BIOL-1116 Practical Lab #1 Bacteria, Protists and Fungi
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What are the three main domains of life
Archaea
Bacteria
Eukarya
Which domains are all prokaryotes?
Archaea and Bacteria
Distinguishing characteristic of prokaryotes
Do not contain membrane bound organelles
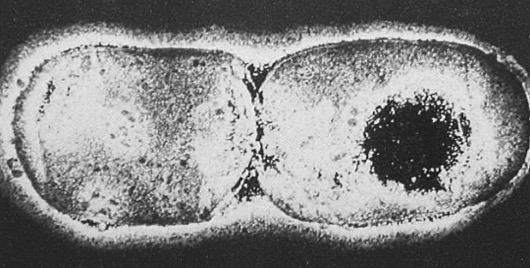
What reproduction is occuring in the photo? And what is reproducing
Binary fission - Bacteria reproduction cell duplicates its components and divides into two cells
Nucleoid region in prokaryotes
A single circular loop of DNA
Peptidoglycan
Network of sugar polymers corss linked by short polypeptides, found in most bacterial cell walls
Heterotrophs
Deriving their energy from organic molecules made by other organisms
Decomposers
Feeding on dead organic matter, u
Pathogens
Heterotrophs which cause disease to plants and animals
Symbionts
Heterotrophs which form partnerships with other organisms which they both benefit i
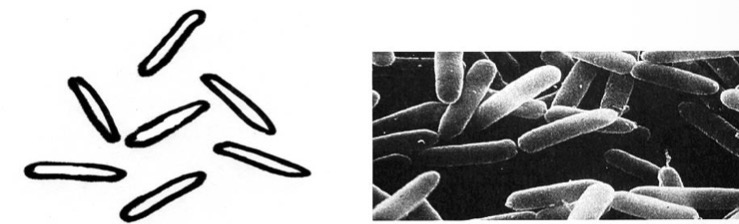
What is the shape of this bacteria
Bacilli
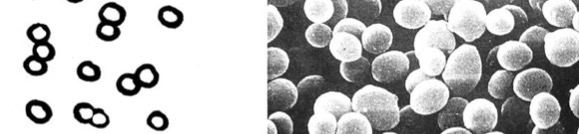
What is the shape of the bacteria shown?
Cocci
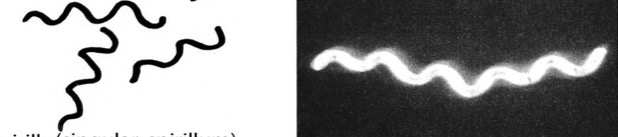
What is the shape of the bacteria shown
Spirilla
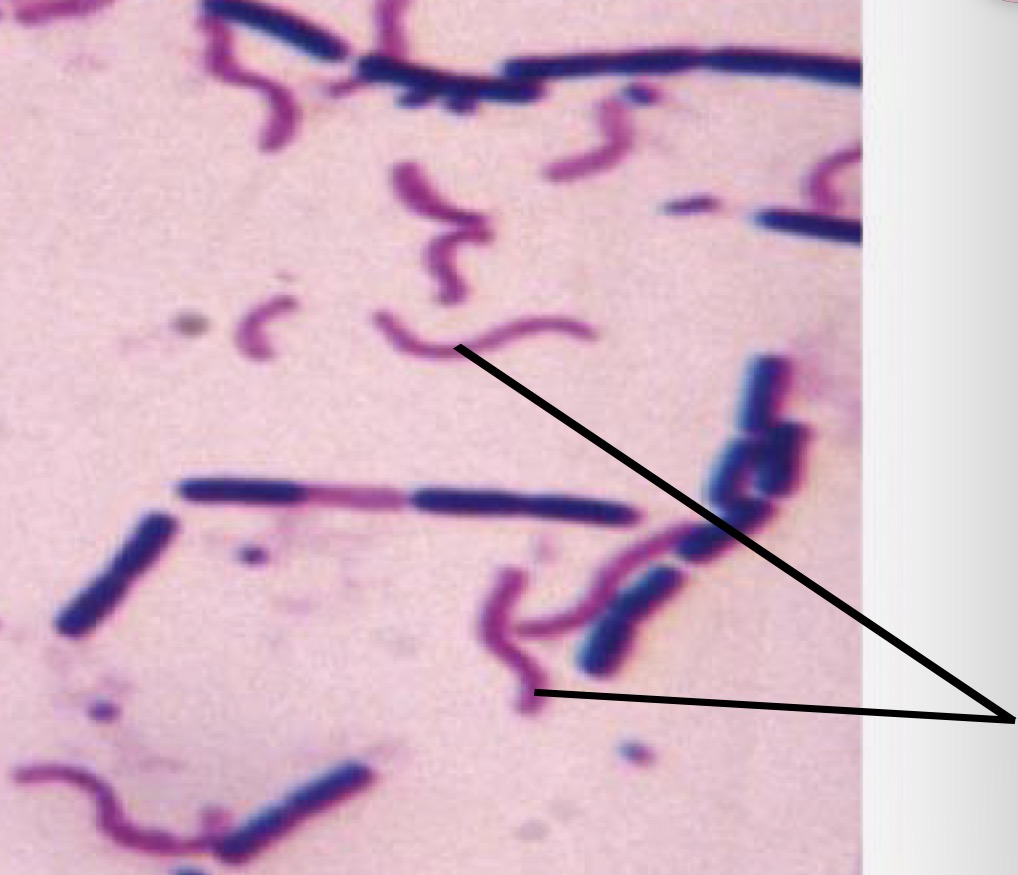
Is the bacteria pointed at gram positive or negative
Gram negative bacteria
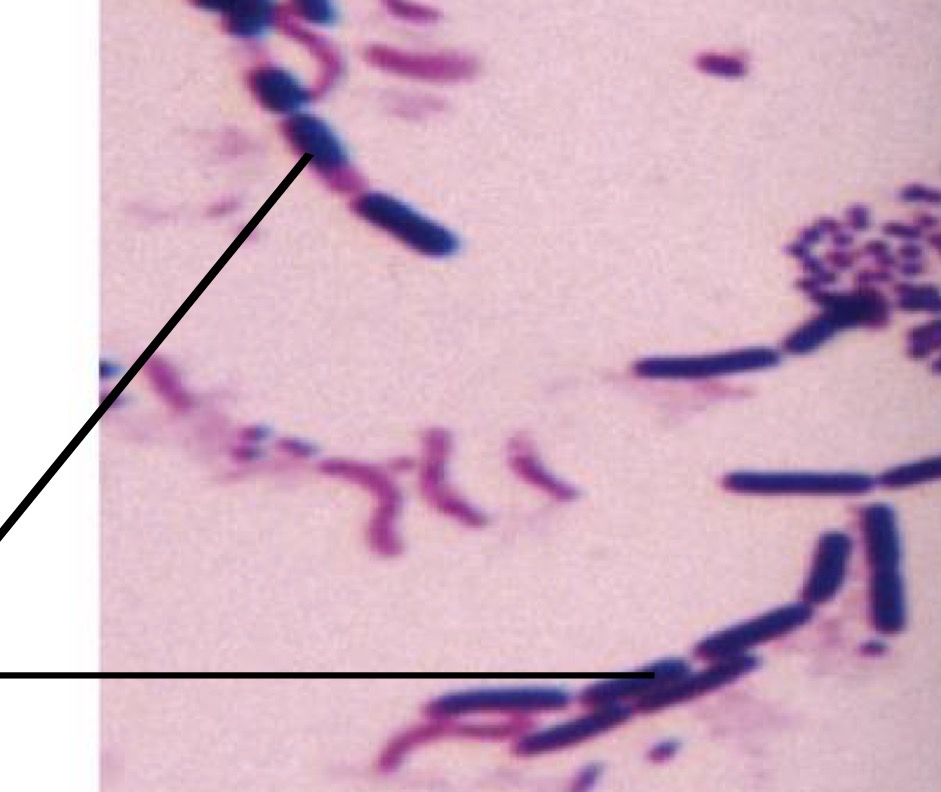
Is the bacteria pointed at gram positive or gram negative
Gram positive
What is cyanobacteria
Autotrophic blue green algae deriving energy from photosynthesis
The cells of cyanobacteria are _____
Prokaryotic
Heterocysts
Specialized nitrogen fixing cells
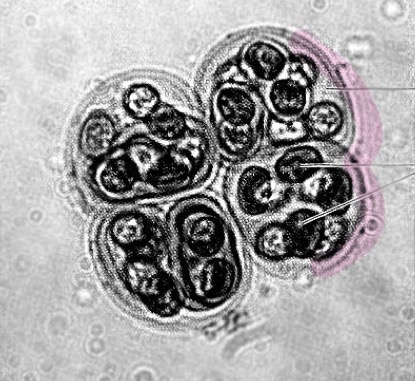
What is the structure highlighted by pink
Gelatinous sheath
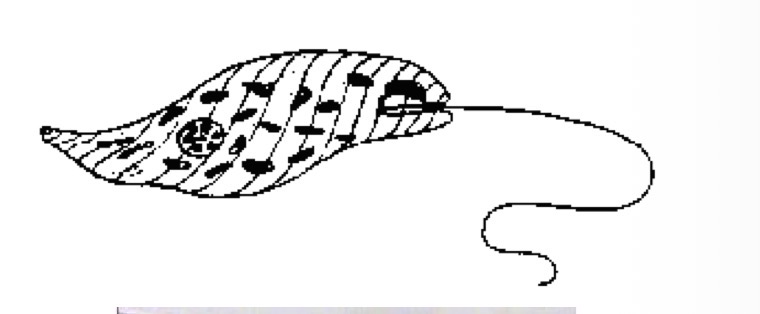
Pellicle
A flexible layer of protein bands, rather than a cell wall allowing for euglenozoans to swim
Mixotrophs
In sunlight they are autotrophic
Without sunlight they are heterotrophic
Silica
Silicon dioxide embedded in an organic matrix
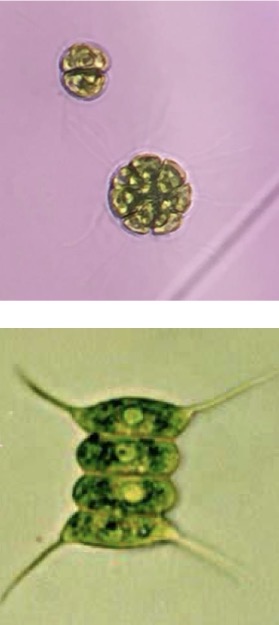
What are the three basic morphological types of green algae
Unicellular
Colonial
Filamentous
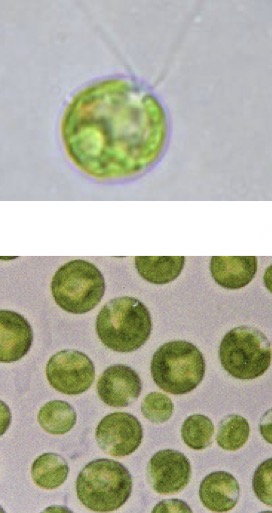
What morphological type is being shown
Unicellular
What morphological type is being shown
Colonial
Mucilage
Less dense than water, aiding in buoyancy
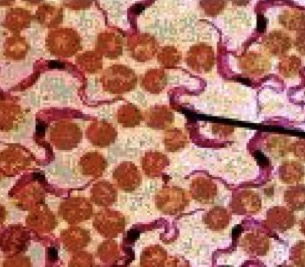
True/false; the organism being pointed at is parasitic
True
Kinetoplast
A single, large mitochondrion that contains an organized mass of DNA in a parasite
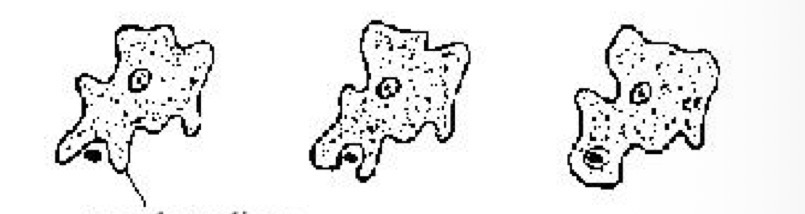
The ameboid protozoa flowing extensions of the body is called
Pseudopodia - engulfs food and aids locomotion
Cilia
Small hair like structures which are used in movement and feeding

What is occurring in this picture
Transverse fission - Division of an organism in two
Plasomodium
Brightly coloured cytoplasm containing diploid nuclei
Coenocytic
NOT multicellular, growing as nuclei divide
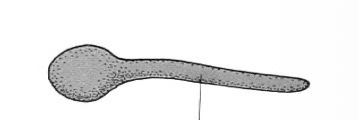
What is being shown in the picture
Hyphae
Gametangia
Gamete producing structures
What develops in the same diploid mycelium to produce spherical eggs (oospheres)
Oogonia (female) and antheridia (male)
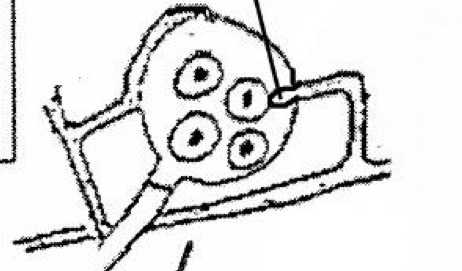
The growth of tubular processes toward the oogonia are called? (Structure being pointed to)
Fertilization tubes
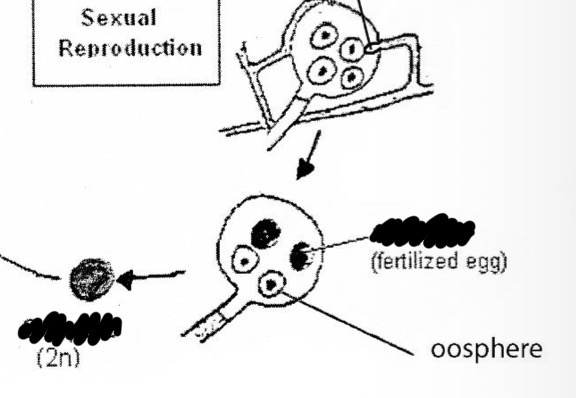
What developes after the combining of the oosphere and the fertilization tubes?
Oospores 2n
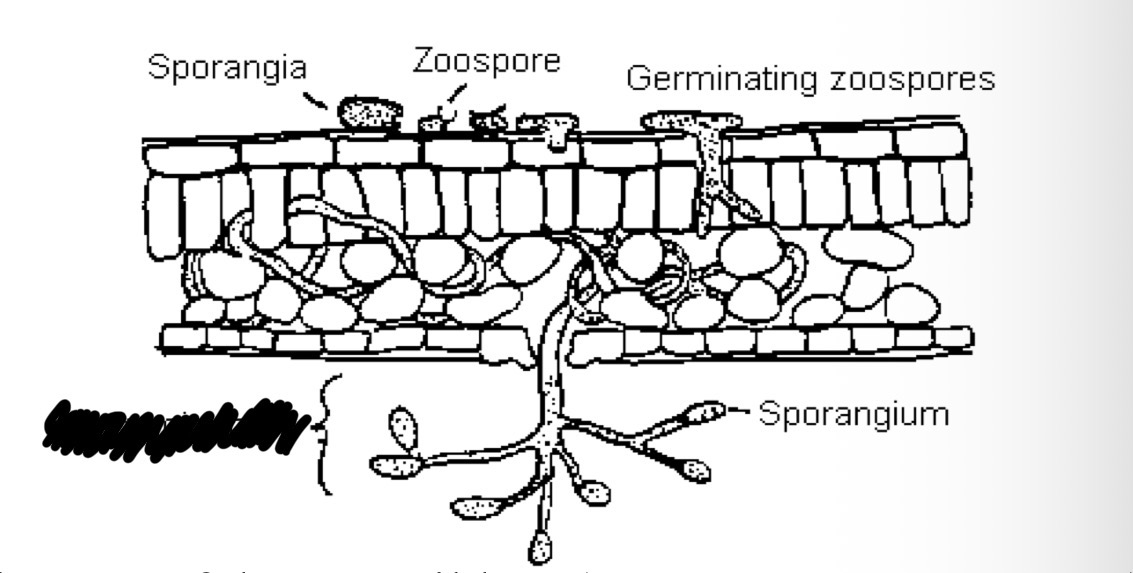
What is the structure which cover the surface of downy mildew infected leaves of plants (term covered in the photo) called?
Sporangiophores
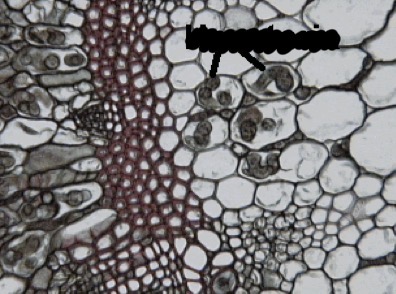
What cells are being pointed at, and what do they do?
Haustoria penetrate the living hosts cells, absorbing nutrients and passing them to growing hyphae
What is mycorrhizae
Fungi which increase absorptive surfaces of plants and roots which aid mineral exchange between soil and plant
Mycelium
An individual organism made of mass of hyphae
Saprophytes (fungi)
Fungi feed on living organisms and are parasites
Septa
cross walls that separate cytoplasm and nuclei into cells
Chitin
Polysaccharide that makes up cell walls of fungi which comprises the exoskeletons of crustaceans
Budding
Form of asexual reproduction, uneven distribution of cytoplasm common in yeast
Fragmentation
Asexual reproduction involbing the breaking an organism into one or more pieces which can develop into a new organism
Union of the cytoplasm of two parent mycelia (gametes)
Plasmogamy
Nuclei contributed by two gametes is known as
Karyogamy
Zygomyota produce what
Zygospores are produced
Basidiomycota produce
Diploid structure called basidium
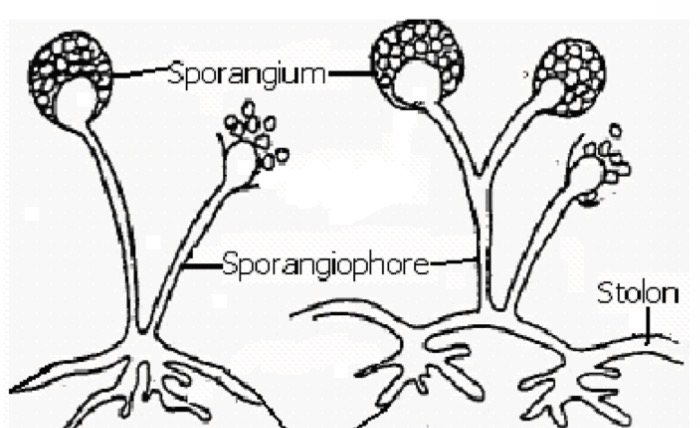
Which structure is formed from submerged hyphae aerial hyphae
Stoloni
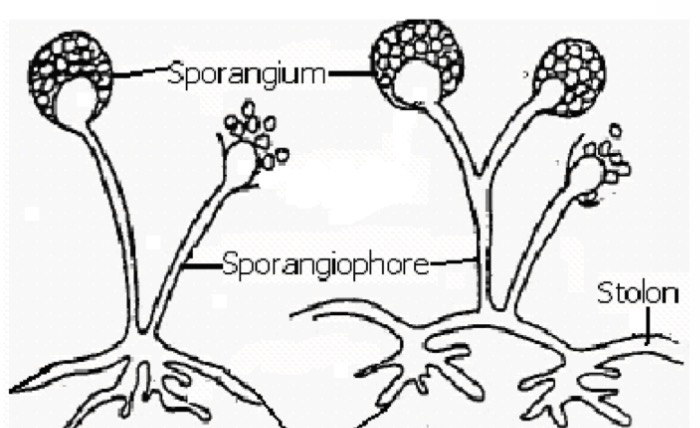
Which structure is formed by the touching of stolons whenever tips come in contact with substrate
Rhizoids y
Basidiomycota produces what from sexual reproduction (meiosis)
Basidiospores
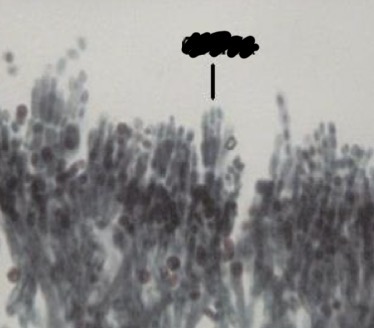
What specific structure is being pointed at in the picture
Conidia