2.3 MANUEL The Trait Controversy: Mischel's Challenge
1/28
Earn XP
Description and Tags
The Trait Controversy: Mischel's Challenge
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
Traditional personality theories
are trait and psychodynamic approaches
view individual differences as broad, consistent characteristics influencing diverse behaviors
social learning theory
posits that behavior varies across situations depending on consequences like rewards and punishments
Consistency arise
when similar consequences occur across situations or when an individual cannot differentiate contexts
Example of Consistency
punishment - decrease behaviour
reward - reinforce behaviour
A child consistently rewarded for speaking across different settings learns to generalize that behavior
Sophisticated models
how traits affect behavior in situations, developed by Mischel
Example of situational context of behavior
aggressive people don't hit and yell all the time
helpful people may act no different from others unless they see someone in need
relationship between traits and behavior takes situations into account.
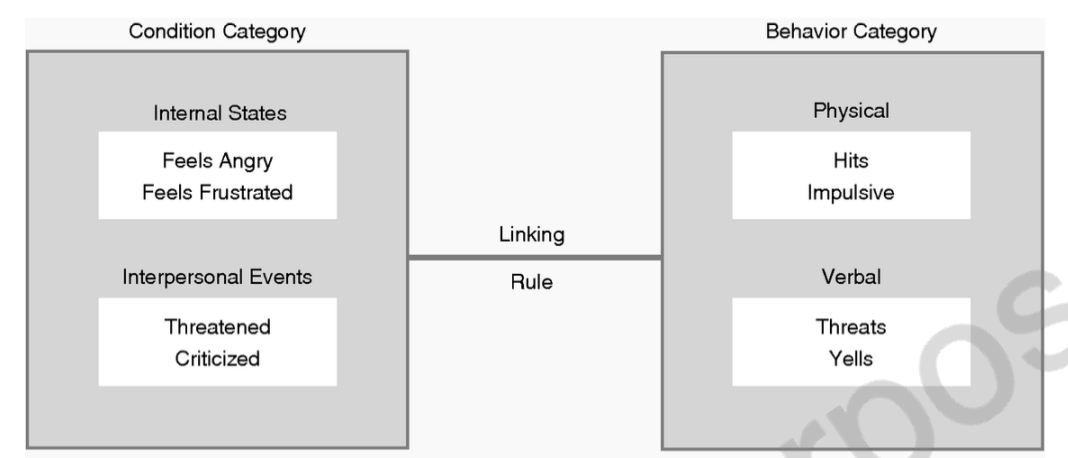
trait of aggressiveness, influences behavior only under certain conditions = when a person feels angry or frustrated
situational context of behavior
refers to how a person's actions are influenced by the environment or circumstances they are in, rather than just their personality traits or internal characteristics.
Thoughts & emotions results of prior experience with that situatsion.
Moods, fantasies, plans, goals, and other internal reactions are triggered by specific situations.
situational approach
it is consistent with people's everyday descriptions of behavior.
Person does x when y
there are consistent individual differences in situation-behavior relationships: study shows different expressions of aggression among children in different situastions
Statistical analyses suggest that reactions to specific situations are influenced by both genetics and experience.
Another theoretical development suggests = trait-related behavior example
Consider conscientiousness behavior:
An individual may be very conscientious sometimes (carefully proofreading a term paper)
Moderately conscientious at other times
And not at all careful at others.
The situational context influences this variability
Cognitive Person Variables
derived from cognition and from social learning
adaptation to the environment, in the unique style of an individual.
Encoding strategies
personal constructs
concepts for describing situations and events.
personal constructs
Trait terms, which people use to describe themselves and other people
They are personal both in the sense that they describe individuals and in the sense that they vary from one person to another
Self-system
Personal constructs that people use to describe themselves
They are unique to each person.
concepts for describing situations and events
people have different learning histories, thus the meaning of situations varies from person to person
personality prototypes
abstract representations of particular personality types
e.g. extroverts & introverts
based on the prototype we can judge whether a particular individual is an introvert
includes social stereotypes & prototypes of various kinds of love
prototypes ranges from very broad categories to narrow ones
Cognitive & behavioral construction competencies
what a person can do
what a person can think
competencies
Include many learned behaviors and concepts
Refer to what a person knows or is able to do
requires providing incentives/reward for the performance of the behavior
Examples of cognitive and behavioral construction competencies
Sexual gender identity
Knowing the structure of the physical world
Social rules and conversations
Personal constructs about self and others
Rehearsal strategies for learning
Expectancies
behavior-outcome expectancies
stimulus-outcome expectancies
self-efficacy expectancies
they develop from experience in various situations
stimulus-outcome expectancies
how events will develop in the world, aside from their own actions
e.g. “If Jerry is shouting, he may soon hit someone”
Self-efficacy expectancies
whether one actually can do the behavior are termed
Central to the cognitive social learning approach (Bandura & Mischel)
low self-efficacy expectancy example
believes that behaviour in a certain situation would not be possible
high behavior-outcome expectancy exmaple
Student knows who believes that 12 hours of straight study would result in an A on an exam
SUBJECTIVE STIMULUS VALUES
Refers to the extent to which a person regards an outcome as desirable or undesirable
A person´s goal or values
In learning terms, it is the value of the reward
SELF-REGULATORY SYSTEMS AND PLANS
These are internal mechanisms that have powerful implications for behavior.
important self-regulatory system is the ability to delay gratification
Examples of SELF-REGULATORY SYSTEMS
People set performance goals for themselves
They reward themselves
They criticize themselves
Delay of Gratification
the ability to postpone present gratification for larger future goal
skill that develops in childhood
Study of children with marshmellows showed that (Mischel)
Delay is more difficult if the rewards are visible = and if the child is thinking about how wonderful the marshmallow will taste.
The marshmallows are out of sight = ) and if the child is thinking about something else.
delay of gratification is easier
this basically suggests that: Adolescents who have difficulty controlling aggression can be taught to use imagery as a technique for increasing self-control.
Personality is adaptational, and the personality characteristics = prepare an individual to cope with situations.
Mischel's model of personality = two competing approaches in personality
approach that seeks to identify personality traits
approach that minimizes individual differences (personality dynamics)
delay of gratification shows how individual children learn to overcome the power of situations to gain self-control