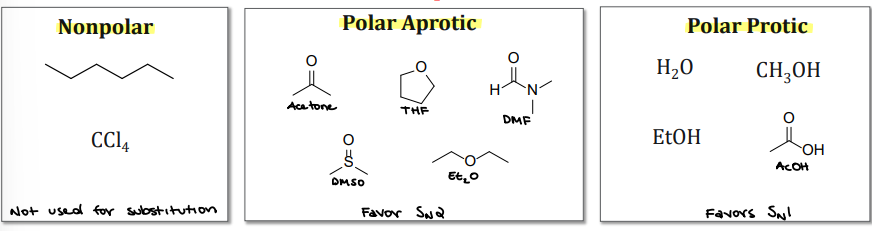
Reaction solvent: most reactions are performed in a solvent
Carbon attached to leaving group MUST be what hybridized?
sp³ !!
Nucleophile
SN2: requires strong nucleophiles
SN1: strength does not matter
Strong Nucleophile
X-, OH-, SR-, NR2-, -C=-N, -C=-C-R, RSH
Neutral Nucleophile
H2O, ROH, RSH, RNH2
Substrate
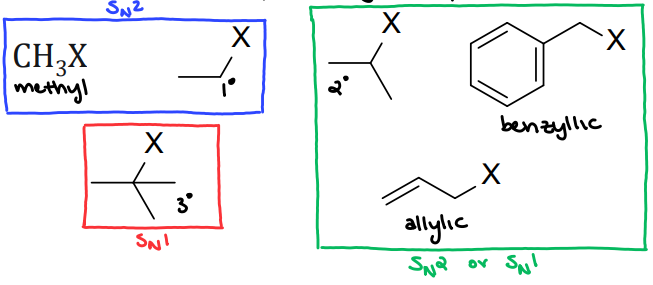
Leaving Group
The better the leaving group, the more stable the leading group, the faster the reaction
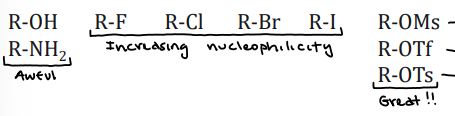
Reaction solvent: most reactions are performed in a solvent