Properties of Matter and Chemical Bonding
1/70
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
71 Terms
What are the two types of compositions in physical properties of matter?
Homogenous (the same) and heterogeneous (different) compositions.
What are some examples of physical properties of matter?
Colour, magnetism, particle size, melting points, and boiling points.
How is density defined in chemistry?
Density is defined as the mass per unit of volume.
What are the typical units for expressing density?
Grams per millilitre (g/mL) or kilograms per cubic metre (kg/m³).
How is density calculated?
Density (d) is calculated using the formula d = m/v, where m is mass and v is volume.
What is filtration used for in separation methods?
Filtration is used to separate insoluble solids from liquids based on particle size.
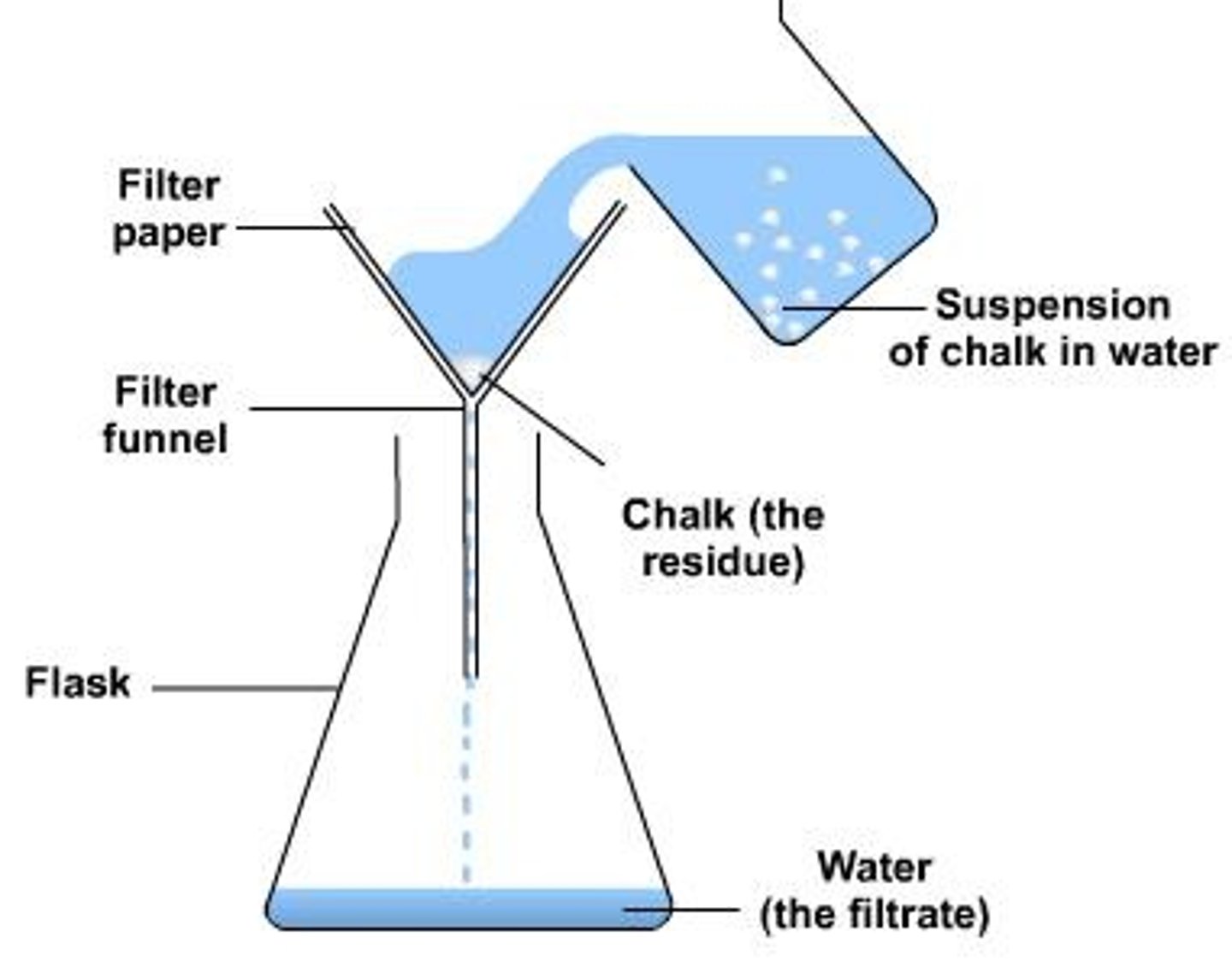
What is the principle behind separating two solids based on differing solubility?
One solid is soluble in a solvent while the other is not.
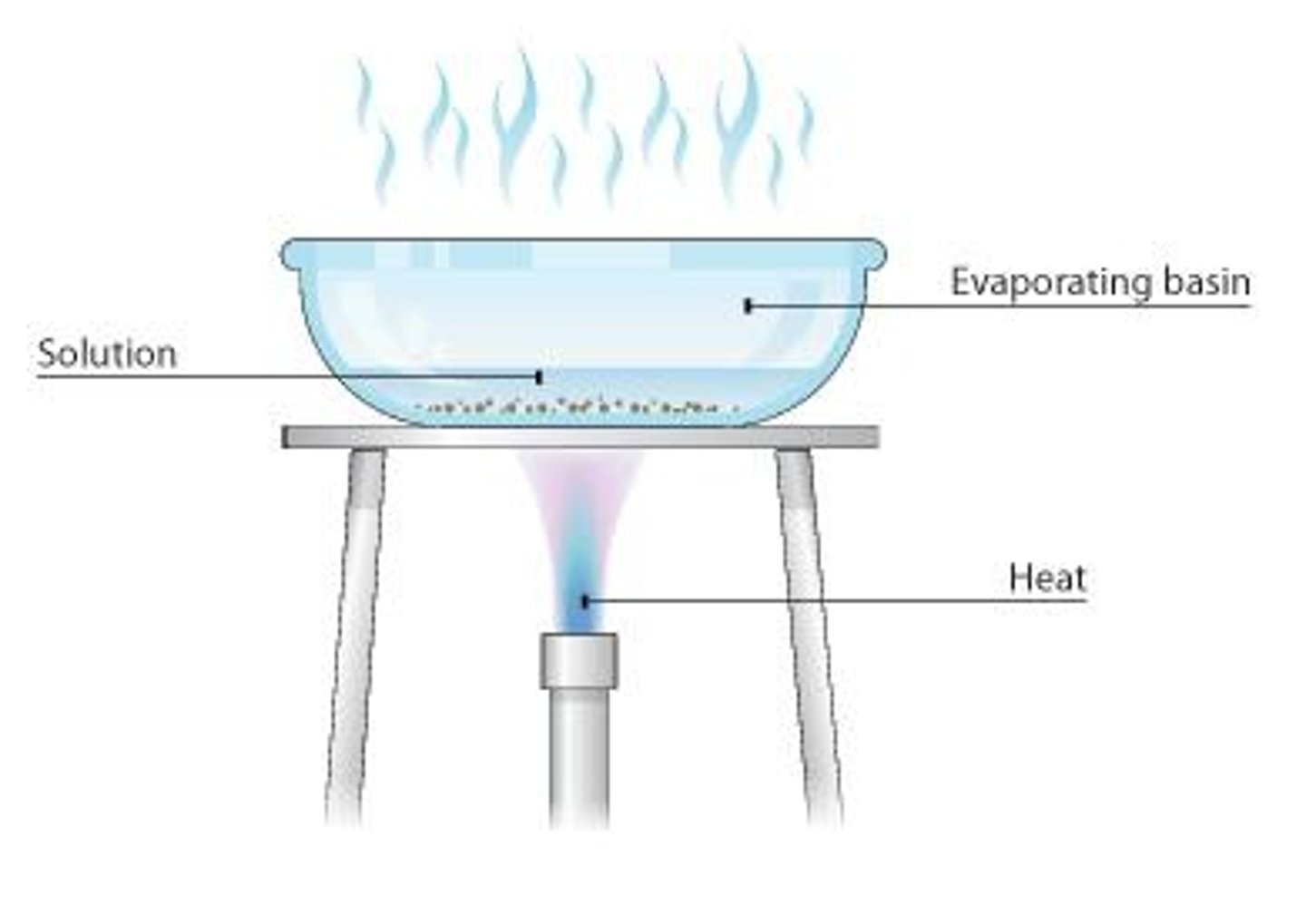
What is evaporation used for in separation methods?
Evaporation is used to separate a dissolved solid (solute) from a solution.
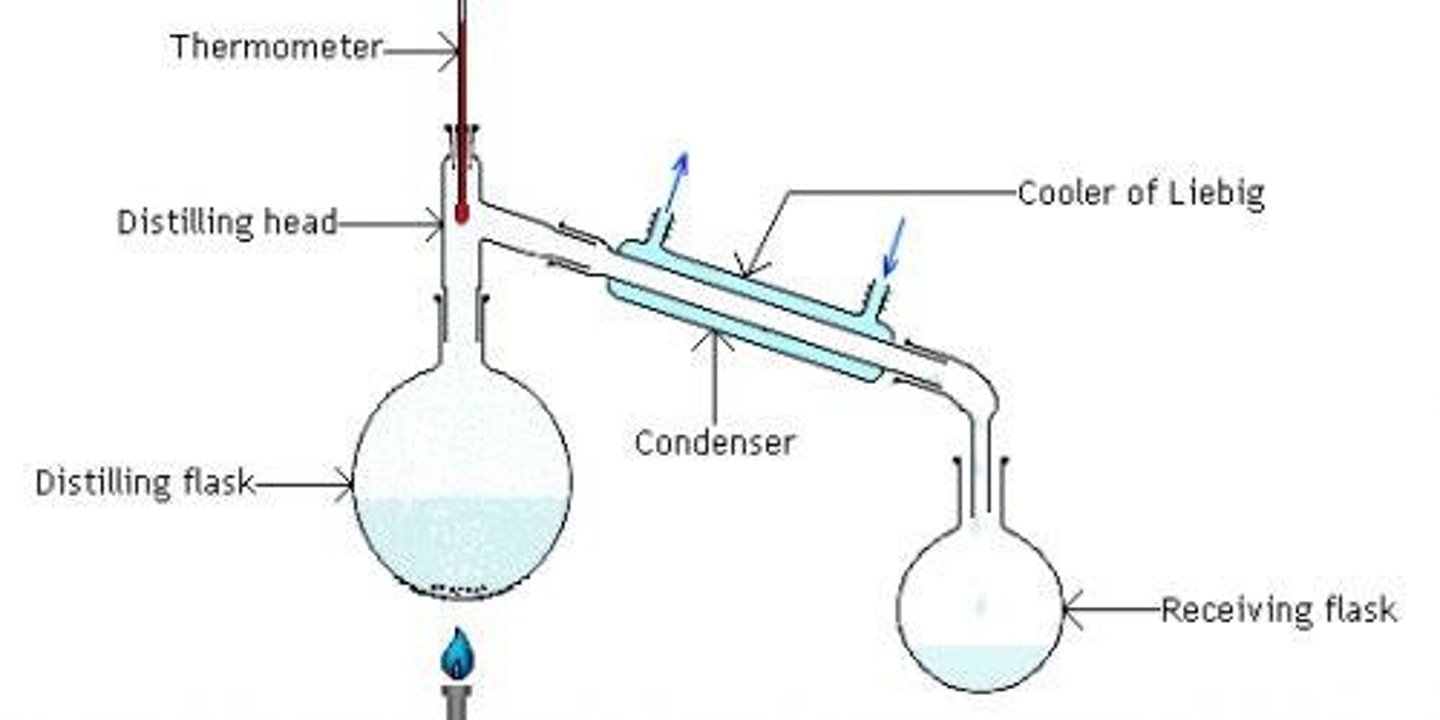
What is distillation?
Distillation involves boiling a mixture of liquids, where the solute is non-volatile, and condensing the volatile vapour to collect it as distillate.
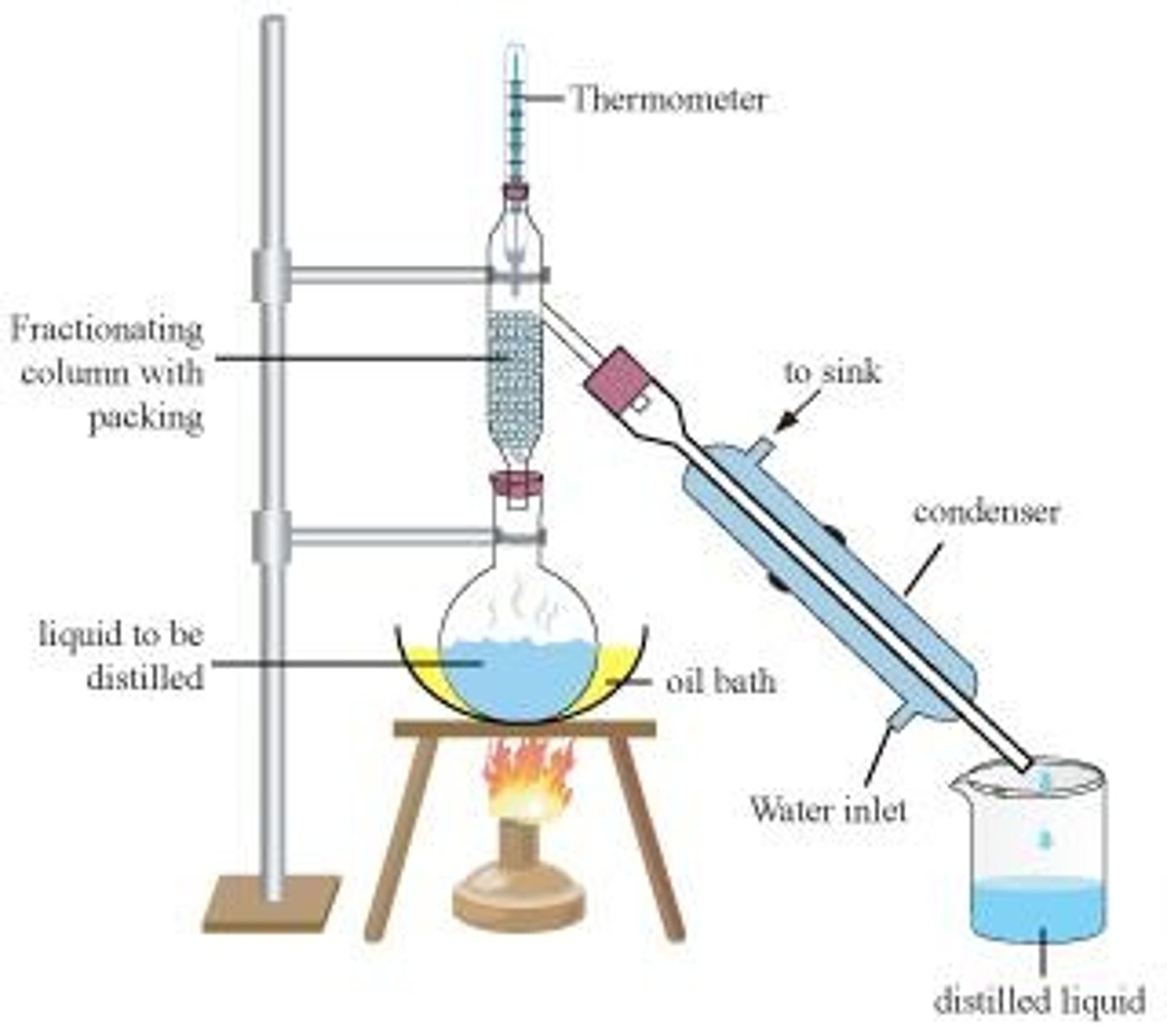
What is fractional distillation?
Fractional distillation is the separation of two volatile liquids based on differing boiling points.
What does sedimentation allow in the context of density?
Sedimentation allows the separation of heavier particles, which can then be collected by decantation.
What is gravimetric analysis?
Gravimetric analysis involves separating substances in a mixture and weighing them, often expressed as a percentage.
What are the characteristics of metals in the periodic table?
Metals are typically solids at room temperature, have a shiny appearance, good conductivity, and are malleable.
What do the columns and rows represent in the periodic table?
Columns (groups) represent elements with the same number of valence electrons, while rows (periods) represent elements with the same number of shells.
What are the three subatomic particles in an atom?
Electrons (e) with a -1 charge, protons (p) with a +1 charge, and neutrons (n) with no charge.
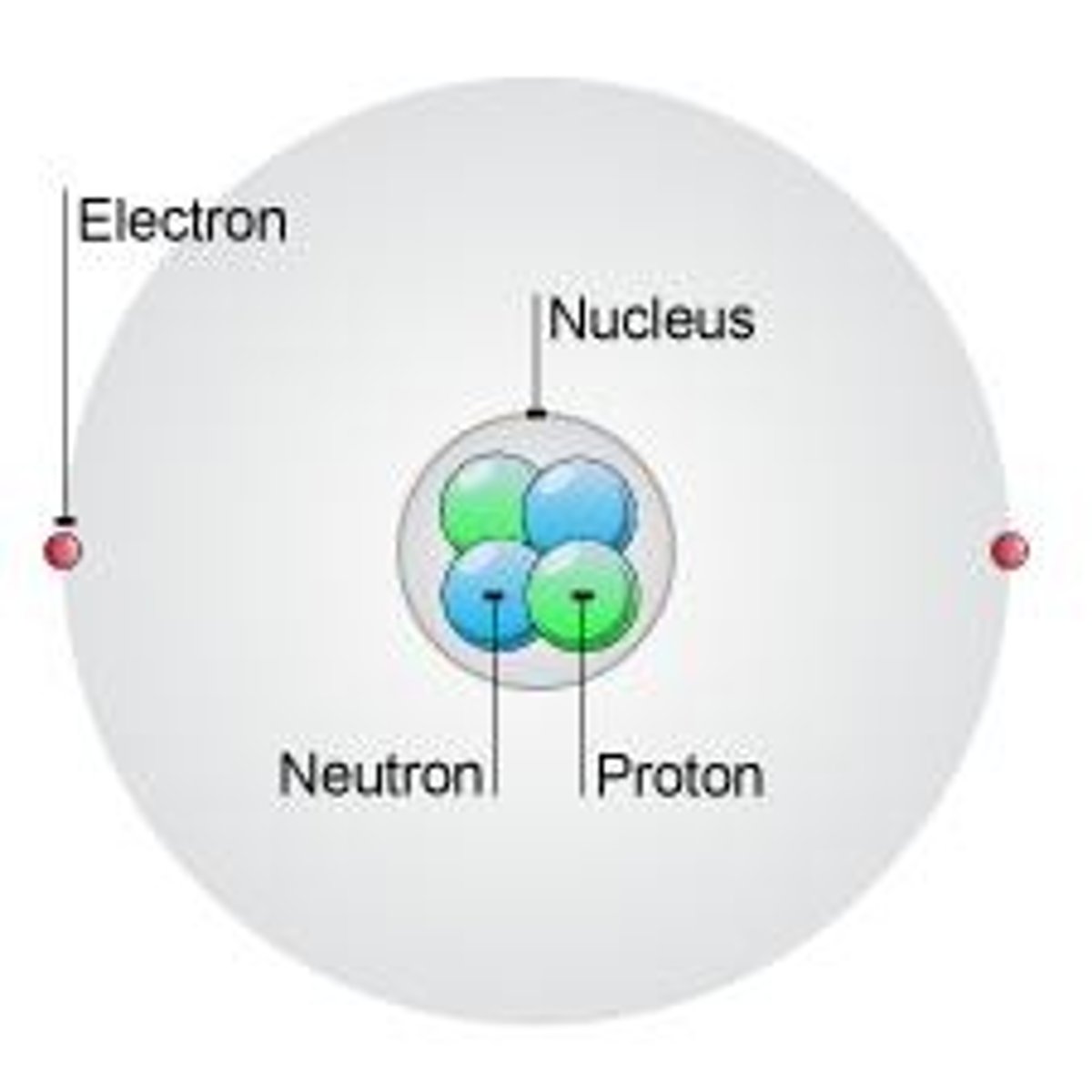
What constitutes the nucleus of an atom?
The nucleus consists of protons and neutrons.
What are isotopes?
Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of neutrons in their nuclei.
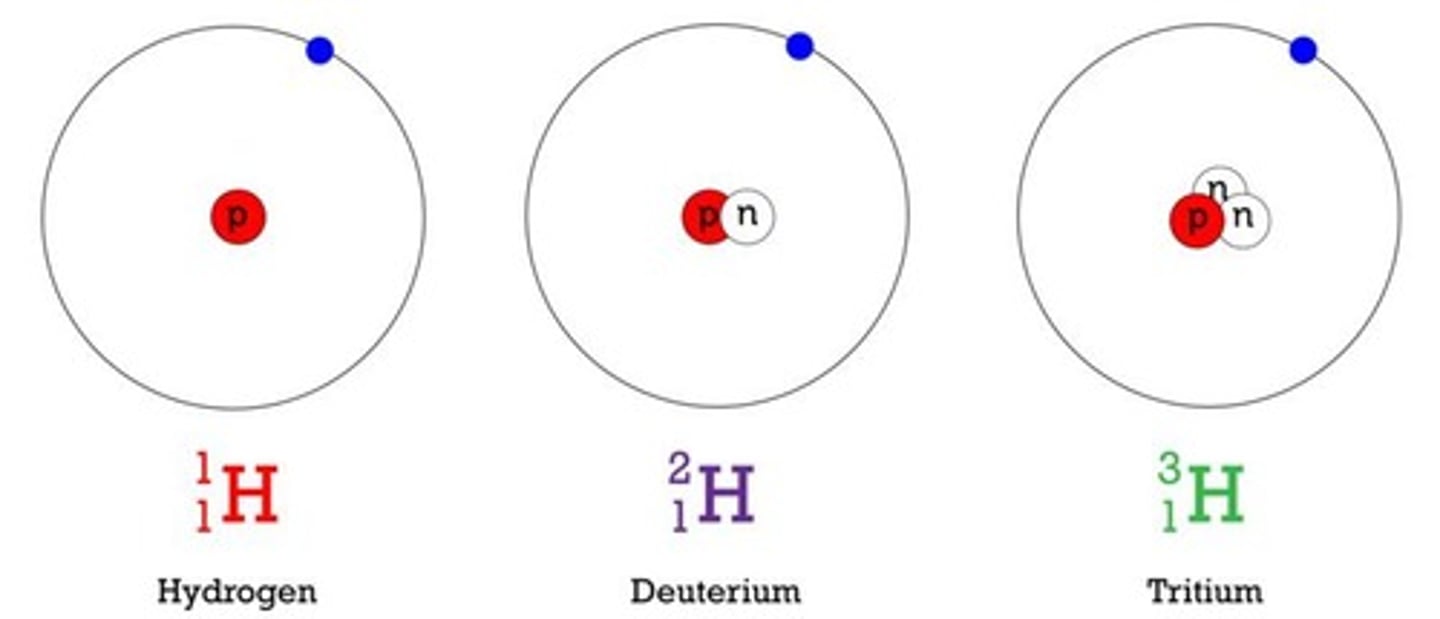
What does 'relative abundance' of an isotope refer to?
Relative abundance refers to the percentage of that isotope in naturally occurring elements.
Do isotopes of the same element have different chemical properties?
No, isotopes of the same element have the same chemical properties and very similar physical properties.
What is the formula for representing an element's atomic mass, atomic number, and symbol?
The formula is A/ZM, where A = Atomic mass (protons + neutrons), Z = Atomic Number (protons), and M is the elemental symbol.
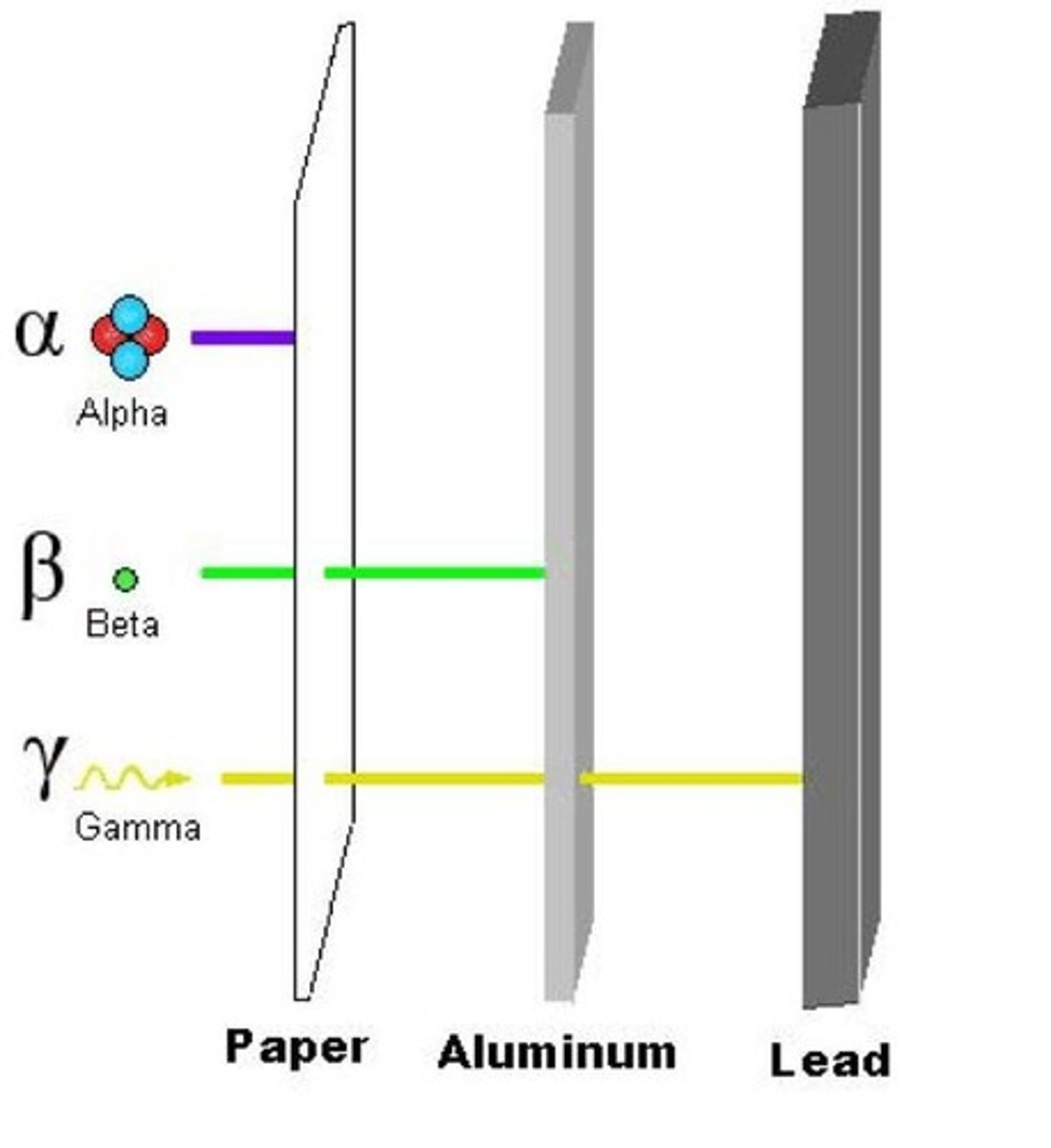
What is radioactivity?
Radioactivity is the spontaneous emission of radiation that occurs with certain isotopes due to their instability.
What are the three types of radiation?
The three types of radiation are Alpha (helium particle), Beta (electron), and Gamma (similar properties to X-rays).
What is electron configuration?
Electron configuration refers to the arrangement of electrons into shells or energy levels around the nucleus of an atom.
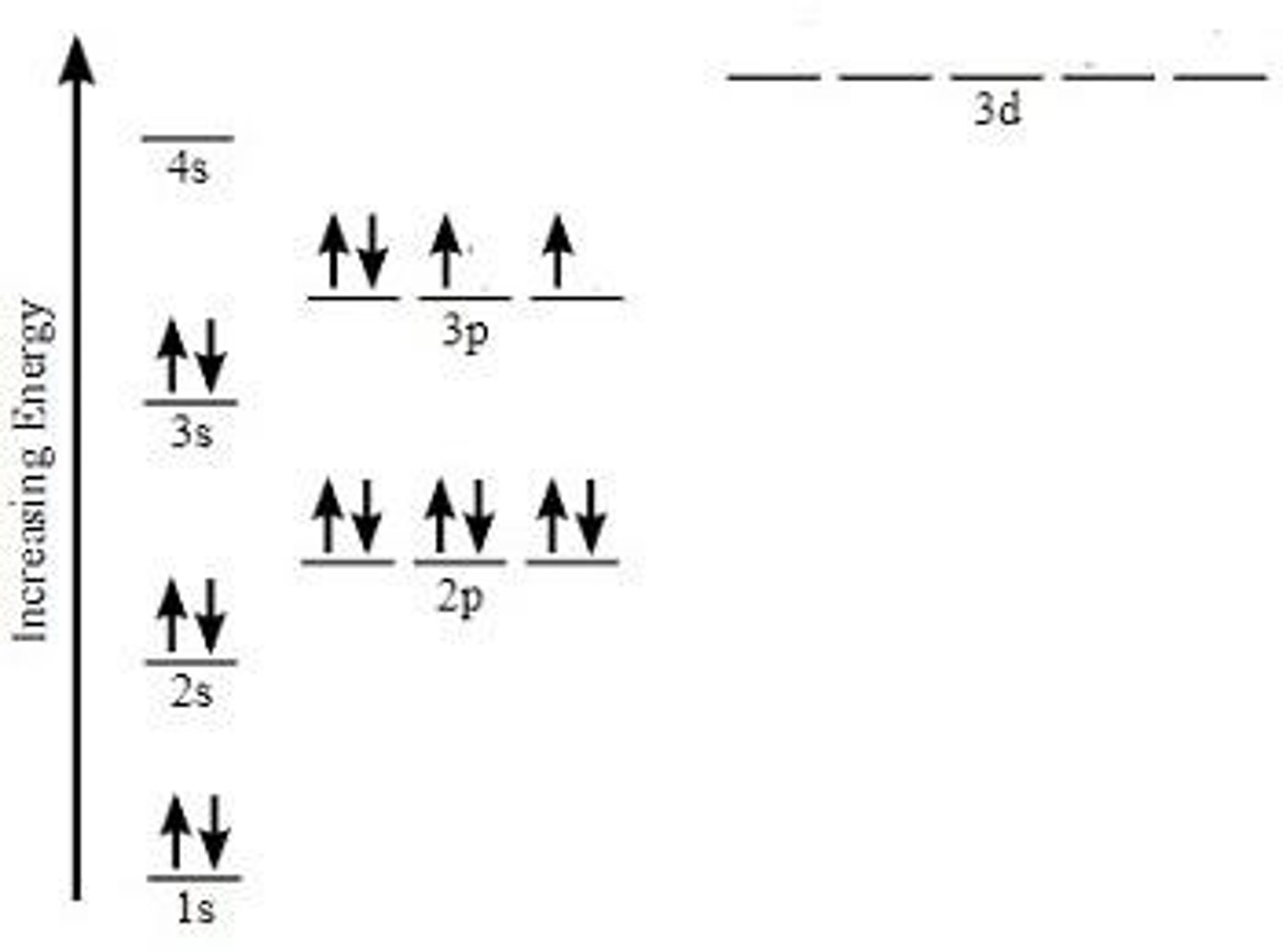
What rule applies to the arrangement of electrons in energy levels?
The Rules of 2.8.8 apply, meaning the first shell holds 2 electrons, the second shell holds 8, the third shell holds 8 before the fourth shell can hold electrons.
What is the electron configuration of Titanium (22 electrons)?
The electron configuration of Titanium is 2.8.9.2.
What is the driving force behind chemical reactivity in atoms?
The driving force is the atom's desire to achieve stable electron configurations, i.e., a full outside shell.
What are valence electrons?
Valence electrons are the electrons in the outermost shell (highest energy level) of an atom.
What is an orbital?
An orbital is defined as a volume of space surrounding the nucleus of an atom through which one or two electrons may randomly move.
What are the sublevels of main energy levels?
The sublevels are s, p, d, and f.
How many electrons can each type of orbital hold?
s can hold 2 electrons, p can hold 6 (3 sets of 2), d can hold 10 (5 sets of 2), and f can hold 14 (7 sets of 2).
What is the filling order of orbitals?
The filling order is 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p, 4s, 3d, 4p, 5s, 4d.
What is the electron configuration of Nitrogen?
The electron configuration of Nitrogen is 2.5.
What is orbital notation for Nitrogen?
The orbital notation for Nitrogen is 1s² 2s² 2p³.
What happens when atoms are given extra energy (e.g., heating above 1500°C)?
Electrons jump up energy levels, and when they fall back to their original configuration, they release energy as emitted light.
What types of light can be emitted when electrons fall back to their correct configuration?
The emitted light can be visible, ultraviolet (UV), or infrared (IR).
What is the relationship between energy released and wavelength according to Planck's Constant?
The relationship is inversely proportional, expressed as ΔE = hc/λ, where h is Planck's constant and c is the velocity of light.
What does the emission spectrum represent for each element?
It is specific to each element, similar to a fingerprint, and corresponds to the energy required to excite a particular electron in an atom.
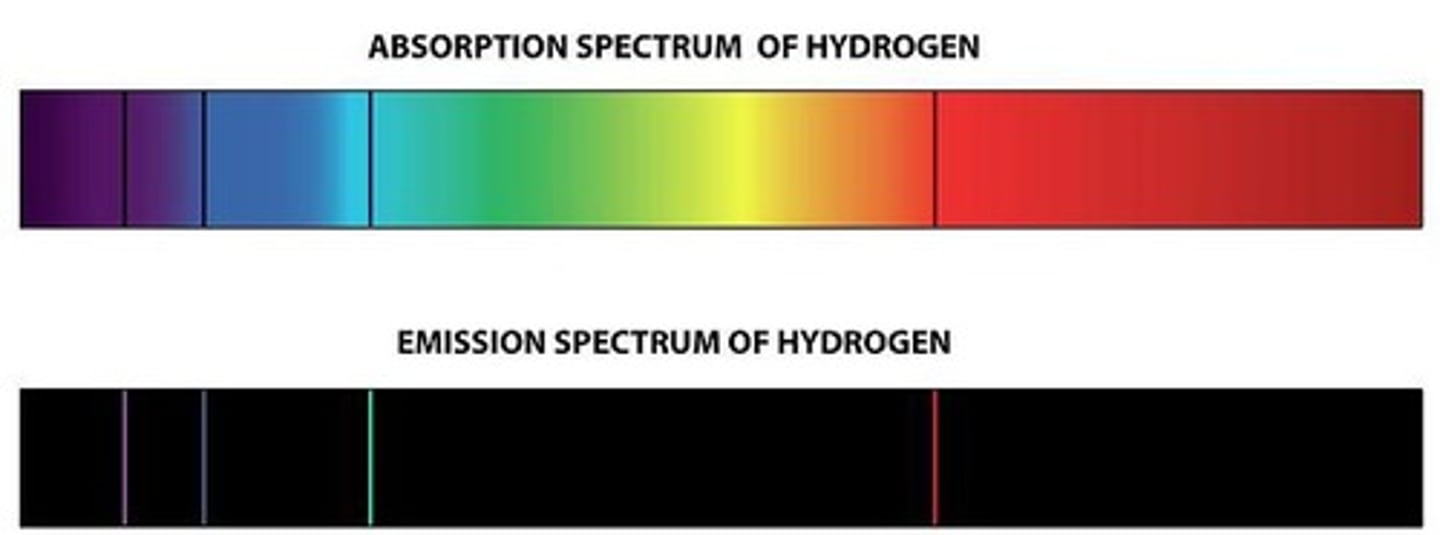
How does atomic radius change when moving down a group in the periodic table?
The atomic radius increases.
How does ionization energy change when moving right across a period in the periodic table?
The ionization energy increases.
What trend occurs in reactivity with water when moving down a group in the periodic table?
Reactivity with water increases.
What happens to electronegativity when moving right across a period?
Electronegativity increases.
What is the general trend for metallic character when moving down a group?
Metallic character increases.
What are ions and how are they formed?
Ions are charged atoms formed by gaining or losing electrons.
What are the two types of ions and how are they named?
Positive ions are called cations, and negative ions are called anions. Ionic compounds are named by combining the metal and non-metal with the non-metal ending in -ide.
What is the structure of ionic compounds?
Ionic compounds form a lattice structure due to the attraction between opposite charges.
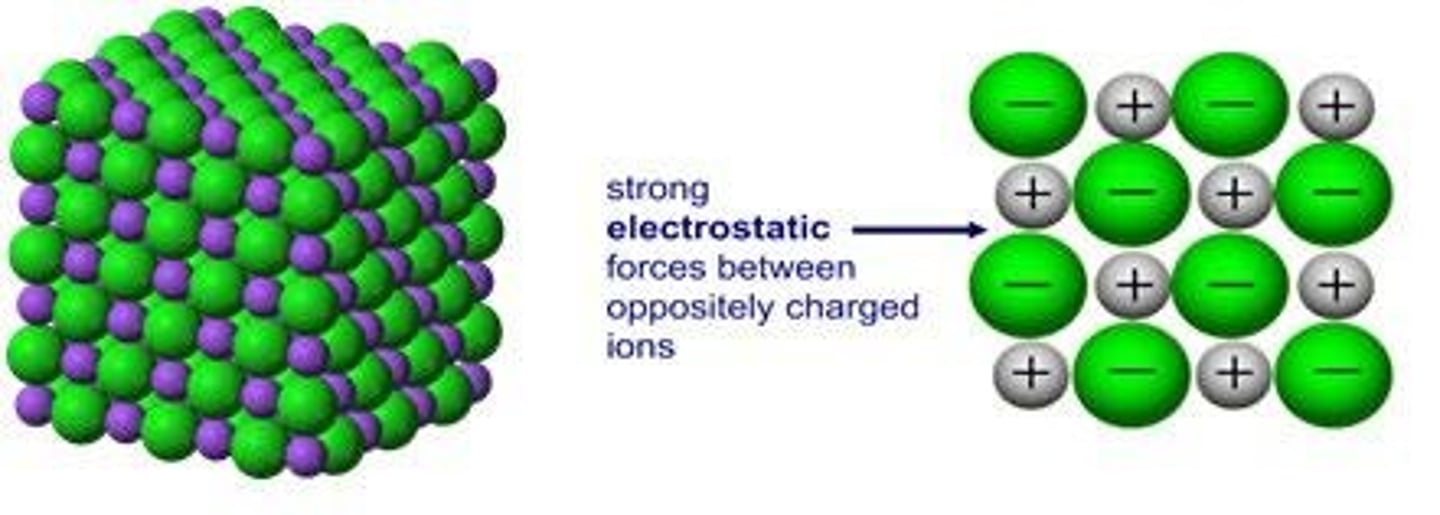
What defines the valency of an ion?
The valency is the charge calculated by the difference in protons and electrons.
What is the main characteristic of covalent bonding?
Covalent bonds are formed when electrons are shared to fill the outer shell of the atoms involved.
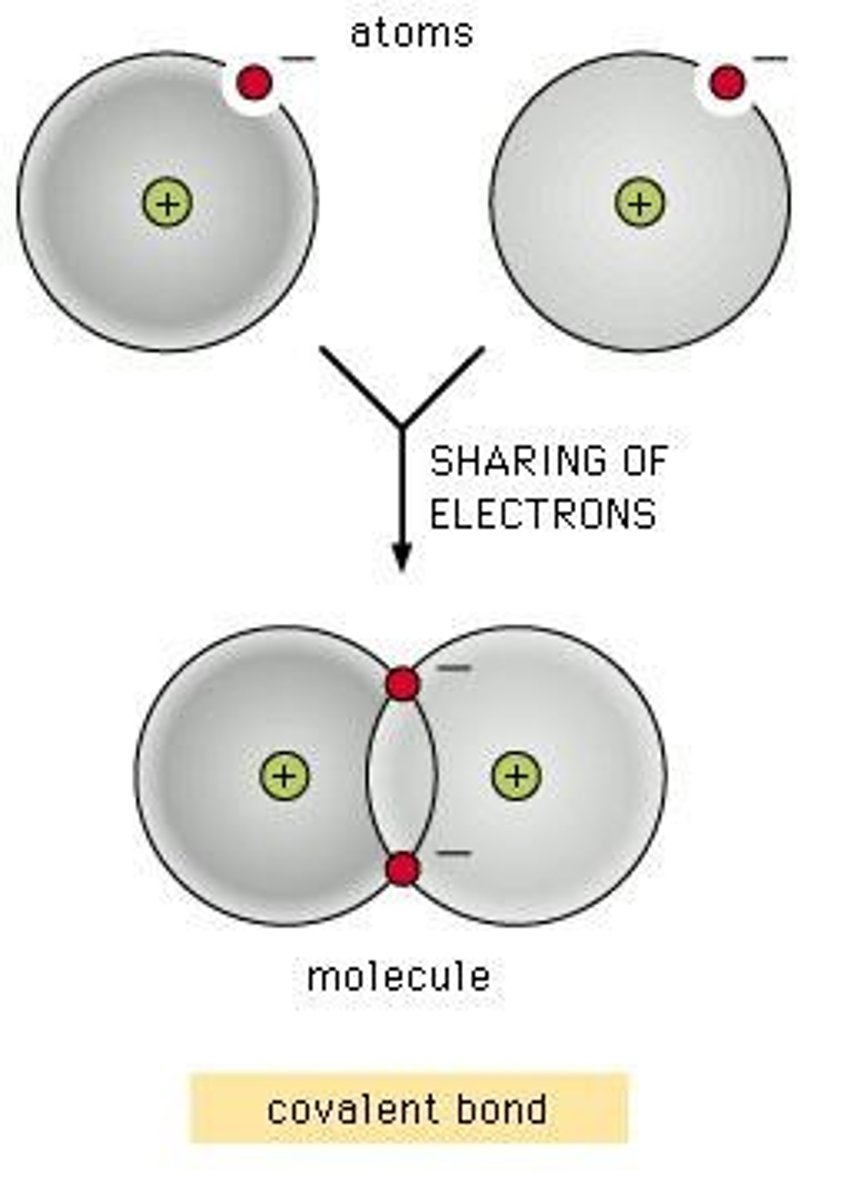
What type of formula do covalent compounds have?
Covalent compounds have a molecular formula that specifies the number of atoms of each substance within a molecule.
What is an example of a covalent molecule and its bonding behavior?
Oxygen (O2) molecule, where oxygen's ion is O2- and it forms two bonds to fill its outer shell.
What are the properties of ionic substances?
Ionic substances are solids at room temperature, have high melting points, are hard, do not conduct electricity as solids, and are brittle.
What are the properties of covalent substances?
Covalent substances are generally gases at room temperature, have low melting and boiling points, are soft solids, and do not conduct electricity as solids or liquids.
What are covalent network solids?
Covalent network solids are solids where covalent bonding occurs indefinitely, resulting in empirical formulae rather than molecular formulae.
Give examples of covalent network solids.
Examples include silica (SiO2, quartz) and diamond (carbon).
What happens when covalent lattices melt?
Melting involves breaking many strong covalent bonds.
What temperature range is required for the process mentioned in the notes?
Very high temperatures (>1000°C)
What characterizes metallic bonding?
Positive ions immersed in a sea of electrons.
What property of metals is attributed to mobile electrons?
High conductivity, as electrons can flow through the structure.
How do mobile electrons contribute to the malleability and ductility of metals?
They hold the positive ions of metals together even when the metal is distorted.
What happens to electrons in a covalent bond when the two elements have different electronegativities?
The electrons are dispersed unevenly, attracted to the more electronegative atom.
What charge does the more electronegative atom acquire in a polar covalent bond?
Slightly negative charge.
What charge does the less electronegative atom acquire in a polar covalent bond?
Slightly positive charge.
What are dipole-dipole forces?
Attractive forces that occur between polar molecules, where opposite poles attract.
What are dispersion forces?
Weak electrostatic attractions between instantaneous dipoles in neighboring molecules.
How do dispersion forces arise?
Due to the uneven distribution of the electron cloud, creating temporary dipoles.
What is hydrogen bonding?
An attraction between hydrogen and highly electronegative atoms like Oxygen, Nitrogen, or Fluorine in another molecule.
What happens to the charge of hydrogen in a hydrogen bond?
It becomes positively charged due to the attraction to the more electronegative atom.
What is allotropy?
The existence of two or more physically distinct forms of one element in the same physical state.
What are some properties that differ among allotropes?
Color, density, hardness, and electrical conductivity.
What causes the differences in properties among allotropes?
The different structure or packing of atoms.
Name three typical allotropes mentioned in the notes.
Phosphorous, Sulfur, Oxygen.
What are some allotropes of carbon?
Diamond, graphite, and fullerenes.