29 Chromatography and Spectroscopy
1/36
Earn XP
Description and Tags
hasn't got any Qs and missing 29.2/3/4/5/6
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
37 Terms
what is chromatography used for
separating individual components from a mixture of substances
what do all forms of chromatography have
a stationary phase
doesn’t move, is normally a solid/liquid supported on a solid
a mobile phase
does move, normally a liquid or a gas
what is chromatography used for
Used in analysis of drugs, plastics, flavourings, air samples, and has applications in forensic science.
what is thin layer chromatography (TLC)
Quick and inexpensive analytical technique that indicates how many components are in a mixture
how does TLC work
absorbent substance (usually silica)
In TLC the absorbent is the stationary phase.
The different components in the mixture have different affinities for the absorbent that bind with differing strengths to its surface.
Adsorption is the process by which the solid silica holds the different substances in the mixture to its surface.
Separation is achieved by the relative adsorptions of substances with the stationary phase.
how to carry out TLC

Rf equation
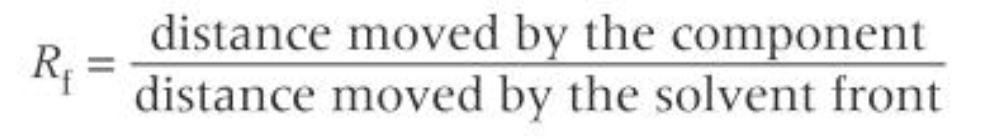
what is gas chromatography (GC) used for
Useful for separating and identifying volatile organic compounds in a mixture.
GC schematic diagram
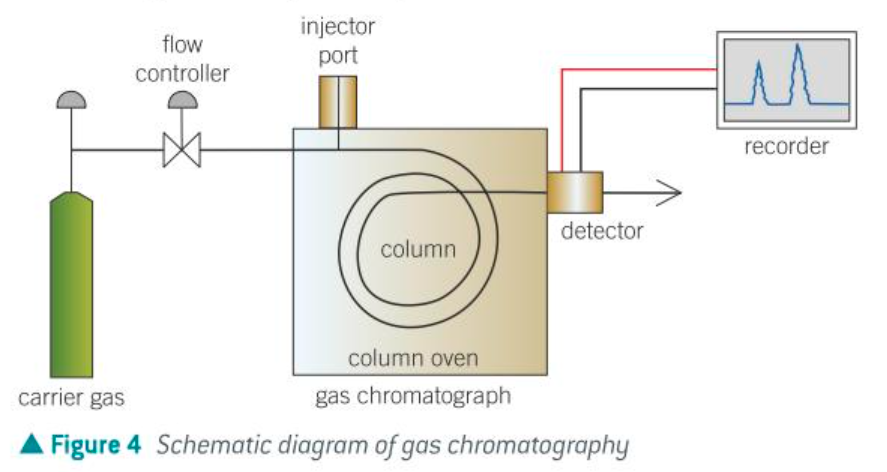
how does GC work
The stationary phase is a high boiling liquid absorbed onto an inert solid support. The mobile phase in an inert carrier gas such as helium or neon.
A small amount of the volatile mixture is injected into the apparatus (Called a gas chromatograph)
The mobile carrier gas carries the components in the sample through the capillary column which contains the liquid stationary phase absorbed onto the solid support.
The components slow down as they interact with the liquid stationary phase inside the column. The more soluble the component is in the liquid stationary phase, the slower it moves through the capillary column.
The components of the mixture are separated depending on their solubility in the liquid stationary phase.
The compounds in the mixture reach the detector at different times depending on their interactions with the stationary phase in the column.
The compound retained in the column for the shortest time has the lowest retention time and is detected first.
The retention time is the time taken for each component to travel through the column.
what is the stationary phase in TLC
the absorbent
what is the process by which the solid silica holds the different substances in the mixture to its surface in TLC?
adsorption
how is separation achieved in TLC
Separation is achieved by the relative adsorptions of substances with the stationary phase.
what is the the stationary phase in GC
a high boiling liquid absorbed onto an inert solid support.
column coated in thin layer of hydrocarbon liquid
kept at constant temp
what is the mobile phase in GC
an inert carrier gas e.g. He or Ne
what happens to the components in GC as they interact w the liquid stationary phase inside the column
they slow down
the more soluble the component is in the liquid stationary phase, the slower it moves through the capillary column
what effects the speed with which the components move through the capillary column
the solubility in the liquid stationary phase
relative interactions w mobile phase (carrier)
compared to interactions w stationary phase (liquid hydrocarbon coating the column)
how are components of a mixture separated in GC
depending on their solubility in the liquid stationary phase
they reach the detector at diff times depending on their interactions w the stationary phase in the column
what is the retention time in GC
the time taken for each component to travel through the column to the detector
The compound retained in the column for the shortest time has the lowest retention time and is detected first.
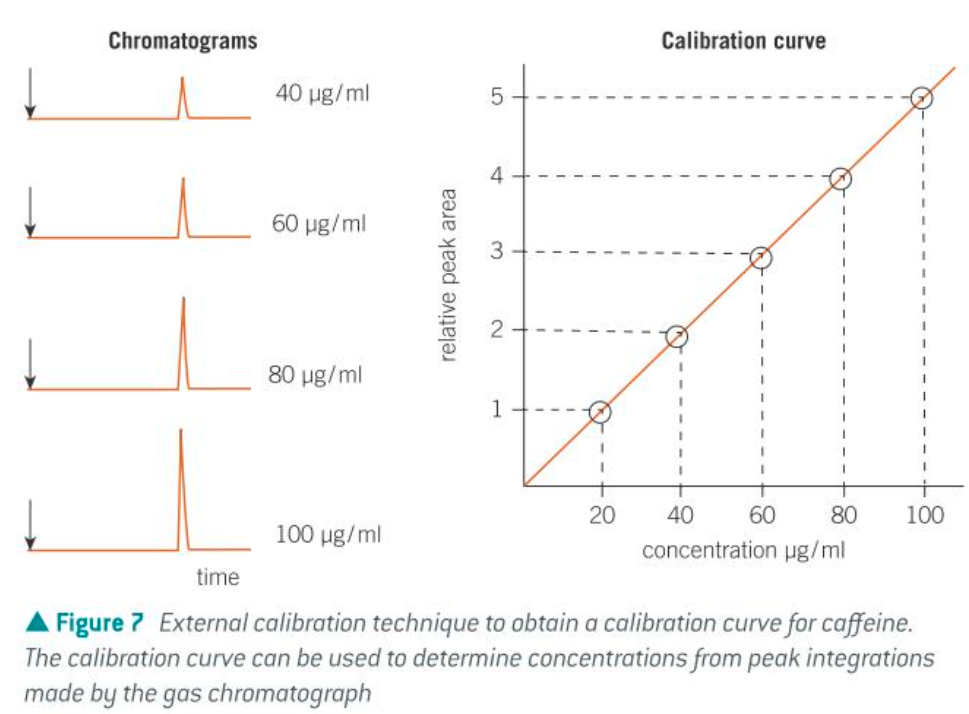
how can you determine the [components] in the sample in GC
using a gas chromatogram:
the peak integrations (area under each peak) can be calculated to determine the [components] in the sample
comparing the peak integrations w values obtained from standard solutions of the component
method for determining concentration of compounds

calibration curve
what effects retention time in GC
temperature: (increased temp so gas moves faster)
flow rate
length of capillary tube/column
liquid in stationary phase
carrier gas
why would a component move very slowly down the liquid coating column/stationary phase
if it’s very soluble
diff times for diff components to move through the column
time taken to emerge is related to the structure of component
what does a large peak on a chromotagram say about the component
highest concentration (greatest area under peak)
how to calculate peak on gas chromatogram
½ base x height
if a peak has a high retention time on a gas chromatogram what does that say about the component
longer retention time
slow to emerge
interacted more w/ stationary phase
advantages vs disadvantages of GC
advantages:
can find the exact proportions using a calibration curve
linked to mass spec: can identify compound straight away
disadvantages:
(more expensive equipment)
only for volatile organic compounds
if you have an unknown compound and unknown retention time, it can’t be identified
similar compounds w similar IMF will have similar retention times
uses of GC testing
steroid testing in athletes
F1 motor racing - fuel testing
advantages and disadvantages of TLC
advantages:
cheap
quick
can change solvent for better separation
same amount of sample
disadvantages:
can’t do gas
don’t know Rf value of compound
don’t know concentration
similar functional group → similar Rf values → difficult to find good solvent
test + observation for alkene
add bromine water drop-wise
bromine water decolourised from orange to colourless
test + observation for haloalkane
+ AgNO3 + ethanol
warm to 50°C in water bath
Cl-: white ppt
Br-: cream ppt
I-: yellow ppt
test + observation for carbonyl
add 2,4-DNP
orange ppt
test + observation for aldehyde
+ Tollen’s reagent
warm
silver mirror
test + observation for primary and secondary alcohol and aldehyde
add K2Cr2O7/H2SO4(aq)
warm in water bath
colour change from orange to green
(doesn’t work if XS K2Cr2O7/H2SO4(aq))
test + observation for c-acid
+ Na2CO3(aq)
effervescence
how to identify a phenol
add Br2
room temp
Br2 decolourises and white ppt forms